Hemp Protein Hydrolysates Modulate Inflammasome-Related Genes in Microglial Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Samples
2.2. Preparation of Hemp Protein Isolate
2.3. Hydrolysis of Hemp Protein Isolate
2.4. BV-2 Cell Culture and Treatments
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Determination of NO in Supernatant
2.7. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.8. Determination of Protein Levels by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
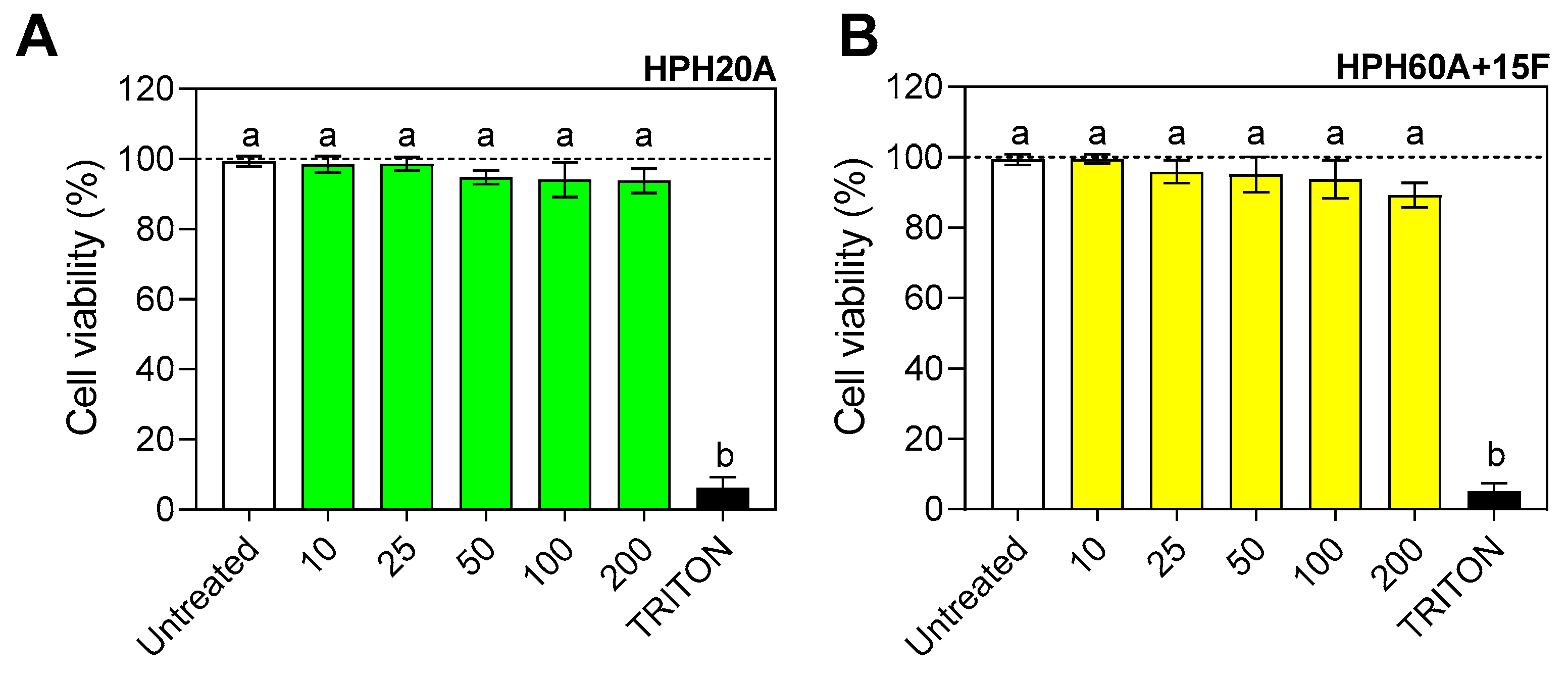
3.1. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of Hemp Protein Hydrolysates in BV2 Cells
3.2. Determination of the Antioxidant Activity of Hemp Products
3.3. Neuroprotective Properties of Hemp Protein Hydrolysates in BV-2 Cells
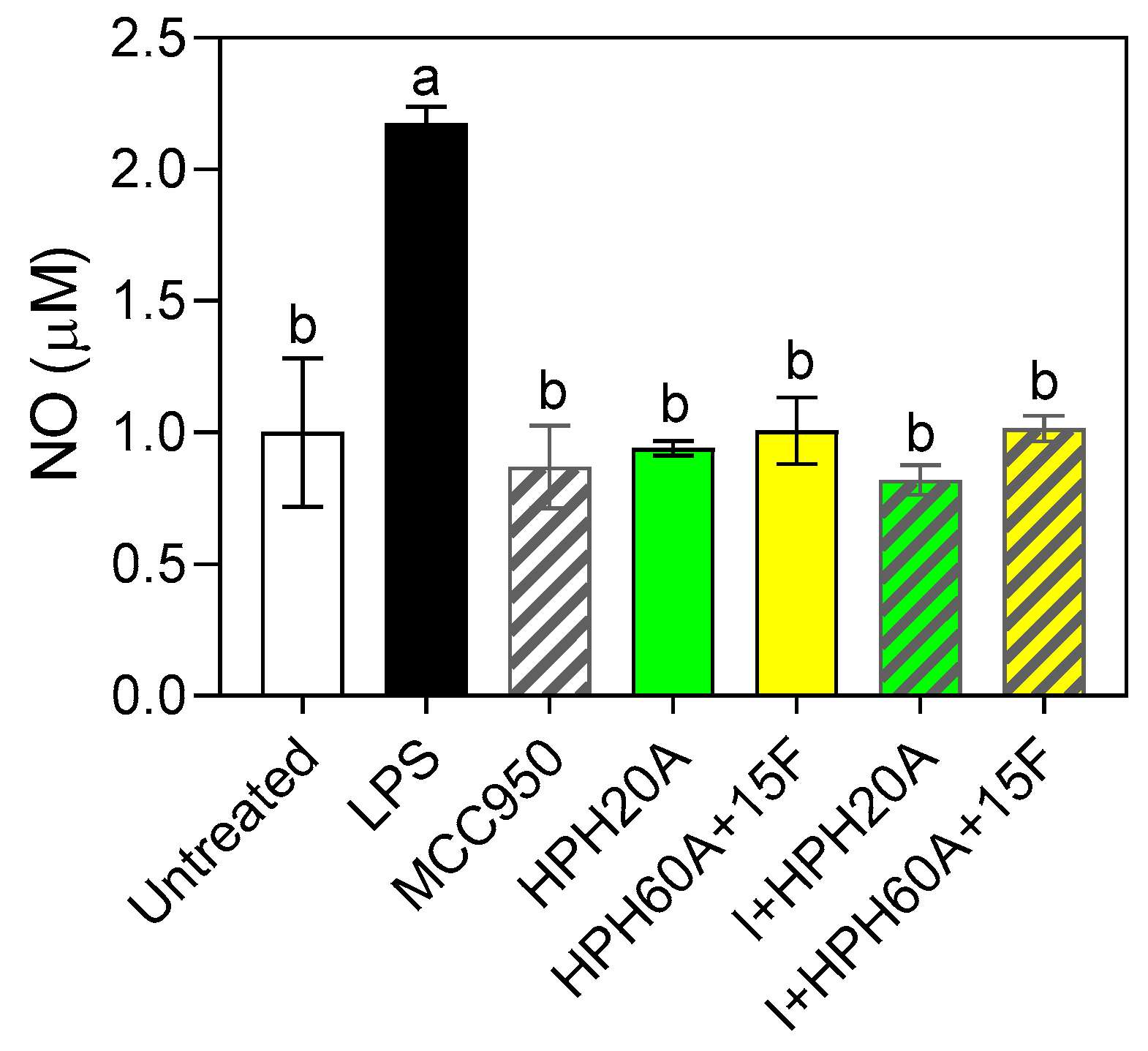
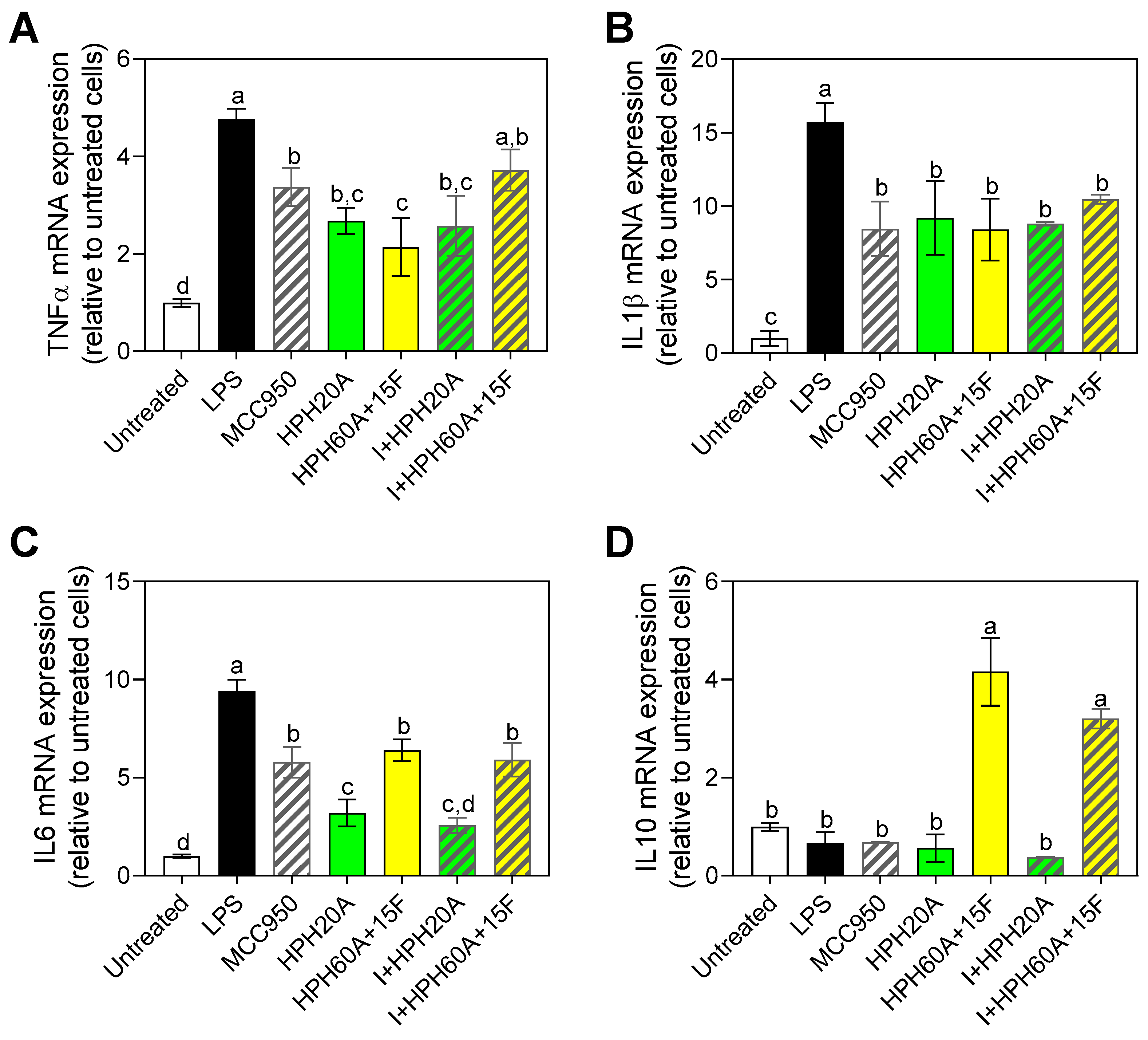
3.4. Effect of Hemp Protein Hydrolysates on Microglial Polarization
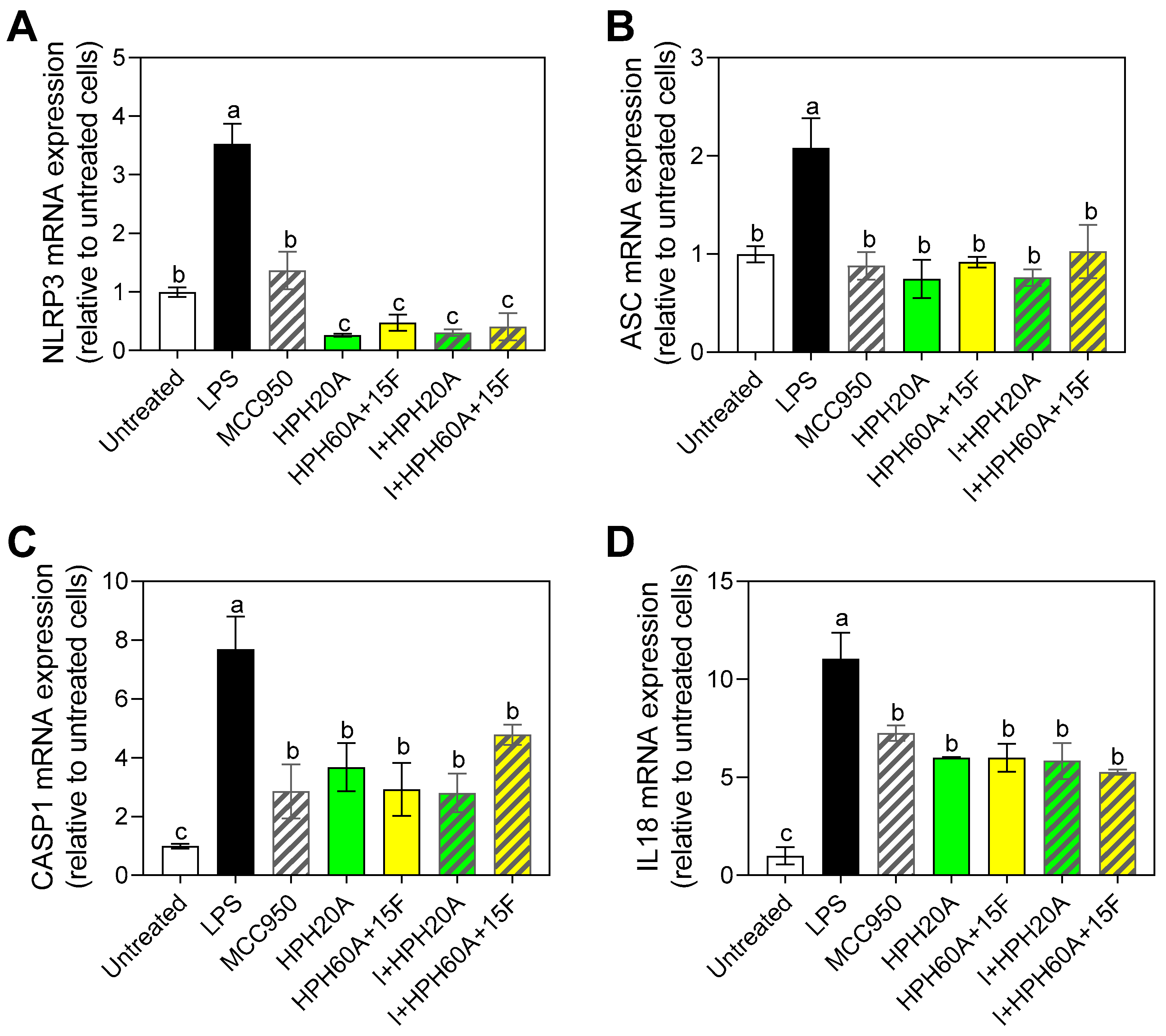
3.5. Effect of Hemp Protein Products on Components of Inflammasome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Nutrient (g/100 g Product) | Hemp Seeds | Hemp Protein Isolate (HPI) | Hemp Protein Hydrolysate: HPH20A | Hemp Protein Hydrolysate: HPH 60A + 15F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteins | 24.2 ± 1.0 | 96.5 ± 0.9 | 83.0 ± 0.2 | 82.3 ± 0.0 |
| Carbs | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Fat | 32.4 ± 0.6 | --------- | --------- | --------- |
| Humidity | 4.5 ± 0.0 | 2.2 ± 0.0 | 8.8 ± 0.0 | 7.5 ± 0.3 |
| Ash | 5.1 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 8.1 ± 0.8 | 10.1 ± 0.3 |
| Fiber | 29.7 ± 1.4 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Polyphenols | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Amino Acids (mg/g Protein) | Hemp Protein Isolate (HPI) | Hemp Protein Hydrolysate: HPH20A | Hemp Protein Hydrolysate: HPH60A+15F |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid + asparagine | 151.7 ± 0.8 | 142.2 ± 2.3 | 146.1 ± 1.7 |
