Endothelin Modulates Rhythm Disturbances and Autonomic Responses to Acute Emotional Stress in Rats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Study Population and Ethics
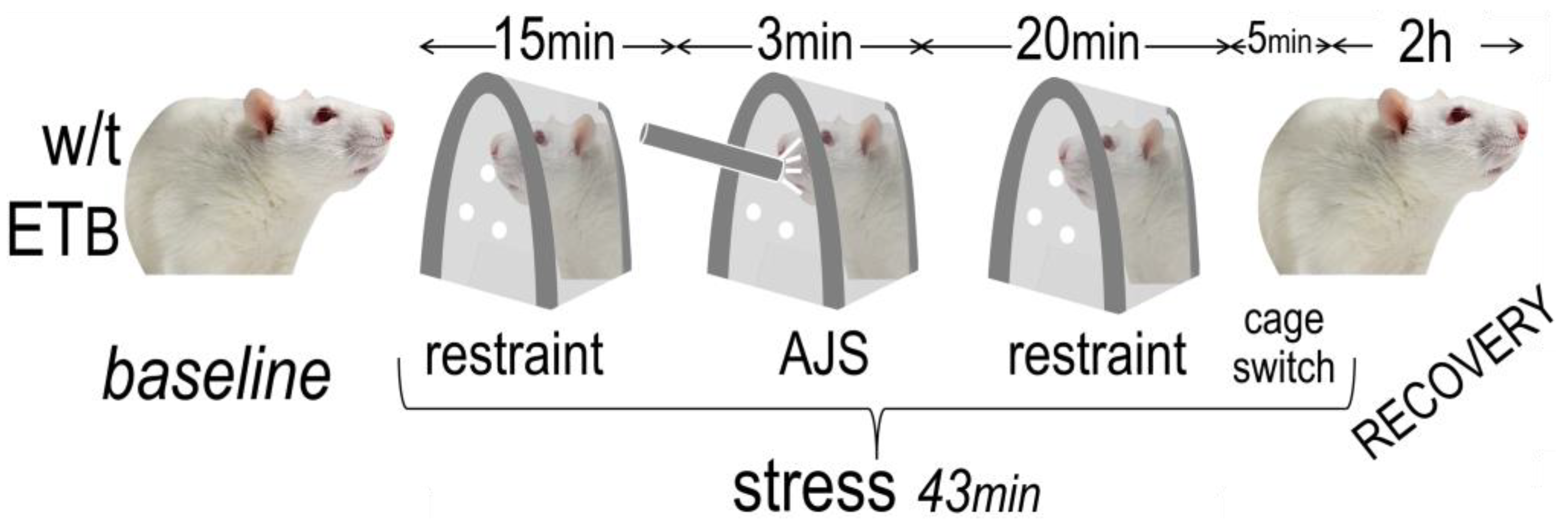
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Induction of AES
2.4. Heart Rate Variability Analysis
2.5. Arrhythmia Analysis
2.6. Voluntary Activity
2.7. Blood Pressure Protocol
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Differences between the Two Rat Strains
3.2. Autonomic Responses in Wild-Type Rats
3.3. Autonomic Responses in ETB-Deficient Rats
3.4. Between-Group Comparison: Heart Rate
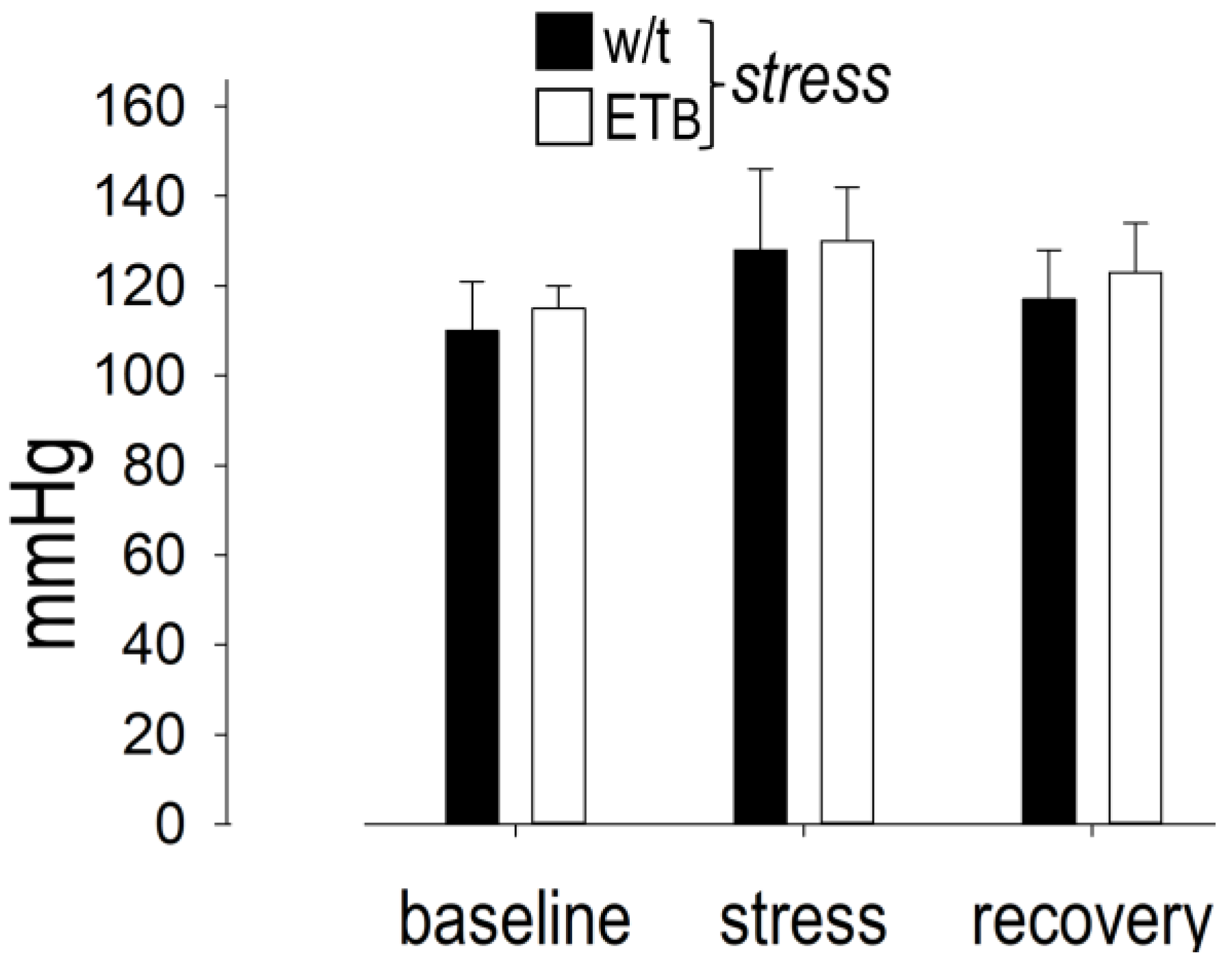
3.5. Between-Group Comparison: Blood Pressure
3.6. Between-Group Comparison: Sympathetic Activity
3.7. Between-Group Comparison: Vagal Activity
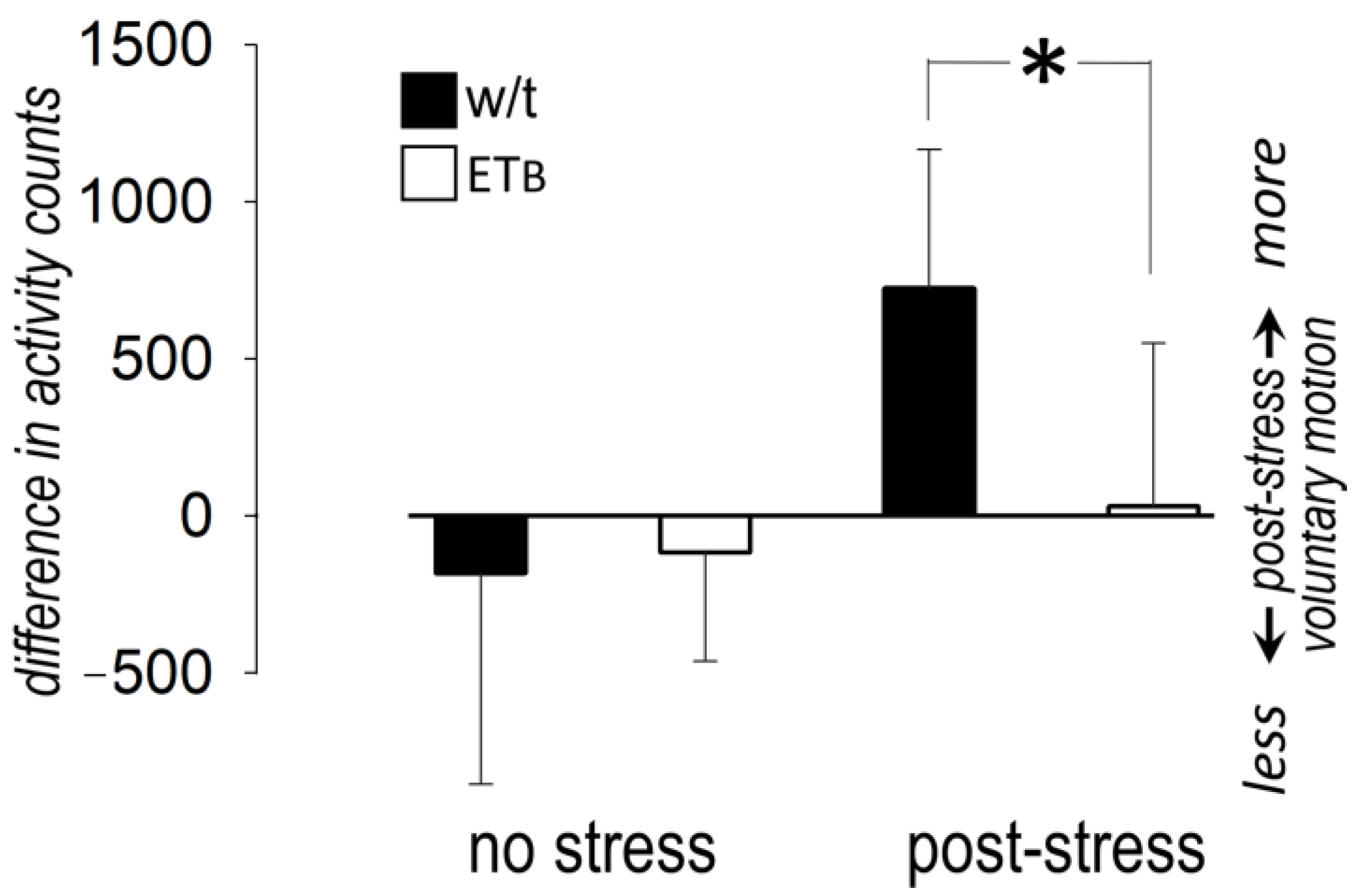
3.8. Between-Group Comparison: Voluntary Motion
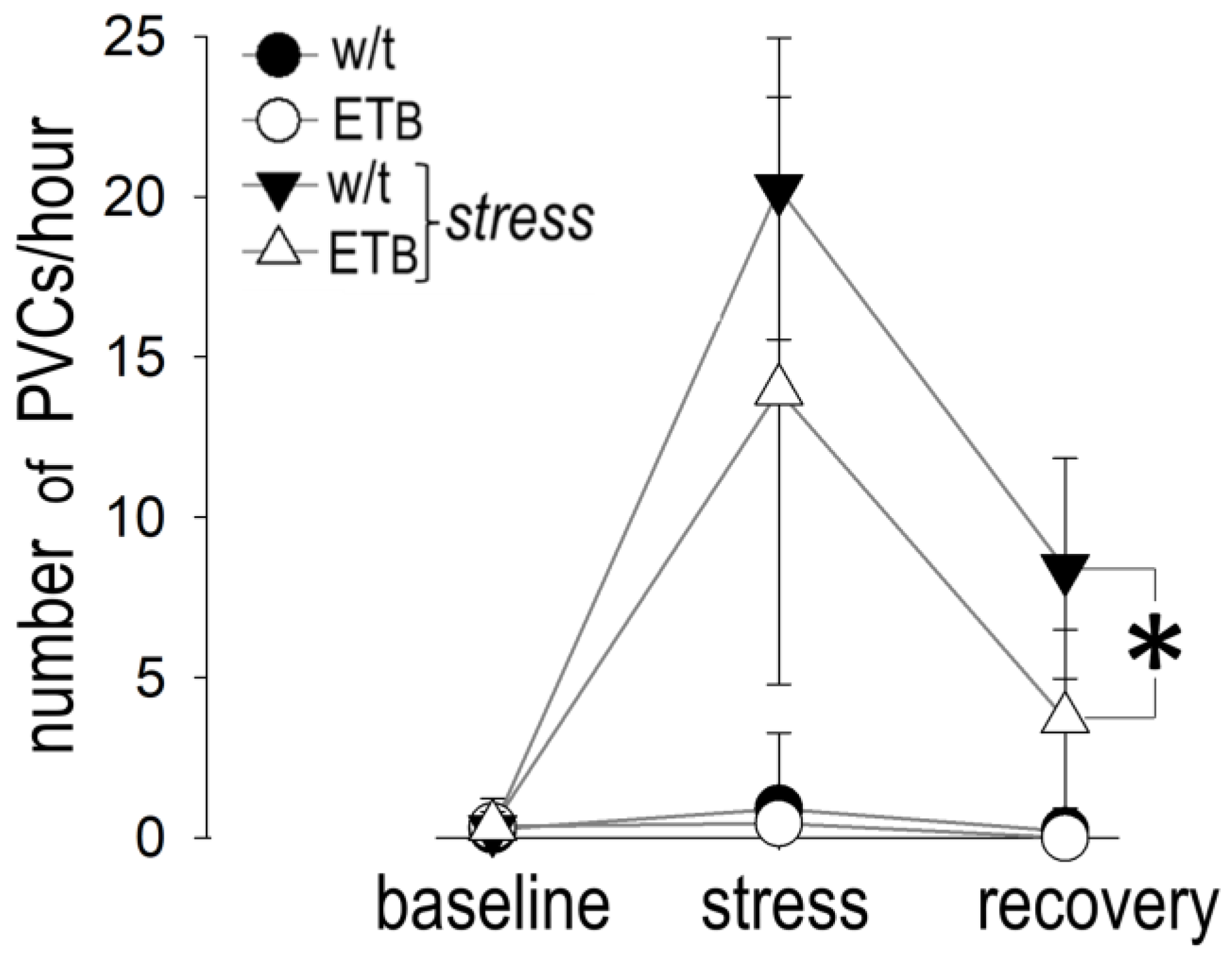
3.9. Between-Group Comparison: Premature Ventricular Contractions
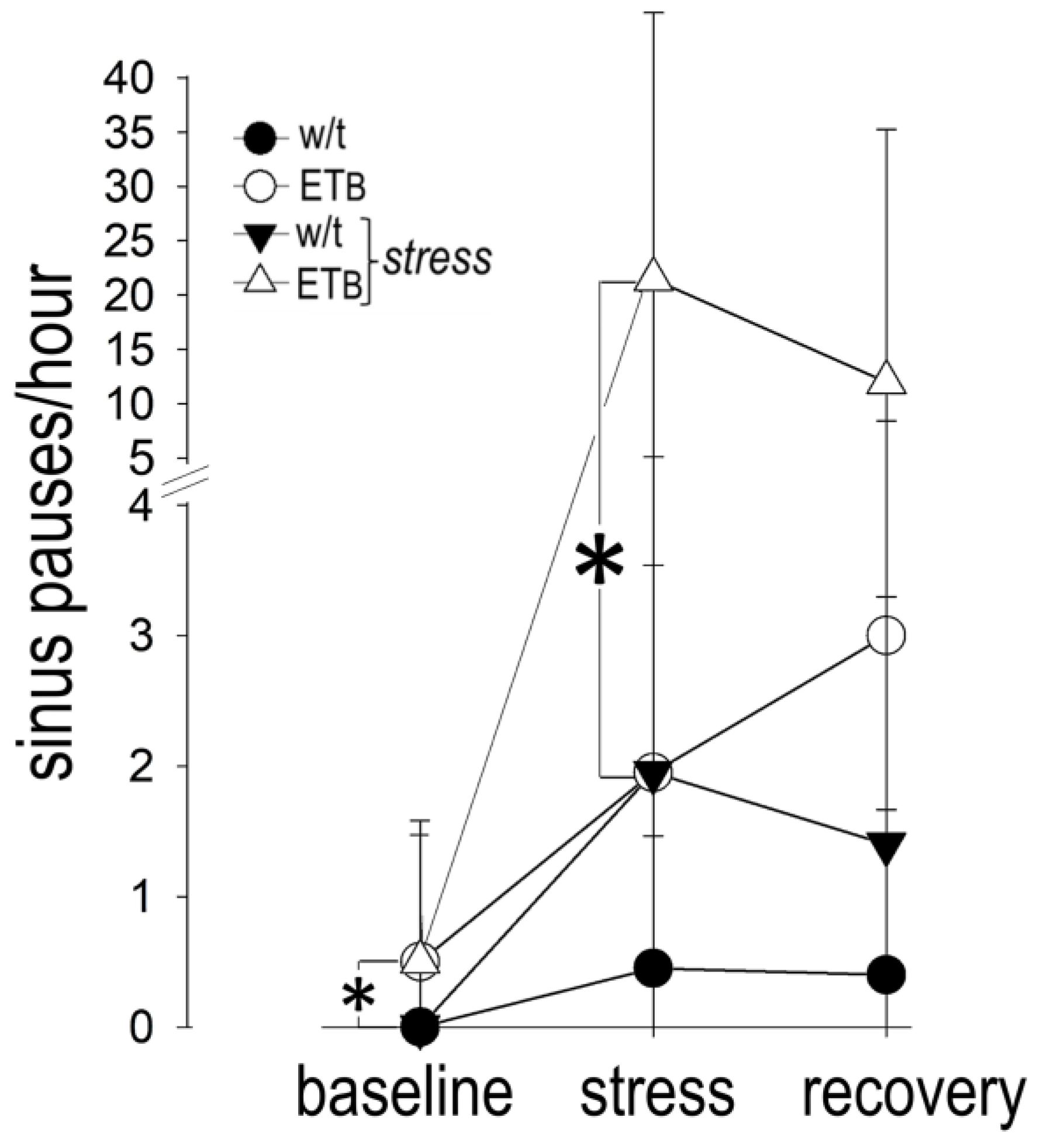
3.10. Comparison between Groups: Bradyarrhythmias
4. Discussion
4.1. Autonomic Responses in Wild-Type Rats
4.2. Observational Period Duration
4.3. Baseline Autonomic Characteristics of ETB-Deficient Rats
4.4. Sympathetic Responses in ETB-Deficient Rats
4.5. Vagal Responses in ETB-Deficient Rats
4.6. Rhythm Disturbances in Wild-Type and ETB-Deficient Rats
4.7. Freezing Reactions to Fear
4.8. Neurocardiogenic Syncope
4.9. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding

Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Herman, J.P. Neural regulation of endocrine and autonomic stress responses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, P.; Boyett, M.R.; Logantha, S.J.; Lambiase, P.D. Anger, emotion, and arrhythmias: From brain to heart. Front. Physiol. 2011, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.A.; Xavier, C.H.; Marins, F.R.; Limborco-Filho, M.; Vaz, G.C.; Muller-Ribeiro, F.C.; Nalivaiko, E. Emotional stress and sympathetic activity: Contribution of dorsomedial hypothalamus to cardiac arrhythmias. Brain Res. 2014, 1554, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekios, K.C.; Mouchtouri, E.