Effects of Doxycycline Treatment on Hematological Parameters, Viscosity, and Cytokines in Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
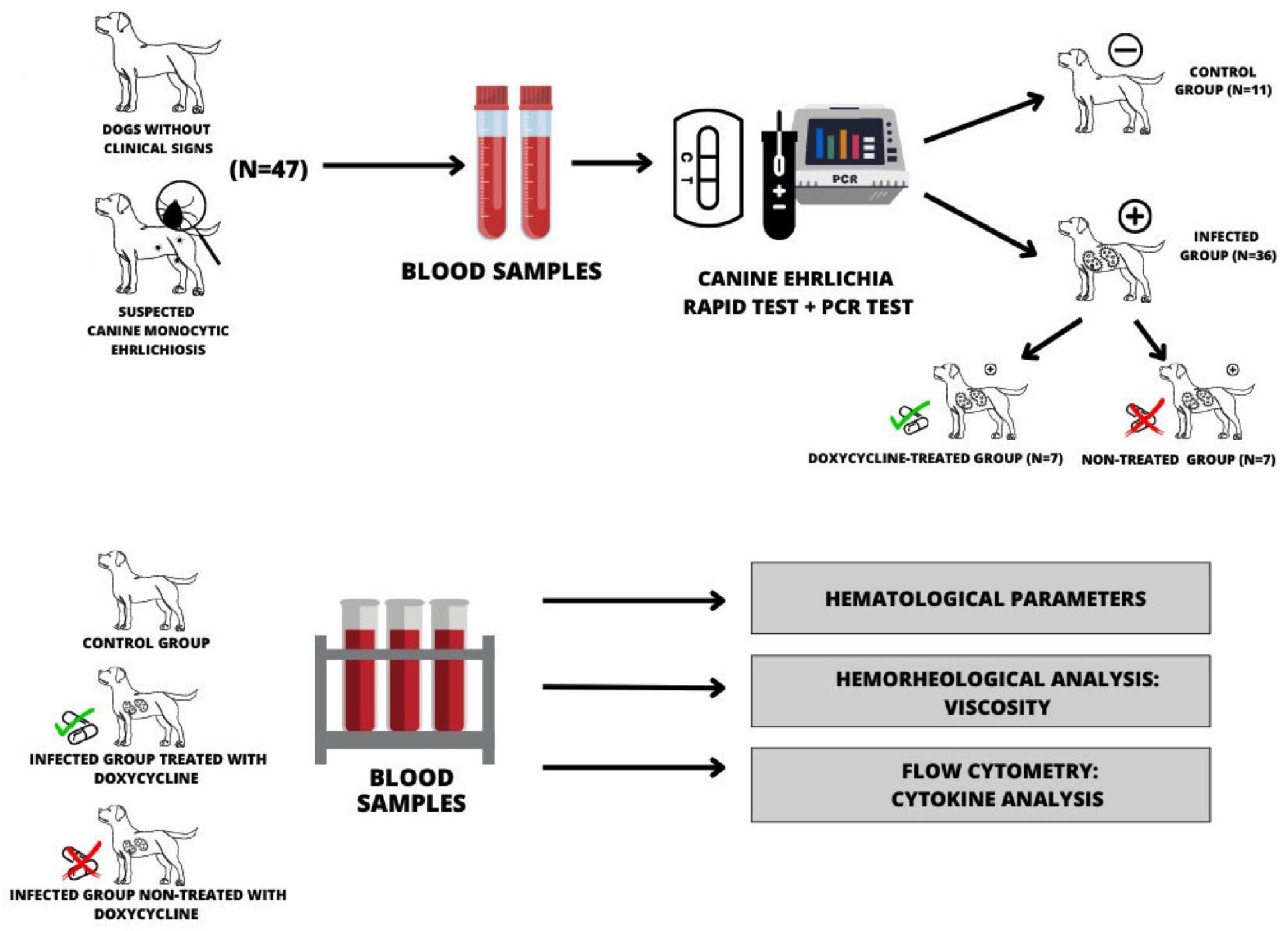
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Serological Tests
2.3. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.4. Hematological Parameters
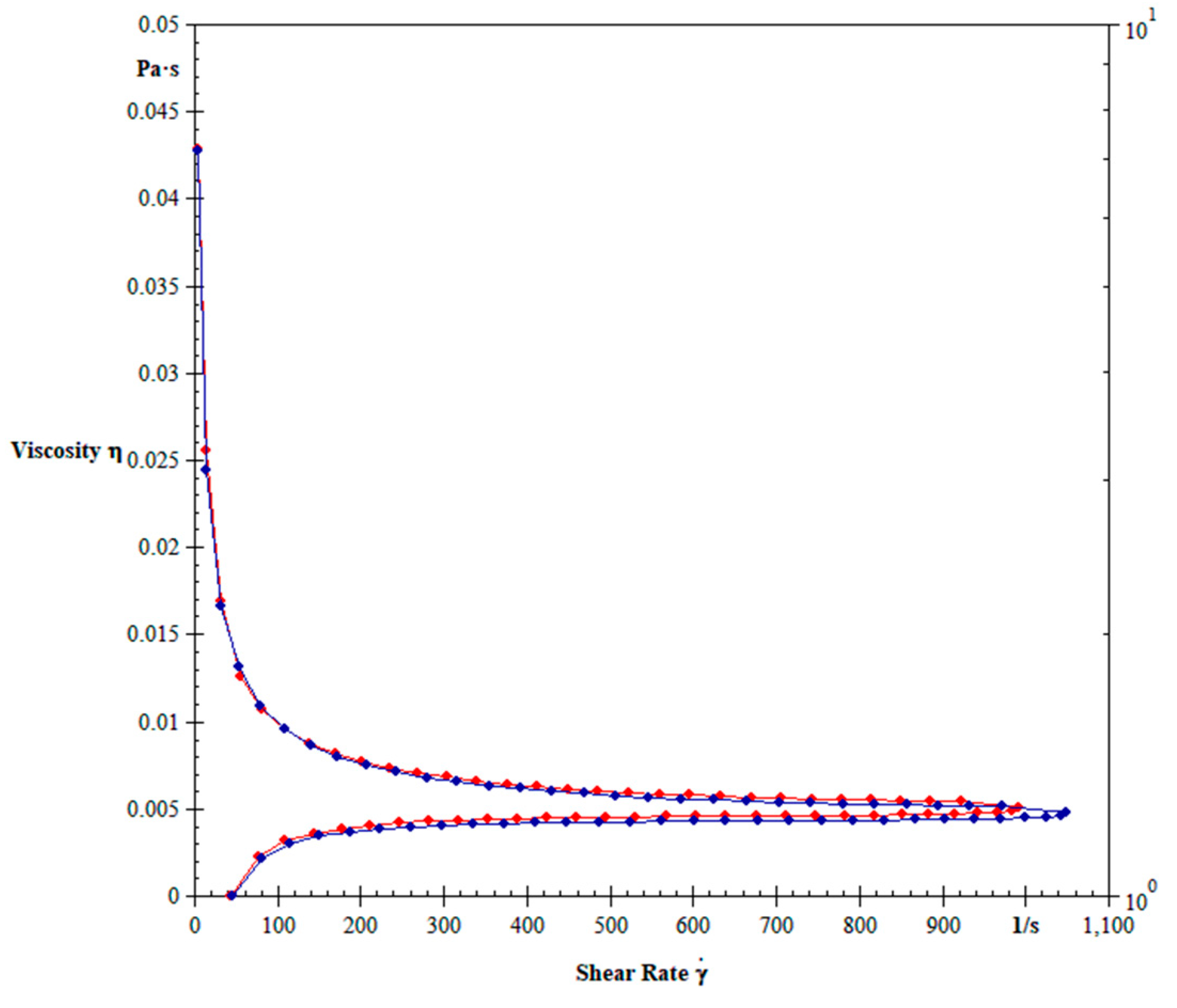
2.5. Hemorheological Parameters
2.6. Cytokines
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sainz, Á.; Roura, X.; Miró, G.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Kohn, B.; Harrus, S.; Solano-Gallego, L. Guideline for Veterinary Practitioners on Canine Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis in Europe. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavromatis, K.; Doyle, C.K.; Lykidis, A.; Ivanova, N.; Francino, M.P.; Chain, P.; Shin, M.; Malfatti, S.; Larimer, F.; Copeland, A.; et al. The Genome of the Obligately Intracellular Bacterium Ehrlichia canis Reveals Themes of Complex Membrane Structure and Immune Evasion Strategies. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 4015–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, P.E.B.; De Andrade Oliveira, T.N.; Carvalho, F.S.; Carlos, R.S.A.; Albuquerque, G.R.; Munhoz, A.D.; Wenceslau, A.A.; Silva, F.L. Canine Ehrlichiosis: Prevalence and Epidemiology in Northeast Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2015, 24, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula, W.V.d.F.; Taques, Í.I.G.G.; Miranda, V.C.; Barreto, A.L.G.; de Paula, L.G.F.; Martins, D.B.; Damasceno, A.D.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Sevá, A.P.; Dantas-Torres, F.; et al. Seroprevalence and Hematological Abnormalities Associated with Ehrlichia canis in Dogs Referred to a Veterinary Teaching Hospital in Central-Western Brazil. Cienc. Rural 2022, 52, e20201131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.F.C.; Biondo, A.W.; Guimarães, M.A.S.; Santos, A.P.; Santos, R.P.; Dutra, L.H.; Diniz, P.P.V.P.; Morais, H.A.; Messick, J.B.; Labruna, M.B.; et al. Ehrlichiosis in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2011, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Figueredo, L.A.; Sales, K.G.S.; Miranda, D.E.O.; Alexandre, J.L.A.; Silva, Y.Y.; Silva, L.G.; Valle, G.R.; Ribeiro, V.M.; Otranto, D.; et al. Prevalence and incidence of vector-borne pathogens in unprotected dogs in two Brazilian regions. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, T.A.; Maerle, M.O.; Witter, R.; Meneguzzi, M.; Melo, A.L.T.; Nakazato, L.; Dutra, V.; Aguiar, D.M.; Pacheco, R.C. Serological and molecular survey of tick-borne pathogens among dogs in Northern Brazil. Arch. Vet. Sci. 2021, 26, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakant, R.K.; Verma, H.C.; Diwakar, R.P. Canine ehrlichiosis: A review. J. Entomol. Zool. 2020, 8, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Mylonakis, M.E.; Theodorou, K.N. Canine monocytic ehrlichiosis: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Act. Vet. 2017, 67, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonakis, M.E.; Koutinas, A.F.