Dissolved Carbon Dioxide: The Lifespan of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis in Bottled Carbonated Mineral Water
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Reference Strains for Inoculation
2.2. Preparation of Artificial Contaminated Water Samples
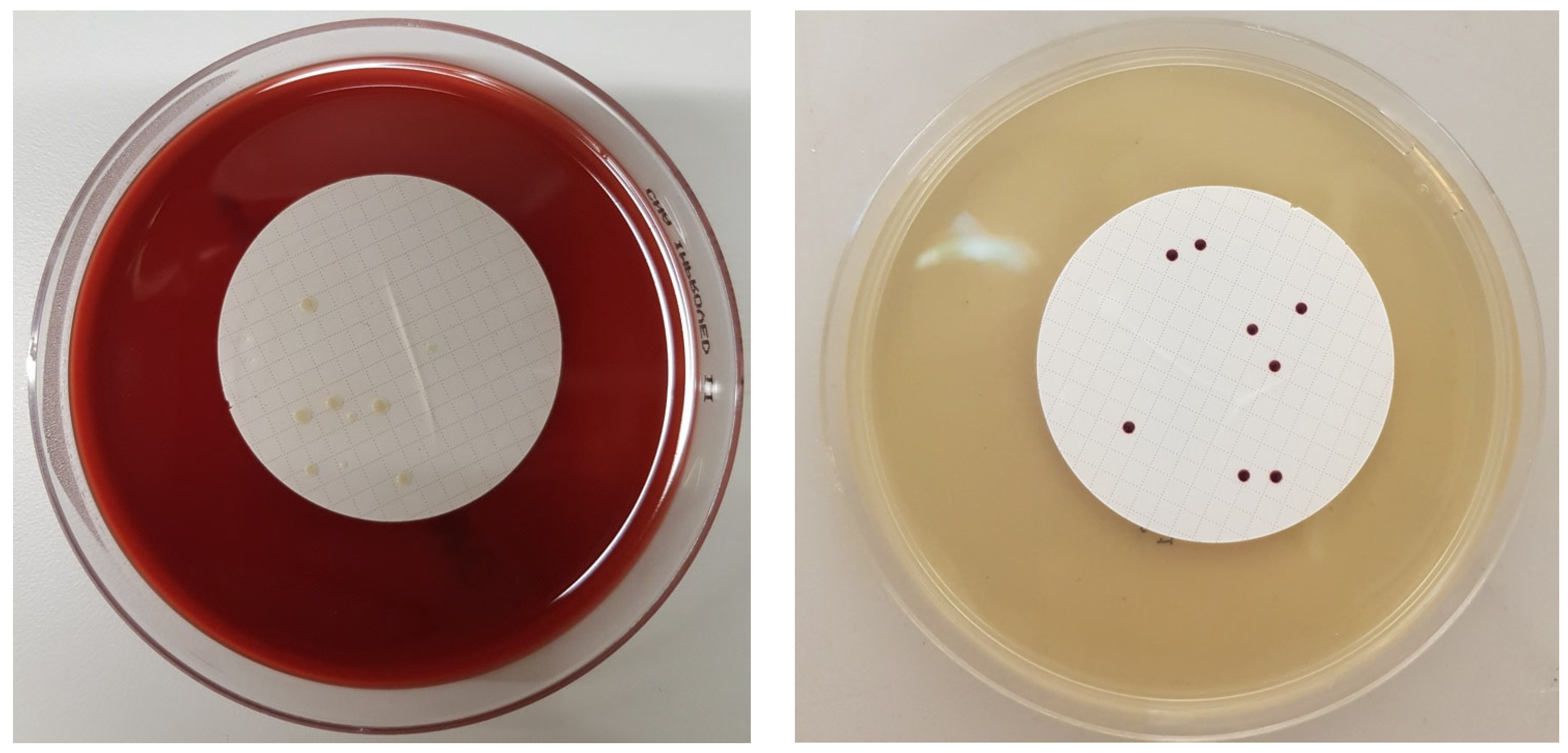
2.3. Cultivation of Target Bacteria
2.4. Gram Staining
2.5. Data Analysis
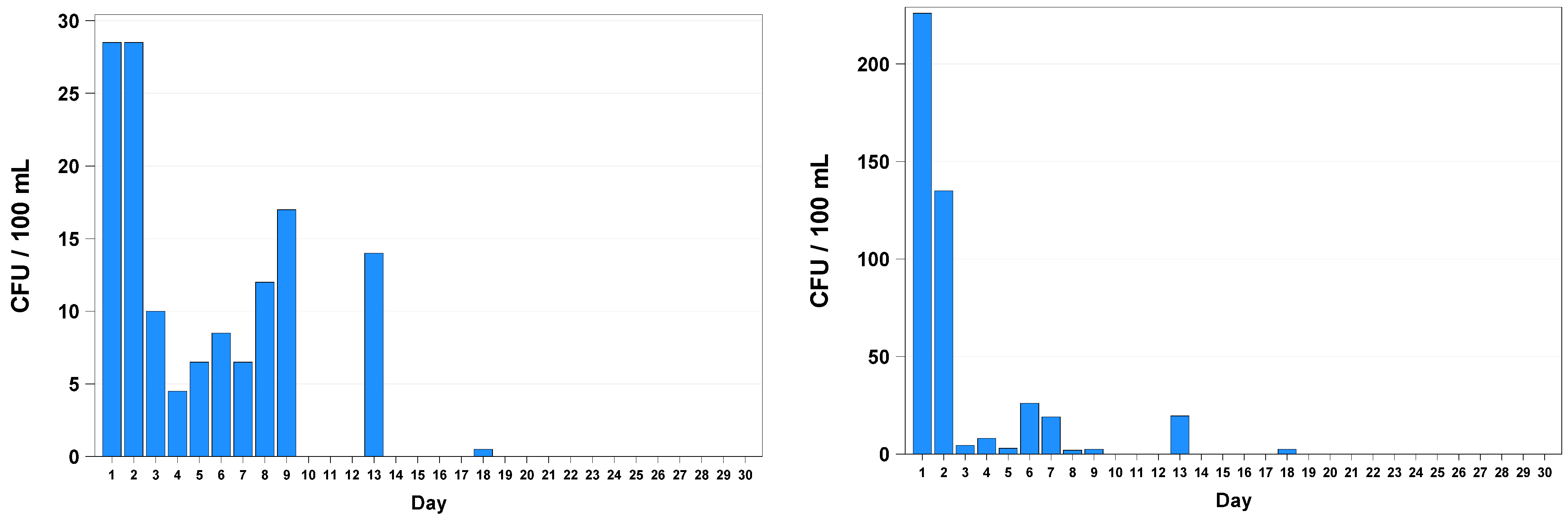
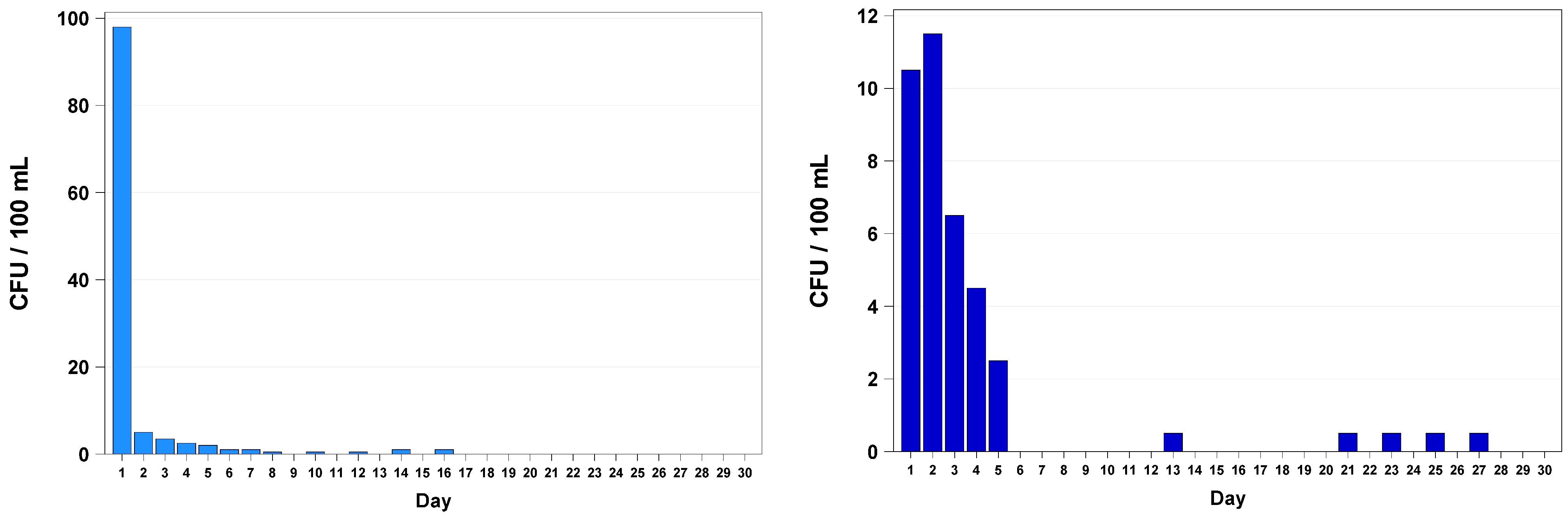
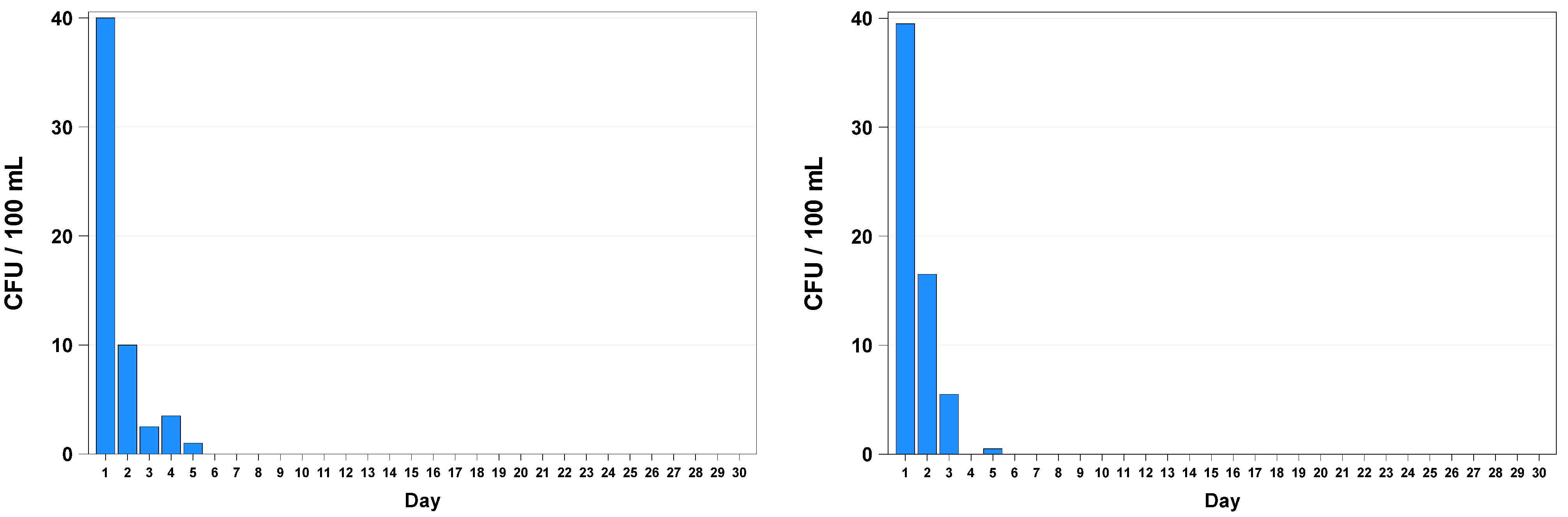
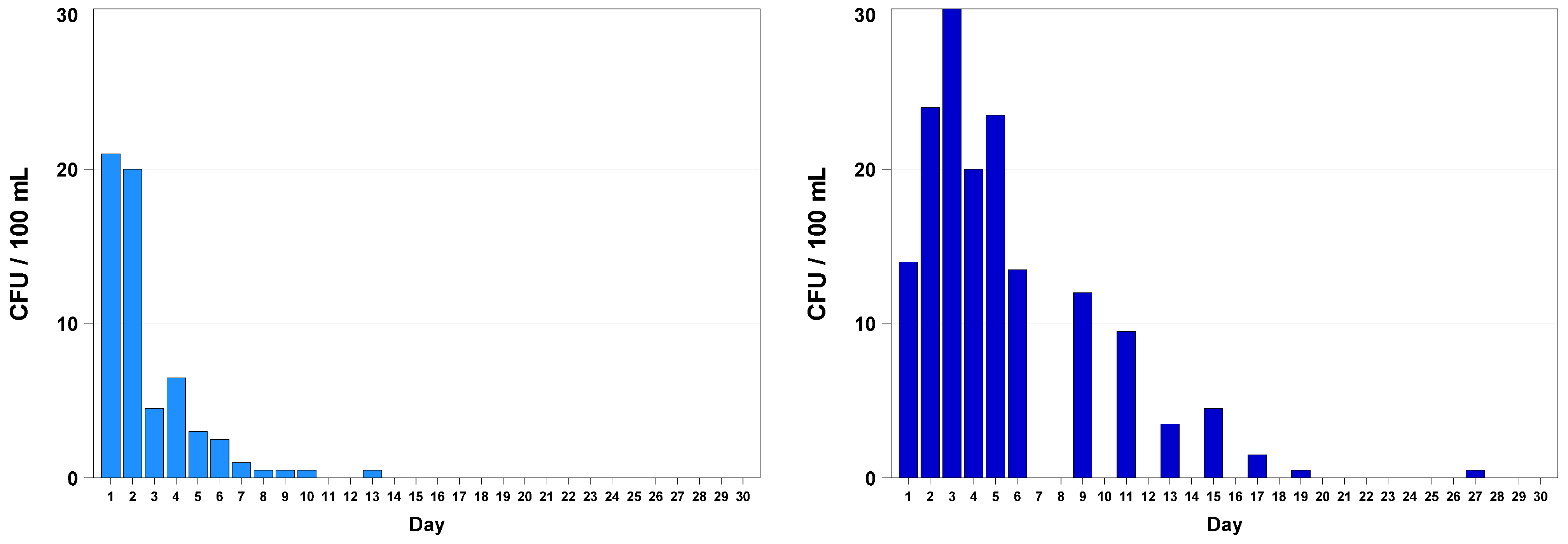
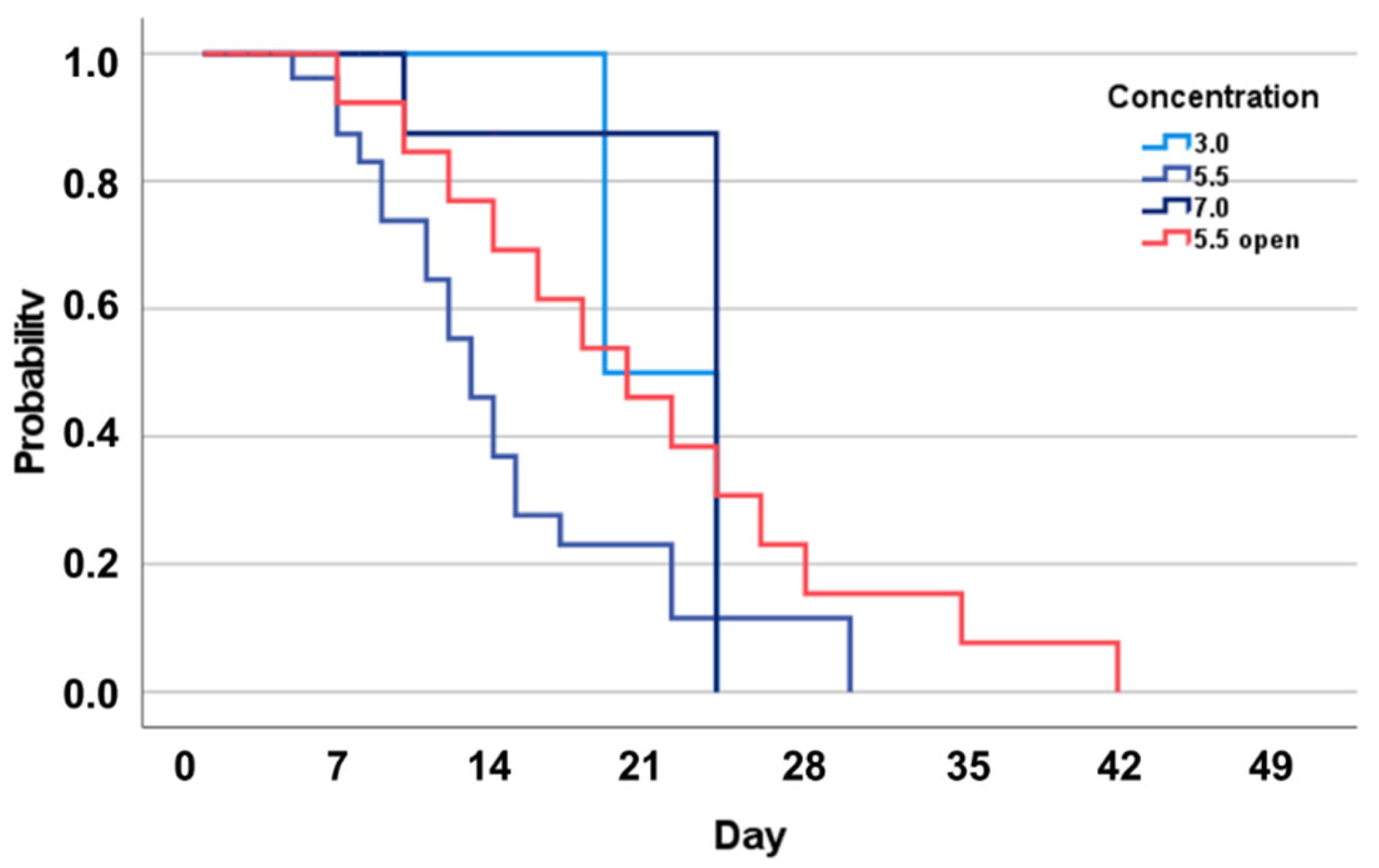
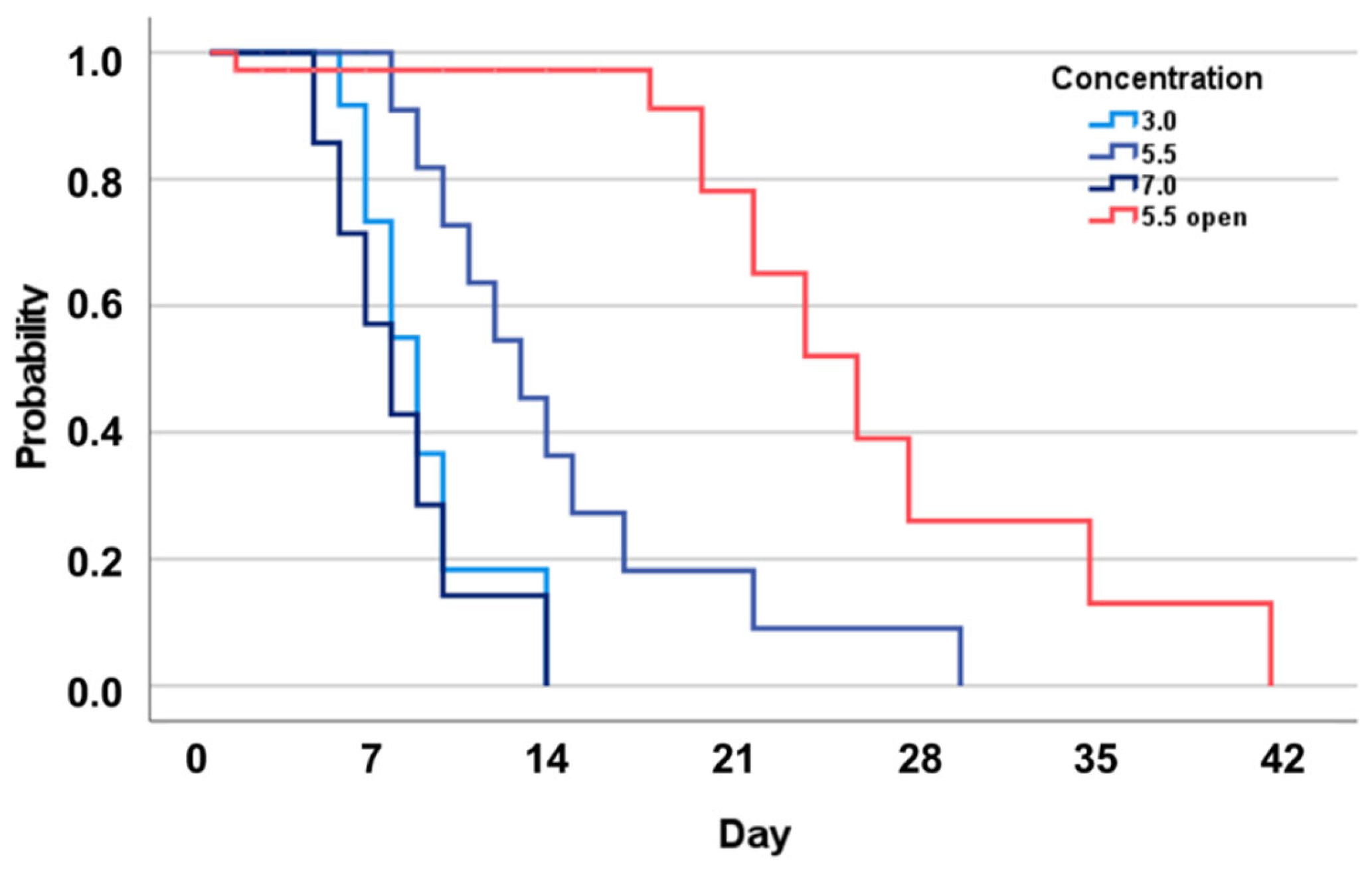
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Österreichisches Lebensmittelbuch (ÖLMB) Kapitel B17 Abgefüllte Wässer. Available online: https://www.verbrauchergesundheit.gv.at/Lebensmittel/buch/codex/B17_Abgefuellte_Waesser.pdf?8ksx23 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Mineral und Quellwasserverordnung. Available online: https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung/Bundesnormen/20000003/Mineralwasser-%20und%20Quellwasserverordnung%2c%20Fassung%20vom%2002.01.2023.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Iyer, V.; Raut, J.; Dasgupta, A. Impact of pH on growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus in vitro. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 001421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, M.; Svenarud, P.; Flock, J.I.; van der Linden, J. Carbon dioxide inhibits the growth rate of Staphylococcus aureus at body temperature. Surg. Endosc. 2005, 19, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, J.T.; Bayu, A.; Aryati, W.D.; Fernandes, C.; Yanuar, A.; Kijjoa, A.; Putra, M.Y. Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Bacteria with Antibiotic and Antibiofilm Activities against Drug-Resistant Pathogens. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, D. A Visible Light-Induced and ROS-Dependent Method for the Rapid Formation of a MOF Composite Membrane with Antibacterial Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambreen, J.; Haleem, A.; Shah, A.A.; Mushtaq, F.; Siddiq, M.; Bhatti, M.A.; Shah