Aerosol Nutrients and Their Biological Influence on the Northwest Pacific Ocean (NWPO) and Its Marginal Seas
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Global Patterns of Atmospheric Input to the Ocean
3. Features of East Asian Aerosols
4. Key Species of Atmospheric Nutrients
4.1. Atmospheric Nitrogen (N) Input to the Ocean
4.2. Atmospheric Fe and Other Trace Metals Deposition
4.3. Atmospheric Phosphorus (P) Deposition
4.4. Atmospheric Deposition of Oorganic Matters
5. Effect of East Asian Aerosol on Phytoplankton in NWPO and Its Marginal Seas
5.1. Fertilizing Effect
5.2. Stimulation of N2 Fixation
5.3. Change of Nutrient Stoichiometry
5.4. Shift of Community Composition and Struture
5.5. Inhibitory Effect
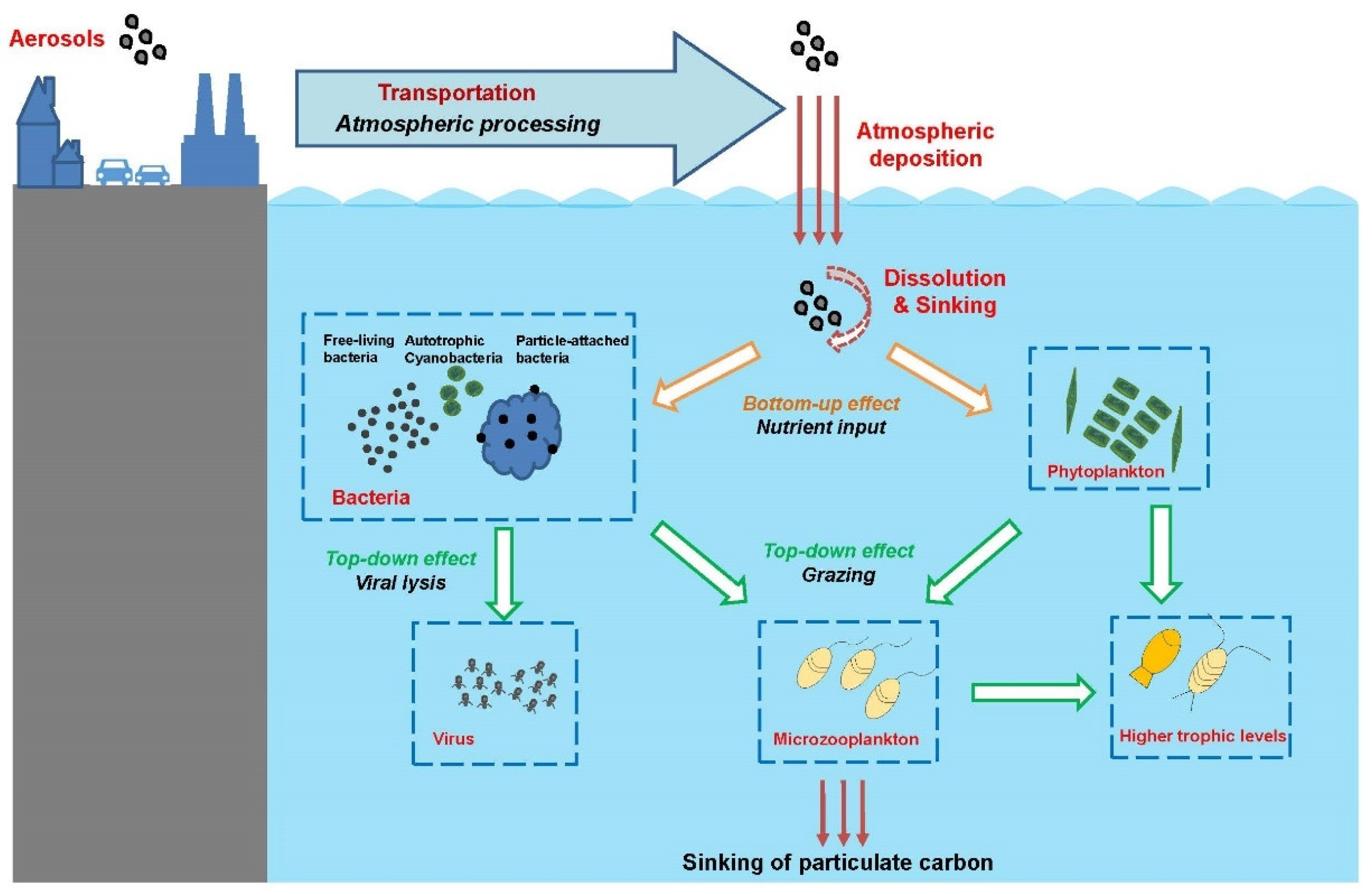
6. Effect of East Asian Aerosol on Bacteria
7. Future Perspectives
- (1)
- Improved modeling of future trends in atmospheric deposition and human impacts, and a better understanding of the responses of marine microbial ecosystems to perturbations by atmospheric inputs are required. More detailed studies of the atmospheric chemistry of EA aerosol deposition and the response of the microbial community, including microzooplankton, phytoplankton, bacteria and viruses, both in short and long terms, are needed, particularly as oceanic and atmospheric records of sufficient length to investigate long-term changes are limited. Thus, time series observations in key regions need to be maintained.
