Mendelian Randomization and GWAS Meta Analysis Revealed the Risk-Increasing Effect of Schizophrenia on Cancers
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
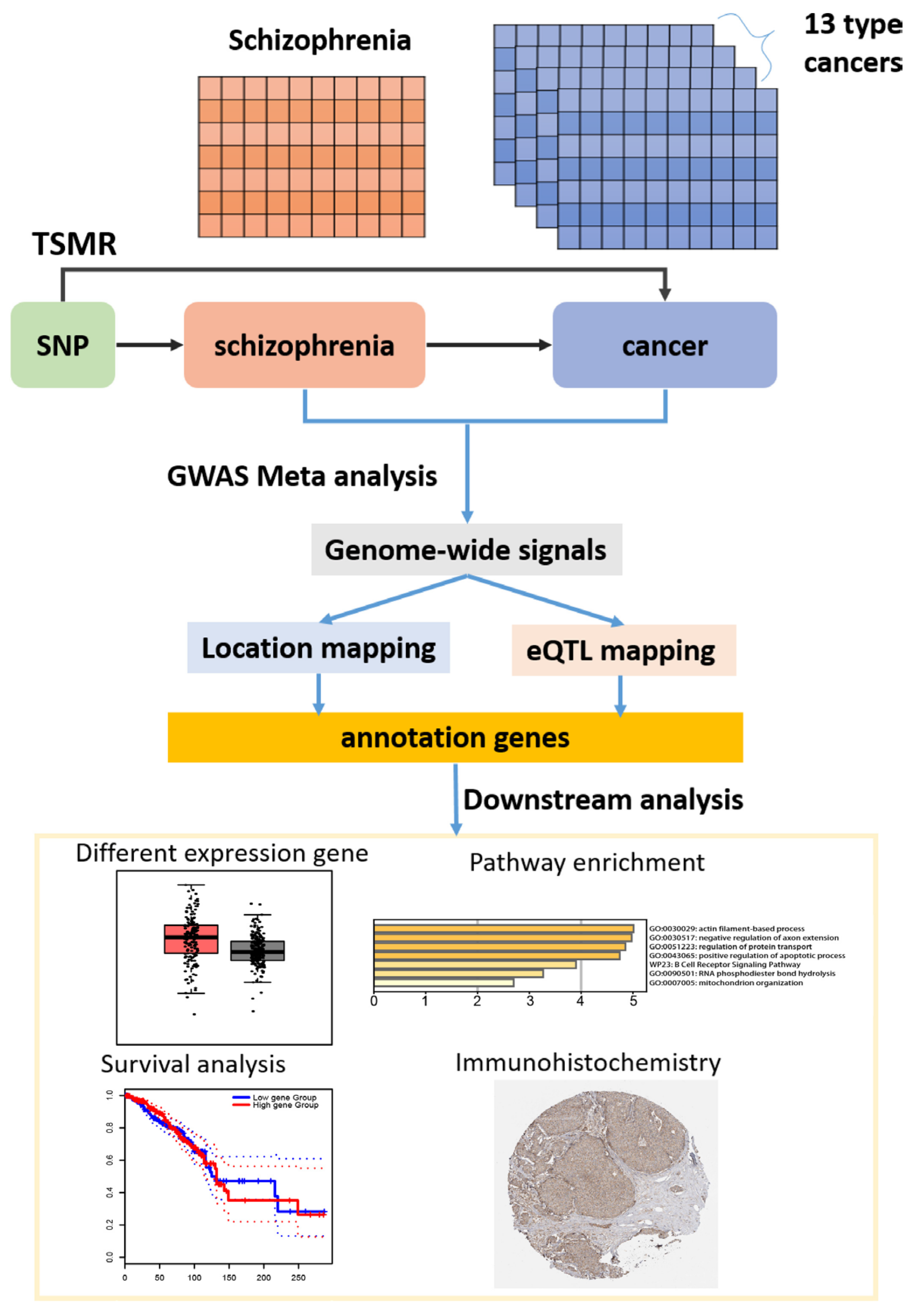
2.1. Conceptual Framework
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Power Calculation
2.4. Two-Sample MR
2.5. Sensitivity Analyses
2.5.1. Heterogeneity Test
2.5.2. Pleiotropy Test
2.5.3. Leave-One-Out Sensitivity Test
2.6. GWAS Meta-Analysis
2.7. Identification of Candidate SNPs, Gene Mapping, and Functional Annotation
2.8. MAGMA Gene-Based Tests
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
3. Results
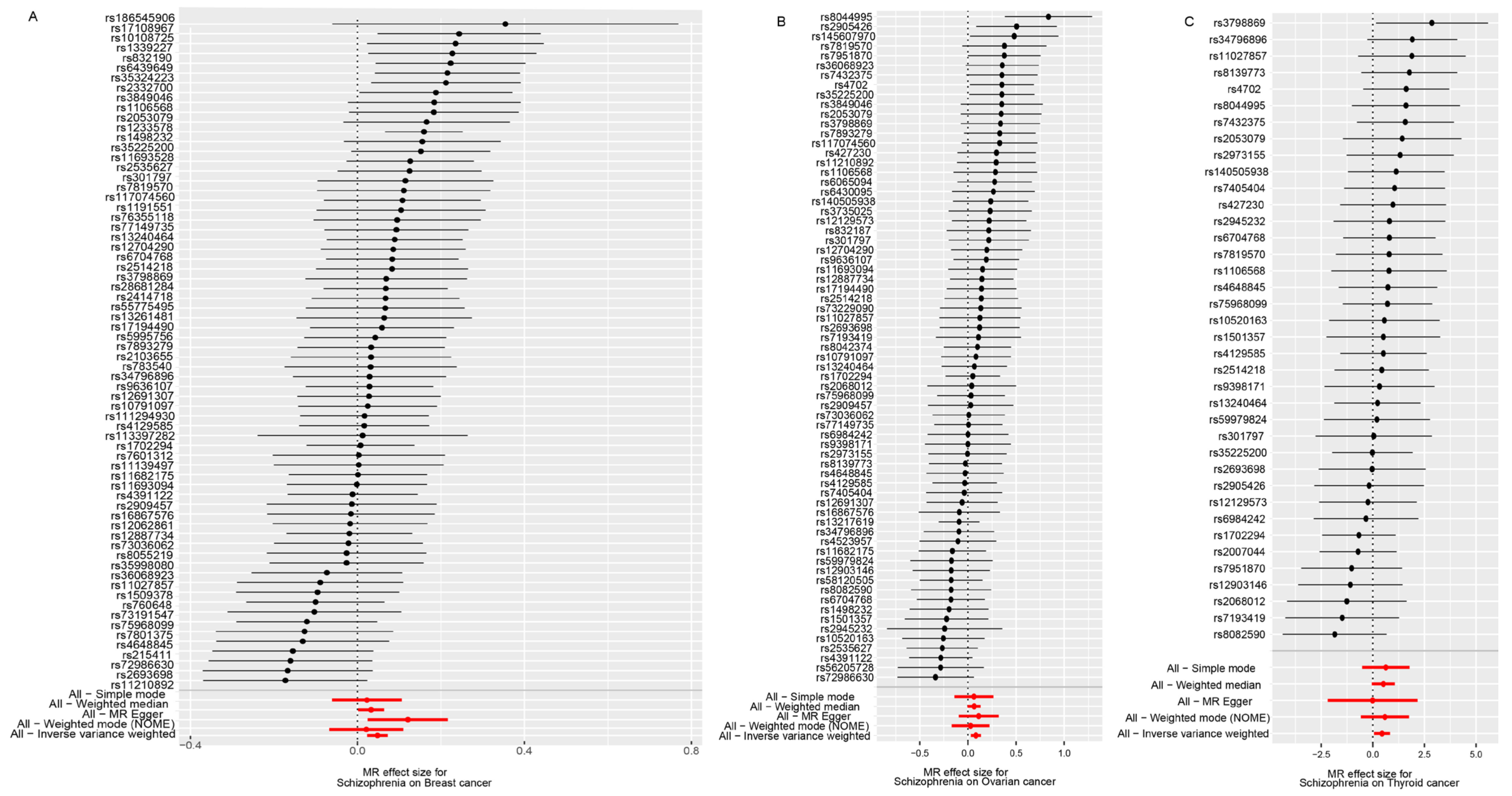
3.1. SMR Results of SCZ and Cancers
3.2. SMR Results of SCZ and Subtypes of Three Cancers
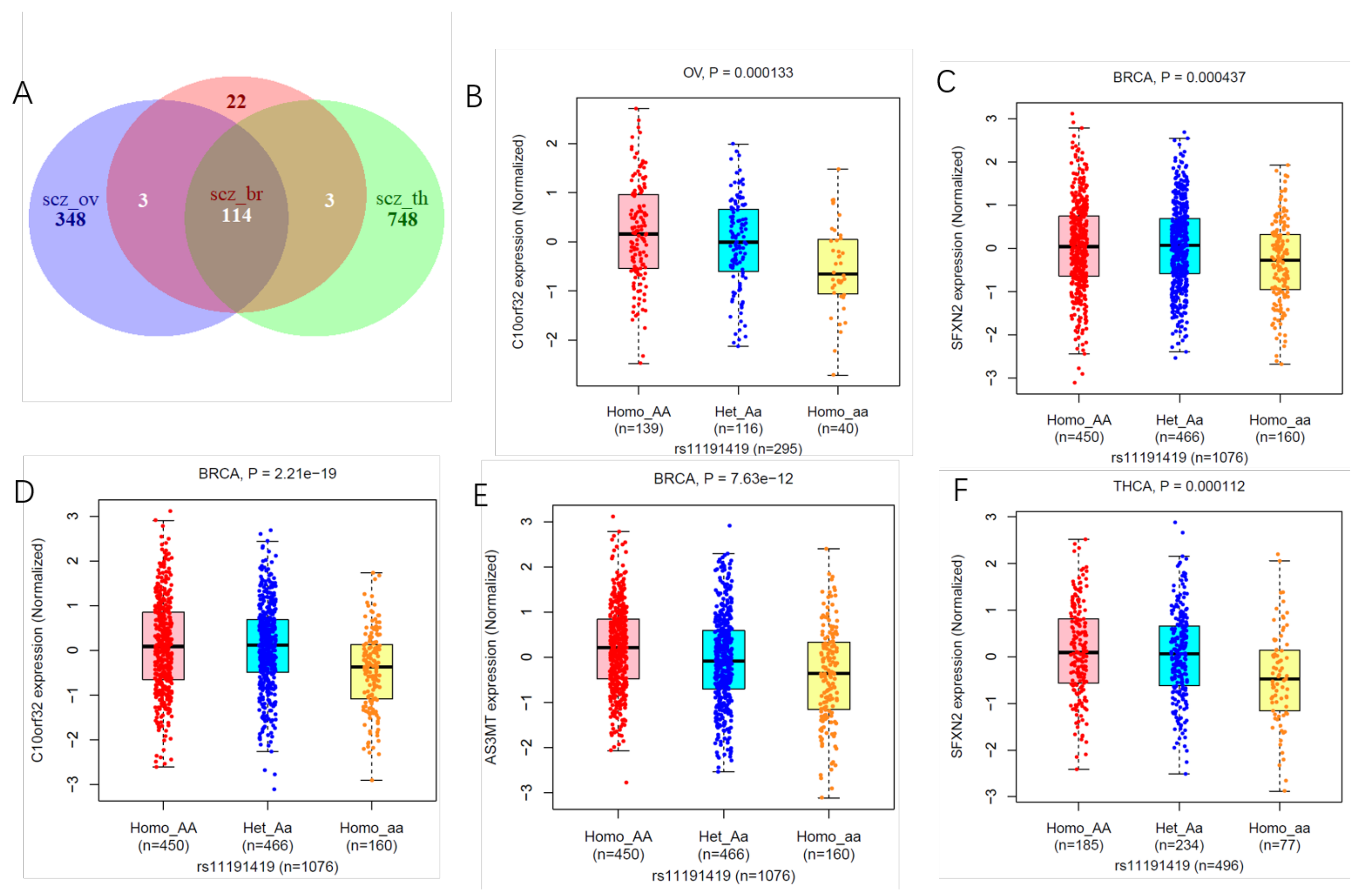
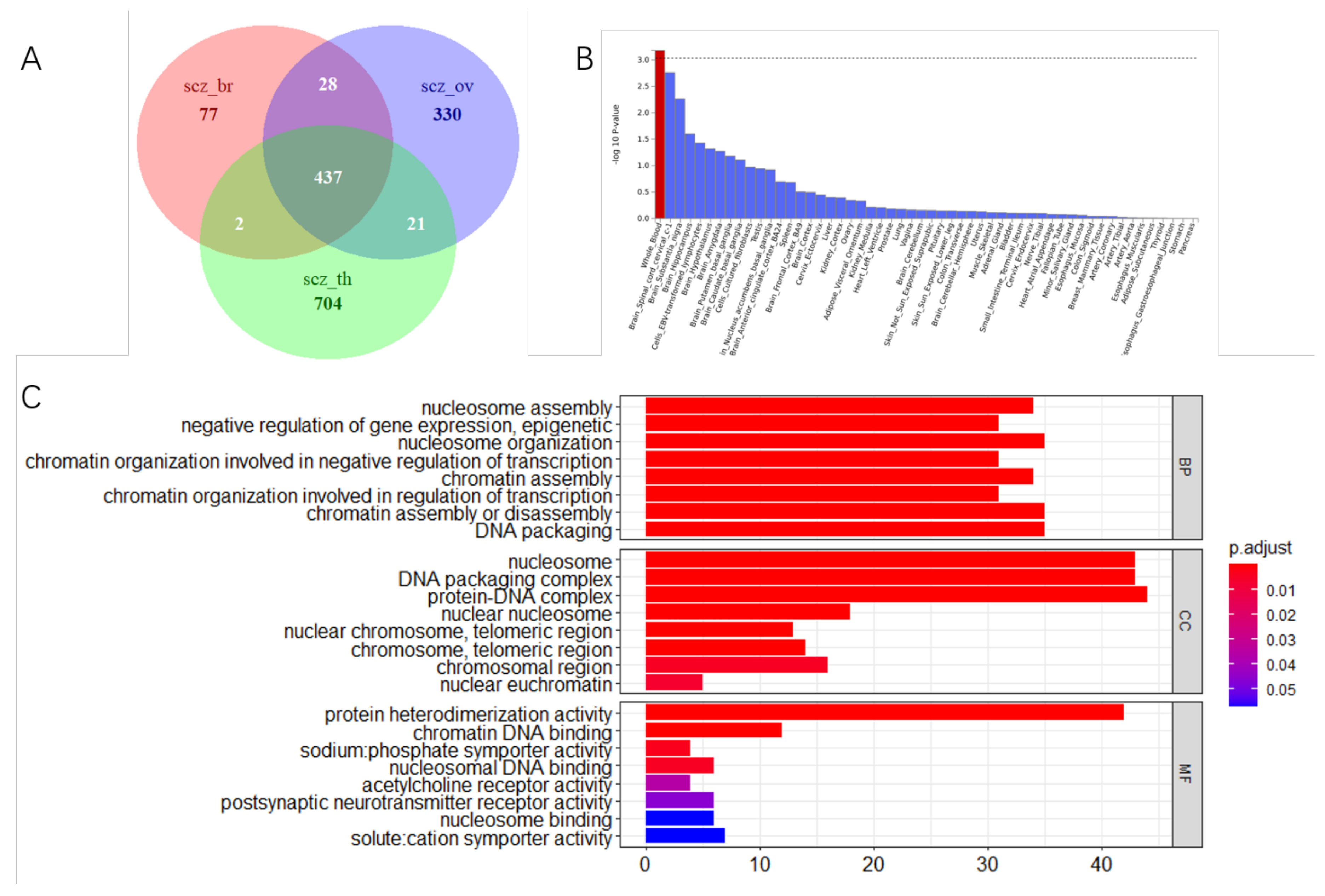
3.3. Shared Genetic Variants of SCZ with Three Cancers
3.4. Tissue Expression Specific and Gene Mapping
3.5. The Level of the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Could Be Affected by SCZ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SCZ | Schizophrenia |
| 2SMR | Two-sample Mendelian randomization |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association studies |
| eQTL | Expression quantitative trait loci |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| IVW | inverse-variance weighted method |
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| MR-PRESSO | Mendelian randomization Pleiotropy RESidual Sum and Outlier |
| OR | odds ratio |
| IV | Instrumental variable; |
| CI | Confidence interval. |
| TSH | Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
References
- Hodgson, R.; Wildgust, H.J.; Bushe, C.J. Cancer and schizophrenia: Is there a paradox? J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24 (Suppl. 4), 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyauchi, M.; Kishida, I.; Suda, A.; Shiraishi, Y.; Fujibayashi, M.; Taguri, M.; Ishii, C.; Ishii, N.; Moritani, T.; Hirayasu, Y. Long term effects of smoking cessation in hospitalized schizophrenia patients. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cather, C.; Pachas, G.N.; Cieslak, K.M.; Evins, A.E. Achieving Smoking Cessation in Individuals with Schizophrenia: Special Considerations. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidou, K.; Lindstrom, S.; Dennis, J.; Beesley, J.; Hui, S.; Kar, S.; Lemacon, A.; Soucy, P.; Glubb, D.; Rostamianfar, A.; et al. Association analysis identifies 65 new breast cancer risk loci. Nature 2017, 551, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-K. Impact of additive alcohol and substance use disorders on the mortality of people with schizophrenia and mood disorders. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2016, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, G.; Zhang, G.; Walss-Bass, C.; Quevedo, J.; Soares, J.C.; Xia, H.; Li, X.; et al. The prevalence, risk factors and clinical correlates of obesity in Chinese patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 251, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, B.; Chen, L.J.; Chung, M.S.; Ku, P.W. Physical activity ameliorates the association between sedentary behavior and cardiometabolic risk among inpatients with schizophrenia: A comparison versus controls using accelerometry. Compr. Psychiatry 2017, 74, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalá-López, F.; Suárez-Pinilla, M.; Suárez-Pinilla, P.; Valderas, J.M.; Gómez-Beneyto, M.; Martinez, S.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Climent, J.; Valencia, A.; McGrath, J.; et al. Inverse and direct cancer comorbidity in people with central nervous system disorders: A meta-analysis of cancer incidence in 577,013 participants of 50 observational studies. Psychother. Psychosom. 2014, 83, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, C.; Triplett, P.T. Association of Schizophrenia With the Risk of Breast Cancer Incidence: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Zheng, H.; Sun, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Bi, X. The incidence rate of cancer in patients with schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 195, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Vinogradova, Y.C.; Coupland, C.; Parker, C. Risk of Malignancy in Patients With Schizophrenia or Bipolar Disorder: Nested Case-Control Study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, C.; Tao, R.; Jiang, R.; Lin, X.; Shao, M. Cancer mortality in patients with schizophrenia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry. 2017, 211(1), 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordentoft, M.; Plana-Ripoll, O.; Laursen, T.M. Cancer and schizophrenia. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skou, S.T.; Lind, M.; Hölmich, P.; Jensen, H.P.; Jensen, C.; Afzal, M.; Jørgensen, U.; Thorlund, J.B. Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial of meniscal surgery compared with exercise and patient education for treatment of meniscal tears in young adults. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Warren Andersen, S.; Shu, X.O.; Michailidou, K.; Bolla, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Garcia-Closas, M.; Milne, R.L.; Schmidt, K.M.; Chang-Claude, J.; et al. Genetically Predicted Body Mass Index and Breast Cancer Risk: Mendelian Randomization Analyses of Data from 145,000 Women of European Descent. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Bakshi, A.; Robinson, M.R.; Powell, J.E.; Montgomery, G.W.; Goddard, M.E.; Wray, N.R.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Integration of summary data from GWAS and eQTL studies predicts complex trait gene targets. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauquet, S.; Zhu, Z.; O’Donovan, M.C.; Walters, J.T.R.; Wray, N.R.; Shah, S. Association of Antihypertensive Drug Target Genes With Psychiatric Disorders: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wu, L.; Zheng, W.; Wen, W.; Wang, S.; Shu, X.; Long, J.; Shen, C.Y.; Wu, P.E.; Saloustros, E.; et al. Genetic Evidence for the Association between Schizophrenia and Breast Cancer. J. Psychiatr. Brain Sci. 2018, 3, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kim, K.; Myung, W.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.K.; Won, H.-H. Two-sample Mendelian randomization study for schizophrenia and breast cancer. Precis. Future Med. 2020, 4, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.D.; Neuhausen, S.L. Bi-directional Mendelian randomization of epithelial ovarian cancer and schizophrenia and uni-directional Mendelian randomization of schizophrenia on circulating 1- or 2-glycerophosphocholine metabolites. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2019, 21, 100539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardiñas, A.F.; Holmans, P.; Pocklington, A.J.; Escott-Price, V.; Ripke, S.; Carrera, N.; Legge, S.E.; Bishop, S.; Cameron, D.; Hamshere, M.L.; et al. Common schizophrenia alleles are enriched in mutation-intolerant genes and in regions under strong background selection. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripke, S.; Neale, B.M.; Corvin, A.; Walters, J.T.R.; Farh, K.-H.; Holmans, P.A.; Lee, P.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Collier, D.A.; Huang, H.; et al. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature 2014, 511, 421–427. [Google Scholar]
