Simple Summary
Blastocystis is a neglected enteric pathogen that is highly prevalent in humans and animals worldwide. Studies have reported that Blastocystis infection frequently coexists with other infectious pathogens in humans. However, dual infection by Blastocystis and Echinococcus multilocularis, which causes the severe parasitic disease echinococcosis has not been reported. In this study, the authors investigated the clinical prevalence, risk factors, and genotypes of Blastocystis in Tibetan patients with liver echinococcosis and Tibetan healthy controls from the Qinghai province in China, and also tested whether E. multilocularis infection increases host susceptibility to Blastocystis using a mouse model. The results found a significantly higher prevalence of genetically divergent Blastocystis in Tibetans with liver echinococcosis. E. multilocularis infection in Balb/c mice increased the host susceptibility to Blastocystis and aggravated intestinal pathology with higher disease severity and higher mortality. Taken together, these findings provide new insights into dual infections by Blastocystis and helminths in humans.
Abstract
Blastocystis is a common human intestinal protozoan parasite. Little is known about its prevalence in echinococcosis. This study tested whether Echinococcus multilocularis infection would increase host susceptibility to Blastocystis. A total of 114 fecal samples (68 hydatid disease patients and 46 healthy people) were collected from Tibetans in the Qinghai province in China. The presence of Blastocystis was identified by sequencing of the small subunit (SSU) rRNA gene. Balb/c mice were co-infected with Blastocystis and E. multilocularis and tested for host susceptibility to Blastocystis. The overall Blastocystis prevalence was 12.3%; 16.2% in the patients and 4.4% in healthy people (p < 0.05). Sequence analysis identified three known Blastocystis genotypes, including ST1, ST2, and ST3, and one unknown genotype. Experimental dual infection significantly reduced mouse survival rate (20%), induced more severe signs, and increased intestinal damages with a higher intestinal colonization level of Blastocystis. The mouse model showed that E. multilocularis infection increases host susceptibility to Blastocystis. Our study shows a significantly higher prevalence of Blastocystis in patients with liver echinococcosis and reveals that non-intestinal E. multilocularis infection increases host susceptibility to the Blastocystis. Our results highlight that E. multilocularis infection is associated with Blastocystis. These findings remind us that more attention should be paid to the gut health of the patients with a helminth infection during clinical patient care.
1. Introduction
Blastocystis is one of the most common intestinal organisms found in humans worldwide. This parasite is genetically diverse with at least 22 identified valid genotypes, 10 of which (ST1-ST9 and ST12) have been reported in humans and animals [1,2,3]. Hosts are usually infected with Blastocystis via the fecal–oral route through the ingestion of contaminated water or food [4,5]. Today, Blastocystis is a common part of the healthy gut microbiota [6,7]. However, intestinal symptoms may emerge in presence of Blastocystis, and thus it may be considered pathogenic when other agents are eliminated [8]. Infection with Blastocystis has been reported to coincide with other parasitic diseases, and to be more common in patients with immune deficiency or chronic immunosuppression than in healthy people [9,10]. Chronic helminth infections typically induce suppression of host immunity [11]. Thus, helminth diseases can potentially increase the risk of Blastocystis infection in the gut. However, we still know little about dual infection prevalence and causal mechanisms with Blastocystis and helminths. Moreover, whether a chronic helminth infection can exacerbate Blastocystis infection pathogenesis remains unknown.
Among the most severe of the zoonotic helminth diseases, hydatid disease (echinococcosis), which includes alveolar echinococcosis (AE) and cystic echinococcosis (CE), represents a substantial disease burden; globally, AE and CE are the second and third most important food-borne parasitic diseases, respectively [12]. The worldwide prevalence of hydatid disease is estimated at 1 million with an annual incidence of 200,000 [13]. Each year, hydatid disease is estimated to claim 19,300 lives and result in around 871,000 disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) globally (WHO FERG, 2015). The Chinese Qinghai province (hereon Qinghai) belongs to the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau region located in western China, which is the main epidemic region for human echinococcosis around the world.
