Effects of “Bacuri” Seed Butter (Platonia insignis Mart.), a Brazilian Amazon Fruit, on Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus-Related Parameters in STZ-Diabetic Rats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
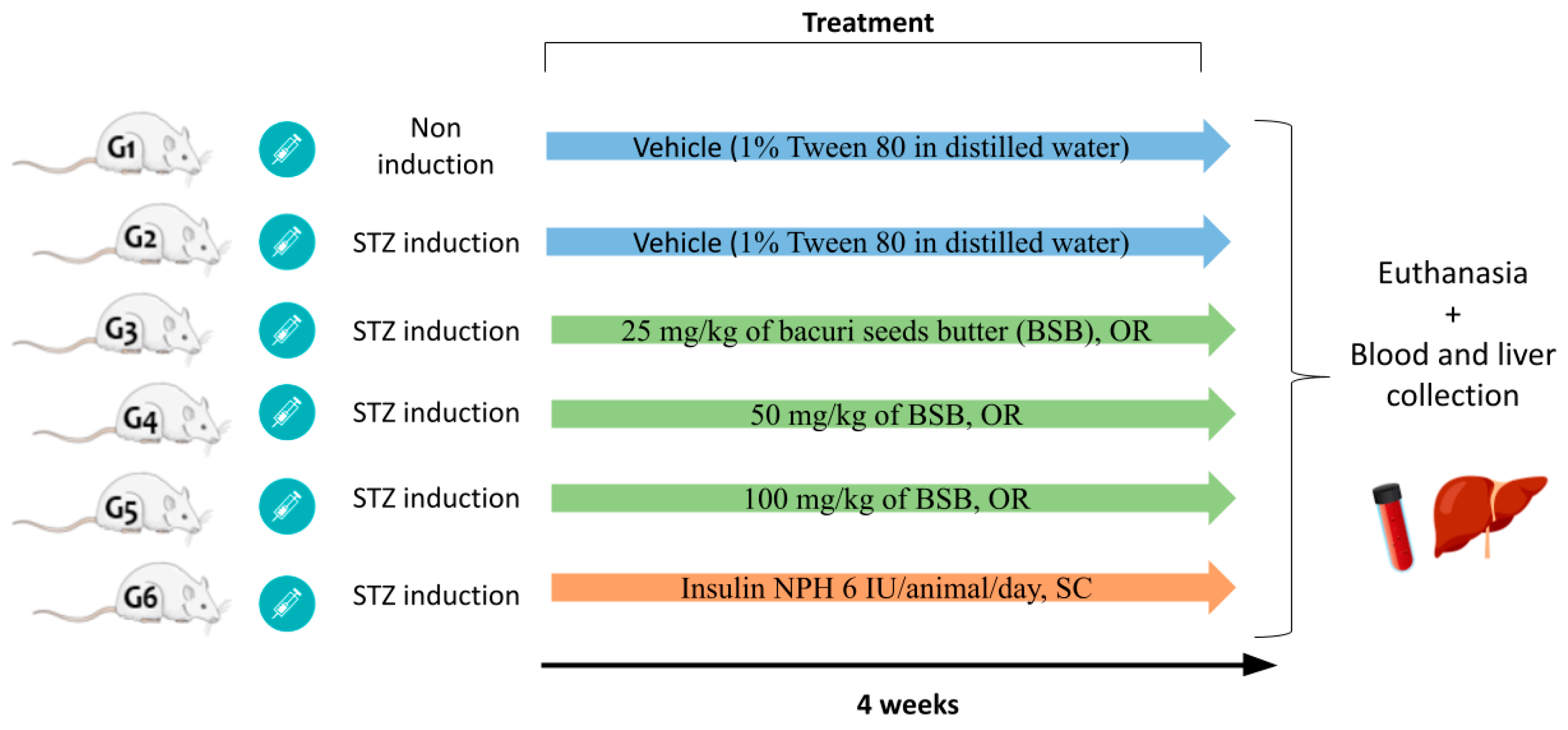
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. The Seed Butter from “Bacuri” (Platonia insignis Mart.)
