Bioelectrical, Anthropometric, and Hematological Analysis to Assess Body Fluids and Muscle Changes in Elite Cyclists during the Giro d’Italia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Bioelectrical Assessment
2.4. Anthropometric Assessment
2.5. Hematological Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Athlete’s Characterization
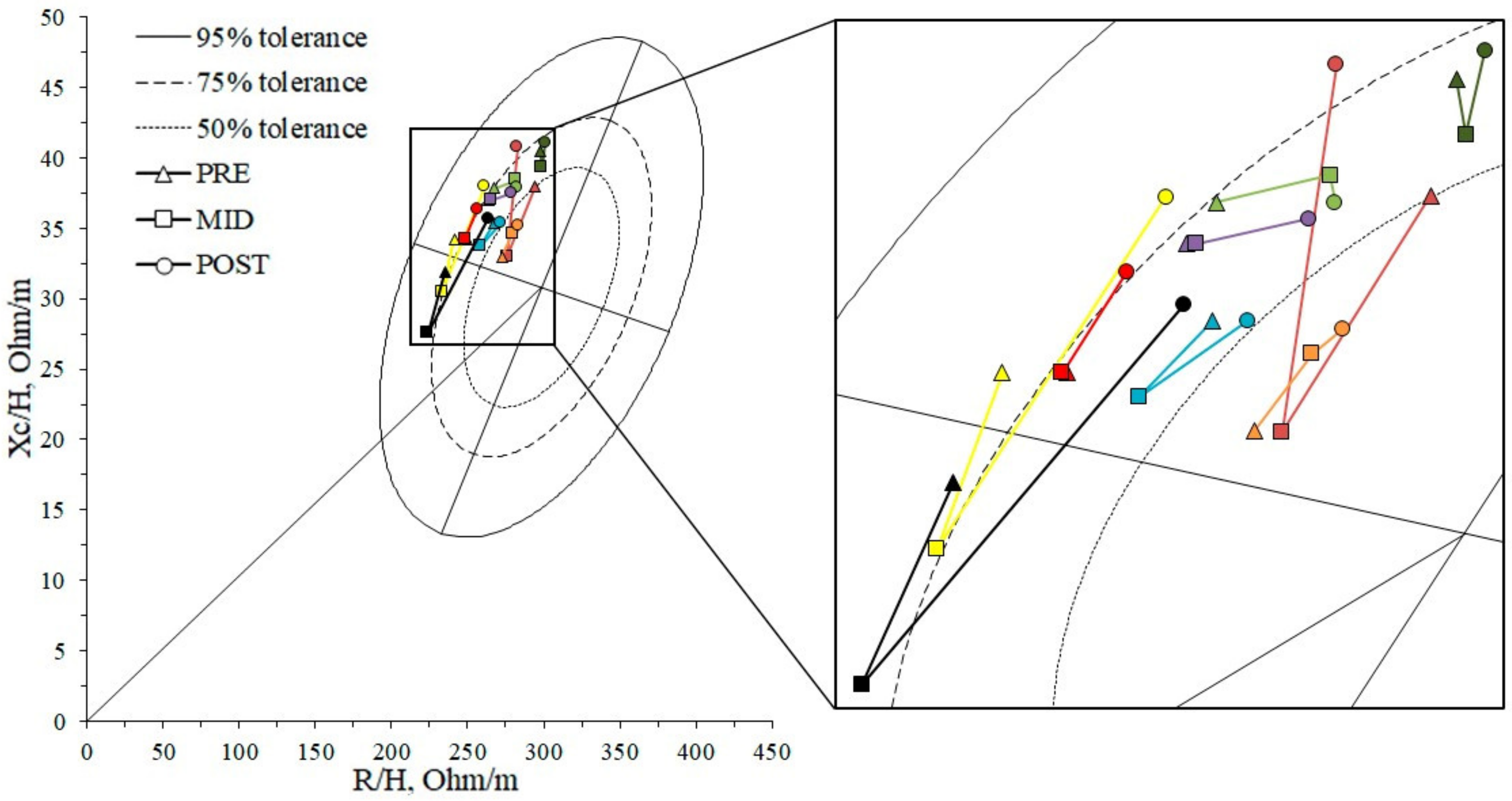
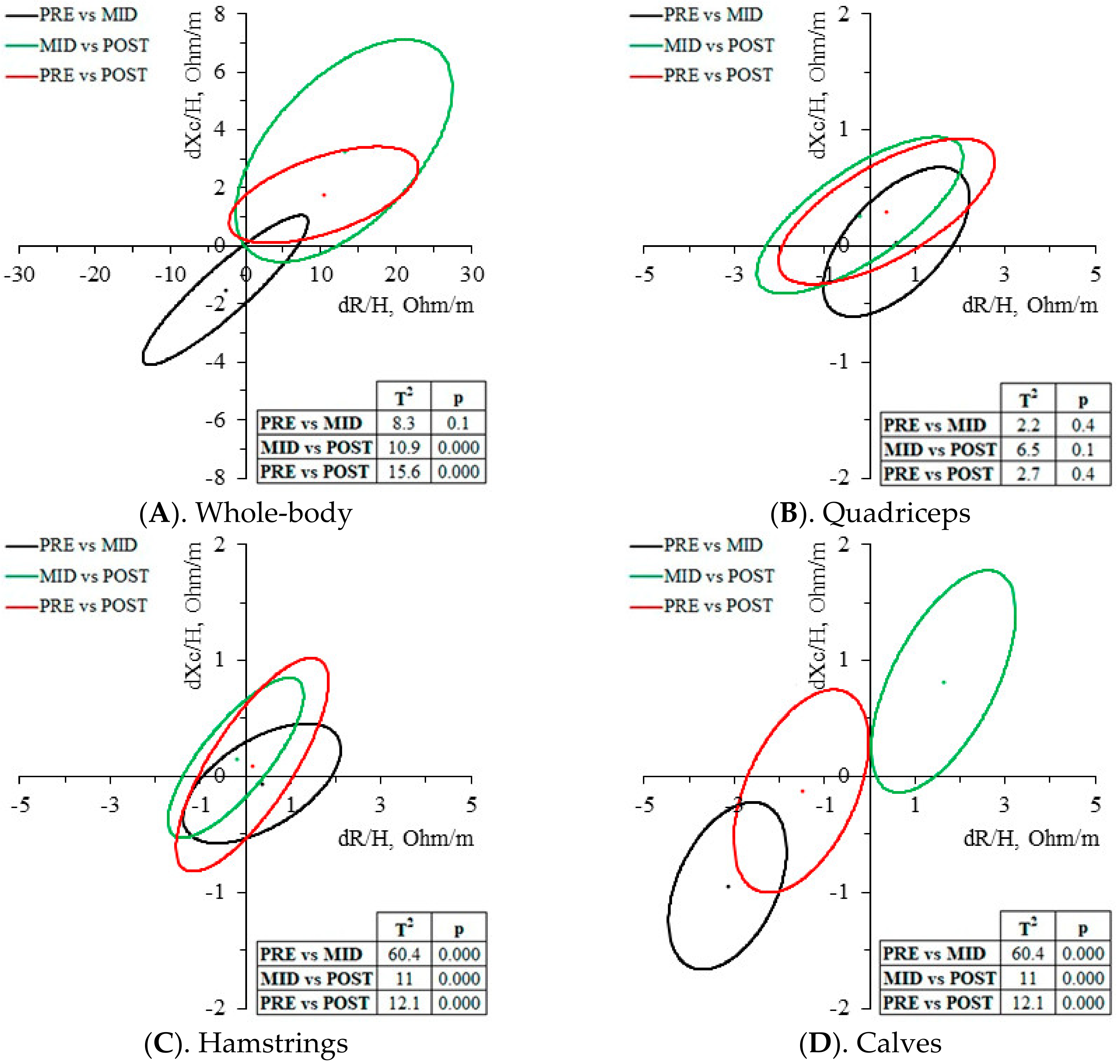
4.2. Whole-Body Changes
4.3. Muscle-Localized Changes
4.4. Hematological Changes
4.5. Practical Applications and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corsetti, R.; Barassi, A.; Perego, S.; Sansoni, V.; Rossi, A.; Damele, C.A.L.; Melzi D’Eril, G.; Banfi, G.; Lombardi, G. Changes in Urinary Amino Acids Excretion in Relationship with Muscle Activity Markers over a Professional Cycling Stage Race: In Search of Fatigue Markers. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollastri, L.; Lanfranconi, F.; Tredici, G.; Schenk, K.; Burtscher, M.; Gatterer, H. Body Fluid Status and Physical Demand during the Giro d’Italia. Res. Sports Med. 2016, 24, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollastri, L.; Lanfranconi, F.; Tredici, G.; Burtscher, M.; Gatterer, H. Body Water Status and Short-Term Maximal Power Output during a Multistage Road Bicycle Race (Giro d’Italia 2014). Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, G.; Corsetti, R.; Lanteri, P.; Grasso, D.; Vianello, E.; Marazzi, M.G.; Graziani, R.; Colombini, A.; Galliera, E.; Corsi Romanelli, M.M.; et al. Reciprocal Regulation of Calcium-/Phosphate-Regulating Hormones in Cyclists during the Giro d’Italia 3-Week Stage Race. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2014, 24, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, N.; Noakes, T.D. The Quantification of Body Fluid Allostasis during Exercise. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Gobbo, L.A.; Stagi, S.; Cyrino, L.T.; Toselli, S.; Marini, E.; Coratella, G. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis versus Reference Methods in the Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 122, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, A. Bioelectric Impedance Measurement for Fluid Status Assessment. In Fluid Overload; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 164, pp. 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Castizo-Olier, J.; Irurtia, A.; Jemni, M.