Benthic Heterotrophic Protist Communities of the Southern Baltic Analyzed with the Help of Curated Metabarcoding Studies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. DNA and RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. PCR Amplification and High-Throughput Sequencing
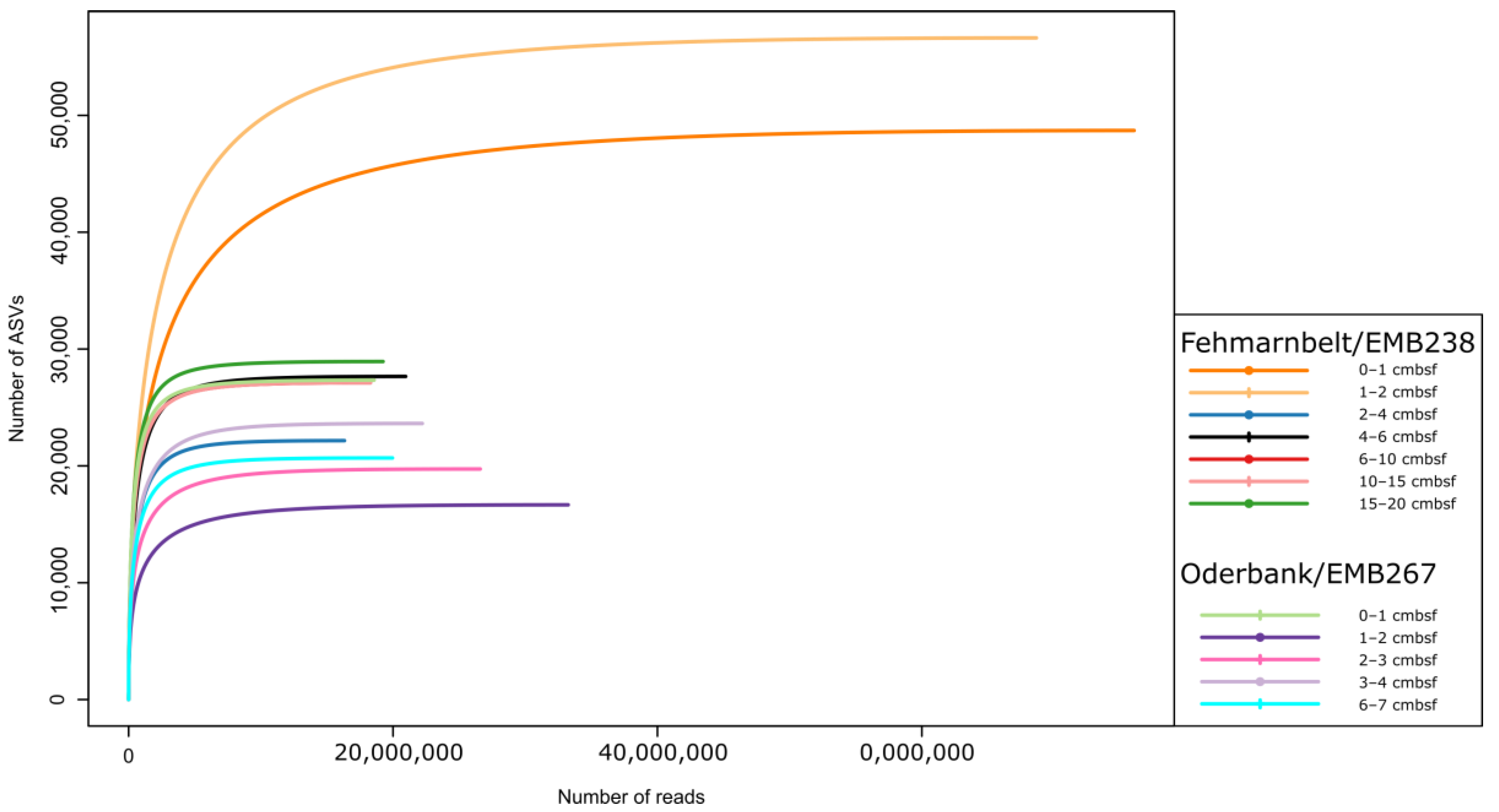
2.4. Bioinformatic Processing
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Alpha Diversity of Benthic Protists in the Southern Baltic
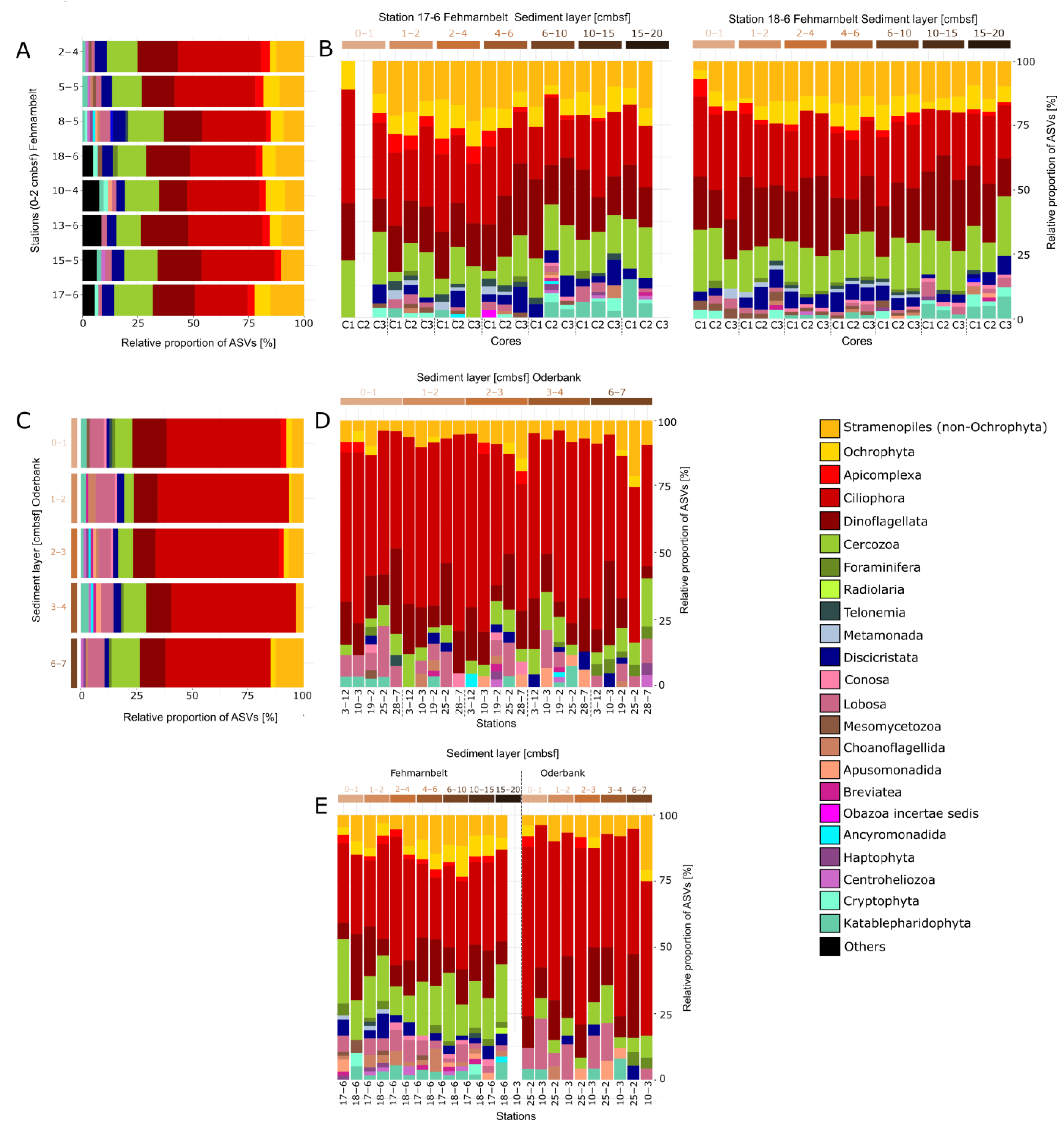
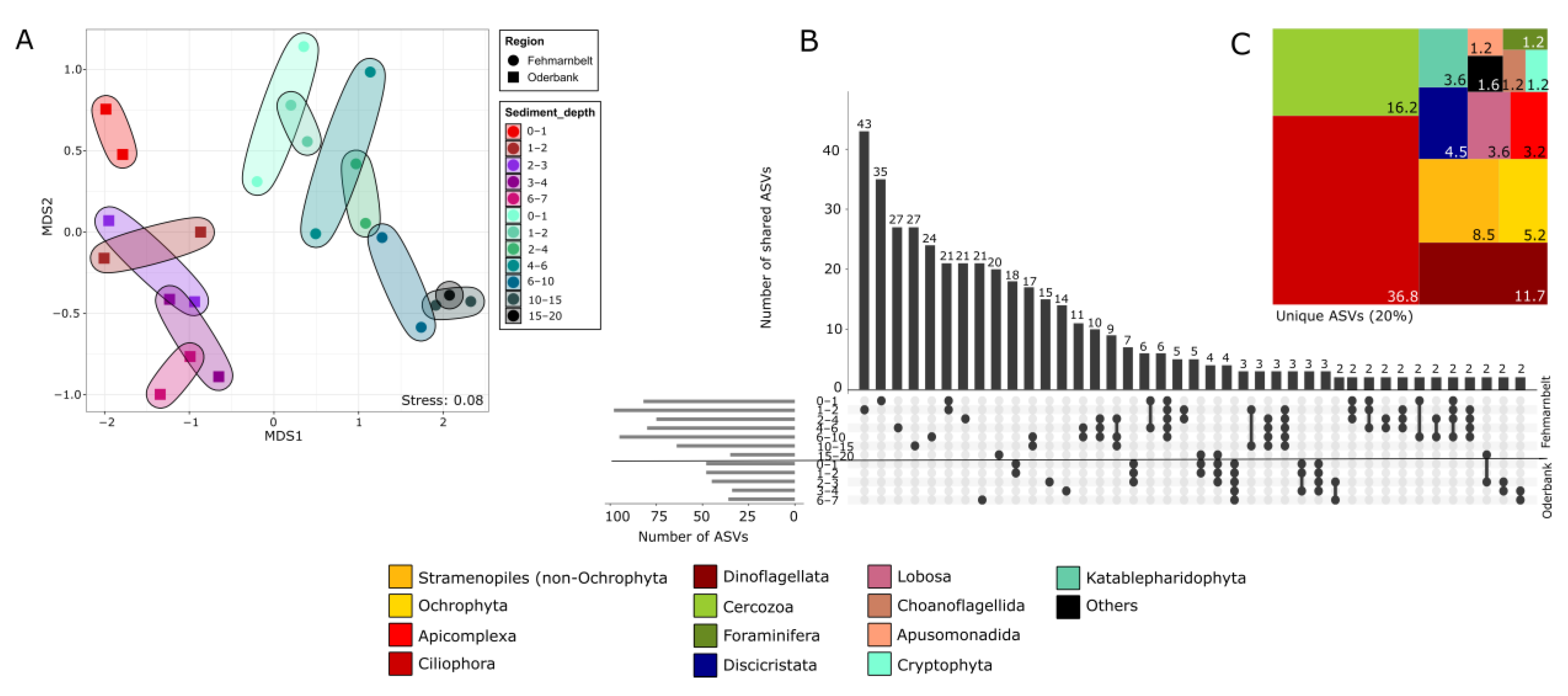
3.2. Protist Community Composition at Different Regions and Sediment Depths
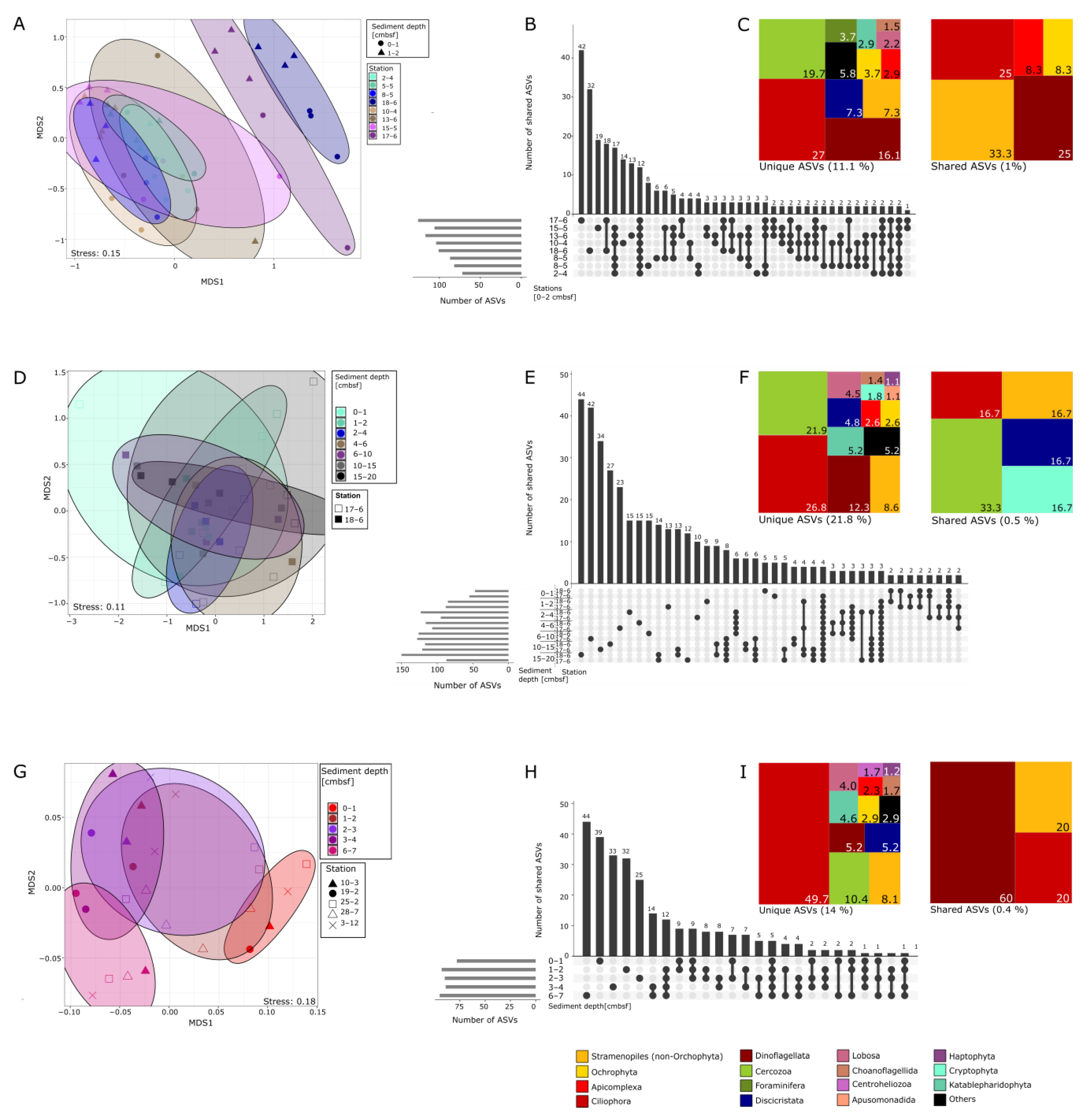
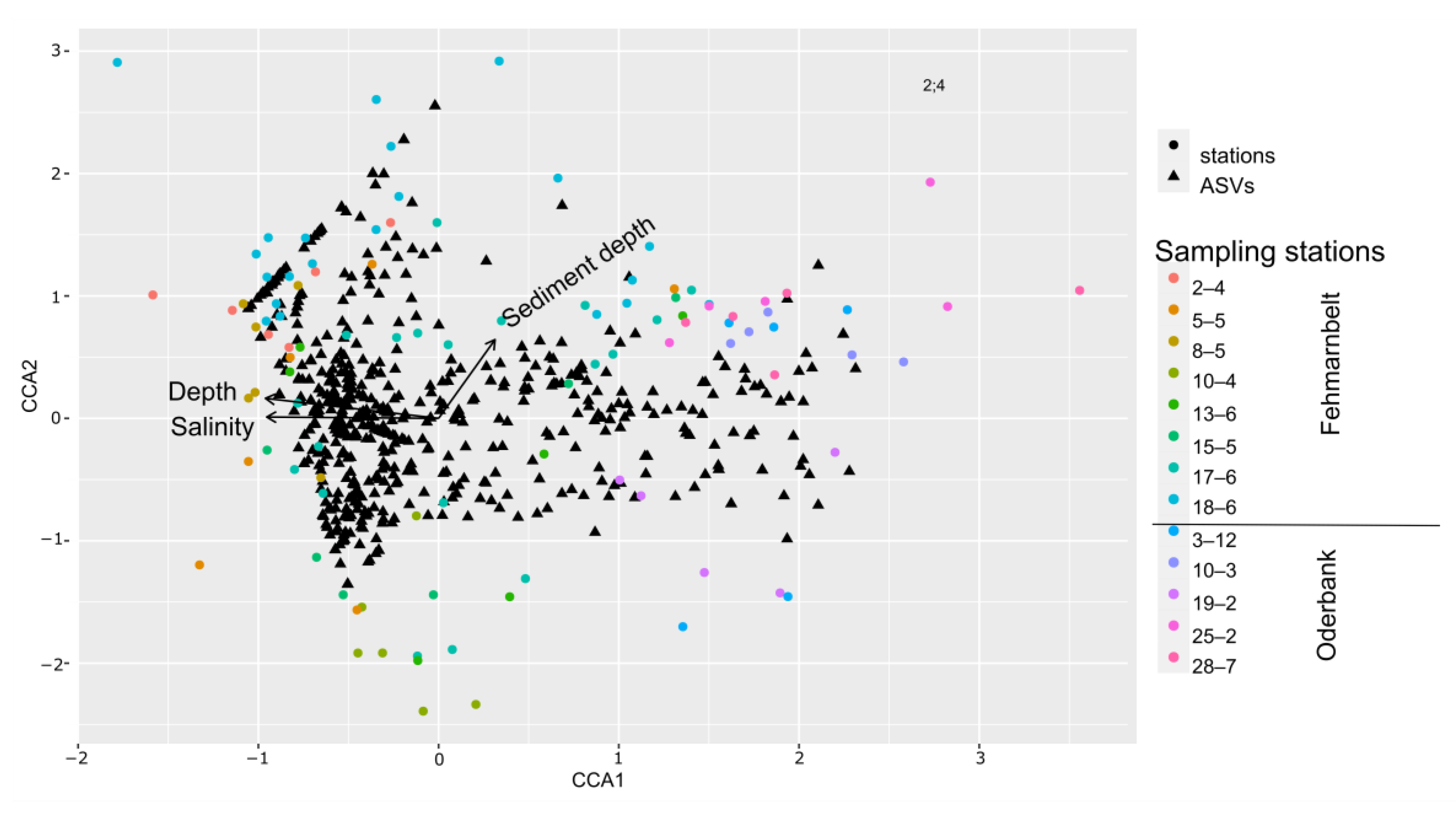
3.3. Protist Beta-Diversity in Relation to Sediment Depth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marcus, N.H.; Boero, F. Minireview The Importance of Benthic-Pelagic Coupling and the Forgotten Role of Life Cycles in Coastal Aquatic Systems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; Leonard, G.; Milner, D.S.; Sudek, S.; Conway, M.; Moore, K.; Hudson, T.; Mahé, F.; Keeling, P.J.; Santoro, A.E.; et al. Controlled Sampling of Ribosomally Active Protistan Diversity in Sediment-Surface Layers Identifies Putative Players in the Marine Carbon Sink. ISME J. 2020, 14, 984–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vargas, C.; Audic, S.; Henry, N.; Decelle, J.; Mahé, F.; Logares, R.; Lara, E.; Berney, C.; Le Bescot, N.; Probert, I.; et al. Eukaryotic Plankton Diversity in the Sunlit Ocean. Science 2015, 348, 1261605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, H.; Dietrich, D.; Auer, B.; Cleven, E.-J.; Gräfenhan, T.; Weitere, M.; Mynikov, A. Functional Diversity of Heterotrophic Flagellates in Aquatic Ecosystems. In The Flagellates; Leadbeater, B.S.C., Green, J.C., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 2000; pp. 240–268. [Google Scholar]
