Interindividual Brain and Behavior Differences in Adaptation to Unexpected Uncertainty
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
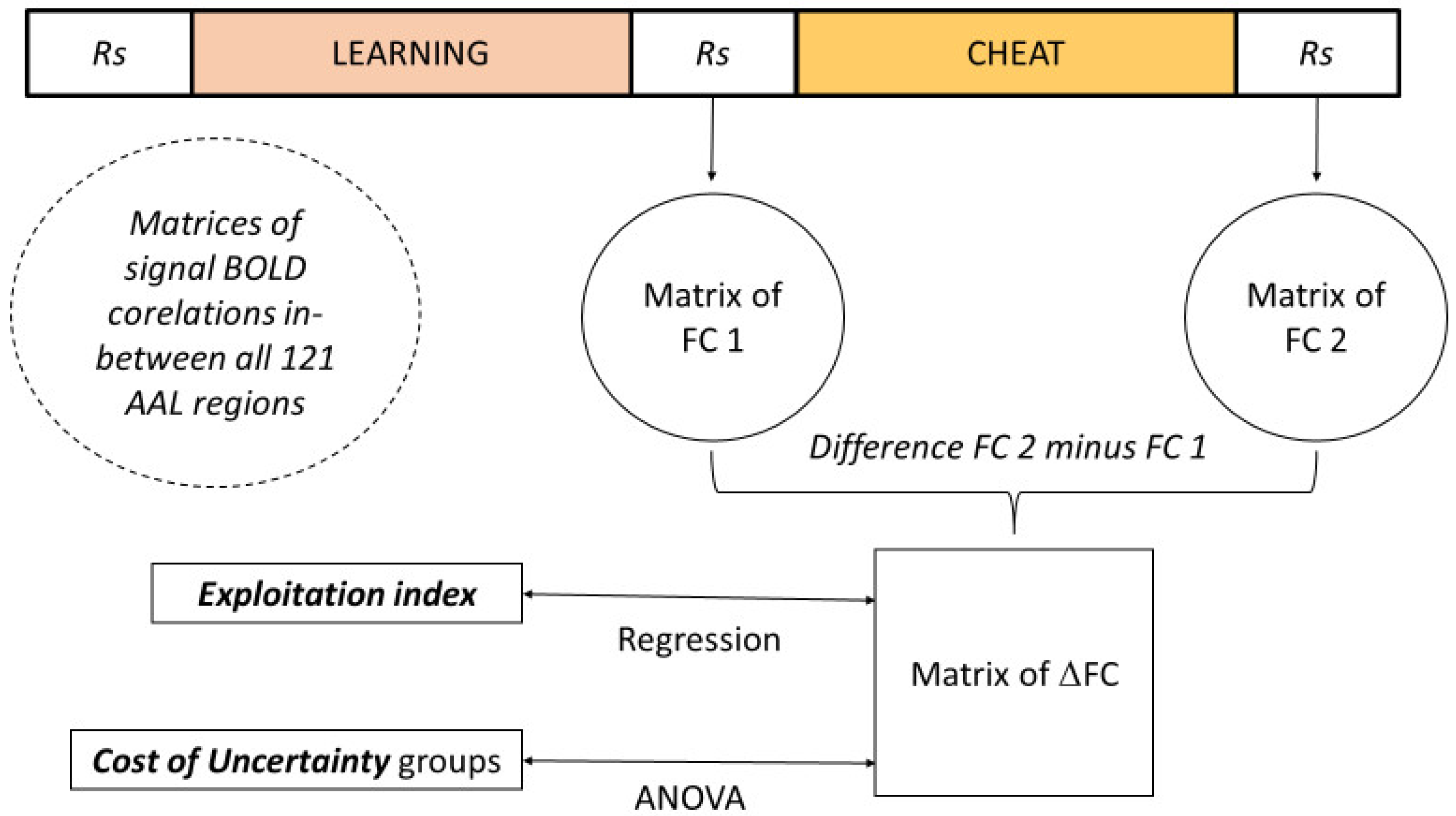
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Neuropsychological Tests and Psychometric Scales
2.3. Associative Learning Task and MRI Protocol
2.4. MRI Acquisition
2.4.1. Acquisition
2.4.2. Preprocessing
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.5.1. Behavioral Data
2.5.2. fMRI Data
2.5.3. Interindividual Variability