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Fernández-García, R.; Rodríguez, F.A. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) in Sport and Exercise: Systematic Review and Future Perspectives. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, E.; Campa, F.; Buffa, R.; Stagi, S.; Matias, C.N.; Toselli, S.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Phase Angle and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis in the Evaluation of Body Composition in Athletes. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaski, H.C. Body Composition: Health and Performance in Exercise and Sport, 1st ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Orlando, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cebrián-Ponce, Á.; Irurtia, A.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Saco-Ledo, G.; Girabent-Farrés, M.; Castizo-Olier, J. Electrical Impedance Myography in Health and Physical Exercise: A Systematic Review and Future Perspectives. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 740877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Da Prat, B.; Montagnese, C.; Caldara, A.; Sammarco, R.; Pasanisi, F.; Corsetti, R. Segmental Bioimpedance Analysis in Professional Cyclists during a Three Week Stage Race. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsetti, R.; Lombardi, G.; Lanteri, P.; Colombini, A.; Graziani, R.; Banfi, G. Haematological and Iron Metabolism Parameters in Professional Cyclists during the Giro d’Italia 3-Weeks Stage Race. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2012, 50, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, E.; Toselli, S. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis of Body Composition—Applications in Sports Science; UNICApress: Cagliari, Italy, 2021; ISBN 9788833120324. [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli, A.; Nigrelli, S.; Caberlotto, A.; Bottazzo, S.; Rossi, B.; Pillon, L.; Maggiore, Q. Bivariate Normal Values of the Bioelectrical Impedance Vector in Adult and Elderly Populations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association (WMA). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, C.N.; Santos, D.A.; Júdice, P.B.; Magalhães, J.P.; Minderico, C.S.; Fields, D.A.; Lukaski, H.C.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Estimation of Total Body Water and Extracellular Water with Bioimpedance in Athletes: A Need for Athlete-Specific Prediction Models. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Marfell-Jones, M.; Olds, T.; de Ridder, H. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Portsmouth, UK, 2011; ISBN 0-620-36207-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, A.A. A Simple and Accurate Method for Prescribing Plasma Exchange. ASAIO Trans. 1990, 36, M597–M599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siekmann, L.; Bonora, R.; Burtis, C.A.; Ceriotti, F.; Clerc-Renaud, P.; Férard, G.; Ferrero, C.A.; Forest, J.-C.; Franck, P.F.H.; Gella, F.-J.; et al. IFCC Primary Reference Procedures for the Measurement of Catalytic Activity Concentrations of Enzymes at 37 °C. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2002, 40, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, A.; Pastori, G. BIVA Software; University of Padova: Padova, Italy, 2002; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Pirlich, M.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Bioelectrical Phase Angle and Impedance Vector Analysis—Clinical Relevance and Applicability of Impedance Parameters. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertow, G.M.; Lowrie, E.G.; Wilmore, D.W.; Gonzalez, J.; Lew, N.L.; Ling, J.; Leboff, M.S.; Gottlieb, M.N.; Huang, W.; Zebrowski, B.; et al. Nutritional Assessment with Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1995, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castizo-Olier, J.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Roy, A.; Chaverri, D.; Iglesias, X.; Pérez-Chirinos, C.; Rodríguez, F.; Irurtia, A. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) and Body Mass Changes in an Ultra-Endurance Triathlon Event. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2018, 17, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Castizo-Olier, J.; Rodríguez-Zamora, L.; Iglesias, X.; Rodríguez, F.A.; Chaverri, D.; Brotons, D.; Irurtia, A. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) for Measuring the Hydration Status in Young Elite Synchronized Swimmers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, A.; Vicini, M.; Pollastri, L.; Lombardi, E.; Magni, E.; Andreazzoli, A.; Orsini, M.; Bonifazi, M.; Lukaski, H.; Gatterer, H. Bioimpedance Patterns and Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) of Road Cyclists. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 2608–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrián-Ponce, Á.; Garnacho-Castaño, M.V.; Castellano-Fàbrega, M.; Castizo-Olier, J.; Carrasco-Marginet, M.; Serra-Paya, N.; Irurtia, A. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector and Creatine Phosphokinase Changes Induced by a High-Intensity Training Session in Rink Hockey Players. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, K.R. Use of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Measurements as an Evaluation for Participating in Sports. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington-Rauth, M.; Leu, C.G.; Júdice, P.B.; Correia, I.R.; Magalhães, J.P.; Sardinha, L.B. Whole Body and Regional Phase Angle as Indicators of Muscular Performance in Athletes. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2021, 21, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetherington-Rauth, M.; Baptista, F.; Sardinha, L.B. BIA-Assessed Cellular Hydration and Muscle Performance in Youth, Adults, and Older Adults. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.; Fields, D.A.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Sardinha, L.B. Body Composition and Power Changes in Elite Judo Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2010, 31, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.E.; Johnson, E.C.; McKenzie, A.L.; Ellis, L.A.; Williamson, K.H. Endurance Cyclist Fluid Intake, Hydration Status, Thirst, and Thermal Sensations: Gender Differences. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2016, 26, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Da Prat, B.; Montagnese, C.; Sgroi, M.; Sicilia, G.; Caldara, A.; Santarpia, L.; Corsetti, R. Body Composition Changes in Professional Cyclists during the 2011 Giro d’Italia, a 3-Week Stage Race. Nutr. Ther. Metab. 2014, 32, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.E.; Rosenberg, I.; Armstrong, L.; Manz, F.; Dal Canton, A.; Barclay, D.; Ritz, P.; Sawka, M.; Shirreffs, S.; Ferry, M. Hydration Assessment Techniques. Nutr. Rev. 2005, 63, S40–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress: Cellular Mechanisms and Impact on Muscle Force Production. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascherini, G.; Petri, C.; Galanti, G. Integrated Total Body Composition and Localized Fat-Free Mass Assessment. Sport Sci. Health 2015, 11, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingwell, J.B.; Joubert, J.E.; Diefenthaeler, F.; Trinity, J.D. Changes in Muscle Activity and Kinematics of Highly Trained Cyclists During Fatigue. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 2666–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørkeberg, J.S.; Belhage, B.; Damsgaard, R. Changes in Blood Values in Elite Cyclist. Int. J. Sports Med. 2009, 30, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsworth, R.E.; Cho, Y.I.; Weidman, J. Effect of Hydration on Whole Blood Viscosity in Firefighters. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2013, 19, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Costill, D.L.; Fink, W.J. Plasma Volume Changes Following Exercise and Thermal Dehydration. J. Appl. Physiol. 1974, 37, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, A.; Sanders, D.; Vicini, M.; Lukaski, H.; Gatterer, H. Body Fluid Status, Plasma Volume Change and Its Relationship to Physical Effort during a Multistage Professional Road Cycling Race. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2018, 18, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Day | Stage (#) | Length (km) | Accumulated Slope (m) | Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 * | – | – | – | – |
| 1 | 1 | 130.0 | 1274 | F |
| 2 | 2 | 17.4 | 329 | Team TT |
| 3 | 3 | 222.0 | 3308 | MM |
| 4 | 4 | 246.0 | 2528 | MM |
| 5 | 5 | 203.0 | 981 | F |
| 6 | 6 | 169.0 | 399 | F |
| 7 | 7 | 177.0 | 3664 | MM |
| 8 | 8 | 54.8 | 889 | Individual TT |
| 9 | 9 | 170.0 | 4786 | MM |
| 10 * | Rest | – | – | – |
| 11 | 10 | 167.0 | 4183 | HM |
| 12 | 11 | 182.0 | 4235 | MM |
| 13 | 12 | 134.0 | 1411 | F |
| 14 | 13 | 254.0 | 2390 | F |
| 15 | 14 | 180.0 | 2790 | HM |
| 16 | Rest | – | – | – |
| 17 | 15 | 145.0 | 7095 | HM |
| 18 | 16 | 238.0 | 5798 | MM |
| 19 | 17 | 214.0 | 1136 | F |
| 20 | 18 | 20.6 | 1045 | Individual TT |
| 21 | 19 (Cancelled) | – | – | – |
| 22 | 20 | 210.0 | 3354 | HM |
| 23 * | 21 | 206.0 | 575 | F |
| Total | 21 | 3455.0 | 52,170 | |
| Mean | 164.5 | 2609 |
| PRE-MID | MID-POST | PRE-POST | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | MID | POST | ∆ (%) | p | ∆ (%) | p | ∆ (%) | p | |
| Body composition | |||||||||
| BM (kg) | 70.5 ± 6.1 | 70.4 ± 6.2 | 70.7 ± 5.9 | −0.1 ± 1.2 | 0.574 | 0.4 ± 1.3 | 0.400 | 0.3 ± 1.6 | 0.499 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.4 ± 0.8 | 21.4 ± 0.8 | 21.4 ± 0.7 | −0.1 ± 1.2 | 0.589 | 0.4 ± 1.3 | 0.443 | 0.3 ± 1.6 | 0.673 |
| TBW (L) | 45.9 ± 3.7 | 46.1 ± 4.0 | 45.5 ± 3.3 | 0.3 ± 1.6 | 0.398 | −1.2 ± 2.1 | 0.075 | −1.0 ± 1.5 | 0.086 |