- Michailidou, K.; Hall, P.; Gonzalez-Neira, A.; Ghoussaini, M.; Dennis, J.; Milne, R.L.; Schmidt, M.K.; Chang-Claude, J.; Bojesen, S.E.; Bolla, M.K.; et al. Large-scale genotyping identifies 41 new loci associated with breast cancer risk. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michailidou, K.; Beesley, J.; Lindstrom, S.; Canisius, S.; Dennis, J.; Lush, M.J.; Maranian, M.J.; Bolla, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Shah, M.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of more than 120,000 individuals identifies 15 new susceptibility loci for breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Mei, S.; Liu, C.; Xiang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, J.; Liu, R.; Diao, L.; Guo, A.-Y.; et al. PancanQTL: Systematic identification of cis-eQTLs and trans-eQTLs in 33 cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, L.J.; Price, A.L. Distinguishing genetic correlation from causation across 52 diseases and complex traits. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D971–D976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco M, F.; Minelli, C.; Smith, G.D.; Sheehan, N.; Thompson, J. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 1783–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastani, Z.; Hivert, M.F.; Timpson, N.; Perry, J.R.; Yuan, X.; Scott, R.A.; Henneman, P.; Heid, I.M.; Kizer, J.R.; Lyytikainen, L.P.; et al. Novel loci for adiponectin levels and their influence on type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits: A multi-ethnic meta-analysis of 45,891 individuals. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, D.I.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Shah, S.; Sofat, R.; Holmes, M.V.; White, J.; Mindell, J.S.; Kivimaki, M.; Brunner, E.J.; Whittaker, J.C.; et al. Selecting instruments for Mendelian randomization in the wake of genome-wide association studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1600–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Smith, G.D. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: A guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ 2018, 362, k601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bakker, P.I.; Ferreira, M.A.; Jia, X.; Neale, B.M.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Voight, B.F. Practical aspects of imputation-driven meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, R122–R128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skol, A.D.; Scot, L.J.; Abecasis, G.R.; Boehnke, M. Optimal designs for two-stage genome-wide association studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 2007, 31, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, C.J.; Li, Y.; Abecasis, G.R. METAL: Fast and efficient meta-analysis of genomewide association scans. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2190–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.R.; Altshuler, D.M.; Durbin, R.M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Bentley, D.R.; Chakravarti, A.G.; Donelly, C.P.; Eichler, E.E. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GTEx Consortium. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Science 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, C.A.; Mooij, J.M.; Heskes, T.; Posthuma, D. MAGMA: Generalized gene-set analysis of GWAS data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thul, P.J.; Lindskog, C. The human protein atlas: A spatial map of the human proteome. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, C.M.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Tyrer, J.P.; Kar, S.P.; Lawrenson, K.; Winham, S.J.; Dennis, J.; Pirie, A.; Riggan, M.J.; Chornokur, G.; et al. Identification of 12 new susceptibility loci for different histotypes of epithelial ovarian cancer. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, R.R.R.; Troakes, C.; Nolan, M.; Srivastava, D.P.; Murray, R.M.; Bray, N.J. Genome-wide significant schizophrenia risk variation on chromosome 10q24 is associated with altered cis-regulation of BORCS7, AS3MT, and NT5C2 in the human brain. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2016, 171, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamboa-Loira, B.; Cebrian, M.E.; Salinas-Rodriguez, A.; Lopez-Carrillo, L. Genetic susceptibility to breast cancer risk associated with inorganic arsenic exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 56, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddaskho, F.; Eyvani, H.; Ghadami, M.; Tavakkoly-Bazzaz, J.; Alimoghaddam, K.; Ghavamzadeh, A.; Ghaffari, S.H. Demethylation and alterations in the expression level of the cell cycle-related genes as possible mechanisms in arsenic trioxide-induced cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer cells. Tumour. Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317692255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A. The role of microrna-449 in human breast cancer. J. Stud. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Subramanian, V.S.; Constantinescu, A.R.; Benke, P.J.; Said, H.M. Mutations in SLC5A6 associated with brain, immune, bone, and intestinal dysfunction in a young child. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kory, N.; Wyant, G.A.; Prakash, G.; de Bos, J.U.; Bottanelli, F.; Pacold, M.E.; Chan, S.H.; Lewis, C.A.; Wang, T.; Keys, H.R.; et al. SFXN1 is a mitochondrial serine transporter required for one-carbon metabolism. Science 2018, 362, eaat9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Song, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiong, W.; Chen, H.; Sun, C.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H. TERT rs10069690 polymorphism and cancers risk: A meta-analysis. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2019, 7, e00903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoussaini, M.; French, J.D.; Michailidou, K.; Nord, S.; Beesley, J.; Canisus, S.; Hillman, K.M.; Kaufmann, S.; Sivakumaran, H.; Marjaneh, M.M.; et al. Evidence that the 5p12 Variant rs10941679 Confers Susceptibility to Estrogen-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer through FGF10 and MRPS30 Regulation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, W.; Liyanarachchi, S.; Srinivas, M.; Wang, Y.; Akagi, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, Q.; Jin, V.; et al. Multiple functional variants in long-range enhancer elements contribute to the risk of SNP rs965513 in thyroid cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6128–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, X.; Rong, R.; Gao, Y.; Tang, X.; Chen, Y. High expression of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) predicts poor outcome in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, O.H.; Gerend, P.L.; Davis, M.; Goretzki, P.E.; Hoffman, G.P. Estrogen