Caveolin-1: A Review of Intracellular Functions, Tissue-Specific Roles, and Epithelial Tight Junction Regulation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
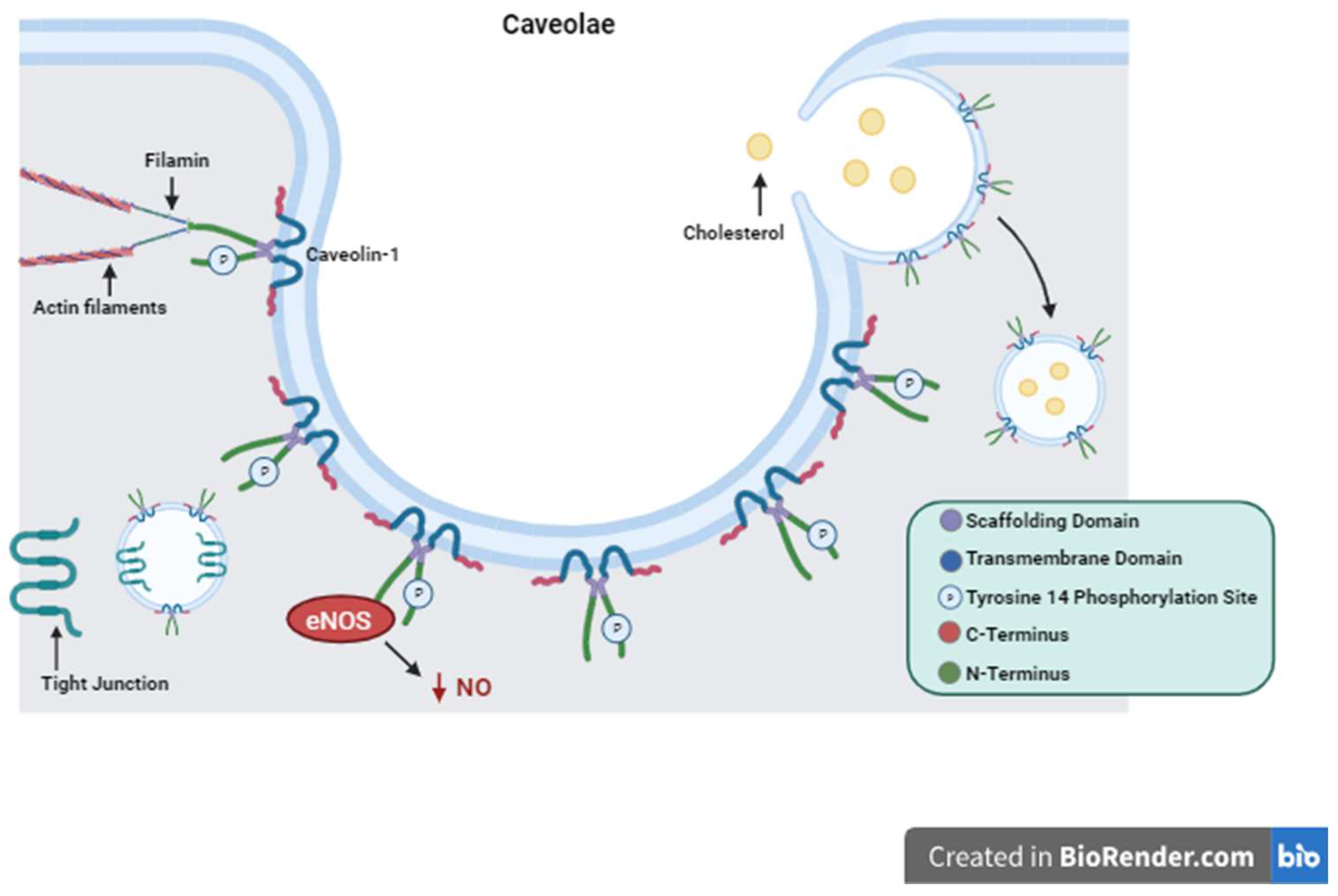
2. Caveolin-1 Structure and Function
3. Cellular Signaling
4. Cell Proliferation, Differentiation, Migration and Survival
4.1. Proliferation
4.2. Differentiation
4.3. Migration
4.4. Survival
4.5. Caveolin-1 Role in Cancer Cell Death and Survival
5. Caveolin-1 Tissue-Specific Roles
5.1. Vascular
5.2. Adipose
5.3. Brain
5.4. Pneumocytes
6. Caveolin-1 and the Intestinal Barrier
7. Conclusions
8. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, V. T cells and their immunometabolism: A novel way to understanding sepsis immunopathogenesis and future therapeutics. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 97, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michell, D.L.; Shihata, W.A.; Andrews, K.L.; Abidin, N.A.Z.; Jefferis, A.-M.; Sampson, A.K.; Lumsden, N.G.; Huet, O.; Parat, M.-O.; Jennings, G.L.; et al. High intraluminal pressure promotes vascular inflammation via caveolin-1. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.; Zhang, G.; You, Y.; Tuan, R.S. Caveolin-1 regulates proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 3773–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-S.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, H.-W.; Chae, G.-N.; Oh, H.-T.; Park, J.-Y.; Shim, H.; Seo, M.; Shin, E.Y.; Kim, E.G.; et al. Increased caveolin-1, a cause for the declined adipogenic potential of senescent human mesenchymal stem cells. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2005, 126, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volonte, D.; Zhang, K.; Lisanti, M.P.; Galbiati, F. Expression of Caveolin-1 Induces Premature Cellular Senescence in Primary Cultures of Murine Fibroblasts. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 2502–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Ryu, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Han, H.J. Lipid rafts play an important role for maintenance of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, K.; Toomre, D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Discher, D.E.; Mooney, D.J.; Zandstra, P.W. Growth Factors, Matrices, and Forces Combine and Control Stem Cells. Science 2009, 324, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.S.; Lee, H.; Frank, P.G.; Razani, B.; Nguyen, A.V.; Parlow, A.F.; Russell, R.G.; Hulit, J.; Pestell, R.G.; Lisanti, M.P.; et al. Caveolin-1-deficient Mice Show Accelerated Mammary Gland Development During Pregnancy, Premature Lactation, and Hyperactivation of the Jak-2/STAT5a Signaling Cascade. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 3416–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratliff, B.B.; Singh, N.; Yasuda, K.; Park, H.-C.; Addabbo, F.; Ghaly, T.; Rajdev, M.; Jasmin, J.F.; Plotkin, M.; Lisanti, M.P.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Used as Bait, Disclose Tissue Binding Sites: A Tool in the Search for the Niche? Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbaa, E.; DeWever, J.; Martinive, P.; Bouzin, C.; Frérart, F.; Balligand, J.-L.; Dessy, C.; Feron, O. Caveolin Plays a Central Role in Endothelial Progenitor Cell Mobilization and Homing in SDF-1–Driven Postischemic Vasculogenesis. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande-García, A.; Echarri, A.; de Rooij, J.; Alderson, N.B.; Waterman-Storer, C.M.; Valdivielso, J.M.; del Pozo, M.A. Caveolin-1 regulates cell polarization and directional migration through Src kinase and Rho GTPases. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 177, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parat, M.-O.; Anand-Apte, B.; Fox, P.L.; Meng, F.; Saxena, S.; Liu, Y.; Joshi, B.; Wong, T.H.; Shankar, J.; Foster, L.J.; et al. Differential Caveolin-1 Polarization in Endothelial Cells during Migration in Two and Three Dimensions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3156–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.; Tuan, R.S. The less-often-traveled surface of stem cells: Caveolin-1 and caveolae in stem cells, tissue repair and regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nah, J.; Yoo, S.-M.; Jung, S.; Jeong, E.I.; Park, M.; Kaang, B.