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive of Psychological Variable
3.2. Behavioral Analyses
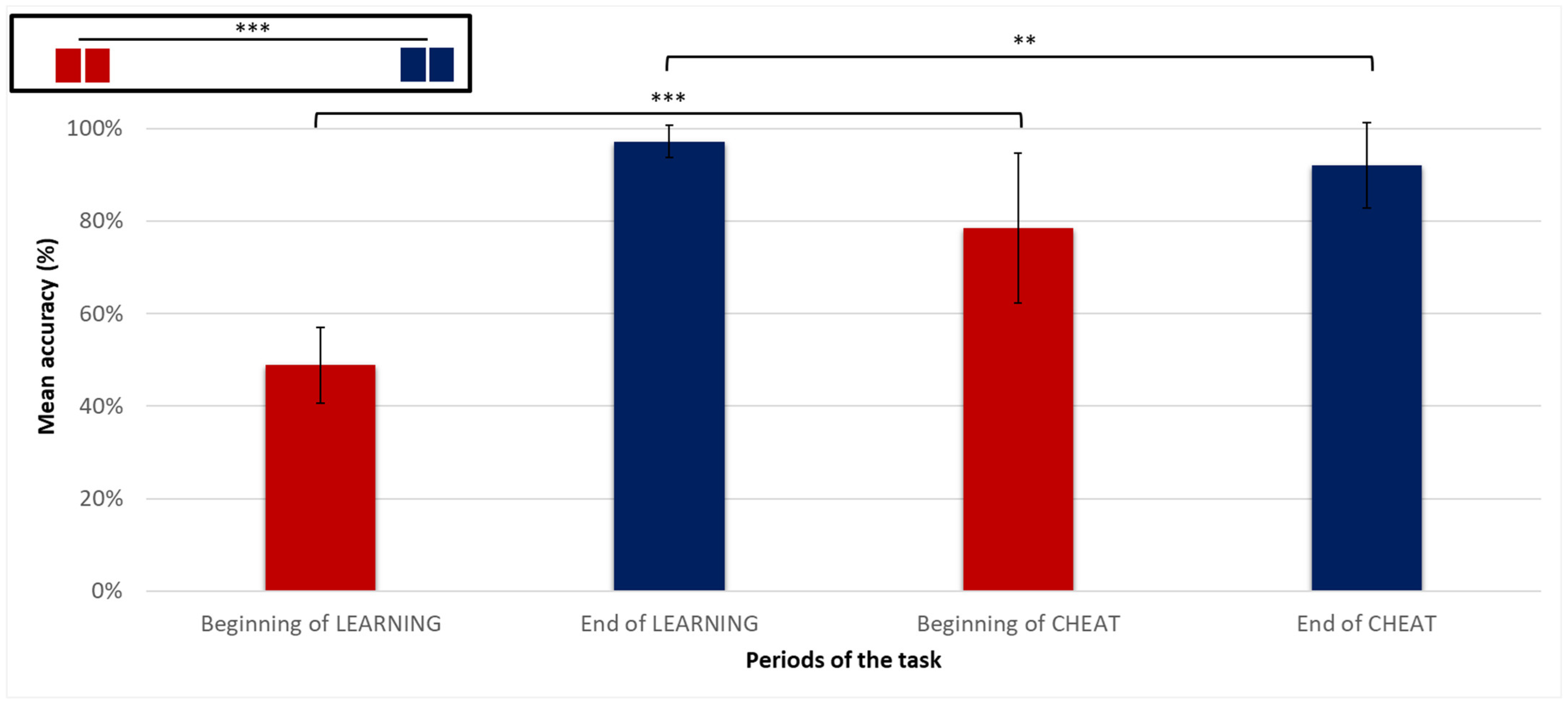
3.2.1. Overall Accuracy
3.2.2. Cost of Uncertainty and Exploitation Indices
3.3. Resting-State Functional Connectivity
- (i).
- The ΔFC between the right caudate and left lingual gyrus (T(26) = 4.52, p < 0.001, p(FDRCorr) = 0.01, d = 1.17), where connectivity increased in the “Cost+” (ΔFC = 0.09 ± 0.17) but decreased in the “Cost−” (ΔFC = −0.12 ± 0.15) group;
- (ii).