| Glutamic acid + Glutamine | 194.2 ± 1.7 | 191.9 ± 2.3 | 189.8 ± 3.6 |
| Alanine | 47.6 ± 0.4 | 43.4 ± 0.5 | 44.7 ± 1.0 |
| Arginine | 126.5 ± 0.9 | 131.0 ± 1.2 | 131.6 ± 1.6 |
| Cysteine | 11.7 ± 0.3 | 5.8 ± 0.3 | 6.6 ± 0.3 |
| Glycine | 40.1 ± 0.2 | 36.7 ± 0.4 | 36.9 ± 1.0 |
| Histidine | 28.6 ± 0.2 | 28.5 ± 0.1 | 27.1 ± 0.1 |
| Isoleucine | 23.8 ± 0.0 | 41.0 ± 0.4 | 39.2 ± 0.7 |
| Leucine | 62.9 ± 0.4 | 62.3 ± 0.5 | 64.6 ± 0.9 |
| Lysine | 29.2 ± 0.2 | 33.1 ± 0.5 | 33.4 ± 0.4 |
| Methionine | 17.9 ± 6.2 | 24.2 ± 0.0 | 18.5 ± 0.4 |
| Phenylalanine + Tyrosine | 78.7 ± 0.7 | 78.6 ± 0.7 | 80.3 ± 1.2 |
| Proline | 58.6 ± 10.7 | 45.4 ± 9.5 | 28.8 ± 0.4 |
| Serine | 59.6 ± 0.4 | 50.0 ± 0.4 | 54.1 ± 0.8 |
| Threonine | 34.1 ± 0.4 | 32.1 ± 0.2 | 34.4 ± 0.5 |
| Tryptophan | 11.9 ± 0.2 | 10.7 ± 0.0 | 11.1 ± 0.5 |
| Valine | 34.8 ± 1.1 | 43.4 ± 0.5 | 42.6 ± 1.0 |
References
- Mayasari, N.R.; Ho, D.K.; Lundy, D.J.; Skalny, A.V.; Tinkov, A.A.; Teng, I.-C.; Wu, M.-C.; Faradina, A.; Mohammed, A.Z.; Park, J.M.; et al. Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Food Security and Diet-Related Lifestyle Behaviors: An Analytical Study of Google Trends-Based Query Volumes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farinon, B.; Molinari, R.; Costantini, L.; Merendino, N. The Seed of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): Human Health and Nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Davis, A.; Kumar, S.K.; Murray, B.; Zheljazkov, V.D. Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa subsp. sativa) as an Emerging Source for Value-Added Functional Food Ingredients and Nutraceuticals. Molecules 2020, 25, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campiglia, E.; Gobbi, L.; Marucci, A.; Rapa, M.; Ruggieri, R.; Vinci, G. Hemp Seed Production: Environmental Impacts of Cannabis sativa L. Agronomic Practices by Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and Carbon Footprint Methodologies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Pino, F.; Millan-Linares, M.C.