The main aims of our study were to investigate the prevalence of Blastocystis in patients with hydatid diseases from the Qinghai Tibetans population and explore whether helminth infection increases host susceptibility to Blastocystis infection. This work will help provide scientific support to develop better preventive and control strategies in dual infections between E. multilocularis and Blastocystis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Fresh fecal samples were collected from 114 people recruited from the Qinghai People’s Hospital. These included 68 patients with liver echinococcosis and 46 healthy individuals. A diagnosis of liver echinococcosis was based on HD-specific IgG ELISA, ultrasonographic features, computed tomography, and surgical findings. Healthy controls did not have liver echinococcosis as determined by negative tests for hydatid antibodies. Individuals with chronic diseases (such as cancers and diabetes), chronic viral diseases, and those who had used antiparasitic medications within the last 3 months were excluded. The fresh fecal samples were stored at −80 °C immediately after collection and kept frozen until DNA extraction to test whether echinococcosis would increase host susceptibility to Blastocystis. The fecal DNA was extracted from inpatients with liver echinococcosis and 46 healthy individuals were examined for the positivity of Blastocystis. In addition, venous blood was collected from 68 patients with liver echinococcosis and routine clinical tests were performed to test for an association with Blastocystis infection. The blood specimens were collected from 68 patients with liver echinococcosis from January 2021 to December 2021. The blood routines were retrieved from the diagnosis step at admission. Stool samples for each participant were also collected at the same time.
2.2. Mouse Model
We used 7–9-week-old female-specific pathogen-free (SPF) Balb/c mice (females) purchased from the Laboratory Animals Center of Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. A total of 14 Balb/c mice were divided into four groups, including (1) a dual infection group (n = 5) that was infected with E. multilocularis (2000 protoscolex per mouse) and Blastocystis ST1 strain (1 × 105 cells per mouse), (2) a Blastocystis infection group (n = 3) that was infected with the ST1 strain (1 × 105 cells per mouse), (3) an E. multilocularis infection group (n = 3) that was infected with E. multilocularis protoscolex (n = 2000), and (4) a control group (n = 3) that was treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Mice were inoculated with E. multilocularis using the E. multilocularis protoscolex (n = 2000) from hydatid cysts collected from a Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) that had been infected with E. multilocularis for five months. The protoscolex was collected and filtered through an 80-mesh copper mesh, followed by two washes with PBS supplemented with 1% penicillin/streptomycin. We used the ST1 Blastocystis strain to infect our mice as it has been demonstrated to cause an asymptomatic phenotype in rodents [14]. The Blastocystis strain (ST1) was a gift from Dr. Lei Ma at Hebei Normal University. Mice were infected with either the E. multilocularis protoscolex or treated with PBS depending on group assignment. The dual infection and Blastocystis infection groups were gavaged with Blastocystis (1 × 105 cells per mouse). The E. multilocularis infection and negative control mice were euthanized after three months, and their intestinal tissues and lamina propria cells were collected for histopathological staining and T lymphocyte isolation, respectively. After infection with Blastocystis, feces from the dual infection and Blastocystis infection mice were collected every two days and used to detect Blastocystis colonization. The dual infection and Blastocystis infection mice were euthanized on day 14 post infection. The feces and intestinal tissues of the mice were collected and used for DNA extraction and histopathological staining, respectively. The tissue was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 48 h, dehydrated, and then embedded in paraffin. Slices were dewaxed, rehydrated, and stained with hematoxylin-eosin. The symptoms of piloerection and torpidity were estimated by observation of “absence” and “presence”.
2.3. T Lymphocyte Isolation
Flow cytometry analyses of T lymphocytes in the lamina propria of the small intestine were performed in samples taken from mice infected with either 2000 E. multilocularis protoscolex or PBS on day 90 post infection, according to the protocol described in a previous study [15]. Briefly, intestines were harvested from mice, cut open longitudinally, and washed in PBS. The fat tissues and Peyer’s Patches (PPs) were removed. Intestines were then cut into 2 cm pieces and washed on a shaker in PBS containing 1 mM DTT for 10 min at 37 °C. After that, the intestines were incubated twice with shaking in PBS containing 30 mM EDTA at 37 °C for 10 min; the fluid was replaced between cycles. Then, the intestines were further cut into 0.5 cm pieces. The tissues were then digested with shaking in RPMI1640 medium (Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA) containing DNase I (Solarbio, Beijing, China) (150 μg/mL) and collagenase VIII (Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA) (200 U/mL) at 37 °C for 70 min. The digested tissues were homogenized by vigorous shaking and then passed through a 70 μm cell strainer to remove large debris. The flow-through was centrifuged in a Percoll gradient at 800× g for 20 min at room temperature and the mononuclear T lymphocytes were harvested from the 40%/80% interphase. Flow cytometry was performed to analyze regulatory T cells (Treg) according to a previous study [16].