- Nagano, N.; Matsui, S.; Kuramura, T.; Taoka, Y.; Honda, D.; Hayashi, M. The Distribution of Extracellular Cellulase Activity in Marine Eukaryotes, Thraustochytrids. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.R.; Harvey, E.L. Temporal Variability and Ecological Interactions of Parasitic Marine Syndiniales in Coastal Protist Communities. mSphere 2020, 5, e00209-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worden, A.Z.; Follows, M.J.; Giovannoni, S.J.; Wilken, S.; Zimmerman, A.E.; Keeling, P.J. Rethinking the Marine Carbon Cycle: Factoring in the Multifarious Lifestyles of Microbes. Science 2015, 347, 1257594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, M.; Shibuvardhan, Y.; Manilal, V.B. Response of Anaerobic Protozoa to Oxygen Tension in Anaerobic System. Int. Microbiol. 2019, 22, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, H.-U.; Matthäus, W. General Oceanography of the Baltic Sea. In State and Evolution of the Baltic Sea, 1952–2005: A Detailed 50-Year Survey of Meteorology and Climate, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Marine Environment; Feistel, R., Naush, G., Wasmund, N., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 5–44. ISBN 978-0-471-97968-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ojaveer, H.; Jaanus, A.; MacKenzie, B.R.; Martin, G.; Olenin, S.; Radziejewska, T.; Telesh, I.; Zettler, M.L.; Zaiko, A. Status of Biodiversity in the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Mylnikov, A.P.; Jürgens, K.; Wylezich, C. Culturing Heterotrophic Protists from the Baltic Sea: Mostly the “Usual Suspects” but a Few Novelties as Well. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, H. On the Importance of Planktonic Protozoans in the Eutrophication Process of the Baltic Sea. Int. Rev. Der Gesamten Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1991, 76, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Del Campo, J.; Wylezich, C.; Massana, R.; Jürgens, K. Unveiling Trophic Functions of Uncultured Protist Taxa by Incubation Experiments in the Brackish Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.; Jürgens, K.; Bunge, J.; Stoeck, T. Protistan Diversity in Suboxic and Anoxic Waters of the Gotland Deep (Baltic Sea) as Revealed by 18S RRNA Clone Libraries. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 55, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwosz, K.; Całkiewicz, J.; Gołębiewski, M.; Creer, S. Diversity and Community Composition of Pico- and Nanoplanktonic Protists in the Vistula River Estuary (Gulf of Gdańsk, Baltic Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 207, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.O.O.; Karlson, B.; Charvet, S.; Andersson, A.F. Diversity of Pico- to Mesoplankton along the 2000 Km Salinity Gradient of the Baltic Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sich, H. Die Benthische Ciliatenfauna bei Gabelsflach (Kieler Bucht) und deren Beeinflussung durch Bakterien—Eine Studie über Menge, Biomasse, Produktion, Bakterieningestion und Ultrastruktur von Mikroorganismen. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kiel, Kiel, Germany, 1989. Berichte aus dem Institut für Meereskunde Kiel, Nr. 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garstecki, T.; Verhoeven, R.; Wickham, S.A.; Arndt, H. Benthic-Pelagic Coupling: A Comparison of the Community Structure of Benthic and Planktonic Heterotrophic Protists in Shallow Inlets of the Southern Baltic: Benthic and Pelagic Protistan Community Structure. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garstecki, T.; Arndt, H. Seasonal Abundances and Community Structure of Benthic Rhizopods in Shallow Lagoons of the Southern Baltic Sea. Eur. J. Protistol. 2000, 36, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Soetaert, K.; Xu, Y. The Relative Roles of Multiple Drivers on Benthic Ciliate Communities in an Intertidal Zone. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Stumm, K.; Wickham, S.A.; Berninger, U. Distributions and Biomass of Benthic Ciliates, Foraminifera and Amoeboid Protists in Marine, Brackish, and Freshwater Sediments. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2014, 61, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, D.; Arndt, H. Biomass Partitioning of Benthic Microbes in a Baltic Inlet: Relationships between Bacteria, Algae, Heterotrophic Flagellates and Ciliates. Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.; Kooistra, W.; Levialdighiron, J.; Mann, D.; Pröschold, T.; Montresor, M. Reproductive Isolation among Sympatric Cryptic Species in Marine Diatoms. Protist 2007, 158, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, L.; Viprey, M.; Chambouvet, A.; Welsh, R.M.; Kirkham, A.R.; Massana, R.; Scanlan, D.J.; Worden, A.Z. Widespread Occurrence and Genetic Diversity of Marine Parasitoids Belonging to Syndiniales( Alveolata ). Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 3349–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massana, R.; Del Campo, J.; Sieracki, M.E.; Audic, S.; Logares, R. Exploring the Uncultured Microeukaryote Majority in the Oceans: Reevaluation of Ribogroups within Stramenopiles. ISME J. 2014, 8, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlitzer, R. Ocean Data View. Available online: odv.awi.de (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Danovaro, R. Methods for the Study of Deep-Sea Sediments, Their Functioning and Biodiversity; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, N.; Beaumier, D.; Lee, K.; Greer, C.W. Soil Washing Improves the Recovery of Total Community DNA from Polluted and High Organic Content Sediments. J. Microbiol. Methods 2004, 56, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; McCliment, E.A.; Ducklow, H.W.; Huse, S.M. A Method for Studying Protistan Diversity Using Massively Parallel Sequencing of V9 Hypervariable Regions of Small-Subunit Ribosomal RNA Genes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michu, E.; Mráčková, M.; Vyskot, B.; Žlůvová, J. Reduction of Heteroduplex Formation in PCR Amplification. Biol. Plant. 2010, 54, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Park, J.S. Comparative Analyses of the V4 and V9 Regions of 18S RDNA for the Extant Eukaryotic Community Using the Illumina Platform. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods. 