The Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress during the Interaction between Calcium Oxalate Crystals and Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. RNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Construction of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
2.7. Validation of DEGs in the Public Dataset
2.8. Cell Viability and Apoptosis Assays
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.10. Western Blot (WB)
3. Results
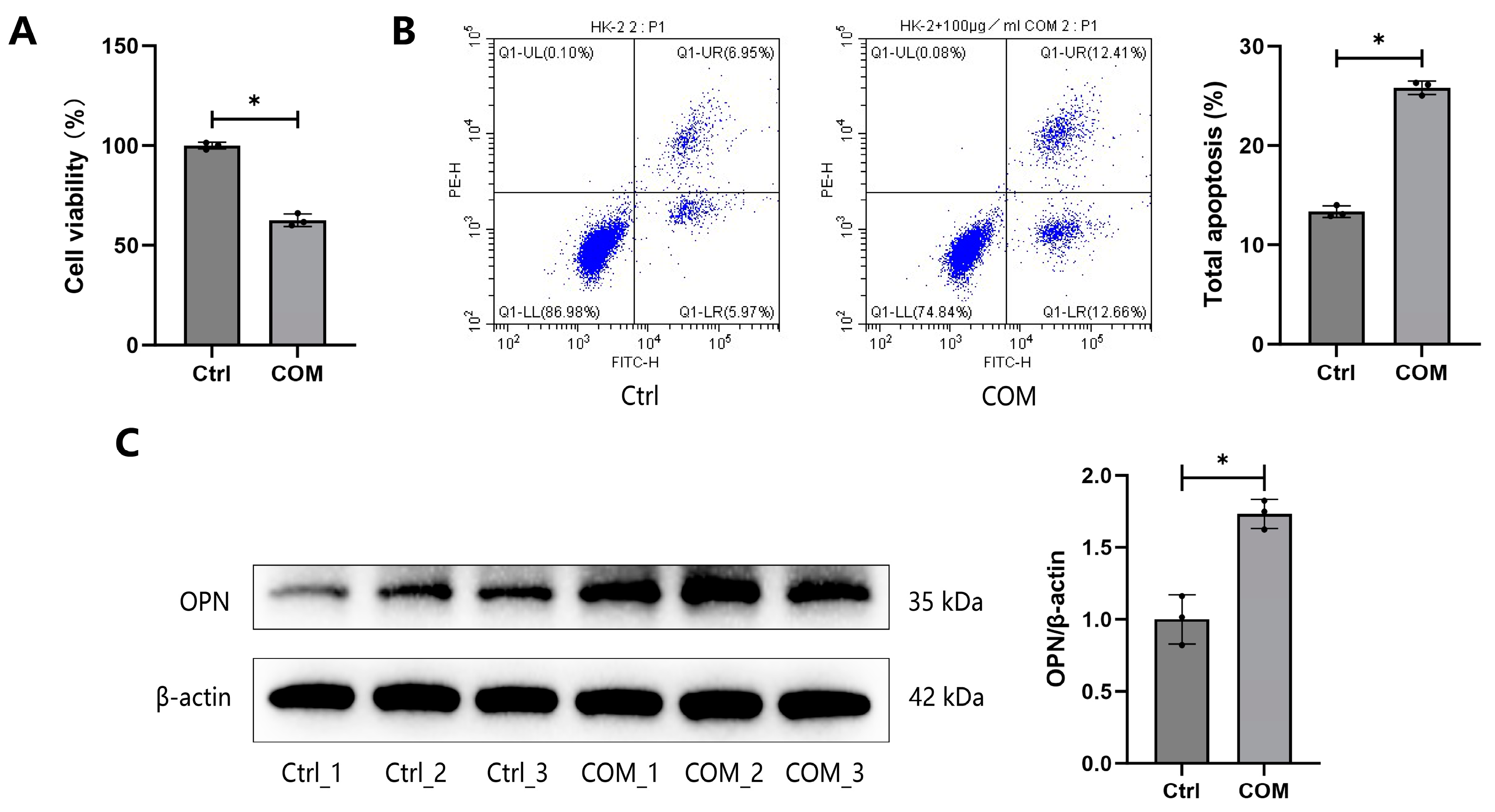
3.1. Validation of the Cell–Crystal Interaction Model
3.2. Alignment Statistic of Reads Aligned with Reference Genome
3.3. Identification of DEGs
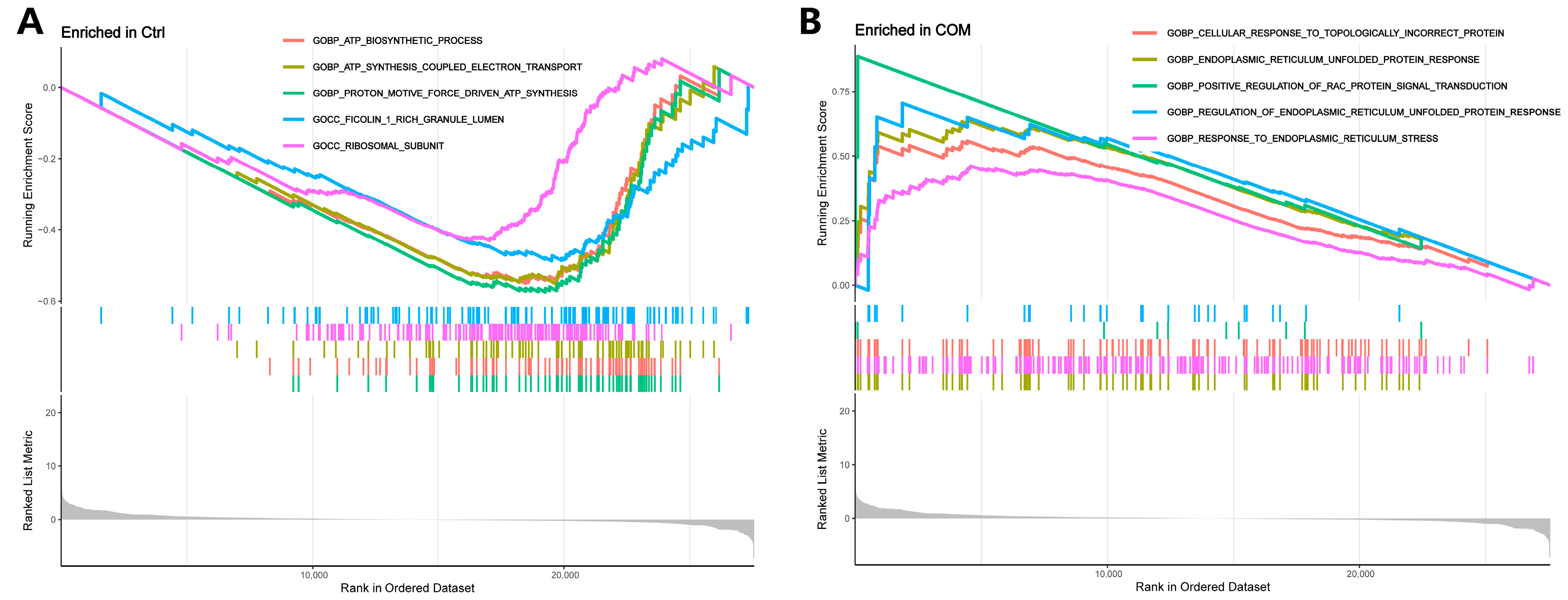
3.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis
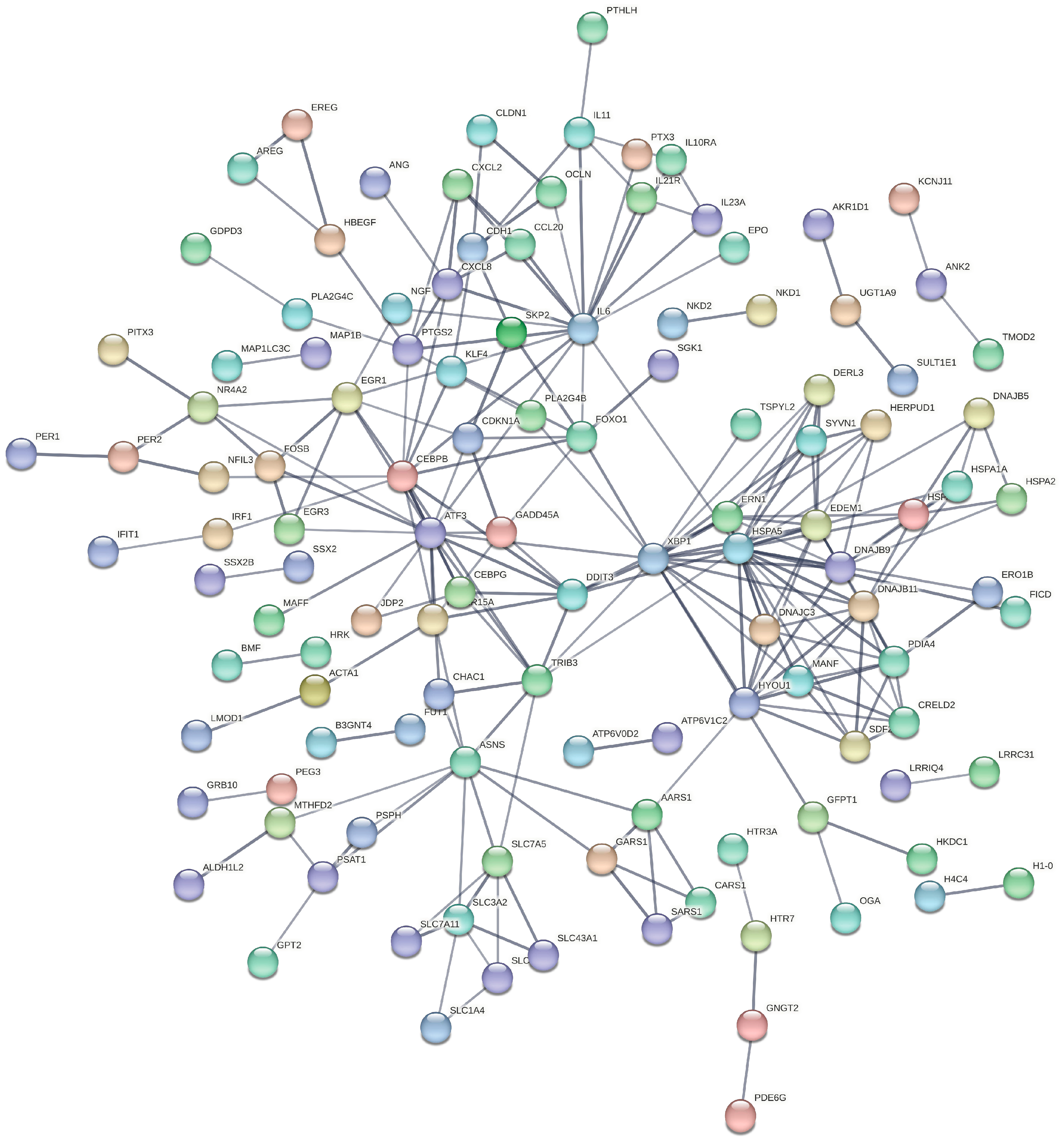
3.5. Construction of PPI Network
3.6. Validation of DEGs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.R.; Pearle, M.S.; Robertson, W.G.; Gambaro, G.; Canales, B.K.; Doizi, S.; Traxer, O.; Tiselius, H.G. Kidney stones. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, N. Crystal-membrane interaction in kidney stone disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1994, 5, S37–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.R. Crystal-induced inflammation of the kidneys: Results from human studies, animal models, and tissue-culture studies. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2004, 8, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, K.P.; Narula, S.; Kakkar, M.; Tandon, C. Nephrolithiasis: Molecular mechanism of renal stone formation and the critical role played by modulators. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 292953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, D.C.; Ares, M., Jr.; Hannon, G.J.; Nilsen, T.W. Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2010, 2010, pdb.prot5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.A.; Clark, J.; Ireland, A.; Lomax, J.; Ashburner, M.; Foulger, R.; Eilbeck, K.; Lewis, S.; Marshall, B.; Mungall, C.; et al. The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D258–D261. [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Hamamoto, S.; Okada, A.; Unno, R.; Kamisawa, H.; Naiki, T.; Ando, R.; Mizuno, K.; Kawai, N.; Tozawa, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Gene Expression Profiling of Randall’s Plaques in Calcium Oxalate Stone Formers. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. From endoplasmic-reticulum stress to the inflammatory response. Nature 2008, 454, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Zhang, K.; Kaufman, R.J. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.; Schröder, M. The Unfolded Protein Response: An Overview. Biology 2021, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Lerner, A.G.; Vande Walle, L.; Upton, J.P.; Xu, W.; Hagen, A.; Backes, B.J.; Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R. IRE1alpha kinase activation modes control alternate endoribonuclease outputs to determine divergent cell fates. Cell 2009, 138, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.J.; Kopp, M.C.; Larburu, N.; Nowak, P.R.; Ali, M.M.U. Structure and Molecular Mechanism of ER Stress Signaling by the Unfolded Protein Response Signal Activator IRE1. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Bertolotti, A.; Zeng, H.; Ron, D. Perk is essential for translational regulation and cell survival during the unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yu, H.; Ding, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Fu, R. Molecular mechanism of ATF6 in unfolded protein response and its role in disease. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnain, S.Z.; Lourie, R.; Das, I.; Chen, A.C.; McGuckin, M.A. The interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.V.; Peel, A.; Logvinova, A.; del Rio, G.; Hermel, E.; Yokota, T.; Goldsmith, P.C.; Ellerby, L.M.; Ellerby, H.M.; Bredesen, D.E. Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program: Role of the ER chaperone GRP78. FEBS Lett. 2002, 514, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S. The ER chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78/BiP as a monitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Methods 2005, 35, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek, A.; Benita, S.; Kumari, M.; Ganesan, D.; Paul, E.; Sasikumar, P.; Mahesh, A.; Yuvaraj, S.; Ramprasath, T.; Selvam, G.S. Molecular analysis of oxalate-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis in the pathogenesis of kidney stone disease. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 73, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Naura, A.S.; Singla, S.K. Modulatory effect of 4-phenyl butyric acid on hyperoxaluria-induced renal injury and inflammation. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 451, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, R.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kaur, T. Amelioration of hyperoxaluria-induced kidney dysfunction by chemical chaperone 4-phenylbutyric acid. Urolithiasis 2019, 47, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Naura, A.S.; Singla, S.K. A deleterious interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and its functional linkage to mitochondria in nephrolithiasis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 168, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kang, J.; Tao, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Guan, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y. Effect of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated excessive autophagy on apoptosis and formation of kidney stones. Life Sci. 2020, 244, 117232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kang, J.; Guan, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y. Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress on the damage and apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells induced by calcium oxalate crystals. Urolithiasis 2021, 49, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, R.R.; Prescott, E.T.; Sylvester, C.F.; Higdon, A.N.; Shan, J.; Kilberg, M.S.; Mungrue, I.N. Human CHAC1 Protein Degrades Glutathione, and mRNA Induction Is Regulated by the Transcription Factors ATF4 and ATF3 and a Bipartite ATF/CRE Regulatory Element. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15878–15891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungrue, I.N.; Pagnon, J.; Kohannim, O.; Gargalovic, P.S.; Lusis, A.J. CHAC1/MGC4504 is a novel proapoptotic component of the unfolded protein response, downstream of the ATF4-ATF3-CHOP cascade. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Tang, Z.; Mo, F.; Li, X.C.; Mao, H.; Wei, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Crosstalk between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Oxidative Stress in Heat Exposure-Induced Apoptosis Is Dependent on the ATF4-CHOP-CHAC1 Signal Pathway in IPEC-J2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 15495–15511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, D.; Fu, Q.; Hao, S.