2.4. Genomic DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
Approximately 200 mg of fecal sample was extracted for genomic DNA using the E.Z.N.A. Stool DNA kit (OMEGA, Norcross, Georgia) and eluted into a final volume of 100 μL according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Genomic DNA from each sample was stored at −20 °C for further PCR amplification. Blastocystis positivity was screened by PCR targeting a fragment of the SSU rRNA with primers (RD5: 5′-ATCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGT-3′ and BhRDr: 5′-GAGCTTTTTAACTGCAACAACG-3′) [17]. The 25 μL reaction system consisted of 2 μL genomic DNA, 0.2 mM dNTP mixture, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 2.5 μL of 10 × buffer, 1.25 U of TaKaRa Ex Taq® (Takara Dalian, China), and 0.25 μL of primers (10 mol/μL). The PCR reaction conditions were set as follows: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min, 35 cycles including 94 °C for 45 s, 59 °C for 45 s, and 72 °C for 1 min; finally, an additional 72 °C extension for 3 min. Each PCR reaction included negative and positive controls.
2.5. DNA Samples for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay
For Quantitative Real-time PCR (qPCR) analysis, all the fecal DNA in the mice was standardized to 100 ng/μL. The qPCR amplifications were performed using an Applied Biosystems (ABI) 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) in a 20 μL reaction volume containing 10 μL of 2x GoTaq@ qPCR Master Mix (Promega Corporation, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA), 3.65 mM MgCl2, 0.2 μM of each primer (BL18SPPF1: 5′-AGTAGTCATACGCTCGTCTCAAA-3′ and BL18SR2PP: 5′-TCTTCGTTACCCGTTACTGC-3′) [18], and 3 μL of DNA template. The qPCR reaction consisted of pre-denaturation at 95 °C for 3 min and 35 cycles for 45 s of denaturation at 95 °C, 45 s of annealing at 65 °C, and 1 min of extension at 72 °C. For normalization, genomic DNA (Blastocystis-positive DNA) from an in vitro culture of Blastocystis strain (ST1) was used to establish a standard curve line for DNA concentration of Blastocystis according to the method in the literature [18]. A Ct value < 35 was considered positive [19]
2.6. Phylogenetic Groups of Blastocystis
The PCR-positive products were subject to DNA sequencing in the TSINGKE Bio-logical Technology Company (Xian, China). Obtained sequences were checked with their DNA peak form graph by Chromas v.2.6, and the genotypes of Blastocystis were identified by aligning the sequences with the corresponding genotype sequences retrieved from the GenBank database (http://www.ncbi.lm.nih.gov/GenBank/ accessed on 26 July 2021). The sequences of the Blastocystis were aligned with the Clustal W algorithm using MEGA 7 (http://www.megasoftware.net/ accessed on 26 July 2021). Because the nucleotide sequences of Blastocystis used in this study differ in length, ends of sequences were trimmed by Clustal X v.2.0. The phylo-genetic analyses were performed using maximum likelihood (ML) methods (Ki-mura-2-parameter model with 1000 bootstrap replicates) implemented in MEGA7 to infer the genetic relationships.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis for the prevalence of Blastocystis was performed using chi-squared tests in SPSS 24.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. Odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were used to identify risk factors of Blastocystis infection. The difference was considered significant when p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Increased Prevalence of Blastocystis Infection in Patients with Hydatid Diseases
A total of 13 (11.4%, 95% CI: 5.57–17.24) of 114 samples were positive for Blastocystis infection. Tibetan females (18.0%) were marginally more susceptible to infection with Blastocystis than males (6.3%, p = 0.05). Additionally, the highest prevalence of Blastocystis was observed in older Tibetans aged over 65 years (33.3%), followed by 10.5% in Tibetans aged 18–65 years, and 7.7% in those aged less than 18 years (Table 1). Notably, the prevalence of Blastocystis in hydatidosis patients (16.2%) was significantly higher than that in healthy individuals (4.4%) (p < 0.05) (Table 2). Routine blood tests and biochemical indices were used to test for associations with Blastocystis in hydatidosis patients. We found that lipase (LPS) and total bilirubin (TBIL) were associated with the prevalence of Blastocystis in these patients, and the odds ratios were 3.9 and 6.1, respectively (Table 3). These results indicate that liver hydatid disease is associated with a higher rate of intestinal Blastocystis infection in Tibetans.

Table 1.
Prevalence and factors associated with Blastocystis infection in Tibetan people in Qinghai, China.

Table 2.
Prevalence and factors associated with Blastocystis infection in hydatidosis patients and healthy people in Qinghai, China.

Table 3.
Prevalence and factors associated with Blastocystis infection in blood routine and blood biochemical indexes of hydatidosis patients in Qinghai, China.