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Available online: http://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=vegan (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R Package for the Visualization of Intersecting Sets and Their Properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a Dual-Index Sequencing Strategy and Curation Pipeline for Analyzing Amplicon Sequence Data on the MiSeq Illumina Sequencing Platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore-Donno, A.M.; Rixen, C.; Rippin, M.; Glaser, K.; Samolov, E.; Karsten, U.; Becker, B.; Bonkowski, M. New Barcoded Primers for Efficient Retrieval of Cercozoan Sequences in High-Throughput Environmental Diversity Surveys, with Emphasis on Worldwide Biological Soil Crusts. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennartz, A.E.; Nitsche, F.; Schoenle, A.; Voigt, C.; Staubwasser, M.; Arndt, H.; Arndt, H. High Diversity and Isolated Distribution of Aquatic Heterotrophic Protists in Salars of the Atacama Desert at Different Salinities. Eur. J. Protistol. 2023, 89, 125987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.A.-T.; Pawlowski, J. Can Abundance of Protists Be Inferred from Sequence Data: A Case Study of Foraminifera. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Fan, X.; Warren, A.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H. Functional Diversity of Benthic Ciliate Communities in Response to Environmental Gradients in a Wetland of Yangtze Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azovsky, A.I.; Tikhonenkov, D.V.; Mazei, Y.A. An Estimation of the Global Diversity and Distribution of the Smallest Eukaryotes: Biogeography of Marine Benthic Heterotrophic Flagellates. Protist 2016, 167, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesh, I.; Schubert, H.; Skarlato, S. Revisiting Remane’s Concept: Evidence for High Plankton Diversity and a Protistan Species Maximum in the Horohalinicum of the Baltic Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 421, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remane, A. Die Brackwasserfauna. In Verhandlungen der Deutschen Zoologischen Gesellschaft. Deutschen Zoologischen Gesellschaft im Frankfurt am Main; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1934; pp. 34–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Shi, F.; Ma, B.; Dong, J.; Pachiadaki, M.; Zhang, X.; Edgcomb, V.P. Depth Shapes