Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Signaling at the Skin Barrier Interface
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
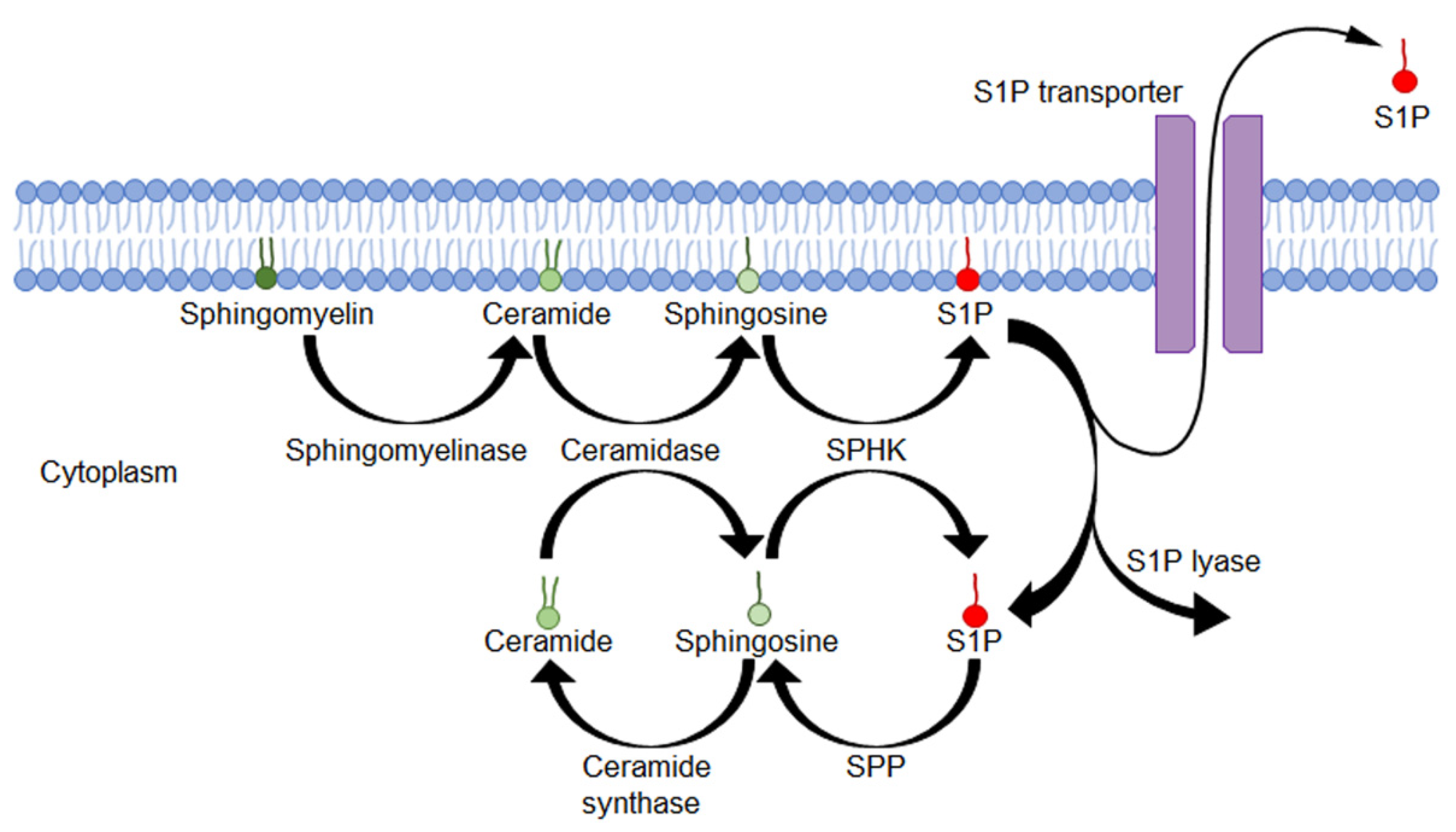
2. S1P Formulation and Secretion
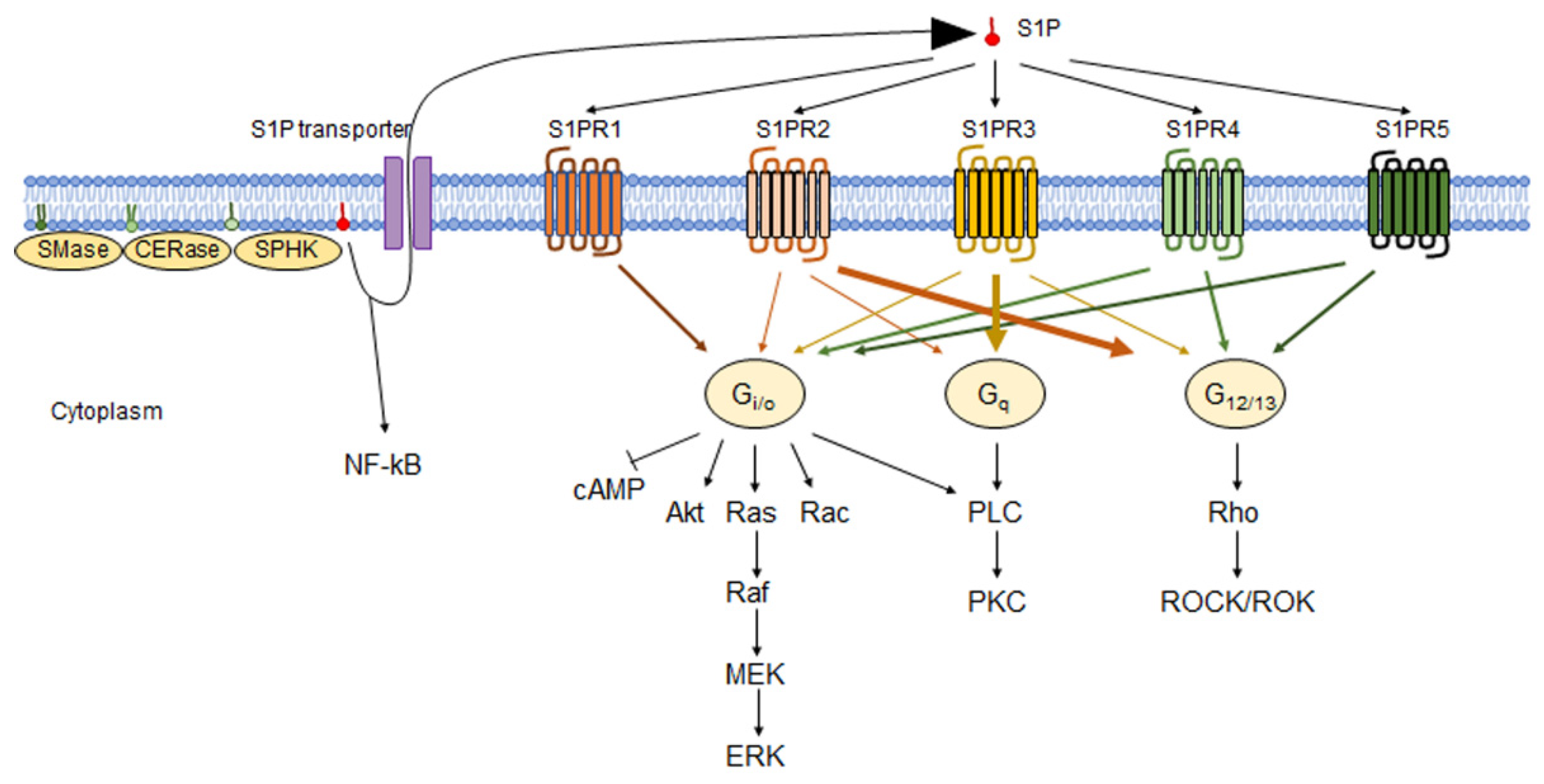
3. S1P Receptors
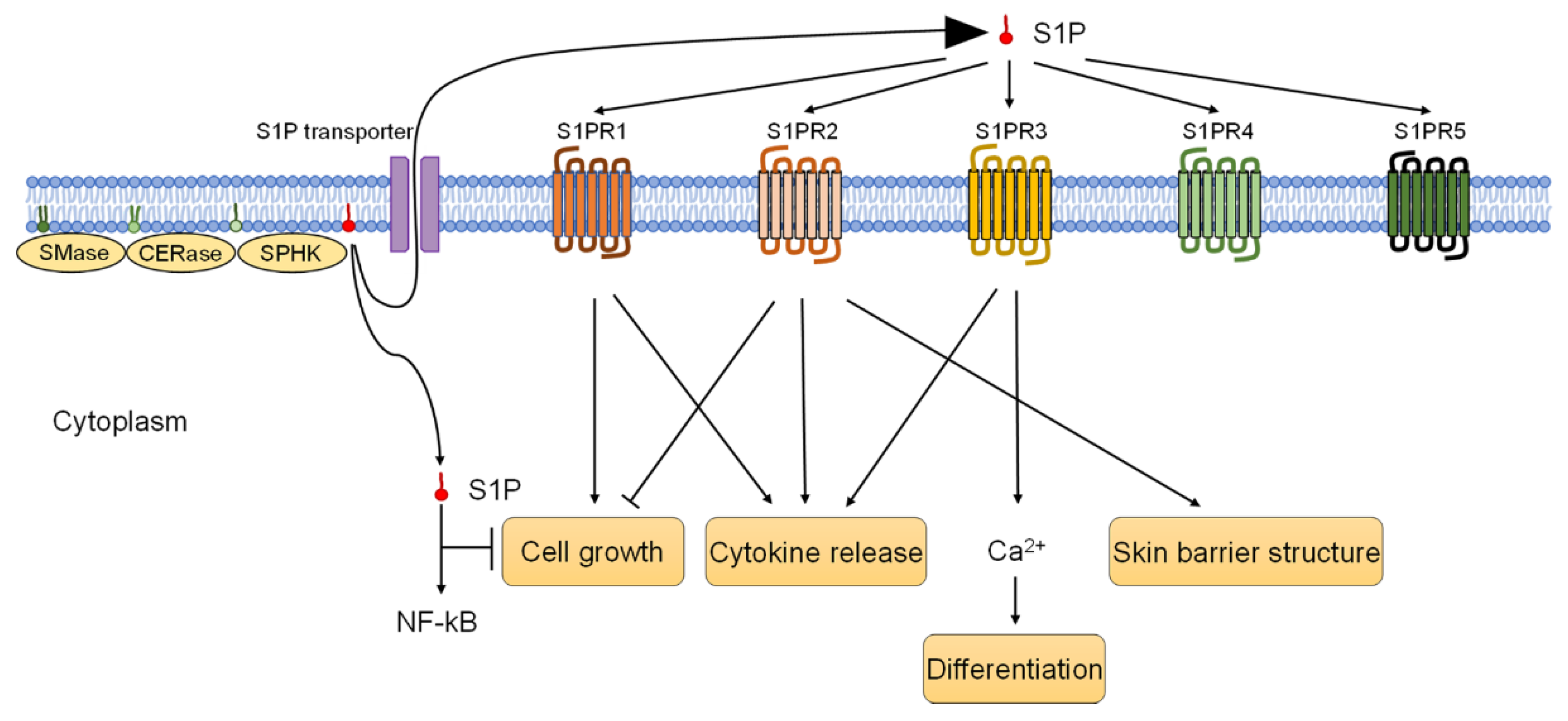
4. S1P and S1P-S1PR Pathways on Human Keratinocytes
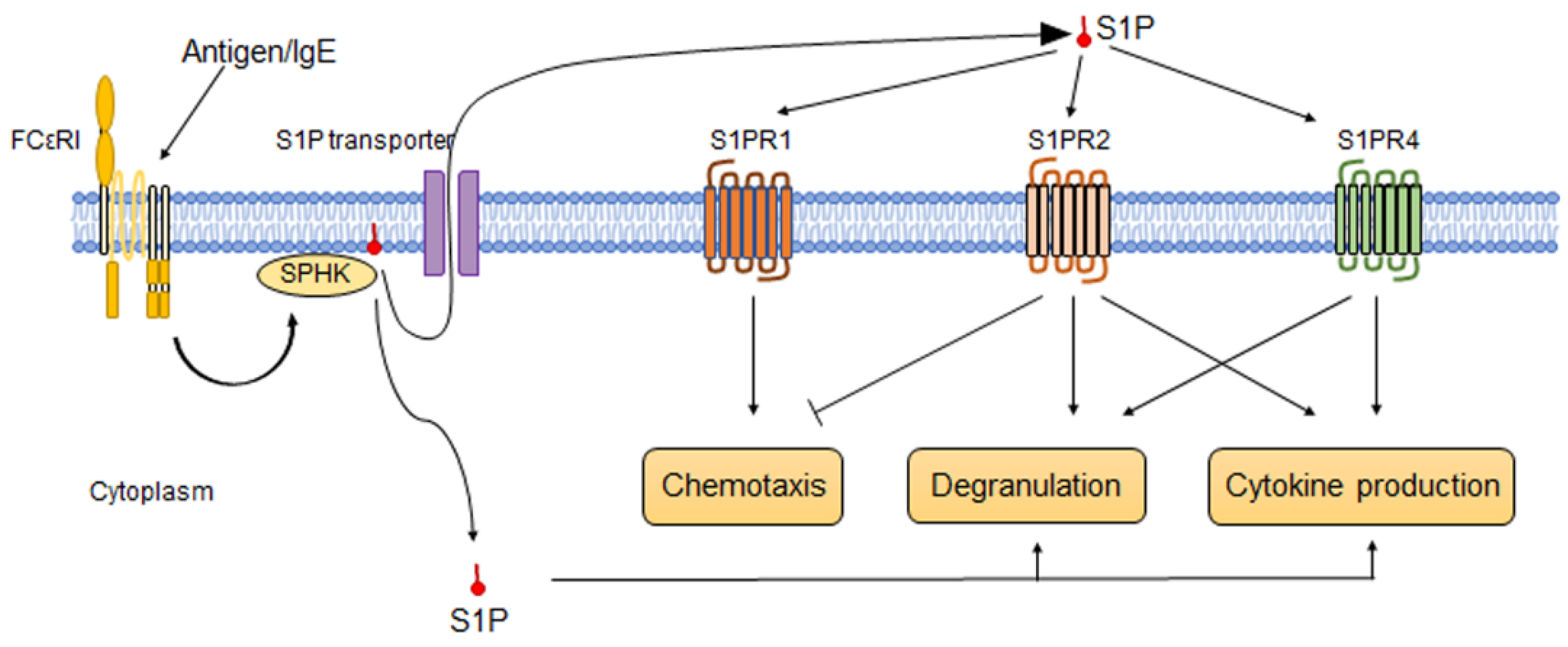
5. S1P and S1P-S1PR Pathways on Human Mast Cells
6. S1P-S1PR Signaling and Skin Diseases
7. S1P and S1PR Modulators for Skin Diseases
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spiegel, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate: A ligand for the EDG-1 family of G-protein-coupled receptors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 905, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, J.; Proia, R.L.; Olivera, A. The alliance of sphingosine-1-phosphate and its receptors in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Desai, N.N.; Olivera, A.; Seki, T.; Brooker, G.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a novel lipid, involved in cellular proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 114, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, T.; Hla, T. Structural and functional characteristics of S1P receptors. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 92, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, M.; Aoki, H.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Tsuge, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsumoto, N.M.; Toyohara, E.; Okubo, Y.; Ogawa, R.; Takabe, K. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Facilitates Skin Wound Healing by Increasing Angiogenesis and Inflammatory Cell Recruitment with Less Scar Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Qi, D.; Xu, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Shang, Z.; Zhang, G. The S1PR1 agonist SEW2871 promotes the survival of skin flap. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieschl, E.E.; Csonga, R.; Novotny, V.; Kikuchi, G.E.; Baumruker, T. The balance between sphingosine and sphingosine-1-phosphate is decisive for mast cell activation after Fc epsilon receptor I triggering. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolly, P.S.; Rosenfeldt, H.M.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. The roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate in asthma. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 38, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper, K.; Dickhaut, J.; Japtok, L.; Kietzmann, M.; Mischke, R.; Kleuser, B.; Baumer, W. Sphingosine-1-phosphate exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects in mouse models of psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 71, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Cho, K.A.; Hahn, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Woo, S.Y.; Ryu, K.H.; Park, W.J.; Park, J.W. Inhibiting Sphingosine Kinase 2 Derived-sphingosine-1-phosphate Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Disease via Blocking Th17 Differentiation of Naive CD4 T Lymphocytes in Mice. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2019, 99, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Japtok, L.; Bäumer, W.; Kleuser, B. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as signaling molecule in the skin: Relevance in atopic dermatitis. Allergo J. Int. 2014, 23, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kano, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Date, M.; Tennichi, M.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Strasser, D.S.; Takehara, K.; Matsushita, T. Attenuation of murine sclerodermatous models by the selective S1P1 receptor modulator cenerimod. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igawa, S.; Choi, J.E.; Wang, Z.; Chang, Y.L.; Wu, C.C.; Werbel, T.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Di Nardo, A. Human Keratinocytes Use Sphingosine 1-Phosphate and its Receptors to Communicate Staphylococcus aureus Invasion and Activate Host Defense. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1743–1752.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igawa, S.; Ohzono, A.; Pham, P.; Wang, Z.; Nakatsuji, T.; Dokoshi, T.; Di Nardo, A. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 2 Is Central to Maintaining Epidermal Barrier Homeostasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1188–1197.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Mannaerts, G.P. Subcellular localization and membrane topology of sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase in rat liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 12502–12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peest, U.; Sensken, S.C.; Andréani, P.; Hänel, P.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Gräler, M.H. S1P-lyase independent clearance of extracellular sphingosine 1-phosphate after dephosphorylation and cellular uptake. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 756–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatomi, Y.; Igarashi, Y.; Yang, L.; Hisano, N.; Qi, R.; Asazuma, N.; Satoh, K.; Ozaki, Y.; Kume, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate, a bioactive sphingolipid abundantly stored in platelets, is a normal constituent of human plasma and serum. J. Biochem. 1997, 121, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Sato, K.; Kuwabara, A.; Tomura, H.; Ishiwara, M.; Kobayashi, I.; Ui, M.; Okajima, F. Sphingosine 1-phosphate may be a major component of plasma lipoproteins responsible for the cytoprotective actions in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31780–31785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappu, R.; Schwab, S.R.; Cornelissen, I.; Pereira, J.P.; Regard, J.B.; Xu, Y.; Camerer, E.; Zheng, Y.W.; Huang, Y.; Cyster, J.G.; et al. Promotion of lymphocyte egress into blood and lymph by distinct sources of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 2007, 316, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, K.; Lee, Y.M.; Michaud, J.; Thangada, S.; Ai, Y.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Parikh, N.S.; Habrukowich, C.; Hla, T. Vascular endothelium as a contributor of plasma sphingosine 1-phosphate. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olivera, A.; Mizugishi, K.; Tikhonova, A.; Ciaccia, L.; Odom, S.; Proia, R.L.; Rivera, J. The sphingosine kinase-sphingosine-1-phosphate axis is a determinant of mast cell function and anaphylaxis. Immunity 2007, 26, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, K.; Elias, P.M.; Shin, K.O.; Lee, Y.M.; Hupe, M.; Borkowski, A.W.; Gallo, R.L.; Saba, J.; Holleran, W.M.; Uchida, Y. A novel role of a lipid species, sphingosine-1-phosphate, in epithelial innate immunity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.J.; Van Brocklyn, J.R.; Thangada, S.; Liu, C.H.; Hand, A.R.; Menzeleev, R.; Spiegel, S.; Hla, T. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1. Science 1998, 279, 1552–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Takuwa, N.; Gonda, K.; Okazaki, H.; Chang, K.; Yatomi, Y.; Shigematsu, H.; Takuwa, Y. EDG1 is a functional sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor that is linked via a Gi/o to multiple signaling pathways, including phospholipase C activation, Ca2+ mobilization, Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, and adenylate cyclase inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27104–27110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonda, K.; Okamoto, H.; Takuwa, N.; Yatomi, Y.; Okazaki, H.; Sakurai, T.; Kimura, S.; Sillard, R.; Harii, K.; Takuwa, Y. The novel sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor AGR16 is coupled via pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive G-proteins to multiple signalling pathways. Biochem. J. 1999, 337 Pt 1, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Takuwa, N.; Yatomi, Y.; Gonda, K.; Shigematsu, H.; Takuwa, Y. EDG3 is a functional receptor specific for sphingosine 1-phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine with signaling characteristics distinct from EDG1 and AGR16. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 260, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takuwa, Y. Subtype-specific differential regulation of Rho family G proteins and cell migration by the Edg family sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2002, 1582, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodemote, K.A.; Mattie, M.E.; Berger, A.; Spiegel, S. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein in the mitogenic signaling pathways of sphingosine 1-phosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 10272–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.J.; Thangada, S.; Liu, C.H.; Thompson, B.D.; Hla, T. Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates the G-protein-coupled receptor EDG-1 as a low affinity agonist. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 22105–22112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obinata, H.; Hla, T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and inflammation. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzikonstantinou, S.; Poulidou, V.; Arnaoutoglou, M.; Kazis, D.; Heliopoulos, I.; Grigoriadis, N.; Boziki, M. Signaling through the S1P-S1PR axis in the Gut, the Immune and the Central Nervous System in Multiple Sclerosis: Implication for Pathogenesis and Treatment. Cells 2021, 10, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: An enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Takuwa, N.; Yokomizo, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Sakurada, S.; Shigematsu, H.; Takuwa, Y. Inhibitory regulation of Rac activation, membrane ruffling, and cell migration by the G protein-coupled sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor EDG5 but not EDG1 or EDG3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 9247–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Jia, G.; Wu, C.; Wang, W.; Cheng, L.