Effects of 4.9 GHz Radiofrequency Field Exposure on Brain Metabolomic and Proteomic Characterization in Mice
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Radiofrequency Field Exposure
2.3. Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. Proteomic Analysis
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
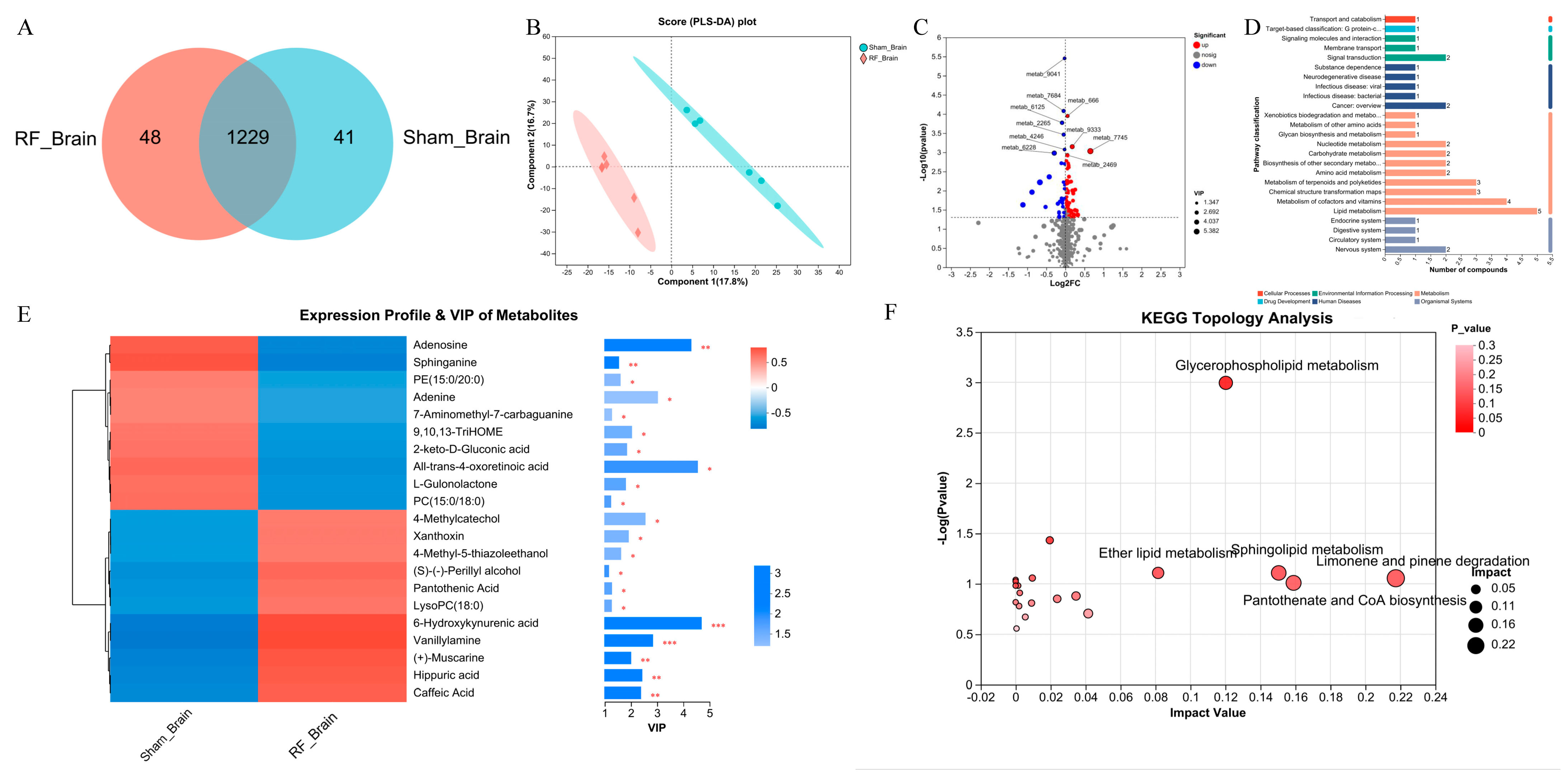
3.1. 4.9 GHz Radiofrequency Exposure Altered Metabolism Profile in Brain
3.2. 4.9 GHz Radiofrequency Exposure Induced Disturbance of Metabolism in Serum
3.3. 4.9 GHz Radiofrequency Exposure Caused Deregulation of Proteins in Brain
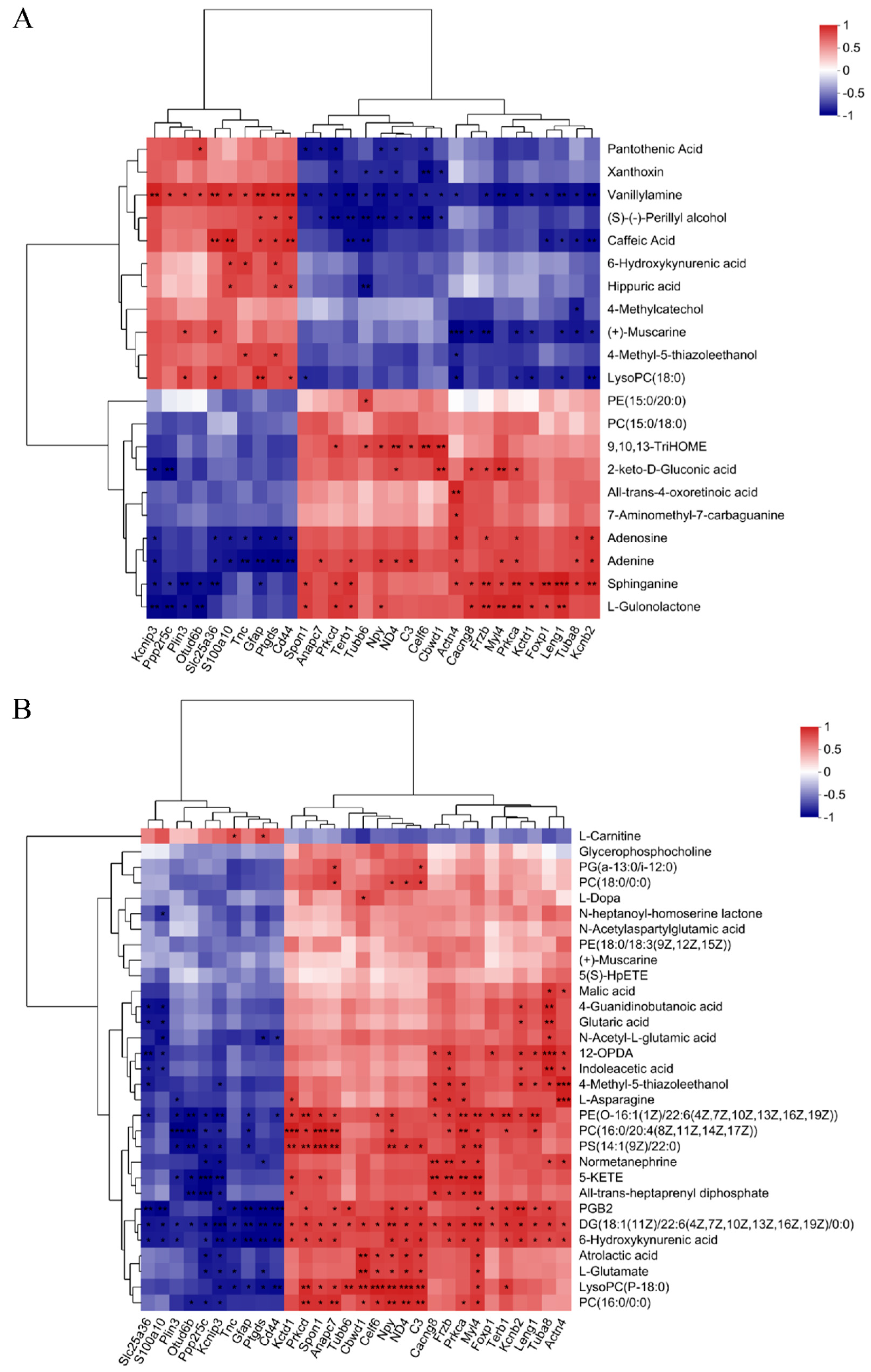
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Metabolomics and Proteomics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, R.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Gao, D.; Gong, W.; Zhang, C.; Dong, G.; Li, Z. Biological effects of exposure to 2650 MHz electromagnetic radiation on the behavior, learning, and memory of mice. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Guidelines for Limiting Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz). Health Phys. 2020, 118, 483–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Patel, S.K.; Tomar, M.S.; Singh, S.K.; Mesharam, M.K.; Krishnamurthy, S. Long-term exposure of 2450 MHz electromagnetic radiation induces stress and anxiety like behavior in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Gan, P.; Luo, X.; Zhong, S.; Zuo, W. Effects of Acute Exposure to 3500 MHz (5G) Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Radiation on Anxiety-Like Behavior and the Auditory Cortex in Guinea Pigs. Bioelectromagnetics 2022, 43, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altun, G.; Deniz, O.G.; Yurt, K.K.; Davis, D.; Kaplan, S. Effects of mobile phone exposure on metabolomics in the male and female reproductive systems. Env. Res. 2018, 167, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savchenko, L.; Martinelli, I.; Marsal, D.; Batkivska, O.; Zhdan, V.; Kaidashev, I.; Pizzinat, N.; Boal, F.; Tronchere, H.; Tao, J.; et al. Metabolic, Apoptotic and Fibro-Inflammatory Profiles of the Heart Exposed to Environmental Electromagnetic Fields. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Tian, S.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Yan, H.L.; Hu, X.G.; Shao, Q.; Guo, J.M. Transcriptomic and metabolomic studies on the protective effect of molecular hydrogen against nuclear electromagnetic pulse-induced brain damage. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1103022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, R.; Maan, K.; Khushu, S.; Rana, P. Urine metabolomics based prediction model approach for radiation exposure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yao, C.; Wang, H.