Time-Dependent Changes of Laboratory Parameters as Independent Predictors of All-Cause Mortality in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Groups
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Outcome Measures and Operational Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
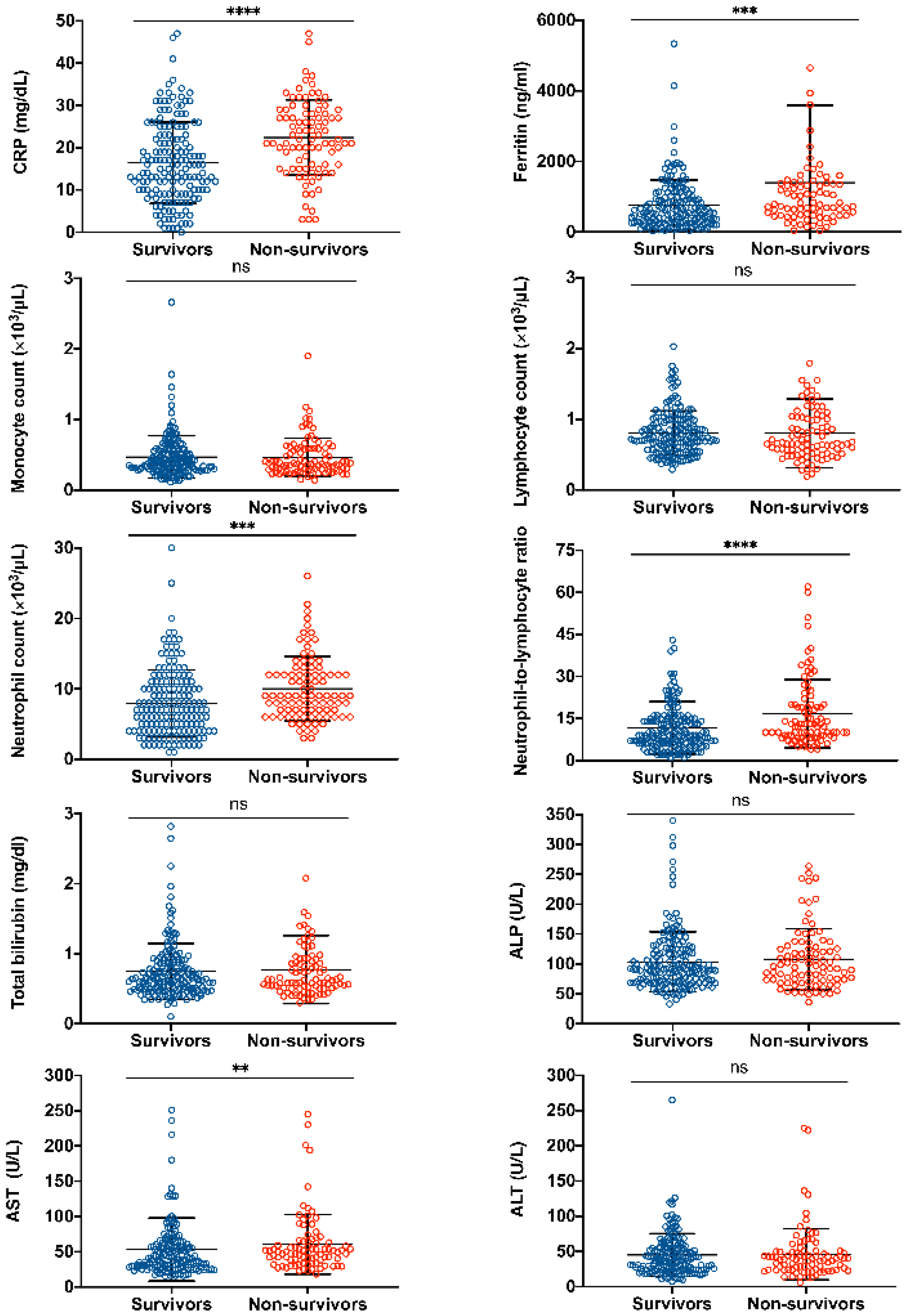
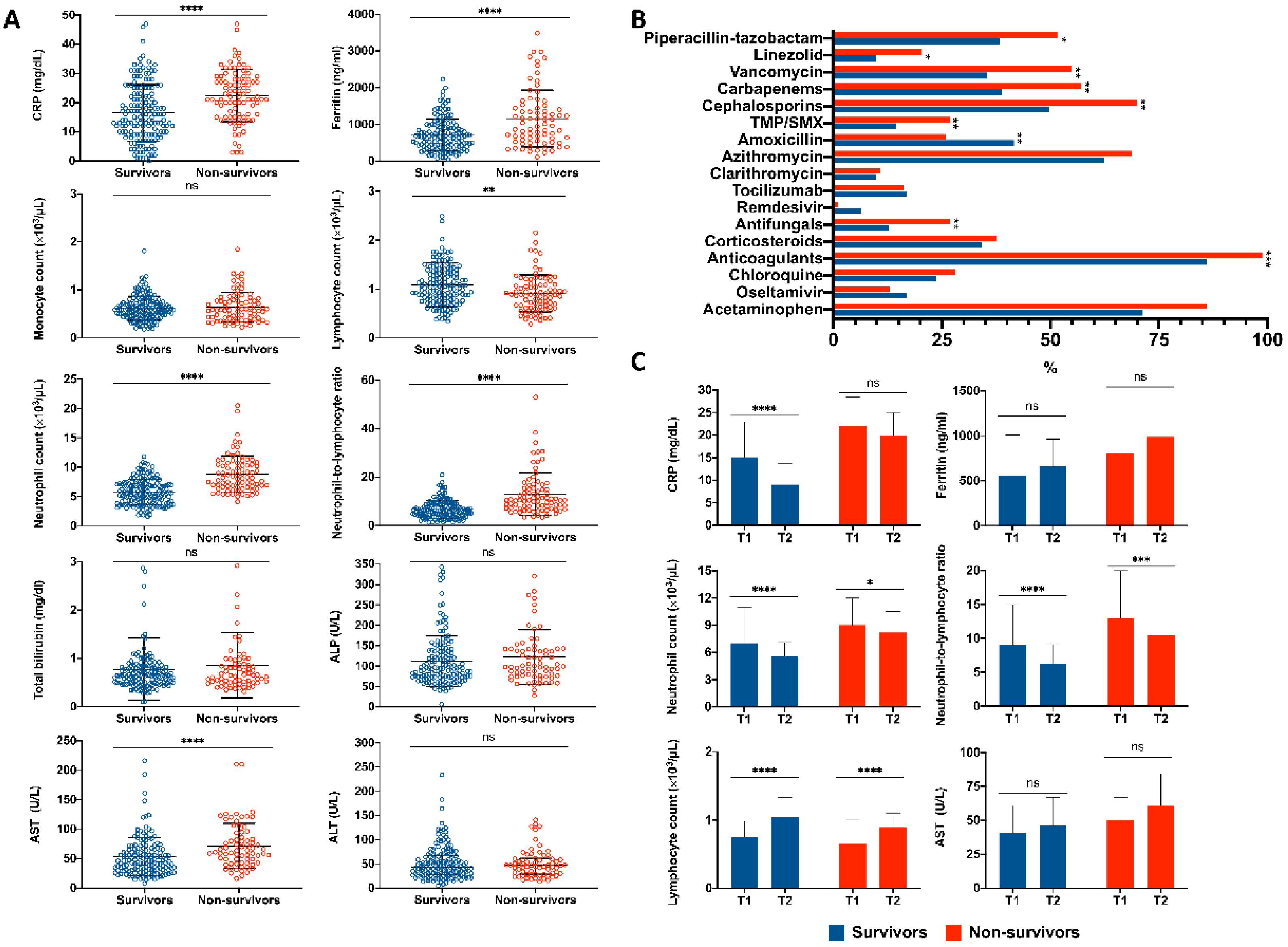
3.2. Abnormal Laboratory Findings upon Admission Related to a Higher Mortality Risk
3.3. Abnormal Laboratory Findings during Hospital Stay Related to a Higher Mortality Risk
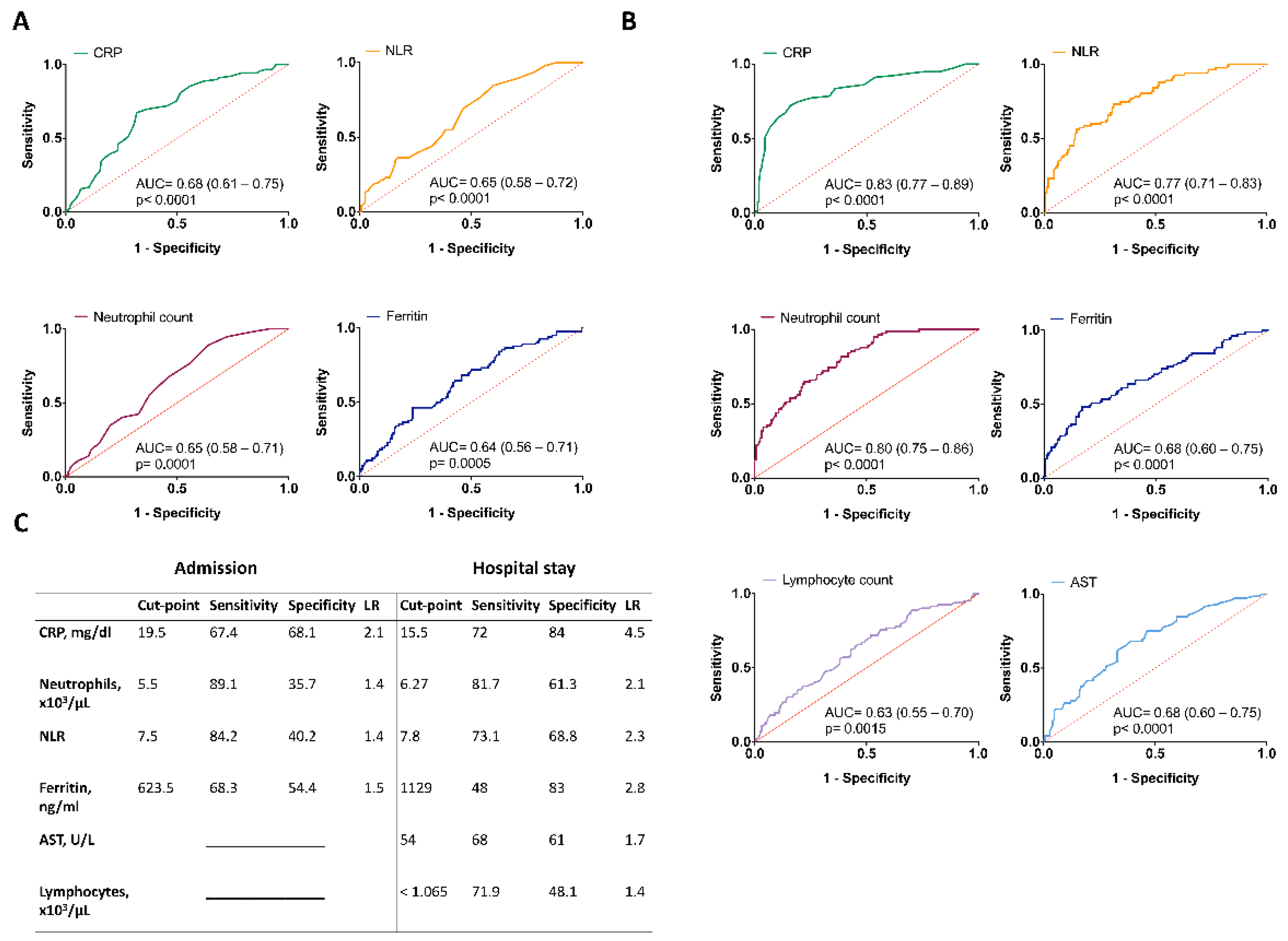
3.4. Clinical and Laboratory Predictors Associated with Mortality Due to COVID-19
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 Pandemic Planning Scenarios. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/planning-scenarios.html (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Sanyaolu, A.; Okorie, C.; Marinkovic, A.; Patidar, R.; Younis, K.; Desai, P.; Hosein, Z.; Padda, I.; Mangat, J.; Altaf, M. Comorbidity and its Impact on Patients with COVID-19. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Lin, R.; Han, K. Clinical features of COVID-19 in elderly patients: A comparison with young and middle-aged patients. J. Infect. 2020, 80, e14–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Hajat, C.; Stein, E. The global burden of multiple chronic conditions: A narrative review. Prev. Med. Rep. 2018, 12, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baksh, M.; Ravat, V.; Zaidi, A.; Patel, R.S. A Systematic Review of Cases of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. Cureus 2020, 12, e8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Beitler, J.R.; Brochard, L.; Calfee, C.S.; Ferguson, N.D.; Slutsky, A.S.; Brodie, D. COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: Is a different approach to management warranted? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Shang, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Du, H.; et al. Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A large cohort study. Ann. Intensive Care 2020, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshazli, R.M.; Toraih, E.A.; Elgaml, A.; El-Mowafy, M.; El-Mesery, M.; Amin, M.N.; Hussein, M.H.; Killackey, M.T.; Fawzy, M.S.; Kandil, E. Diagnostic and prognostic value of hematological and immunological markers in COVID-19 infection: A meta-analysis of 6320 patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Huang, Y.; Shi, F.; Tan, K.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, X. C-reactive protein correlates with computed tomographic findings and predicts severe COVID-19 early. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.; Zhou, W.; Yan, X.; Guo, T.; Wang, B.; Xia, H.; Ye, L.; Xiong, J.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Prognostic value of C-reactive protein in patients with COVID-19. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2174–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; De Oliveira, M.H.S.; Benoit, S.; Plebani, M.; Lippi, G. Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, F.; Yu, B.; Lv, J.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Level May Predict the Risk of COVID-19 Aggravation. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabatchian, F.; Ashtiani, M.; Davoudi, M.; Teimourpour, A.; Davoudi, N. A Multivariate Analysis Model of Changes in Some Laboratory Parameters in Response to COVID-19, Diabetes, Gender, and Age. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Huang, L.; Hoffmann, D.; Lu, M.; Qiu, Y. Excessive Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escadafal, C.; Incardona, S.; Fernandez-Carballo, B.L.; Dittrich, S. The good and the bad: Using C reactive protein to distinguish bacterial from non-bacterial infection among febrile patients in low-resource settings. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e002396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feld, J.; Tremblay, D.; Thibaud, S.; Kessler, A.; Naymagon, L. Ferritin levels in patients with COVID-19: A poor predictor of mortality and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 42, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Tao, Y.; Xie, C.; Ma, K.; Shang, K.; Wang, W.; et al. Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, G.; Manelli, F.; Patroni, A.; Bettinardi, A.; Borrelli, G.; Fiordalisi, G.; Marino, A.; Menolfi, A.; Saggini, S.; Volpi, R.; et al. Laboratory predictors of death from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the area of Valcamonica, Italy. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2020, 58, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galani, I.E.; Andreakos, E. Neutrophils in viral infections: Current concepts and caveats. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, B.; Hu, J.; Zuo, X.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.; Shi, X.; Deng, A. Predictors of progression from moderate to severe coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ju, M.; Chen, C.; Yang, D.; Hou, D.; Tang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Ji, S.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients: A retrospective study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mancilla-Galindo, J.; García-Méndez, J.Ó.; Márquez-Sánchez, J.; Reyes-Casarrubias, R.E.; Aguirre-Aguilar, E.; Rocha-González, H.I.; Kammar-García, A. All-cause mortality among patients treated with repurposed antivirals and antibiotics for COVID-19 in Mexico City: A real-world observational study. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course, and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappetta, S.; Sharma, A.M.; Bottino, V.; Stier, C. COVID-19 and the role of chronic inflammation in patients with obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1790–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Ren, H.; Zhang, S.; Shi, X.; Yu, X.; Dong, K. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with severe Covid-19 with diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhl, M.; Grubelnik, V.; Magdič, M.; Markovič, R. Diabetes and metabolic syndrome as risk factors for COVID-19. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.B.; Lalbakhsh, A.; Talla, J.; Peroutka, Z.; Hadjilooei, F.; Lalbakhsh, P.; Jamshidi, M.; Spada, L.; Mirmozafari, M.; Dehghani, M.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and COVID-19: Deep Learning Approaches for Diagnosis and Treatment. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 109581–109595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, O.; Zhang, X.; Xu, K.; Suo, C.; Wang, Q.; Song, Y.; Yu, K.; et al. Early prediction of mortality risk among patients with severe COVID-19, using machine learning. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 49, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laatifi, M.; Douzi, S.; Bouklouz, A.; Ezzine, H.; Jaafari, J.; Zaid, Y.; El Ouahidi, B.; Naciri, M. Machine learning approaches in Covid-19 severity risk prediction in Morocco. J. Big Data 2022, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, V.; Phelps, S.; Ryono, R.; Lee, C.; Parekh, H.; Mewton, J.; Sedghi, F.; Etminani, P.; Holodniy, M. A Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Prediction Model From Standard Laboratory Tests. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e2901–e2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 266) | Survivors (n = 173) | Non-Survivors (n = 93) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr.)—mean (SD) | 53 (13) | 52 (13) | 55 (13) | 0.099 |
| Sex, male—No. (%) | 175 (66) | 106 (61) | 69 (74) | 0.034 |
| Weight (kg)—median (IQR) | 82 (73–92) | 82 (73–;90) | 84 (70–95) | 0.256 |
| Smoking history—No. (%) | ||||
| Current | 29 (11) | 18 (10) | 11 (12) | 0.477 |
| Former | 60 (23) | 39 (23) | 21 (23) | 0.459 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2)—median (IQR) | 30 (27–34) | 30 (28–33) | 31 (27–34) | 0.424 |
| Normal (%) | 34 (13) | 24 (14) | 10 (11) | 0.786 |
| Overweight (%) | 88 (33) | 57 (33) | 31 (33) | |
| Obesity (%) | 144 (54) | 92 (53) | 52 (56) | |
| Days from symptom onset to admission—median (IQR) | 8 (5–13) | 8 (5–14) | 7 (5–11) | 0.504 |
| Days from admission to discharge—median (IQR) | 10 (6–23) | 12 (7–25) | 9 (5–17) | 0.004 |
| Pre-existing diseases—No. (%) | ||||
| Diabetes | 74 (28) | 40 (23) | 34 (37) | 0.023 |
| Hypertension | 87 (33) | 57 (33) | 30 (32) | 0.892 |
| Hepatic disease | 12 (5) | 7 (4) | 5 (5) | 0.758 |
| Alcoholism | 23 (9) | 13 (8) | 10 (11) | 0.239 |
| Asthma | 4 (2) | 3 (2) | 1 (1) | 0.999 |
| Cancer | 8 (3) | 5 (3) | 3 (3) | 0.999 |
| Symptomatic treatment prior admission—No. (%) | ||||
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and acetaminophen | 145 (55) | 101 (58) | 44 (47) | 0.094 |