- (2)
- Except for the LNLC regions primarily limited by N, and the HNLC areas significantly affected by Fe, our understanding of the importance and the mechanisms of atmospheric deposition in many areas is still not clear. This is mainly due to uncertainties in the bioavailability and specific composition of atmospheric deposition, and the complexity of the “supply” and “demand” between atmospheric deposition and ocean biota. Moreover, the impact of aerosol deposition on the microbial community is closely related to the nutrient stoichiometry of atmospheric input, initial microbial assemblage, metabolic and trophic state, and the hydrological condition of the investigated water. Therefore, how to quantify the similarities and differences in the responses of marine biota to atmospheric deposition from different sources in different areas and how to determine the controlling factors have become the keys to understanding the impacts of atmospheric deposition on marine primary production processes.
- (3)
- More research on biological mechanisms should be carried out in the future. For example, the detailed mechanisms of the plankton responses on community, individual, and molecular levels and how they influence C, N, P, and S cycles; and the dynamics of microbial food webs, including the bottom-up and top-down effects in response to aerosol input. Moreover, in addition to atmospheric N, P, and Fe, the effects of other trace metals and organic compounds should also be extensively studied. Considering the long residential time and complex chemical and biological interactions of metals and organic matters in the seawater, it is necessary to conduct more experiments to directly assess their impact and combined effect with nutrients on microbes.
- (4)
- As the climate of East Asia is affected by anthropogenic aerosols [130], the combined effects of atmospheric deposition with other environmental changes, such as warming and acidification, should be considered. It has been suggested that predicted warming and acidification will intensify these responses [129], affecting food web processes and biogeochemical cycles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jickells, T.D.; An, Z.S.; Andersen, K.K.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Cao, J.; Boyd, P.W.; Duce, R.A.; Hunter, K.A.; et al. Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate. Science 2005, 308, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chappell, A.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; McTainsh, G.H.; Mikami, M.; Tanaka, T.Y.; Wang, X.; Yoon, S. Dust cycle: An emerging core theme in Earth system science. Aeolian Res. 2011, 2, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.D.; Moore, C.M. The importance of atmospheric deposition for ocean productivity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2015, 46, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duce, R.A.; LaRoche, J.; Altieri, K.; Arrigo, K.R.; Baker, A.R.; Capone, D.G.; Cornell, S.; Dentener, F.; Galloway, J.; Ganeshram, R.S.; et al. Impacts of atmospheric anthropogenic nitrogen on the open ocean. Science 2008, 320, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakidou, M.; Duce, R.A.; Prospero, J.M.; Baker, A.R.; Benitez-Nelson, C.; Dentener, F.J.; Hunter, K.A.; Liss, P.S.; Mahowald, N.; Okin, G.S.; et al. Atmospheric fluxes of organic N and P to the global ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26, GB3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Scanza, R.; Brahney, J.; Goodale, C.L.; Hess, P.G.; Moore, J.K.; Neff, J. Aerosol deposition impacts on land and ocean carbon cycles. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2017, 3, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A.; Prospero, J.M.; Mackie, D.; Gaiero, D.; Hesse, P.P.; Balkanski, Y. Global connections between aeolian dust, climate and ocean biogeochemistry at the present day and at the last glacial maximum. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 61–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duce, R.A.; Liss, P.S.; Merrill, J.T.; Atlas, E.L.; Buat-Menard, P.; Hicks, B.B.; Miller, J.M.; Prospero, J.M.; Arimoto, R.; Church, T.M.; et al. The atmospheric input of trace species to the world ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1991, 5, 193–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duce, R.A.; Tindale, N.W. Atmospheric transport of iron and its deposition in the ocean. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Lee, K.; Najjar, R.G.; Jeong, H.D.; Jeong, H.J. Increasing N abundance in the northwestern Pacific Ocean due to atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Science 2011, 334, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.I.; Chen, J.-P.; Wong, G.T.F.; Huang, C.-W.; Lien, C.-C. Aerosol input to the South China Sea: Results from the MODerate resolution imaging spectro-radiometer, the quick scatterometer, and the measurements of pollution in the troposphere sensor. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Duce, R.A.; Jickells, T.D.; Kubilay, N.; Prospero, J.M.; Tegen, I. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridame, C.; Guieu, C. Saharan input of phosphate to the oligotrophic water of the open western Mediterranea Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, B.; Sarin, M.M. Atmospheric deposition of N, P and Fe to the Northern Indian Ocean: Implications to C- and N-fixation. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, A.; Bopp, L.; Aumont, O. Evaluating the importance of atmospheric and sedimentary iron sources to Southern Ocean biogeochemistry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L13601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Chin, M.; Tegen, I.; Prospero, J.M.; Holben, B.; Dubovik, O.; Lin, S.-J. Sources and distributions of dust aerosols simulated with the GOCART model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 20255–20273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C. Sensitivity study of meteorological parameters on mineral aerosol mobilization, transport, and distribution. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Barrett, K.; Church, T.; Dentener, F.; Duce, R.A.; Galloway, J.N.; Levy, H.; Moody, J.; Quinn, P. Atmospheric deposition of nutrients to the North Atlantic Basin. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 27–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegen, I.; Werner, M.; Harrison, S.P.; Kohfeld, K.E. Relative importance of climate and land use in determining present and future global soil dust emission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L05105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zender, C.S. Mineral Dust Entrainment and Deposition (DEAD) model: Description and 1990s dust climatology. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, R.; Tie, X.; Li, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, Z.; Han, Y.; Gu, Z.; et al. Severe haze in northern China: A synergy of anthropogenic emissions and atmospheric processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019, 116, 8657–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.C.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, J.Y. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Arimoto, R.; Duce, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; An, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhou, M.; Gu, D. Temporal and spatial distributions of dust and its deposition to the China Sea. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 1997, 49, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.D. Multielemental analysis and characterization of fine aerosols at several key ACE-Asia sites. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D19S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, M.I.; Song, C.K.; Kim, K.M.; da Silva, A.M. Interannual variation of the East Asia jet stream and its impact on the horizontal distribution of aerosol in boreal spring. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Niggemann, J.; Luo, L.; Dittmar, T.; Kao, S.J. Aerosols as a source of dissolved black carbon to the ocean. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paytan, A.; Mackey Katherine, R.M.; Chen, Y.; Lima Ivan, D.; Doney Scott, C.; Mahowald, N.; Labiosa, R.; Post Anton, F. Toxicity of atmospheric aerosols on marine phytoplankton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4601–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, C.F.; Baker, A.R.; Jickells, T.D.; Bange, H.W.; Chance, R.J.; Yodle, C. Estimation of the atmospheric flux of nutrients and trace metals to the eastern tropical North Atlantic Ocean. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 4029–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boreddy, S.K.R.; Kawamura, K. A 12-year observation of water-soluble ions in TSP aerosols collected at a remote marine location in the western North Pacific: An outflow region of Asian dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6437–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhuang, G.; Guo, J.; Yin, K.; Zhang, P. Characterization of aerosol over the Northern South China Sea during two cruises in 2003. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7821–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Dennis, R.L.; Whitall, D.R. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen: Implications for nutrient over-enrichment of coastal waters. Estuaries 2002, 25, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Whitall, D.R. Anthropogenically-derived atmospheric nitrogen deposition, marine eutrophication and harmful algal bloom expansion: Is there a link? Ambio 1999, 28, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Cornell, S.; Randell, A.; Jickells, T. Atmospheric inputs of dissolved organic nitrogen to the oceans. Nature 1995, 376, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, S.E.; Jickells, T.D.; Cape, J.N.; Rowland, A.P.; Duce, R.A. Organic nitrogen deposition on land and coastal environments: A review of methods and data. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2173–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-X.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wang, W.; Yeh, J.-X.; Chou, W.-C.; Gong, G.-C.; Tsai, F.-J.; Huang, S.-J.; Lin, C.-T. Dissolved organic nitrogen in wet deposition in a coastal city (Keelung) of the southern East China Sea: Origin, molecular composition and flux. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.M.; Ridame, C.; Davey, M.; Roche, J.; Geider, R.J. Iron and phosphorus co-limit nitrogen fixation in the eastern tropical North Atlantic. Nature 2004, 429, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Howarth, R.W.; Michaels, A.F.; Nixon, S.W.; Prospero, J.M.; Dentener, F.J. Nitrogen and phosphorus budgets of the North Atlantic Ocean and its watershed. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzinger, S.P.; Mayorga, E.; Bouwman, A.F.; Kroeze, C.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Billen, G.; Van Drecht, G.; Dumont, E.; Fekete, B.M.; Garnier, J.; et al. Global river nutrient export: A scenario analysis of past and future trends. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, GB0A08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.D.; Buitenhuis, E.; Altieri, K.; Baker, A.R.; Capone, D.; Duce, R.A.; Dentener, F.; Fennel, K.; Kanakidou, M.; LaRoche, J.; et al. A reevaluation of the magnitude and impacts of anthropogenic atmospheric nitrogen inputs on the ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakidou, M.; Myriokefalitakis, S.; Daskalakis, N.; Fanourgakis, G.; Nenes, A.; Baker, A.R.; Tsigaridis, K.; Mihalopoulos, N. Past, present and future atmospheric nitrogen deposition. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Luo, K.; Liu, H.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Fan, J.; Yao, X.; Gao, H.; Nagashima, T. Impacts of climate change and emissions on atmospheric oxidized nitrogen deposition over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, L.E.; Sunda, W.G.; Guillard, R.R.L. Reduction of marine phytoplankton reproduction rates by copper and cadmium. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1986, 96, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, C.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Sigman, D.M.; Gruber, N.; Dunne, J.P. Spatial coupling of nitrogen inputs and losses in the ocean. Nature 2007, 445, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaffey, C.; Michaels, A.; Capone, D. The conundrum of marine N2 fixation. Amer. J. Sci. 2005, 305, 546–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.K.; Doney, S.C.; Lindsay, K.; Mahowald, N.; Michaels, A.F. Nitrogen fixation amplifies the ocean biogeochemical response to decadal timescale variations in mineral dust deposition. Tellus B 2006, 58, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, A.; Moore, J.K.; Zender, C.S.; Luo, C. Effects of atmospheric inorganic nitrogen deposition on ocean biogeochemistry. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, G02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.K.; Doney, S.C. Iron availability limits the ocean nitrogen inventory stabilizing feedbacks between marine denitrification and nitrogen fixation. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21, GB2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Lee, K.; Duce, R.; Liss, P. Impact of atmospheric nitrogen deposition on phytoplankton productivity in the South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3156–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhao, H.; Chen, F.; Xiao, H. The distribution of aerosols and their impacts on chlorophyll—A distribution in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2020, 125, e2019JG005490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.H.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, D.; Lee, K.; Kang, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Kim, T.W. Atmospheric deposition of anthropogenic inorganic nitrogen in airborne particles and precipitation in the East Sea in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 681, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, P.W.; Jickells, T.; Law, C.S.; Blain, S.; Boyle, E.A.; Buesseler, K.O.; Coale, K.H.; Cullen, J.J.; de Baar, H.J.; Follows, M.; et al. Mesoscale iron enrichment experiments 1993–2005: Synthesis and future directions. Science 2007, 315, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkowski Paul, G.; Barber Richard, T.; Smetacek, V. Biogeochemical controls and feedbacks on ocean primary production. Science 1998, 281, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, I.Y.; Meyn, S.K.; Tegen, I.; Doney, S.C.; John, J.G.; Bishop, J.K.B. Iron supply and demand in the upper ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H.; Gordon, M.; Fitzwater, S.E. The case for iron. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld Michael, J.; Kolber Zbigniew, S. Widespread iron limitation of phytoplankton in the south Pacific Ocean. Science 1999, 283, 840–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Mills, M.M.; Arrigo, K.R.; Berman-Frank, I.; Bopp, L.; Boyd, P.W.; Galbraith, E.D.; Geider, R.J.; Guieu, C.; Jaccard, S.L.; et al. Processes and patterns of oceanic nutrient limitation. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Engelstaedter, S.; Luo, C.; Sealy, A.; Artaxo, P.; Benitez-Nelson, C.; Bonnet, S.; Chen, Y.; Chuang, P.Y.; Cohen, D.D.; et al. Atmospheric iron deposition: Global distribution, variability, and human perturbations. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2009, 1, 245–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-P.; Ho, T.-Y.; Tsai, I.C. Atmospheric iron deposition in the northwestern Pacific Ocean and its adjacent marginal seas: The importance of coal burning. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 29, 138–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Hamilton, D.S.; Mackey, K.R.M.; Moore, J.K.; Baker, A.R.; Scanza, R.A.; Zhang, Y. Aerosol trace metal leaching and impacts on marine microorganisms. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, K.N.; Moffett, J.; Barbeau, K.A.; Bundy, R.M.; Kondo, Y.; Wu, J. The organic complexation of iron and copper: An intercomparison of competitive ligand exchange-adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry (CLE-ACSV) techniques. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 496–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.; Jickells, T.D.; Baker, A.R.; Artaxo, P.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R.; Bergametti, G.; Bond, T.C.; Chen, Y.; Cohen, D.D.; Herut, B.; et al. Global distribution of atmospheric phosphorus sources, concentrations and deposition rates, and anthropogenic impacts. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2008, 22, GB4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.; Hamilton, D.; Baker, A.R.; Jickells, T.D.; Bromley, T.; Nojiri, Y.; Quack, B.; Boyd, P.W. Western Pacific atmospheric nutrient deposition fluxes, their impact on surface ocean productivity. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 712–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okin, G.S.; Baker, A.R.; Tegen, I.; Mahowald, N.M.; Dentener, F.J.; Duce, R.A.; Galloway, J.N.; Hunter, K.; Kanakidou, M.; Kubilay, N. Impacts of atmospheric nutrient deposition on marine productivity: Roles of nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2011, 25, GB2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yu, J.; Ho, T.Y.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Kong, L.; Liu, H. Dynamics of phytoplankton community structure in the South China Sea in response to the East Asian aerosol input. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1519–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herut, B.; Zohary, T.; Krom, M.D.; Mantoura, R.F.C.; Pitta, P.; Psarra, S.; Rassoulzadegan, F.; Tanaka, T.; Frede Thingstad, T. Response of East Mediterranean surface water to Saharan dust: On-board microcosm experiment and field observations. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2005, 52, 3024–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myriokefalitakis, S.; Nenes, A.; Baker, A.R.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kanakidou, M. Bioavailable atmospheric phosphorous supply to the global ocean: A 3-D global modeling study. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 6519–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, N.; Gao, H.; Baker, A.R.; Yao, X.; Zhang, D. Phosphorus solubility in aerosol particles related to particle sources and atmospheric acidification in Asian continental outflow. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, E.; Dachs, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Simó, R. Atmospheric deposition of organic and black carbon to the global oceans. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7931–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.R.T. Aerosol particles collected on aircraft flights over the northwestern Pacific region during the ACE-Asia campaign: Composition and major sources of the organic compounds. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D19S09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanCuren, R.A. Asian aerosols in North America: Extracting the chemical composition and mass concentration of the Asian continental aerosol plume from long-term aerosol records in the western United States. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, I.; Nunes, S.; Sanchez-Perez, E.D.; Aparicio, F.L.; Estrada, M.; Marrase, C.; Moreno, T.; Wagener, T.; Querol, X.; Peters, F. Anthropogenic versus mineral aerosols in the stimulation of microbial planktonic communities in coastal waters of the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pérez, E.D.; Marín, I.; Nunes, S.; Aparicio, F.L.; Fernández-González, L.; Peters, F.; Pujo-Pay, M.; Conan, P.; Marrasé, C. Aerosol inputs affect the optical signatures of dissolved organic matter in NW Mediterranean coastal waters. Sci. Mar. 2016, 80, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, T.; Chen, Y.-L.L. Different mechanisms controlling interannual phytoplankton variation in the South China Sea and the western North Pacific subtropical gyre: A satellite study. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 52, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-C.; Yao, X.; Gao, H.-W.; Shi, G.-Y.; Yue, X. Variability in the correlation between Asian dust storms and chlorophyll a concentration from the north to equatorial Pacific. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.C.; Shi, G.Y.; Shi, J.H.; Gao, H.W.; Yao, X. Correlation of Asian dust with chlorophyll and primary productivity in the coastal seas of China during the period from 1998 to 2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, G02029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; Lin, N.H.; Sayer, A.M.; Huang, S.J.; Lau, W.K. Can Asian dust trigger phytoplankton blooms in the oligotrophic northern South China Sea? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L05811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.E.; Kim, K.; Macdonald, A.M.; Park, K.T.; Kim, H.C.; Yoo, K.C.; Yoon, H.I.; Yang, E.J.; Jung, J.; Lim, J.H. Spatial and temporal variabilities of spring Asian dust events and their impacts on chlorophyll—A concentrations in the western North Pacific Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.I.; Wong, G.T.F.; Lien, C.-C.; Chien, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-W.; Chen, J.-P. Aerosol impact on the South China Sea biogeochemistry: An early assessment from remote sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-H.; Gao, H.-W.; Zhang, J.; Tan, S.-C.; Ren, J.-L.; Liu, C.-G.; Liu, Y.; Yao, X. Examination of causative link between a spring bloom and dry/wet deposition of Asian dust in the Yellow Sea, China. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D17304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Che, H.; Chen, B. Satellite-observed transport of dust to the East China Sea and the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre: Contribution of dust to the increase in chlorophyll during spring 2010. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-C.; Wang, H. The transport and deposition of dust and its impact on phytoplankton growth in the Yellow Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onitsuka, G.; Uno, I.; Yanagi, T.; Yoon, J.