Effects of New Btk-Based Formulations BLB1 and Lip on Aquatic Non-Target Organisms
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Btk-Based Biopesticide Formulations
2.2. Acute Toxicity Assay on Daphnia Magna
2.3. Acute Toxicity Assay on Aliivibrio Fischeri
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
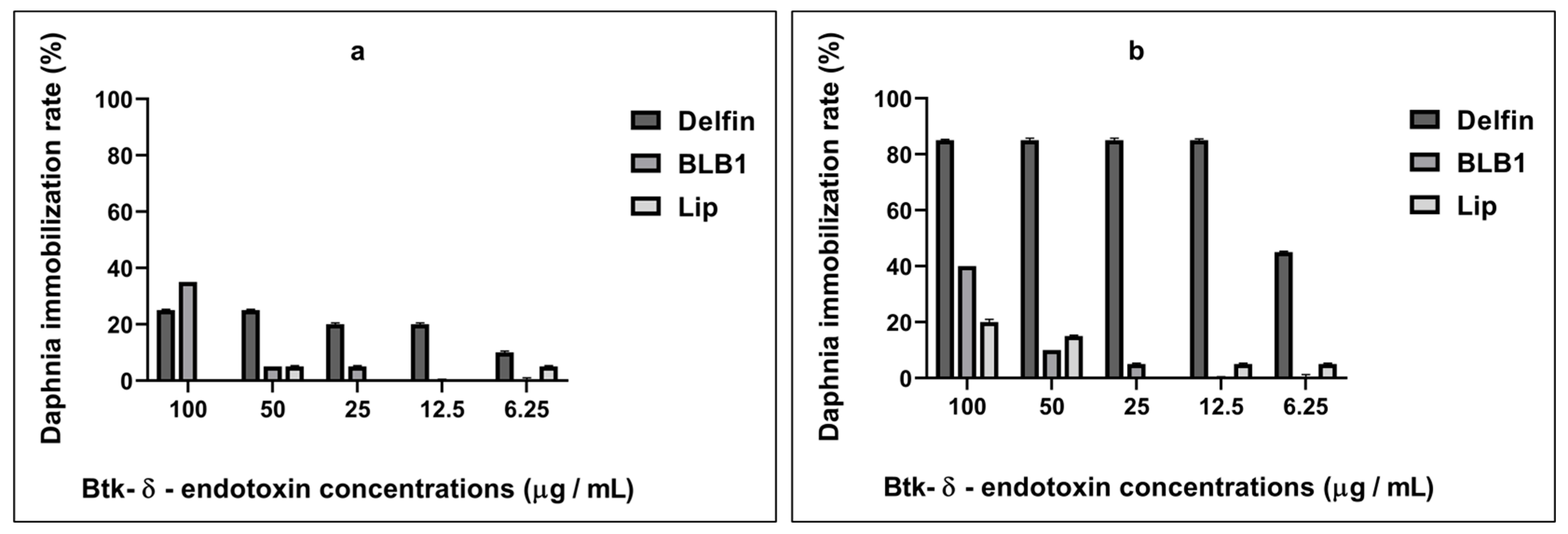
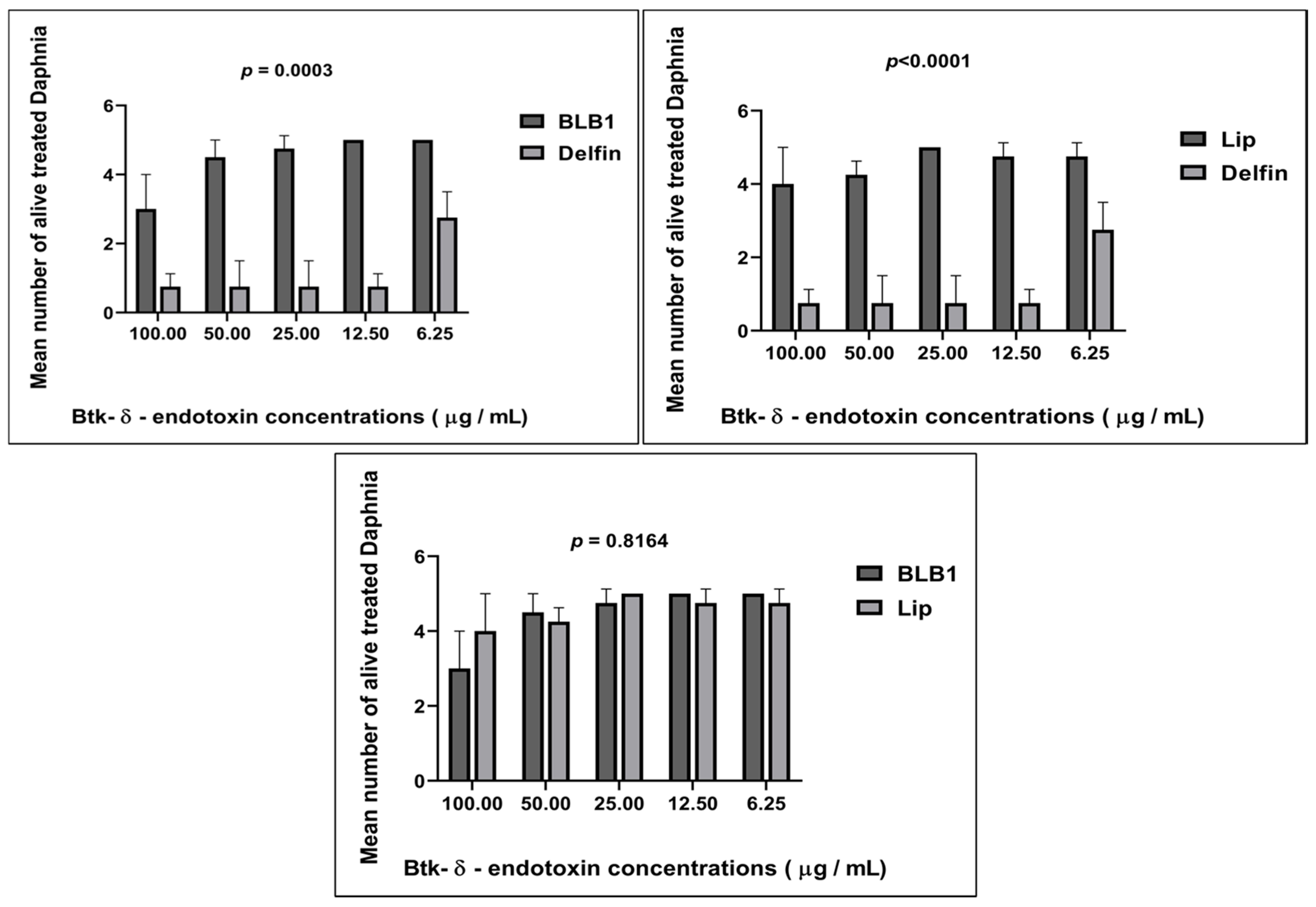
3.1. Sensitivity Response of D. magna toward Various Concentrations of BLB1, Lip, and Delfin®
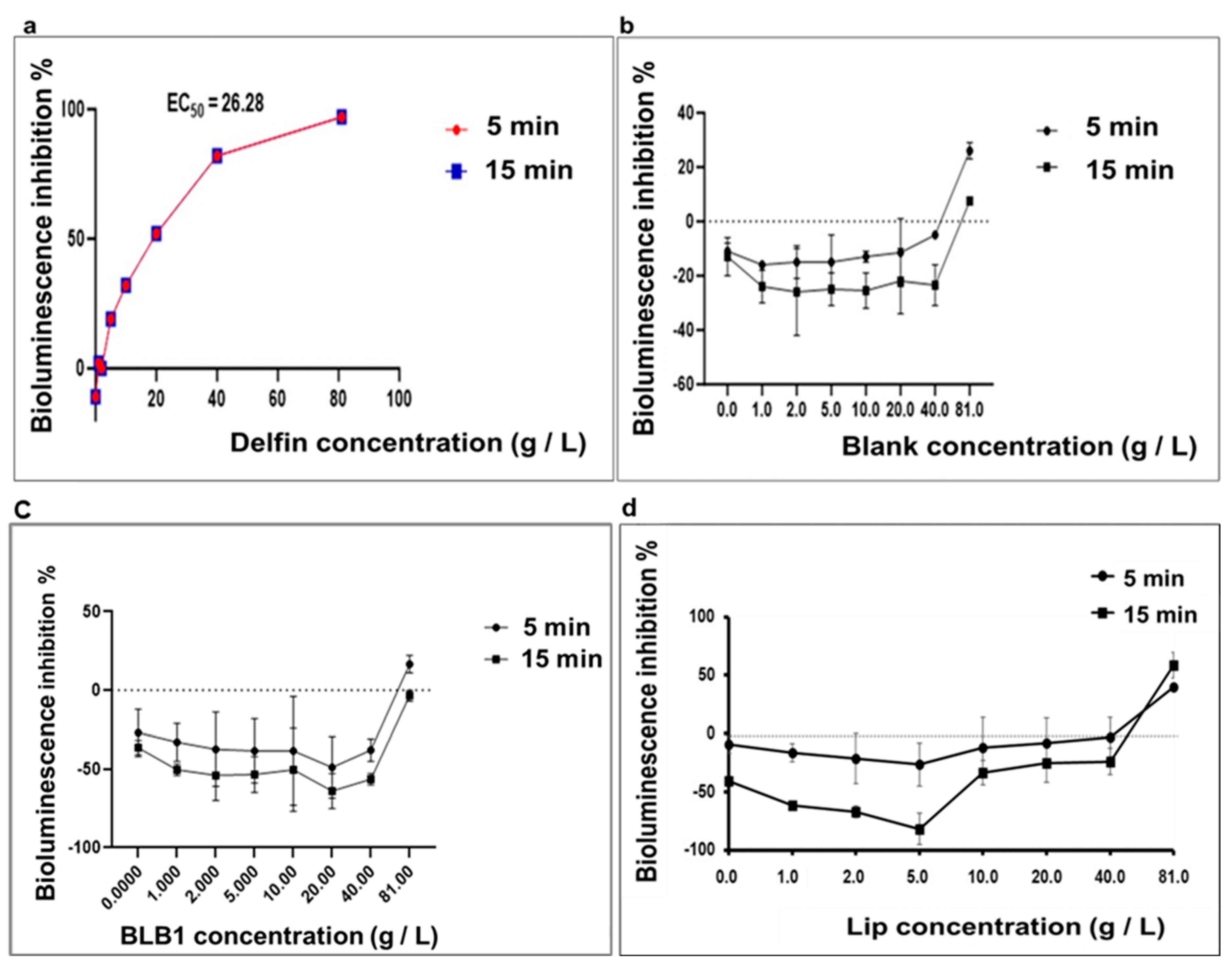
3.2. Sensitivity of A. fischeri to New BLB1, Lip, and Delfin®
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lew, S.; Marcin, L.; Józef, S.; Tomasz, M. Effect of pesticides on soil and aquatic environmental microorganisms—A short review. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2009, 18, 8. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Causal Analysis/Diagnosis Decision Information System (CADDIS)—Insecticides. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/caddis/insecticides (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Kumar, J.; Ayyagari, R.; Dharmendra, M.; Vachaspati, M. An Overview of Some Biopesticides and Their Importance in Plant Protection for Commercial Acceptance. Plants 2021, 10, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamani, M.; Aditi, N. Biopesticides for Pest Management. In Sustainable Bioeconomy; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 239–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino-Otín, M.R.; Diego, B.; Enrique, N.; Azucena, G.C.; Jonatan, V.; Ana, M.M. Ecotoxicity of a Novel Biopesticide from Artemisia Absinthium on Non-Target Aquatic Organisms. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.; Eduardo, C.; Cesar, K.G. The Ecotoxicology of Microbial Insecticides and Their Toxins in Genetically Modified Crops: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Cowles, A.E.; Pietrantonio, V.P. The Mode of Action of Bacillus thuringiensis Endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Enlamal 1992, 37, 615–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Mode of Action of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry and Cyt Toxins and Their Potential for Insect Control. Toxicon 2007, 49, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.; Likitvivatanavong, S.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Bacillus thuringiensis: A Story of a Successful Bioinsecticide. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfersberger, M.G. The toxicity of two Bacillus thuringiensis 6-endotoxins to gypsy moth larvae is inversely related to the affinity of binding sites on midgut brush border membranes for the toxins. Experienti 1990, 46, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisvert, M.; Boisvert, J. Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis Var. Israelensis on Target and Nontarget Organisms: A Review of Laboratory and Field Experiments. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 517–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, H.; Kebaili-Ghribi, J.; Ben Farhat-Touzri, D.; Daoud, D.; Fakhfakh, I.; Tounsi, S.; Jaoua, S. Selection and Characterisation of an HD-1-like Bacillus Thuringiensis Isolate with a High Insecticidal Activity against Spodoptera Littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadaoui, I.; Rouis, R.; Jaoua, S. A New Tunisian Strain of Bacillus thuringiensis Kurstaki Having High Insecticidal Activity and δ-Endotoxin Yield. Arch. Microbiol. 2009, 191, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, M.; Azzouz, H.; Chavanieu, A.; Abdelmalak, N.; Chopineau, J.; Awad, M.K. Isolation and Characterization of a New Bacillus thuringiensis Strain Lip Harboring a New cry1Aa Gene Highly Toxic to Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Larvae. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charbonneau, C.S.; Drobney, R.D.; Charles, F.R. Effects of Bacillus Thuringiensis Var. Israelensis on Nontarget Benthic Organisms in a Lentic Habitat and Factors Affecting the Efficacy of the Larvicide. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1994, 13, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brausch, J.M.; Salice, J.C. Effects of an Environmentally Realistic Pesticide Mixture on Daphnia magna Exposed for Two Generations. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 61, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.S.; Ranville, J.F.; Pontasch, M.; Gorsuch, J.W.; Adams, W.J. Acute Toxicity of Binary and Ternary Mixtures of Cd, Cu, and Zn to Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Vijver, G.M.; Chen, G.; Peijnenburg, J.G.M.W. Toxicity and Accumulation of Cu and ZnO Nanoparticles in Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4657–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.A.; Abdel-Hamid, A.A.; Ibrahim, W.A.; Mahmoud, H.N.; Moselhy, A.W. Toxicity of Some Pesticides, Heavy Metals and Their Mixtures to Vibrio fischeri Bacteria and Daphnia magna: Comparative Study. J. Biol. Life Sci. 2015, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6341:2012; Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibition of the Mobility of Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea)—Acute Toxicity Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zouari, N.; Dhouib, A.; Ellouz, R.; Jaoua, S. Nutritional Requirements of a Strain of Bacillus thuringiensis Subsp, Kurstaki and Use of Gruel Hydrolysate for the Formulation of a New Medium for 8-Endotoxin Production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1998, 69, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11348; Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio fischeri (Luminescent Bacteria Test). Parts 1, 2, and 3. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- Jallouli, W.; Sellami, S.; Sellami, M.; Tounsi, S. Impact of Liquid Formulation Based on Ultrafiltration-Recovered Bioactive Components on Toxicity of Bacillus Thuringiensis Subsp. Kurstaki Strain BLB1 against Ephestia Kuehniella. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 2010–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2022.962619/full (accessed on 14 August 2024). [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M.; Daniel, R.H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D. Agriculture Development, Pesticide Application and Its Impact on the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1112. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/18/3/1112 (accessed on 14 August 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.F.; Ahmad, F.A.; Alsayegh, A.A.; Zeyaullah Md AlShahrani, A.M.; Muzammil, K. Pesticides impacts on human health and the environment with their mechanisms of action and possible countermeasures. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29128. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2405844024051594 (accessed on 18 August 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, K.; Anderson, J.; Bachman, P.; De Schrijver, A.; Dively, G.; Federici, B. Genetically modified crops and aquatic ecosystems: Considerations for environmental risk assessment and non-target organism testing. Transgenic Res. 2012, 21, 813–842. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11248-011-9569-8 (accessed on 14 August 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Romeis, J.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X. Safety of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1C Protein for Daphnia magna Based on Different Functional Traits. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraretti, M.; Siciliano, A.; Carraturo, F.; Cimmino, A.; De Natale, A.; Guida, M. Ecotoxicological evaluation of four fungal metabolites with potential application as biocides for the conservation of cultural heritage. Toxins 2022, 14, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, D.P.; Butarewicz, A.J.; Andraka, M. Use of toxicity tests to assess the harmfulness of selected herbicides. J. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 25, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, O.; Cyrino, E.; Muniz, F.H.D.; Freire, S.I.; Ramos, R.F.; Alves, T.R.; Jonsson, M.C.; Grisolia, K.C.; Monnerat, G.R. Susceptibility of Non-Target Invertebrates to Brazilian Microbial Pest Control Agents. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Stępniewska, Z.; Skowroński, T. Effects of ectoine on behavioural, physiological and biochemical parameters of Daphnia magna. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 168, 2–10. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1532045614001409 (accessed on 14 August 2024). [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A. Daphnia swimming behaviour as a biomarker in toxicity assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 194, 601–602. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0048969717313062 (accessed on 14 August 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ismaiel, M.M.S. Effect of nitrogen regime on antioxidant parameters of selected prokaryotic and eukaryotic microalgal species. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 154. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11738-016-2170-2 (accessed on 14 August 2024). [CrossRef]
- Krewski, D.; Acosta, D.; Andersen, M.; Anderson, H.; Bailar, C.J.; Boekelheide, K.; Brent, R. Toxicity Testing in the 21st Century: A Vision and a Strategy. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2010, 13, 51–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butu, M.; Rodino, S.; Butu, A. Biopesticide formulations-current challenges and future perspectives. In Biopesticides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Nuruzzaman, M.d.; Liu, Y.; Rahman, M.M.; Dharmarajan, R.; Duan, L.; Jamal Uddin, M.d.A.F.; Naidu, R. Nanobiopesticides: Composition and Preparation Methods. Nano-Biopestic. Today Future Perspect. 2019, 69–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zou, X.; Yao, Z.; Tian, D.; Wang, D.; Yin, D. Model of Hormesis and Its Toxicity Mechanism Based on Quorum Sensing: A Case Study on the Toxicity of Sulfonamides to Photobacterium Phosphoreum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7746–7754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J. Hormesis Is Central to Toxicology, Pharmacology and Risk Assessment. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brack, A.; Strube, J.; Stolz, P.; Decker, H. Effects of Ultrahigh Dilutions of 3,5-Dichlorophenol on the Luminescence of the Bacterium Vibrio Fischeri. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1621, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulladosa, E.J.C.; Villaescusa, M.I. Effect of Cadmium (II), Chromium (VI), and Arsenic (V) on Long-Term Viability- and Growth-Inhibition Assays Using Vibrio Fischeri Marine Bacteria. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 49, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Shen, C.; Lu, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Lin, Q.; Chen, Y. Hormesis Response of Marine and Freshwater Luminescent Bacteria to Metal Exposure. Biol. Res. 2009, 42, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavicoli, I.; Fontana, L.; Agathokleous, E.; Santocono, C.; Russo, F.; Vetrani, I.; Fedele, M.; Calabrese, J.E. Hormetic Dose Responses Induced by Antibiotics in Bacteria: A Phantom Menace to Be Thoroughly Evaluated to Address the Environmental Risk and Tackle the Antibiotic Resistance Phenomenon. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Test | Trophic Level | Group of Organisms | Type of Test | Test Duration | Test Criterion | Test Principle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microtox * (Aliivibrio fischeri) | Decomposer | Bacteria | acute | 15 min | Bioluminescence inhibition | Measure of luminescence reduction with luminometer |
| Daphtox * (Daphnia magna) | Primary consumer | Crustaceans | acute | 48 h | Immobility/Mortality | Counting of immobilized/dead and alive crustacean |
| Bioproduct | EC5 | EC10 | EC15 | EC20 | EC50 | TU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delfin® | Optimal | 14.855110814 | 20.280975727 | 24.592538668 | 28.43358065 | 50.66287994 | 1.97 |
| Average | 14.855111017 | 20.280975848 | 24.592539295 | 28.43357995 | 50.6628789 | ||
| Median | 14.855111122 | 20.280975341 | 24.592538833 | 28.4335804 | 50.66287994 | ||
| BLB1 | Optimal | 53.936655407 | 61.635712778 | 66.943755933 | 71.2397125 | 91.25 | 1.095 |
| Average | 53.936656564 | 61.635710299 | 66.943757236 | 71.2397173 | 91.25000238 | ||
| Median | 53.936655951 | 61.635711669 | 66.943756103 | 71.23971558 | 91.25 | ||
| Lip | Optimal | 70.335694387 | 76.286681764 | 80.22085677 | 83.31619615 | 96.86585999 | 1.032 |
| Average | 70.335693657 | 76.286680996 | 80.22085577 | 83.31619203 | 96.86586261 | ||
| Median | 70.335693359 | 76.286682128 | 80.22085571 | 83.31619263 | 96.86585999 |
