Closing the Gap: Horizontal Transfer of Mariner Transposons between Rhus Gall Aphids and Other Insects
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Availability
2.2. Identification and Annotation of MLEs in Targeted Species
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Estimating the Minimal Number of Horizontal Transfer Events
3. Results
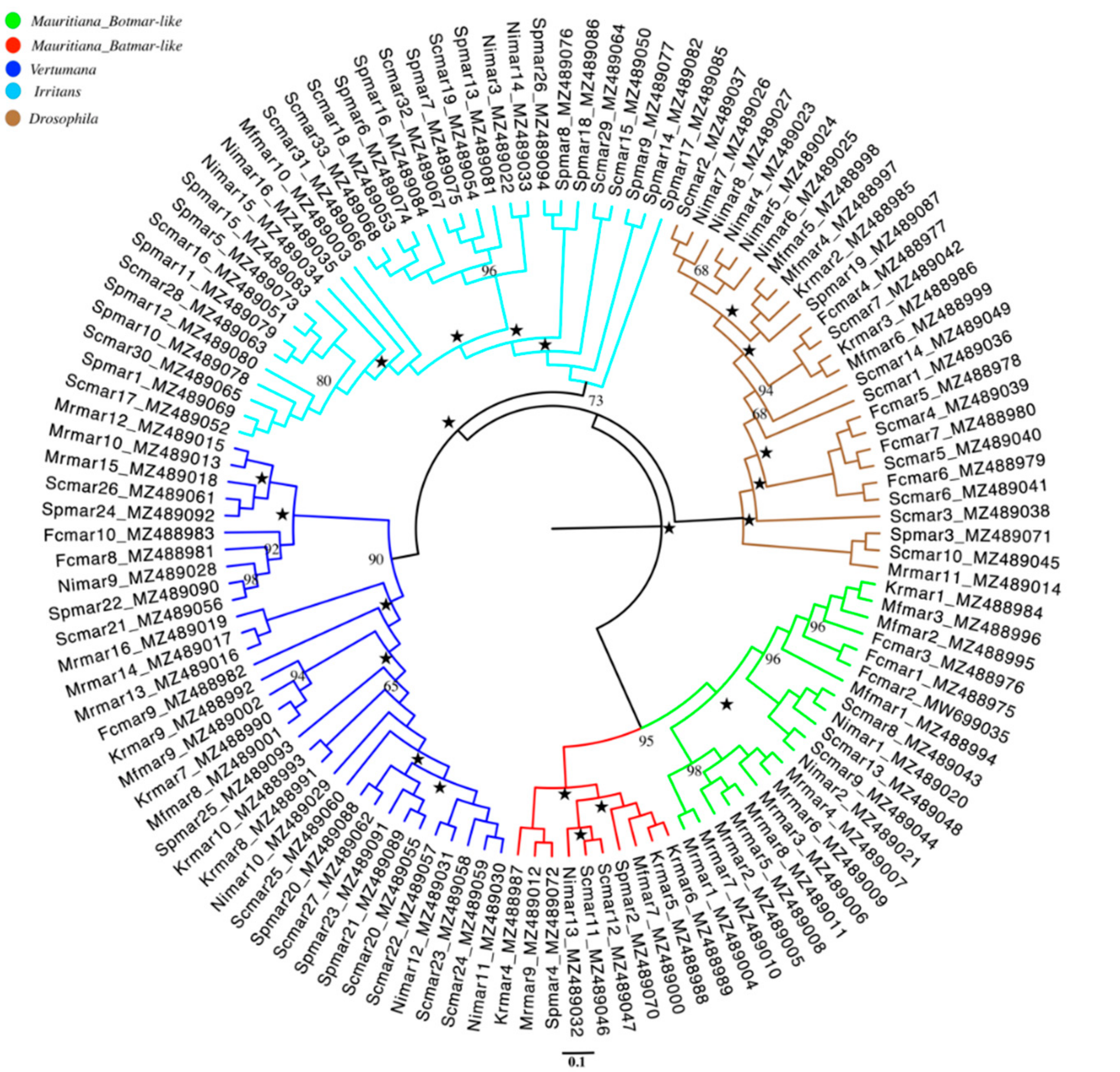
3.1. Phylogenetic Relationship of the Rhus Gall Aphids MLEs
3.2. Selection of the MLEs Representative Sequence for HTT
3.3. Inference of Horizontal Transfer between Rhus Gall TEs with Other Insects
3.4. Inference of HTT Based on Nucleotides Sequence Similarities
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of HTT among Rhus Gall Aphids and Other Insects
3.6. Estimation of Divergence Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Koning, A.J.; Gu, W.; Castoe, T.A.; Batzer, M.A.; Pollock, D.D. Repetitive elements may comprise over two-thirds of the human genome. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicker, T.; Gundlach, H.; Spannagl, M.; Uauy, C.; Borrill, P.; Ramírez-González, R.H.; De Oliveira, R.; Mayer, K.F.; Paux, E.; Choulet, F. Impact of transposable elements on genome structure and evolution in bread wheat. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feschotte, C.; Jiang, N.; Wessler, S.R. Plant transposable elements: Where genetics meets genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourque, G. Transposable elements in gene regulation and in the evolution of vertebrate genomes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2009, 19, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, I.A.; Naville, M.; Chalopin, D.; Levin, P.; Berger, C.S.; Galiana, D.; Volff, J.-N. Evolutionary impact of transposable elements on genomic diversity and lineage-specific innovation in vertebrates. Chromosome Res. 2015, 23, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion-Côté, A.-M.; Renaut, S.; Normandeau, E.; Bernatchez, L. RNA-seq reveals transcriptomic shock involving transposable elements reactivation in hybrids of young lake whitefish species. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, A.; Marsano, R.M. Transposable elements: A jump toward the future of expression vectors. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebriaei, P.; Izsvák, Z.; Narayanavari, S.A.; Singh, H.; Ivics, Z. Gene therapy with the sleeping beauty transposon system. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnik, F.; McCutcheon, J.P. Functional horizontal gene transfer from bacteria to eukaryotes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.A.; Li, J.; Davidson, W.S.; Davies, P.L. Smelt was the likely beneficiary of an antifreeze gene laterally transferred between fishes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, L.; Boulain, H.; Gauthier, J.; Hua-Van, A.; Musset, K.; Jakubowska, A.K.; Aury, J.-M.; Volkoff, A.-N.; Huguet, E.; Herrero, S. Recurrent domestication by Lepidoptera of genes from their parasites mediated by bracoviruses. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.F. Too much eukaryote LGT. BioEssays 2017, 39, 1700115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, M.M.; Eme, L.; Stairs, C.W.; Roger, A.J. Demystifying eukaryote lateral gene transfer (Response to Martin 2017 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201700115). BioEssays 2018, 40, 1700242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, L.T.; Olofsson, J.K.; Parisod, C.; Choudhury, R.R.; Moreno-Villena, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Dionora, J.; Quick, W.P.; Park, M.; Bennetzen, J.L. Lateral transfers of large DNA fragments spread functional genes among grasses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4416–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.B.; Peterson, K.R.; Strausbaugh, L.D.; Kidwell, M.G.; Chovnick, A. Evidence for horizontal transmission of the P transposable element between Drosophila species. Genetics 1990, 124, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicker, T.; Sabot, F.; Hua-Van, A.