-K.; Jung, Y.-K. Phosphorylated CAV1 activates autophagy through an interaction with BECN1 under oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; He, W.; Li, Z.; Chang, W.; Xin, Y.; Huang, T. Caveolin-1 functions as a key regulator of 17β-estradiol-mediated autophagy and apoptosis in BT474 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Shi, W.; Lv, P.; Meng, W.; Mao, G.; Gong, C.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Critical role of caveolin-1 in aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity via the regulation of oxidation and autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargalovic, P.; Dory, L. Cellular apoptosis is associated with increased caveolin-1 expression in macrophages. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidlow, J.H.; Sessa, W.C. Caveolae, caveolins, and cavins: Complex control of cellular signalling and inflammation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 86, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotgia, F.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Howell, A.; Pestell, R.G.; Pavlides, S.; Lisanti, M.P. Caveolin-1 and Cancer Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment: Markers, Models, and Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2012, 7, 423–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Ishiguro, H.; Kimura, M.; Mitsui, A.; Mori, Y.; Sugito, N.; Tomoda, K.; Mori, R.; Harada, K.; Katada, T.; et al. The overexpression of caveolin-1 and caveolin-2 correlates with a poor prognosis and tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ho, C.-C.; Kuo, S.-H.; Huang, P.-H.; Huang, H.-Y.; Yang, C.-H.; Yang, P.-C. Caveolin-1 expression is significantly associated with drug resistance and poor prognosis in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2008, 59, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shao, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Gong, L.; Yang, P. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Induces Invasion and Migration of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Decreasing the Expression of E-cadherin, β-catenin, and Caveolin-1. Anat. Rec. 2010, 293, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleske, A.J.; Baltimore, D.; Lisanti, M.P. Reduction of caveolin and caveolae in oncogenically transformed cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1381–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.M.; Lisanti, M.P. Caveolin-1 in oncogenic transformation, cancer, and metastasis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 288, C494–C506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-P.; Liu, P.; Pilcher, B.K.; Anderson, R.G.W. Cell-specific targeting of caveolin-1 to caveolae, secretory vesicles, cytoplasm or mitochondria. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzchalia, T.V.; Dupree, P.; Parton, R.G.; Kellner, R.; Virta, H.; Lehnert, M.; Simons, K. VIP21, a 21-kD membrane protein is an integral component of trans-Golgi-network-derived transport vesicles. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 118, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, E.J.; Ying, Y.S.; Conrad, P.A.; Anderson, R.G. Caveolin moves from caveolae to the Golgi apparatus in response to cholesterol oxidation. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ramírez, C.M.; Aryal, B.; Madrigal-Matute, J.; Liu, X.; Diaz, A.; Torrecilla-Parra, M.; Suárez, Y.; Cuervo, A.M.; Sessa, W.C.; et al. Cav-1 (Caveolin-1) Deficiency Increases Autophagy in the Endothelium and Attenuates Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1510–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Oliveira, S.D.S.; Zimnicka, A.M.; Jiang, Y.; Sharma, T.; Chen, S.; Lazarov, O.; Bonini, M.G.; Haus, J.M.; Minshall, R.D.; et al. Reciprocal regulation of eNOS and caveolin-1 functions in endothelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2018, 29, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-M.; Yao, Y.-Z.; Zhu, Z.-H.; Sun, X.-T.; Qiu, Y.-D.; Ding, Y.-T. Caveolin-1 is important for nitric oxide-mediated angiogenesis in fibrin gels with human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Lin, M.I.; Huang, Y.; Yu, J.; Bauer, P.M.; Giordano, F.J.; Sessa, W.C. Reexpression of caveolin-1 in endothelium rescues the vascular, cardiac, and pulmonary defects in global caveolin-1 knockout mice. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, P.E.; Lisanti, M.P.; Baldini, G.; Sargiacomo, M.; Mastick, C.C.; Lodish, H.F. Induction of caveolin during adipogenesis and association of GLUT4 with caveolin-rich vesicles. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Lay, S.; Hajduch, E.; Lindsay, M.R.; Le Lièpvre, X.; Thiele, C.; Ferré, P.; Parton, R.G.; Kurzchalia, T.; Simons, K.; Dugail, I. Cholesterol-Induced Caveolin Targeting to Lipid Droplets in Adipocytes: A Role for Caveolar Endocytosis. Traffic 2006, 7, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, A.; Martin, S.; Ingelmo-Torres, M.; Ferguson, C.; Enrich, C.; Parton, R.G.; Nishimura, T.; Uchida, Y.; Yachi, R.; Kudlyk, T.; et al. Cholesterol and Fatty Acids Regulate Dynamic Caveolin Trafficking through the Golgi Complex and between the Cell Surface and Lipid Bodies. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 2091–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razani, B.; Combs, T.P.; Wang, X.B.; Frank, P.G.; Park, D.S.; Russell, R.G.; Li, M.; Tang, B.; Jelicks, L.A.; Scherer, P.E.; et al. Caveolin-1-deficient Mice Are Lean, Resistant to Diet-induced Obesity, and Show Hypertriglyceridemia with Adipocyte Abnormalities*. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 8635–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.W.; Combs, T.P.; Scherer, P.E.; Lisanti, M.P. Role of caveolin and caveolae in insulin signaling and diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2003, 285, E1151–E1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brännmark, C.; Palmér, R.; Glad, S.T.; Cedersund, G.; Strålfors, P. Mass and Information Feedbacks through Receptor Endocytosis Govern Insulin Signaling as Revealed Using a Parameter-free Modeling Framework. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 20171–20179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, D.; Al Madhoun, A.; Nizam, R.; Al-Mulla, F. Role of Caveolin-1 in Diabetes and Its Complications. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 9761539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, M.-S.; Lee, E.-B.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, J.-T.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, M.-C.; Lee, H.-J.; Cho, K.-H. Overexpression of caveolin-1 attenuates brain edema by inhibiting tight junction degradation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67857–67867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmin, J.-F.; Malhotra, S.; Dhallu, M.S.; Mercier, I.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Lisanti, M.P. Caveolin-1 Deficiency Increases Cerebral Ischemic Injury. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Ge, S.; Pachter, J.S. Caveolin-1 regulates expression of junction-associated proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Blood 2006, 109, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, B.P.; Peart, J.N.; Panneerselvam, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Pearn, M.L.; Niesman, I.R.; Bonds, J.A.; Schilling, J.M.; Miyanohara, A.; Headrick, J.; et al. Loss of Caveolin-1 Accelerates Neurodegeneration and Aging. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.-Y.; Choi, Y.R.; Noh, H.R.; Cha, S.-H.; Kim, J.-B.; Park, S.M. Age-related increase in caveolin-1 expression facilitates cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein in neurons. Mol. Brain 2021, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.C. Alveolar Type I Cells: Molecular Phenotype and Development. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 65, 669–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J. Number and distribution of plasmalemmal vesicles in the lung. Fed. Proc. 1983, 42, 2414–2418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stoeber, M.; Schellenberger, P.; Siebert, C.A.; Leyrat, C.; Helenius, A.; Grünewald, K. Model for the architecture of caveolae based on a flexible, net-like assembly of Cavin1 and Caveolin discs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E8069–E8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannes-Costa, P.S.; Pimentel, B.A.d.S.; Nagao, P.E. Role of Caveolin-1 in Sepsis—A Mini-Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 902907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Kim, H.P.; Song, R.; Choi, A.M. Caveolin-1 confers antiinflammatory effects in murine macrophages via the MKK3/p38 MAPK pathway. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 34, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Cai, J.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Teng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tao, M.; Xia, A.; et al. Hypoxic trophoblast HMGB1 induces endothelial cell hyperpermeability via the TRL-4/caveolin-1 pathway. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5000–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.H.; Tam, K.; Chen, S.F.; Liou, J.Y.; Tsai, Y.C.; Lee, Y.M.; Huang, T.Y.; Shyue, S.K. Deletion of caveolin-1 attenuates LPS/GalN-induced acute liver injury in mice. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5573–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Yi, F.; Dai, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.D.; Mirza, M.K.; Xu, J.; Vogel, S.M.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Loss of caveolin-1 and adiponectin induces severe inflammatory lung injury following LPS challenge through excessive oxidative/nitrative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L566–L573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettele, J.; Klein, D. Caveolin-1, cancer and therapy resistance. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, A.; Nichols, B.J.; Sandin, S. Architecture of the caveolar coat complex. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibel, E.R.; West, J.B.; Quirk, J.D.; Sukstanskii, A.L.; Woods, J.C.; Lutey, B.A.; Conradi, M.S.; Gierada, D.S.; Yusen, R.D.; Castro, M.; et al. Morphological basis of alveolar-capillary gas exchange. Physiol. Rev. 1973, 53, 419–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xue, X.; You, K.; Fu, J. Caveolin-1 regulates the expression of tight junction proteins during hyperoxia-induced pulmonary epithelial barrier breakdown. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvo Romero, E.; Alonso Cotoner, C.; Pardo Camacho, C.; Casado Bedmar, M.; Vicario, M. The intestinal barrier function and its involvement in digestive disease. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2015, 107, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groschwitz, K.R.; Hogan, S.P. Intestinal barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, M.D.; Denning, P.W. The role of intestinal epithelial barrier function in the development of NEC. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e1000707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.J.; Leaphart, C.L.; Mollen, K.P.; Hackam, D.J. The Role of The Intestinal Barrier in The Pathogenesis of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Shock 2007, 27, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruewer, M.; Utech, M.; Ivanov, A.I.; Hopkins, A.M.; Parkos, C.A.; Nusrat, A. Interferon-gamma induces internalization of epithelial tight junction proteins via a macropinocytosis-like process. Faseb J. 2005, 19, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayburgh, D.R.; Barrett, T.A.; Tang, Y.; Meddings, J.B.; Van Eldik, L.J.; Watterson, D.M.; Clarke, L.L.; Mrsny, R.J.; Turner, J.R. Epithelial myosin light chain kinase-dependent barrier dysfunction mediates T cell activation-induced diarrhea in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2702–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, A.I.; Nusrat, A.; Parkos, C.A. Endocytosis of Epithelial Apical Junctional Proteins by a Clathrin-mediated Pathway into a Unique Storage Compartment. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Kubo, A.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. A peculiar internalization of claudins, tight junction-specific adhesion molecules, during the intercellular movement of epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, B.T.; Wang, F.; Shen, L.; Clayburgh, D.R.; Su, L.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Turner, J.R. LIGHT Signals Directly to Intestinal Epithelia to Cause Barrier Dysfunction via Cytoskeletal and Endocytic Mechanisms. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2383–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Turner, J.R.; Van Itallie, C.M.; Tietgens, A.J.; Anderson, J.M.; Nusrat, M.E.A.; Lu, R.; Dalgalan, D.; Mandell, E.K.; Parker, S.S.; et al. Actin Depolymerization Disrupts Tight Junctions via Caveolae-mediated Endocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 3919–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, L.E.; Shen, L.; Ogden, S.; Romero–Gallo, J.; Lapierre, L.A.; Israel, D.A.; Turner, J.R.; Peek, R.M. Helicobacter pylori Dysregulation of Gastric Epithelial Tight Junctions by Urease-Mediated Myosin II Activation. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeissig, S.; Bürgel, N.; Günzel, D.; Richter, J.; Mankertz, J.; Wahnschaffe, U.; Kroesen, A.J.; Zeitz, M.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5 and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction in active Crohn’s disease. Gut 2007, 56, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchiando, A.M.; Shen, L.; Graham, W.V.; Weber, C.R.; Schwarz, B.T.; Austin, J.R., II; Raleigh, D.R.; Guan, Y.; Watson, A.J.; Montrose, M.H.; et al. Caveolin-1–dependent occludin endocytosis is required for TNF-induced tight junction regulation in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, T.D.; Cai, X.; Liebe, H.; Golubkova, A.; Schlegel, C.B.; Hunter, C.M. Caveolin-1 and Tight Junction Expression in Human Intestine as a Susceptibility Marker of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2022, 235, S173–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronstein, R.; Seebach, J.; Großklaus, S.; Minten, C.; Engelhardt, B.; Drab, M.; Liebner, S.; Arsenijevic, Y.; Abu Taha, A.; Afanasieva, T.; et al. Caveolin-1 opens endothelial cell junctions by targeting catenins. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 93, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ares, G.; Buonpane, C.; Sincavage, J.; Yuan, C.; Wood, D.R.; Hunter, C.J. Caveolin 1 is Associated with Upregulated Claudin 2 in Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.M.; Tatum, R.; Ravisankar, S.; Shekhawat, P.S.; Chen, Y.-H. Necrotizing enterocolitis in a mouse model leads to widespread renal inflammation, acute kidney injury, and disruption of renal tight junction proteins. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günzel, D.; Yu, A.S.L. Claudins and the Modulation of Tight Junction Permeability. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 525–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quest, A.F.G.; Gutierrez-Pajares, J.L.; Torres, V.A. Caveolin-1: An ambiguous partner in cell signalling and cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 1130–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, C.; Carnino, J.; Jin, Y. The Evolving Role of Caveolin-1: A Critical Regulator of Extracellular Vesicles. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luissint, A.-C.; Artus, C.; Glacial, F.; Ganeshamoorthy, K.; Couraud, P.-O. Tight junctions at the blood brain barrier: Physiological architecture and disease-associated dysregulation. Fluids Barriers CNS 2012, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Shen, L.; Clayburgh, D.R.; Nalle, S.C.; Sullivan, E.A.; Meddings, J.B.; Abraham, C.; Turner, J.R. Targeted Epithelial Tight Junction Dysfunction Causes Immune Activation and Contributes to Development of Experimental Colitis. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscher, C.; Nabi, I.R. CAVEOLIN-1: Role in Cell Signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 729, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couet, J.; Li, S.; Okamoto, T.; Ikezu, T.; Lisanti, M.P. Identification of peptide and protein ligands for the caveolin-scaffolding domain: Implications for the interaction of caveolin with caveolae-associated proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6525–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineo, C.; James, G.L.; Smart, E.J.; Anderson, R.G. Localization of Epidermal Growth Factor-stimulated Ras/Raf-1 Interaction to Caveolae Membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 11930–11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venema, V.J.; Zou, R.; Ju, H.; Marrero, M.B.; Venema, R.C. Caveolin-1 Detergent Solubility and Association with Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Is Modulated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Toya, Y.; Schwencke, C.; Lisanti, M.P.; Myers, M.G.; Ishikawa, Y. Caveolin Is an Activator of Insulin Receptor Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26962–26968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, P.E.; Chau, P.; Liu, D.; Spencer, T.A.; Fielding, C.J. Mechanism of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-Dependent Caveolin-1 Phosphorylation: Relationship to Sterol Binding and the Role of Serine-80. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 2578–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, A.; Arvan, P.; Lisanti, M.P. Caveolin-1 binding to endoplasmic reticulum membranes and entry into the regulated secretory pathway are regulated by serine phosphorylation: Protein sorting at the level of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4398–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, E. The fine structure of the gall bladder epithelium of the mouse. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 1955, 1, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.; Sengupta, D. Interplay between Membrane Curvature and Cholesterol: Role of Palmitoylated Caveolin-1. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinger, K.R.T.; Woolfrey, K.M.; Swanson, S.P.; Schnell, S.A.; Meitzen, J.; Dell’Acqua, M.; Mermelstein, P.G. Palmitoylation of caveolin-1 is regulated by the same DHHC acyltransferases that modify steroid hormone receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15901–15911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohi, M.D.; Kenworthy, A.K. Emerging Insights into the Molecular Architecture of Caveolin-1. J. Membr. Biol. 2022, 255, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, A.; Stoeber, M.; Bissig, C.; Helenius, A. Biogenesis of Caveolae: Stepwise Assembly of Large Caveolin and Cavin Complexes. Traffic 2010, 11, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariotti, N.; Rae, J.; Leneva, N.; Ferguson, C.; Loo, D.; Okano, S.; Hill, M.M.; Walser, P.; Collins, B.M.; Parton, R.G. Molecular Characterization of Caveolin-induced Membrane Curvature. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24875–24890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khater, I.M.; Liu, Q.; Chou, K.C.; Hamarneh, G.; Nabi, I.R. Super-resolution modularity analysis shows polyhedral caveolin-1 oligomers combine to form scaffolds and caveolae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamaze, C.; Tardif, N.; Dewulf, M.; Vassilopoulos, S.; Blouin, C.M. The caveolae dress code: Structure and signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2017, 47, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khailova, L.; Dvorak, K.; Arganbright, K.M.; Williams, C.S.; Halpern, M.D.; Dvorak, B. Changes in Hepatic Cell Junctions Structure During Experimental Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Effect of EGF Treatment. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itallie, C.M.V.; Anderson, J.M. Caveolin binds independently to claudin-2 and occludin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1257, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.M.; Lisanti, M.P. The caveolin proteins. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalton, C.M.; Schlegel, C.; Hunter, C.J. Caveolin-1: A Review of Intracellular Functions, Tissue-Specific Roles, and Epithelial Tight Junction Regulation. Biology 2023, 12, 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111402
Dalton CM, Schlegel C, Hunter CJ. Caveolin-1: A Review of Intracellular Functions, Tissue-Specific Roles, and Epithelial Tight Junction Regulation. Biology. 2023; 12(11):1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111402
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalton, Cody M., Camille Schlegel, and Catherine J. Hunter. 2023. "Caveolin-1: A Review of Intracellular Functions, Tissue-Specific Roles, and Epithelial Tight Junction Regulation" Biology 12, no. 11: 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111402
APA StyleDalton, C. M., Schlegel, C., & Hunter, C. J. (2023). Caveolin-1: A Review of Intracellular Functions, Tissue-Specific Roles, and Epithelial Tight Junction Regulation. Biology, 12(11), 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111402





