MicroRNAs Signature Panel Identifies Heavy Drinkers with Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis from Heavy Drinkers without Liver Injury
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Human Samples
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. OpenArray® Panels—Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Pathway Analysis of the Dysregulated microRNAs
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of Global Profiling of the Serum microRNA Expression in Heavy Alcohol Users
3.3. microRNA Signature Distinguished Patients with Alcoholic Hepatitis
3.4. Correlation of Downregulated microRNAs with Traditional Biomarkers of Liver Disease
3.5. Diagnostic Performance of Conventional Biomarkers and Selected microRNAs to Distinguish Cases from Drinking Controls
3.6. Association of miRNAs with Genetic Variants Linked to Risk of Cirrhosis
3.7. Identification of Target Genes and Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AH | Alcoholic hepatitis |
| ALD | Alcohol-associated liver disease |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| AUC-ROC | Area Under The Curve of Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| AUDIT | Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test |
| Ct | Threshold cycle |
| Cq | Quantitation Cycle |
| F | Female |
| Fx | Disease and function pathway |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| GWAS | Genome wide association studies |
| Hb | Haemoglobin |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HREC | Human Research Ethics Committee |
| INR | International Normalised Ratio |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| M | Male |
| MELD | Mortality end-stage liver disease |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| Tx | Toxic function pathway |
References
- Mendez-Sanchez, N.; Almeda-Valdes, P.; Uribe, M. Alcoholic liver disease. An update. Ann. Hepatol. 2005, 4, 32–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-C.; Mo, L.-R.; Chang, C.-Y.; Perng, D.-S.; Hsu, C.-C.; Lo, G.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Yen, Y.-C.; Hu, J.-T.; Yu, M.-L.; et al. Heavy alcohol consumption increases the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Tsai, I.