Osseous Bridges of the Sphenoid Bone: Frequency, Bilateral and Sex Distribution
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
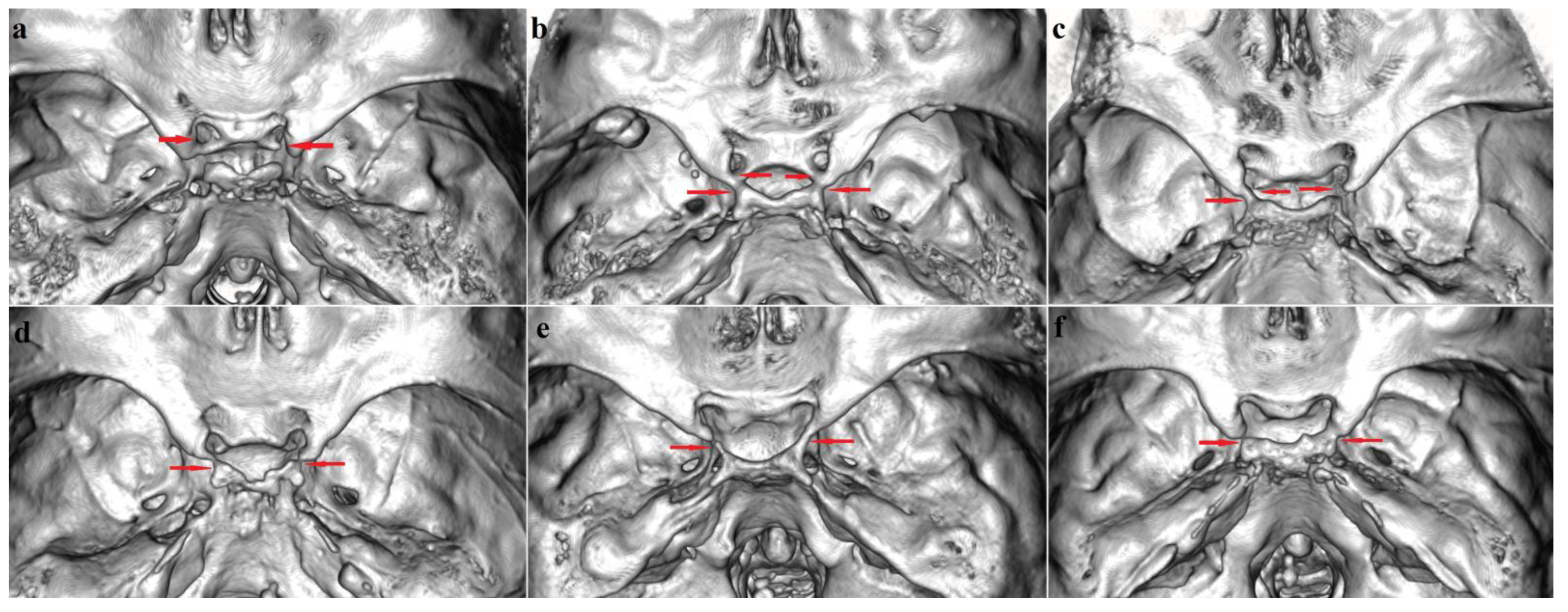
3.1. Sellar (Caroticoclinoid and Interclinoid) Bridges
3.1.1. Frequency
3.1.2. Bilateral and Sex Distribution
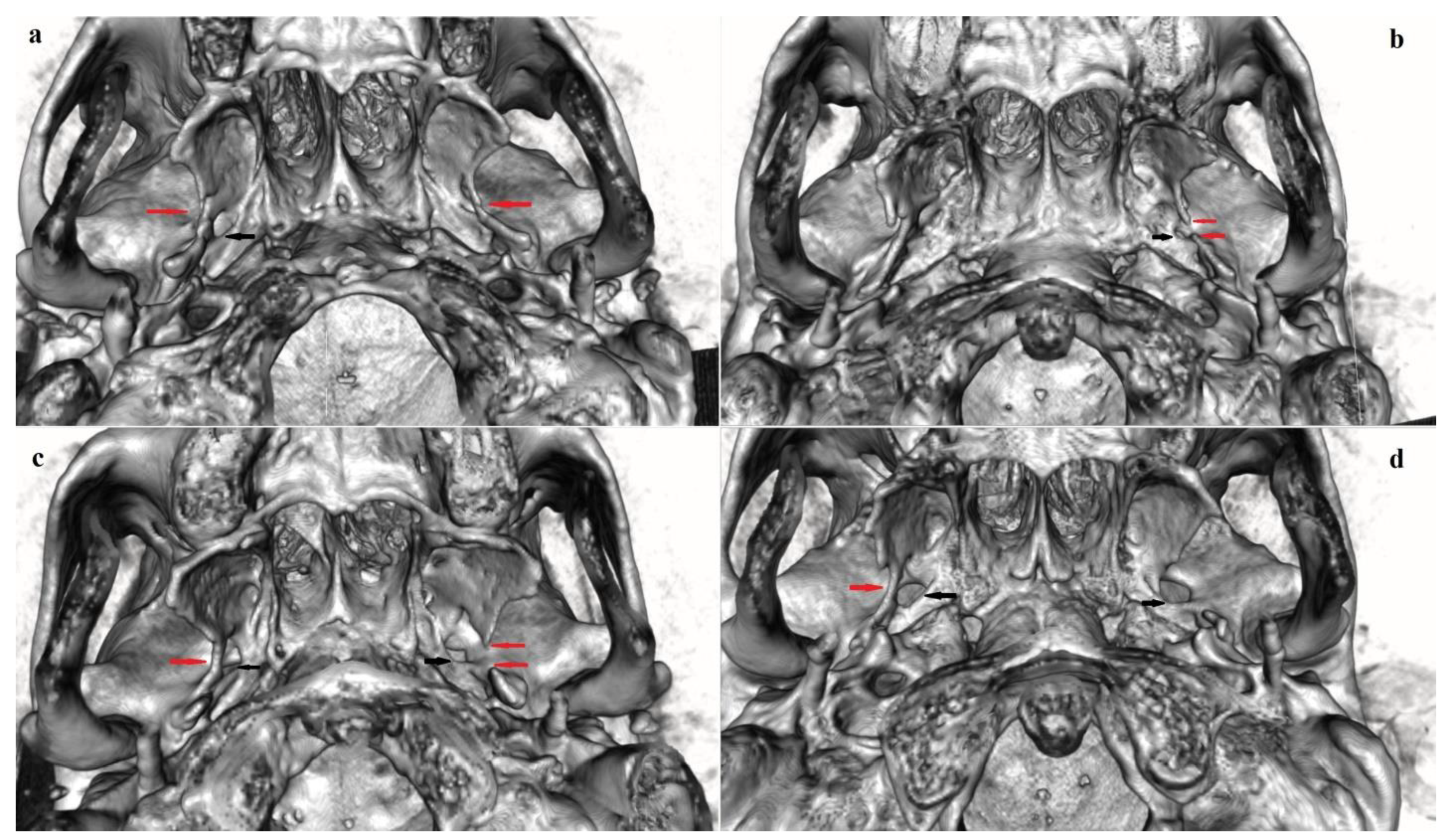
3.2. Pterygospinous Bridge
3.2.1. Frequency
3.2.2. Bilateral and Sex Distribution
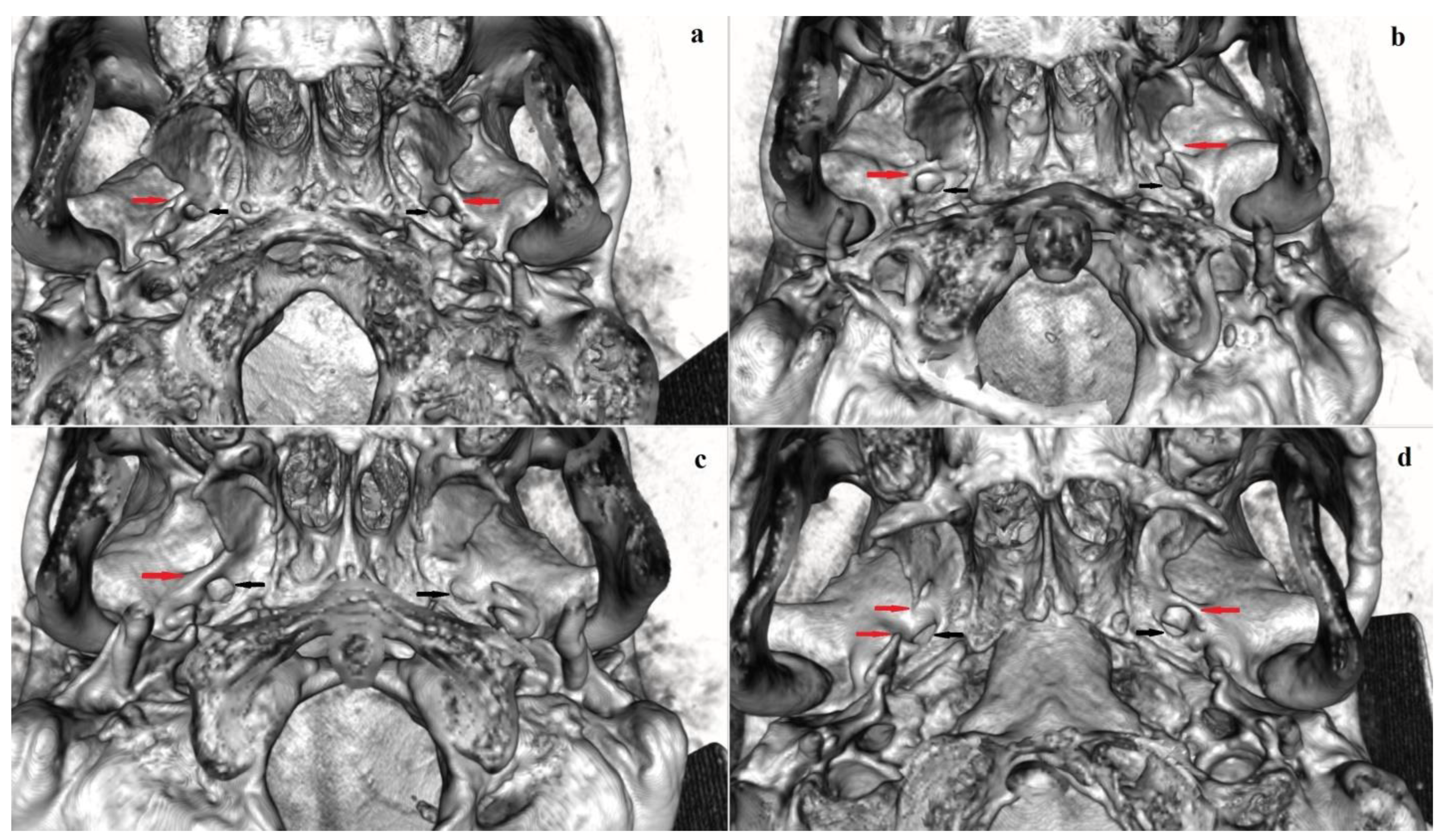
3.3. Pterygoalar Bridge
3.3.1. Frequency
3.3.2. Bilateral and Sex Distribution
3.4. Correlation Analysis
3.5. Sphenoid Bridges Co-Occurrence
4. Discussion
4.1. Frequency and Distribution
4.1.1. Sellar (Caroticoclinoid and Interclinoid) Bridges
Caroticoclinoid Bridge (Type I)
Interclinoid Bridges (Types II, III and IV)
4.1.2. Pterygospinous Bridge
4.1.3. Pterygoalar Bridge
4.1.4. Sphenoid Bridges Co-Occurrence and Correlation Analysis
4.2. Etiology
4.3. A Phylogenetic Aspect of the Development and Relationship between the Spinous Process, Processus Angularis and the Prominence of the Lateral Pterygoid Plate
4.4. Clinical Significance
4.4.1. Sellar (Caroticoclinoid and Interclinoid) Bridges
4.4.2. Pterygospinous and Pterygoalar Bridges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Tormenti, M.; Latorre, F.; Gardner, P.; Snyderman, C. Endoscopic endonasal middle clinoidectomy. Oper. Neurosurg. 2012, 71 (Suppl. S2), 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Rieth, G.E.; Tanenbaum, J.E.; Williams, J.S.; Ota, N.; Chakravarthi, S.; Manjila, S.; Kassam, A.; Yapicilar, B. A morphometric survey of the parasellar region in more than 2700 skulls: Emphasis on the middle clinoid process variants and implications in endoscopic and microsurgical approaches. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouké, K.S. On the incidence of the foramen of Civinini and the Porus crotaphitico-buccinatorius in American whites and negroes. Am. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 1946, 4, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Lüdinghausen, M.; Kageyama, I.; Miura, M.; Alkhatib, M. Morphological peculiarities of the deep infratemporal fossa in advanced age. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2006, 28, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyes, J.E.L. Observations on four thousand optic foramina in human skulls of known origin. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1935, 13, 538–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepp, F.H.; Sandner, M.O. Anatomic-radiographic study of ossified pterygospinous and “innominate” ligaments. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1968, 26, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archana, R.; Anita, R.; Jyoti, C.; Punita, M.; Rakesh, D. Incidence of osseous interclinoid bars in Indian population. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2010, 32, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, D.E.; Wiersma, W.; Jurs, S.G. Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences, 5th ed.; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, B.; Gupta, M.; Kumar, H. Ossified ligaments of the skull. J. Anat. Soc. India 2012, 61, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprasanna, K.; Kumar, A. Surgically relevant bony anatomical variations in paraclinoid aneurysms-three-dimensional multi-detector row computed tomography-based study. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2017, 8, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chung, I.H.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, K.S. Anterior clinoid process and optic strut in Koreans. Yonsei Med. J. 1997, 38, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, N.; Tanikawa, R.; Miyazaki, T.; Miyata, S.; Oda, J.; Noda, K.; Tsuboi, T.; Takeda, R.; Kamiyama, H.; Tokuda, S. Surgical microanatomy of the anterior clinoid process for paraclinoid aneurysm surgery and efficient modification of extradural anterior clinoidectomy. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, E.; Mehić, A. Anatomical variations and morphometric study of the optic strut and the anterior clinoid process. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2012, 12, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touska, P.; Hasso, S.; Oztek, A.; Chinaka, F.; Connor, S.E.J. Skull base ligamentous mineralisation: Evaluation using computed tomography and a review of the clinical relevance. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Ray, B.; Ghosh, S. A study on anterior clinoid process and optic strut with emphasis on variations of caroticoclinoid foramen. Nepal Med. Coll. J. 2005, 7, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peker, T.; Karaköse, M.; Anil, A.; Turgut, H.B.; Gülekon, N. The incidence of basal sphenoid bony bridges in dried crania and cadavers: Their anthropological and clinical relevance. Eur. J. Morphol. 2002, 40, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyan, N.; Ozsahin, E.; Kizilkanat, E.; Tekdemir, I.; Soames, R.; Oguz, O. Surgical importance of the morphometry of the anterior clinoid process, optic strut, caroticoclinoid foramen, and interclinoid osseous bridge. Neurosurg. Q. 2011, 21, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturk, M.; Kayalioglu, G.; Govsa, F. Anatomy of the clinoidal region with special emphasis on the caroticoclinoid foramen and interclinoid osseous bridge in a recent Turkish population. Neurosurg. Rev. 2004, 27, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsis, K.; Piagkou, M.; Lazaridis, N.; Totlis, T.; Anastasopoulos, N.; Constantinidis, J. Incidence and morphometry of sellar bridges and related foramina in dry skulls: Their significance in middle cranial fossa surgery. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthymiou, E.; Thanopoulou, V.; Kozompoli, D.; Kanellopoulou, V.; Fratzoglou, M.; Mytilinaios, D.; Piagkou, M.; Johnson, E.O. Incidence and morphometry of caroticoclinoid foramina in Greek dry human skulls. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibelli, D.; Cellina, M.; Gibelli, S.; Panzeri, M.; Oliva, A.G.; Termine, G.; Sforza, C. Sella turcica bridging and ossified carotico-clinoid ligament: Correlation with sex and age. Neuroradiol. J. 2018, 31, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagtekin, A.; Avci, E.; Uzmansel, D.; Kurtoglu, Z.; Kara, E.; Uluc, K.; Akture, E.; Baskaya, M.K. Regional microsurgical anatomy and variations of the anterior clinoid process. Turk. Neurosurg. 2014, 24, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzat, J.; Mroz, I.; Marchewka, J. Bridges of the sella turcica–anatomy and topography. Folia Med. Crac. 2012, 52, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C.; Chamoun, R.; Beahm, D. Morphometric analysis of the middle clinoid process using maxillofacial computed tomography scans. Oper. Neurosurg. 2016, 13, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadanoff, D.; Mutafov, S. The Human Skull in a Medico-Anthropological Aspect: Form, Dimensions and Variability; Prof. Marin Drinov Academic Publishing House: Sofia, Bulgaria, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Kucia, A.; Jankowski, T.; Siewniak, M.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Grocholewicz, K.; Szych, Z.; Wilk, G. Sella turcica anomalies on lateral cephalometric radiographs of Polish children. Dentomaxillofacial. Radiol. 2014, 43, 20140165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdoğmuş, Ö.; Saka, E.; Tulay, C.; Gürdal, E.; Uzün, I.; Cavdar, S. The anatomy of the carotico-clinoid foramen and its relation with the internal carotid artery. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2003, 25, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederberg, R.A.; Benson, B.W.; Nunn, M.; English, J.D. Calcification of the interclinoid and petroclinoid ligaments of sella turcica: A radiographic study of the prevalence. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2003, 6, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribante, A.; Sfondrini, M.F.; Cassani, M.; Fraticelli, D.; Beccari, S.; Gandini, P. Sella turcica bridging and dental anomalies: Is there an association? Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2017, 27, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbs, R.S.; May, W.R.; Apaydin, N.; Shoja, M.M.; Shokouhi, G.; Loukas, M.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A. Ossification of ligaments near the foramen ovale: An anatomic study with potential clinical significance regarding transcutaneous approaches to the skull base. Neurosurgery 2009, 65 (Suppl. S1), ons60–ons64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.S.; Ananthi, K.S.; Subramaniam, A.; Balaji, M.T.; Vinaitha, D.; Vaithianathan, G. Foramen of Civinini: A new anatomical guide for maxillofacial surgeons. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; Saralaya, V.; Prabhu, L.V.; Pai, M.M.; Vadgaonkar, R.; D’Costa, S. Pterygospinous bar and foramina in Indian skulls: Incidence and phylogenetic significance. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2007, 29, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar, V.; Niranjan, R. Pterygospinous bar and foramen in the adult human skulls of North India: Its incidence and clinical relevance. Anat. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 286794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, K.; Kuberappa, V. Anatomical study of pterygospinous and pterygoalar bar in human skulls with their phylogeny and clinical significance. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, AC10–AC13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Jain, A. An anatomical study of the pterygospinous bar and foramen of Civinini. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2016, 38, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.P. Pterygospinous and pterygoalar foramina: A role in the etiology of trigeminal neuralgia? Clin. Anat. 1993, 6, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.J.; Park, M.K.; Lee, U.Y.; Kwak, H.H. Incidence of pterygospinous and pterygoalar bridges in dried skulls of Koreans. Anat. Cell Biol. 2016, 49, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Piagou, M.; Anagnostopoulou, S. An anatomical study of the pterygospinous and pterygoalar bars and foramina–their clinical relevance. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 36, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.R.; Faig-Leite, H.; Faig-Leite, F.S.; Moraes, L.C.; Moraes, M.E.L.; Filho, E.M. Radiographic study of ossification of the pterygospinous and pterygoalar ligaments by the Hirtz axial technique. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2010, 23, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chouké, K.S. On the incidence of the foramen of Civinini and the porus crotaphitico-buccinatorius in American whites and negroes; observations on 2745 additional skulls. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1947, 5, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, H.G. The pterygospinous bar in panoramic roentgenography. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1968, 26, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krmpotić-Nemanić, J.; Vinter, I.; Hat, J.; Jalsovec, D. Mandibular neuralgia due to anatomical variations. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 1999, 256, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Pękala, P.A.; Frączek, P.A.; Pękala, J.R.; Natsis, K.; Piagkou, M.; Tomaszewski, K.A.; Tomaszewska, I.M. Prevalence, morphology, and morphometry of the pterygospinous bar: A meta-analysis. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2020, 42, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Paul, S. Ossified pterygospinous ligament and its clinical implications. Bratisl. Lek Listy 2007, 108, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, V.S.; Mallikarjun, M.; Patil, R. A study on an ossified pterygospinous ligament. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2011, 5, 978–979. [Google Scholar]
- Natsis, K.; Piagkou, M.; Skotsimara, G.; Totlis, T.; Apostolidis, S.; Panagiotopoulos, N.A.; Skandalakis, P. The ossified pterygoalar ligament: An anatomical study with pathological and surgical implications. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, e266–e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pękala, P.A.; Henry, B.M.; Pękala, J.R.; Frączek, P.A.; Taterra, D.; Natsis, K.; Piagkou, M.; Skrzat, J.; Tomaszewska, I.M. The pterygoalar bar: A meta-analysis of its prevalence, morphology and morphometry. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossenberg, N.S. The Influence of Artificial Cranial Deformation on Discontinuous Morphological Traits. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1970, 33, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kier, E.L. Embryology of the normal optic canal and its anomalies. An anatomic and roentgenographic study. Investig. Radiol. 1966, 1, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahara, H.; Inui, M.; Lotz, M.K. Tendons and Ligaments: Connecting Developmental Biology to Musculoskeletal Disease Pathogenesis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, D.; Wang, H.; Tan, J. Heterotopic ossification of tendon and ligament. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5428–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osakabe, T.; Hayashi, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Okuaki, T.; Ritty, T.M.; Mecham, R.P.; Wachi, H.; Seyama, Y. Age- and gender-related changes in ligament components. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2001, 38, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasawa, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Sawada, T.; Okada, A.; Ueyama, K.; Motomura, S.; Harata, S.; Inoue, I.; Toh, S.; Furukawa, K.I. Pathophysiological role of endothelin in ectopic ossification of human spinal ligaments induced by mechanical stress. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2006, 79, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J. Skull Base and Related Structures: Atlas of Clinical Anatomy, 2nd ed.; Shattauer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, J. Structure and postnatal organization of heretofore uninvestigated and infrequent ossifications of the sella turcica region. Acta Anat. 1977, 99, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esen, K.; Özgür, A.; Balcı, Y.; Ten, B. Pterygospinous and pterygoalar bars in children. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2022, 44, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.; Scheuer, L.; Black, S. Developmental Juvenile Osteology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Frazer, J.E. The Anatomy of the Human Skeleton; J&A Churchill: London, UK, 1920. [Google Scholar]
- Wood-Jones, F. The Non-metrical Morphological Characters of the Skull as Criteria for Racial Diagnosis: Part I: General Discussion of the Morphological Characters Employed in Racial Diagnosis. J. Anat. 1931, 65, 179–195. [Google Scholar]
- Erdogmus, S.; Pinar, Y.; Celik, S. A cause of entrapment of the lingual nerve: Ossified pterygospinous ligament–a case report. Neuroanatomy 2009, 8, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Peuker, E.T.; Fischer, G.; Filler, T.J. Entrapment of the lingual nerve due to an ossified pterygospinous ligament. Clin. Anat. 2001, 14, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; Rai, R.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Prabhu, L.V.; Ranade, A.V.; Mansur, D.I.; Kumar, S. An unusual course and entrapment of the lingual nerve in the infratemporal fossa. Bratisl. Lek Listy 2008, 109, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chouké, K.S.; Hodes, P.J. The ptergoalar bar and its recognition by roentgen methods in trigeminal neuralgia. Am. J. Roentgenol. Radium Ther. 1951, 65, 180–182. [Google Scholar]
| Sellar Bridges | Males | Females | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Left | R + L | Right | Left | R + L | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Type 1 | 19 | 12.8 | 15 | 10.1 | 34 | 11.5 | 31 | 18.6 | 26 | 15.6 | 57 | 17.1 |
| complete | 12 | 8.1 | 9 | 6.1 | 21 | 7.1 | 15 | 9.0 | 15 | 9.0 | 30 | 9.0 |
| contact | 2 | 1.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 0.7 | 4 | 2.4 | 3 | 1.8 | 7 | 2.1 |
| incomplete | 5 | 3.4 | 6 | 4.0 | 11 | 3.7 | 12 | 7.2 | 8 | 4.8 | 20 | 6.0 |
| Type 2 | 9 | 6.1 | 6 | 4.0 | 15 | 5.1 | 8 | 4.8 | 7 | 4.2 | 15 | 4.5 |