2.3. Experimental Diabetes Induction
2.4. Biochemical Assays
2.5. Histopathology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Bacuri Seed Butter (Platonia insignis Mart.) Treatment on Body Weight and Food Intake
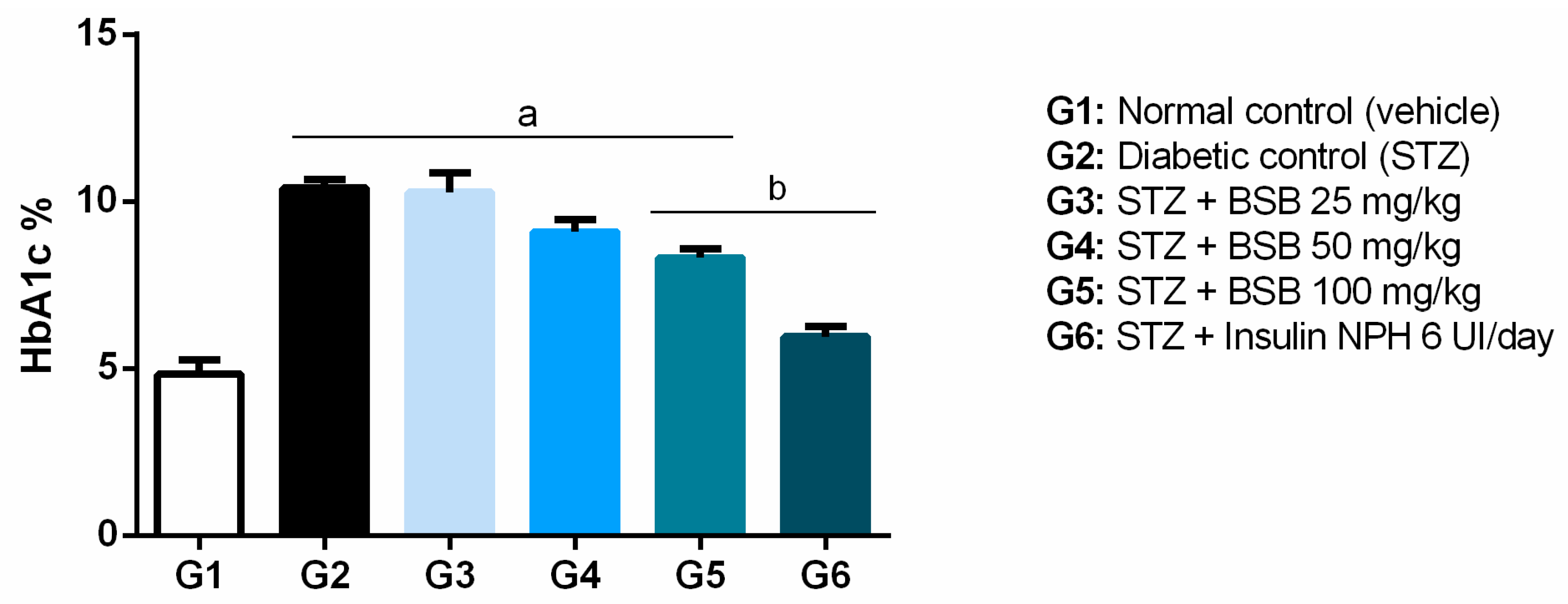
3.2. Effects of Bacuri Seed Butter (BSB) (Platonia insignis Mart.) on Fast Blood Glucose Levels and Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Percentage
3.3. Effects of Bacuri Seed Butter (BSB) (Platonia insignis Mart.) on Biomarkers of Liver and Kidney Function
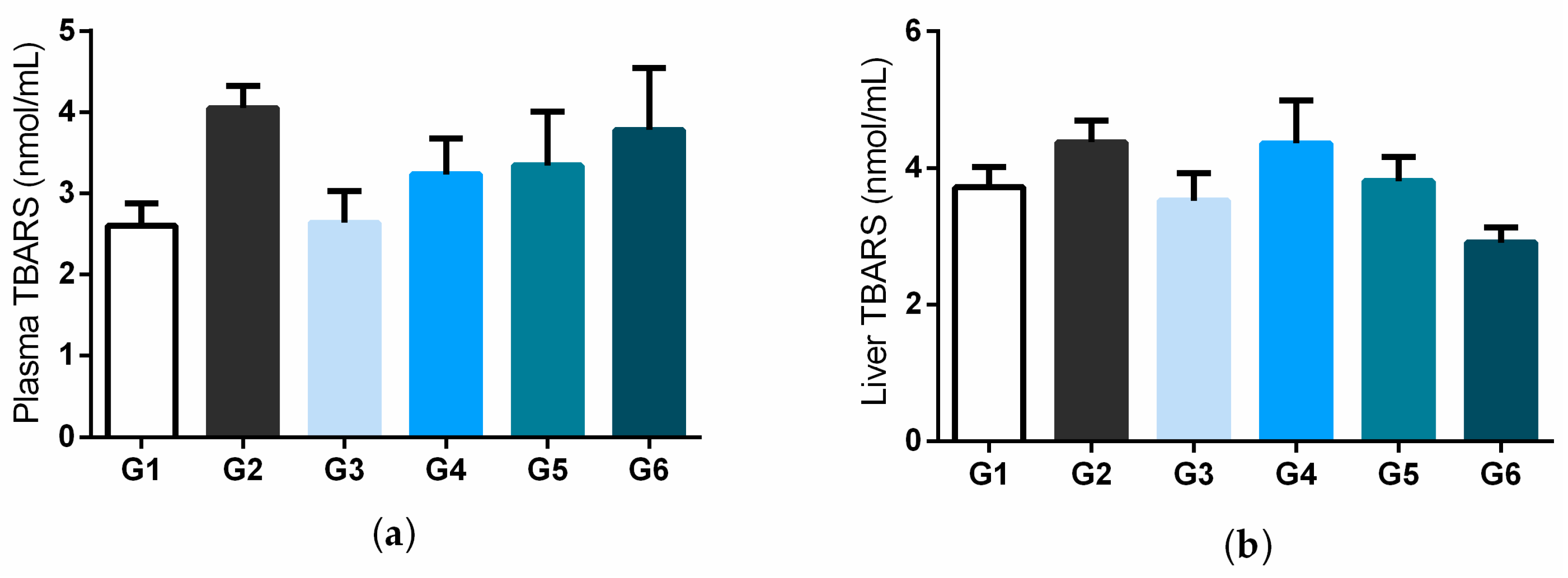
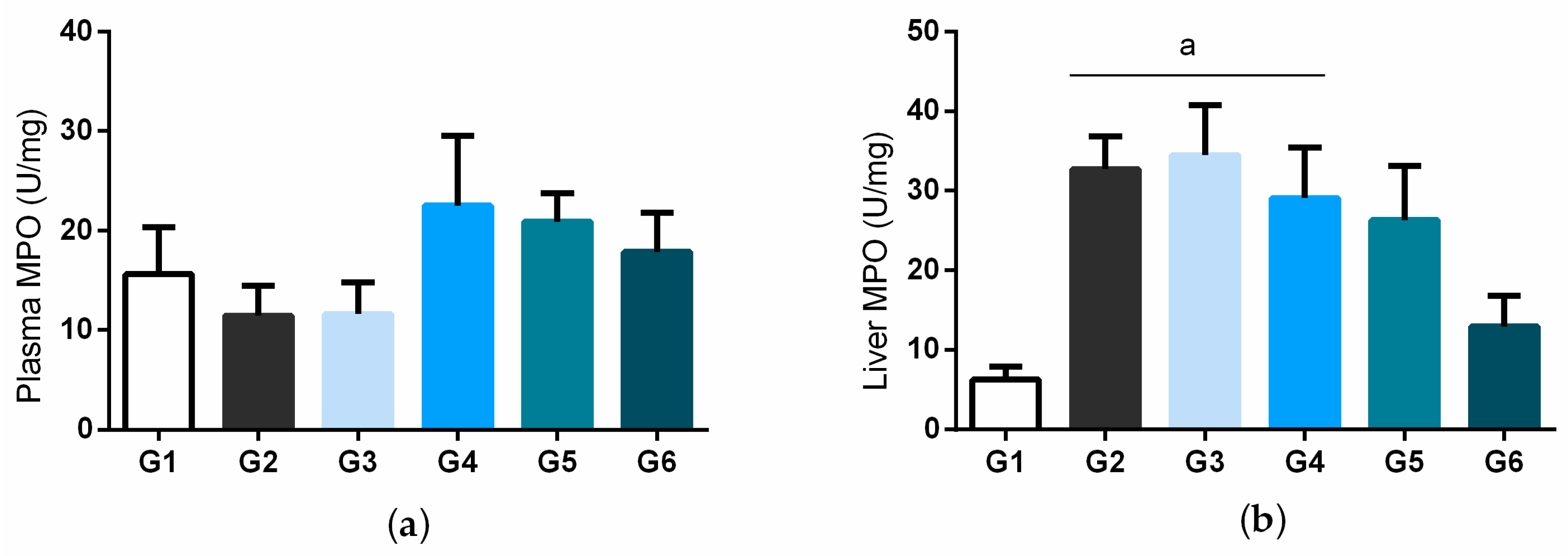
3.4. Effects of Bacuri Seed Butter (BSB) (Platonia insignis Mart.) on Lipid Peroxidation and Myeloperoxidase Activity in Plasma and Liver
3.5. Effect of Bacuri Seed Butter (Platonia insignis Mart.) on Antioxidant Compounds
3.6. Morphological Changes in Liver Tissue of Diabetic Animals Treated with Bacuri Seed Butter (BSB) (Platonia insignis Mart.)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souza, V.A.B.; Vasconcelos, L.F.L.; Araújo, E.C.E.; Alves, R.E. Bacurizeiro: Platonia insignis Mart.; Funep: São Paulo, Brazil, 2000; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, M.C.C.L.; Homma, A.K.O.; Menezes, A.J.E.A.; Carvalho, A.C.P.P.; Ferreira, A.; Benbadis, A.K.; Muller, C.H.; Fereira, C.A.P.; Cruz, C.D.; Araújo, E.C.E.; et al. Bacuri: Agrobiodiversidade; Instituto Interamericano de Cooperação para a Agricultura: São Luís, Brazil, 2007; p. 210. [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, W.M.O.; Carvalho, J.E.U.; Muler, C.H. Ocorrência e distribuição geográfica do bacurizeiro. Rev. Bras. De Frutic. 2007, 29, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, A.; Cicero, N. Development of Food Chemistry, Natural Products, and Nutrition Research: Targeting New Frontiers. Foods 2020, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, P.E.N. Caracterização Química e Nutricional de Algumas Frutas do Estado do Maranhão. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Maranhão, São Luis, Brazil, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, G.H.A. Frutos do Bacurizeiro (Platonia insignis Mart.): Caracterização, Qualidade e Conservação. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista, São Paulo, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Bernini, R.; Campo, M.; Vita, C.; Souto, E.B.; Lombardi-Boccia, G.; Ramadan, M.F.; Santini, A.; Romani, A. Fruit Wastes as a Valuable Source of Value-Added Compounds: A Collaborative Perspective. Molecules 2021, 26, 6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feitosa, C.M.; Dos Santos, P.R.P.; De Freitas, R.M.; Rodrigues, A.M.X.; De, G.A.L.O.; Junior, J.S.D.C.; Cavalcante, A.D.N. Ensaios pré-clínicos em ratos tratados com 1,3-diestearil-2-oleil-glicerol, constituinte isolado de Platonia insiginis. ConSci. Saúde 2015, 14, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Júnior, J.S.; Ferraz, A.B.F.; Filho, B.A.B.; Feitosa, C.M.