| Bioproduct | EC5 | EC10 | EC15 | EC20 | EC50 | TU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delfin® | Optimal | 932.3414516 | 952.2753551 | 964.8300967 | 974.3915958 | 1013.395661 | 0.09867 |
| Average | 968.3056653 | 993.0435114 | 1008.840638 | 1020.989531 | 1071.710124 | ||
| Median | 914.4064941 | 937.2280884 | 954.8158569 | 967.4196167 | 1012.115662 | ||
| BLB1 | Optimal | 1216.949498 | 1228.692693 | 1236.019997 | 1241.565502 | 1263.884835 | 0.07912129 |
| Average | 1360.461129 | 1373.301712 | 1381.325891 | 1387.405276 | 1411.930563 | ||
| Median | 1216.949341 | 1228.692505 | 1236.019775 | 1241.565308 | 1263.884644 | ||
| Lip | Optimal | 1211. 38623 | 1222. 83924 | 1229.83385 | 1235.24384 | 1256.74177 | 0.07619 |
| Average | 1211.4529137 | 1222.772556 | 1229.76717 | 1235.17715 | 1256.67509 | ||
| Median | 1211.5196 | 1222.77256 | 1229.70048 | 1235.11047 | 1256.60841 | ||
| Blank | Optimal | 1249.645277 | 1265.305134 | 1275.098841 | 1282.522459 | 1312.5 | 0.07619 |
| Average | 1249.645233 | 1265.305161 | 1275.09892 | 1282.52244 | 1312.5 | ||
| Median | 1249.645264 | 1265.305176 | 1275.098877 | 1282.522461 | 1312.5 | ||
| Species | Ranking | Significance (*) |
|---|---|---|
| Daphnia magna | Delfin® > BLB1 > Lip | Delfin versus BLB1 (p = 0.0259) Delfin versus Lip (p < 0.0001) |
| Aliivibrio fischeri | Delfin® > Lip > BLB1 | Delfin versus BLB1 (p = 0.0002) Delfin versus Lip (p = 0.0029) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhaouadi, S.; Jeni, R.E.; Kraiem, H.; Ayyildiz, G.; Filik-Iscen, C.; Yurtkuran-Ceterez, Z.; Bouhaouala-Zahar, B. Effects of New Btk-Based Formulations BLB1 and Lip on Aquatic Non-Target Organisms. Biology 2024, 13, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100824
Dhaouadi S, Jeni RE, Kraiem H, Ayyildiz G, Filik-Iscen C, Yurtkuran-Ceterez Z, Bouhaouala-Zahar B. Effects of New Btk-Based Formulations BLB1 and Lip on Aquatic Non-Target Organisms. Biology. 2024; 13(10):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100824
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhaouadi, Sayda, Rim El Jeni, Hazar Kraiem, Gul Ayyildiz, Cansu Filik-Iscen, Zeynep Yurtkuran-Ceterez, and Balkiss Bouhaouala-Zahar. 2024. "Effects of New Btk-Based Formulations BLB1 and Lip on Aquatic Non-Target Organisms" Biology 13, no. 10: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100824
APA StyleDhaouadi, S., Jeni, R. E., Kraiem, H., Ayyildiz, G., Filik-Iscen, C., Yurtkuran-Ceterez, Z., & Bouhaouala-Zahar, B. (2024). Effects of New Btk-Based Formulations BLB1 and Lip on Aquatic Non-Target Organisms. Biology, 13(10), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100824






