MicroRNA (miR)-124: A Promising Therapeutic Gateway for Oncology
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biological Functions of miR-124
3. Role of miR-124 in Cancer
3.1. Neurological Cancers
3.2. Breast Cancer
3.3. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
3.4. Lung Cancer
3.5. Other Cancer Types
4. miR-124: Clinical Prospects
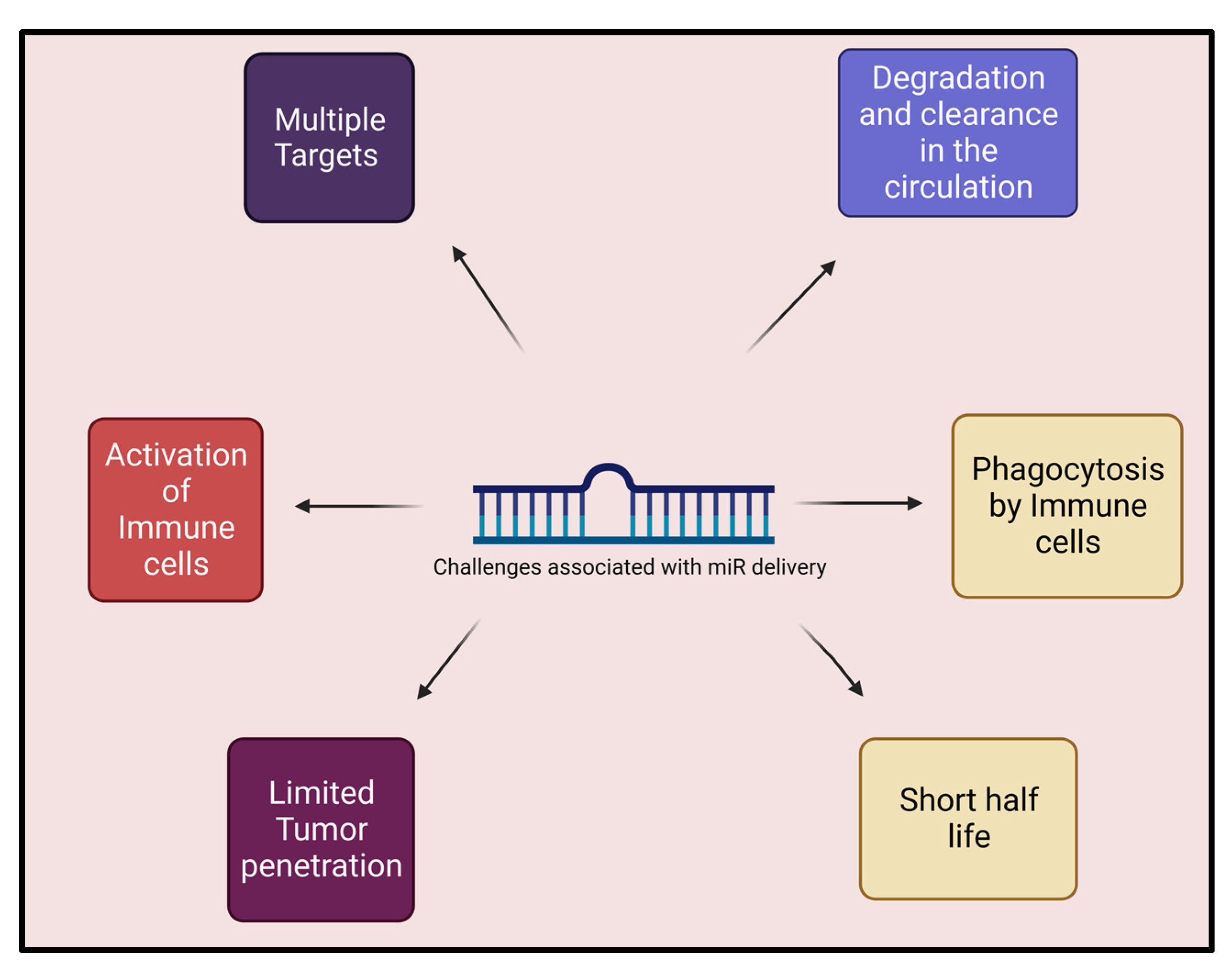
5. Hurdles and Challenges to Delivery of miR
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, Z.; Wang, P.Y.; Su, D.F.; Liu, X. miRNA-124 in Immune System and Immune Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Yalcin, A.; Meyer, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Tuschl, T. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerkova, K.; Hudcova, K.; Vlahova, V.; Vaculovicova, M.; Pekarik, V.; Masarik, M.; Adam, V.; Klzek, R. Label-free and amplification-free miR-124 detection in human cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 46, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Ji, J.; Lou, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, W.; Guo, M.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; et al. MicroRNA-124: An emerging therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 5638–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in Control of Gene Expression: An Overview of Nuclear Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Urrutia, E.; Bustamante Montes, L.P.; Ladrón de Guevara Cervantes, D.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Campos-Parra, A.D. Crosstalk Between Long Non-coding RNAs, Micro-RNAs and mRNAs: Deciphering Molecular Mechanisms of Master Regulators in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, L.; Höck, J.; Ivacevic, T.; Ohrt, T.; Mütze, J.; Schwille, P.; Kremmer, E.; Benes, V.; Urlaub, H.; Meister, G. Importin 8 is a gene silencing factor that targets argonaute proteins to distinct mRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, A.R.; Vizinha, D.; Morais, H.; Colaço, A.R.; Loch-Neckel, G.; Barbosa, M.; Brites, D. Overexpression of miR-124 in Motor Neurons Plays a Key Role in ALS Pathological Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, N.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, D.; Lin, R.; Wang, X.; Shi, B. Anticancer effects of miR-124 delivered by BM-MSC derived exosomes on cell proliferation, epithelial mesenchymal transition, and chemotherapy sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells. Aging 2020, 12, 19660–19676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, N.; Jia, B.; He, Y.; Luan, W.; Bao, W.; Han, X.; Gao, W.; Gao, Y.; Cha, N.; Jia, B.; et al. MicroRNA-124 suppresses the invasion and proliferation of breast cancer cells by targeting TFAP4. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pircs, K.; Petri, R.; Jakobsson, J. Crosstalk between MicroRNAs and Autophagy in Adult Neurogenesis: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Brain Plast. 2018, 3, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Dong, Z. Downregulation of miR-124 predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 73, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Hou, X.; Ren, G.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, H. Dynamic changes in miR-124 levels in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Int. J. Neurosci. 2019, 129, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Liu, X. miR-124, a potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanuki, R.; Yamamura, T. Tumor Suppressive Effects of miR-124 and Its Function in Neuronal Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottiers, V.; Naar, A.M. MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 13, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.A.; Singaravelu, R.; Powdrill, M.H.; Nhan, J.; Ahmed, N.; Ozcelik, D.; Pezacki, J.P. MicroRNA-124 Regulates Fatty Acid and Triglyceride Homeostasis. iScience 2018, 10, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Patil, N.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, iv1–iv96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarese, R.; Harsh, G.R.t.; Yadav, A.K.; Bug, E.; Maticzka, D.; Reichardt, W.; Dombrowski, S.M.; Miller, T.E.; Masilamani, A.P.; Dai, F.; et al. Lineage-specific splicing of a brain-enriched alternative exon promotes glioblastoma progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2861–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Kong, X.; Gong, S.