3.2. Genotyping and Phylogenetic Analysis
Using SSU rRNA sequence analysis, we identified four genotypes of Blastocystis in the 13 Blastocystis-positive samples, including three known genotypes, ST1 (n = 6, 46.15%), ST2 (n = 1, 7.69%), ST3 (n = 5, 38.46%), and one unknown genotype (n = 1, 7.69%). Genotype sequences were used to infer the phylogenetic relationships (Figure 1). The phylogenetic tree revealed that the sequences of Blastocystis from this study were highly similar to those of other Blastocystis isolates previously deposited in GenBank. Moreover, no mixed infections of Blastocystis were detected in any of the examined samples.
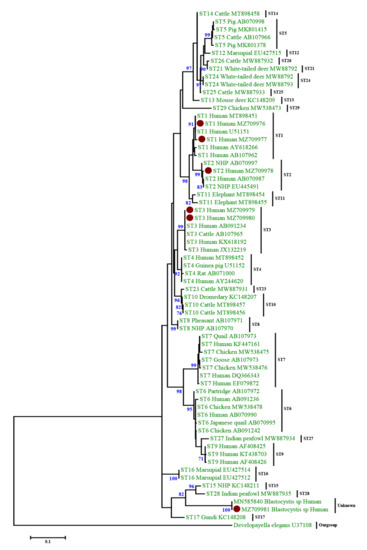
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of Blastocystis using maximum likelihood method based on the SSU rRNA gene sequences. Developayella elegans was used as outgroup taxon to root the tree. Analysis was conducted by a maximum likelihood method. Genetic distances were calculated using the Kimura two-parameter model. This analysis involved 66 nucleotide sequences. Bootstrap values lower than 60% are not displayed. The Blastocystis sequences determined in this study are indicated with a red circle.
3.3. E. multilocularis Infection Increases Host Susceptibility to Blastocystis in a Balb/c Mouse Model
To confirm whether liver hydatid disease increases host susceptibility to Blastocystis infection, we used a mouse model that can be colonized by a human ST1 isolate (Figure S1). Balb/c mice were pre-infected with E. multilocularis, which is a causative agent for liver hydatid disease. Consistent with the findings in the previous studies that chronic E. multilocularis infection typically suppresses host immunity [20], we also observed an expansion of regulatory T cells (Treg) (Figure 2a), suggestive of an immune state of suppression. After inoculation with Blastocystis (ST1 isolate), 80% of the mice in the dual infection group died within 14 days post infection. Conversely, all control mice survived following Blastocystis infection (Figure 2b). Moreover, Balb/c mice that had been pre-infected with E. multilocularis developed a more severe illness, with typical symptoms of piloerection and torpidity, than the mice that were only infected with Blastocystis (Figure 2c). The qPCR quantification of fecal Blastocystis indicated that the colonization was significantly higher in the dual infection group than in control mice (Table S1). This suggests that Blastocystis colonized and proliferated more easily in the gut of the dual-infected mice (Figure 2d). Moreover, the mice singly infected with E. multilocularis and negative control mice did not show any detected level of Blastocystis in their feces (data not shown). H&E staining also showed more extensive pathology in the jejunum tissue in the dual infection mice (Figure 2e). Collectively, these results suggest that chronic E. multilocularis infection increases host susceptibility to gut pathogen colonization and aggravates the pathogenesis caused by Blastocystis.
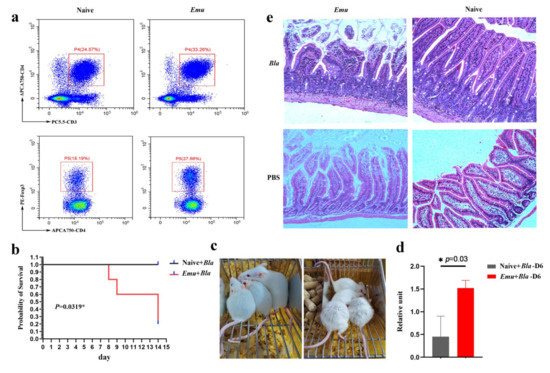
Figure 2.
E. multilocularis (Emu) infection increased the susceptibility to Blastocystis (Bla) in a mouse model. (a) Flow cytometry analysis revealed that regulatory T cells (Treg) were expanded in the Balb/c mice that were pre-infected with E. multilocularis 3 months ago. (b) The survival rate of mice with dual infection (E. multilocularis and Blastocystis) and single infection (Blastocystis). (c) Symptoms of mice with a single infection (left) and with dual infection (right). The piloerection and torpidity were observed in mice with dual infection (right) but not in the mice with a single infection (left). (d) qPCR detection of Blastocystis in feces of the mice at day 6 post-infection. (e) H&E staining of jejunum in for the naive mice, and the mice with single (E. multilocularis or Blastocystis) or dual infection (E. multilocularis and Blastocystis). The * represents the difference was statistically significant.