α- and β-Diversities of Microbial Eukayryotes in Surficial Sediments of Coastal Ecosystems. Environ. Biol. 2015, 17, 3722–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamels, I.; Sabbe, K.; Muylaert, K.; Vyverman, W. Quantitative Importance, Composition, and Seasonal Dynamics of Protozoan Communities in Polyhaline versus Freshwater Intertidal Sediments. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 47, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamels, I.; Muylaert, K.; Sabbe, K.; Vyverman, W. Contrasting Dynamics of Ciliate Communities in Sandy and Silty Sediments of an Estuarine Intertidal Flat. Eur. J. Protistol. 2005, 41, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Barucca, M.; Luna, G.M.; Dell’Anno, A. Preservation, Origin and Genetic Imprint of Extracellular DNA in Permanently Anoxic Deep-Sea Sediments. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenle, A.; Hohlfeld, M.; Rybarski, A.; Sachs, M.; Freches, E.; Wiechmann, K.; Nitsche, F.; Arndt, H. Cafeteria in Extreme Environments: Investigations on C. Burkhardae and Three New Species from the Atacama Desert and the Deep Ocean. Eur. J. Protistol. 2022, 85, 125905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, T.; Takasugi, H.; Kimura, H. Abundance of Thraustochytrids in Coastal Plankton. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 162, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorni, L.; Pusceddu, A.; Danovaro, R. Enzymatic Activities of Epiphytic and Benthic Thraustochytrids Involved in Organic Matter Degradation. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 41, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenchel, T.; Finlay, B. Oxygen and the Spatial Structure of Microbial Communities. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenchel, T.; Finlay, B.J. The Biology of Free-Living Anaerobic Ciliates. Eur. J. Protistol. 1991, 26, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massana, R.; Unrein, F.; Rodríguez-Martínez, R.; Forn, I.; Lefort, T.; Pinhassi, J.; Not, F. Grazing Rates and Functional Diversity of Uncultured Heterotrophic Flagellates. ISME J. 2009, 3, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Xiang, S.