and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptors in neoplastic and nonneoplastic human thyroid tissue. J. Surg. Res. 1985, 38, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, D.S.A.; Watters, K.F.; Carpenter, A.D.; Ladenson, P.W.; Cooper, D.S.; Ding, E.L. Thyrotropin and thyroid cancer diagnosis: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 8, 2682–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, J.; Borgquist, S.; Almquist, M.; Manjer, J. Thyroid function and survival following breast cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.A.-O.; Labrecque, J.A. Mendelian randomization with a binary exposure variable: Interpretation and presentation of causal estimates. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hert, M.; Peuskens, J.; Sabbe, T.; Mitchell, A.J.; Stubbs, B.; Neven, P.; Wildiers, H.; Detraux, J. Relationship between prolactin, breast cancer risk, and antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia: A critical review. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2016, 133, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Datasets Num | Cancer Name | MR Results (IVW-p Value) | FDR | Heterogeneity Statistics | OR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ieu-a-1126 | Breast cancer | 0.00012 * | 0.0015 | 0.054 | 1.049 (1.023–1.075) |
| ieu-a-1120 | Ovarian cancer | 0.0007 * | 0.0045 | 0.2821 | 1.326 (1.267–1.387) |
| ieu-a-1082 | Thyroid cancer | 0.0285 * | 0.123 | 0.3841 | 1.575 (1.048–2.365) |
| ieu-a-822 | Pancreatic cancer | 0.1638 | 0.3549 | 0.7246 | 1.155 (0.943–1.415) |
| ieu-a-816 | Neuroblastoma | 0.504 | 0.655 | 0.6306 | 0.939 (0.782–1.128) |
| ieu-a-1057 | Gallbladder cancer | 0.843 | 0.843 | 0.095 | 0.876 (0.235–3.264) |
| ieu-a-1013 | Glioma | 0.225 | 0.417 | 0.274 | 0.880 (0.716–1.081) |
| ieu-a-966 | Lung cancer | 0.073 | 0.237 | 2.12 × 10−34 | 1.130 (0.989–1.290) |
| ieu-b-85 | Prostate cancer | 0.418 | 0.603 | 2.98 × 10−15 | 1.019 (0.973–1.068) |
| ieu-b-90 | Oral cavity and pharyngeal cancer | 0.681 | 0.804 | 0.00024 | 1.042 (0.858–1.265) |
| ukb-b-16713 | Secondary malignant neoplasm of liver | 0.158 | 0.332 | 0.4327 | 1.000 (0.999–1.0001) |
| ukb-b-20145 | Colon cancer | 0.812 | 0.879 | 0.8691 | 1.000 (0.999–1.0005) |
| ukb-b-19425 | Rectum cancer | 0.67 | 0.871 | 0.3638 | 0.9998 (0.9994–1.0003) |