-T.; Hsu, Y.-C. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cequera, A.; Garcia de Leon Mendez, M.C. Biomarkers for liver fibrosis: Advances, advantages and disadvantages. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2014, 79, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Schwantes-An, T.; Darlay, R.; Mathurin, P.; Masson, S.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Mueller, S.; Aithal, G.P.; Eyer, F.; Gleeson, D.; Thompson, A.; et al. Genome-wide Association Study and Meta-analysis on Alcohol-Associated Liver Cirrhosis Identifies Genetic Risk Factors. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1920–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, S.; Stickel, F.; Trépo, E.; Way, M.; Herrmann, A.; Nischalke, H.D.; Brosch, M.; Rosendahl, J.; Berg, T.; Ridinger, M.; et al. A genome-wide association study confirms PNPLA3 and identifies TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 as risk loci for alcohol-related cirrhosis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulyaeva, L.F.; Kushlinskiy, N.E. Regulatory mechanisms of microRNA expression. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Chen, J.; Tao, Z.; Miao, L.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J. Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: Coordination between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Mackowiak, B.; Gao, B. MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Gut 2021, 70, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaddaq, G.; Shahzad, N.; Ashraf, M.A.; Arshad, M.I. Circulating liver-specific microRNAs as noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers of hepatic diseases in human. Biomarkers 2019, 24, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Szabo, G. MicroRNA Signature in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 498232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, J.B.; Masson, S.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Mueller, S.; Aithal, G.P.; Eyer, F.; Gleeson, D.; Thompson, A.; Stickel, F.; Soyka, M.; et al. Obesity, Diabetes, Coffee, Tea, and Cannabis Use Alter Risk for Alcohol-Related Cirrhosis in 2 Large Cohorts of High-Risk Drinkers. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, J.B.; Rahman, K.; Haber, P.S.; Day, C.P.; Masson, S.; Daly, A.K.; Cordell, H.J.; Mueller, S.; Seitz, H.K.; Liangpunsakul, S.; et al. Brief Report: Genetics of Alcoholic Cirrhosis—GenomALC Multinational Study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shihana, F.; Joglekar, M.V.; Raubenheimer, J.; Hardikar, A.A.; Buckley, N.A.; Seth, D. Circulating human microRNA biomarkers of oxalic acid-induced acute kidney injury. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1725–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shihana, F.; Wong, W.K.M.; Joglekar, M.V.; Mohamed, F.; Gawarammana, I.B.; Isbister, G.K.; Hardikar, A.A.; Seth, D.; Buckley, N.A. Urinary microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for toxic acute kidney injury in humans. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shihana, F.; Joglekar, M.V.; Hardikar, A.A.; Seth, D.; Buckley, N.A. Serum microRNA as biomarkers for acute kidney injury following poisoning with potassium permanganate and oxalic acid. Clin. Toxicol. 2019, 57, 1175. [Google Scholar]
- Crabb, D.W.; Bataller, R.; Chalasani, N.P.; Kamath, P.S.; Lucey, M.; Mathurin, P.; McClain, C.; McCullough, A.; Mitchell, M.C.; Morgan, T.R.; et al. Standard Definitions and Common Data Elements for Clinical Trials in Patients with Alcoholic Hepatitis: Recommendation from the NIAAA Alcoholic Hepatitis Consortia. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Itoh, Y. Limitations of liver biopsy and non-invasive diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soresi, M.; Giannitrapani, L.; Cervello, M.; Licata, A.; Montalto, G. Non invasive tools for the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18131–18150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Saini, M.; Das, R.; Gupta, S.; Joshi, T.; Mehta, D.K. Circulating MicroRNAs: Diagnostic Value as Biomarkers in the Detection of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. MicroRNA 2023, 12, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, K.; Venugopal, S.K. Circulating microRNAs: Possible role as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers in liver disease. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enache, L.S.; Enache, E.L.; Ramière, C.; Diaz, O.; Bancu, L.; Sin, A.; André, P. Circulating RNA Molecules as Biomarkers in Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 17644–17666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Lin, Y.; Yu, C. Circulating miRNAs as Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 2096161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Kaur, M.; Saini, N.; Mir, A.; Duseja, A.; Sinha, S.; Sharma, S. Altered expressions of circulating microRNAs 122 and 192 during antitubercular drug induced liver injury indicating their role as potential biomarkers. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjay, S.; Girish, C. Role of miRNA and its potential as a novel diagnostic biomarker in drug-induced liver injury. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueller, F.; Roy, S.; Vucur, M.; Trautwein, C.; Luedde, T.; Roderburg, C. The Role of miRNAs in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases and Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Kusumanchi, P.; Tang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Radaeva, S.; Peiffer, B.; Shah, V.H.; Kamath, P.; Gores, G.J.; et al. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the MicroRNAs Responsible for Liver Regeneration Associated with Mortality in Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2436–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doghish, A.S.; Elballal, M.S.; Elazazy, O.; Elesawy, A.E.; Elrebehy, M.A.; Shahin, R.K.; Midan, H.M.; Sallam, A.-A.M. The role of miRNAs in liver diseases: Potential therapeutic and clinical applications. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 243, 154375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, A.S.A.; Rudayni, H.A.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Ali, M.A.M. MicroRNAs: Small molecules with big impacts in liver injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 32–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

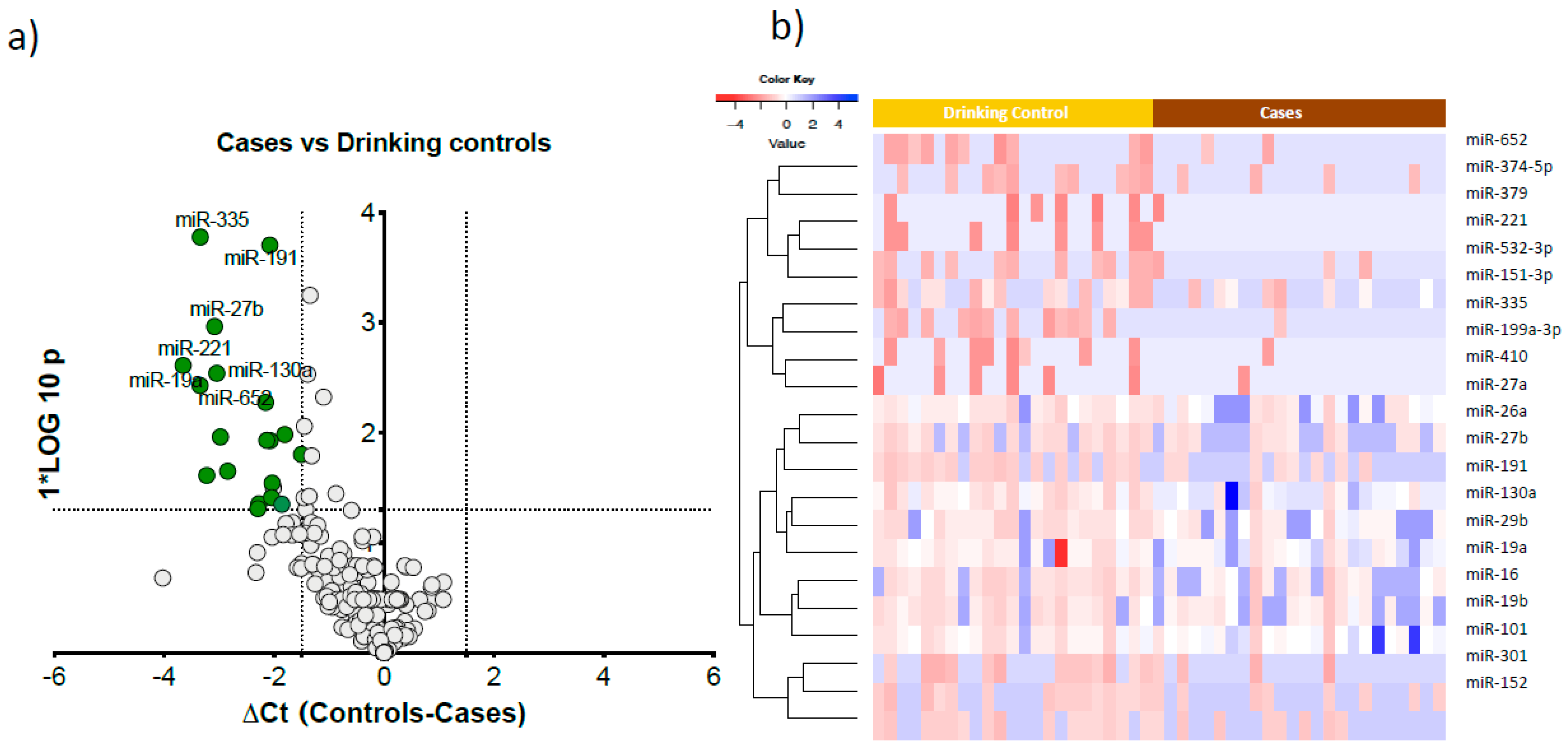
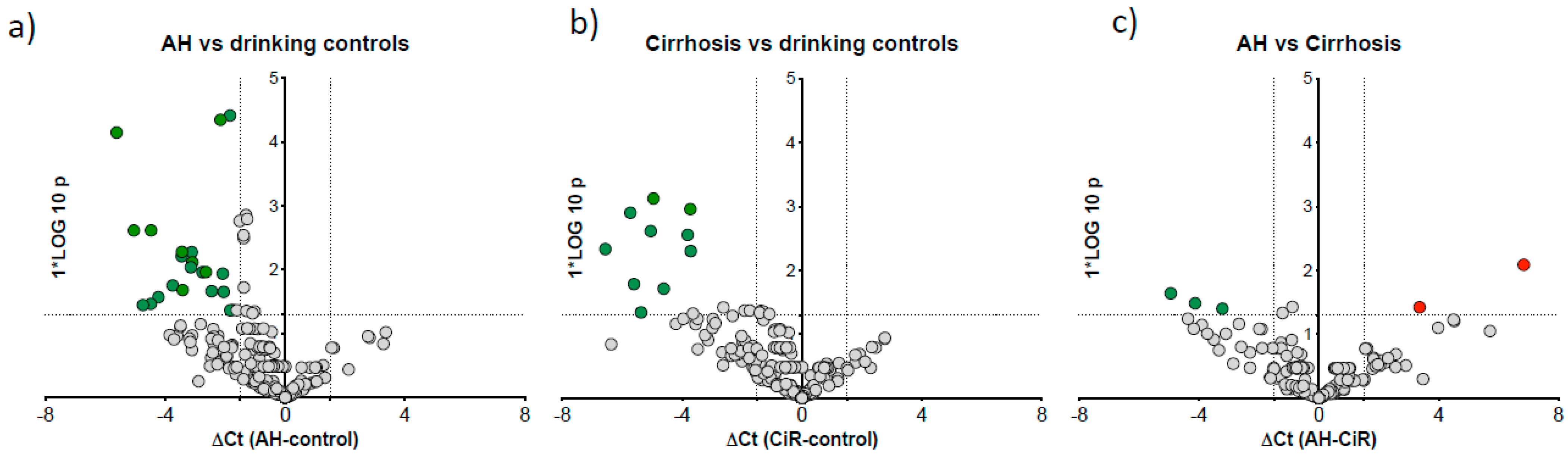