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Freitas, R.M.; Saffi, J. Evaluation of antioxidant effects in vitro of garcinielliptone FC (GFC) isolated from Platonia insignis Mart. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Costa Júnior, J.S.; Almeida, A.A.C.; Costa, J.P.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Saffi, J.; Freitas, R.M. Superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in rat hippocampus pretreated with garcinielliptone FC from Platonia insignis. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, É.A.; Alves, M.M.D.M.; Amorim, L.V.; Carvalho, R.D.C.V.; Cruz, L.P.L.; Costa-Júnior, J.S.; Oliveira, M.D.D.A.; Neto, J.D.S.L.; Carvalho, F.A.D.A.; Citó, A.M.D.G.L.; et al. Garcinielliptone FC: Selective anti-amastigote and immunomodulatory effects on macrophages infected by Leishmania amazonensis. Toxicol. Vitr. 2020, 63, 104750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcanjo, D.D.R.; Costa Júnior, J.S.; Moura, L.H.P.; Ferraz, A.B.F.; Rossatto, R.R.; David, J.M.; Quintans Júnior, L.J.; Oliveira, R.C.M.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; de Oliveira, A.P. Garcinielliptone FC, a polyisoprenylated benzophenone from Platonia insignis Mart., promotes vaso-relaxant effect on rat mesenteric artery. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agra, M.D.F.; Silva, K.N.; Basílio, I.J.L.D.; De Freitas, P.F.; Filho, J.M.B. Survey of medicinal plants used in the region Northeast of Brazil. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2008, 18, 472–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agra, M.; De Freitas, P.F.; Filho, J.M.B. Synopsis of the plants known as medicinal and poisonous in Northeast of Brazil. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2007, 17, 114–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, J.S.D.C.; Feitosa, C.M.; Cito, A.M.D.G.; de Freitas, R.M.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Saffi, J. Evaluation of Effects of Ethanolic Extract from Platonia insignis Mart. on Pilocarpine-induced Seizures. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 10, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lustosa, A.K.M.F.; Silva, F.V.; Silva, E.R.S.; Mendes, A.N.; Sousa, L.R.; Carvalho, A.L.M.; Citó, A.M.G.L. Lecithin-based organogel for an industrialized butter from Platonia insignis Mart. seeds and its anti-inflammatory potential: Formulation and preclinical studies. J. Glob. Innov. 