Bukhari, S.N.U.; Chandio, A.D.; Mahdi, W.A.; Alshehri, S. Facile Synthesis and Fabrication of NIPAM-Based Cryogels for Environmental Remediation. Gels 2023, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, G.; Tong, Y.; Zen, M.; Liang, Z.; Li, M.; Yan, R.; Wang, Y. Green Synthesis of Anti-bacterial Nano Silver by Polysaccharide from Bletilla Striata. Inorganics 2023, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altran Costa, B.; Abuçafy, M.P.; Barbosa, T.W.L.; da Silva, B.L.; Fulindi, R.B.; Isquibola, G.; da Costa, P.I.; Chiavacci, L.A. ZnO@ZIF-8 Nanoparticles as Nanocarrier of Ciprofloxacin for Antimicrobial Activity. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, G.M.; Garcia-Teodoro, B.; Martins, C.P.; Schmitt, P.; Guzmán, F.; de Freitas, A.C.O.; Stoco, P.H.; Ferreira, F.A.; Stadnik, M.J.; Robl, D.; et al. Antimicrobial Spectrum of Activity and Mechanism of Action of Linear Alpha-Helical Peptides Inspired by Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legiawati, L.; Halim, P.A.; Fitriani, M.; Hikmahrachim, H.G.; Lim, H.W. Microbiomes in Acne Vulgaris and Their Susceptibility to Antibiotics in Indonesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghataty, D.S.; Amer, R.I.; Amer, M.A.; Abdel Rahman, M.F.; Shamma, R.N. Green Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Bovine Serum Albumin for Linezolid Drug Delivery as Potential Wound Healing Biomaterial: Bio-Synergistic Approach, Antibacterial Activity, and In Vitro and Ex Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, L.; Agostinho, P.; Morais, P.V.; da Costa, M.S. Survival of allochthonous bacteria in still mineral water bottled in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and glass. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1994, 77, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechmechani, S.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Karam, L.; EL Omari, K.; Fadel, A.; Hamze, M.; Chihib, N.-E. Pepsin and Trypsin Treatment Combined with Carvacrol: An Efficient Strategy to Fight Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterococcus faecalis Biofilms. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, M.S.; Urushibara, N.