| Datasets Num | Cancer Name | sample Size | MR results (IVW-p Value) | FDR | Heterogeneity Statistics | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ieu-a-1125 | Endometrioid ovarian cancer | 43,751 | 0.8596 | 0.86 | 0.2153 | 1.0096 (0.908–1.122) |
| Ieu-a-1124 | Clear cell ovarian cancer | 42,307 | 0.1522 | 0.254 | 0.207 | 1.114 (0.961–1.291) |
| Ieu-a-1123 | Invasive mucinous ovarian cancer | 42,358 | 0.548 | 0.685 | 0.1659 | 1.046 (0.902–1.213) |
| ieu-a-1122 | Low-grade serous ovarian cancer | 41,953 | 0.02374 * | 0.06 | 0.101 | 1.235 (1.029–1.483) |
| ieu-a-1121 | High-grade serous ovarian cancer | 53,978 | 0.006 (0.017) * | 0.03 | 0.1742 | 1.085 (1.015–1.160) |
| Datasets Num | Hormone Name | Samples Size | MR Results (IVW-p Value) | FDR | Heterogeneity Statistics | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prot-a-2974 | thyroid hormone receptor alpha | 3301 | 0.3866 | 0.644 | 0.1852 | 1.040(0.952–1.134) |
| prot-a-2892 | estrogen sulfotransferase | 3301 | 0.9762 | 0.992 | 0.5922 | 1.001 (0.923–1.086) |
| prot-a-991 | estrogen receptor | 3301 | 0.3628 | 0.644 | 0.7841 | 0.963 (0.887–1.045) |
| prot-a-530 | thyroid-stimulating hormone | 3301 | 0.03536 * | 0.177 | 0.3254 | 1.0999 (1.011–1.197) |
| prot-a-2432 | parathyroid horm-related protein | 3301 | 0.9921 | 0.992 | 0.1516 | 1.0004 (0.916–1.093) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, K.; Song, W.; Liu, Z.; Lin, G.N.; Yu, S. Mendelian Randomization and GWAS Meta Analysis Revealed the Risk-Increasing Effect of Schizophrenia on Cancers. Biology 2022, 11, 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091345
Yuan K, Song W, Liu Z, Lin GN, Yu S. Mendelian Randomization and GWAS Meta Analysis Revealed the Risk-Increasing Effect of Schizophrenia on Cancers. Biology. 2022; 11(9):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091345
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Kai, Weichen Song, Zhe Liu, Guan Ning Lin, and Shunying Yu. 2022. "Mendelian Randomization and GWAS Meta Analysis Revealed the Risk-Increasing Effect of Schizophrenia on Cancers" Biology 11, no. 9: 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091345
APA StyleYuan, K., Song, W., Liu, Z., Lin, G. N., & Yu, S. (2022). Mendelian Randomization and GWAS Meta Analysis Revealed the Risk-Increasing Effect of Schizophrenia on Cancers. Biology, 11(9), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11091345