-Z.; Yan, Y.; Yang, R.; Lin, M.-P.; Wang, X.-M.; Xue, Y.-L.; Guan, X.-Y. Sediment Microbial Communities and Their Potential Role as Environmental Pollution Indicators in Xuande Atoll, South China Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissner, W. Protist Diversity and Distribution: Some Basic Considerations. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 17, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlfeld, M.; Schoenle, A.; Arndt, H. Horizontal and Vertical Small-Scale Patterns of Protist Communities at the Atlantic Deep-Sea Floor. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2021, 171, 103515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
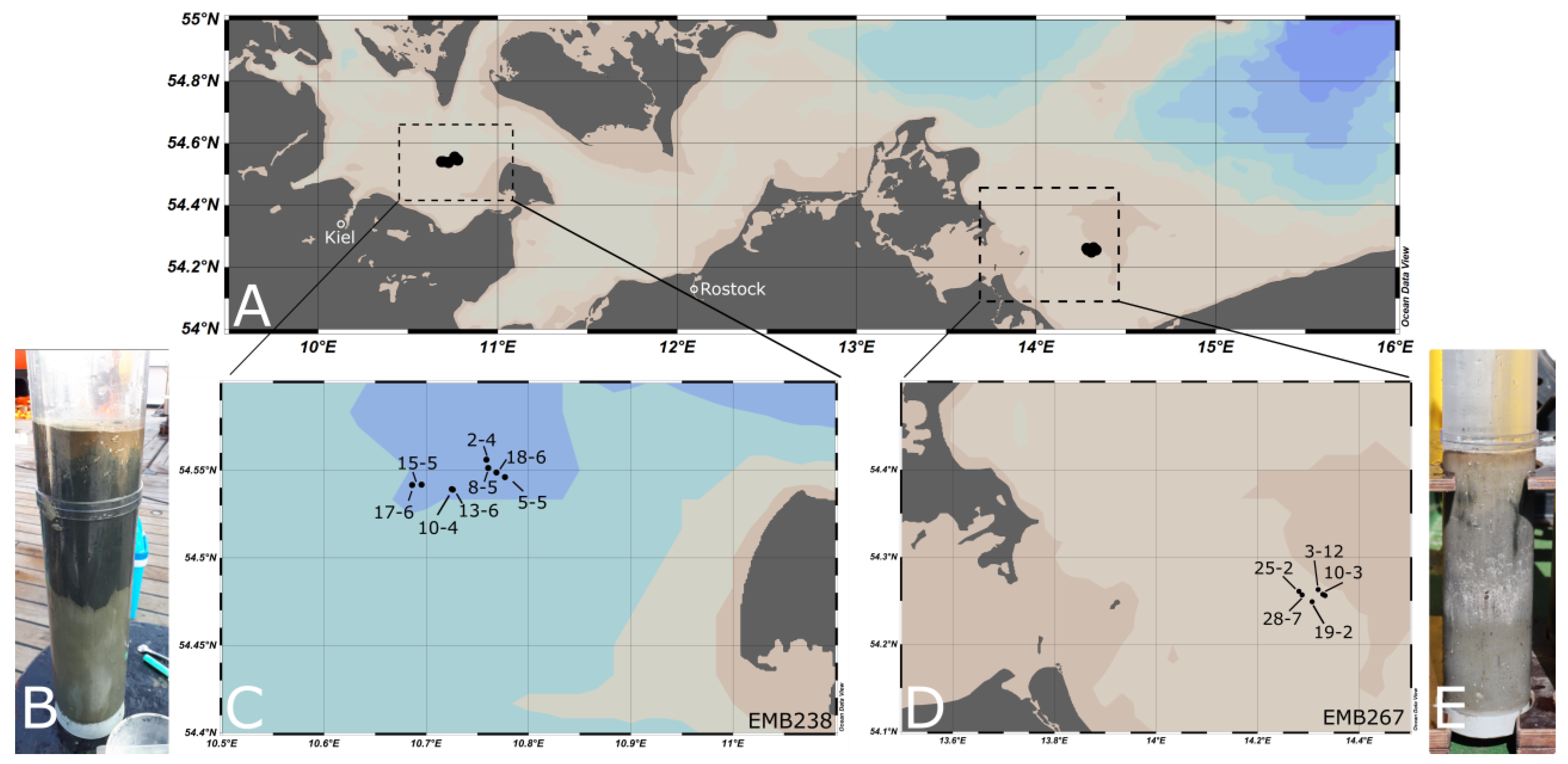


| Region | Station/Cast | Area | Longitude/Latitude | Depth Intervals [cmbsf] | Depth [m] | Cruise | Sediment Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB | 2-4 | MPA | 54°33.37′ 10°45.52′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10,10–15,15–20 | 23.5 | EMB238 | muddy |
| FB | 5-5 | MPA | 54°32.77′ 10°46.61′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10,10–15,15–20 | 23 | EMB238 | muddy |
| FB | 8-5 | MPA | 54°33.08′ 10°45.63′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10,10–15,15–20 | 23.9 | EMB238 | muddy |
| FB | 10-4 | Ref. area | 54°32.36′ 10°43.49′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10,10–15,15–20 | 22.8 | EMB238 | muddy |
| FB | 13-6 | Ref. area | 54°32.34′ 10°43.55′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10,10–15,15–20 | 23 | EMB238 | muddy |
| FB | 15-5 | Ref. area | 54°32.51′ 10°41.71′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10,10–15,15–20 | 23.2 | EMB238 | muddy |
| FB | 17-6 | Ref. area | 54°32.5′ 10°41.16′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10,10–15,15–20 | 23 | EMB238 | muddy |
| FB | 18-6 | MPA | 54°32.93′ 10°46.11′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–4, 4–6, 6–10,10–15,15–20 | 24.4 | EMB238 | muddy |
| OB | 3-12 | MPA | 54°15.774′ 14°19.148′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–3, 3–4, 6–7, 8–9, 10–11 | 15.3 | EMB267 | sandy |