-H. Modeling the effects of atmospheric nitrogen input on biological production in the Japan Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2009, 65, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, P.; Chai, F. Impact of atmospheric deposition on carbon export to the deep ocean in the subtropical northwest Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL089640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-C.; Gong, G.-C.; Chung, W.-C.; Kuo, W.-T.; Lin, F.-C. Enhancement of particulate organic carbon export flux induced by atmospheric forcing in the subtropical oligotrophic northwest Pacific Ocean. Mar. Chem. 2009, 113, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, C.; Gong, X.; Yao, X.; Guo, X.; Gao, H. Promotion Effect of Asian Dust on Phytoplankton Growth and Potential Dissolved Organic Phosphorus Utilization in the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 1101–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Yao, X.; Shi, Z.; Shi, J.; Yu, Y.; Meng, L.; Guo, X. Phytoplankton growth response to Asian dust addition in the northwest Pacific Ocean versus the Yellow Sea. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; He, J.; Yao, X.; Mu, Y.; Guo, X.; Ding, X.; Yu, Y.; Shi, J.; Gao, H. Dynamics of phytoplankton and nutrient uptake following dust additions in the northwest Pacific. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ito, A.; Shi, Z.; Aita, M.N.; Yao, X.; Chu, Q.; Shi, J.; Gong, X.; Gao, H. Fertilization of the northwest Pacific Ocean by East Asia air pollutants. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2019, 33, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman-Frank, I.; Cullen, J.T.; Shaked, Y.; Sherrell, R.M.; Falkowski, P.G. Iron availability, cellular iron quotas, and nitrogen fixation in Trichodesmium. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, P.D.; Moffett, J.W.; Hynes, A.M.; Webb, E.A. Molecular evidence of iron limitation and availability in the global diazotroph Trichodesmium. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohm, J.A.; Webb, E.A.; Capone, D.G. Emerging patterns of marine nitrogen fixation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridame, C.; Guieu, C.; L’Helguen, S. Strong stimulation of N2 fixation in oligotrophic Mediterranean Sea: Results from dust addition in large in situ mesocosms. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7333–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridame, C.; Le Moal, M.; Guieu, C.; Ternon, E.; Biegala, I.C.; L’Helguen, S.; Pujo-Pay, M. Nutrient control of N2 fixation in the oligotrophic Mediterranean Sea and the impact of Saharan dust events. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahav, E.; Cheung, S.-Y.; Guo, C.; Liu, H.; Tsagaraki, T.M.; Giannakourou, A.; Tsiola, A.; Psarra, S.; Lagaria, A.; Mulholland, M.R.; et al. Evaluating the impact of atmospheric depositions on springtime dinitrogen fixation in the Cretan Sea (Eastern Mediterranean)—A mesocosm approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Browning Thomas, J.; Cai, Y.; Dai, R.; Zhang, R.; Du, C.; Jiang, R.; Lin, W.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; et al. Nutrient regulation of biological nitrogen fixation across the tropical western North Pacific. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.R.; Weston, K.; Kelly, S.D.; Voss, M.; Streu, P.; Cape, J.N. Dry and wet deposition of nutrients from the tropical Atlantic atmosphere: Links to primary productivity and nitrogen fixation. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2007, 54, 1704–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.; Berman-Frank, I.; Shaked, Y. Dust- and mineral-iron utilization by the marine dinitrogen-fixer Trichodesmium. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, N.; Armoza-Zvuloni, R.; Wang, S.; Basu, S.; Weber, P.K.; Stuart, R.K.; Shaked, Y. Selective collection of iron-rich dust particles by natural Trichodesmium colonies. ISME J. 2020, 14, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Koedooder, C.; Zhang, F.; Kessler, N.; Eichner, M.; Shi, D.; Shaked, Y. Colonies of the marine cyanobacterium Trichodesmium optimize dust utilization by selective collection and retention of nutrient-rich particles. iScience 2022, 25, 103587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Gledhill, M.; de Beer, D.; Prabhu Matondkar, S.G.; Shaked, Y. Colonies of marine cyanobacteria Trichodesmium interact with associated bacteria to acquire iron from dust. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, S.; Guieu, C.; Chiaverini, J.; Ras, J.; Stock, A. Effect of atmospheric nutrients on the autotrophic communities in a low nutrient, low chlorophyll system. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Liu, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.J. Role of microzooplankton grazing in regulating phytoplankton biomass and community structure in response to atmospheric aerosol input. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 507, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yao, X.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Shi, J.; Gao, H. Variations in the phytoplankton community due to dust additions in eutrophication, LNLC and HNLC oceanic zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Ma, Q.W.; Wang, F.J. Responses of phytoplankton community to the input of different aerosols in the East China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7081–7088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.R.; Shi, J.H.; Gao, H.W.; Yao, X.H. Responses of chlorophyll a to added nutrients, Asian dust, and rainwater in an oligotrophic zone of the Yellow Sea: Implications for promotion and inhibition effects in an incubation experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Q.P.; Wu, Z. Coastal phytoplankton responses to atmospheric deposition during summer. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 66, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.-Y.; Wang, J.-T.; Tan, L.-J.; Dong, Z.-Y. Impact of atmospheric wet deposition on phytoplankton community structure in the South China Sea. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2016, 173, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, K.R.; Buck, K.N.; Casey, J.R.; Cid, A.; Lomas, M.W.; Sohrin, Y.; Paytan, A. Phytoplankton responses to atmospheric metal deposition in the coastal and open-ocean Sargasso Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeveste, P.; Agusti, S.; Tovar-Sanchez, A. Toxic thresholds of cadmium and lead to oceanic phytoplankton: Cell size and ocean basin-dependent effects. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.; Ahlgren, N.; Moffett, J.; Chisholm, S. Copper toxicity and cyanobacteria ecology in the Sargasso Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 976–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, H. Impacts of aerosol copper on marine phytoplankton: A review. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Guo, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, H.; Xia, X.; He, H.; McMinn, A.; Wang, M. Effect of East Asian atmospheric particulate matter deposition on bacterial activity and community structure in the oligotrophic Northwest Pacific. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.-H.; Yang, S.-C.; Ho, T.-Y. Trace metal composition of size-fractionated plankton in the Western Philippine Sea: The impact of anthropogenic aerosol deposition. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 2243–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Z.G.; Gao, H.W.; Mackey, K.R.; Yao, X.H.; Zhuang, G.S.; Paytan, A. Combined effects of iron and copper from atmospheric dry deposition on ocean productivity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2546–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, R.K.; Dupont, C.L.; Johnson, D.A.; Paulsen, I.T.; Palenik, B. Coastal strains of marine Synechococcus species exhibit increased tolerance to copper shock and a distinctive transcriptional response relative to those of open-ocean strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5047–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, N.S.; Jones, G.J.; Nelson, D.M. Effects of copper and zinc on growth, morphology, and metabolism of Asterionella japonica (Cleve). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1981, 51, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.M.; Moore, C.M.; Langlois, R.; Milne, A.; Achterberg, E.; Nachtigall, K.; Lochte, K.; Geider, R.J.; La, R.J. Nitrogen and phosphorus co-limitation of bacterial productivity and growth in the oligotrophic subtropical North Atlantic. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Xia, X.; Pitta, P.; Herut, B.; Rahav, E.; Berman-Frank, I.; Giannakourou, A.; Tsiola, A.; Tsagaraki, T.M.; Liu, H. Shifts in microbial community structure and activity in the ultra-oligotrophic eastern Mediterranean Sea driven by the deposition of Saharan dust and European aerosols. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghdass, M.; Blain, S.; Besseling, M.; Catala, P.; Guieu, C.; Obernosterer, I. Effects of Saharan dust on the microbial community during a large in situ mesocosm experiment in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekunberri, I.; Lefort, T.; Romero, E.; Vazquez-Dominguez, E.; Romera-Castillo, C.; Marrase, C.; Peters, F.; Weinbauer, M.; Gasol, J.M. Effects of a dust deposition event on coastal marine microbial abundance and activity, bacterial community structure and ecosystem function. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marañén, E.; Fernández, A.; Mouriño-Carballido, B.; MartÍnez-GarcÍa, S.; Teira, E.; Cermeño, P.; Chouciño, P.; Huete-Ortega, M.; Fernández, E.; Calvo-DÍaz, A.; et al. Degree of oligotrophy controls the response of microbial plankton to Saharan dust. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 2339–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Beltran, I.; Logue, J.B.; Andersson, A.F.; Peters, F. Atmospheric deposition impact on bacterial community composition in the NW Mediterranean. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahav, E.; Belkin, N.; Paytan, A.; Herut, B. Phytoplankton and bacterial response to desert dust deposition in the coastal waters of the southeastern Mediterranean Sea: A four-year in situ survey. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, I.; Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Romera, O.; Villena, E.P.; Baquero, R.M.; Casamayor, E.O. Effect of Saharan dust inputs on bacterial activity and community composition in Mediterranean lakes and reservoirs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Jing, H.; Kong, L.; Liu, H. Effect of East Asian aerosol enrichment on microbial community composition in the South China Sea. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maki, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Kobayashi, F.; Kakikawa, M.; Aoki, K.; Mastunaga, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Iwasaka, Y. Effects of Asian dust (KOSA) deposition event on bacterial and microalgal communities in the Pacific Ocean. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 5, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Mastunaga, T.; Pointing, S.B.; Saito, Y.; Kasai, T.; Watanabe, K.; Aoki, K.; Horiuchi, A.; Lee, K.C.; et al. Atmospheric aerosol deposition influences marine microbial communities in oligotrophic surface waters of the western Pacific Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 118, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahav, E.; Paytan, A.; Mescioglu, E.; Bar-Zeev, E.; Martínez Ruiz, F.; Xian, P.; Herut, B. Bio-aerosols negatively affect Prochlorococcus in oligotrophic aerosol-rich marine regions. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinasquet, J.; Bigeard, E.; Gazeau, F.; Azam, F.; Guieu, C.; Maranon, E.; Ridame, C.; Wambeke, F.; Obernosterer, I.; Baudoux, A.C. Impact of dust addition on the microbial food web under present and future conditions of pH and temperature. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 1303–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samset, B.H.; Lund, M.T.; Bollasina, M.; Myhre, G.; Wilcox, L. Emerging Asian aerosol patterns. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Area | Stations | Trophic State | Type of Atmospheric Input | Amendment Concentration (Dry Deposition: mg/L; Wet Deposition: mL/L) | Response Ratio of Chl a Concentration | Beneficial Phytoplankton Taxa | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry deposition | SCS | A3, A6 | mesotrophic | Dust (Qingdao, TSP) | 1.09 | ↑2.1–2.9 | ↑Chaetoceros spp. | [85] |
| WG2 | oligotrophic | Dust (Qingdao, TSP) | 1.09 | ↑3 | ↑Nitzschia spp. | |||
| SCS | PM7, C3a, A1 | mesotrophic | Aerosol (Hong Kong, PM2.5) | 0.019 0.19 | → ↑1.7–2.5 | Pico- and nano-→ micro-phytoplankton | [64] | |
| SEATs | oligotrophic | Aerosol (Hong Kong, PM2.5) | 0.019 0.19 | → ↑3.5 | ||||
| YS | A2 | mesotrophic | Dust (Qingdao, TSP) | 2 20 | → ↑1.4 | Pico-and nano- → micro-phytoplankton | [105] | |
| ECS | ECS | eutrophic | Mineral dust (Huaniao Island, TSP) | 1 | ↑3 | ↑Haptophyceae | [104] | |
| Aerosol (Huaniao Island, TSP) | 1 | ↑2 | ||||||
| Secondary aerosol (Huaniao Island, TSP) | 1 | ↑1.8 | ↑Bacillarophyceae, Dinophyceae, Cryptophyceae | |||||
| Kuroshio Extension (KE) | M1 | mesotrophic | Dust (Tengger Desert, soil dust) | 0.5 | ↑1.8 | Pico- → nano- and micro-phytoplankton | [87] | |
| M1B | mesotrophic | 0.5 1 | ↑2.5 ↑3 | |||||
| Kuroshio-Oyashio transition region (TR) | E10M | eutrophic | Dust (Tengger Desert, soil dust) | 0.3 0.5 1 | ↑1.5 ↑1.7 ↑2.3 | |||
| E2 | mesotrophic | 0.3 0.5 1 | ↑2.3 ↑2.8 ↑4.5 | |||||
| S-NWPO | Ar4, G7 | mesotrophic | Haze particles (Qingdao, TSP) | 2 | ↓0.3–0.8 | Pico- → nano- and micro-phytoplankton | [103] | |
| Kuroshio Extension (KE) | M1B | mesotrophic | Haze particles (Qingdao, TSP) | 0.03 0.06 | ↑2.1 ↑2.6 | |||
| M1 | mesotrophic | Haze particles (Qingdao, TSP) | 0.1 0.3 0.6 | ↑1.1 ↑2.0 ↑2.9 | ||||
| S-NWPO | A1-b | mesotrophic | Haze particles (Qingdao, TSP) | 0.4 | ↑2.7 | |||
| YS | H10, B7 | eutrophic | Haze particles (Qingdao, TSP) | 2 | ↓0.6 | |||
| YS1 | mesotrophic | Haze particles (Qingdao, TSP) | 0.05 0.1 | → | ||||
| ECS | PN3 | eutrophic | Haze particles (Qingdao, TSP) | 0.4 | → | |||
| S-NWPO | Ar4, G7, K4 | mesotrophic | Treated soil dust (Gobi Desert, surface soil) | 2 | ↑1.3–2.8 | Pico- → nano- or micro-phytoplankton | [86] | |
| YS | B7, H10 | eutrophic | Treated soil dust (Gobi Desert, surface soil) | 2 | → | |||
| S-NWPO | A1-b | mesotrophic | Dust (Mu Us Desert, soil) | 0.2 1 | ↑1.5 ↑2.8 | Pico- → nano- and micro-phytoplankton | [88] | |
| Kuroshio-Oyashio transition region (TR) | B1 | mesotrophic | Dust (Mu Us Desert, soil) | 0.2 1 2 | → ↑2.0 ↑2.0 | |||
| ECS | C1 | eutrophic | Dust (Mu Us Desert, soil) | 0.2 1 2 | → ↑1.4 ↑1.6 | |||
| SCS | A7, B2 | eutrophic | Aerosols (Guangzhou, TSP) | 3.3 | ↑1.2–1.9 | Pico- → micro-phytoplankton | [106] | |
| C4, A13, B6 C8 | mesotrophic | Aerosols (Guangzhou, TSP) | 3.3 | ↑1.2–2.5 ↓0.3 | ||||
| Wet deposition | SCS | A3, A6 | Mesotrophic | Rainwater (SCS) | 0.4 | → | [85] | |
| WG2 | oligotrophic | Rainwater (SCS) | 0.4 | ↑3 | ||||
| SCS | R | mesotrophic | Rainwater (SCS R) | 50 100 | ↑1.7 ↑1.9 | Pico- → micro- phytoplankton | [107] | |
| 0.7 μm filtered Rainwater (SCS R) | 100 | ↑1.6 | ||||||
| YS | A2 | mesotrophic | Rainwater (SYS) | 2 | ↑1.9 | ↓Nano-phytoplanton | [105] | |
| SCS | A7, B2 | mesotrophic | Rainwater (Shanwei) | 100 | ↑2–2.5 | Pico- → nano- and micro-phytoplankton | [106] | |
| C4 C8 | mesotrophic | Rainwater (Shanwei) | 100 | ↑2.5 ↓0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, H.; Su, C.; Kong, L. Aerosol Nutrients and Their Biological Influence on the Northwest Pacific Ocean (NWPO) and Its Marginal Seas. Biology 2022, 11, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060842
Guo C, Zhou Y, Zhou H, Su C, Kong L. Aerosol Nutrients and Their Biological Influence on the Northwest Pacific Ocean (NWPO) and Its Marginal Seas. Biology. 2022; 11(6):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060842
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Cui, Yao Zhou, Hongyan Zhou, Chang Su, and Liangliang Kong. 2022. "Aerosol Nutrients and Their Biological Influence on the Northwest Pacific Ocean (NWPO) and Its Marginal Seas" Biology 11, no. 6: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060842
APA StyleGuo, C., Zhou, Y., Zhou, H., Su, C., & Kong, L. (2022). Aerosol Nutrients and Their Biological Influence on the Northwest Pacific Ocean (NWPO) and Its Marginal Seas. Biology, 11(6), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060842