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Hegarty, B.C.; Billinis, C.D.; Leontides, L.S.; Kontos, V.S. Chronic canine ehrlichiosis (Ehrlichia canis): A retrospective study of 19 natural cases. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2004, 40, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, T.T.; Farris, T.; Luo, T.; Mitra, S.; Zhu, B.; McBride, J.W. Hacker within! Ehrlichia chaffeensis Effector Driven Phagocyte Reprogramming Strategy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palacios, M.; Arteaga, R.; Calvo, G. High-Dose Filgrastim Treatment of Nonregenerative Pancytopenia Associated With Chronic Canine Ehrlichiosis. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2017, 32, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Gutiérrez-Grajales, E.J.; Osorio-Navia, D.; Chacón-Peña, M.; Trejos-Mendoza, A.E.; Pérez-Vargas, S.; Valencia-Mejía, L.; MarínArboleda, L.F.; Martínez-Hidalgo, J.P.; Reina-Mora, M.A.; et al. Hematological Alterations Associated with Selected Vector-Borne Infections and Exposure in Dogs from Pereira, Risaralda, Colombia. Animals 2022, 12, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.N.; Cotrim, A.C.; Conceição, L.A.V.; Marins, C.M.F.; Marchi, P.G.F.; Honório-França, A.C.; Almeida, A.B.P.F.; França, E.L.; Sousa, V.R.F. Immunohaematological and rheological parameters in canine visceral leishmaniasis. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2018, 27, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhas, Y.; Banerjee, J.; Mishra, N. Blood Viscosity, Glycemic Markers and Blood Pressure: A Study in Middle-Aged Normotensive and Hypertensive Type 2 Diabetics. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 35, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutzouri, A.G.; Athanassiou, G.A.; Dimitropoulou, D.; Skoutelis, A.T.; Gogos, C.A. Severe Sepsis and Diabetes Mellitus Have Additive Effects on Red Blood Cell Deformability. J. Infect. 2008, 57, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, E.L.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Scherer, E.F.; Cantarini, D.G.; Pessôa, R.S.; França, F.L.; Honório-França, A.C. Effects of Momordica charantia L. on the blood rheological properties in diabetic patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 840379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.P.; Paludo, G.R.; Silva, J.N.; Honório-França, A.C.; França, E.L. Hemorheological Evaluation and Cytokine Production in Dogs Naturally Infected with Anaplasmataceae. In Parasitology and Microbiology Research, 1st ed.; Pacheco, G.A.B., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrales, P.; Intaglietta, M.; Tsai, A.G. Increased plasma viscosity sustains microcirculation after resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock and continuous bleeding. Shock 2005, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrales, P.; Tsai, A.G.; Intaglietta, M. Is resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock limited by blood oxygen-carrying capacity or blood viscosity? Shock 2007, 27, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, E.F.; Cantarini, D.G.; Siqueira, R.