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S. Hemp Protein. In Sustainable Food Science: A Comprehensive Approach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; ISBN 978-0-08-100596-5. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, G.; Lammi, C.; Boschin, G.; Zanoni, C.; Arnoldi, A. Exploration of Potentially Bioactive Peptides Generated from the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Hempseed Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10174–10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Bollati, C.; Bartolomei, M.; Li, J.; Arnoldi, A.; Lammi, C. Hempseed (Cannabis sativa) Peptides WVSPLAGRT and IGFLIIWV Exert Anti-inflammatory Activity in the LPS-Stimulated Human Hepatic Cell Line. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Martin, N.M.; Montserrat-De la Paz, S.; Toscano, R.; Grao-Cruces, E.; Villanueva, A.; Pedroche, J.; Millan, F.; Millan-Linares, M.C. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein hydrolysates promote anti-inflammatory response in primary human monocytes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Martin, N.M.; Toscano, R.; Villanueva, A.; Pedroche, J.; Millan, F.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Millan-Linares, M.C. Neuroprotective protein hydrolysates from hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6732–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Bollati, C.; Gelain, F.; Arnoldi, A.; Pugliese, R. Enhancement of the stability and anti-DPPIV activity of hempseed hydrolysates through self-assembling peptide-based hydrogels. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, M.; Ben-Shaanan, T.L.; Rolls, A. Neuronal regulation of immunity: Why, how and where? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.M.; Gómez Lahoz, A.M.; Martín, R.O. Role of the immune system in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Immunopathology of COVID-19. Medicine 2021, 13, 1917–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, J.; Blander, J.M. Increasing complexity of NLRP3 inflammasome regulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, N.A.; Oliveira, G.A.L.; de Oliveira, A.P.; Lopes, A.L.F.; Iles, B.; Nogueira, K.M.; Araújo, T.S.L.; Souza, L.K.M.; Araújo, A.R.; Ramos-Jesus, J.; et al. Novel Ocellatin Peptides Mitigate LPS-induced ROS Formation and NF-kB Activation in Microglia and Hippocampal Neurons. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; McManus, R.M.; Latz, E. Inflammasome signalling in brain function and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Inflammasome activation and regulation: Toward a better understanding of complex mechanisms. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, G.; Cárdenas, G.; Espinosa, A.; Rassy, D.; Pérez-Osorio, I.N.; Bárcena, B.; Fleury, A.; Besedovsky, H.; Fragoso, G.; Sciutto, E. Sepsis: Developing new alternatives to reduce neuroinflammation and attenuate brain injury. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1437, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Dong, Q.; Song, Z.; Shen, F.; Shi, J.; Li, Y. NLRP3 inflammasome: A promising target in ischemic stroke. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catale, C.; Bisicchia, E.; Carola, V.; Viscomi, M.T. Early life stress exposure worsens adult remote microglia activation, neuronal death, and functional recovery after focal brain injury. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 94, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lqari, H.; Vioque, J.; Pedroche, J.; Millán, F. Lupinus angustifolius protein isolates: Chemical composition, functional properties and protein characterization. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the MTT Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Naranjo, M.C.; Lopez, S.; Abia, R.; Muriana, F.J.G.; Bermudez, B. Niacin and its metabolites as master regulators of macrophage activation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 39, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toopcham, T.; Mes, J.J.; Wichers, H.J.