| ECW (L) | 15.3 ± 1.2 | 15.3 ± 1.2 | 15.1 ± 1.0 | 0.3 ± 1.7 | 0.683 | −1.3 ± 2.2 | 0.105 | −1.1 ± 1.6 | 0.064 |
| ICW (L) | 30.7 ± 2.5 | 30.8 ± 2.8 | 30.3 ± 2.2 | 0.3 ± 1.4 | 0.458 | −1.0 ± 1.9 | 0.090 | −0.8 ± 1.4 | 0.079 |
| ECW/ICW ratio | 0.50 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.00 | −0.1 ± 0.3 | 1.000 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.083 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.083 |
| Whole-body BIVA | |||||||||
| R/H (Ω/m) | 265.5 ± 21.5 | 262.8 ± 24.4 | 275.9 ± 13.9 | −1.0 ± 3.7 | 0.515 | 5.4 ± 5.9 | 0.008 * | 4.2 ± 4.6 | 0.038 |
| Xc/H (Ω/m) | 35.8 ± 2.8 | 34.3 ± 3.7 | 37.5 ± 2.2 | −4.3 ± 6.8 | 0.108 | 10.5 ± 11.8 | 0.013 * | 5.1 ± 4.6 | 0.018 |
| Z/H (Ω/m) | 267.9 ± 21.6 | 265.0 ± 24.6 | 278.4 ± 13.9 | −1.1 ± 3.8 | 0.515 | 5.5 ± 6.0 | 0.008 * | 4.2 ± 4.6 | 0.038 |
| PhA (°) | 7.7 ± 0.4 | 7.4 ± 0.4 | 7.8 ± 0.4 | −3.4 ± 4.0 | 0.048 * | 4.7 ± 7.7 | 0.089 | 1.0 ± 4.9 | 0.623 |
| Mean quadriceps BIVA | |||||||||
| R/H (Ω/m) | 14.7 ± 1.3 | 15.3 ± 1.3 | 15.1 ± 2.4 | 4.6 ± 10.6 | 0.236 | −1.4 ± 13.6 | 1.000 | 2.8 ± 15.9 | 0.624 |
| Xc/H (Ω/m) | 5.1 ± 0.5 | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 5.4 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 12.2 | 0.671 | 5.8 ± 12.5 | 0.256 | 6.4 ± 11.2 | 0.122 |
| Z/H (Ω/m) | 15.6 ± 1.4 | 16.1 ± 1.3 | 16.0 ± 2.4 | 4.2 ± 10.4 | 0.236 | −0.6 ± 13.1 | 0.722 | 3.2 ± 14.9 | 0.553 |
| PhA (°) | 19.4 ± 1.6 | 18.7 ± 1.3 | 20.1 ± 2.0 | −3.1 ± 8.4 | 0.314 | 7.7 ± 10.3 | 0.085 | 4.2 ± 11.9 | 0.477 |
| Mean hamstrings BIVA | |||||||||
| R/H (Ω/m) | 14.5 ± 2.0 | 14.9 ± 1.1 | 14.6 ± 1.6 | 3.9 ± 13.7 | 0.463 | −1.4 ± 9.4 | 0.766 | 2.0 ± 13.1 | 0.675 |
| Xc/H (Ω/m) | 4.9 ± 0.4 | 4.9 ± 0.5 | 5.0 ± 0.9 | −1.1 ± 9.3 | 0.608 | 3.3 ± 13.0 | 0.440 | 2.3 ± 17.0 | 0.866 |
| Z/H (Ω/m) | 15.3 ± 2.0 | 15.6 ± 1.1 | 15.5 ± 1.7 | 3.3 ± 12.6 | 0.574 | −0.9 ± 9.6 | 0.953 | 2.0 ± 13.2 | 0.722 |
| PhA (°) | 18.9 ± 1.9 | 18.1 ± 2.0 | 18.9 ± 2.1 | −3.9 ± 9.3 | 0.262 | 4.2 ± 6.1 | 0.050 * | 0.0 ± 8.8 | 0.953 |
| Mean calves BIVA | |||||||||
| R/H (Ω/m) | 36.2 ± 3.3 | 33.1 ± 3.3 | 34.7 ± 3.4 | −8.7 ± 3.2 | 0.008 * | 5.0 ± 4.5 | 0.017 * | −4.2 ± 3.7 | 0.018 * |
| Xc/H (Ω/m) | 8.6 ± 1.2 | 7.6 ± 1.2 | 8.5 ± 1.2 | −10.9 ± 7.3 | 0.007 * | 11.5 ± 12.7 | 0.028 * | −1.1 ± 9.8 | 0.357 |
| Z/H (Ω/m) | 37.2 ± 3.4 | 33.9 ± 3.4 | 35.7 ± 3.6 | −8.8 ± 3.3 | 0.008 * | 5.3 ± 4.7 | 0.013 * | −4.1 ± 3.7 | 0.017 * |
