Intra- and Interspecific Foraging and Feeding Interactions in Three Sea Stars and a Gastropod from the Deep Sea
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Focal Species, Collection, and Holding Conditions
2.2. Experimental Designs
2.3. Experimental Conditions and Procedures
2.4. Morphometric Measurements
2.5. Response Variables and Data Processing
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
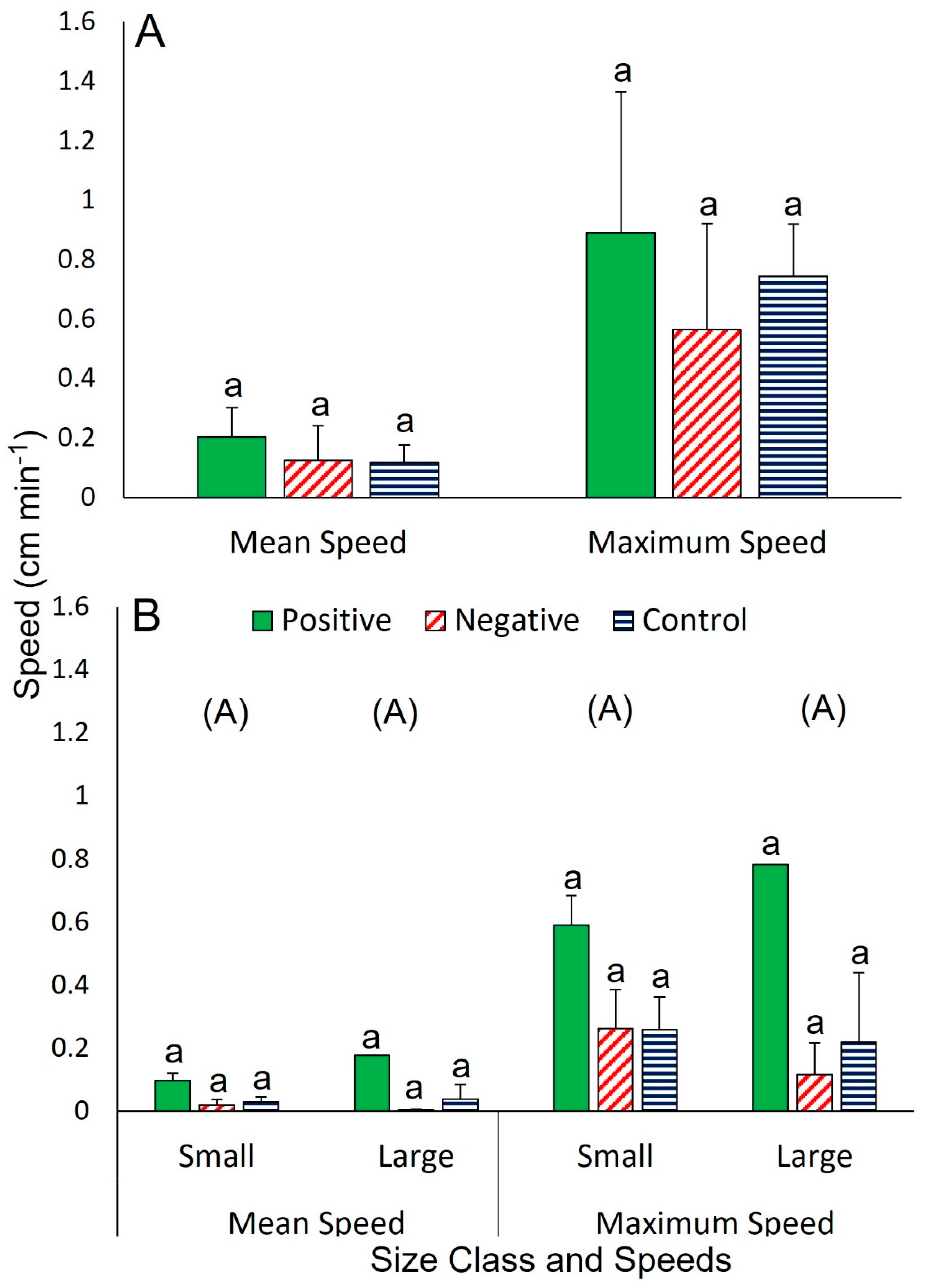
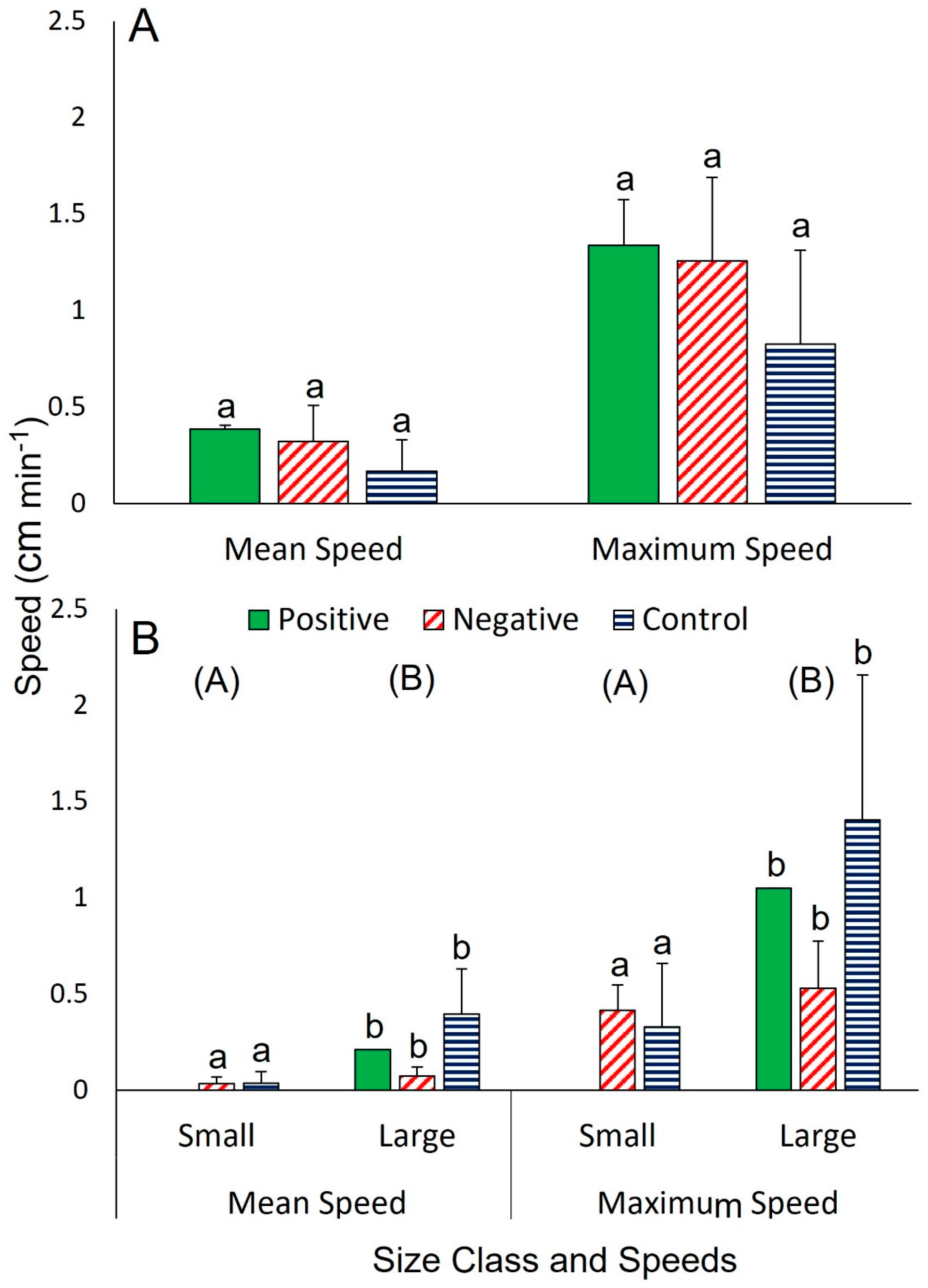
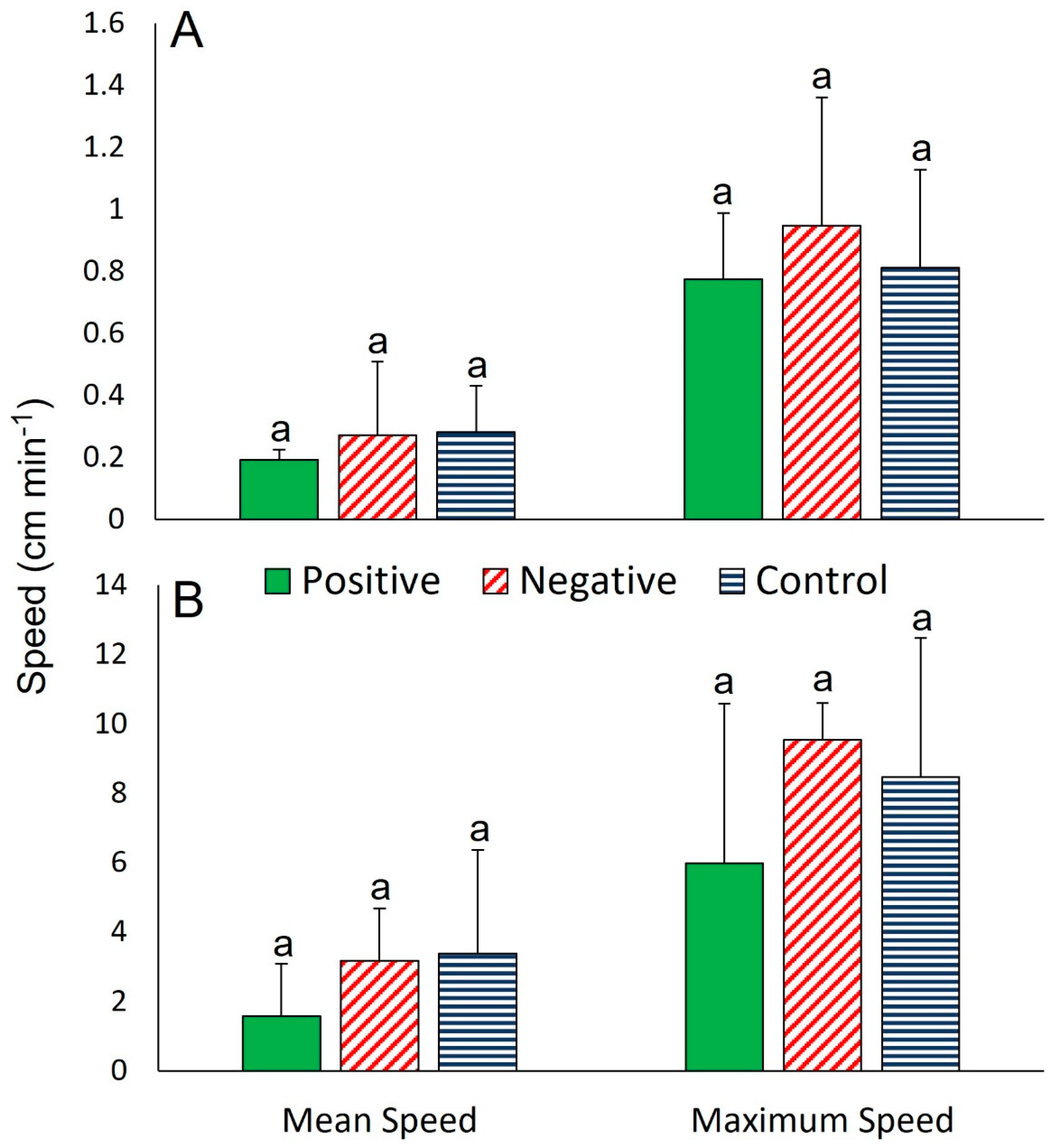
3.1. Interspecific Interactions
3.1.1. The Sea Star Ceramaster granularis
3.1.2. The Sea Star Hippasteria phrygiana
3.1.3. The Sea Star Henricia lisa
3.1.4. The Gastropod Buccinum scalariforme
3.2. Interspecific Interactions
3.2.1. The Sea Star C. granularis with the Sea Star H. lisa
3.2.2. The Sea Star C. granularis with the Gastropod B. scalariforme
3.2.3. The Sea Star C. granularis with the Sea Star H. lisa and the Gastropod B. scalariforme
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McClintock, J.B.; Angus, R.A.; Ho, C.P.; Amsler, C.D.; Baker, B.J. Intraspecific agonistic arm-fencing behavior in the Antarctic keystone sea star Odontaster validus influences prey acquisition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 371, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, R.; Tétreault, F.; Himmelman, J.H. Aggregation of whelks, Buccinum undatum, near feeding predators: The role of reproductive requirements. Anim. Behav. 2001, 61, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menge, J.L.; Menge, B.A. Role of resource allocation, aggression and spatial heterogeneity in coexistence of two competing intertidal starfish. Ecol. Monogr. 