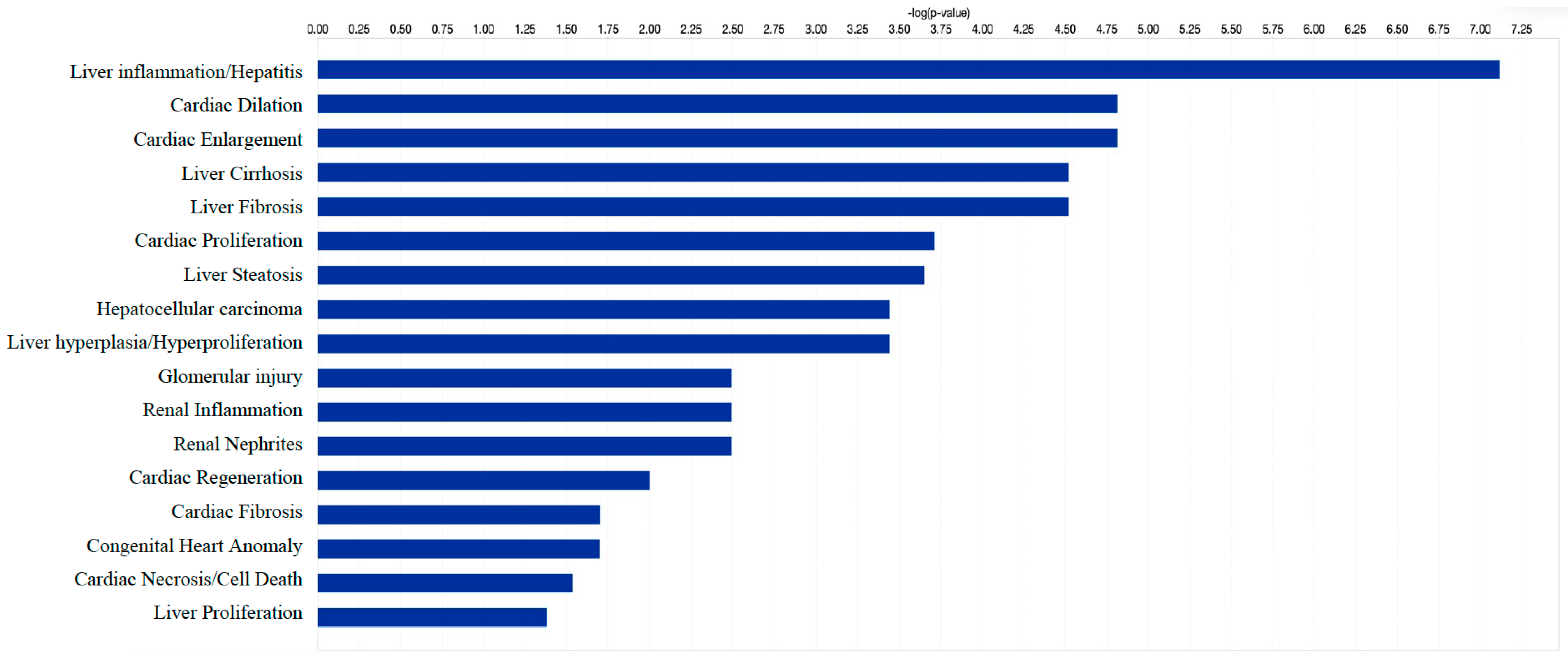
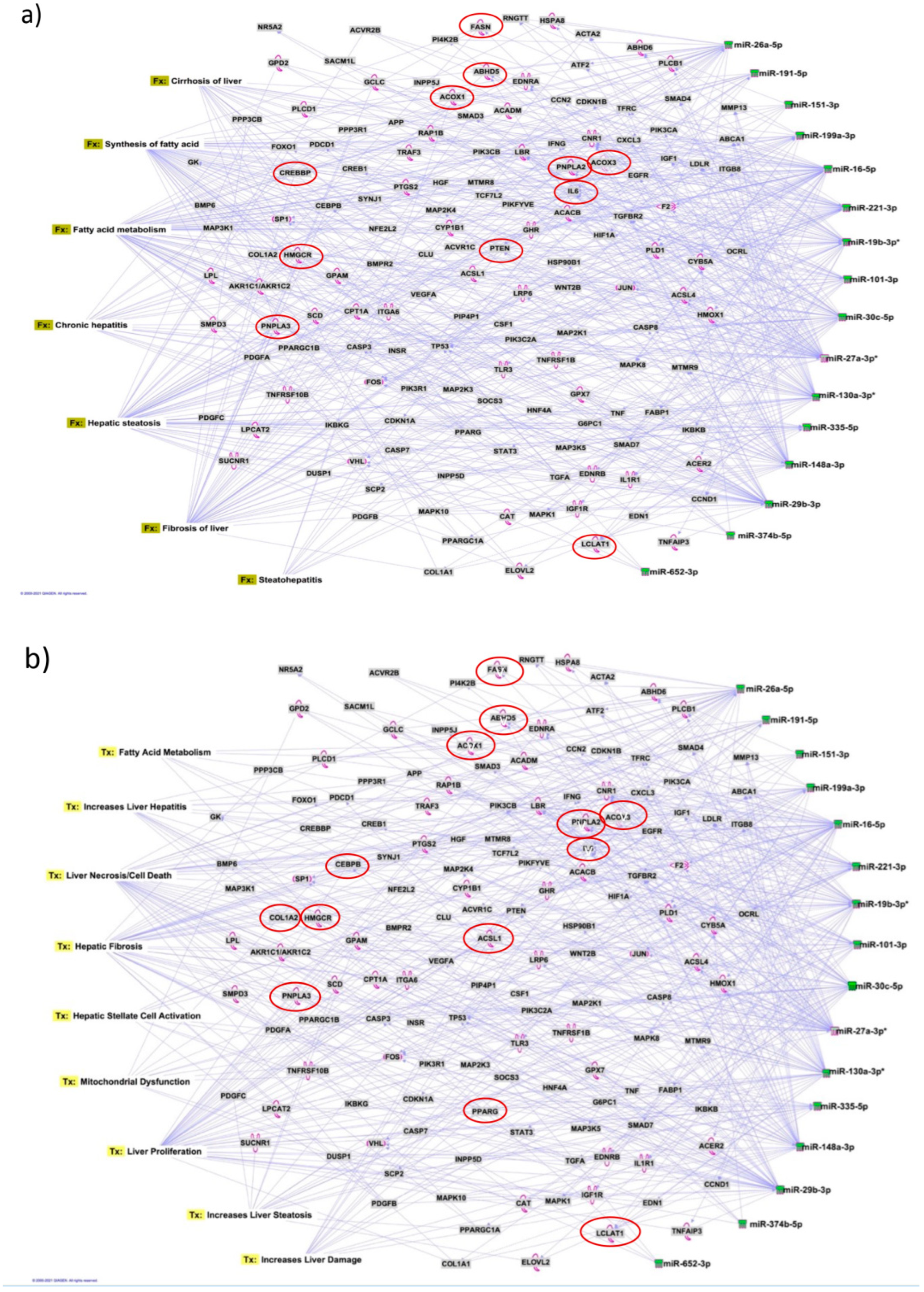
| Cases (n = 24) | Drinking Controls (n = 23) | p-Value (Case Group vs. Drinking Control Group) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male n = 16 | Female n = 8 | Male n = 15 | Female n = 8 | |||
| Demographics | European Caucasian ethnicity/race (%) | 100% | 100% | 93% | 100% | 0.674 |
| Males (%) | 66 | 34 | 65 | 35 | 0.864 | |
| Age | 51 (46–57) | 49 (40–51) | 56 (49–64) | 52 (48–55) | 0.156 | |
| Alcohol use | Alcohol intake (g/day) | 236 ± 106 | 148 ± 89 | 228 ± 110 | 178 ± 84 | 0.779 |
| Years of high-risk drinking | 30 (22–33) | 21 (19–24) | 22 (17–31) | 16 (15–23) | 0.133 | |
| Life-time alcohol intake (Kg) | 2497 ± 1542 | 1287 ± 1167 | 1952 ±1033 | 1267 ± 688 | 0.790 | |
| Audit score | 14 (2–33) | 5 (3–21) | 29 (29–36) | 33 (29–33) | 0.04 * | |
| Lab results | Haemoglobin (g/L) | 126 ± 20 | 118 ± 21 | 153 ±7.9 | 131 ± 6 | 0.001 * |
| WBC | 6.9 ± 2.7 | 6.0 ± 1.7 | 6.8 ± 2.7 | 8 ± 3 | 0.456 | |
| Platelet count (109/L) | 151 ± 97 | 104 ± 37 | 254 ± 100 | 255 ± 72 | <0.0001 * | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 34 ± 12 | 35 ± 5 | 44 ± 3 | 45 ± 4 | <0.0001 * | |
| Bilirubin (umol/L) | 44 ± 37 | 62 ± 34 | 9 ± 5 | 8 ± 4 | <0.0001 * | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 71 (58–94) | 64 ± 21 | 82 ± 11 | 63 ±13 | 0.594 | |
| ALT (IU/L) | 43 ± 22 | 30 ± 10 | 38 ± 32 | 23 ± 11 | 0.623 | |
| AST (IU/L) | 74 ± 37 | 63 ± 40 | 35 ± 23 | 28 ±14 | 0.001 * | |
| GGT (U/L) | 142 ± 127 | 127 ± 183 | 148 ± 181 | 62 ± 87 | 0.179 | |
| Liver disease severity | INR | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | <0.0001 * |
| MELD score | 10.1 ± 5.8 | 12 ± 5.2 | 2.3 ± 2.1 | −0.7 ± 4.1 | <0.0001 * | |
| miRs | ALT (IU/L) | AST (IU/L) | Bilirubin (mg/dL) | INR | MELD Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-16 | 0.01 (−0.2 to 0.30) | 0.18 (−0.12 to 0.45) | 0.39 ** (0.11 to 0.62) | 0.51 *** (0.26 to 0.71) | 0.48 *** (0.21 to 0.68) |
| miR-19a | 0.26 (−0.03 to 0.51) | 0.39 ** (0.11 to 0.61) | 0.44 ** (0.16 to 0.65) | 0.50 *** (0.24 to 0.69) | 0.53 *** (0.27 to 0.71) |