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Immunomodulatory activity of protein hydrolysates derived from Virgibacillus halodenitrificans SK1-3-7 proteinase. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalamaiah, M.; Yu, W.; Wu, J. Immunomodulatory and anticancer protein hydrolysates (peptides) from food proteins: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savran, M.; Aslankoc, R.; Ozmen, O.; Erzurumlu, Y.; Savas, H.B.; Temel, E.N.; Kosar, P.A.; Boztepe, S. Agomelatine could prevent brain and cerebellum injury against LPS-induced neuroinflammation in rats. Cytokine 2020, 127, 154957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.; Faria, A.; Calhau, C.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N. Bioavailability of anthocyanins and derivatives. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Rodriguez-Martin, N.M.; Villanueva, A.; Pedroche, J.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Millan, F.; Millan-Linares, M.C. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory and Atheroprotective Properties of Wheat Gluten Protein Hydrolysates in Primary Human Monocytes. Foods 2020, 9, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, G.C.; Ren, X.; Vodnala, S.K.; Lu, J.; Coppo, L.; Leepiyasakulchai, C.; Holmgren, A.; Kristensson, K.; Rottenberg, M.E. Nitric Oxide Protects against Infection-Induced Neuroinflammation by Preserving the Stability of the Blood-Brain Barrier. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuste, J.E.; Tarragon, E.; Campuzano, C.M.; Ros-Bernal, F. Implications of glial nitric oxide in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Kim, O.Y.; Jo, G.; Shin, M.-J. Alterations in Circulating Amino Acid Metabolite Ratio Associated with Arginase Activity Are Potential Indicators of Metabolic Syndrome: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Pangloli, P.; Meng, X.; Dia, V.P. Effect of heating on the digestibility of isolated hempseed (Cannabis sativa L.) protein and bioactivity of its pepsin-pancreatin digests. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollati, C.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Aiello, G.; Li, J.; Bartolomei, M.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Ranaldi, G.; Ferruzza, S.; Sambuy, Y.; Arnoldi, A.; et al. Investigation of the intestinal trans-epithelial transport and antioxidant activity of two hempseed peptides WVSPLAGRT (H2) and IGFLIIWV (H3). Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merz, M.; Eisele, T.; Berends, P.; Appel, D.; Rabe, S.; Blank, I.; Stressler, T.; Fischer, L. Flavourzyme, an Enzyme Preparation with Industrial Relevance: Automated Nine-Step Purification and Partial Characterization of Eight Enzymes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5682–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cian, R.E.; Hernández-Chirlaque, C.; Gámez-Belmonte, R.; Drago, S.R.; Sánchez de Medina, F.; Martínez-Augustin, O. Green Alga Ulva spp. Hydrolysates and Their Peptide Fractions Regulate Cytokine Production in Splenic Macrophages and Lymphocytes Involving the TLR4-NFκB/MAPK Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgih, A.T.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. In Vitro Antioxidant Properties of Hemp Seed (Cannabis sativa L.) Protein Hydrolysate Fractions. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbub, R.; Callcott, E.; Rao, S.; Ansari, O.; Waters, D.L.E.; Blanchard, C.L.; Santhakumar, A.B. The effect of selected hemp seed protein hydrolysates in modulating vascular function. Food Biosci. 2022, 45, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, L.; González-Rogel, D.; Heres, A.; Toldrá, F. Iberian dry-cured ham as a potential source of α-glucosidase-inhibitory peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhramanyam, C.S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Dheen, S.T. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 94, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Bao, X.; Wang, R. Clinical PET Imaging of Microglial Activation: Implications for Microglial Therapeutics in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano-Silva, M.E.; Rund, L.A.; Vailati-Riboni, M.; Pacheco, M.T.B.; Johnson, R.W. Copper-Binding Peptides Attenuate Microglia Inflammation through Suppression of NF-kB Pathway. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, H.; Ji, X.; Wang, J.; Pang, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Protective effects of bioactive peptides in foxtail millet protein hydrolysates against experimental colitis in mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2594–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, N.P.; Kirwan, A.M.; McArdle, M.A.; Holohan, K.; Nongonierma, A.B.; Keane, D.; Kelly, S.; Celkova, L.; Lyons, C.L.; McGillicuddy, F.C.; et al. A casein hydrolysate protects mice against high fat diet induced hyperglycemia by attenuating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation and improving insulin signaling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguchem, R.N.; Okagu, I.U.; Okagu, O.D.; Ndefo, J.C.; Udenigwe, C.C. A review on the techno-functional, biological, and health-promoting properties of hempseed-derived proteins and peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khavinson, V.K.; Popovich, I.G.; Linkova, N.S.; Mironova, E.S.; Ilina, A.R. Peptide Regulation of Gene Expression: A Systematic Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Target | GenBank Accession Number | Forward Reverse | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tnfα | NM_000594 | Forward Reverse | TCCTTCAGACACCCTCAACC AGGCCCCAGTTTGAATTCTT |
| Il1β | NM_000576 | Forward Reverse | GGGCCTCAAGGAAAAGAATC TTCTGCTTGAGAGGTGCTGA |
| Il6 | NM_000600 | Forward Reverse | TACCCCCAGGAGAAGATTCC TTTTCTGCCAGTGCCTCTTT |
| Il10 | NM_000572 | Forward Reverse | GCCTAACATGCTTCGAGATC TGATGTCTGGGTCTTGGTTC |