1974, 44, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, R.J. Indirect interactions between prey: Apparent competition, predator aggregation, and habitat segregation. Ecology 1987, 68, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaymer, C.F.; Himmelman, J.H.; Johnson, L.E. Effect of intra- and interspecific interactions on the feeding behavior of two subtidal sea stars. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 232, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, A.P.; Moreland, H.R.; Gagnon, P. Body size and competitor identity modulate prey consumption and feeding behaviour in a slow-moving benthic predator (Asterias rubens, Linneaus). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2018, 507, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Su, X.; Wang, F.; Zhong, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D. Starvation intensifies the impacts of interspecific interactions on foraging behavior of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus). Aquaculture 2019, 504, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbragaglia, V.; Leiva, D.; Arias, A.; Garcia, J.A.; Aguzzi, J.; Breithaupt, T. Fighting over burrows: The emergence of dominance hierarchies in the Norway lobster (Nephrops norvegicus). J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 4624–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, B.A. Competition for food between two intertidal starfish species and its effect on body size and feeding. Ecology 1972, 53, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, R.; Hamel, J.-F.; Himmelman, J.H. Foraging strategy of the asteroid Leptasterias polaris: Role of prey odors, current and feeding status. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 106, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.L.; Schultz, H.K.; Elliott, J.K. Size-dependent interference competition between two sea star species demographically affected by wasting disease. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 589, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, R.A.; Harley, C.D.G. Quantifying the effects of predator and prey body size on sea star feeding behaviors. Biol. Bull. 2015, 228, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, C.; Honkoop, P.; van der Meer, J. Small is profitable: No support for the optimal foraging theory in sea stars Asterias rubens foraging on the blue edible mussel Mytilus edulis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 94, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.H.; Schaerer, R. Predator-prey interaction between two competing sea star species of the genus Astropecten. Mar. Ecol. 1981, 2, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.C.; Barbeau, M.A. Effects of substrate on interactions between juvenile sea scallops (Placopecten magellanicus Gmelin) and predatory sea stars (Asterias vulgaris Verrill) and rock crabs (Cancer irroratus Say). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 287, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, K.S.P.; Hamel, J.-F.; Mercier, A. Trophic ecology of deep-sea Asteroidea (Echinodermata) from eastern Canada. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2013, 80, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckless, B.; Hamel, J.-F.; Aguzzi, J.; Mercier, A. Foraging strategies in four deep-sea benthic species. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2021, 542–543, 151607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.L.; Kaiser, M.J.; Hughes, R.N. Behaviour and energetics of whelks, Buccinum undatum (L.), feeding on animals killed by beam trawling. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 197, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelman, J.H.; Hamel, J.-R. Diet, behaviour and reproduction of the whelk Buccinum undatum in the northern Gulf of St. Lawrence, eastern Canada. Mar. Biol. 1993, 116, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilano, A.S.; Miranda, R.M.T.; Fujinaga, K.; Nakao, S. Feeding behaviour and food consumption of Japanese whelk, Buccinum isaotakii (Neogastropoda: Buccinidae). Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, S.; Himmelman, J.H. Subtidal food thieves: Interactions of four invertebrate kleptoparasites with the sea star Leptasterias polaris. Anim. Behav. 2000, 60, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, K.S.P.; Gilkinson, K.; Hamel, J.-F.; Mercier, A. Patterns and drivers of asteroid abundances and assemblages on the continental margin of Atlantic Canada. Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 734–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, C. Ceramaster granularis (Retzius, 1783). 2019. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=124020 (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- Mah, C.; Neill, K.; Eléaume, M.; Foltz, D. New species and global revision of Hippasteria (Hippasterinae: Goniasteridae; Asteroidea; Echinodermata). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 171, 422–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, C. Henricia lisa A.H. Clark, 1949. 2019. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=123969 (accessed on 12 February 2019).