| miR-19b | 0.11 (0.18 to 0.39) | 0.23 (−0.06 to 0.49) | 0.32 * (0.13 to 0.63) | 0.36 * (0.19 to 0.66) | 0.47 *** (0.20 to 0.67) |
| miR-26a | 0.21 (−0.09 to 0.47) | 0.27 (−0.03 to 0.52) | 0.30 * (0.12 to 0.62) | 0.30 * (0.01 to 0.54) | 0.40 ** (0.15 to 0.64) |
| miR-27a | 0.13 (−0.17 to 0.40) | 0.18 (−0.11 to 0.45) | 0.38 ** (0.04 to 0.57) | 0.39 ** (0.01 to 0.53) | 0.39 ** (0.11 to 0.62) |
| miR-27b | 0.16 (−0.14 to 0.43) | 0.28 (−0.01 to 0.53) | 0.38 * (0.09 to 0.60) | 0.41 ** (0.13 to 0.63) | 0.36 * (0.07 to 0.59) |
| miR-29b | 0.24 (0.05 to 0.50) | 0.20 (−0.09 to 0.47) | 0.39 ** (0.07 to 0.59) | 0.49 *** (0.22 to 0.68) | 0.53 *** (0.27 to 0.71) |
| miR-30c | 0.08 (−0.21 to 0.37) | 0.27 (−0.03 to 0.52) | 0.36 * (0.18 to 0.66) | 0.40 ** (0.12 to 0.62) | 0.42 ** (0.26 to 0.71) |
| miR-101 | 0.22 (−0.08 to 0.48) | 0.30 * (0.01 to 0.54) | 0.39 ** (0.04 to 0.57) | 0.44 ** (0.16 to 0.64) | 0.52 *** (0.27 to 0.71) |
| miR-130a | 0.27 (0.02 to 0.52) | 0.34 * (0.052 to 0.58) | 0.43 ** (0.14 to 0.64) | 0.53 *** (0.27 to 0.71) | 0.43 ** (0.15 to 0.64) |
| miR-151-3p | 0.45 ** (0.18 to 0.65) | 0.43 ** (0.16 to 0.65) | 0.41 ** (0.13 to 0.63) | 0.25 (0.01 to 0.51) | 0.28 (−0.01 to 0.53) |
| miR-191 | 0.29 * (0.01 to 0.54) | 0.44 ** (0.16 to 0.65) | 0.54 **** (0.29 to 0.72) | 0.59 **** (0.35 to 0.75) | 0.60 **** (0.37 to 0.76) |
| miR-199a-3p | 0.29 * (0.01 to 0.54) | 0.39 ** (0.11 to 0.61) | 0.33 * (0.04 to 0.57) | 0.30 * (0.02 to 0.54) | 0.32 * (0.02 to 0.56) |
| miR-221 | 0.17 (−0.13 to 0.44) | 0.32 * (0.03 to 0.56) | 0.50 *** (0.24 to 0.69) | 0.35 * (0.06 to 0.58) | 0.45 ** (0.17 to 0.66) |
| miR-335 | 0.13 (−0.16 to 0.41) | 0.25 (−0.05 to 0.50) | 0.36 * (0.06 to 0.59) | 0.40 ** (0.12 to 0.62) | 0.35 * (0.06 to 0.58) |
| miR-374-5p | 0.08 (−0.36 to 0.21) | 0.11 (−0.19 to 0.39) | 0.40 ** (0.11 to 0.62) | 0.34 * (0.04 to 0.57) | 0.34 * (0.05 to 0.58) |
| miR-532-3p | 0.15 (−0.15 to 0.42) | 0.26 (−0.04 to 0.51) | 0.34 * (0.05 to 0.58) | 0.34 * (0.04 to 0.57) | 0.39 ** (0.10 to 0.62) |
| miR-652 | 0.26 (−0.03 to 0.51) | 0.42 ** (0.14 to 0.63) | 0.33 * (0.04 to 0.57) | 0.39 ** (0.11 to 0.61) | 0.31 * (0.01 to 0.55) |
| AUC-ROC (95%CI) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional biomarkers | INR | 0.97 (0.92–1) | <0.0001 |