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Ohashi, N.; Hirose, M.; Kudo, K.; Tsukamoto, N.; Ito, M.; Kobayashi, N. Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Factors, and Genotypes of Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium Clinical Isolates in Northern Japan: Identification of optrA in ST480 E. faecalis. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, S. WHO warns against ‘post-antibiotic’ era. Nature 2014, 244, 1356–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam Mohamed, S.; Nyerere, A.; Sang, W.K.; Ngayo, M. Bottled water brands are contaminated with multidrug resistant bacteria in Nairobi, Kenya. F1000Research 2020, 9, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompré, A.; Servais, P.; Baudart, J.; de-Roubin, M.R.; Laurent, P. Detection and enumeration of coliforms in drinking water: Current methods and emerging approaches. J. Microbiol. Methods 2002, 49, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalli, M.; Inwinkl, S.M.; Platzer, S.; Baumert, R.; Reinthaler, F.F.; Ofner-Kopeinig, P.; Haas, D. Cefsulodin and Vancomycin: A Supplement for Chromogenic Coliform Agar for Detection of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria from Different Water Sources. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurliyana, M.R.; Sahdan, M.Z.; Wibowo, K.M.; Muslihati, A.; Saim, H.; Ahmad, S.A.; Sari, Y.; Mansor, Z. The Detection Method of Escherichia coli in Water Resources: A Review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 995, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumfield, K.D.; Hasan, N.A.; Leddy, M.B.; Cotruvo, J.A.; Rashed, S.M.; Colwell, R.R.; Huq, A. A comparative analysis of drinking water employing metagenomics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Gupta, R.; Sekhri, S. A convolutional neural network approach for detection of E. coli bacteria in water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 60778–60786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, S.M.; Shah, P.; Nair, A. Flow cytometry: Principles, applications and recent advances. Bioanalysis 2021, 3, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manaia, C.M.; Nunes, O.C.; Morais, P.V.; da Costa, M.S. Heterotrophic plate counts and the isolation of bacteria from mineral waters on selective and enrichment media. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 69, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi Kouchesfahani, M.; Alimohammadi, M.; Nabizadeh Nodehi, R.; Aslani, H.; Rezaie, S.; Asadian, S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Heterotrophic Bacteria Count in Bottled Waters in Iran. Iran. J. Public Health 2015, 44, 1514–1519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reasoner, D.J. Heterotrophic plate count methodology in the United States. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 92, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranceau, S.J.; Emerson, H.P.; Wilder, R.J. Impact of bottled water storage duration and location on bacteriological quality. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2012, 22, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venieri, D.; Vantarakis, A.; Komninou, G.; Papapetropoulou, M. Microbiological evaluation of bottled non-carbonated (“still”) water from domestic brands in Greece. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 107, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florina, R.; Calin, A.; Raluca, M. Physico-Chemical and Microbiological Differences between Mains and Bottled Water, in an Area in the Central Area of Romania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.A.C.; Dropa, M.; Rocha, S.M.; Peternella, F.A.S.; Razzolini, M.T.P. Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in drinking water fountains in urban parks. J. Water Health 2020, 18, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeChevallier, M.W.; Seidler, R.J. Staphylococcus aureus in rural drinking water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1980, 39, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesoji, A.T.; Onuh, J.P.; Bagu, J.; Itohan, S.A. Prevalence and antibiogram study of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical and selected drinking water of Dutsin-Ma, Katsina state, Nigeria. Afr. Health Sci. 2019, 19, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.S.; Choong, M.Y.; Wu, S.F.; Chen, K.J. Irrigating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus—Colonized and infected chronic wounds. Int. Wound J. 2013, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagoba, B.S.; Selkar, S.P.; Mule, J.B. Irrigating methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-colonised and -infected chronic wounds—Why use tap water? Int. Wound J. 2015, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, S.; Bagale, K.; Patel, S.; Kooyers, N.J.; Kulkarni, R. Human Urine Alters Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Virulence and Transcriptome. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0074421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, H.; Yamasaki, O.; Tada, J.; Kubota, K.; Arata, J. Antimicrobial effects of acidic hot-spring water on Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from atopic dermatitis patients. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2000, 24, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Tango, C.N.; Chelliah, R.; Oh, D.H. Sanitization Efficacy of Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water against pure cultures of Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica, Typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus spores, in Comparison with Different Water Hardness. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchon, S.; Gaillard-Martinie, B.; Dordet-Frisoni, E.; Bellon-Fontaine, M.N.; Leroy, S.; Labadie, J.; Hébraud, M.; Talon, R. Formation of biofilm by Staphylococcus xylosus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Meira, Q.G.; de Medeiros Barbosa, I.; Athayde, A.J.A.A.; de Siqueira-Júnior, J.P.; de Souza, E.L. Influence of temperature and surface kind on biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus from food-contact surfaces and sensitivity to sanitizers. Food Contr. 2012, 25, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tango, C.N.; Akkermans, S.; Hussain, M.S.; Khan, I.; Van Impe, J.; Jin, Y.G.; Oh, D.H. Modeling the effect of pH, water activity, and ethanol concentration on biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.; Pérez-Rodríguez, F.; Carrasco, E.; Fuentes-Alventosa, J.M.; García-Gimeno, R.M.; Zurera, G. Modelling the growth boundaries of Staphylococcus aureus: Effect of temperature, pH and water activity. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 133, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedada, T.L.; Dera, F.A.; Edicho, R.M.; Gebre, S.G.; Asefa, Y.B.; Sima, W.G.; Maheder, R.F.; Negassi, T.Y.; Biegna, A.G. Mycological and Bacteriological Quality and Safety of Bottled Water in Ethiopia. Open Microbiol. J. 2018, 12, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igbeneghu, O.A.; Lamikanra, A. The bacteriological quality of different brands of bottled water available to consumers in Ile-Ife, south-western Nigeria. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, J.A.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Rizvi, S.S.H. A Review of Effects of Carbon Dioxide on Microbial Growth and Food Quality. J. Food Prot. 1985, 48, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams-Campbell, A.M.; Jay, J.M. Effects of diacetyl and carbon dioxide on spoilage microflora in ground beef. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.D.; Werner, B.G.; Hotchkiss, J.H. Effects of carbon dioxide on bacterial growth parameters in milk as measured by conductivity. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Chen, Y. Effects of elevated carbon dioxide on environmental microbes and its mechanisms: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Bååth, E. Contrasting soil pH effects on fungal and bacterial growth suggest functional redundancy in carbon mineralization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beer, D.; Haeckel, M.; Neumann, J.; Wegener, G.; Inagaki, F.; Boetius, A. Saturated CO2 inhibits microbial processes in CO2-vented deep-sea sediments. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 5639–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, L.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Spilimbergo, S.; Elst, K.; Van Ginneken, L.; Debevere, J.; Van Impe, J.F.; Devlieghere, F. High pressure carbon dioxide inactivation of microorganisms in foods: The past, the present and the future. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, L.