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Braga, É.M.; Honório-França, A.C.; França, E.L. Cytokine Modulation of Human Blood Viscosity from Vivax Malaria Patients. Acta Trop. 2016, 158, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza-Perea, M.; Kumthekar, S.M.; Sabarinath, A.; Karpathy, S.E.; Sharma, R.N.; Stone, D.M. Doxycycline treatment of asymptomatic dogs seropositive for Ehrlichia canis. West Indian Vet. J. 2009, 9, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- McClure, J.C.; Crothers, M.L.; Schaefer, J.J.; Stanley, P.D.; Needham, G.R.; Ewing, S.A.; Stich, R.W. Efficacy of a doxycycline treatment regimen initiated during three different phases of experimental ehrlichiosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5012–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourie, J.J.; Horak, I.; Crafford, D.; Erasmus, H.L.; Botha, O.J. The Efficacy of a generic doxycycline tablet in the treatment of canine monocytic ehrlichiosis. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2015, 86, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonakis, M.E.; Harrus, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. An update on the treatment of canine monocytic ehrlichiosis (Ehrlichia canis). Vet. J. 2019, 246, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; 2100p. [Google Scholar]
- Quaresma, P.F.; Murta, S.M.; Ferreira, E.C.; Rocha-Lima, A.C.; Xavier, A.A.; Gontijo, C.M. Molecular diagnosis of canine visceral leishmaniasis: Identification of Leishmania species by PCR-RFLP and quantification of parasite DNA by real-time PCR. Acta Trop. 2009, 111, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolovschi, C.; Gomez, J.; Marié, J.L.; Davoust, B.; Guigal, P.M.; Raoult, D.; Parolla, P. Ehrlichia canis in Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks in the Ivory Coast. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirois, M. Automated Analyzers. In Laboratory Procedures for Veterinary Technicians, 7th ed.; Sirois, M., Ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzi, T.E.; Meinkoth, J.H.; Clinkenbeard, K.D. Normal hematology of the dog. In Schalm’s Veterinary Hematology and Clinical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Weiss, D.J., Wardrop, K.J., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Ames, IA, USA, 2010; pp. 799–810. [Google Scholar]