-T.; Lekkas, P.; Nikas, D.N.; Kolettis, T.M. Sympathetic activation and arrhythmogenesis after myocardial infarction: Where do we stand? J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulos, D.; Katsouyanni, K.; Zavitsanos, X.; Tzonou, A.; Dalla-Vorgia, P. Psychological stress and fatal heart attack: The Athens (1981) earthquake natural experiment. Lancet 1983, 1, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, A.J.; Alexander, H.M.; Malcolm, J.A.; Steele, P.L.; Miles, T.A. Heart attacks and the Newcastle earthquake. Med. J. Aust. 1991, 155, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leor, J.; Poole, W.K.; Kloner, R.A. Sudden cardiac death triggered by an earthquake. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgoifo, A.; de Boer, S.F.; Westenbroek, C.; Maes, F.W.; Beldhuis, H.; Suzuki, T.; Koolhaas, J.M. Incidence of arrhythmias and heart rate variability in wild-type rats exposed to social stress. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, H1754–H1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, R.; Joska, T.; Burg, M.M.; Batsford, W.P.; McPherson, C.A.; Jain, D. Emotional and physical precipitants of ventricular arrhythmia. Circulation 2002, 106, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, J.S.; Arshad, A.; Kowalski, M.; Kukar, A.; Suma, V.; Vloka, M.; Ehlert, F.; Herweg, B.; Donnelly, J.; Philip, J.; et al. Increased incidence of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias in implantable defibrillator patients after the World Trade Center attack. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchtouri, E.T.; Konstantinou, T.; Lekkas, P.; Kolettis, T.M. Endothelin system and ischemia-induced ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Life 2022, 12, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawa, M.; Fukumoto, T.; Ohkita, M.; Matsumura, Y. Role of endogenous endothelin-1 in post-ischemic cardiac dysfunction and norepinephrine overflow in rat hearts. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, R.M.; Sudano, I.; Ghiadoni, L.; Masi, L.; Taddei, S. Interactions between sympathetic nervous system and endogenous endothelin in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 2011, 57, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolettis, T.M.; Baltogiannis, G.G.; Tsalikakis, D.G.; Tzallas, A.T.; Agelaki, M.G.; Fotopoulos, A.