| OB | 10-3 | MPA | 54°15.438′ 14°19.733′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–3, 3–4, 6–7, 9–10, 10–15 | 14.9 | EMB267 | sandy |
| OB | 19-2 | Ref. area | 54°14.934′ 14°18.435′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–3, 3–4, 6–7, 9–10, 14–15 | 15.5 | EMB267 | sandy |
| OB | 25-2 | Ref. area | 54°15.655′ 14°16.873′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–3, 3–4, 6–7, 9–10, 13.5–14.5 | 15.9 | EMB267 | sandy |
| OB | 28-7 | Ref. area | 54°15.406′ 14°17.241′ | 0–1, 1–2, 2–3, 3–4, 6–7, 9–10, 14–15 | 15.5 | EMB267 | sandy |
| HFCC No. | Species | Protist Group |
|---|---|---|
| 171 | Rhynchomonadidae undet. | Kinetoplastida |
| 175 | Fabomonas tropica | Ancyromonadida |
| 176 | Massisteria marina | Cercozoa |
| 178 | Ministeria vibrans | Opisthokonta |
| 203 | Cafeteria burkhardae | Stramenopiles |
| 744 | Aristerostoma sp. | Ciliophora |
| 766 | Protocruzia sp. | Ciliophora |
| 768 | Halocafeteria sp. | Stramenopiles |
| 828 | Neobodo sp. | Kinetoplastida |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sachs, M.; Dünn, M.; Arndt, H. Benthic Heterotrophic Protist Communities of the Southern Baltic Analyzed with the Help of Curated Metabarcoding Studies. Biology 2023, 12, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12071010
Sachs M, Dünn M, Arndt H. Benthic Heterotrophic Protist Communities of the Southern Baltic Analyzed with the Help of Curated Metabarcoding Studies. Biology. 2023; 12(7):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12071010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSachs, Maria, Manon Dünn, and Hartmut Arndt. 2023. "Benthic Heterotrophic Protist Communities of the Southern Baltic Analyzed with the Help of Curated Metabarcoding Studies" Biology 12, no. 7: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12071010
APA StyleSachs, M., Dünn, M., & Arndt, H. (2023). Benthic Heterotrophic Protist Communities of the Southern Baltic Analyzed with the Help of Curated Metabarcoding Studies. Biology, 12(7), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12071010