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, S.; Sheng, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; et al. CHAC1 as a Novel Contributor of Ferroptosis in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells with Oxidative Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.S.; Lu, X.H.; Xiao, Y.C.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ding, T.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; et al. ATF4- and CHOP-dependent induction of FGF21 through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 807874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Cui, Z.; Yao, D.; Huang, Z.; Xu, M.; Chen, M.; et al. FGF21 attenuates hypoxia-induced dysfunction and apoptosis in HPAECs through alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, M.J.; Back, S.H.; Konishi, M.; Itoh, N.; Lee, M.S. Fibroblast growth factor 21 participates in adaptation to endoplasmic reticulum stress and attenuates obesity-induced hepatic metabolic stress. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Yang, M.; Chen, H.; He, C.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Zhuo, J.; Lin, Z.; Hu, Z.; Lu, D.; et al. FGF21-mediated autophagy: Remodeling the homeostasis in response to stress in liver diseases. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample Name | Total Reads | Total Mapped (%) | Uniquely Mapped (%) | Multiple Mapped (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl_1 | 47,390,414 | 45,949,461 (96.96%) | 41,796,275 (88.20%) | 4,153,186 (8.76%) |
| Ctrl_2 | 42,219,656 | 41,042,552 (97.21%) | 37,366,844 (88.51%) | 3,675,708 (8.71%) |
| Ctrl_3 | 49,909,816 | 48,541,929 (97.26%) | 43,884,870 (87.93%) | 4,657,059 (9.33%) |
| COM_1 | 50,143,150 | 48,635,137 (96.99%) | 44,239,250 (88.23%) | 4,395,887 (8.77%) |
| COM_2 | 43,001,784 | 41,721,455 (97.02%) | 37,877,062 (88.08%) | 3,844,393 (8.94%) |
| COM_3 | 47,134,688 | 45,793,724 (97.16%) | 41,409,278 (87.85%) | 4,384,446 (9.30%) |
| ERS-Related DEGs | Our RNA-Seq Data | Public Dataset GSE73680 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log2 FC (the COM Groups Versus the Control Group) | p-Value | Log2 FC (CaOx Renal Papillary Tissues Versus Normal Renal Papillary Tissues) | p-Value | |
| ATF3 | 3.7524 | 0.000000 | −0.0216 | 0.972784 |
| CEBPB | 1.0315 | 0.000000 | −0.6940 | 0.165201 |
| CHAC1 | 2.6641 | 0.000003 | 1.1802 | 0.001305 |
| CTH | 2.2632 | 0.000000 | 0.0204 | 0.959321 |
| CXCL8 | 1.7993 | 0.000000 | 0.4042 | 0.655936 |
| DDIT3 | 3.5863 | 0.000000 | −0.7056 | 0.048815 |