- Montgomery, E.M.; Hamel, J.-F.; Mercier, A. The deep-sea neogastropod Buccinum scalariforme: Reproduction, development and growth. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2017, 119, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meigering, E.; Dzyubachyk, O.; Smal, I. Methods for cell and particle tracking. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 504, 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserstein, R.L.; Schirm, A.L.; Lazar, N.A. Moving to a world beyond “p < 0.05”. Am. Stat. 2019, 73, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushoff, J.; Kain, M.P.; Bolker, B.M. I can see clearly now: Reinterpreting statistical significance. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2019, 10, 756–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, J.J. Are there physiological and biochemical adaptations of metabolism in deep-sea animals? Trends Ecol. Evol. 1995, 10, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooday, A.J.; Turley, C.M. Responses by benthic organisms to inputs of organic material to the ocean floor: A review. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1990, 331, 119–138. [Google Scholar]
- Higgs, N.D.; Gates, A.R.; Jones, D.O.B. Fish food in the deep sea: Revisiting the role of large food-falls. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga-Henriques, A.; Carreiro-Silva, M.; Tempera, F.; Porteiro, F.M.; Jakobsen, K.; Jakobsen, J.; Albuquerque, M.; Santos, R.S. Carrying behavior in the deep-sea crab Paromola cuvieri (Northeast Atlantic). Mar. Biodivers. 2011, 42, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elner, R.W.; Koshio, S.; Hurley, G.V. Mating behavior of the deep-sea red crab, Geryon quinquedens Smith (Decapoda, Brachyura, Geryonidae). Crustaceana 1987, 52, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.M.; Hamel, J.-F.; Mercier, A. Feeding in deep-sea demosponges: Influence of abiotic and biotic factors. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2017, 127, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzi, J.; Jamieson, A.J.; Fujii, T.; Sbragaglia, V.; Costa, C.; Menesatti, P.; Fujiwara, Y. Shifting feeding behaviour of deep-sea buccinid gastropods at natural and simulated food falls. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 458, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.M.; Alexander Jr, J.E. Group foraging in a marine gastropod predator: Benefits and costs to individuals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 112, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowbridge, C.D. Group membership facilitates feeding of the herbivorous sea slug Placida dendritica. Ecology 1991, 72, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, J.A.; Herbert, G.S. No honor among snails: Conspecific competition leads to incomplete drill holes by a naticid gastropod. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 379–380, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, J.-F.; Mercier, A. Evidence of chemical communication during the gametogenesis of holothuroids. Ecology 1996, 77, 1600–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennebert, E. Adhesion mechanisms developed by sea stars: A review of the ultrastructure and composition of tube feet and their secretion. In Biological Adhesive Systems; von Byern, J., Grunwald, I., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2010; pp. 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo, F.J.; Muñoz, P.D.; Cristobo, J.; Ríos, P.; González, C.; Kenchington, E.; Serrano, A. Deep-sea sponge grounds of the Flemish Cap, Flemish Pass and the Grand Banks of Newfoundland (Northwest Atlantic Ocean): Distribution and species composition. Mar. Biol. Res. 2012, 8, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, F.J.; Serrano, A.; Kenchington, E.; Mora, J. Epibenthic assemblages of the Tail of the Grand Bank and Flemish Cap (Northwest Atlantic) in relation to environmental parameters and trawling intensity. Deep-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 109, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheild, C.J.; Witman, J.D. The impact of Henricia sanguinolenta (O. F. Müller) (Echinodermata: Asteroidea) predation on the finger sponges, Isodictya spp. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1993, 166, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, M.H.; Blicher, M.E.; Garm, A. Deep-sea starfish from the Arctic have well-developed eyes in the dark. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamel, J.-F.; Mercier, A. Prespawning behaviour, spawning and development of the brooding starfish Leptasterias polaris. Biol. Bull. 1995, 188, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, G.A.; Glazer, R.A.; Stewart, N.J. Predator-induced behavioral and morphological plasticity in the tropical marine gastropod Strombus gigas. Biol. Bull. 2002, 203, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, V.; Cabral, H.N.; Bishop, M.J. Prior exposure influences the behavioural avoidance by an intertidal gastropod, Bembicium auratum, of acidified waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 136, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez, F.; Nieto Vilela, R.A.; Lozada, M.; Bigatti, G. Morphological and behavioral differences in the gastropod Trophon geversianus associated to distinct environmental conditions, as revealed by a multidisciplinary approach. J. Sea Res. 2015, 95, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, M.; Holm, C.; Lubin, Y.; Bilde, T. Cooperative foraging expands dietary niche but does not offset intra-group competition for resources in social spiders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menge, B.A. Foraging strategy of a starfish in relation to actual prey availability and environmental predictability. Ecol. Monogr. 1972, 42, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danovaro, R.; Snelgrove, P.V.; Tyler, P. Challenging the paradigms of deep-sea ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A.; Le Bris, N. The deep ocean under climate change. Science 2015, 350, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, N.C.; Calado, R.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Exploitation of deep-sea resources: The urgent need to understand the role of high pressure in the toxicity of chemical pollutants to deep-sea organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Llodra, E.; Tyler, P.A.; Baker, M.C.; Bergstad, O.A.; Clark, M.R.; Escobar, E.; Levin, L.A.; Menot, L.; Rowden, A.A.; Smith, C.R.; et al. Man and the last great wilderness: Human impact on the deep sea. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Treatment * | Min ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramaster granularis | Two same-sized individuals | 21.0 ± 10.0 |
| Two differently sized individuals | 40.0 ± 8.3 | |
| Five differently sized individuals | 45.0 ± 150.8 | |
| C. granularis and B. scalariforme (short) | 31.0 ± 17.0 | |
| C. granularis and B. scalariforme (long) | 17.5 ± 0.7 | |
| C. granularis, H. lisa, and B. scalariforme | 188.0 ± 341.7 | |
| Across all treatments | 39.0 ± 161.7 | |
| Hippasteria phrygiana | Two same-sized individuals | 35.5 ± 11.3 |
| Two differently sized individuals | 58.0 | |
| Five differently sized individuals | 50.0 ± 444.1 | |
| Across all treatments | 45.5 ± 318.0 | |
| Henricia lisa | Two same-sized individuals | 26.0 ± 22.5 |
| C. granularis and H. lisa (long) | 12.0 ± 8.5 | |
| C. granularis, H. lisa, and B. scalariforme | 65 ± 145.2 | |
| Across all treatments | 22.0 ± 93.2 | |
| Buccinum scalariforme | Two same-sized individuals | 3.0 ± 22.8 |
| C. granularis, H. lisa, and B. scalariforme | 103.0 ± 79.4 | |
| Across all treatments | 48.5 ± 78.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stuckless, B.; Hamel, J.-F.; Aguzzi, J.; Mercier, A. Intra- and Interspecific Foraging and Feeding Interactions in Three Sea Stars and a Gastropod from the Deep Sea. Biology 2023, 12, 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060774
Stuckless B, Hamel J-F, Aguzzi J, Mercier A. Intra- and Interspecific Foraging and Feeding Interactions in Three Sea Stars and a Gastropod from the Deep Sea. Biology. 2023; 12(6):774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060774
Chicago/Turabian StyleStuckless, Brittney, Jean-François Hamel, Jacopo Aguzzi, and Annie Mercier. 2023. "Intra- and Interspecific Foraging and Feeding Interactions in Three Sea Stars and a Gastropod from the Deep Sea" Biology 12, no. 6: 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060774
APA StyleStuckless, B., Hamel, J.-F., Aguzzi, J., & Mercier, A. (2023). Intra- and Interspecific Foraging and Feeding Interactions in Three Sea Stars and a Gastropod from the Deep Sea. Biology, 12(6), 774. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060774