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Elst, K.; Van Ginneken, L.; Van Impe, J.F.; Devlieghere, F. Influence of type of microorganism, food ingredients and food properties on high-pressure carbon dioxide inactivation of microorganisms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 129, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, L.; Geeraerd, A.H.; Mast, J.; Briers, Y.; Elst, K.; Van Ginneken, L.; Van Impe, J.F.; Devlieghere, F. Membrane permeabilization and cellular death of Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae as induced by high pressure carbon dioxide treatment. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, X.; Bi, W.; Jiang, C. Relationship between membrane damage, leakage of intracellular compounds, and inactivation of Escherichia coli treated by pressurized CO2. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Rhee, M.S.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, K.H. Modeling the inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and generic Escherichia coli by supercritical carbon dioxide. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 118, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastelli, E.; Corinaldesi, C.; Dell’Anno, A.; Amaro, T.; Greco, S.; Lo Martire, M.; Carugati, L.; Queirós, A.M.; Widdicombe, S.; Danovaro, R. CO2 leakage from carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS) systems affects organic matter cycling in surface marine sediments. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 122, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; An, H.; Hao, Y.; Hu, X.; Liao, X. New Insights into the Formation of Viable but Nonculturable Escherichia coli O157:H7 Induced by High-Pressure CO2. mBio 2016, 7, e00961-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, R.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Su, Y.; Li, M. Effect of CO2 on Microbial Denitrification via Inhibiting Electron Transport and Consumption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9915–9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ÖNORM EN ISO 10523; Wasserbeschaffenheit–Bestimmung des pH-Wertes. Austrian Standards Institute: Vienna, Austria, 2012.