| complete | 3 | 2.0 | 4 | 2.7 | 7 | 2.4 | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 1.2 | 4 | 1.2 |
| contact | 1 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| incomplete | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 1.2 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 0.6 |
| mixed | 5 | 3.4 | 2 | 1.3 | 7 | 2.4 | 4 | 2.4 | 5 | 3.0 | 9 | 2.7 |
| Type 3 | 5 | 3.4 | 7 | 4.7 | 12 | 4.0 | 1 | 0.6 | 3 | 1.8 | 4 | 1.2 |
| complete | 4 | 2.7 | 1 | 0.7 | 5 | 1.7 | 1 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.3 |
| contact | 1 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.3 |
| incomplete | 0 | 0.0 | 6 | 4.0 | 6 | 2.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 2 | 1.2 | 2 | 0.6 |
| Type 4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Types 1–4 | 33 | 22.3 | 28 | 18.9 | 61 | 20.6 | 40 | 24.0 | 36 | 21.6 | 76 | 22.8 |
| Absence | 115 | 77.7 | 120 | 81.1 | 235 | 79.4 | 127 | 76.0 | 131 | 78.4 | 258 | 77.2 |
| Total | 148 | 100.0 | 148 | 100.0 | 296 | 100.0 | 167 | 100.0 | 167 | 100.0 | 334 | 100.0 |
| PsB/Types | Males | Females | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Left | R + L | Right | Left | R + L | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| PsB | 21 | 14.2 | 29 | 19.6 | 50 | 16.9 | 14 | 8.4 | 14 | 8.4 | 28 | 8.4 |
| complete | 8 | 5.4 | 10 | 6.8 | 18 | 6.1 | 3 | 1.8 | 6 | 3.6 | 9 | 2.7 |
| incomplete | 13 | 8.8 | 19 | 12.8 | 32 | 10.8 | 11 | 6.6 | 8 | 4.8 | 19 | 5.7 |
| Absence | 127 | 85.8 | 119 | 80.4 | 246 | 83.1 | 153 | 91.6 | 153 | 91.6 | 306 | 91.6 |
| Total | 148 | 100.0 | 148 | 100.0 | 296 | 100.0 | 167 | 100.0 | 167 | 100.0 | 334 | 100.0 |
| PaB/Types | Males | Females | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Left | R + L | Right | Left | R + L | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| PaB | 5 | 3.4 | 4 | 2.8 | 9 | 3.0 | 4 | 2.4 | 2 | 1.2 | 6 | 1.8 |
| complete | 3 | 2.0 | 2 | 1.4 | 5 | 1.6 | 3 | 1.8 | 1 | 0.6 | 4 | 1.2 |
| incomplete | 2 | 1.4 | 2 | 1.4 | 4 | 1.4 | 1 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.6 | 2 | 0.6 |
| Absence | 143 | 96.6 | 144 | 97.2 | 287 | 97.0 | 163 | 97.6 | 165 | 98.8 | 328 | 98.2 |
| Total | 148 | 100.0 | 148 | 100.0 | 296 | 100.0 | 167 | 100.0 | 167 | 100.0 | 334 | 100.0 |
| Males | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SB-R | SB-L | PsB-R | PsB-L | PaB-R | PaB-L | |||
| Spearman’s rho | SB-R | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | 0.653 | −0.078 | −0.019 | −0.100 | −0.089 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | 0.000 | 0.344 | 0.818 | 0.226 | 0.281 | ||
| SB-L | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | −0.048 | 0.022 | −0.090 | −0.081 | ||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.562 | 0.788 | 0.275 | 0.331 | ||||