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Capy, P.; Chalhoub, B.; Flavell, A.; Leroy, P.; Morgante, M.; Panaud, O. A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, D.J.; Witherspoon, D.J.; Soto-Adames, F.N.; Robertson, H.M. Recent horizontal transfer of mellifera subfamily mariner transposons into insect lineages representing four different orders shows that selection acts only during horizontal transfer. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallau, G.L.; Capy, P.; Loreto, E.; Le Rouzic, A.; Hua-Van, A. VHICA, a new method to discriminate between vertical and horizontal transposon transfer: Application to the mariner family within Drosophila. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1094–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccoud, J.; Loiseau, V.; Cordaux, R.; Gilbert, C. Massive horizontal transfer of transposable elements in insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4721–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, D.; Mialdea, G.; Miele, V.; De Vienne, D.M.; Peccoud, J.; Gilbert, C.; Duret, L.; Charlat, S. Global survey of mobile DNA horizontal transfer in arthropods reveals Lepidoptera as a prime hotspot. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.C.; Loreto, E.L.; Clark, J.B. Factors that affect the horizontal transfer of transposable elements. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2004, 6, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Houck, M.A.; Clark, J.B.; Peterson, K.R.; Kidwell, M.G. Possible horizontal transfer of Drosophila genes by the mite Proctolaelaps regalis. Science 1991, 253, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.; Schaack, S.; Pace, J.K., II; Brindley, P.J.; Feschotte, C. A role for host–parasite interactions in the horizontal transfer of transposons across phyla. Nature 2010, 464, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.; Cordaux, R. Viruses as vectors of horizontal transfer of genetic material in eukaryotes. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 25, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loiseau, V.; Peccoud, J.; Bouzar, C.; Guillier, S.; Fan, J.; Gueli Alletti, G.; Meignin, C.; Herniou, E.A.; Federici, B.A.; Wennmann, J.T. Monitoring insect transposable elements in large double-stranded DNA viruses reveals host-to-virus and virus-to-virus transposition. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3512–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herédia, F.; Loreto, E.L.S.; Valente, V.L.S. Complex evolution of gypsy in Drosophilid species. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ludwig, A.; Valente, V.d.S.; Loreto, E. Multiple invasions of Errantivirus in the genus Drosophila. Insect Mol. Biol. 2008, 17, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Setta, N.; Van Sluys, M.-A.; Capy, P.; Carareto, C. Multiple invasions of Gypsy and Micropia retroelements in genus Zaprionus and melanogaster subgroup of the genus Drosophila. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sormacheva, I.; Smyshlyaev, G.; Mayorov, V.; Blinov, A.; Novikov, A.; Novikova, O. Vertical evolution and horizontal transfer of CR1 non-LTR retrotransposons and Tc1/mariner DNA transposons in Lepidoptera species. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 3685–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-H.; Li, G.-Y.; Xiong, X.-M.; Han, M.-J.; Zhang, X.-G.; Dai, F.-Y. TRT, a vertebrate and protozoan Tc1-like transposon: Current activity and horizontal transfer. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 2994–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrat, I.; Mezghani, M.; Casse, N.; Denis, F.; Caruso, A.; Makni, H.; Capy, P.; Rouault, J.-D.; Chénais, B.; Makni, M. Characterization of mariner-like transposons of the mauritiana subfamily in seven tree aphid species. Genetica 2015, 143, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouallègue, M.; Filée, J.; Kharrat, I.; Mezghani-Khemakhem, M.; Rouault, J.