- ÖNORM EN 27888; Wasserbeschaffenheit–Bestimmung der elektrischen Leitfähigkeit. Österreichisches Normungsinstitut: Vienna, Austria, 1993.
- DIN EN ISO 19036; Mikrobiologie der Lebensmittelkette—Feststellung von Messunsicherheiten bei Quantitativen Bestimmungen. Deutsches Institut für Normung e. V.: Berlin, Germany, 2019.
- Levallois, P.; Barn, P.; Valcke, M.; Gauvin, D.; Kosatsky, T. Public Health Consequences of Lead in Drinking Water. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalli, M.; Kogler, B.; Miorini, T.; Gehrer, M.; Reinthaler, F.F. High-Speed Dental Instruments: An Investigation of Protein-Contaminated Dental Handpieces with the Bicinchoninic Acid Assay in Dental Offices in Styria, Austria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in Drinking Water—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Dobaradaran, S.; Schmidt, T.C.; Nabipour, I.; Spitz, J. Worldwide bottled water occurrence of emerging contaminants: A review of the recent scientific literature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalli, M.; Weber, P.; Nasseri, S.A.; Gomez, A.T.; Müller, P.; Stütz, A.E.; Withers, S.G.; Wolfsgruber, A.; Wrodnigg, T.M. Biologically active branched-chain aminocyclopentane tetraols from d-galactose. Monatsh. Chem. 2019, 150, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Edberg, S.C.; Clancy, J.L.; Hrudey, S.E. Drinking water microbial myths. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 41, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staphylococcal (Staph) Food Poisoning. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/diseases/staphylococcal.html (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Korting, H.C.; Lukacs, A.; Vogt, N.; Urban, J.; Ehret, W.; Ruckdeschel, G. Influence of the pH-value on the growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus and Propionibacterium acnes in continuous culture. Zentralbl. Hyg. Umweltmed. 1992, 193, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borjac, J.; Zeino, W.; Matar, A.; Khawaja, S.; Merheb, M.; Matar, R. Prevalence of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Domestic Water Storage Tanks in Sidon, Lebanon. Water 2023, 15, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.D. Bottled water: How safe is it? Water Environ. Res. 2005, 77, 3013–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Ohnishi, T.; Araki, E.; Kanda, T.; Tomita, A.; Ozawa, K.; Goto, K.; Sugiyama, K.; Konuma, H.; Hara-Kudo, Y. Characteristics of bacterial and fungal growth in plastic bottled beverages under a consuming condition model. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2014, 49, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, C.P.; Zhang, P.; Michalek, S.; Eleazer, P.D. pH required to kill Enterococcus faecalis in vitro. J. Endod. 2004, 30, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salze, M.; Giard, J.C.; Riboulet-Bisson, E.; Hain, T.; Rincé, A.; Muller, C. Identification of the general stress stimulon related to colonization in Enterococcus faecalis. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, D.; Wu, Z. Transcriptome analysis of Cyclocarya paliurus flavonoids regulation of differently expressed genes in Enterococcus faecalis under low pH stress. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2147–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Da, R.; Tuo, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, J.; Jiang, K.; Lv, J.; Adediji, O.M.; Han, B. Probiotic and Safety Properties Screening of Enterococcus faecalis from Healthy Chinese Infants. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkman, O. Antimicrobial effect of pressurised carbondioxide on Enterococcus faecalis in physiological saline and foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH). Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/water-sanitation-and-hygiene-wash#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
| Number of Bottles (250 mL) | Concentration of CO2 (g/L) | Bacterial Strain |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 3.0 | Ent. faecalis ATCC 6057 |
| 40 | 5.5 | Ent. faecalis ATCC 6057 |
| 20 | 7.0 | Ent. faecalis ATCC 6057 |
| 20 | 3.0 | S. aureus ATCC 25923 |
| 40 | 5.5 | S. aureus ATCC 25923 |
| 20 | 7.0 | S. aureus ATCC 25923 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schalli, M.; Platzer, S.; Schmutz, R.; Ofner-Kopeinig, P.; Reinthaler, F.F.; Haas, D. Dissolved Carbon Dioxide: The Lifespan of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis in Bottled Carbonated Mineral Water. Biology 2023, 12, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030432
Schalli M, Platzer S, Schmutz R, Ofner-Kopeinig P, Reinthaler FF, Haas D. Dissolved Carbon Dioxide: The Lifespan of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis in Bottled Carbonated Mineral Water. Biology. 2023; 12(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030432
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchalli, Michael, Sabine Platzer, Rainer Schmutz, Petra Ofner-Kopeinig, Franz F. Reinthaler, and Doris Haas. 2023. "Dissolved Carbon Dioxide: The Lifespan of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis in Bottled Carbonated Mineral Water" Biology 12, no. 3: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030432
APA StyleSchalli, M., Platzer, S., Schmutz, R., Ofner-Kopeinig, P., Reinthaler, F. F., & Haas, D. (2023). Dissolved Carbon Dioxide: The Lifespan of Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis in Bottled Carbonated Mineral Water. Biology, 12(3), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030432