| PsB-R | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | 0.433 | −0.076 | 0.052 | |||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | 0.000 | 0.358 | 0.533 | ||||
| PsB-L | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | −0.092 | −0.082 | ||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.264 | 0.320 | ||||||
| PaB-R | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | 0.430 | |||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | 0.000 | ||||||
| PaB-L | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | ||||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | |||||||
| Females | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SB-R | SB-L | PsB-R | PsB-L | PaB-R | PaB-L | |||
| Spearman’s rho | SB-R | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | 0.729 | −0.069 | −0.069 | −0.088 | 0.067 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | 0.000 | 0.379 | 0.379 | 0.259 | 0.388 | ||
| SB-L | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | −0.001 | −0.001 | −0.082 | 0.076 | ||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | 0.990 | 0.990 | 0.291 | 0.328 | |||
| PsB-R | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | 0.610 | −0.047 | −0.033 | |||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | 0.000 | 0.543 | 0.669 | ||||
| PsB-L | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | −0.047 | −0.033 | ||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | 0.543 | 0.669 | |||||
| PaB-R | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | 0.343 | |||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | 0.000 | ||||||
| PaB-L | Correlation Coefficient | 1.000 | ||||||
| Sig. (2-tailed) | . | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolova, S.; Toneva, D.; Zlatareva, D.; Fileva, N. Osseous Bridges of the Sphenoid Bone: Frequency, Bilateral and Sex Distribution. Biology 2023, 12, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12040492
Nikolova S, Toneva D, Zlatareva D, Fileva N. Osseous Bridges of the Sphenoid Bone: Frequency, Bilateral and Sex Distribution. Biology. 2023; 12(4):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12040492
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolova, Silviya, Diana Toneva, Dora Zlatareva, and Nevena Fileva. 2023. "Osseous Bridges of the Sphenoid Bone: Frequency, Bilateral and Sex Distribution" Biology 12, no. 4: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12040492
APA StyleNikolova, S., Toneva, D., Zlatareva, D., & Fileva, N. (2023). Osseous Bridges of the Sphenoid Bone: Frequency, Bilateral and Sex Distribution. Biology, 12(4), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12040492