| MELD score | 0.94 (0.87–1) | <0.0001 | |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.89 (0.79–0.98) | <0.0001 | |
| Platelet count | 0.85 (0.74–0.96) | <0.0001 | |
| Albumin/µmol/L | 0.83 (0.70–0.96) | 0.0001 | |
| AST (U/L) | 0.76 (0.62–0.90) | 0.0023 | |
| MicroRNAs | miR-191 | 0.85 (0.73–0.96) | <0.0001 |
| miR-27a | 0.80 (0.67–0.93) | 0.0004 | |
| miR-130a | 0.78 (0.64–0.92) | 0.0009 | |
| miR-19a | 0.77 (0.63–0.92) | 0.0013 | |
| miR-19b | 0.76 (0.61–0.91) | 0.0022 | |
| miR-16 | 0.74 (0.59–0.89) | 0.0050 | |
| miR-29b | 0.71 (0.56–0.87) | 0.0128 | |
| miR-101 | 0.68 (0.54–0.82) | 0.0316 |
| Target mRNA | Functions of Genes/Coded Molecule | miRNA Association from Pathway Analysis | Gene Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABHD5 | Activates ATGL; dynamic interactions of ABHD5 with PNPLA3 regulate triacylglycerol metabolism in brown adipocytes | miR-26a, miR-27a, miR-19b, miR-27b | a/b hydrolase domain containing 5 |
| ABHD6 | Inactivation of ABHD6 protects against HFD-induced obesity, liver steatosis and insulin resistance | miR-151, miR-30c, miR-27a | a/b hydrolase domain containing 6 |
| ABHD3 | A lipase that selectively cleaves medium-chain and oxidatively truncated phospholipids | miR-130a, miR-221 | a/b hydrolase domain containing 3 |
| ACOX1 | A rate-limiting enzyme in peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation, regulates metabolism, spontaneous hepatic steatosis and hepatocellular damage over time. | miR-199a, miR-16 | Acyl-CoA Oxidase 1 |
| ACOX3 | Related to lipid metabolism | miR-151, miR-19a | Acyl-CoA Oxidase 3 |
| CREBP | Key modulator of glycolytic, lipogenic and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (Mttp) gene expression, thereby controlling both fatty acid accumulation and VLDL export from the liver | miR-191, miR-26a | carbohydrate response element binding protein |
| HMGCR | Transmembrane glycoprotein that is the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis as well as in the biosynthesis of nonsterol isoprenoids that are essential for normal cell function, including ubiquinone and geranylgeranyl proteins | miR-29b, miR-27a | 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase |
| IL6 | Liver inflammation | miR-26a, miR-148a, miR-19b, miR-16, miR-30c, miR-191 | Interleukin 6 |
| LBR | Cholesterol synthesis via sterol reductase function | miR-221, miR-101, miR-27a, miR-130a | Lamin B receptor |
| PNPLA2/ATGL | The key enzyme for intracellular hydrolysis of stored triglycerides and determines FA signalling through PPARα; we explored the role of ATGL in hepatic inflammation in mouse models of NASH and endotoxemia | miR-148a, miR-27a | Adipose triglyceride lipase |
| PNPLA3 | Exhibits a dual function in LD metabolism, and that it participates in the restoration of lipid | miR-29b, miR-27a | Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 |
| TCF7L2 | Susceptibility gene for type-2 diabetes | miR-191, miR-26a, miR-221 | Transcription factor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shihana, F.; Joglekar, M.V.; Schwantes-An, T.-H.; Hardikar, A.A.; Seth, D. MicroRNAs Signature Panel Identifies Heavy Drinkers with Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis from Heavy Drinkers without Liver Injury. Biology 2023, 12, 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101314
Shihana F, Joglekar MV, Schwantes-An T-H, Hardikar AA, Seth D. MicroRNAs Signature Panel Identifies Heavy Drinkers with Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis from Heavy Drinkers without Liver Injury. Biology. 2023; 12(10):1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101314
Chicago/Turabian StyleShihana, Fathima, Mugdha V. Joglekar, Tae-Hwi Schwantes-An, Anandwardhan A. Hardikar, and Devanshi Seth. 2023. "MicroRNAs Signature Panel Identifies Heavy Drinkers with Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis from Heavy Drinkers without Liver Injury" Biology 12, no. 10: 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101314
APA StyleShihana, F., Joglekar, M. V., Schwantes-An, T.-H., Hardikar, A. A., & Seth, D. (2023). MicroRNAs Signature Panel Identifies Heavy Drinkers with Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis from Heavy Drinkers without Liver Injury. Biology, 12(10), 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12101314