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Kyriakides, Z.S. Effects of dual endothelin receptor blockade on sympathetic activation and arrhythmogenesis during acute myocardial infarction in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 580, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, D.L.; Haywood, J.R.; Hinojosa-Laborde, C. Endothelin enhances and inhibits adrenal catecholamine release in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2000, 35, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yamamoto, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Kanazawa, M.; Fujita, M.; Takaoka, M.; Gariepy, C.E.; Yanagisawa, M.; Matsumura, Y. Different contributions of endothelin-A and endothelin-B receptors in postischemic cardiac dysfunction and norepinephrine overflow in rat hearts. Circulation 2005, 111, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltogiannis, G.G.; Tsalikakis, D.G.; Mitsi, A.C.; Hatzistergos, K.E.; Elaiopoulos, D.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Kyriakides, Z.S.; Kolettis, T.M. Endothelin receptor-A blockade decreases ventricular arrhythmias after myocardial infarction in rats. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 67, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lekkas, P.; Georgiou, E.S.; Kontonika, M.; Mouchtouri, E.T.; Mourouzis, I.; Pantos, C.; Kolettis, T.M. Intracerebroventricular endothelin receptor-A blockade in rats decreases phase-II ventricular tachyarrhythmias during acute myocardial infarction. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekkas, P.; Kontonika, M.; Georgiou, E.S.; La Rocca, V.; Mouchtouri, E.T.; Mourouzis, I.; Pantos, C.; Kolettis, T.M. Endothelin receptors in the brain modulate autonomic responses and arrhythmogenesis during acute myocardial infarction in rats. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, G.; Loria, A.S.; Pollock, D.M.; Pollock, J.S. Endothelin activation of reactive oxygen species mediates stress-induced pressor response in Dahl salt-sensitive prehypertensive rats. Hypertension 2010, 56, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, B.M.; Becker, B.K.; Loria, A.S.; Hyndman, K.A.; Jin, C.; Clark, H.; Johns, R.; Yanagisawa, M.; Pollock, D.M.; Pollock, J.S. Acute pressor response to psychosocial stress is dependent on endothelium-derived endothelin-1. J. Am. Heart. Assoc. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Yan, H.H.; Shu, S.; Pei, L.; Zang, L.K.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Wan, Q.; Bi, L.L. Amygdalar endothelin-1 regulates pyramidal neuron excitability and affects anxiety. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piira, O.P.; Miettinen, J.A.; Hautala, A.J.; Huikuri, H.V.; Tulppo, M.P. Physiological responses to emotional excitement in healthy subjects and patients with coronary artery disease. Auton. Neurosci. 2013, 177, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiafico, R.A.; Malatino, L.S.; Attina, T.; Messina, R.; Fiore, C.E. Exaggerated endothelin release in response to acute mental stress in patients with intermittent claudication. Angiology 2002, 53, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Wolff, G.; Young, M.L.; Mas, M.S.; Escobar, A.; Gelband, H. Usefulness of endothelin-1 as a predictor of response to head-up tilt-table testing in children with syncope. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995, 76, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouchtouri, E.T.; Lekkas, P.; Delis, F.; Pantelakis, E.; Mourouzis, I.; Pantos, C.; Kolettis, T.M. Sympathetic and vagal responses elicited by acute stress in rats. Cureus 2020, 12, e11602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariepy, C.E.; Williams, S.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Hammer, R.E.; Yanagisawa, M. Transgenic expression of the endothelin-B receptor prevents congenital intestinal aganglionosis in a rat model of Hirschsprung disease. J. Clin. Investg. 1998, 102, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, M.G.; Molero, M.M.; Giulumian, A.D.; Katakam, P.V.; Pollock, J.S.; Pollock, D.M.; Fuchs, L.C. ET(B) receptor-deficient rats exhibit reduced contraction to ET-1 despite an increase in ET(A) receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 281, H2680–H2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uji, M.; Yoshida, K.; Shintani-Ishida, K.; Morimoto, K. Sex difference in norepinephrine surge in response to psychological stress through nitric oxide in rats. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepke, J.P.; DiBona, G.F. Central beta-adrenergic receptors mediate renal nerve activity during stress in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1985, 7, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciosi, S.; Perry, F.K.G.; Roston, T.M.; Armstrong, K.R.; Claydon, V.E.; Sanatani, S. The role of the autonomic nervous system in arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Auton. Neurosci. 2017, 205, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Morimoto, A.; Sakata, Y.; Tan, N.; Morimoto, K.; Murakami, N. Running training attenuates the ACTH responses in rats to swimming and cage-switch stress. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 73, 2452–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarvainen, M.P.; Niskanen, J.P.; Lipponen, J.A.; Ranta-Aho, P.O.; Karjalainen, P.A. Kubios HRV—heart rate variability analysis software. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2014, 113, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, M.J.; Hancox, J.C.; Farkas, A.; Wainwright, C.L.; Stables, C.L.; Saint, D.A.; Clements-Jewery, H.; Lambiase, P.D.; Billman, G.E.; Janse, M.J.; et al. The Lambeth Conventions (II): Guidelines for the study of animal and human ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 213–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezak, K.R.; Missig, G.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Behavioral methods to study anxiety in rodents. Dialog. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 19, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erken, H.A.; Erken, G.; Genc, O. Blood pressure measurement in freely moving rats by the tail cuff method. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2013, 35, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, Y.; Kurihara, H.; Morita, H.; Cao, W.H.; Ling, G.Y.; Kumada, M.; Kimura, S.; Nagai, R.; Yazaki, Y.; Kuwaki, T. Role of endothelin-1 in stress response in the central nervous system. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R515–R521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.; Walker, D.L.; Miles, L.; Grillon, C. Phasic vs sustained fear in rats and humans: Role of the extended amygdala in fear vs anxiety. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 105–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevali, L.; Trombini, M.; Porta, A.; Montano, N.; de Boer, S.F.; Sgoifo, A. Vagal withdrawal and susceptibility to cardiac arrhythmias in rats with high trait aggressiveness. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tung, I.; Krafty, R.T.; Delcourt, M.L.; Melhem, N.M.; Jennings, J.R.; Keenan, K.; Hipwell, A.E. Cardiac vagal control in response to acute stress during pregnancy: Associations with life stress and emotional support. Psychophysiology 2021, 58, e13808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, K. Freeze for action: Neurobiological mechanisms in animal and human freezing. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulat, P.; D’Orleans-Juste, P.; de Champlain, J.; Yano, M.; Couture, R. Cardiovascular effects of intrathecally administered endothelins and big endothelin-1 in conscious rats: Receptor characterization and mechanism of action. Brain Res. 1994, 648, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Habuchi, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Nishio, M.; Morikawa, J.; Yoshimura, M. Negative chronotropic actions of endothelin-1 on rabbit sinoatrial node pacemaker cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, H.C.; Terzini, G.C.; da Silva, V.J.; Martins-Pinge, M.C.; Salgado, H.C.; Salgado, M.C. Increased cardiac sympathetic drive and reduced vagal modulation following endothelin receptor antagonism in healthy conscious rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 35, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, K.; Becker, B.K.; Johnston, J.G.; Young, C.; Torres Rodriguez, A.A.; Jin, C.; Pollock, D.M. Endothelin B receptors impair baroreflex function and increase blood pressure variability during high salt diet. Auton. Neurosci. 2021, 232, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, G.; Pollock, J.S.; Pollock, D.M. Endogenous endothelin attenuates the pressor response to acute environmental stress via the ETA receptor. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H1829–H1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, A.S.; D’Angelo, G.; Pollock, D.M.; Pollock, J.S. Early life stress downregulates endothelin receptor expression and enhances acute stress-mediated blood pressure responses in adult rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, R185–R191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, S.M.; Compton, A.M.; Kemp, P.A.; Bennett, T. Regional and cardiac haemodynamic responses to glyceryl trinitrate, acetylcholine, bradykinin and endothelin-1 in conscious rats: Effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 101, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, S.; van den Buuse, M. Sensitization of baroreceptor reflex by central endothelin in conscious rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 260, H1106–H1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krowicki, Z.K.; Nathan, N.A.; Hornby, P.J. Excitatory gastric motor and cardiovascular effects of endothelins in the dorsal vagal complex are mediated through ET(A) receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 282, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burg, M.M.; Soufer, A.; Lampert, R.; Collins, D.; Soufer, R. Autonomic contribution to endothelin-1 increase during laboratory anger-recall stress in patients with coronary artery disease. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanselow, M.S. Neural organization of the defensive behavior system responsible for fear. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 1994, 1, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magerkurth, C.; Riedel, A.; Braune, S. Permanent increase in endothelin serum levels in vasovagal syncope. Clin. Auton. Res 2005, 15, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazurova, Z.; Habalova, V.; Mitro, P. Association of polymorphisms in endothelin-1 and endothelin receptor A genes with vasovagal syncope. Physiol. Res. 2022, 71, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyphantis, T.N.; Pappas, A.I.; Vlahos, A.P.; Carvalho, A.F.; Levenson, J.L.; Kolettis, T.M. Depressive symptoms and neurocardiogenic syncope in children: A 2-year prospective study. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, M.M.; Martens, E.J.; Collins, D.; Soufer, R. Depression predicts elevated endothelin-1 in patients with coronary artery disease. Psychosom. Med. 2011, 73, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Variables | Wild-Type | ETB-Deficient | p Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sympatho-vagal balance | Mean HR (bpm) | 314 ± 53 | 337 ± 34 | 0.1029 |