4. Discussion
Previous studies have shown that Blastocystis can co-occur with protozoa [21,22], HIV [23], malignant tumor [24], tuberculosis [25], and urticaria [26] in humans. However, no cases of combined Blastocystis and hydatidosis have been reported. The prevalence of hydatid disease was 4.5%, 4.7%, and 1.2% in the Qinghai province in 2012, 2014, and 2018, respectively, which represents one of the most prevalent regions around the world [27,28,29]. In this study, we found a Blastocystis prevalence in Tibetans of 12.3% (95% CI: 5.57–17.24). The prevalence was significantly higher in patients with hydatidosis (16.2%) than in healthy individuals (4.4%), suggesting that the former have an increased susceptibility to Blastocystis infection. Our prevalence data for the healthy population agree with a comprehensive review by Zhang et al. in which the average infection rate of Blastocystis worldwide was 4.4% (20,236/457,501) [30]. The prevalence of Blastocystis is influenced by multiple epidemiological factors. Jiménez et al. have proposed that Blastocystis in humans is associated with poor conditions and poor access to clean drinking water [31]. Additional factors such as lifestyle and dietary habits, poultry or livestock farming, poor immune function, poor nutritional status, female sex, low body mass index < 19, anemia, and barefoot farm work are risks associated with Blastocystis infection in humans [32,33,34,35]. In this study, we found that almost all these factors were present in our participants who originate from the same region and share similar lifestyles and animal-based diets. We found that the prevalence of Blastocystis in females was marginally significantly higher than that in males (p = 0.05); this concurs with previously published data. Furthermore, there was no statistical difference in prevalence among age groups in the present study (p = 0.17).
By excluding these sex factors, the higher prevalence of Blastocystis found in hydatidosis patients is likely to be related to immunocompetence. Previous studies have reported a higher Blastocystis infection rate in patients with malignant tumors due to a weakened immune system [36,37]. Chronic E. multilocularis infection is marked by significant suppression of host immunity [22,38,39], which may provide a permissive environment for invasion by other pathogens. Indeed, Blastocystis infection is frequently observed in immunocompromised individuals, with a high reported prevalence of 15.0–72.4% [10]. Here, we speculate that hydatid disease increased the susceptibility to Blastocystis in our cohort. Interestingly, routine blood tests revealed marginal associations with Blastocystis infection; patients with an abnormal lipase index (OR = 3.90, 95% CI: 0.78–19.58) were more likely to infect with Blastocystis compared to those with a normal index. Such elevation of lipase is regularly observed during immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) [40]. We speculate that the elevation seen in our cohort might reflect such immune suppression. Furthermore, immunocompromised individuals had a higher prevalence of Blastocystis [10], so the abnormal lipase index could also have been related to Blastocystis infection. In contrast, total bilirubin levels in hydatidosis patients were marginally associated with Blastocystis infection (OR = 6.11, 95% CI: 0.76–49.05). It has been demonstrated that serum bilirubin has substantial anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties [41,42]. Blood levels of total bilirubin are also normally present in the gut and can cross the gut cell membranes [43]. Thus, bilirubin might protect the gut, resulting in a lower prevalence of Blastocystis in hydatidosis. The observed marginal association between blood routines and Blastocystis infection might reflect some cause or consequences, but no previous studies have reported this relationship. Thus, further research is needed to profoundly investigate it.
At least 22 valid genotypes (STs) of Blastocystis have been described among mammalian and avian isolates [1,5,30], of which nine genotypes (ST1-ST9 and ST12) are reported in the human population [4]. In Asia, the most prevalent genotypes include ST1, ST2, and ST3. In China, ST1-ST7, ST12, and unknown genotypes have also been identified in humans [30]. Consistent with these prior studies, we identified three genotypes, ST1 (n = 6), ST2 (n = 1), and ST3 (n = 5), and one unknown genotype (n = 1) in our cohort. The unknown genotype was clustered into a separate branch that is relatively far from the ST1, ST2, and ST3 and is more closely related to ST15 and ST28 (Figure 1).