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Luo, K.; Yang, S.; Yan, W.; et al. Structures of signaling complexes of lipid receptors S1PR1 and S1PR5 reveal mechanisms of activation and drug recognition. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, I.; Fukushima, N.; Ye, X.; Chun, J. Lysophospholipid receptors: Signaling and biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 321–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, N.; Takuwa, N.; Okamoto, H.; Sakurada, S.; Takuwa, Y. Inhibitory and stimulatory regulation of Rac and cell motility by the G12/13-Rho and Gi pathways integrated downstream of a single G protein-coupled sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor isoform. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, M.; Urbano, M.; Velaparthi, S.; Schaeffer, M.T.; Brown, S.J.; Crisp, M.; Ferguson, J.; Hodder, P.; Rosen, H.; Oldstone, M.; et al. Identification of a Novel Agonist of the Sphingosine 1-phosphate Receptor 4 (S1P4). In Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vogler, R.; Sauer, B.; Kim, D.S.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kleuser, B. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and its potentially paradoxical effects on critical parameters of cutaneous wound healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kleuser, B.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.C. Sphingosine-1-phosphate inhibits human keratinocyte proliferation via Akt/protein kinase B inactivation. Cell. Signal. 2004, 16, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichte, K.; Rossi, R.; Danneberg, K.; ter Braak, M.; Kürschner, U.; Jakobs, K.H.; Kleuser, B.; Meyer zu Heringdorf, D. Lysophospholipid receptor-mediated calcium signaling in human keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uchida, Y.; Houben, E.; Park, K.; Douangpanya, S.; Lee, Y.M.; Wu, B.X.; Hannun, Y.A.; Radin, N.S.; Elias, P.M.; Holleran, W.M. Hydrolytic pathway protects against ceramide-induced apoptosis in keratinocytes exposed to UVB. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriue, T.; Igarashi, J.; Yoneda, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Nakai, K.; Kosaka, H.; Kubota, Y. Sphingosine 1-phosphate attenuates peroxide-induced apoptosis in HaCaT cells cultured in vitro. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 38, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Elias, P.M.; Hupe, M.; Borkowski, A.W.; Gallo, R.L.; Shin, K.O.; Lee, Y.M.; Holleran, W.M.; Uchida, Y. Resveratrol stimulates sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling of cathelicidin production. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, K.; Ikushiro, H.; Seo, H.S.; Shin, K.O.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Yano, T.; Holleran, W.M.; Elias, P.; et al. ER stress stimulates production of the key antimicrobial peptide, cathelicidin, by forming a previously unidentified intracellular S1P signaling complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1334–E1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.K.; Kim, Y.I.; Shin, K.O.; Kim, B.W.; Lee, S.H.; Jeon, J.E.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Mauro, T.M.; Elias, P.M.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 activation enhances epidermal innate immunity through sphingosine-1-phosphate stimulation of cathelicidin production. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 79, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, K.O.; Kim, K.P.; Cho, Y.; Kang, M.K.; Kang, Y.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Ikushiro, H.; Yokota, M.; Yano, T.; Choe, S.J.; et al. Both Sphingosine Kinase 1 and 2 Coordinately Regulate Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide Production during Keratinocyte Differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oizumi, A.; Nakayama, H.; Okino, N.; Iwahara, C.; Kina, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Ogawa, H.; Takamori, K.; Ito, M.; Suga, Y.; et al. Pseudomonas-derived ceramidase induces production of inflammatory mediators from human keratinocytes via sphingosine-1-phosphate. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herzinger, T.; Kleuser, B.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Korting, H.C. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and the skin. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 8, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.O.; Choe, S.J.; Uchida, Y.; Kim, I.; Jeong, Y.; Park, K. Ginsenoside Rb1 Enhances Keratinocyte Migration by a Sphingosine-1-Phosphate-Dependent Mechanism. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüppel, M.; Kürschner, U.; Kleuser, U.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Kleuser, B. Sphingosine 1-phosphate restrains insulin-mediated keratinocyte proliferation via inhibition of Akt through the S1P2 receptor subtype. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, E.I.; Potteck, H.; Schüppel, M.; Manggau, M.; Wahydin, E.; Kleuser, B. Sphingosine 1-phosphate protects primary human keratinocytes from apoptosis via nitric oxide formation through the receptor subtype S1P3. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 371, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yin, X.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Q. The lncRNA H19/miR-766-3p/S1PR3 Axis Contributes to the Hyperproliferation of Keratinocytes and Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis via the AKT/mTOR Pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9991175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, P.S.; Bektas, M.; Olivera, A.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C.; Proia, R.L.; Rivera, J.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Transactivation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors by FcepsilonRI triggering is required for normal mast cell degranulation and chemotaxis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Resh, M.D. Fyn, a Src family tyrosine kinase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 30, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, A.; Urtz, N.; Mizugishi, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Gilfillan, A.M.; Furumoto, Y.; Gu, H.; Proia, R.L.; Baumruker, T.; Rivera, J. IgE-dependent activation of sphingosine kinases 1 and 2 and secretion of sphingosine 1-phosphate requires Fyn kinase and contributes to mast cell responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2515–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitra, P.; Oskeritzian, C.A.; Payne, S.G.; Beaven, M.A.