A Novel Method to Screen Strong Constitutive Promoters in Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens for Industrial Applications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Cultivation
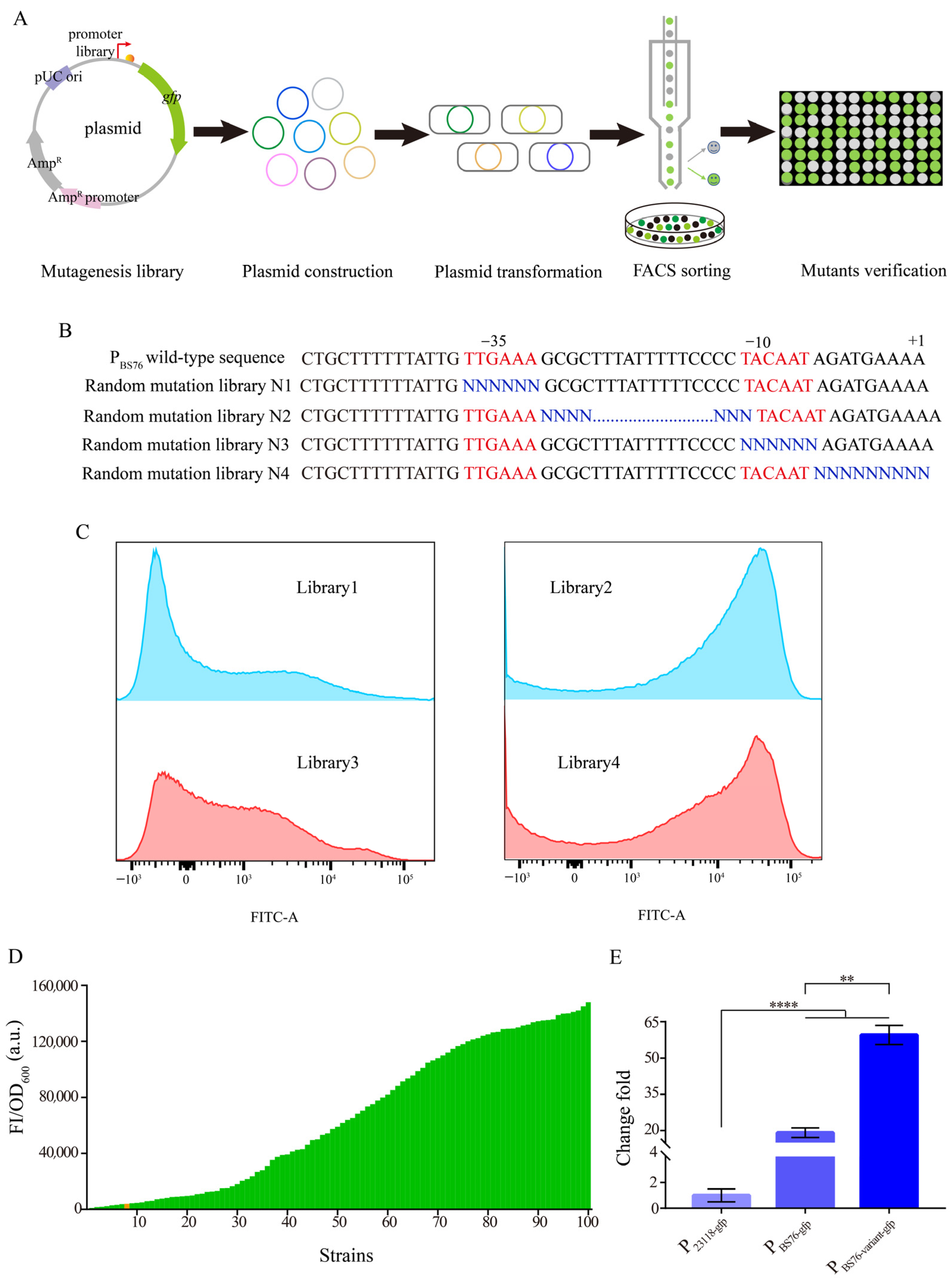
2.2. Design and Construction of Random Library to Isolate Strong Constitutive Promoters Based on Random Genomic Interruption
2.3. Construction of the Promoter PBS76 Library
2.4. Construction of Recombinant Strains
2.5. Fluorescence Assays
2.6. Cultivation in Shake Flasks
2.7. Analytical Methods
3. Results
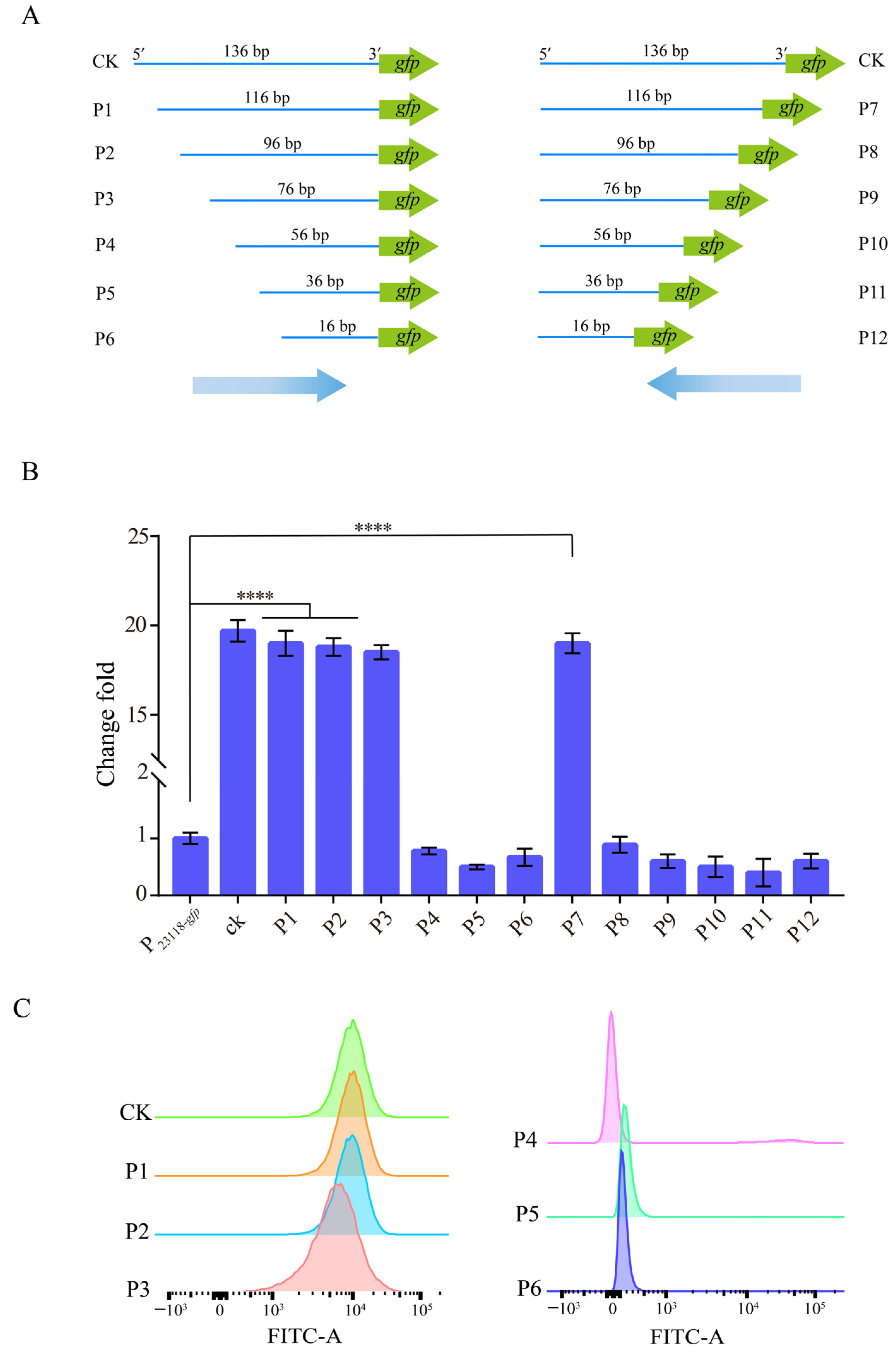
3.1. Screening of Potential Strong Constitutive Promoters Based on a Novel Approach of Random Genomic Interruption and FACS Technology
3.2. Characterization of the Identified Strong Constitutive Promoter from B. subtilis 168
3.3. Construction of a Gradient Promoter Library via Modifying Promoter PBS76
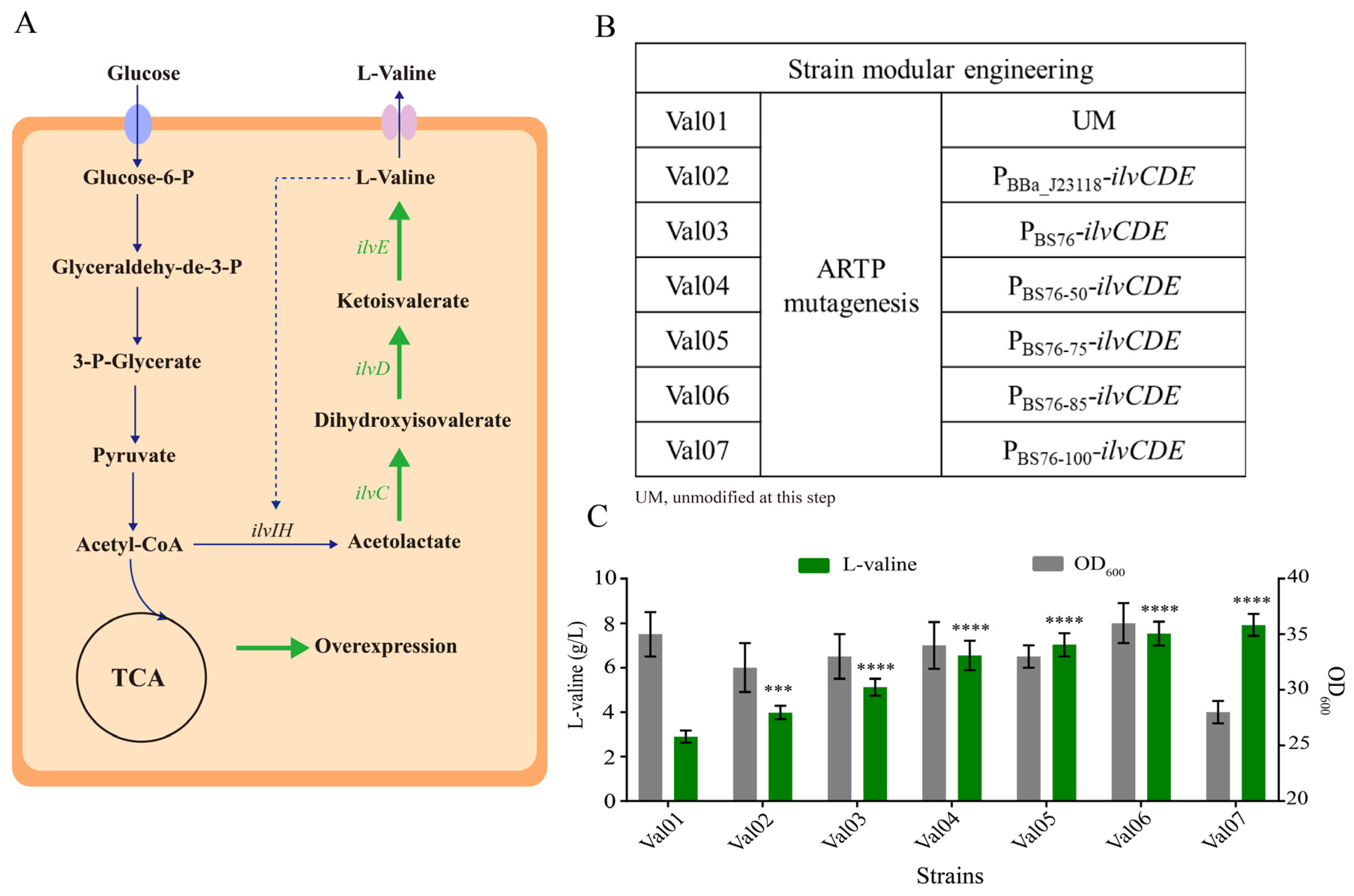
3.4. Application of the Identified Regulatory Elements for L-Valine Overproduction in E. coli W3110
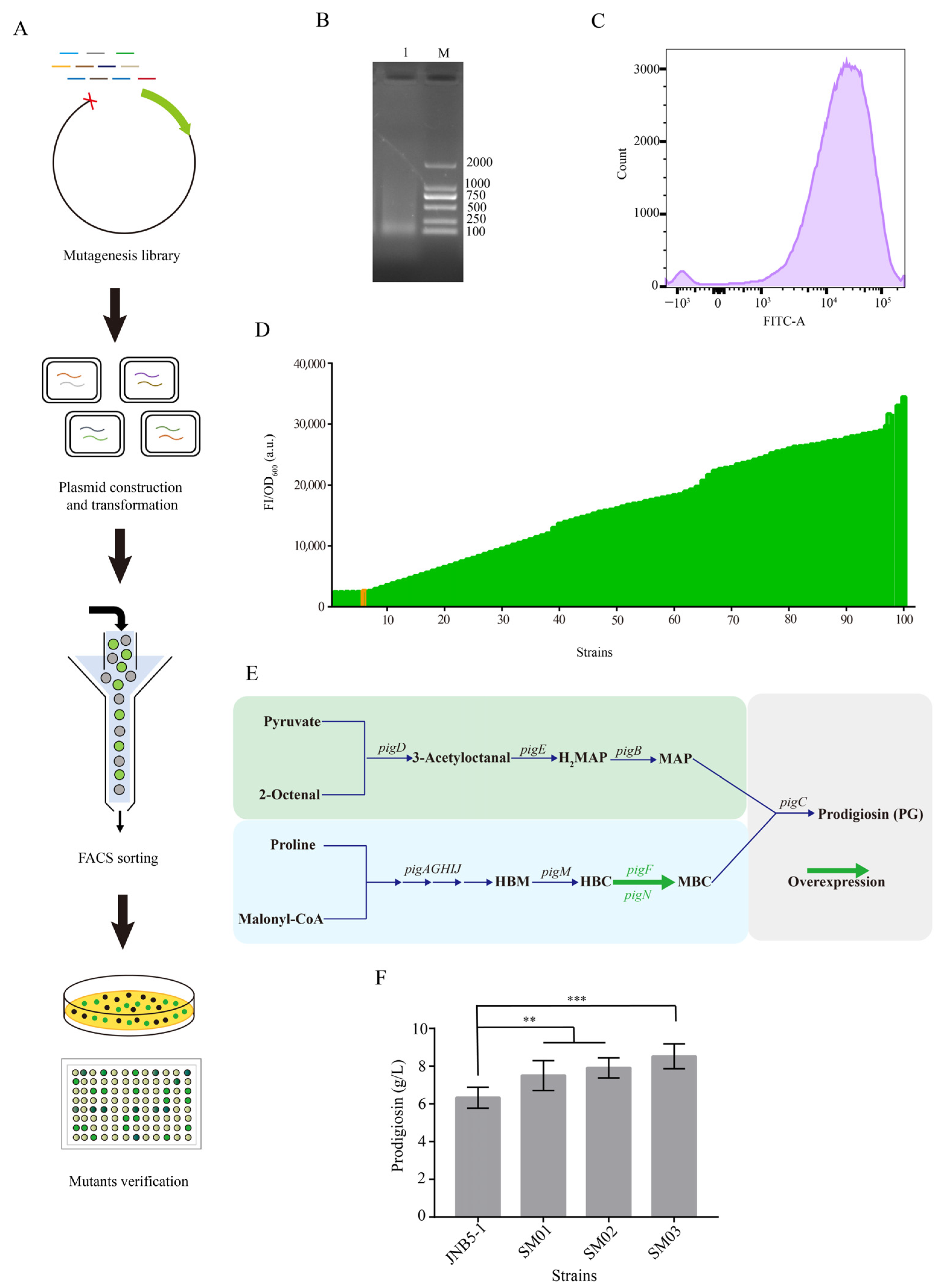
3.5. Screening of Strong Constitutive Promoter Applicable for S. marcescens by Random Genomic Disruption and FACS Technology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ko, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.A.; Han, T.; Kim, G.B.; Park, J.E.; Lee, S.Y. Tools and strategies of systems metabolic engineering for the development of microbial cell factories for chemical production. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4615–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.-S.; Park, J.M.; Choi, S.; Choi, Y.J.; Seung, D.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, S.Y. Engineering of microorganisms for the production of biofuels and perspectives based on systems metabolic engineering approaches. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Prabowo, C.P.S.; Eun, H.; Park, S.Y.; Cho, I.J.; Jiao, S.; Lee, S.Y. Escherichia coli as a platform microbial host for systems metabolic engineering. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuan, N.H.; Tatipamula, V.B.; Canh, N.X.; Giang, N.V. Recent advances in microbial co-culture for production of value-added compounds. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzotto, E.; Tong, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Weber, T. Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering of actinomycetes for natural product discovery. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.R.; Shin, J.H.; Cho, J.S.; Yang, D.; Lee, S.Y. Systems Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2017, 7, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, M.; Smith, D.; Selvarajoo, K. Systems biology approaches integrated with artificial intelligence for optimized metabolic engineering. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2020, 11, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, N.S.; Ledesma-Amaro, R. Synthetic Biology Tools to Engineer Microbial Communities for Biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.Q. Synthetic Biology and Genome-Editing Tools for Improving PHA Metabolic Engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.R.; Jang, W.D.; Yang, D.; Cho, J.S.; Park, D.; Lee, S.Y. Systems Metabolic Engineering Strategies: Integrating Systems and Synthetic Biology with Metabolic Engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 817–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillier, M.; Repoila, F. RNA and gene control in bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Synthetic N-terminal coding sequences for fine-tuning gene expression and metabolic engineering in Bacillus subtilis. Metab. Eng. 2019, 55, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, J.A.; Voigt, C.A. Principles of genetic circuit design. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redden, H.; Alper, H.S. The development and characterization of synthetic minimal yeast promoters. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiziou, S.; Sauveplane, V.; Chang, H.J.; Clerte, C.; Declerck, N.; Jules, M.; Bonnet, J. A part toolbox to tune genetic expression in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7495–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall-Shapiro, T.H.; Sontag, E.D.; Voigt, C.A. Engineered promoters enable constant gene expression at any copy number in bacteria. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.J.; Hu, Y.L.; Xiang, S.H.; Miao, J.; Lou, C.B.; Zhang, L.X. Exploiting a precise design of universal synthetic modular regulatory elements to unlock the microbial natural products in Streptomyces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12181–12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.S.; Kim, M.W.; Kim, M.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, E.J.; Cho, B.K.; Kim, B.G. A Novel Approach for Gene Expression Optimization through Native Promoter and 5’ UTR Combinations Based on RNA-seq, Ribo-seq, and TSS-seq of Streptomyces coelicolor. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkanoglu Ozcelik, A.; Yilmaz, S.; Inan, M. Pichia pastoris Promoters. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1923, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, R.; Sandelin, A. Determinants of enhancer and promoter activities of regulatory elements. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.-H.; Xiong, Z.-Q.; Song, X.; Xia, Y.-J.; Zhang, N.; Ai, L.-Z. Characterization of a Panel of Strong Constitutive Promoters from Streptococcus thermophilus for Fine-Tuning Gene Expression. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 8, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.O.; Gonzalez-Villanueva, M.; Tee, K.L.; Wong, T.S. An Engineered Constitutive Promoter Set with Broad Activity Range for Cupriavidus necator H16. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartner, F.S.; Ruth, C.; Langenegger, D.; Johnson, S.N.; Hyka, P.; Lin-Cereghino, G.P.; Lin-Cereghino, J.; Kovar, K.; Cregg, J.M.; Glieder, A. Promoter library designed for fine-tuned gene expression in Pichia pastoris. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.S.; An, S.J.; Kang, M.; Lee, J.; Jeong, K.J. Isolation of fully synthetic promoters for high-level gene expression in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 2959–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegl, T.; Tokovenko, B.; Myronovskyi, M.; Luzhetskyy, A. Design, construction and characterisation of a synthetic promoter library for fine-tuned gene expression in actinomycetes. Metab. Eng. 2013, 19, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Yin, J.; Ye, J.-W.; Xiang, R.-J.; Ning, Z.-Y.; Huang, W.-Z.; Chen, G.-Q. Promoter Engineering for Enhanced P(3HB- co-4HB) Production by Halomonas bluephagenesis. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Zhong, L.; Liu, J.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, X. Promoter Screening Facilitates Heterologous Production of Complex Secondary Metabolites in Burkholderiales Strains. ACS Synth. Biol. 2020, 9, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Li, P.; Xie, X.; Li, J.; Liao, Y.; Ma, X.; Cai, D.; Chen, S. Construction and Characterization of a Gradient Strength Promoter Library for Fine-Tuned Gene Expression in Bacillus licheniformis. ACS Synth. Biol. 2021, 10, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, D.; Pu, Z.; Bao, Y. Integration of metabolic pathway manipulation and promoter engineering for the fine-tuned biosynthesis of malic acid in Bacillus coagulans. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 2597–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, M.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Lin, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, N.; Zhang, C. High-level production of L-homoserine using a non-induced, non-auxotrophic Escherichia coli chassis through metabolic engineering. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 327, 124814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhu, X.; Nie, T.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Lu, Y.; Trouth, F.; Lu, Z. Enhanced Expression of Pullulanase in Bacillus subtilis by New Strong Promoters Mined From Transcriptome Data, Both Alone and in Combination. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Kong, A.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Ma, T.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, C. Screening of endogenous strong promoters for enhanced production of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates in Pseudomonas mendocina NK-01. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, L.; Liang, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; He, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; et al. Screening and engineering of high-activity promoter elements through transcriptomics and red fluorescent protein visualization in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Syn. Syst. Biotechnol. 2021, 6, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Barton, K.W.; Zhao, H. Systematic Identification of a Panel of Strong Constitutive Promoters from Streptomyces albus. ACS Synth. Biol. 2015, 4, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Wu, S.; Tao, Y. Isolating promoters from Corynebacterium ammoniagenes ATCC 6871 and application in CoA synthesis. BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Nikoloff, J.M.; Fu, G.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Xie, N.; Zheng, P.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D. Promoter Screening from Bacillus subtilis in Various Conditions Hunting for Synthetic Biology and Industrial Applications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; You, J.; Tang, M.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Yang, T.; Rao, Z. Improving prodigiosin production by transcription factor engineering and promoter engineering in Serratia marcescens. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 977337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.O.; Bignon, J.; Rapoport, G.; Debarbouille, M. Regulation of the acetoin catabolic pathway is controlled by sigma L in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.A.; Schulze, M.B.; Klaus, S.; Weitkunat, K. The branched-chain amino acids valine and leucine have differential effects on hepatic lipid metabolism. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 9727–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Tuyishime, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Xu, M.; Rao, Z. Engineering of microbial cells for L-valine production: Challenges and opportunities. Microb. Cell Factories 2021, 20, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Pan, X.; Xing, R.; You, J.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, M.; Rao, Z. High-level production of L-valine in Escherichia coli using multi-modular engineering. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 359, 127461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, H.; Crow, M.; Everson, L.; Salmond, G.P. Phosphate availability regulates biosynthesis of two antibiotics, prodigiosin and carbapenem, in Serratia via both quorum-sensing-dependent and -independent pathways. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 47, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanks, R.M.Q.; Stella, N.A.; Lahr, R.M.; Aston, M.A.; Brothers, K.M.; Callaghan, J.D.; Sigindere, C.; Liu, X. Suppressor analysis of eepR mutant defects reveals coordinate regulation of secondary metabolites and serralysin biosynthesis by EepR and HexS. Microbiology 2017, 163, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Tang, M.; You, J.; Osire, T.; Sun, C.; Fu, W.; Yi, G.; Yang, T.; Yang, S.T.; Rao, Z. PsrA is a novel regulator contributes to antibiotic synthesis, bacterial virulence, cell motility and extracellular polysaccharides production in Serratia marcescens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Jiang, T.; Li, M.; Zou, Y.; Yan, Y. Fine-tuning gene expression for improved biosynthesis of natural products: From transcriptional to post-translational regulation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 54, 107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Shi, T.; Sun, G.; Gao, N.; Zhao, X.; Guo, X.; Ni, X.; Yuan, Q.; Feng, J.; et al. CRISPR-assisted rational flux-tuning and arrayed CRISPRi screening of an L-proline exporter for L-proline hyperproduction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Lyu, Y.; Li, H.; Koffas, M.A.; Zhou, J. Fine-tuning the (2S)-naringenin synthetic pathway using an iterative high-throughput balancing strategy. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.W.; Lee, J.; Ko, Y.S.; Lee, S.Y. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 3-aminopropionic acid. Metab. Eng. 2015, 30, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.; Shen, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Yuan, Q. Synergetic utilization of glucose and glycerol for efficient myo-inositol biosynthesis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ye, B.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yan, X. Promoter engineering enables overproduction of foreign proteins from a single copy expression cassette in Bacillus subtilis. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, T.; Ni, X.; Pu, W.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, N.; Han, S.; et al. Development of a Hyperosmotic Stress Inducible Gene Expression System by Engineering the MtrA/MtrB-Dependent NCgl1418 Promoter in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, H.C.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, S.G. Screening of a novel strong promoter by RNA sequencing and its application to H2 production in a hyperthermophilic archaeon. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4085–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, J.-Z.; Wang, B.; Rao, Z.-M.; Zhang, W.-G. L-valine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum based on systematic metabolic engineering: Progress and prospects. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1301–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Jang, Y.S.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.Y. Escherichia coli W as a New Platform Strain for the Enhanced Production of L-Valine by Systems Metabolic Engineering. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, S.Y. Fed-Batch Culture of Escherichia coli for L-Valine Production Based on In Silico Flux Response Analysis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savrasova, E.A.; Stoynova, N.V. Application of leucine dehydrogenase Bcd from Bacillus subtilis for l-valine synthesis in Escherichia coli under microaerobic conditions. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, X.; Fan, X.; Men, J.; Wu, H.; Jiang, S.; Tian, D.; Xiong, B.; Xie, X. High-yield production of L-valine in engineered Escherichia coli by a novel two-stage fermentation. Metab. Eng. 2020, 62, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, N.R.; Fineran, P.C.; Leeper, F.J.; Salmond, G.P. The biosynthesis and regulation of bacterial prodiginines. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.H.; Yarkoni, O.; Ajioka, J.; Wan, K.L.; Nathan, S. Recent advancements in high-level synthesis of the promising clinical drug, prodigiosin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Pan, X.; Osire, T.; Fang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.T.; Yang, T.; Rao, Z. Improved Prodigiosin Production by Relieving CpxR Temperature-Sensitive Inhibition. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Osire, T.; Fu, W.; Yi, G.; Yang, S.T.; Yang, T.; Rao, Z. Enhanced Prodigiosin Production in Serratia marcescens JNB5-1 by Introduction of a Polynucleotide Fragment into the pigN 3’ Untranslated Region and Disulfide Bonds into O-Methyl Transferase (PigF). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0054321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, X.; Tang, M.; You, J.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Rao, Z. A Novel Method to Screen Strong Constitutive Promoters in Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens for Industrial Applications. Biology 2023, 12, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010071
Pan X, Tang M, You J, Hao Y, Zhang X, Yang T, Rao Z. A Novel Method to Screen Strong Constitutive Promoters in Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens for Industrial Applications. Biology. 2023; 12(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010071
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Xuewei, Mi Tang, Jiajia You, Yanan Hao, Xian Zhang, Taowei Yang, and Zhiming Rao. 2023. "A Novel Method to Screen Strong Constitutive Promoters in Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens for Industrial Applications" Biology 12, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010071
APA StylePan, X., Tang, M., You, J., Hao, Y., Zhang, X., Yang, T., & Rao, Z. (2023). A Novel Method to Screen Strong Constitutive Promoters in Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens for Industrial Applications. Biology, 12(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010071







