Multigenerational Social Housing and Group-Rearing Enhance Female Reproductive Success in Captive Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Ethical Statement
2.4. Measures
2.5. Age Interaction Maternal Age and Group Type
2.6. Statistics
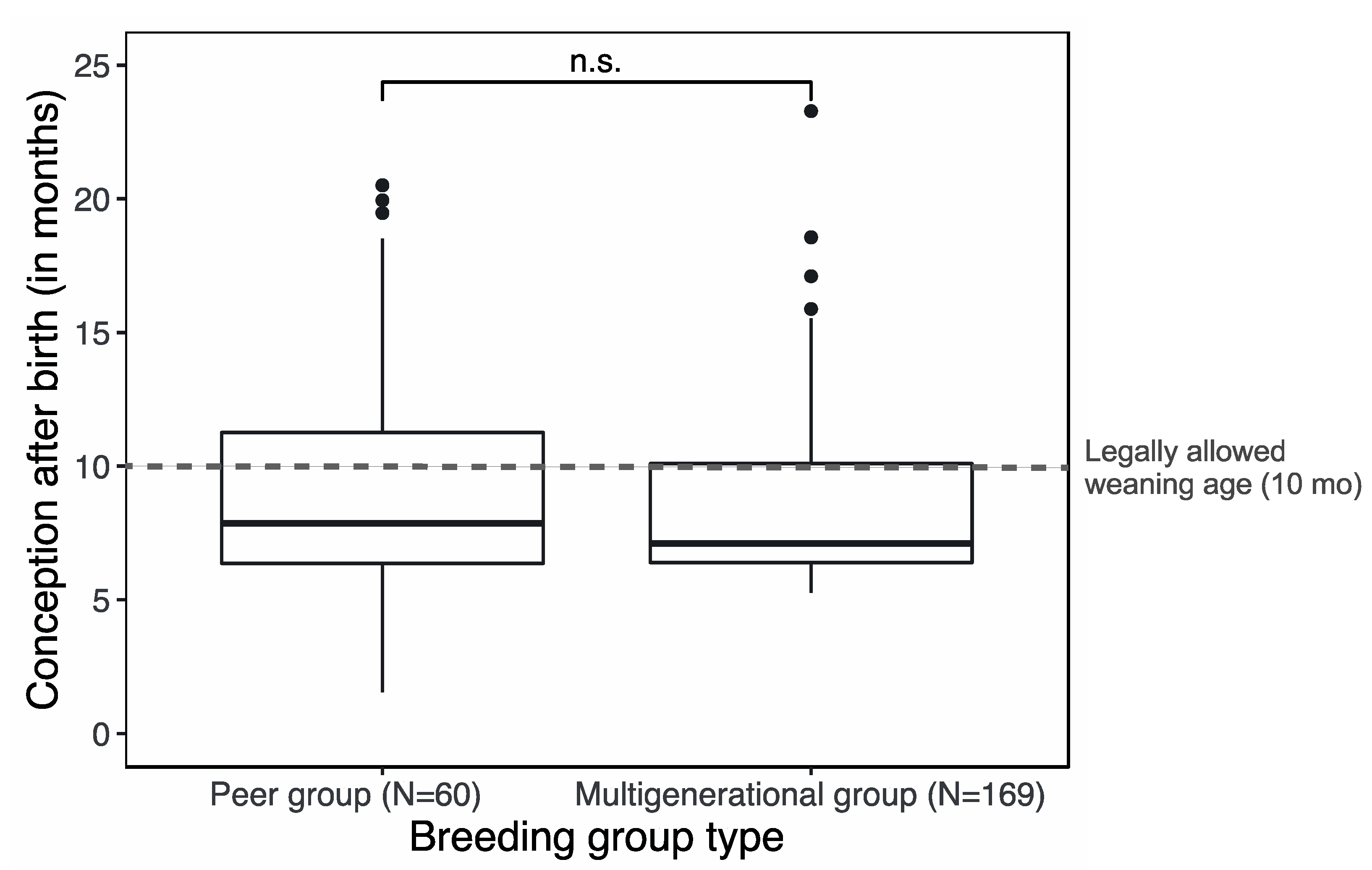
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Breeding Group Type
4.2. Maternal Rearing History
4.3. No Trade-off between Female Reproductive Success and Welfare
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, K.C.; Bloomsmith, M.A.; Oettinger, B.; Neu, K.; Griffis, C.; Schoof, V.; Maloney, M. Benefits of pair housing are consistent across a diverse population of rhesus macaques. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 137, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, K.C.; Bloomsmith, M.A.; Oettinger, B.; Neu, K.; Griffis, C.; Schoof, V.A. Comparing options for pair housing rhesus macaques using behavioral welfare measures. Am. J. Primatol. 2014, 76, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, M.H.; Baker, K.C. Social buffering in adult male rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta): Effects of stressful events in single vs. pair housing. J. Med. Primatol. 2011, 40, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannibal, D.L.; Bliss-Moreau, E.; Vandeleest, J.; McCowan, B.; Capitanio, J. Laboratory rhesus macaque social housing and social changes: Implications for research. Am. J. Primatol. 2017, 79, e22528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eaton, G.G.; Kelley, S.T.; Axthelm, M.K.; Iliff-Sizemore, S.A.; Shiigi, S.M. Psychological well-being in paired adult female rhesus (Macaca mulatta). Am. J. Primatol. 1994, 33, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, C.K.; Novak, M.A. Environmental enrichment for nonhuman primates: Theory and application. Ilar J. 2005, 46, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goo, G.P.; Fugate, J.K. Effects of weaning age on maternal reproduction and offspring health in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Lab. Anim. Sci. 1984, 34, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, M.J.; Nixon, M.E.; Farningham, D.A.; Naiken, S.; Griffiths, M.A. Laboratory macaques: When to wean? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 137, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomendio, M. Suckling behaviour and fertility in rhesus macaques (Macaca multatta). J. Zool. 1989, 217, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.J.; Agoramoorthy, G.; Lin, J.F. Birth seasonality and interbirth intervals in free-ranging Formosan macaques, Macaca cyclopis, at Mt. Longevity, Taiwan. Primates 2001, 42, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Ruiz-Lambides, A.V.; Higham, J.P. Higher offspring mortality with short interbirth intervals in free-ranging rhesus macaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6057–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rox, A.; van Vliet, A.H.; Sterck, E.H.; Langermans, J.A.; Louwerse, A.L. Factors determining male introduction success and long-term stability in captive rhesus macaques. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempes, M.M.; Gulickx, M.M.C.; van Daalen, H.J.C.; Louwerse, A.L.; Sterck, E.H.M. Social competence is reduced in socially deprived rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). J. Comp. Psychol. 2008, 122, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempes, M.M.; Den Heijer, E.; Korteweg, L.; Louwerse, A.L.; Sterck, E.H.M. Socially deprived rhesus macaques fail to reconcile: Do they not attempt or not accept reconciliation? Anim. Behav. 2009, 78, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommeck, I.; Gottlieb, D.H.; Strand, S.C.; McCowan, B. The effects of four nursery rearing strategies on infant behavioral development in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2009, 48, 395–401. [Google Scholar]