To test whether E. multilocularis infection is able to increase host susceptibility to Blastocystis, we constructed an E. multilocularis and Blastocystis dual infection Balb/c mouse model. Consistent with previous findings that chronic Echinococcus infection modulates host immunity by inducing the proliferation of Treg cell proliferation [44,45], we found a significant expansion of CD4+ FoxP3+ Treg cells in the E. multilocularis infection model (Figure 2a); this indicates that immune suppression was induced by the helminth infection. This may explain why susceptibility to Blastocystis is increased in this model. In addition, we found that Blastocystis induced higher mortality with increased gut inflammation and more severe pathogenic damage in the intestinal tissue in mice that were pre-infected with E. multilocularis (Figure 2c,e), further suggesting that the host immunity was suppressed after E. multilocularis. Similarly, the level of Blastocystis infection in mouse feces was higher in the dual infection group (Figure 2d). A high level of Blastocystis infection has also been shown in HIV/AIDS patients in the Anhui province of China [46]. Together, our data suggest that the E. multilocularis infection could increase host susceptibility to Blastocystis and aggravate the resultant pathological damage in the gut.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to report a higher co-occurrence of E. multilocularis and Blastocystis in the Tibetan population. Findings from our dual infection mouse model provide direct evidence that links non-intestinally parasitic helminth E. multilocularis infection and increased host susceptibility to the intestinal protozoan Blastocystis. Further work is needed to more clearly elucidate the mechanisms underlying this dual infection.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology11050773/s1, Figure S1: PCR amplification of Blastocystis in mice feces; Table S1: The results of qPCR detection of Blastocystis in mice feces. COIN represents the dual infection group (E. multilocularis and Blastocystis), SIN represents a single infection group (Blastocystis). The Ct value < 35 was considered positive. Lane M represents DL2000-bp DNA marker, Lane A represents the PCR amplification product of Blastocystis in dual infection mice feces, Lane B/C/D represents the PCR amplification product of Blastocystis in the fecal samples of the mice with the single infection of Blastocystis, Lane E represents positive control of Blastocystis DNA, and Lane F represents native control for Blastocystis DNA.
Author Contributions
conceptualization: S.W., X.-M.H. and Y.Z.; formal analysis: Y.Z. and Y.-G.W.; funding acquisition: S.W.; investigation: Y.Z., Y.-G.W. and Z.-L.L.; methodology: Y.Z., Y.-G.W., Z.-L.L., A.-J.G., X.-L.L. and Z.-Q.S.; project administration: S.W.; resources: Y.Z., Y.-G.W., A.-J.G. and S.W.; software: Y.Z. and Y.-G.W.; supervision: A.-J.G., X.-M.H. and S.W.; validation: S.W.; writing—original draft preparation: Y.Z. and Y.-G.W.; writing—review and editing: X.-L.L., Z.-Q.S., X.-Q.Z. and S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China (No. 21JR7RA027, Funder: Shuai Wang and Funding number: RMB 300,000), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32172878, Funder: Shuai Wang and Funding number: RMB 600,000).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was approved by Qinghai People’s Hospital Ethics Committees (Reference No. 2021-161). Animal work was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (LVRIAEC-2020-019). All animals were handled strictly according to the Animal Ethics Procedures and Guidelines of the People’s Republic of China.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the findings of this article are included within the article. The sequences obtained in the study are deposited in GenBank under the accession numbers: MZ709976-MZ709981 (https://submit.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/subs/genbank/SUB10154998/overview/, accessed on 5 August 2021).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all healthcare workers in Qinghai Provincial People’s Hospital for their assistance in this study, including sample collection, inventory, and processing. We would like to express our gratitude to EditSprings (https://www.editsprings.cn) for the expert linguistic services provided.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Stensvold, C.R.; Clark, C.G. Pre-Empting Pandora’s Box: Blastocystis Subtypes Revisited. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, J.G.; Santin, M. Mind the Gap: New Full-Length Sequences of Subtypes Generated via Oxford Nanopore Minion Sequencing Allow for Comparisons between Full-Length and Partial Sequences of the Small Subunit of the Ribosomal RNA Gene. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, J.G.; Jang, Y.; Molokin, A.; George, N.S.; Santin, M. Wide Genetic Diversity of in White-Tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus) from Maryland, USA. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Clark, C.G. Current Status of Blastocystis: A Personal View. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, J.G.; Lombard, J.E.; Urie, N.J.; Shivley, C.B.; Santin, M. Zoonotic and Genetically Diverse Subtypes of Blastocystis in US Pre-Weaned Dairy Heifer Calves. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tito, R.Y.; Chaffron, S.; Caenepeel, C.; Lima-Mendez, G.; Wang, J.