Comparative Analysis of the Upper Respiratory Bacterial Communities of Pigs with or without Respiratory Clinical Signs: From Weaning to Finishing Phase
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Herds
2.2. Study Design and Sampling
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Sequencing
2.4. 16S rRNA Reads Processing
2.5. Microbial Communities and Statistical Analysis
2.6. Functional Prediction
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Diversity
3.2. Microbial Composition and Distribution
3.3. Core and Rare Microbiota
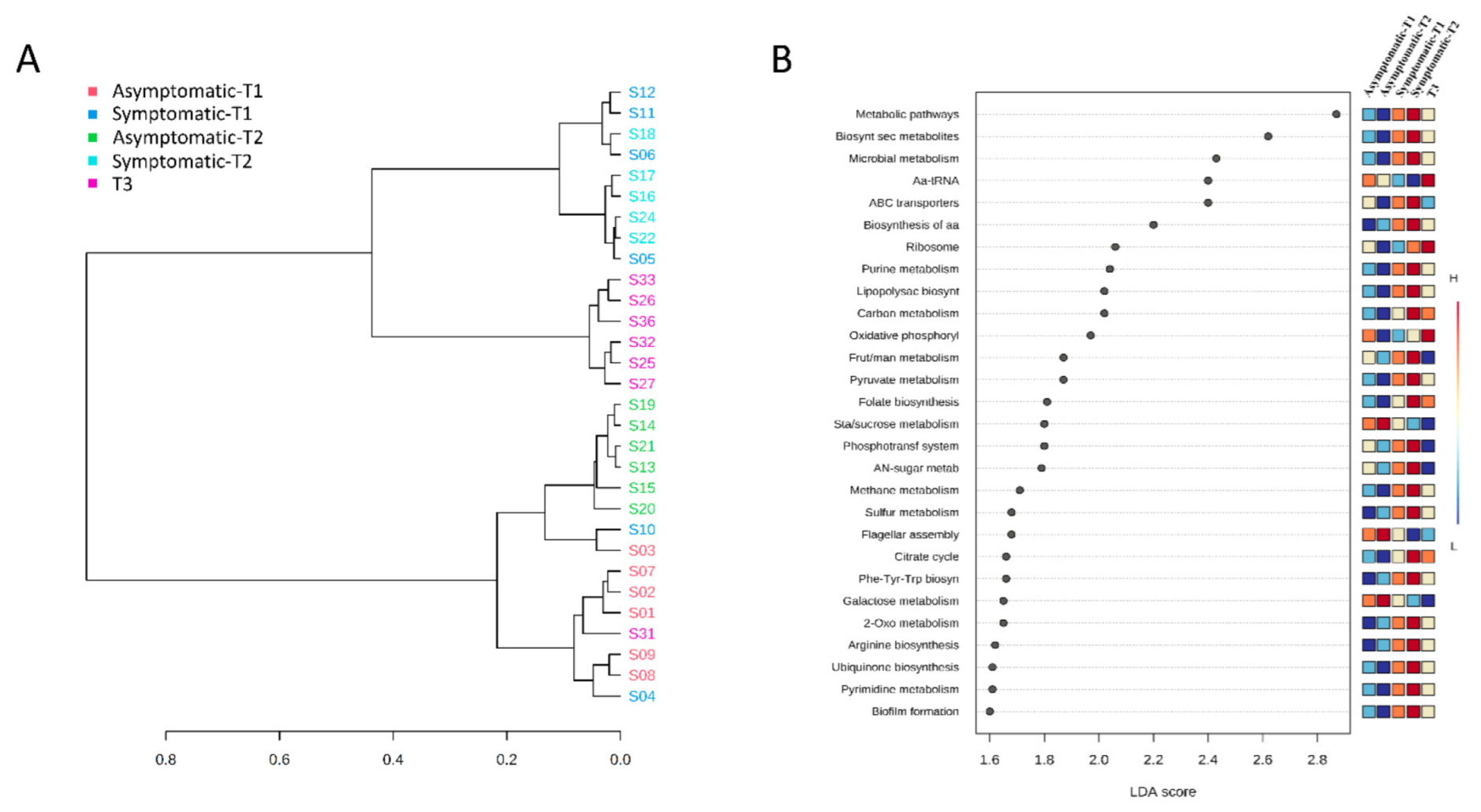
3.4. Functional Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pieters, M.; Maes, D. Mycoplasmosis. In Diseases of Swine, 11th ed.; Zimmerman, J.J., Karriker, L.A., Ramirez, A., Schwartz, K.J., Stevenson, G.W., Zhang, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 863–883. [Google Scholar]
- Stärk, K.D.C. Epidemiological investigation of the influence of environmental risk factors on respiratory diseases in swine—A literature review. Vet. J. 2000, 159, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opriessnig, T.; Giménez-Lirola, L.G.; Halbur, P.G. Polymicrobial respiratory disease in pigs. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2011, 12, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Donovan, S.M. Human microbiota-associated swine: Current progress and future opportunities. ILAR J. 2015, 56, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluthge, N.D.; Van Sambeek, D.M.; Carney-Hinkle, E.E.; Li, Y.S.; Fernando, S.C.; Burkey, T.E. The pig microbiota and the potential for harnessing the power of the microbiome to improve growth and health1. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 3741–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowland, T.L.; Plush, K.J.; Barton, M.; Kirkwood, R.N. Development and function of the intestinal microbiome and potential implications for pig production. Animals 2019, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Seok, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, B.N.; Johnson, T.J.; Isaacson, R.E.; Kim, H.B. Piglet gut microbial shifts early in life: Causes and effects. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, M.; Tiezzi, F.; Howard, J.; Huang, Y.J.; Gray, K.A.; Schillebeeckx, C.; McNulty, N.P.; Maltecca, C. Gut microbiome composition differences among breeds impact feed efficiency in swine. Microbiome 2020, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, D.; Cholewińska, P.; Jankowska-Mąkosa, A.; Czyż, K. Development of swine’s digestive tract microbiota and its relation to production indices—A review. Animals 2020, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slifierz, M.J.; Friendship, R.M.; Weese, J.S. Longitudinal study of the early-life fecal and nasal microbiotas of the domestic pig. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Fiz, F.; Fraile, L.; Aragon, V. Piglet nasal microbiota at weaning may influence the development of Glässer’s Disease during the rearing period. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirolo, M.; Espinosa-Gongora, C.; Bogaert, D.; Guardabassi, L. The porcine respiratory microbiome: Recent insights and future challenges. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, B.A.; Marsh, T.L.; Isaacs-Cosgrove, N.; Kirkwood, R.N.; Kiupel, M.; Mulks, M.H. Defining the “core microbiome” of the microbial communities in the tonsils of healthy pigs. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederwerder, M.C. Role of the microbiome in swine respiratory disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 209, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm, N.W.; de Zoete, M.R.; Flavell, R.A. Immune-microbiota interactions in health and disease. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 159, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weese, J.S.; Slifierz, M.; Jalali, M.; Friendship, R. Evaluation of the nasal microbiota in slaughter-age pigs and the impact on nasal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) carriage. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morés, N.; Barioni Junior, W.; Sobestansky, J.; Dalla Costa, A.O.; Piffer, A.I.; Paiva, D.P.; Guzzo, R.; Coimbra, J.B.S. Estimating of pneumonia by coughing and atrophic rhinitis by sneezing indices in swine. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária Zootec. 2001, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, M.; Daniels, J.; Rovira, A. Comparison of sample types and diagnostic methods for in vivo detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae during early stages of infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 203, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumgam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, S.; Weinmaier, T.; Schmidt, B.L.; Albertson, D.G.; Poloso, N.J.; Dabbagh, K.; DeSantis, T.Z. Piphillin: Improved prediction of metagenomic content by direct inference from human microbiomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Di, D.; Pan, R.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, B.; Wei, J.; Liu, K.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Comparative analysis of the pulmonary microbiome in healthy and diseased pigs. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2021, 296, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Fiz, F.; dos Santos, J.M.G.; Illas, F.; Aragon, V. Antimicrobial removal on piglets promotes health and higher bacterial diversity in the nasal microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeineldin, M.; Aldridge, B.; Blair, B.; Kancer, K.; Lowe, J. Microbial shifts in the swine nasal microbiota in response to parenteral antimicrobial administration. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 121, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Johnson, T.A.; Su, J.Q.; Qiao, M.; Guo, G.X.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Hashsham, S.A.; Tiedje, J.M. Diverse and abundant antibiotic resistance genes in Chinese swine farms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3435–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeineldin, M.; Aldridge, B.; Lowe, J. Antimicrobial effects on swine gastrointestinal microbiota and their accompanying antibiotic resistome. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, P.A. Alternatives to antibiotics as growth promoters for use in swine production: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.B.; Melo, A.D.B.; Cruz, D.R.; Garbossa, A.C.P.; Andrade, C.; Cantarelli, C.S.; Costa, L.B. Alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters for weanling pigs. Cienc. Rural 2015, 45, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Cai, R.; Huang, A.; Wang, X.; Qu, W.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Yan, H. Comparison of oropharyngeal microbiota in healthy piglets and piglets with respiratory disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Fang, S.; He, M.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Huang, L. Age-based dynamic changes of phylogenetic composition and interaction networks of health pig gut microbiome feeding in a uniformed condition. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.Y.; Song, E.J.; Kang, K.S.; Nam, Y.D. Age-related compositional and functional changes in micro-pig gut microbiome. Geroscience 2019, 41, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, D.B.; Gzyl, K.E.; Mou, K.T.; Allen, H.K. Weaning age and its effect on the development of the swine gut microbiome and resistome. mSystems 2021, 6, e0068221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowland, T.L.; Kirkwood, R.N.; Pluske, J.R. Review: Can early-life establishment of the piglet intestinal microbiota influence production outcomes? Animal 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeger, M.J.; Van Alstine, W.G. Respiratory System. In Diseases of Swine, 11th ed.; Zimmerman, J.J., Karriker, L.A., Ramirez, A., Schwartz, K.J., Stevenson, G.W., Zhang, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 393–407. [Google Scholar]
- Vigre, H.; Ersbøll, A.K.; Sørensen, V. Decay of acquired colostral antibodies to Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in pigs. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2003, 50, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, R.; Maturrano, L.; Azevedo, V.; Aburjaile, F. Pathogenomics insights for understanding Pasteurella multocida adaptation. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baums, C.G.; Bruggemann, C.; Kock, C.; Beineke, A.; Waldmann, K.H.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Immunogenicity of an autogenous Streptococcus suis bacterin in preparturient sows and their piglets in relation to protection after weaning. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M. Streptococcosis. In Diseases of Swine, 11th ed.; Zimmerman, J.J., Karriker, L.A., Ramirez, A., Schwartz, K.J., Stevenson, G.W., Zhang, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 934–950. [Google Scholar]
- Obradovic, M.R.; Segura, M.; Segalés, J.; Gottschalk, M. Review of the speculative role of co-infections in Streptococcus suis-associated diseases in pigs. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Carrou, J.; Laurentie, M.; Kobisch, M.; Gautier-Bouchardon, A.V. Persistence of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in experimentally infected pigs after marbofloxacin treatment and detection of mutations in the parC gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeris-Chacin, R.; Sponheim, A.; Fano, E.; Isaacson, R.; Singer, R.S.; Nerem, J.; Leite, F.L.; Pieters, M. Relationships among fecal, air, oral, and tracheal microbial communities in pigs in a respiratory infection disease model. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, J.G. Anaerobic bacterial infection of the lung. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Majaz, S.; Nouroz, F. Two-component systems regulate ABC transporters in antimicrobial peptide production, immunity and resistance. Microbiology 2020, 166, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.J.; Song, S.; Mason, K.; Pinkett, H.W. Selective substrate uptake: The role of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) importers in pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
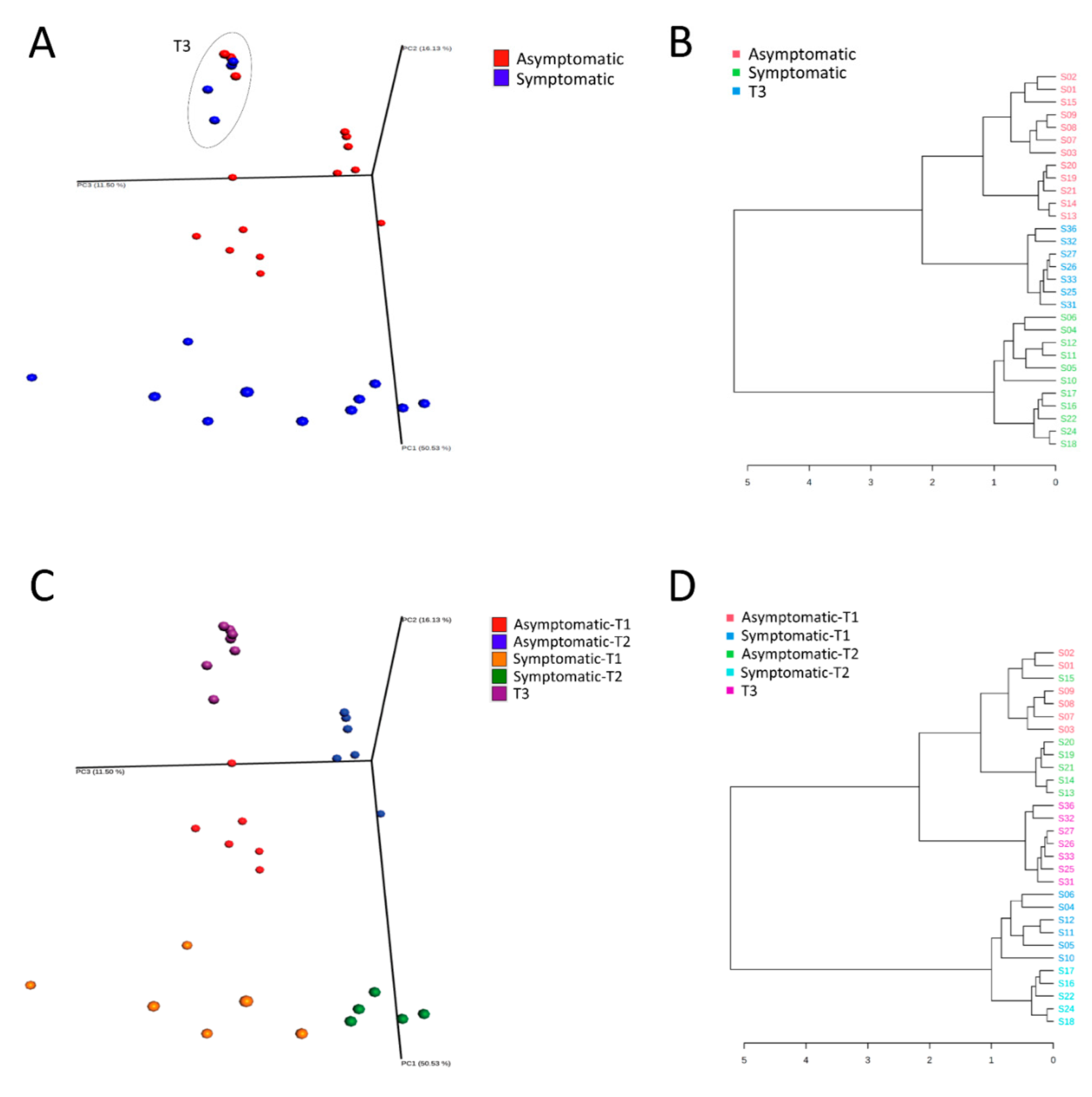
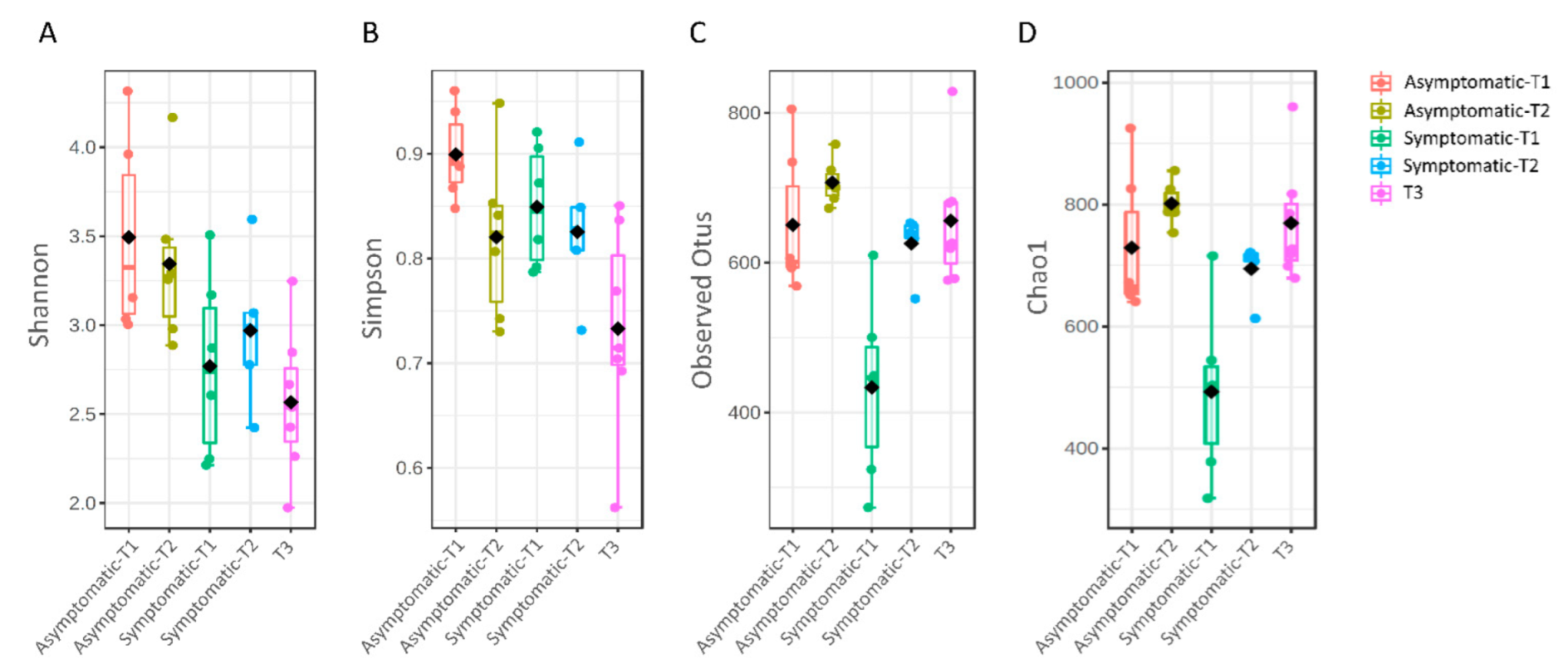
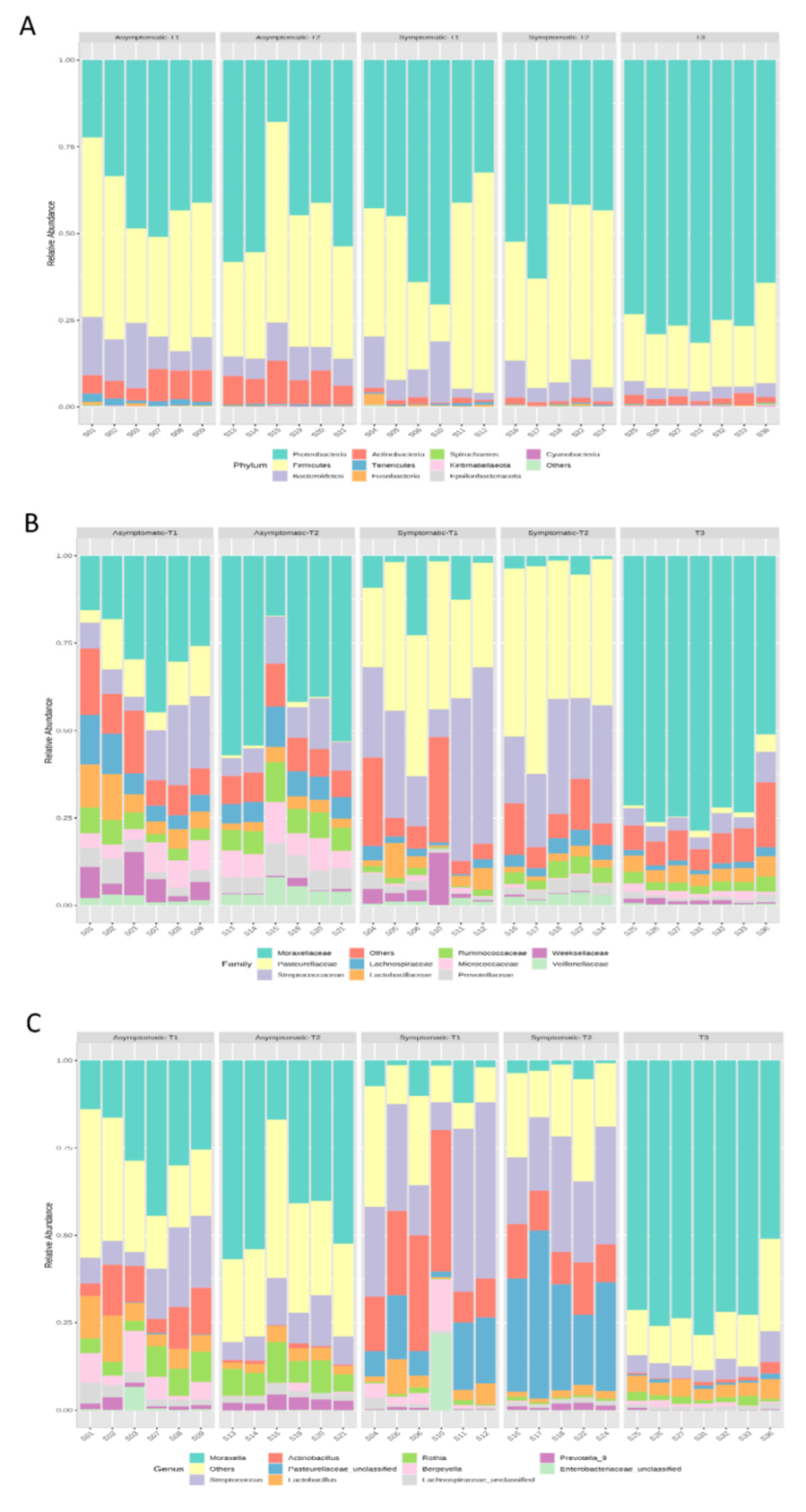


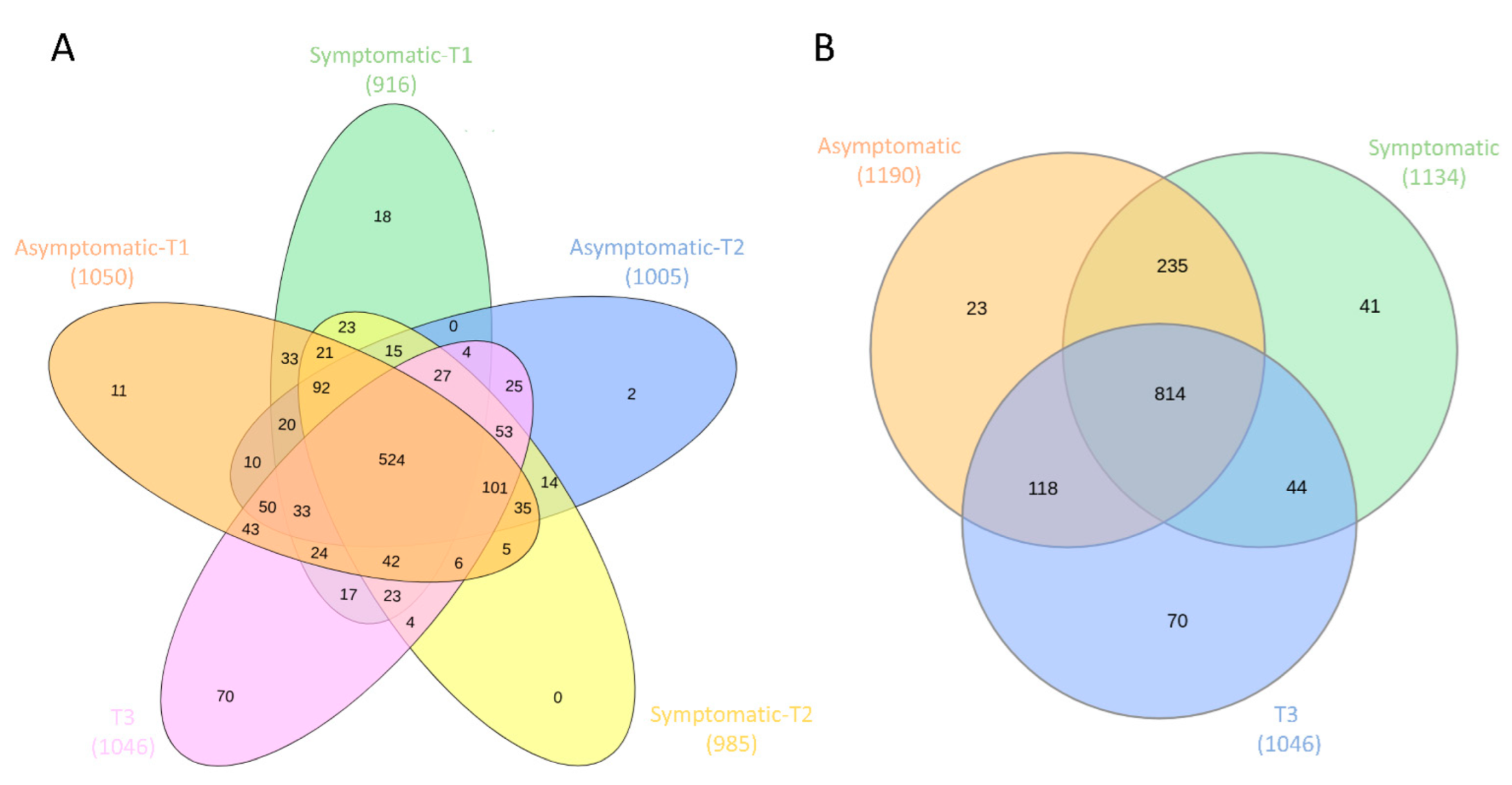
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Sample Size | q-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic | Asymptomatic | 23 | 0.001 |
| Symptomatic | T3 | 18 | 0.001 |
| Asymptomatic | T3 | 19 | 0.001 |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Sample Size | q-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptomatic-T1 | Symptomatic-T2 | 11 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T1 | Symptomatic-T3 | 10 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T1 | Asymptomatic-T1 | 12 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T1 | Asymptomatic-T2 | 12 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T1 | Asymptomatic-T3 | 9 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T2 | Symptomatic-T3 | 9 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T2 | Asymptomatic-T1 | 11 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T2 | Asymptomatic-T2 | 11 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T2 | Asymptomatic-T3 | 8 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T3 | Asymptomatic-T1 | 10 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T3 | Asymptomatic-T2 | 10 | 0.01 |