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Yao, B.; Ren, K.; Sun, L.; et al. Immune Responses to Multi-Frequencies of 1.5 GHz and 4.3 GHz Microwave Exposure in Rats: Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Ren, K.; Dong, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Yao, B.; Zhou, H.; et al. The Biological Effects of Compound Microwave Exposure with 2.8 GHz and 9.3 GHz on Immune System: Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis. Cells 2022, 11, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.V.; Arya, R.; Nirala, J.P.; Sahu, D.; Nanda, R.K.; Rajamani, P. Effects of mobile phone electromagnetic radiation on rat hippocampus proteome. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dong, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Yao, B.; Zhao, L.; et al. Changes in cognitive function, synaptic structure and protein expression after long-term exposure to 2.856 and 9.375 GHz microwaves. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, W.-J.; Wang, L.-F.; Hu, X.-J. Recent advances in the effects of microwave radiation on brains. Mil. Med. Res. 2017, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Ruiz, M.; Suárez, O.J.; López, V.; Marina, P.; Sanchis, A.; Liste, I.; de Alba, M.; Ramos, V. Effects of 700 and 3500 MHz 5G radiofrequency exposure on developing zebrafish embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 169475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Qin, T.Z.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Z.W.; Huang, Z.F.; Lin, J.J.; Jing, Y.T.; Wang, H.N.; et al. Intestinal microbiota via NLRP3 inflammasome dependent neuronal pyroptosis me-diates anxiety-like behaviour in mice exposed to 3.5 GHz radiofrequency radiation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.Z.; Wang, X.; Du, J.Z.; Lin, J.J.; Xue, Y.Z.; Guo, L.; Lai, P.P.; Jing, Y.T.; Zhang, Z.W.; Ding, G.R. Effects of radiofrequency field from 5G communications on the spatial memory and emotionality in mice. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 34, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endle, H.; Horta, G.; Stutz, B.; Muthuraman, M.; Tegeder, I.; Schreiber, Y.; Snodgrass, I.F.; Gurke, R.; Liu, Z.W.; Sestan-Pesa, M.; et al. AgRP neurons control feeding behaviour at cortical synapses via peripherally derived lysophospholipids. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; Lin, J.; Qin, T.; Du, J.; Guo, L.; Lai, P.; Jing, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Effects of radiofrequency field from 5G communication on fecal microbiome and metabolome profiles in mice. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karipidis, K.; Mate, R.; Urban, D.; Tinker, R.; Wood, A. 5G mobile networks and health—A state-of-the-science review of the research into low-level RF fields above 6 GHz. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 585–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.S.; Gallucci, S.; Siervo, B.; Hartwig, V. Numerical Analysis of Electromagnetic Field Exposure from 5G Mobile Communications at 28 GHZ in Adults and Children Users for Real-World Exposure Scenarios. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simko, M.; Mattsson, M.O. 5G Wireless Communication and Health Effects-A Pragmatic Review Based on Available Studies Regarding 6 to 100 GHz. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozek, K.; Wei, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liu, X.; Xiong, J.; Sugimoto, M.; Tomita, M.; Pääbo, S.; Sherwood, C.C.; Hof, P.R.; et al. Organization and Evolution of Brain Lipidome Revealed by Large-Scale Analysis of Human, Chimpanzee, Macaque, and Mouse Tissues. Neuron 2015, 85, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.S.; Tiwari, N.K. Lipid Integration in Neurodegeneration: An Overview of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.-m.; Li, Q.; Zhou, C.; Yu, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.-w.; Ding, G.; Shang, H.; Zou, Z.M. Chronic unpredictive mild stress leads to altered hepatic metabolic profile and gene expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.; Hou, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, P.; Xu, G. Plasma lipidomics reveals potential lipid markers of major depressive disorder. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6497–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, H.; Zeng, N.; Li, H.; Yao, G.; Liu, K.; Yan, C.; Wu, L. Luteolin alleviates depression-like behavior by modulating glycerophospholipid metabolism in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of LOD rats. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 30, e14455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Perry, S.W.; Yin, B.; Tan, X.; Chai, T.; Liang, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. The gut microbiome modulates gut-brain axis glycerophospholipid metabolism in a region-specific manner in a nonhuman primate model of depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 2380–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Pu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Teng, T.; Tian, L.; et al. Integrated Metabolomics and Proteomics Analysis of Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Depression. Neuroscience 2018, 371, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogswell, D.; Bisesi, P.; Markwald, R.R.; Cruickshank-Quinn, C.; Quinn, K.; McHill, A.; Melanson, E.L.; Reisdorph, N.; Wright, K.P., Jr.; Depner, C.M. Identification of a Preliminary Plasma Metabolome-based Biomarker for Circadian Phase in Humans. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2021, 36, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.K.; Sisodia, R.; Bhatia, A.L. Radioprotective Role of Amaranthus gangeticus Linn.: A Biochemical Study on Mouse Brain. J. Med. Food 2002, 5, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sisodia, R.; Bhatnagar, D.; Saxena, V.K. Spatial memory and learning performance and its relationship to protein synthesis of Swiss albino mice exposed to 10 GHz microwaves. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2014, 90, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragopoulou, A.F.; Samara, A.; Antonelou, M.H.; Xanthopoulou, A.; Papadopoulou, A.; Vougas, K.; Koutsogiannopoulou, E.; Anastasiadou, E.; Stravopodis, D.J.; Tsangaris, G.T.; et al. Brain proteome response following whole body exposure of mice to mobile phone or wireless DECT base radiation. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2012, 31, 250–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaev, I.Y.; Koch, C.B.; Terenius, O.; Roxström-Lindquist, K.; Malmgren, L.O.; Sommer, W.H.; Salford, L.G.; Persson, B.R. Exposure of rat brain to 915 MHz GSM microwaves induces changes in gene expression but not double stranded DNA breaks or effects on chromatin conformation. Bioelectromagnetics 2006, 27, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.P.; Reichel, M.; Mühle, C.; Rhein, C.; Gulbins, E.; Kornhuber, J. Brain membrane lipids in major depression and anxiety disorders. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulbins, E.; Walter, S.; Becker, K.A.; Halmer, R.; Liu, Y.; Reichel, M.; Edwards, M.J.; Müller, C.P.; Fassbender, K.; Kornhuber, J. A central role for the acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide system in neurogenesis and major depression. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornhuber, J.; Müller, C.P.; Becker, K.A.; Reichel, M.; Gulbins, E. The ceramide system as a novel antidepressant target. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, S.; Futerman, A.H. The metabolism and function of sphingolipids and glycosphingolipids. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2270–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbins, E.; Palmada, M.; Reichel, M.; Lüth, A.; Böhmer, C.; Amato, D.; Müller, C.P.; Tischbirek, C.H.; Groemer, T.W.; Tabatabai, G.; et al. Acid sphingomyelinase–ceramide system mediates effects of antidepressant drugs. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.G.; Chan, R.B.; Bravo, F.V.; Miranda, A.; Silva, R.R.; Zhou, B.; Marques, F.; Pinto, V.; Cerqueira, J.J.; Di Paolo, G.; et al. The impact of chronic stress on the rat brain lipidome. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 21, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Rassoulpour, A.; Goodman, J.H.; Scharfman, H.E.; Bertram, E.H.