2020, 2, eJGI000011. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, G.D.M.; Brito, A.K.D.S.; de Farias, L.M.; Rodrigues, L.A.R.L.; Pereira, C.F.D.C.; Lima, S.K.R.; Frota, K.D.M.G.; Rizzo, M.D.S.; Nunes, P.H.M.; Lucarini, M.; et al. Effects of “Bacuri” Seed Butter (Platonia insignis Mart.) on Metabolic Parameters in Hamsters with Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5584965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustosa, A.K.M.; Arcanjo, D.D.; Ribeiro, R.G.; Rodrigues, K.A.F.; Passos, F.F.B.; Piauilino, C.A.; Silva-Filho, J.C.; Araújo, B.Q.; Lima-Neto, J.S.; Costa-Júnior, J.S.; et al. Immunomodulatory and toxicological evaluation of the fruit seeds from Platonia insignis, a native species from Brazilian Amazon Rainforest. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2016, 26, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustosa, A.K.M.F.; Bezerra, É.A.; Rodrigues, K.A.F.; Amorim, L.V.; Lima-Neto, J.S.; Araújo, B.Q.; Costa Junior, J.S.; Mendes, A.N.; Carvalho, F.A.A.; Arcanjo, D.D.R. Efeito antileishmania de sementes de frutos de Platonia insignis contra formas amastigotas internalizadas por macrófagos de Leishmania amazonensis. Rev. Cuba. Plantas Med. 2018, 23, 2018. Available online: http://www.revplantasmedicinales.sld.cu/index.php/pla/article/view/639 (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Lustosa, A.K.M.F.; Coêlho, A.G.; dos Santos, A.A.; Barros, Y.S.O.; Rodrigues, K.A.d.F.; Amorim, L.V.; Alves, M.M.D.M.; Carvalho, A.L.M.; Mendes, A.N.; Carvalho, F.A.D.A.; et al. Formulações tópicas à base de manteiga das sementes de Platonia insignis Mart. para o tratamento de lesões relacionadas à leishmaniose cutânea experimental. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e52310413665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.H.P.; Oliveira, S.L.; Seara, L.T. O papel dos produtos finais da glicação avançada (AGEs) no desenvolvimento de com-plicações vasculares do diabetes. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 52, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M.C. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Biochemistry of oxidative stress. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genestra, M. Oxyl radicals, redox-sensitive signalling cascades and antioxidants. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Atlas, 7th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 40 (Suppl. 