| Symptomatic-T3 | Asymptomatic-T3 | 7 | 0.89 |
| Asymptomatic-T1 | Asymptomatic-T2 | 12 | 0.01 |
| Asymptomatic-T1 | Asymptomatic-T3 | 9 | 0.01 |
| Asymptomatic-T2 | Asymptomatic-T3 | 9 | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rampelotto, P.H.; dos Santos, A.C.R.; Muterle Varela, A.P.; Takeuti, K.L.; Loiko, M.R.; Mayer, F.Q.; Roehe, P.M. Comparative Analysis of the Upper Respiratory Bacterial Communities of Pigs with or without Respiratory Clinical Signs: From Weaning to Finishing Phase. Biology 2022, 11, 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081111
Rampelotto PH, dos Santos ACR, Muterle Varela AP, Takeuti KL, Loiko MR, Mayer FQ, Roehe PM. Comparative Analysis of the Upper Respiratory Bacterial Communities of Pigs with or without Respiratory Clinical Signs: From Weaning to Finishing Phase. Biology. 2022; 11(8):1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081111
Chicago/Turabian StyleRampelotto, Pabulo Henrique, Anne Caroline Ramos dos Santos, Ana Paula Muterle Varela, Karine Ludwig Takeuti, Márcia Regina Loiko, Fabiana Quoos Mayer, and Paulo Michel Roehe. 2022. "Comparative Analysis of the Upper Respiratory Bacterial Communities of Pigs with or without Respiratory Clinical Signs: From Weaning to Finishing Phase" Biology 11, no. 8: 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081111
APA StyleRampelotto, P. H., dos Santos, A. C. R., Muterle Varela, A. P., Takeuti, K. L., Loiko, M. R., Mayer, F. Q., & Roehe, P. M. (2022). Comparative Analysis of the Upper Respiratory Bacterial Communities of Pigs with or without Respiratory Clinical Signs: From Weaning to Finishing Phase. Biology, 11(8), 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081111