- Parashar, R.; Sudan, V.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Srivastava, A.; Shanker, D. Evaluation of clinical, biochemical and hematological markers in natural infection of canine monocytic ehrlichiosis. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, E.R.; Silva, W.M.; Teixeira, M.N.; da Silva, V.C.L.; Marinho, M.L.; van der Linden, L.A.; Oliveira, R.A.S. Clinical and laboratory aspects in dogs naturally infected with Ehrlichia canis. Braz. J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2021, 4, 3471–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shropshire, S.; Olver, C.; Lappin, M. Characteristics of hemostasis during experimental Ehrlichia canis infection. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.; Waner, T. Diagnosis of canine monocytotropic ehrlichiosis (Ehrlichia canis): An overview. Vet. J. 2011, 187, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrus, S.; Waner, T.; Aizenberg, I.; Bark, H. Therapeutic effect of doxycycline in experimental subclinical canine monocytic ehrlichiosis: Evaluation of a 6-week course. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2140–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, D.M.; Rodrigues, F.P.; Ribeiro, M.G.; Santos, B.; Muraro, L.S.; Taques, I.I.G.G.; Campos, A.N.S.; Dutra, V.; Nakazato, L.; da Costa Vieira, R.F.; et al. Uncommon Ehrlichia canis Infection Associated with Morulae in Neutrophils from Naturally Infected Dogs in Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaescusa, A.; García-Sancho, M.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Tesouro, M.; Sainz, T. Effects of Doxycycline on Haematology, Blood Chemistry and Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte Subsets of Healthy Dogs and Dogs Naturally Infected with Ehrlichia canis. Vet. J. 2015, 204, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadesiya, C.M.; Raval, S.K. Hematobiochemical Changes in Ehrlichiosis in Dogs of Anand Region, Gujarat. Vet. World 2015, 8, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.C.T.; Santos, J.R.S.; Silva, R.M.N.; Santana, V.L.; Martins, F.S.M.; Falcão, B.M.R.; Tanikawa, A.; Almeida, T.M.; Vaz, A.F.M.; Souza, A.P. Prednisolone Associated with Doxycycline on the Hematological Parameters and Serum Proteinogram of Dogs with Ehrlichiosis. Cienc. Rural 2021, 51, e20200335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.N.; Shobhamani, B.; Rao, V.; Subramanyam, K.V. Comparative Efficacy of Doxycycline and Imidocarb Diprionate in Treatment of Ehrlichiosis in Dogs. J. Pharm. Innov. 2022, 11, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Nader, E.; Skinner, S.; Romana, M.; Fort, R.; Lemoine, N.; Guillot, N.; Gauthier, A.; Antoine-Jonville, S.; Renoux, C.; Hardy-Dessources, M.D.; et al. Blood Rheology: Key Parameters, Impact on Blood Flow, Role in Sickle Cell Disease and Effects of Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.L.M.; Munhoz, T.D.; João, C.F.; Vargas-Herández, G.; André, M.R.; Pereira, W.A.B.; Machado, R.Z.; Tinucci-Costa, M. Ehrlichia canis (Jaboticabal strain) induces the expression of TNF-α in leukocytes and splenocytes of experimentally infected dogs. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2011, 20, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Stevenson, H.L.; Walker, D.H. Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) and Interleukin-10 in the Pathogenesis of Severe Murine Monocytotropic Ehrlichiosis: Increased Resistance of TNF Receptor P55- and P75-Deficient Mice to Fatal Ehrlichial Infection. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.L.; Santos, G.J.L.; Roatt, B.M.; Reis, A.B.; Freitas, J.C.C.; Nunes-Pinheiro, D.C.S. Serum TNF-α and IL-10 in Ehrlichia spp. naturally infected dogs. Act. Sci. Vet. 2015, 43, 1322. [Google Scholar]
- Dastjerdi, A.V.; Torkan, S.; Jafarian, M. Evaluation of the immunological changes in the use of Sumac herb powder (Rhus coriaria) compared with Levamisole in dogs. J. Herb. Drug 2018, 9, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Tang, Y.; Hua, S. Immunological approaches towards cancer and inflammation: A cross-talk. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.; Kanneganti, T.D. Function and regulation of IL-1α in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leisewitz, A.; Goddard, A.; De Gier, J.; Van Engelshoven, J.; Clift, S.; Thompson, P.; Schoeman, J.P. Disease Severity and Blood Cytokine Concentrations in Dogs with Natural Babesia rossi Infection. Parasite Immunol. 2019, 41, e12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.O.; Costa, S.F.; Souza, F.S.; Mendes, J.M.F.; Pinheiro, C.G.M.; Moreira, D.R.M.; Silva, L.K.; Lima, V.M.F.; Oliveira, G.G.S. Blocking IL-10 signaling with soluble IL-10 receptor restores in vitro specific lymphoproliferative response in dogs with leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania infantum. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0239171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, A.S.; Reid, H.L.; Greenidge, A.; Landis, C.; Reid, M. Blood Viscosity and the Expression of Inflammatory and Adhesion Markers in Homozygous Sickle Cell Disease Subjects with Chronic Leg Ulcers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H. White blood cell and platelet counts could affect whole blood viscosity. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2004, 67, 394–397. [Google Scholar]
- Nakaghi, A.C.H.; Machado, R.Z.; Costa, M.T.; André, M.R.; Baldine, C.D. Canine ehrlichiosis: Clinical, hematological, serological, and molecular aspects. Cienc. Rural 2008, 38, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, P.P.V.P.; Aguiar, D.M. Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis: An Update. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2022, 52, 1225–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | E. canis (-) | E. canis (+) | E. canis (+) Doxycycline | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erythrocytes (106/μL) | 6.42 ± 1.82 | 5.73 ± 2.08 | 5.69 ± 1.64 | 0.9545 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.72 ± 3.98 | 13.23 ± 5.36 | 14.06 ± 3.86 | 0.8443 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 43.36 ± 11.85 | 37.58 ± 14.29 | 38.73 ± 11.06 | 0.8654 |