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenate and 7-Chlorokynurenate Formation in Chronically Epileptic Rats. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.K.; Jung, H.A.; Chung, H.Y.; Choi, J.S. In vitro peroxynitrite scavenging activity of 6-hydroxykynurenic acid and other flavonoids from Gingko biloba yellow leaves. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006, 29, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz van Endert, T. Addictive use of digital devices in young children: Associations with delay discounting, self-control and academic performance. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabré-Riera, A.; van Wel, L.; Liorni, I.; Thielens, A.; Birks, L.E.; Pierotti, L.; Joseph, W.; González-Safont, L.; Ibarluzea, J.; Ferrero, A.; et al. Association between estimated whole-brain radiofrequency electromagnetic fields dose and cognitive function in preadolescents and adolescents. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 231, 113659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durusoy, R.; Hassoy, H.; Özkurt, A.; Karababa, A.O. Mobile phone use, school electromagnetic field levels and related symp-toms: A cross-sectional survey among 2150 high school students in Izmir. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, K.; Akgönül, M.; Akpinar, A. Relationship of smartphone use severity with sleep quality, depression, and anxiety in uni-versity students. J. Behav. Addict. 2015, 4, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, T.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z.; Ding, G. Effects of 4.9 GHz Radiofrequency Field Exposure on Brain Metabolomic and Proteomic Characterization in Mice. Biology 2024, 13, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100806
Wang X, Zhou G, Lin J, Zhang Z, Qin T, Guo L, Wang H, Huang Z, Ding G. Effects of 4.9 GHz Radiofrequency Field Exposure on Brain Metabolomic and Proteomic Characterization in Mice. Biology. 2024; 13(10):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100806
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xing, Guiqiang Zhou, Jiajin Lin, Zhaowen Zhang, Tongzhou Qin, Ling Guo, Haonan Wang, Zhifei Huang, and Guirong Ding. 2024. "Effects of 4.9 GHz Radiofrequency Field Exposure on Brain Metabolomic and Proteomic Characterization in Mice" Biology 13, no. 10: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100806
APA StyleWang, X., Zhou, G., Lin, J., Zhang, Z., Qin, T., Guo, L., Wang, H., Huang, Z., & Ding, G. (2024). Effects of 4.9 GHz Radiofrequency Field Exposure on Brain Metabolomic and Proteomic Characterization in Mice. Biology, 13(10), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100806