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Hildebrand, F.; Darzi, Y.; Rymenans, L.; et al. Population-level Analysis of Blastocystis Subtype Prevalence and Variation in the Human Gut Microbiota. Gut 2019, 68, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Sørland, B.A.; Berg, R.P.K.D.; Andersen, L.O.; Van der Giezen, M.; Bowtell, J.L.; El-Badry, A.A.; Belkessa, S.; Kurt, Ö.; Nielsen, H.V. Stool Microbiota Diversity Analysis of Blastocystis-Positive and Blastocystis-Negative Individuals. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.; Cetin, E.S.; Aridoğan, B.C.; Arikan, S.; Demirci, M. Pathogenicity of Blastocystis Hominis, a Clinical Reevaluation. Turkiye Parazitol. Derg. 2007, 31, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, M.V.; Pierrotti, L.C.; Abdala, E.; Clemente, W.T.; Girão, E.S.; Rosa, D.R.T.; Ianhez, L.E.; Bonazzi, P.R.; Lima, A.S.; Fernandes, P.F.C.B.C.; et al. Endemic and Opportunistic Infections in Brazilian Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2011, 16, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.C.; Ong, S.C.; Suresh, K.G. Genetic Variability of Blastocystis Sp. Isolates Obtained from Cancer and HIV/AIDS Patients. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gottstein, B. Immunoregulation in Larval Echinococcus Multilocularis Infection. Parasite Immunol. 2016, 38, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svrckova, P.; Nabarro, L.; Chiodini, P.L.; Jäger, H.R. Disseminated Cerebral Hydatid Disease (multiple Intracranial Echinococcosis). Pract. Neurol. 2019, 19, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, P.R.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Praet, N.; Speybroeck, N.; Willingham, A.L.; Kasuga, F.; Rokni, M.B.; Zhou, X.-N.; Fèvre, E.M.; Sripa, B.; et al. World Health Organization Estimates of the Global and Regional Disease Burden of 11 Foodborne Parasitic Diseases, 2010: A Data Synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E.M.; Hussein, A.M.; Eida, M.M.; Atwa, M.M. Pathophysiological Variability of Different Genotypes of Human Blastocystis Hominis Egyptian Isolates in Experimentally Infected Rats. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 102, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Sheridan, B.S. Isolating Lymphocytes from the Mouse Small Intestinal Immune System. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 28, 57281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Qiu, J.; Ji, Y.; Li, W.; Ding, Z.; Suo, C.; Chang, J.; Wang, J.; He, R.; Qian, Y.; et al. IL-17-Producing ST2+ Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Play a Pathogenic Role in Lung Inflammation. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, e9–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicluna, S.M.; Tawari, B.; Clark, C.G. DNA Barcoding of Blastocystis. Protist. 2006, 157, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, P.; Wawrzyniak, I.; Albert, A.; El Alaoui, H.; Delbac, F.; Livrelli, V. Development and Evaluation of a Real-Time PCR Assay for Detection and Quantification of Blastocystis Parasites in Human Stool Samples: Prospective Study of Patients with Hematological Malignancies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, S.M.; Gazi, M.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Alam, M.A.; Das, S.; Mahfuz, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Haque, R.; Sarker, S.A.; Ahmed, T. Infection with Blastocystis spp. and Its Association with Enteric Infections and Environmental Enteric Dysfunction among Slum-Dwelling Malnourished Adults in Bangladesh. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Song, X.Q.; Li, Y.W.; Shi, H.H. Research on the infection status of Blastocystosis hominis in patients with malignant tumour. Chin. J. Health Lab. Technol. 2015, 25, 1962–1964. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- El-Shazly, L.B.E.-D.; El-Faramawy, A.A.M.; El-Sayed, N.M.; Ismail, K.A.; Fouad, S.M. Intestinal Parasitic Infection among Egyptian Children with Chronic Liver Diseases. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Khalil, S.; Mirdha, B.R. Molecular Appraisal of Intestinal Parasitic Infection in Transplant Recipients. Indian J. Med. Res. 2016, 144, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Lowther, S.A.; Dworkin, M.S.; Hanson, D.L. Entamoeba histolytica/Entamoeba Dispar Infections in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Patients in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşova, Y.; Sahin, B.; Koltaş, S.; Paydaş, S. Clinical Significance and Frequency of Blastocystis Hominis in Turkish Patients with Hematological Malignancy. Acta Med. Okayama. 2000, 54, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, M.F.; Del Castillo, H.; Pereda, Y.; Lecca, L.; Fuertes, J.; Cárdenas, L.; Becerra, M.C.; Bayona, J.; Murray, M. Parasite Infection and Tuberculosis Disease among Children: A Case-Control Study. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hameed, D.M.A.; Hassanin, O.M.; Zuel-Fakkar, N.M. Association of Blastocystis Hominis Genetic Subtypes with Urticaria. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.L.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, Y.F.; Cai, H.X.; Liu, P.Y.; Ma, J.Y.; He, D.L.; Wu, X.H.; et al. An Epidemiological Survey on Echinococcosis in Yushu Prefecture of Qinghai Province in 2012. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 34, 547–551. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Kim, J.-G.; Wang, H.; Cai, H.; Ma, X.; Duong, D.H.; Ahn, C.