| Leukocytes (103/μL) | 10.27 ± 2.98 a | 8.36 ± 2.49 b | 8.70 ± 3.81 b | 0.0119 |
| Neuthrophils (103/μL) | 6.32 ± 2.21 | 6.88 ± 2.61 | 6.35 ± 2.98 | 0.5564 |
| Lymphocytes (103/μL) | 2.84 ± 1.98 a | 1.25 ± 0.79 b | 1.31 ± 0.77 b | 0.0086 |
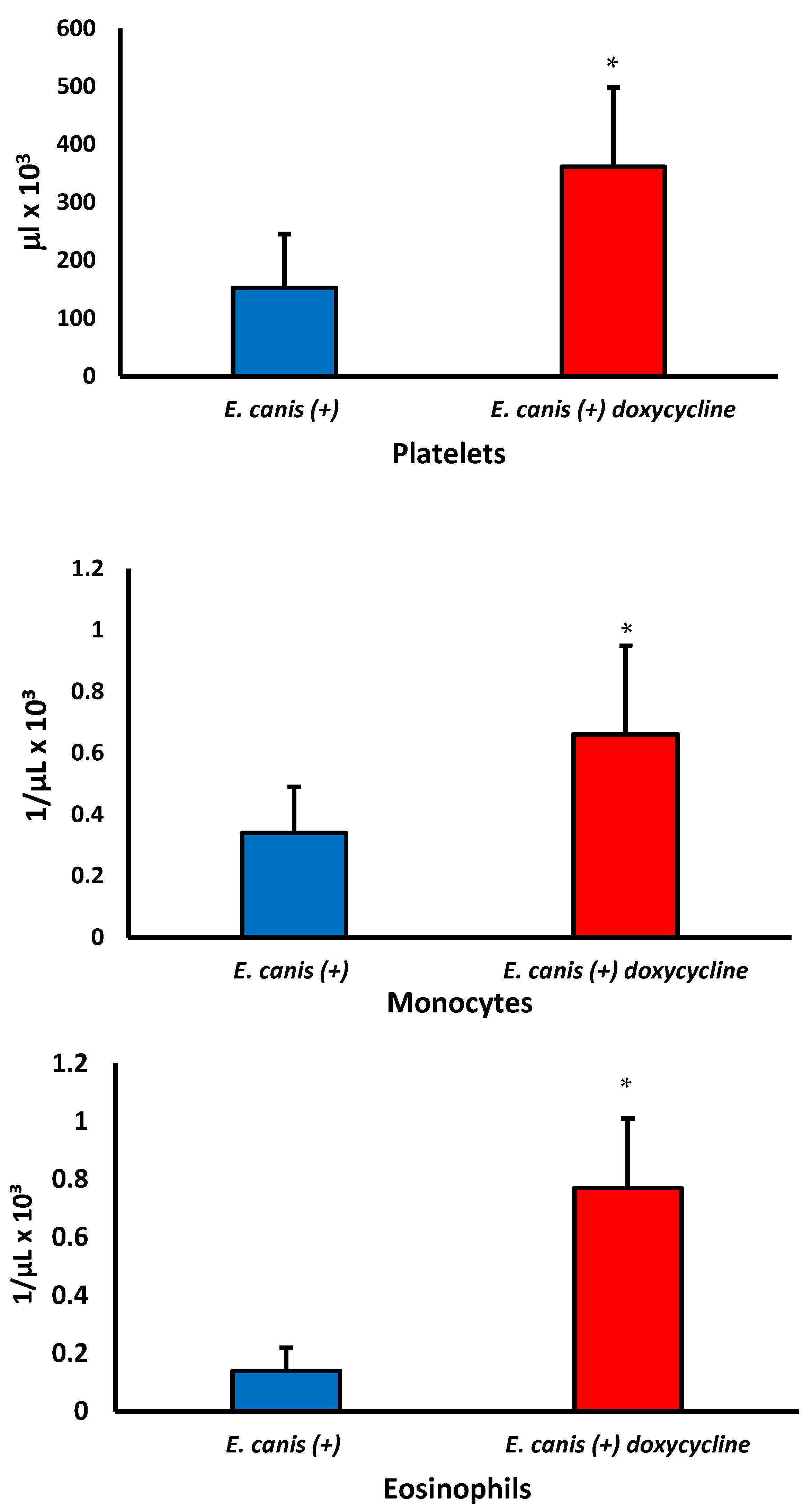
| Monocytes (103/μL) | 0.33 ± 0.12 a | 0.30 ± 0.21 a | 0.64 ± 0.36 b | 0.0257 |
| Eosinophils (103/μL) | 0.67 ± 0.78 a | 0.26 ± 0.28 b | 0.60 ± 0.36 a | 0.0290 |
| Platelets (103μL) | 211.90 ± 161.28 a | 183.68 ± 113.72 b | 298.26 ± 178.50 c | 0.0124 |
| Cytokines (pg/mL) | E. canis (-) | E. canis (+) | E. canis (+) Doxycycline | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 25.59 ± 8.61 | 56.72 ± 24.75 a | 55.38 ± 30.76 a | 0.0150 |
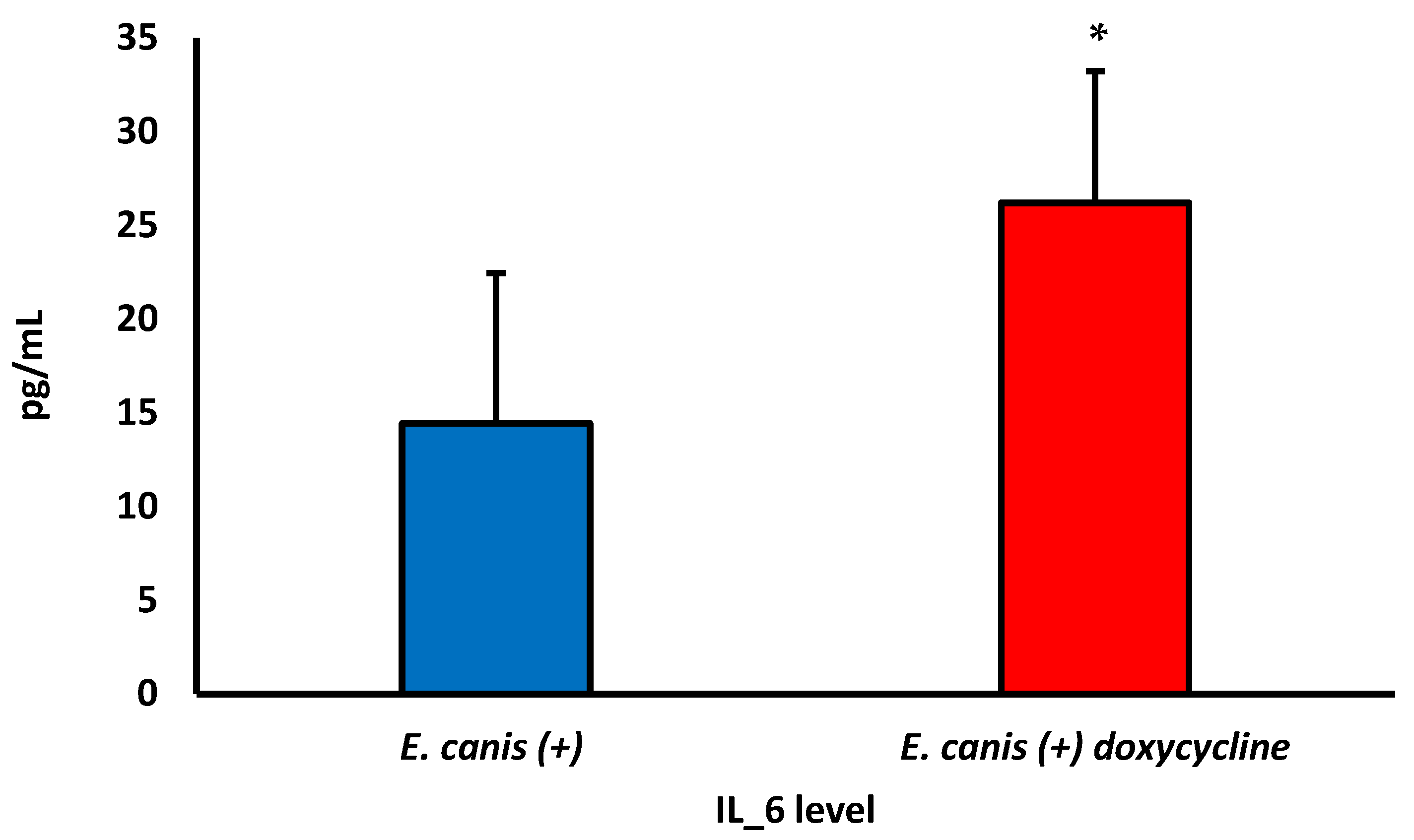
| IL-6 | 28.66 ± 14.04 | 14.42 ± 8.03 | 23.63 ± 13.85 | 0.1588 |
| IL-8 | 20.40 ± 3.60 | 31.17 ± 20.51 | 33.95 ± 22.62 | 0.5416 |
| IL-10 | 34.39 ± 12.60 | 30.46 ± 30.59 | 46.83 ± 26.45 | 0.3815 |
| IL-12 | 28.38 ± 9.16 | 32.47 ± 11.97 | 25.24 ± 8.86 | 0.4985 |
| TNF-α | 589.75 ± 197.56 a | 32.97 ± 37.09 b | 340.40 ± 26.65 c | 0.0001 |
| Parameters | Group | IL-1β | IL-6 | IL-8 | IL-10 | IL-12 | TNF-α | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. canis | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| Erythrocytes | negative | −0.024 | 0.958 | −0.270 | 0.420 | −0.619 | 0.138 | −0.457 | 0.157 | 0.134 | 0.773 | −0.118 | 0.728 |
| positive | −0.248 | 0.591 | −0.190 | 0.683 | −0.711 | 0.073 | −0.244 | 0.597 | −0.738 | 0.057 | −0.660 | 0.106 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.324 | 0.477 | 0.156 | 0.738 | −0.166 | 0.722 | 0.681 | 0.092 | 0.101 | 0.828 | 0.142 | 0.760 | |
| Hematocrit | negative | 0.073 | 0.875 | −0.528 | 0.094 | −0.579 | 0.172 | −0.466 | 0.148 | 0.121 | 0.795 | −0.122 | 0.719 |
| positive | −0.360 | 0.427 | −0.166 | 0.720 | −0.745 | 0.054 | −0.316 | 0.488 | −0.783 | 0.037 * | −0.726 | 0.064 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.578 | 0.173 | −0.165 | 0.722 | 0.057 | 0.902 | 0.668 | 0.100 | 0.219 | 0.637 | −0.113 | 0.808 | |
| Hemoglobin | negative | 0.063 | 0.892 | −0.489 | 0.126 | −0.651 | 0.112 | −0.464 | 0.150 | 0.057 | 0.903 | −0.062 | 0.855 |
| positive | −0.233 | 0.613 | −0.061 | 0.896 | −0.559 | 0.191 | −0.121 | 0.795 | −0.623 | 0.131 | −0.654 | 0.110 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.519 | 0.231 | −0.172 | 0.711 | −0.019 | 0.967 | 0.678 | 0.093 | 0.239 | 0.604 | −0.111 | 0.812 | |
| Leukocytes | negative | 0.113 | 0.809 | 0.037 | 0.912 | −0.594 | 0.159 | 0.015 | 0.964 | 0.353 | 0.436 | −0.463 | 0.150 |
| positive | 0.215 | 0.642 | 0.472 | 0.284 | −0.278 | 0.545 | 0.506 | 0.298 | 0.148 | 0.751 | −0.095 | 0.838 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.500 | 0.252 | 0.243 | 0.599 | −0.145 | 0.755 | −0.757 | 0.048 * | 0.318 | 0.487 | 0.486 | 0.268 | |
| Neutrophils | negative | 0.080 | 0.863 | −0.152 | 0.654 | −0.162 | 0.727 | 0.224 | 0.506 | 0.282 | 0.539 | −0.396 | 0.227 |