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y. Recent advances of the regulation roles of MicroRNA in glioblastoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Soleimani, M. Delivery of Exogenous miR-124 to Glioblastoma Multiform Cells by Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Decreases Cell Proliferation and Migration, and Confers Chemosensitivity. Stem Cell. Rev. Rep. 2018, 14, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabelstrom, H.; Petri, R.; Shchors, K.; Jandial, R.; Schmidt, C.; Sacheva, R.; Masic, S.; Yuan, E.; Fenster, T.; Martinez, M.; et al. Driving Neuronal Differentiation through Reversal of an ERK1/2-miR-124-SOX9 Axis Abrogates Glioblastoma Aggressiveness. Cell. Rep. 2019, 28, 2064–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Finniss, S.; Cazacu, S.; Xiang, C.; Mikkelsen, T.; Poisson, L.; Shackelford, D.B.; Brodie, Z.; Brodie, C. Repurposing phenformin for the targeting of glioma stem cells and the treatment of glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56456–56470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.M.; Hossain, A.; Gumin, J.; Momin, E.N.; Shimizu, Y.; Ledbetter, D.; Shahar, T.; Yamashita, S.; Parker Kerrigan, B.; Fueyo, J.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as natural biofactories for exosomes carrying miR-124a in the treatment of gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, W.; Guo, B.; Zhou, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Dong, B. miR-124 suppresses glioblastoma growth and potentiates chemosensitivity by inhibiting AURKA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, M.F.; Yang, S.; Zhao, C.; Sun, G.; Murai, K.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, H.; Brown, C.E.; Liu, X.; et al. Genome-wide profiling identified a set of miRNAs that are differentially expressed in glioblastoma stem cells and normal neural stem cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, L.; Khan, A.A.; Li, B.; Gu, B.; Lin, F.; Su, X.; Yan, J. miRNA-124-3p/neuropilin-1(NRP-1) axis plays an important role in mediating glioblastoma growth and angiogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Luo, K.; Liu, H.; Nie, X.; Xue, L.; Wang, R.; Xu, Y.; Cui, J.; Shao, N.; Zhi, F. p62 acts as an oncogene and is targeted by miR-124-3p in glioma. Cancer Cell. Int. 2019, 19, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wen, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Yunzhi, L.; Peng, R.; Zhu, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; et al. miR-135a-5p and miR-124-3p Inhibit Malignancy of Glioblastoma by Downregulation of Syndecan Binding Protein. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Da Silva, A.; Arnold, A.; Okeke, L.; Ames, H.; Correa-Cerro, L.S.; Vizcaino, M.A.; Ho, C.Y.; Eberhart, C.G.; Rodriguez, F.J. MicroRNA (miR) 125b regulates cell growth and invasion in pediatric low grade glioma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Dai, J.X.; Pan, Y.B.; Ma, Y.B.; Chu, S.H. Identification of biomarkers and construction of a microRNA-mRNA regulatory network for ependymoma using integrated bioinformatics analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 6079–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneve, P.; Caffarelli, E. The Non-coding Side of Medulloblastoma. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharambe, H.S.; Paul, R.; Panwalkar, P.; Jalali, R.; Sridhar, E.; Gupta, T.; Moiyadi, A.; Shetty, P.; Kazi, S.; Deogharkar, A.; et al. Downregulation of miR-204 expression defines a highly aggressive subset of Group 3/Group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenga, A.; Beard, J.A.; Takwi, A.; Wang, Y.M.; Chen, T. Regulation of Nuclear Receptor Nur77 by miR-124. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.; Hummel, M.; Korfel, A.; Lenze, D.; Joehrens, K.; Thiel, E. Differential micro-RNA expression in primary CNS and nodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 13, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H.; Wang, E.L.; Zhou, H.M.; Yoshimoto, K.; Qian, Z.R. MicroRNAs in Human Pituitary Adenomas. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 435171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Xu, T.; Qiu, P.; Xu, G. Caveolin-1 promotes pituitary adenoma cells migration and invasion by regulating the interaction between EGR1 and KLF5. Exp. Cell. Res. 2018, 367, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hu, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ai, X.; Tang, L.; Xie, L. miR-124-3p acts as a potential marker and suppresses tumor growth in gastric cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2018, 9, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.S.; Cheah, Y.K. Potential miRNAs for miRNA-Based Therapeutics in Breast Cancer. Noncoding RNA 2020, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Han, X.; Tong, J.; Hua, Z. Evaluation of the Role of hsa-mir-124 in Predicting Clinical Outcome in Breast Invasive Carcinoma Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1839205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobini, K.; Banakar, E.; Tamaddon, G.; Mohammadi-Bardbori, A. 6-Formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) Enhances The Expression of Tumor Suppressor miRNAs, miR-22, miR-515-5p, and miR-124-3p in MCF-7 Cells. Cell. J. 2020, 22, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Xu, D.; Tu, C.; Li, W.; Ning, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, S.; Yuan, L.; Xu, N.; Qian, K.; et al. MiR-124 inhibits cell proliferation in breast cancer through downregulation of CDK4. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5987–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, S.; Mannsperger, H.; Zhang, J.D.; Horvat, E.A.; Schmidt, C.; Kublbeck, M.; Henjes, F.; Ward, A.; Tschulena, U.; Zweig, K.; et al. Global microRNA level regulation of EGFR-driven cell-cycle protein network in breast cancer. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2012, 8, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.L.; Chen, L.M.; Wang, W.M.; Zhang, L.M. Decreased expression of microRNA-124 is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor for patients with breast cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Song, G.Q.; Ma, Y.H.; Jin, X.H.; Jin, S.L.; Fang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.C. Interfering cellular lactate homeostasis overcomes Taxol resistance of breast cancer cells through the microRNA-124-mediated lactate transporter (MCT1) inhibition. Cancer Cell. Int. 2019, 19, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Splan, M.F.; Weiss, N.S.; McDonald, G.B.; Beretta, L.; Lee, S.P. Incidence and predictors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Jiang, F.; Zhuang, H.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, C. MicroRNA miR-124-3p suppresses proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma via ARRDC1 (arrestin domain containing 1). Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8255–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.B.; Wu, H.M.; He, Y.C.; Huang, Z.T.; Weng, Y.H.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Yu, W.M.; Chen, W. MiRNA-124-3p.1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib by regulating FOXO3a by targeting AKT2 and SIRT1. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, J. circHIPK3 regulates cell proliferation and migration by sponging miR-124 and regulating AQP3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.Q.; Dong, Y.W.; Wang, R.; Qi, B.; Guo, J.X.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wu, X.Z. MiR-124 inhibits the migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by suppressing integrin alphaV expression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, M.; Matsuda, A.; Diederichs, S.; Patel, T. Non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartorius, K.; Makarova, J.; Sartorius, B.; An, P.; Winkler, C.; Chuturgoon, A.; Kramvis, A. The Regulatory Role of MicroRNA in Hepatitis-B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) Pathogenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lai, Y.; Weng, H.; Tan, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Luo, X.; Ye, Y. MiR-124 sensitizes cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity against CD133+ hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting SIRT1/ROS/JNK pathway. AGING 2019, 11, 2551–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyasamy, P.; Liao, K.; Kook, Y.H.; Niu, F.; Callen, S.E.; Guo, M.L.; Buch, S. Cocaine-Mediated Downregulation of miR-124 Activates Microglia by Targeting KLF4 and TLR4 Signaling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 3196–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X. MiR-124-3p impedes the metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer via extracellular exosome transport and intracellular PI3K/AKT signaling. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Guo, X.; Li, Q.; Ran, P.; Xiang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Dong, T.; Zhu, B.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; et al. Long non-coding RNA 1308 promotes cell invasion by regulating the miR-124/ADAM 15 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6599–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, W.Y.; Xue, J.X.; Xu, Y.; Fan, P.; Caughey, B.A.; Tan, W.W.; Cao, G.Q.; Jiang, L.L.; Lu, Y.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Profile on Solid Subtype of Invasive Lung Adenocarcinoma Reveals a Panel of Four miRNAs to Be Associated with Poor Prognosis in Chinese Patients. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, K.; Yao, G.; Pan, C.; Liu, B.; Xia, Y.; He, Z.; Qi, X.; Li, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-124 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor by Regulating CDH2 and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.Y.; Cao, X.N.; Xu, Q.Z.; Deng, Y.; Lai, S.Y.; Ma, J.; Hu, J.B. miR-124 modulates gefitinib resistance through SNAI2 and STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2016, 36, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, C.; Chu, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhen, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lv, B.; Li, H.; et al. MicroRNA-124 suppresses proliferation and glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting AKT-GLUT1/HKII. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317706215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Nigita, G.; Calore, F.; Saviana, M.; Le, P.; Croce, C.M.; Acunzo, M.; Nana-Sinkam, P. MiR-124a Regulates Extracellular Vesicle Release by Targeting GTPase Rabs in Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Peng, W.; Jiang, H.; Sha, H.; Li, J. LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes proliferation and invasion by targeting miR-124 in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317721440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.K.; Hua, K.; Whipple, W.; Nguyen, M.T.; Liu, C.T.; Haybaeck, J.; Weidhaas, J.; Settleman, J.; Singh, A. Regulation of autophagy, NF-kappaB signaling, and cell viability by miR-124 in KRAS mutant mesenchymal-like NSCLC cells. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Kong, F.; Zong, Z.; Ren, M.; Meng, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z. miR-124 and miR-142 enhance cisplatin sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells through repressing autophagy via directly targeting SIRT1. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5234–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wan, L.; Xiao, C.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, H.T. Inhibition of LHX2 by miR-124 suppresses cellular migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3429–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ai, X.; Shen, S.; Lu, S. NF-κB-mediated miR-124 suppresses metastasis of non-smallcell lung cancer by targeting MYO10. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8244–8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J. Decreased miR-124 contributes to the epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype formation of lung adenocarcinoma cells via targeting enhancer of zeste homolog 2. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, D.; Meng, L.; Wang, B. MicroRNA-124 inhibits proliferation, invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical carcinoma cells by targeting astrocyte-elevated gene-1. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Chen, L.J. The role of miRNAs in the invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G. MicroRNA-124-3p inhibits cell growth and metastasis in cervical cancer by targeting IGF2BP1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, W.; Yang, H.; Xiao, G. Propofol suppresses proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by regulating miR-124-3p.1/AKT3. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Huang, J.; Gao, F.; Lin, X.; He, L.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Ding, Y.; Chen, L. MiR-124 Radiosensitizes human colorectal cancer cells by targeting PRRX1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Yue, X.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wan, J. MiR-124 suppresses growth of human colorectal cancer by inhibiting STAT3. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.H.; Liang, H.; Lu, S.N.; Wang, H.; Su, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.Q.; Guo, M.; Tai, S.; Yu, S. miR-124 Suppresses Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Growth by Regulating Monocarboxylate Transporter 1-Mediated Cancer Lactate Metabolism. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, F.; Shi, D.B.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhao, R.N.; Zhang, H.; Ma, R.R.; He, J.Y.; Gao, P. HRCT1, negatively regulated by miR-124-3p, promotes tumor metastasis and the growth of gastric cancer by activating the ERBB2-MAPK pathway. Gastric Cancer 2023, 26, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierson, J.; Hostager, B.; Fan, R.; Vibhakar, R. Regulation of cyclin dependent kinase 6 by microRNA 124 in medulloblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 90, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Finniss, S.; Cazacu, S.; Bucris, E.; Ziv-Av, A.; Xiang, C.; Bobbitt, K.; Rempel, S.A.; Hasselbach, L.; Mikkelsen, T.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver synthetic microRNA mimics to glioma cells and glioma stem cells and inhibit their cell migration and self-renewal. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.L.; Huang, W.D.; Li, B.; Chen, T.R.; Li, Z.X.; Zhao, C.L.; Li, H.Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Yan, W.J.; Xiao, J.R. microRNA-124 inhibits bone metastasis of breast cancer by repressing Interleukin-11. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.B.; Yang, Z.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Han, Z.C. MicroRNA-124 suppresses breast cancer cell growth and motility by targeting CD151. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 31, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Chang, L.; Chen, H. miRNA-124 modulates lung carcinoma cell migration and invasion. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 54, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Teng, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C. miR-124 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by directly targeting SOX9 in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3115–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Ren, L.; Chen, J.; Cao, R.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. MicroRNA-124 Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Targeting Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Watari, H.; Hanley, S.J.B.; Konno, Y.; Ihira, K.; Suzuki, F.; Yamada, T.; Kudo, M.; Yue, J.; et al. Suppression of iASPP-dependent aggressiveness in cervical cancer through reversal of methylation silencing of microRNA-124. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lin, T.; Xu, C.; Hu, S.; Pan, Y.; Jin, R. miR-124 interacts with the Notch1 signalling pathway and has therapeutic potential against gastric cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhong, H.; Jiao, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, X.; Song, X.; Ying, B. MiR-124-3p inhibits the migration and invasion of Gastric cancer by targeting ITGB3. Pathol.—Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Sun, M.; Gu, W.; Geng, H. Over-expression of mir-124 inhibits MMP-9 expression and decreases invasion of renal cell carcinoma cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 6308–6314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Tang, K.; Liu, H.; Zeng, J.; Li, H.; Yan, L.; Hu, J.; Guan, W.; Chen, K.; Xu, H.; et al. Regulatory Network of Two Tumor-Suppressive Noncoding RNAs Interferes with the Growth and Metastasis of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post-stroke Recovery (PSR_e2020) (PSR_e2020). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04323501?term=NCT04323501&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Allogenic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03384433 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Epigenetic Tools as Prognostic Predictors in COVID-19. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04411563 (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Dose-Ranging Phase 2b Study of ABX464 in Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03760003 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Safety Evaluation of ABX464 in Patients with Moderate to Severe Active Crohn’s Disease. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03905109 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Evaluation of Pain Sensitization in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analysis on a Cohort of Tofacitinib Treated Patients (TOPRA). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03815578 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Curcumin in Treating Patients with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00641147 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- ABX464 in Treating Inflammation and Preventing Acute Respiratory Failure in Patients with COVID-19 (Mir-Age). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04393038 (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Winkle, M.; El-Daly, S.M.; Fabbri, M.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNA therapeutics—Challenges and potential solutions. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2021, 20, 629–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzywa, T.M.; Klicka, K.; Wlodarski, P. Regulators at Every Step—How microRNAs Drive Tumor Cell Invasiveness and Metastasis. Cancers 2020, 12, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, R.; Baghaei, K.; Hashemi, S.M.; Zali, M.R.; Ghanbarian, H.; Amani, D. Tumor-Derived Exosomes Enriched by miRNA-124 Promote Anti-tumor Immune Response in CT-26 Tumor-Bearing Mice. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 619939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Biological Function | Disease | Subtypes | Target Gene | Regulation Pattern | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-cancer activity | Neurological cancers | Medulloblastoma | CDK6 NUR 77 | Regulates cell cycle progression and inhibits cell proliferation | [34,77] |
| Glioblastoma | CDK6 SCP-1 ROCK1 STAT3 MMP-9 | Regulates cell cycle progression and inhibits cell proliferation | [21,78] | ||
| Breast cancer | Triple-negative breast cancer | IL-11 CD-151 CDK-4 EGFR | Inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis | [42,79,80] | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | SP1 STAT3 CAS3 | Increases apoptosis and reduces cell proliferation | [51] | ||
| Lung cancer | NSCLC | ZEB-1 SOX-9 CDH-2 | Prevents migration and invasion | [81,82] | |
| Cervical cancer | - | AEG-1 P53 | Induces apoptosis and decreases cell proliferation | [83,84] | |
| Colorectal cancer | - | AKT-3 DNMT3B DNMT-1 STAT3 | Inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion | [58,72] | |
| Gastric cancer | - | NOTCH-1 PI3/AKT/STAT3 | Inhibits cell proliferation and invasion | [85,86] | |
| Renal cell carcinoma | - | STAT3/MMP-9 MEG/P53 | Regulates apoptosis and decreases cell proliferation | [87,88] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | - | MCT-1 ITGA3 MKK4/JNK/c-Jun | Inhibits cell proliferation and inhibition | [75] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gourishetti, K.; Balaji Easwaran, V.; Mostakim, Y.; Ranganath Pai, K.S.; Bhere, D. MicroRNA (miR)-124: A Promising Therapeutic Gateway for Oncology. Biology 2023, 12, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12070922
Gourishetti K, Balaji Easwaran V, Mostakim Y, Ranganath Pai KS, Bhere D. MicroRNA (miR)-124: A Promising Therapeutic Gateway for Oncology. Biology. 2023; 12(7):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12070922
Chicago/Turabian StyleGourishetti, Karthik, Vignesh Balaji Easwaran, Youssef Mostakim, K. Sreedhara Ranganath Pai, and Deepak Bhere. 2023. "MicroRNA (miR)-124: A Promising Therapeutic Gateway for Oncology" Biology 12, no. 7: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12070922
APA StyleGourishetti, K., Balaji Easwaran, V., Mostakim, Y., Ranganath Pai, K. S., & Bhere, D. (2023). MicroRNA (miR)-124: A Promising Therapeutic Gateway for Oncology. Biology, 12(7), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12070922


_Kwok.png)