-S.; Kang, I.; Kong, Y. Survey of Echinococcoses in Southeastern Qinghai Province, China, and Serodiagnostic Insights of Recombinant Echinococcus Granulosus Antigen B Isoforms. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.P.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.N.; Wang, L.Y.; Zheng, C.J.; Cao, J.P.; Xiao, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.Y.; et al. A nationwide sampling survey on echinococcosis in China during 2012-2016. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2018, 36, 1–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.Q.; Wang, P.; Feng, X.; Mi, Q.M.; Mei, X.F.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, X.R.; Wang, S. Progress of researches on global prevalence of human infections and its subtypes. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi 2020, 33, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, P.A.; Jaimes, J.E.; Ramírez, J.D. A Summary of Blastocystis Subtypes in North and South America. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, N.; Xu, M.; Yang, F.; Tong, L.; Zhou, K.; Cao, J.; Liu, A.; et al. Prevalence and Subtype Distribution of Blastocystis in Ethnic Minority Groups on Both Sides of the China-Myanmar Border, and Assessment of Risk Factors. Parasite 2019, 26, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, L.X.; Tian, L.G.; Zhang, Y.P.; Dong, S.P.; Hu, X.G.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.F.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Intestinal Protozoan and Helminth Infections among Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients without HIV Infection in a Rural County in P. R. China. Acta Trop. 2015, 149, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Chen, J.-X.; Wang, L.-X.; Tian, L.-G.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Dong, S.-P.; Hu, X.-G.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.-F.; Wang, Y.; et al. Intestinal Parasite Co-Infection among Pulmonary Tuberculosis Cases without Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection in a Rural County in China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.-Q.; Hu, Z.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Ai, L.; Tian, L.-G. Epidemiology of Blastocystis Infection from 1990 to 2019 in China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B.; Yan, H.; Shi, H.H.; Liu, D.Y.; Liao, D.J.; Liu, X.Q. Investigating Blastocystis hominis infection of inpatients in two tertiary hospitals of Guangxi. J. Guangxi Med. Univ. (In Chinese). 2016, 3314–3316. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.W.; Tanner, C.E. The Effect of Immunosuppression on Secondary Echinococcus Multilocularis Infections in Mice. Int. J. Parasitol. 1976, 6, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devouge, M.; Ali-Khan, Z. Intraperitoneal Murine Alveolar Hydatidosis: Relationship between the Size of the Larval Cyst Mass, Immigrant Inflammatory Cells, Splenomegaly and Thymus Involution. Tropenmed. Parasitol. 1983, 34, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kizaki, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Ogasawara, K.; Day, N.K.; Good, R.A.; Onoé, K. Immune Suppression Induced by Protoscoleces of Echinococcus Multilocularis in Mice. Evidence for the Presence of CD8dull Suppressor Cells in Spleens of Mice Intraperitoneally Infected with E. multilocularis. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Grimmelmann, I.; Momma, M.; Zimmer, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Heinzerling, L.; Pföhler, C.; Loquai, C.; Ruini, C.; Utikal, J.; Thoms, K.M.; et al. Lipase Elevation and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Related to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy—A Multicentre Study of 90 Patients From the German Dermatooncology Group. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.H.; Wallner, M.; Mölzer, C.; Gazzin, S.; Bulmer, A.C.; Tiribelli, C.; Vitek, L. Looking to The Horizon: The Role of Bilirubin in The Development and Prevention of age-related Chronic diseases. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, T.W.; Saleh, M.; Higginson, D.S.; Paul, B.D.; Juluri, K.R.; Snyder, S.H. Bilirubin and Glutathione Have Complementary Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Roles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5171–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.H.; Shiels, R.G.; Lang, C.A.; Seyed Khoei, N.; Bulmer, A.C. Diagnostic Criteria and Contributors to Gilbert’s Syndrome. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, M.P.; Manfras, B.J.; Margos, M.C.; Eiffler, D.; Hoffmann, W.H.; Schulz-Key, H.; Kern, P.; Soboslay, P.T. Echinococcus Multilocularis Metacestodes Modulate Cellular Cytokine and Chemokine Release by Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Alveolar Echinococcosis Patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 145, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intraperitoneal Echinococcus Multilocularis Infection in Mice Modulates Peritoneal CD4+ and CD8+ Regulatory T Cell Development. Parasitol. Int. 2011, 60, 45–53. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.X.; Yu, Y.F.; Wu, X.P.; Chu, Y.H.; Teng, X.J.; Wang, F.F.; Chen, J.X.; Tian, L.G. Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of infection among patients with HIV/AIDS in Fuyang City Anhui Province. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi 2019, 31, 498–503. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).