-D.; Makni, M.; Capy, P. Diversity and evolution of mariner-like elements in aphid genomes. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallau, G.L.; Vieira, C.; Loreto, É.L.S. Genetic exchange in eukaryotes through horizontal transfer: Connected by the mobilome. Mob. DNA 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Wallau, G.L.; Ren, Z. Characterization of Mariner transposons in seven species of Rhus gall aphids. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Qi, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Shao, S.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, H. A complex nutrient exchange between a gall-forming aphid and its plant host. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Harris, A.; Dikow, R.B.; Ma, E.; Zhong, Y.; Wen, J. Another look at the phylogenetic relationships and intercontinental biogeography of eastern Asian–North American Rhus gall aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae: Eriosomatinae): Evidence from mitogenome sequences via genome skimming. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 117, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Von Dohlen, C.D.; Harris, A.; Dikow, R.B.; Su, X.; Wen, J. Congruent phylogenetic relationships of Melaphidina aphids (Aphididae: Eriosomatinae: Fordini) according to nuclear and mitochondrial DNA data with taxonomic implications on generic limits. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, A.; Escuder, E.; D’Addabbo, P.; Lovero, D.; Marsano, R.M. A genomic survey of Tc1-mariner transposons in nematodes suggests extensive horizontal transposon transfer events. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 158, 107090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurka, J.; Kapitonov, V.V.; Pavlicek, A.; Klonowski, P.; Kohany, O.; Walichiewicz, J. Repbase Update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005, 110, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohany, O.; Gentles, A.J.; Hankus, L.; Jurka, J. Annotation, submission and screening of repetitive elements in Repbase: RepbaseSubmitter and Censor. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.D.; Tomii, K.; Katoh, K. Application of the MAFFT sequence alignment program to large data—Reexamination of the usefulness of chained guide trees. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3246–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Buckley, T.R. Model selection and model averaging in phylogenetics: Advantages of Akaike information criterion and Bayesian approaches over likelihood ratio tests. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree, v1.3.1; Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wallau, G.L.; Capy, P.; Loreto, E.; Hua-Van, A. Genomic landscape and evolutionary dynamics of mariner transposable elements within the Drosophila genus. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.; Feschotte, C. Horizontal acquisition of transposable elements and viral sequences: Patterns and consequences. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 49, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaack, S.; Gilbert, C.; Feschotte, C. Promiscuous DNA: Horizontal transfer of transposable elements and why it matters for eukaryotic evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, B.R.; Carvalho, E.L.; Silva, A.F.; Duarte Silva, L.F.; Pinto, P.M.; Ortiz, M.F.; Wallau, G.L. HTT-DB: Horizontally transferred transposable elements database. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2915–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-H.; Peccoud, J.; Xu, M.-R.-X.; Zhang, X.-G.; Gilbert, C. Horizontal transfer and evolution of transposable elements in vertebrates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimmer, K.; Von Haeseler, A.; Salemi, M. Genetic distances and nucleotide substitution models. In The Phylogenetic Handbook: A Practical Approach to Phylogenetic Analysis and Hypothesis Testing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 111–141. [Google Scholar]