- The ΔFC between the right cerebellar region 3 and the right superior pole of the temporal lobe (T(26) = −4.49, p < 0.001, p(FDRCorr) = 0.01, d = 1.70), where connectivity decreased in the “Cost+” (ΔFC = −0.10 ± 0.15) group but increased in the “Cost−” (ΔFC = 0.10 ± 0.13) group;
- (iii).
- The ΔFC between the right cerebellar region 3 and the orbital part of the right frontal inferior gyrus (T(26) = −3.78, p < 0.001, p(FDRCorr) = 0.05, d = 1.43), where connectivity decreased in the “Cost+” (ΔFC = −0.11 ± 0.07) group, but increased in the “Cost−” (ΔFC = 0.08 ± 0.21) group.

3.4. Associations with the Psychological Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, J.D.; McClure, S.M.; Yu, A.J. Should I Stay or Should I Go? How the Human Brain Manages the Trade-off between Exploitation and Exploration. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.J.; Dayan, P. Uncertainty, Neuromodulation, and Attention. Neuron 2005, 46, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, A.; Schaefer, A. Different Varieties of Uncertainty in Human Decision-Making. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittins, J.C. Bandit Processes and Dynamic Allocation Indices. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1979, 41, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daw, N.D.; O’Doherty, J.P.; Dayan, P.; Seymour, B.; Dolan, R.J. Cortical Substrates for Exploratory Decisions in Humans. Nature 2006, 441, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiez, C.; Sallet, J.; Procyk, E.; Petrides, M. Modulation of Feedback Related Activity in the Rostral Anterior Cingulate Cortex during Trial and Error Exploration. NeuroImage 2012, 63, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroun, K.; Mathar, D.; Wiehler, A.; Ganzer, F.; Peters, J. Dopaminergic Modulation of the Exploration/Exploitation Trade-off in Human Decision-Making. eLife 2020, 9, e51260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureiro-Martínez, D.; Brusoni, S.; Canessa, N.; Zollo, M. Understanding the Exploration-Exploitation Dilemma: An fMRI Study of Attention Control and Decision-Making Performance: Understanding the Exploration-Exploitation Dilemma. Strateg. Manag. J. 2015, 36, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.S.; Baek, K.; Kundu, P.; Harrison, N.A.; Frank, M.J.; Voon, V. Biases in the Explore–Exploit Tradeoff in Addictions: The Role of Avoidance of Uncertainty. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, D.J.; Newell, B.R.; Schulze, C. Learning and Choosing in an Uncertain World: An Investigation of the Explore–Exploit Dilemma in Static and Dynamic Environments. Cognit. Psychol. 2016, 85, 43–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, T.C.; Gershman, S.J. Pure correlates of exploration and exploitation in the human brain. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 18, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlhorn, K.; Newell, B.R.; Todd, P.M.; Lee, M.D.; Morgan, K.; Braithwaite, V.A.; Hausmann, D.; Fiedler, K.; Gonzalez, C. Unpacking the Exploration–Exploitation Tradeoff: A Synthesis of Human and Animal Literatures. Decision 2015, 2, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krypotos, A.-M.; Alves, M.; Crombez, G.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S. The Role of Intolerance of Uncertainty When Solving the Exploration-Exploitation Dilemma. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2022, 181, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, M.R.; Wilson, R.C.; Heasly, B.; Gold, J.I. An Approximately Bayesian Delta-Rule Model Explains the Dynamics of Belief Updating in a Changing Environment. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 12366–12378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, G.P.; Frank, M.J.; Waltz, J.A.; Kasanova, Z.; Herbener, E.S.; Gold, J.M. Deficits in Positive Reinforcement Learning and Uncertainty-Driven Exploration Are Associated with Distinct Aspects of Negative Symptoms in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, M.; Behrens, T.E.; Jocham, G.; O’reilly, J.X.; Bishop, S.J. Anxious Individuals Have Difficulty Learning the Causal Statistics of Aversive Environments. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addicott, M.A.; Pearson, J.M.; Sweitzer, M.M.; Barack, D.L.; Platt, M.L.; Amiez, C.; Sallet, J.; Procyk, E.; Petrides, M. A Primer on Foraging and the Explore/Exploit Trade-Off for Psychiatry Research. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Kirlic, N.; Stewart, J.L.; Touthang, J.; Kuplicki, R.; Khalsa, S.S.; Feinstein, J.; Paulus, M.P.; Aupperle, R.L. Greater Decision Uncertainty Characterizes a Transdiagnostic Patient Sample during Approach-Avoidance Conflict: A Computational Modelling Approach. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2021, 46, E74–E87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiehler, A.; Chakroun, K.; Peters, J. Attenuated Directed Exploration during Reinforcement Learning in Gambling Disorder. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieglitz, N.; Knudsen, T.; Becker, M.C. Adaptation and Inertia in Dynamic Environments. Strateg. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 1854–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston-Jones, G.; Cohen, J.D. Adaptive Gain and the Role of the Locus Coeruleus-Norepinephrine System in Optimal Performance. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 493, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsters, J.H.; Whelan, C.D.; Robertson, I.H.; Ramnani, N. Cerebellum and Cognition: Evidence for the Encoding of Higher Order Rules. Cereb. Cortex 2013, 23, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirokoff, V.; Scala, G.; Swendsen, J.; Dilharreguy, B.; Berthoz, S.; Chanraud, S. Impact of Metacognitive and Psychological Factors in Learning-Induced Plasticity of Resting State Networks. Biology 2022, 11, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, D.S.; Wymbs, N.F.; Porter, M.A.; Mucha, P.J.; Carlson, J.M.; Grafton, S.T. Dynamic Reconfiguration of Human Brain Networks during Learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7641–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.; Zerrin Yetkin, F.; Haughton, V.M.; Hyde, J.S. Functional Connectivity in the Motor Cortex of Resting Human Brain Using Echo-Planar Mri. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.; Castellanos, F.X. Strengthening Connections: Functional Connectivity and Brain Plasticity. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2014, 24, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, N.B.; Robertson, E.M.; Miall, R.C. The Resting Human Brain and Motor Learning. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edde, M.; Di Scala, G.; Dupuy, M.; Dilharreguy, B.; Catheline, G.; Chanraud, S. Learning-Driven Cerebellar Intrinsic Functional Connectivity Changes in Men. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.M.; Baldassarre, A.; Committeri, G.; Romani, G.L.; Corbetta, M. Learning Sculpts the Spontaneous Activity of the Resting Human Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17558–17563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrkanoon, S.; Boonstra, T.W.; Breakspear, M.; Hinder, M.; Summers, J.J. Upregulation of Cortico-Cerebellar Functional Connectivity after Motor Learning. Neuroimage 2016, 128, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, S.; Robertson, E.M.; Miall, R.C. The Time Course of Task-Specific Memory Consolidation Effects in Resting State Networks. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 3982–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, A.; Ritchie, K.; Mulligan, R. The Measurement Properties of a French Language Adaptation of the National Adult Reading Test. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 1999, 8, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.E.; O’Connell, A. Dementia: The Estimation of Premorbid Intelligence Levels Using the New Adult Reading Test. Cortex J. Devoted Study Nerv. Syst. Behav. 1978, 14, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitan, R. Trail Making Test: Manual for Administration, Scoring and Interpretation; Indiana University: Bloomington, IN, USA, 1956; Volume 134. [Google Scholar]