| positive | 0.119 | 0.799 | 0.314 | 0.492 | −0.386 | 0.391 | 0.410 | 0.360 | 0.068 | 0.884 | −0.183 | 0.694 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.686 | 0.088 | 0.366 | 0.418 | −0.229 | 0.619 | −0.747 | 0.053 | 0.155 | 0.739 | 0.525 | 0.225 | |
| Monocytes | negative | 0.051 | 0.913 | 0.168 | 0.620 | −0.579 | 0.172 | 0.296 | 0.376 | −0.001 | 0.997 | −0.226 | 0.502 |
| positive | −0.234 | 0.613 | 0.022 | 0.961 | −0.075 | 0.871 | −0.466 | 0.291 | −0.273 | 0.552 | −0.004 | 0.992 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.753 | 0.050 | −0.337 | 0.459 | 0.191 | 0.681 | 0.2749 | 0.550 | 0.185 | 0.691 | −0.080 | 0.863 | |
| Lymphocytes | negative | −0.555 | 0.195 | 0.190 | 0.573 | 0.461 | 0.297 | 0.015 | 0.964 | 0.512 | 0.239 | −0.073 | 0.831 |
| positive | −0.021 | 0.963 | −0.257 | 0.577 | 0.187 | 0.686 | −0.399 | 0.374 | −0.233 | 0.614 | 0.123 | 0.792 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.313 | 0.493 | −0.368 | 0.416 | −0.077 | 0.868 | −0.201 | 0.664 | 0.692 | 0.084 | 0.095 | 0.838 | |
| Eosinophils | negative | 0.631 | 0.128 | 0.065 | 0.849 | −0.297 | 0.517 | 0.144 | 0.671 | −0.471 | 0.285 | −0.343 | 0.300 |
| positive | 0.506 | 0.246 | 0.388 | 0.389 | 0.177 | 0.703 | 0.523 | 0.227 | 0.784 | 0.036 * | 0.847 | 0.016 * | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.429 | 0.335 | −0.029 | 0.950 | −0.111 | 0.811 | −0.001 | 0.997 | −0.560 | 0.190 | 0.077 | 0.868 | |
| Platelets | negative | −0.184 | 0.692 | −0.040 | 0.906 | −0.388 | 0.388 | 0.240 | 0.645 | −0.090 | 0.846 | −0.035 | 0.918 |
| positive | −0.179 | 0.699 | −0.338 | 0.457 | −0.013 | 0.977 | −0.014 | 0.976 | −0.293 | 0.523 | −0.597 | 0.156 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.160 | 0.730 | −0.175 | 0.706 | 0.409 | 0.361 | 0.113 | 0.808 | −0.005 | 0.991 | −0.600 | 0.154 | |
| Cytokine | Group | Blood Viscosity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. canis | r | p | |
| IL-1β | negative | −0.195 | 0.673 |
| positive | −0.762 | 0.046 * | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.208 | 0.654 | |
| IL-6 | negative | 0.134 | 0.694 |
| positive | −0.082 | 0.860 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.044 | 0.924 | |
| IL-8 | negative | −0.395 | 0.379 |
| positive | −0.697 | 0.081 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.153 | 0.742 | |
| IL-10 | negative | 0.294 | 0.379 |
| positive | −0.797 | 0.031 * | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.882 | 0.019 * | |
| IL-12 | negative | 0.135 | 0.772 |
| positive | −0.838 | 0.018 * | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.598 | 0.155 | |
| TNF-α | negative | −0.930 | >0.001 * |
| positive | −0.672 | 0.097 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.142 | 0.760 | |
| Hematological Parameters | Group | Blood Viscosity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. canis | r | p | |
| Erythrocytes | negative | 0.022 | 0.946 |