| DERL3 | 1.9735 | 0.000000 | 0.6974 | 0.038880 |
| DNAJB9 | 2.572 | 0.000000 | −0.6196 | 0.048469 |
| DNAJC3 | 1.7623 | 0.000000 | 0.1448 | 0.559762 |
| EDEM1 | 1.0806 | 0.000000 | −0.2502 | 0.539455 |
| ERN1 | 2.5113 | 0.000000 | 0.0381 | 0.884129 |
| FGF21 | 5.632 | 0.000253 | 1.4001 | 0.003260 |
| FICD | 2.0538 | 0.000000 | 0.2295 | 0.441651 |
| HERPUD1 | 3.2536 | 0.000000 | −0.8134 | 0.020813 |
| HSPA1A | −1.0059 | 0.000000 | −0.8592 | 0.020964 |
| HSPA5 | 2.479 | 0.000000 | −0.7918 | 0.040477 |
| HYOU1 | 1.7581 | 0.000000 | −0.0876 | 0.719632 |
| MANF | 1.8644 | 0.000000 | −0.1799 | 0.520851 |
| NUPR1 | 1.9967 | 0.000000 | −0.7957 | 0.069520 |
| PDIA4 | 1.008 | 0.000000 | −0.2344 | 0.521433 |
| PPP1R15A | 2.2295 | 0.000000 | −0.4684 | 0.405668 |
| SDF2L1 | 2.5809 | 0.000000 | 0.2598 | 0.420405 |
| SELENOK | 1.0897 | 0.000000 | −0.2884 | 0.263865 |
| SESN2 | 2.0397 | 0.000000 | 0.1554 | 0.538660 |
| STC2 | 1.3444 | 0.000000 | 0.3658 | 0.391225 |
| SYVN1 | 1.3592 | 0.000000 | −0.7824 | 0.064149 |
| TRIB3 | 2.6531 | 0.000000 | 0.6137 | 0.101077 |
| XBP1 | 1.5692 | 0.000000 | −0.1643 | 0.697346 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.-Y.; Miao, L.-T.; Qin, B.-L. The Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress during the Interaction between Calcium Oxalate Crystals and Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Biology 2024, 13, 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100774
Hong S-Y, Miao L-T, Qin B-L. The Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress during the Interaction between Calcium Oxalate Crystals and Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Biology. 2024; 13(10):774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100774
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Sen-Yuan, Lin-Tao Miao, and Bao-Long Qin. 2024. "The Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress during the Interaction between Calcium Oxalate Crystals and Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells" Biology 13, no. 10: 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100774
APA StyleHong, S.-Y., Miao, L.-T., & Qin, B.-L. (2024). The Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress during the Interaction between Calcium Oxalate Crystals and Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Biology, 13(10), 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13100774