| Antibiotics | 173 (65) | 113 (65) | 60 (65) | 0.999 |
| Antihistamines | 19 (7) | 14 (8) | 5 (5) | 0.466 |
| Antivirals | 31 (12) | 26 (15) | 5 (5) | 0.026 |
| Antitussives | 29 (11) | 22 (13) | 7 (8) | 0.222 |
| Antiasthmatics | 30 (11) | 21 (12) | 9 (10) | 0.685 |
| Chloroquine | 8 (3) | 8 (5) | 0 (0) | 0.054 |
| Corticosteroids | 51 (19) | 34 (20) | 17 (18) | 0.871 |
| Others | 75 (28) | 48 (28) | 27 (29) | 0.887 |
| Interventions—No. (%) | ||||
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | 151 (57) | 75 (43) | 76 (82) | <0.0001 |
| Use of vasopressors | 147 (55) | 75 (43) | 72 (77) | <0.0001 |
| Enteral nutrition | 136 (51) | 72 (42) | 64 (69) | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Limon-de la Rosa, N.; Cervantes-Alvarez, E.; Méndez-Guerrero, O.; Gutierrez-Gallardo, M.A.; Kershenobich, D.; Navarro-Alvarez, N. Time-Dependent Changes of Laboratory Parameters as Independent Predictors of All-Cause Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Biology 2022, 11, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040580
Limon-de la Rosa N, Cervantes-Alvarez E, Méndez-Guerrero O, Gutierrez-Gallardo MA, Kershenobich D, Navarro-Alvarez N. Time-Dependent Changes of Laboratory Parameters as Independent Predictors of All-Cause Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Biology. 2022; 11(4):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040580
Chicago/Turabian StyleLimon-de la Rosa, Nathaly, Eduardo Cervantes-Alvarez, Osvely Méndez-Guerrero, Miguel A. Gutierrez-Gallardo, David Kershenobich, and Nalu Navarro-Alvarez. 2022. "Time-Dependent Changes of Laboratory Parameters as Independent Predictors of All-Cause Mortality in COVID-19 Patients" Biology 11, no. 4: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040580
APA StyleLimon-de la Rosa, N., Cervantes-Alvarez, E., Méndez-Guerrero, O., Gutierrez-Gallardo, M. A., Kershenobich, D., & Navarro-Alvarez, N. (2022). Time-Dependent Changes of Laboratory Parameters as Independent Predictors of All-Cause Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Biology, 11(4), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040580