| positive | 0.647 | 0.115 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.266 | 0.563 | |
| Hematocrit | negative | 0.026 | 0.939 |
| positive | 0.722 | 0.066 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.316 | 0.489 | |
| Hemoglobin | negative | −0.033 | 0.922 |
| positive | 0.558 | 0.192 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.350 | 0.441 | |
| Leukocytes | negative | 0.378 | 0.2504 |
| positive | −0.274 | 0.552 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.917 | 0.003 | |
| Neutrophils | negative | 0.351 | 0.289 |
| positive | −0.272 | 0.554 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.804 | 0.029 - | |
| Monocytes | negative | 0.269 | 0.423 |
| positive | 0.577 | 0.174 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.036 | 0.938 | |
| Lymphocytes | negative | 0.032 | 0.924 |
| positive | 0.439 | 0.324 | |
| positive + doxycycline | 0.523 | 0.228 | |
| Eosinophils | negative | 0.247 | 0.462 |
| positive | −0.541 | 0.209 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.578 | 0.173 | |
| Platelets | negative | 0.087 | 0.797 |
| positive | −0.180 | 0.699 | |
| positive + doxycycline | −0.332 | 0.465 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardoso, S.P.; Honorio-França, A.C.; França, D.C.H.; Silva, L.P.S.; Fagundes-Triches, D.L.G.; Neves, M.C.B.; Cotrim, A.C.d.M.; Almeida, A.d.B.P.F.d.; França, E.L.; Sousa, V.R.F. Effects of Doxycycline Treatment on Hematological Parameters, Viscosity, and Cytokines in Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis. Biology 2023, 12, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081137
Cardoso SP, Honorio-França AC, França DCH, Silva LPS, Fagundes-Triches DLG, Neves MCB, Cotrim ACdM, Almeida AdBPFd, França EL, Sousa VRF. Effects of Doxycycline Treatment on Hematological Parameters, Viscosity, and Cytokines in Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis. Biology. 2023; 12(8):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081137
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardoso, Saulo Pereira, Adenilda Cristina Honorio-França, Danielle Cristina Honorio França, Luana Paula Sales Silva, Danny Laura Gomes Fagundes-Triches, Maria Clara Bianchini Neves, Aron Carlos de Melo Cotrim, Arleana do Bom Parto Ferreira de Almeida, Eduardo Luzía França, and Valéria Régia Franco Sousa. 2023. "Effects of Doxycycline Treatment on Hematological Parameters, Viscosity, and Cytokines in Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis" Biology 12, no. 8: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081137
APA StyleCardoso, S. P., Honorio-França, A. C., França, D. C. H., Silva, L. P. S., Fagundes-Triches, D. L. G., Neves, M. C. B., Cotrim, A. C. d. M., Almeida, A. d. B. P. F. d., França, E. L., & Sousa, V. R. F. (2023). Effects of Doxycycline Treatment on Hematological Parameters, Viscosity, and Cytokines in Canine Monocytic Ehrlichiosis. Biology, 12(8), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081137