| LF/HF ** | 0.021 ± 0.011 | 0.011 ± 0.0007 | 0.0005 | |
| SDNN ** (ms) | 4.122 ± 4.638 | 5.309 ± 4.144 | 0.3984 | |
| RMSSD ** (ms) | 7.285 ± 8.242 | 9.562 ± 7.616 | 0.3700 | |
| Sympathetic activity | Power LF | 1.874 ± 0.955 | 1.129 ± 0.0697 | 0.0012 |
| SNSi ** | 451 ± 212 | 325 ± 75 | 0.0172 | |
| Vagal activity | Power HF | 97.82 ± 1.02 | 98.66 ± 0.08 | 0.0007 |
| PNSi ** | −5.459 ± 0.179 | −5.547 ± 0.1056 | 0.0671 | |
| Bradyarrhythmias | Sinus pauses | 0 | 0.50 ± 1.00 | 0.0197 |
| AV ** block episodes | 0 | 0 | (−) | |
| Tachyarrhythmias | PVCs **/h | 0.250 ± 0.55 | 0.35 ± 0.87 | 0.8540 |
| Couplets/h | 0 | 0.10 ± 0.44 | 0.3421 | |
| Triplets/h | 0 | 0.15 ± 0.36 | 0.0803 | |
| Voluntary activity | Activity (counts/h) | 444 ± 572 | 477 ± 428 | 0.8346 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mouchtouri, E.-T.; Konstantinou, T.; Lekkas, P.; Lianopoulou, A.; Kotsaridou, Z.; Mourouzis, I.; Pantos, C.; Kolettis, T.M. Endothelin Modulates Rhythm Disturbances and Autonomic Responses to Acute Emotional Stress in Rats. Biology 2023, 12, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111401
Mouchtouri E-T, Konstantinou T, Lekkas P, Lianopoulou A, Kotsaridou Z, Mourouzis I, Pantos C, Kolettis TM. Endothelin Modulates Rhythm Disturbances and Autonomic Responses to Acute Emotional Stress in Rats. Biology. 2023; 12(11):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111401
Chicago/Turabian StyleMouchtouri, Eleni-Taxiarchia, Thomas Konstantinou, Panagiotis Lekkas, Alexandra Lianopoulou, Zoi Kotsaridou, Iordanis Mourouzis, Constantinos Pantos, and Theofilos M. Kolettis. 2023. "Endothelin Modulates Rhythm Disturbances and Autonomic Responses to Acute Emotional Stress in Rats" Biology 12, no. 11: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111401
APA StyleMouchtouri, E.-T., Konstantinou, T., Lekkas, P., Lianopoulou, A., Kotsaridou, Z., Mourouzis, I., Pantos, C., & Kolettis, T. M. (2023). Endothelin Modulates Rhythm Disturbances and Autonomic Responses to Acute Emotional Stress in Rats. Biology, 12(11), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111401