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Role of ABCC1 in export of sphingosine-1-phosphate from mast cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16394–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dillahunt, S.E.; Sargent, J.L.; Suzuki, R.; Proia, R.L.; Gilfillan, A.; Rivera, J.; Olivera, A. Usage of sphingosine kinase isoforms in mast cells is species and/or cell type determined. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oskeritzian, C.A.; Alvarez, S.E.; Hait, N.C.; Price, M.M.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Distinct roles of sphingosine kinases 1 and 2 in human mast-cell functions. Blood 2008, 111, 4193–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.M.; Kapitonov, D.; Allegood, J.; Milstien, S.; Oskeritzian, C.A.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces development of functionally mature chymase-expressing human mast cells from hematopoietic progenitors. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3506–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivera, A.; Kitamura, Y.; Wright, L.D.; Allende, M.L.; Chen, W.; Kaneko-Goto, T.; Yoshihara, Y.; Proia, R.L.; Rivera, J. Sphingosine-1-phosphate can promote mast cell hyper-reactivity through regulation of contactin-4 expression. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saluja, R.; Kumar, A.; Jain, M.; Goel, S.K.; Jain, A. Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Mast Cell Functions and Asthma and Its Regulation by Non-Coding RNA. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulinski, J.M.; Proia, R.L.; Larson, E.M.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Olivera, A. S1P4 Regulates Passive Systemic Anaphylaxis in Mice but Is Dispensable for Canonical IgE-Mediated Responses in Mast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoo, E.; Yatomi, Y.; Takafuta, T.; Osada, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Ozaki, Y. Sphingosine 1-phosphate inhibits migration of RBL-2H3 cells via S1P2: Cross-talk between platelets and mast cells. J. Biochem. 2004, 135, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, A.; Rivera, J. Sphingolipids and the balancing of immune cell function: Lessons from the mast cell. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, W.J.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, J.H.; Im, D.S. Suppressive Effect of CYM50358 S1P(4) Antagonist on Mast Cell Degranulation and Allergic Asthma in Mice. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, N.; Limberg, M.M.; Brauer, A.U.; Raap, U. Novel functions of S1P in chronic itchy and inflammatory skin diseases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japtok, L.; Schaper, K.; Bäumer, W.; Radeke, H.H.; Jeong, S.K.; Kleuser, B. Sphingosine 1-phosphate modulates antigen capture by murine Langerhans cells via the S1P2 receptor subtype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49427. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.J.; Im, D.S. Blockage of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 attenuates 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.N.; Raue, R.; Weigert, A.; von Knethen, A.; Brune, B. Macrophage S1PR1 Signaling Alters Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis during Skin Inflammation. Cells 2019, 8, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jena, P.K.; Sheng, L.; McNeil, K.; Chau, T.Q.; Yu, S.; Kiuru, M.; Fung, M.A.; Hwang, S.T.; Wan, Y.Y. Long-term Western diet intake leads to dysregulated bile acid signaling and dermatitis with Th2 and Th17 pathway features in mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 95, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, C.; Huard, A.; Sirait-Fischer, E.; Dillmann, C.; Brune, B.; Weigert, A. S1PR4-dependent CCL2 production promotes macrophage recruitment in a murine psoriasis model. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skon, C.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Anderson, K.G.; Masopust, D.; Hogquist, K.A.; Jameson, S.C. Transcriptional downregulation of S1pr1 is required for the establishment of resident memory CD8+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evrard, M.; Wynne-Jones, E.; Peng, C.; Kato, Y.; Christo, S.N.; Fonseca, R.; Park, S.L.; Burn, T.N.; Osman, M.; Devi, S.; et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 5 (S1PR5) regulates the peripheral retention of tissue-resident lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20210116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, O.; Küry, P.; Kieseier, B.; Hartung, H.P. Fingolimod is a potential novel therapy for multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Billich, A.; Baumruker, T.; Heining, P.; Schmouder, R.; Francis, G.; Aradhye, S.; Burtin, P. Fingolimod (FTY720): Discovery and development of an oral drug to treat multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobel, K.; Monnier, L.; Menyhart, K.; Bolinger, M.; Studer, R.; Nayler, O.; Gatfield, J. FTY720 Phosphate Activates Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 2 and Selectively Couples to Gα12/13/Rho/ROCK to Induce Myofibroblast Contraction. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 87, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugita, K.; Kabashima, K.; Sakabe, J.; Yoshiki, R.; Tanizaki, H.; Tokura, Y. FTY720 regulates bone marrow egress of eosinophils and modulates late-phase skin reaction in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Iwatsuki, R.; Inoue, M.; Fujita, T.; Kohno, T. Therapeutic approach to steroid-resistant dermatitis using novel immunomodulator FTY720 (Fingolimod) in combination with betamethasone ointment in NC/Nga mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohno, T.; Tsuji, T.; Hirayama, K.; Watabe, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Kohno, T.; Fujita, T. A novel immunomodulator, FTY720, prevents spontaneous dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1392–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.Y.; Dimasi, D.P.; Pitman, M.R.; Zhuang, Y.; Heddle, R.; Pitson, S.M.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Bonder, C.S. Topical Application of Fingolimod Perturbs Cutaneous Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3854–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reines, I.; Kietzmann, M.; Mischke, R.; Tschernig, T.; Lüth, A.; Kleuser, B.; Bäumer, W. Topical application of sphingosine-1-phosphate and FTY720 attenuate allergic contact dermatitis reaction through inhibition of dendritic cell migration. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamakuwala, M.; Ratna, W.; Joshi, A.; Stagni, G. Fingolimod hydrochloride gel shows promising therapeutic effects in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okura, I.; Kamata, M.; Asano, Y.; Mitsui, A.; Shimizu, T.; Sato, S.; Tada, Y. Fingolimod ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasiform dermatitis by sequestrating interleukin-17-producing ?d T cells in secondary lymph nodes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2021, 102, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao-Draayer, Y.; Sarazin, J.; Fox, D.; Schiopu, E. The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor: A novel therapeutic target for multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 175, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Valle, F.; Gray, E.E.; Cyster, J.G. Inflammation induces dermal Vγ4+ γδT17 memory-like cells that travel to distant skin and accelerate secondary IL-17-driven responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8046–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, F.; Cao, X.; Hu, Z.; Ma, D.; Guo, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Qu, S.; Zhu, J.; et al. Pleiotropic FTY720 Is a Specific and Potent Therapy for Hypertrophic Scars. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, M.; Xue, N.; Lai, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Chen, X. Validating a Selective S1P(1) Receptor Modulator Syl930 for Psoriasis Treatment. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaclavkova, A.; Chimenti, S.; Arenberger, P.; Holló, P.; Sator, P.G.; Burcklen, M.; Stefani, M.; D’Ambrosio, D. Oral ponesimod in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.; Foley, D.; Naylor, C.; Robinson, C.; Riley, J.; Epemolu, O.; Scullion, P.; Shishikura, Y.; Katz, E.; McLean, W.H.I.; et al. Discovery of super soft-drug modulators of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3255–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.; Foley, D.; Naylor, C.; Wood, G.; Robinson, C.; Riley, J.; Epemolu, O.; Ellis, L.; Scullion, P.; Shishikura, Y.; et al. Discovery of Soft-Drug Topical Tool Modulators of Sphingosine-1-phosphate Receptor 1 (S1PR1). ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Xue, N.; Liu, Y.; Fu, R.; Wang, M.; Ji, M.; Lai, F.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Q.; et al. A novel S1P1 modulator IMMH002 ameliorates psoriasis in multiple animal models. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoon, H.S.; Park, W.J.; Adams, D.R.; Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S.; Park, J.W. A Novel Selective Sphingosine Kinase 2 Inhibitor, HWG-35D, Ameliorates the Severity of Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis Model by Blocking Th17 Differentiation of Naïve CD4 T Lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masuda-Kuroki, K.; Di Nardo, A. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Signaling at the Skin Barrier Interface. Biology 2022, 11, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060809
Masuda-Kuroki K, Di Nardo A. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Signaling at the Skin Barrier Interface. Biology. 2022; 11(6):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060809
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasuda-Kuroki, Kana, and Anna Di Nardo. 2022. "Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Signaling at the Skin Barrier Interface" Biology 11, no. 6: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060809
APA StyleMasuda-Kuroki, K., & Di Nardo, A. (2022). Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Signaling at the Skin Barrier Interface. Biology, 11(6), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11060809