| Ccr7 | NM_007719.2 | Forward Reverse | GTGTGCTTCTGCCAAGATGA CCACGAAGCAGATGACAGAA |
| iNos | NM_ 000625 | Forward Reverse | ACCCAGACTTACCCCTTTGG GCCTGGGGTCTAGGAGAGAC |
| Arg1 | NM_007482.3 | Forward Reverse | CGCCTTTCTCAAAAGGACAG ACAGACCGTGGGTTCTTCAC |
| Ym1 | NM_009892.3 | Forward Reverse | ACTTTGATGGCCTCAACCTG AATGATTCCTGCTCCTGTGG |
| Nlrp3 | NM_001359638.1 | Forward Reverse | AAGCAACAGATGGAGACCGG CAAATTCCATCCGCAGCCAG |
| Asc | NM_023258.4 | Forward Reverse | GTCTTAGGGGCGGAAACCAA CCGCGGTCACCTTTTACTCT |
| Casp1 | NM_009807.2 | Forward Reverse | ACTGACTGGGACCCTCAAGT AACTTGAGCTCCAACCCTCG |
| Il18 | NM_001357221.1 | Forward Reverse | TCGCAGCAGGGTTTTCTAGG ACGGGAGGGAGAAAGACTGA |
| Hprt | NM_001289746 | Forward Reverse | ACCCCACGAAGTGTTGGATA AAGCAGATGGCCACAGAACT |
| Gapdh | NM_001289726 | Forward Reverse | AACTTTGGCATTGTGGAAGG ACACATTGGGGGTAGGAACA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Carrillo-Berdasco, G.; Rivero-Pino, F.; Villanueva-Lazo, A.; Millan-Linares, M.C. Hemp Protein Hydrolysates Modulate Inflammasome-Related Genes in Microglial Cells. Biology 2023, 12, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010049
Montserrat-de la Paz S, Carrillo-Berdasco G, Rivero-Pino F, Villanueva-Lazo A, Millan-Linares MC. Hemp Protein Hydrolysates Modulate Inflammasome-Related Genes in Microglial Cells. Biology. 2023; 12(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontserrat-de la Paz, Sergio, Gabriela Carrillo-Berdasco, Fernando Rivero-Pino, Alvaro Villanueva-Lazo, and Maria C. Millan-Linares. 2023. "Hemp Protein Hydrolysates Modulate Inflammasome-Related Genes in Microglial Cells" Biology 12, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010049
APA StyleMontserrat-de la Paz, S., Carrillo-Berdasco, G., Rivero-Pino, F., Villanueva-Lazo, A., & Millan-Linares, M. C. (2023). Hemp Protein Hydrolysates Modulate Inflammasome-Related Genes in Microglial Cells. Biology, 12(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12010049