- Rhéaume, J.; Freeston, M.H.; Dugas, M.J.; Letarte, H.; Ladouceur, R. Perfectionism, Responsibility and Obsessive-Compulsive Symptoms. Behav. Res. Ther. 1995, 33, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, J.; Samson, P.; Turbide, D.; Lawson, J.S. Adaptation française du Social Self-Esteem Inventory. Can. J. Behav. Sci. Can. Sci. Comport. 1981, 13, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardi, C.; Billieux, J.; d’Acremont, M.; Linden, M. A French Adaptation of a Short Version of the Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire (SPSRQ). Personal. Individ. Differ. 2008, 45, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchon-Schweitzer, M.; Paulhan, I. Inventaire D’anxiété état-Trait Forme Y; ECPA: Paris, France, 1993; ISBN 2-7253-0003-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lépine, J.P.; Godchau, M.; Brun, P.; Lempérière, T.H. Évaluation de l’anxiété et de la dépression chez des patients hospitalisés dans un service de médecine interne. In Annales Médico-Psychologiques; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Balsters, J.H.; Ramnani, N. Cerebellar Plasticity and the Automation of First-Order Rules. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Nieto-Castanon, A. Conn: A Functional Connectivity Toolbox for Correlated and Anticorrelated Brain Networks. Brain Connect. 2012, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Landeau, B.; Papathanassiou, D.; Crivello, F.; Etard, O.; Delcroix, N.; Mazoyer, B.; Joliot, M. Automated Anatomical Labeling of Activations in SPM Using a Macroscopic Anatomical Parcellation of the MNI MRI Single-Subject Brain. Neuroimage 2002, 15, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.R.; Navarro, D.J.; Newell, B.R.; Beesley, T. Protection from Uncertainty in the Exploration/Exploitation Trade-Off. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2022, 48, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edde, M.; Dilharreguy, B.; Theaud, G.; Chanraud, S.; Helmer, C.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Amieva, H.; Allard, M.; Descoteaux, M.; Catheline, G. Age-Related Change in Episodic Memory: Role of Functional and Structural Connectivity between the Ventral Posterior Cingulate and the Parietal Cortex. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 2203–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogousslavsky, J.; Miklossy, J.; Deruaz, J.P.; Assal, G.; Regli, F. Lingual and Fusiform Gyri in Visual Processing: A Clinico-Pathologic Study of Superior Altitudinal Hemianopia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1987, 50, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roland, P.E.; Gulyás, B. Visual Memory, Visual Imagery, and Visual Recognition of Large Field Patterns by the Human Brain: Functional Anatomy by Positron Emission Tomography. Cereb. Cortex 1995, 5, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callan, A.M.; Osu, R.; Yamagishi, Y.; Callan, D.E.; Inoue, N. Neural Correlates of Resolving Uncertainty in Driver’s Decision Making. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 2804–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruguier, A.J.; Quartz, S.R.; Bossaerts, P. Exploring the Nature of “Trader Intuition”. J. Financ. 2010, 65, 1703–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziol, L.F.; Budding, D.E.; Chidekel, D. From Movement to Thought: Executive Function, Embodied Cognition, and the Cerebellum. Cerebellum 2012, 11, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D. The Role of the Cerebellum in Cognition and Emotion: Personal Reflections Since 1982 on the Dysmetria of Thought Hypothesis, and Its Historical Evolution from Theory to Therapy. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2010, 20, 236–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M. Bases and Implications of Learning in the Cerebellum—Adaptive Control and Internal Model Mechanism. In Progress in Brain Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 148, pp. 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Walton, M.E.; Rushworth, M.F.S. Learning the Value of Information in an Uncertain World. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulies, D.S.; Kelly, A.C.; Uddin, L.Q.; Biswal, B.B.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P. Mapping the Functional Connectivity of Anterior Cingulate Cortex. NeuroImage 2007, 37, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, H.; Faber, J.; Timmann, D.; Klockgether, T. Update Cerebellum and Cognition. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 3921–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swick, D.; Ashley, V. Left inferior frontal gyrus is critical for response inhibition. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberg, K.C.; Toren, I.; Paz, R. A Neural and Behavioral Trade-off between Value and Uncertainty Underlies Exploratory Decisions in Normative Anxiety. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Gershman, S.J.; Phelps, E.A. Trait Somatic Anxiety Is Associated with Reduced Directed Exploration and Underestimation of Uncertainty. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2023, 7, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhman, A.; Hamm, A.; Hugdahl, K. Cognition and the Autonomic Nervous System: Orienting, Anticipation, and Conditioning. In Handbook of Psychophysiology, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 533–575. ISBN 978-0-521-62634-7. [Google Scholar]
- Luksys, G.; Gerstner, W.; Sandi, C. Stress, Genotype and Norepinephrine in the Prediction of Mouse Behavior Using Reinforcement Learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghunathan, R.; Pham, M.T. All Negative Moods Are Not Equal: Motivational Influences of Anxiety and Sadness on Decision Making. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1999, 79, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, E.T.; Silberman, I. Development of Regulatory Focus: Promotion and Prevention as Ways of Living. In Motivation and Self-Regulation across the Life Span; Dweck, C.S., Heckhausen, J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; pp. 78–113. ISBN 978-0-521-59176-8. [Google Scholar]
- Scholl, J.; Klein-Flügge, M. Understanding Psychiatric Disorder by Capturing Ecologically Relevant Features of Learning and Decision-Making. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 355, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ALL | COST− | COST+ | Group Comparison | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (sd) | n | Mean (sd) | n | Mean (sd) | n | Statistics * | |
| Age (years) | 30.00 (10.87) | 28 | 32.21 (13.47) | 14 | 27.79 (7.32) | 14 | U = 91.00; p = 0.76; r = 0.41 |
| TMT B-A (seconds) | 21.69 (12.93) | 24 | 18.28 (10.26) | 14 | 26.47 (15.22) | 10 | U = 43.00; p = 0.12; r = 0.39 |
| FMPS_CM | 23.00 (8.59) | 25 | 23.23 (9.76) | 13 | 22.75 (7.55) | 12 | t = 0.14; p = 0.89; d = 0.05 |
| FMPS_DA | 11.40 (4.00) | 25 | 11.62 (3.57) | 13 | 11.17 (4.58) | 12 | t = 0.28; p = 0.79; d = 0.11 |
| FMPS_O | 22.24 (5.77) | 25 | 22.92 (5.02) | 13 | 21.50 (6.63) | 12 | t = 0.61; p = 0.55; d = 0.24 |
| FMPS_PS | 22.20 (5.42) | 25 | 21.69 (4.80) | 13 | 22.75 (6.18) | 12 | t = −0.48; p = 0.64; d = 0.13 |
| SPSRQ_P | 43.64 (10.05) | 28 | 42.36 (9.71) | 14 | 44.93 (10.58) | 14 | t = −0.67; p = 0.51; d = 0.11 |
| SPSRQ_R | 37.61 (6.05) | 28 | 37.00 (7.32) | 14 | 38.21 (4.64) | 14 | t = −0.52; p = 0.60; d = -0.20 |
| SSEI | 129.92 (21.67) | 25 | 131.29 (18.92) | 14 | 128.18 (25.60) | 11 | U = 76.00; p = 0.98; r = 0.01 |
| STAI_S | 31.89 (9.69) | 28 | 30.71 (8.51) | 14 | 33.07 (10.94) | 14 | U = 87.00; p = 0.63; r = 0.11 |
| STAI_T | 42.10 (12.88) | 28 | 43.00 (13.93) | 14 | 41.14 (12.19) | 14 | t = 0.36; p = 0.71; d = 0.14 |
| HAD_D | 4.91 (3.79) | 23 | 6.00 (4.59) | 12 | 3.73 (2.323) | 11 | U = 52.50; p = 0.42; r = 0.20 |
| HAD_A | 6.57 (4.25) | 23 | 6.33 (3.37) | 12 | 6.82 (5.21) | 11 | U = 56.50; p = 0.57; r = 0.14 |
| Confidence in learning (%) | 77.37 (6.05) | 28 | 76.55 (6.76) | 14 | 78.18 (5.36) | 14 | U = 83.00; p = 0.50; r = 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soussi, C.; Berthoz, S.; Chirokoff, V.; Chanraud, S. Interindividual Brain and Behavior Differences in Adaptation to Unexpected Uncertainty. Biology 2023, 12, 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101323
Soussi C, Berthoz S, Chirokoff V, Chanraud S. Interindividual Brain and Behavior Differences in Adaptation to Unexpected Uncertainty. Biology. 2023; 12(10):1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101323
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoussi, Célia, Sylvie Berthoz, Valentine Chirokoff, and Sandra Chanraud. 2023. "Interindividual Brain and Behavior Differences in Adaptation to Unexpected Uncertainty" Biology 12, no. 10: 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101323
APA StyleSoussi, C., Berthoz, S., Chirokoff, V., & Chanraud, S. (2023). Interindividual Brain and Behavior Differences in Adaptation to Unexpected Uncertainty. Biology, 12(10), 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101323