1), S11–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Prior, R.L. The Chemistry behind Antioxidant Capacity Assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, E.B.; Santini, A.; Gan, R.-Y.; Jozwik, A.; Grzybek, W.; Horbańczuk, J.O.; et al. Natural products in diabetes research: Quantitative literature analysis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 35, 5813–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A. Plants and Diabetes: Description, Role, Comprehension and Exploitation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Lei n. 11.794, de 8 de Outubro de 2008. Regulamenta o Inciso VII do § 1º do art. 225 da Constituição Federal, Esta-Belecendo Procedimentos para o Uso Científico de Animais; Revoga a Lei n. 6.638, de 8 de Maio de 1979; e dá Outras Providências. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília; (196); SEÇÃO 1:1-4, 2008; Congresso Nacional: Brasilia, Brazil, 2008.
- Brasil. Lei n. 9.605, de 12 de fevereiro de 1998. Dispõe sobre as sanções penais e administrativas derivadas de condutas e atividades lesivas ao meio ambiente, e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília; Congresso Nacional: Brasilia, Brazil, 1998.
- Oliveira, M.D.D.A.D.; Alves, P.E.S.; Sousa, H.G.; Silva, D.D.C.; Rai, M.K.; Lima, N.M.; Andrade, T.D.J.A.D.S.; Feitosa, C.M.; Júnior, J.S.D.C. Genotoxic and cytotoxic activities of hexane extract in seeds from Platonia insignis Mart. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e13911225504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Zhu, J.; Liu, K.-Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, G.-L.; Xu, S.; Lv, W.-H.; Xie, Z.-G. Puerarin enhances superoxide dismutase activity and inhibits RAGE and VEGF expression in retinas of STZ–induced early diabetic rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 5, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, R.H.; Sankaranarayanan, C. B-caryophyllene, a natural sesquiterpene lactone attenuates hyperglycemia mediated oxi-dative and inflammatory stress in experimental diabetic rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 245, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farbood, Y.; Rashno, M.; Ghaderi, S.; Khoshnam, S.E.; Sarkaki, A.; Rashidi, K.; Rashno, M.; Badavi, M. Ellagic acid protects against diabetes-associated behavioral deficits in rats: Possible involved mechanisms. Life Sci. 2019, 225, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.P.; Priebat, D.A.; Christensen, R.D.; Rothstein, G. Measurement of Cutaneous Inflammation: Estimation of Neutrophil Content with an Enzyme Marker. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 78, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.; Samanta, L.; Chainy, G.B.D. A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase using nitrite formation by superoxide radicals. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 37, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb, A.F.S.A. Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1972; Volume 25, p. 457. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, L.G. Routine Staining Procedures. In Manual of Histologic Staining Methods of The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; Luna, L.G., Ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lerco, M.M.; Spadella, C.T.; Machado, J.L.M.; Schellini, S.A.; Padovani, C.R. Caracterização de um modelo experimental de Diabetes mellitus, induzido pela aloxana em ratos. Estudo clínico e laboratorial. Acta Cir. Bras. 2003, 18, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelgassim, A.O. Effect of Acacia nilotica Fruit Extract on Serum Glucose and Lipid Concentrations in Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rats. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ali, Y.; Paul, S.; Tanvir, E.M.; Hossen, S.; Rumpa, N.-E.N.; Saha, M.; Bhoumik, N.; Islam, A.; Hossain, S.; Alam, N.; et al. Antihyperglycemic, Antidiabetic, and Antioxidant Effects of Garcinia pedunculata in Rats. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 2979760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Habori, M.; Raman, A. Antidiabetic and hypocholesterolaemic effects of fenugreek. Phytother. Res. 1998, 12, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konda, P.Y.; Dasari, S.; Konanki, S.; Nagarajan, P. In vivo antihyperglicemic, antihyperlipidemic, antioxidative stress and anti-oxidant potentials activities of Syzygium paniculatum Gaertn. In Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats, Helyon 5; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.K. The potential health benefit of polyisoprenylated benzophenones from Garcinia and related genera: Ethnobotanical and therapeutic importance. Fitoterapia 2013, 89, 86–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoro, S.M.; Aiyelaagbe, O.; Onocha, P.A.; Gloer, J.B. Gakolanone: A new benzophenone derivative from Garcinia kola Heckel stem-bark. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Eid, B.G.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Al-Rabia, M.W.; Khedr, A.I.M.; Nasrullah, M.Z.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. New Alpha-Amylase Inhibitory Metabolites from Pericarps of Garcinia mangostana. Life 2022, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamkhani, F.; Zardooz, H.; Zahediasl, S.; Farrokhi, B. Comparison of the effects of acute and chronic psychological stress on metabolic features in rats. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2012, 13, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyachaturawat, P.; Poprasit, J.; Glinsukon, T.; Wanichanon, C. Gastric mucosal lesions in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 1988, 12, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyachaturawat, P.; Poprasit, J.; Glinsukon, T. Gastric mucosal secretions and lesions by different doses of streptozotocin in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 1991, 55, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, M.S.; Rodrigues, L.S.; Neto, L.S.; Moraes-Souza, R.; Soares, T.S.; Américo, M.F.; Campos, K.E.; Damasceno, D.C.; Volpato, G.T. Effect of Bauhinia holophylla treatment in Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2017, 89, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aratani, Y. Myeloperoxidase: Its role for host defense, inflammation, and neutrophil function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 640, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.-T.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wang, A.-B.; Wu, J.; Basila, D.; Yuan, C.-S. Antihyperglycemic effects of total ginsenosides from leaves and stem of Panax ginseng. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, H.; Goodarzi, M.T.; Salemi, Z.; Seifi, M. Antioxidant Effects of Biochanin A in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2017, 60, e17160741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
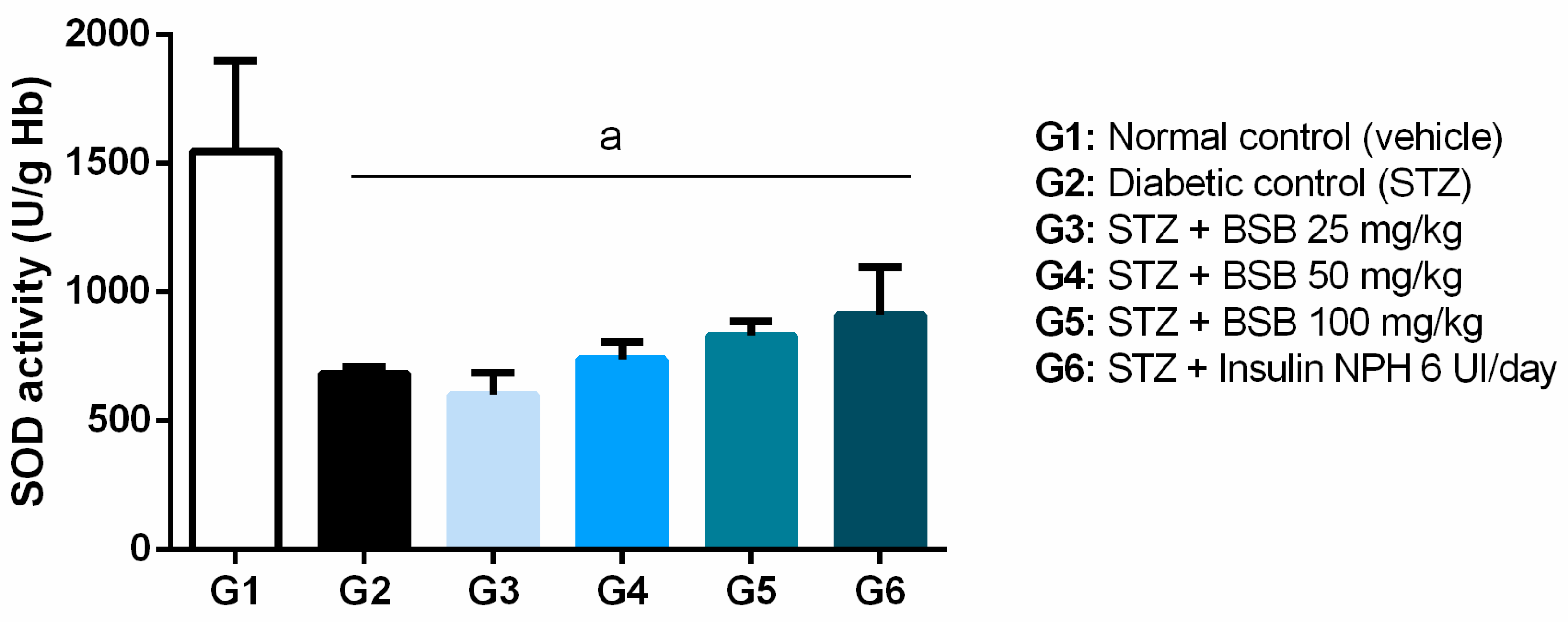
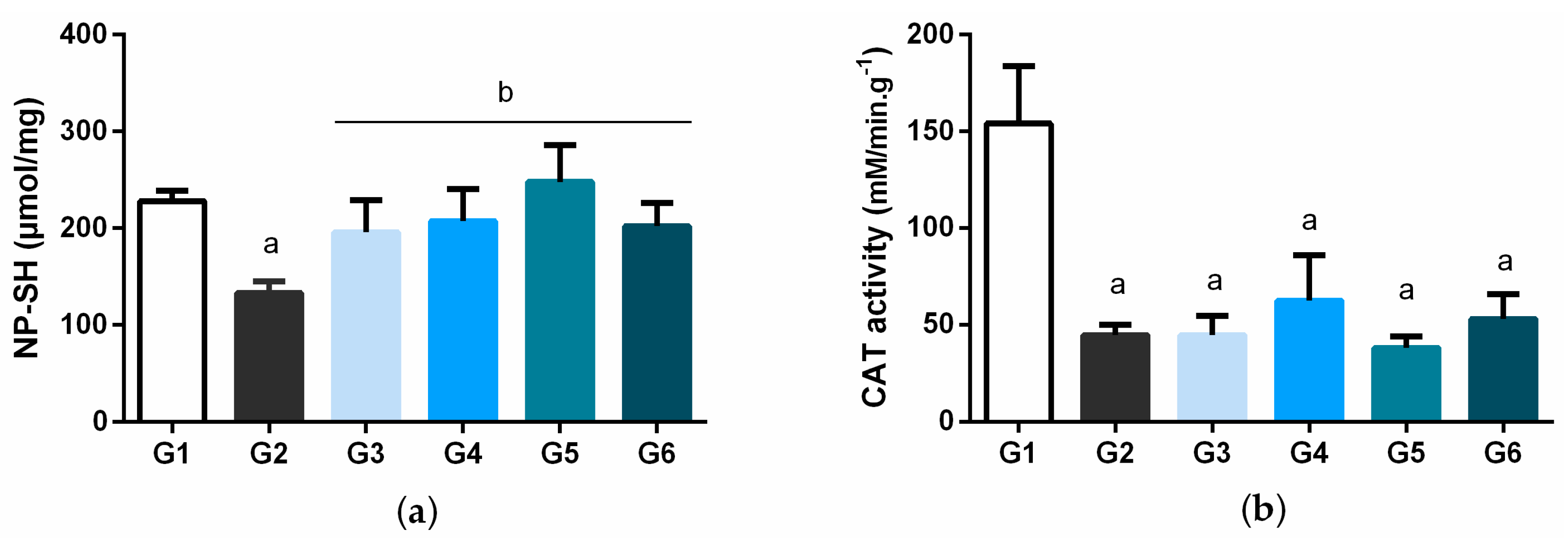

| Normal Control | Diabetic Control | BSB | Insulin NPH 6 UI/Animal/Day | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | 100 mg/kg | ||||
| Body weight gain (g) | 12.4 ± 2.5 | −31.2 ± 4.8 a | −31.6 ± 7.5 a | −25.1 ± 3.1 a | −35.6 ± 6.3 a | 28.4 ± 2.9 b |
| Food Intake (g) | 14.8 ± 0.4 | 35.9 ± 1.07 a | 32.4 ± 1.2 a | 31.7 ± 1.3 a | 32.9 ± 1.4 a | 22.2 ± 0.5 ab |
| Group | Fast Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Week | Second Week | Third Week | Fourth Week | |
| Normal control | 87.8 ± 4.3 | 99.6 ± 2.5 | 95.14 ± 4.1 | 91.43 ± 3.0 |
| Diabetic control | 477.0 ± 18.7 a | 515.0 ± 27.3 a | 515.4 ± 29.7 a | 539.7 ± 29.9 a |
| BSB 25 mg/kg | 509.4 ± 25.4 a | 514.6 ± 22.3 a | 497.8 ± 36.3 a | 470.2 ± 22.3 a |
| BSB 50 mg/kg | 468.8 ± 32.9 a | 543.2 ± 35.6 a | 600.0 ± 0.0 a | 554.2 ± 29.2 a |
| BSB 100 mg/kg | 486.4 ± 34.5 a | 497.8 ± 43.8 a | 532.0 ± 20.7 a | 571.2 ± 16.2 a |
| NPH insulin | 474.6 ± 20.4 a | 477.2 ± 19.4 a | 480.8 ± 30.1 a | 514.0 ± 31.8 a |