- Seay, B.; Alexander, B.K.; Harlow, H.F. Maternal behavior of socially deprived Rhesus monkeys. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 1964, 69, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppenthal, G.C.; Arling, G.L.; Harlow, H.F.; Sackett, G.P.; Suomi, S.J. A 10-year perspective of motherless-mother monkey behavior. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1976, 85, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champoux, M.; Metz, B.; Suomi, S.J. Behavior of nursery/peer-reared and mother-reared rhesus monkeys from birth through 2 years of age. Primates 1991, 32, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, C.; Buchanan-Smith, H.M.; Jones-Engel, L.; Farmer, K.H.; Prescott, M.J.; Fitch-Snyder, H.; Taylor, S. IPS International Guidelines for the Acquisition, Care and Breeding of Nonhuman Primates; International Primatological Society: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2007; Available online: http://internationalprimatologicalsociety.org/docs/IPS_International_Guidelines_for_the_Acquisition_Care_and_Breeding_of_Nonhuman_Primates_Second_Edition_2007.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2022).
- Silk, J.; Short, J.; Roberts, J.; Kusnitz, J. Gestation length in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Int. J. Primatol. 1993, 14, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallapur, A.; Choudhury, B.C. Behavioral abnormalities in captive nonhuman primates. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2003, 6, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, K.J.; Capozzi, D.K.; Newsome, J.T. Effects of maternal and infant characteristics on birth weight and gestation length in a colony of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Comp. Med. 2008, 58, 597–603. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, J.C.; Robinette, R.L.; Sackett, G.P. Social housing and pregnancy outcome in captive pigtailed macaques. Am. J. Primatol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Primatol. 1999, 47, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rox, A.; van Vliet, A.H.; Langermans, J.A.; Sterck, E.H.; Louwerse, A.L. A Stepwise Male Introduction Procedure to Prevent Inbreeding in Naturalistic Macaque Breeding Groups. Animals 2021, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestripieri, D.; Georgiev, A.V. What cortisol can tell us about the costs of sociality and reproduction among free-ranging rhesus macaque females on Cayo Santiago. Am. J. Primatol. 2016, 78, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goin, D.L.; Gust, D.A. Peer-rearing influences subsequent maternal behavior and infant survival in a newly formed herpes B-virus negative rhesus macaque group. Primates 1998, 39, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestripieri, D. Effects of early experience on female behavioural and reproductive development in rhesus macaques. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ljungberg, T.; Westlund, K. Impaired reconciliation in rhesus macaques with a history of early weaning and disturbed socialization. Primates 2000, 41, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, D.N.; Lubach, G.R.; Phillips, G.J.; Lyte, M.; Coe, C.L. Maternal and breast milk influences on the infant gut microbiome, enteric health and growth outcomes of rhesus monkeys. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sade, D.S. Some aspects of parent-offspring and sibling relations in a group of rhesus monkeys, with a discussion of grooming. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1965, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roonwal, M.L.; Mohnot, S.M. Primates of south Asia. In Primates of South Asia; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rox, A.; Waasdorp, S.; Sterck, E.H.M.; Langermans, J.A.M.; Louwerse, A.L. Multigenerational Social Housing and Group-Rearing Enhance Female Reproductive Success in Captive Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Biology 2022, 11, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070970
Rox A, Waasdorp S, Sterck EHM, Langermans JAM, Louwerse AL. Multigenerational Social Housing and Group-Rearing Enhance Female Reproductive Success in Captive Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Biology. 2022; 11(7):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070970
Chicago/Turabian StyleRox, Astrid, Sophie Waasdorp, Elisabeth H. M. Sterck, Jan A. M. Langermans, and Annet L. Louwerse. 2022. "Multigenerational Social Housing and Group-Rearing Enhance Female Reproductive Success in Captive Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta)" Biology 11, no. 7: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070970
APA StyleRox, A., Waasdorp, S., Sterck, E. H. M., Langermans, J. A. M., & Louwerse, A. L. (2022). Multigenerational Social Housing and Group-Rearing Enhance Female Reproductive Success in Captive Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Biology, 11(7), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070970