| PhA (°) | 13.3 ± 1.1 | 13.0 ± 1.2 | 13.7 ± 1.0 | −2.5 ± 5.8 | 0.286 | 6.0 ± 9.2 | 0.097 | 3.1 ± 8.7 | 0.498 |
| Hematological | |||||||||
| Hb (g/dL) | 14.1 ± 0.7 | 13.1 ± 0.9 | 13.6 ± 0.8 | −7.3 ± 3.5 | 0.008 * | 4.1 ± 3.0 | 0.007 * | −3.6 ± 2.6 | 0.012 * |
| Hct (%) | 42.0 ± 2.3 | 39.3 ± 2.3 | 40.6 ± 2.2 | −6.4 ± 2.7 | 0.008 * | 3.6 ± 3.5 | 0.015 * | −3.1 ± 3.3 | 0.028 * |
| EPV (mL) | 2663.3 ± 280.2 | 2785.4 ± 309.4 | 2730.2 ± 257.9 | 13.1 ± 6.2 | 0.011 * | −5.9 ± 4.5 | 0.050 * | 6.2 ± 5.4 | 0.028 * |
| POsm (mOsm/L) | 285.4 ± 6.2 | 292.2 ± 16.9 | 312.2 ± 33.1 | 2.4 ± 5.5 | 0.362 | 7.2 ± 13.0 | 0.155 | 9.3 ± 10.8 | 0.011 * |
| Na+ (mEq/L) | 138.7 ± 1.9 | 141.0 ± 1.4 | 143.4 ± 6.0 | 1.7 ± 1.6 | 0.027 * | 1.7 ± 4.0 | 0.233 | 3.5 ± 4.7 | 0.049 * |
| K+ (mEq/L) | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 4.8 ± 0.3 | −9.3 ± 5.9 | 0.012 * | 3.2 ± 7.3 | 0.396 | −6.7 ± 5.8 | 0.017 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cebrián-Ponce, Á.; Irurtia, A.; Castizo-Olier, J.; Garnacho-Castaño, M.V.; Espasa-Labrador, J.; Noriega, Z.; Carrasco-Marginet, M. Bioelectrical, Anthropometric, and Hematological Analysis to Assess Body Fluids and Muscle Changes in Elite Cyclists during the Giro d’Italia. Biology 2023, 12, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030450
Cebrián-Ponce Á, Irurtia A, Castizo-Olier J, Garnacho-Castaño MV, Espasa-Labrador J, Noriega Z, Carrasco-Marginet M. Bioelectrical, Anthropometric, and Hematological Analysis to Assess Body Fluids and Muscle Changes in Elite Cyclists during the Giro d’Italia. Biology. 2023; 12(3):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030450
Chicago/Turabian StyleCebrián-Ponce, Álex, Alfredo Irurtia, Jorge Castizo-Olier, Manuel Vicente Garnacho-Castaño, Javier Espasa-Labrador, Zeasseska Noriega, and Marta Carrasco-Marginet. 2023. "Bioelectrical, Anthropometric, and Hematological Analysis to Assess Body Fluids and Muscle Changes in Elite Cyclists during the Giro d’Italia" Biology 12, no. 3: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030450
APA StyleCebrián-Ponce, Á., Irurtia, A., Castizo-Olier, J., Garnacho-Castaño, M. V., Espasa-Labrador, J., Noriega, Z., & Carrasco-Marginet, M. (2023). Bioelectrical, Anthropometric, and Hematological Analysis to Assess Body Fluids and Muscle Changes in Elite Cyclists during the Giro d’Italia. Biology, 12(3), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030450