- Dunemann, S.M.; Wasmuth, J.D. Horizontal transfer of a retrotransposon between parasitic nematodes and the common shrew. Mob. DNA 2019, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, A.; Witt, C.C.; Menger, J.; Sadanandan, K.R.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Gerth, M.; Weigert, A.; McGuire, J.A.; Mudge, J.; Edwards, S.V. Ancient horizontal transfers of retrotransposons between birds and ancestors of human pathogenic nematodes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, H.; MacLeod, E. Five major subfamilies of mariner transposable elements in insects, including the Mediterranean fruit fly, and related arthropods. Insect Mol. Biol. 1993, 2, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Rhus Gall Aphid Species | Rhus Gall Aphids MLE | Target Species Element | Species Order | Target Accession | NCBI Blastn Alignment Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Query Coverage | %Identity | E-Value | Bit Score | |||||
| Floraphis choui | Fcmar2 | Myrmica ruginodis | Hymenoptera | AY652426 | 99 | 90.10 | 0 | 1657 |
| Bombus campestris | Hymenoptera | HG995146 | 100 | 87.66 | 0 | 1489 | ||
| Nomada fabriciana | Hymenoptera | OU015690 | 99 | 87.48 | 0 | 1476 | ||
| Ocypus olens | Coleoptera | OU343056 | 99 | 87.55 | 0 | 1469 | ||
| Bombus terrestris | Hymenoptera | OU342929 | 99 | 87.39 | 0 | 1469 | ||
| Bombus pascuorum | Hymenoptera | HG995272 | 99 | 87.25 | 0 | 1454 | ||
| Osmia bicornis | Hymenoptera | OU015504 | 99 | 85.60 | 0 | 1339 | ||
| Kaburagia rhusicola | Krmar4 | Tinea trinotella | Lepidoptera | HG992316 | 99 | 85.39 | 0 | 1315 |
| Krmar5 | Bactrocera tryoni | Diptera | KX931004 | 100 | 94.6 | 0 | 1750 | |
| Meitanaphis flavogallis | Mfmar7 | Bactrocera tryoni | Diptera | KX931004 | 100 | 93.57 | 0 | 1720 |
| Melpahis rhois | Mrmar11 | Mellicta athalia | Lepidoptera | HG992203 | 99 | 96.80 | 0 | 2185 |
| Bactrocera tryoni | Diptera | KX930994 | 100 | 95.67 | 0 | 2108 | ||
| Chrysoperla carnea | Neuroptera | FR997756 | 99 | 91.56 | 0 | 1783 | ||
| Tinea trinotella | Lepidoptera | HG992328 | 99 | 90.98 | 0 | 1307 | ||
| Schlechtendalia chinensis | Scmar11 | Bactrocera tryoni | Diptera | KX931004 | 100 | 93.64 | 0 | 1910 |
| Schlechtendalia peitan | Spmar2 | Bactrocera tryoni | Diptera | KX931004 | 100 | 94.49 | 0 | 1910 |
| Rhus Gall MLEs | Rhus Gall Aphids | Target Species Name | Order | Target MLE Name | Query | Similarity to (Consensus) | Bit Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mrmar16 | Melaphis rhois | Herpegnathos saltator | Hymenoptera | Mariner-33_HS al | 92% | 0.8307 (>97%) | 7128 |
| Fcmar2 | Floraphis choui | Acromyrmex echinatior | Hymenoptera | Mariner-2_AEc | 99% | 0.8925 (89.2%) | 8806 |
| Krmar4 | Kaburagia rhusicola | Drosophila elegans | Diptera | Mariner-7_DEL | 95% | 0.8003 (~96%) | 6914 |
| Krmar5 | Kaburagia rhusicola | Acromyrmex echinator | Hymenoptera | Mariner-18_AEc | 100% | 0.8213 (~96%) | 7732 |
| Mrmar11 | Melaphis rhois | Solenopsis invicta | Hymenoptera | Mariner-5_ Sin | 100% | 0.8088 (>97%) | 6926 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, A.; Su, X.; Harris, A.; Ren, Z. Closing the Gap: Horizontal Transfer of Mariner Transposons between Rhus Gall Aphids and Other Insects. Biology 2022, 11, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050731
Ahmad A, Su X, Harris A, Ren Z. Closing the Gap: Horizontal Transfer of Mariner Transposons between Rhus Gall Aphids and Other Insects. Biology. 2022; 11(5):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050731
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Aftab, Xu Su, AJ Harris, and Zhumei Ren. 2022. "Closing the Gap: Horizontal Transfer of Mariner Transposons between Rhus Gall Aphids and Other Insects" Biology 11, no. 5: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050731
APA StyleAhmad, A., Su, X., Harris, A., & Ren, Z. (2022). Closing the Gap: Horizontal Transfer of Mariner Transposons between Rhus Gall Aphids and Other Insects. Biology, 11(5), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050731