| Normal Control | Diabetic Control | BSB | Insulin NPH 6 UI/Animal/Day | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | 100 mg/kg | ||||
| ALT (U/L) | 47.00 ± 3.6 | 325.2 ± 26.9 a | 229.3 ± 17.3 ab | 195.3 ± 17.7 ab | 137.6 ± 21.6 ab | 62.0 ± 14.97 b |
| AST (U/L) | 111.1 ± 5.3 | 678.3 ± 64.6 a | 329.3 ± 59.1 ab | 287.5 ± 32.8 b | 192.6 ± 20.4 b | 161.2 ± 45.9 b |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 1.77 ± 0.1 a | 1.88 ± 0.1 a | 1.8 ± 0.1 a | 2.2 ± 0.1 b | 2.1 ± 0.1 |
| Liver relative weight (g) | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 4.09 ± 0.1 a | 4.97 ± 0.2 a | 4.8 ± 0.1 a | 4.96 ± 0.1 a | 3.7 ± 0.2 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lindoso, J.V.d.S.; Alencar, S.R.; Santos, A.A.d.; Mello Neto, R.S.; Mendes, A.V.d.S.; Furtado, M.M.; Silva, M.G.d.; Brito, A.K.d.S.; Batista, E.K.F.; Baêta, S.d.A.F.; et al. Effects of “Bacuri” Seed Butter (Platonia insignis Mart.), a Brazilian Amazon Fruit, on Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus-Related Parameters in STZ-Diabetic Rats. Biology 2022, 11, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040562
Lindoso JVdS, Alencar SR, Santos AAd, Mello Neto RS, Mendes AVdS, Furtado MM, Silva MGd, Brito AKdS, Batista EKF, Baêta SdAF, et al. Effects of “Bacuri” Seed Butter (Platonia insignis Mart.), a Brazilian Amazon Fruit, on Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus-Related Parameters in STZ-Diabetic Rats. Biology. 2022; 11(4):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040562
Chicago/Turabian StyleLindoso, Jéssica Vanessa dos Santos, Salmon Rocha Alencar, Andressa Amorim dos Santos, Renato Sampaio Mello Neto, Ana Victória da Silva Mendes, Mariely Mendes Furtado, Maisa Gomes da Silva, Ana Karolinne da Silva Brito, Emanuelle Karine Frota Batista, Silvia de Araújo França Baêta, and et al. 2022. "Effects of “Bacuri” Seed Butter (Platonia insignis Mart.), a Brazilian Amazon Fruit, on Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus-Related Parameters in STZ-Diabetic Rats" Biology 11, no. 4: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040562
APA StyleLindoso, J. V. d. S., Alencar, S. R., Santos, A. A. d., Mello Neto, R. S., Mendes, A. V. d. S., Furtado, M. M., Silva, M. G. d., Brito, A. K. d. S., Batista, E. K. F., Baêta, S. d. A. F., Moreira Nunes, P. H., Lucarini, M., Durazzo, A., Arcanjo, D. D. R., & Martins, M. d. C. d. C. e. (2022). Effects of “Bacuri” Seed Butter (Platonia insignis Mart.), a Brazilian Amazon Fruit, on Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus-Related Parameters in STZ-Diabetic Rats. Biology, 11(4), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040562









