Androgen Glucuronidation in Mice: When, Where, and How
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animal Experiments and Tissue Collection
2.3. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.4. Murine Ugt2b cDNA Cloning and Stable Expression in HEK293 Cells
2.5. Microsome Isolation, Western-Blotting, and Glucuronidation Assays
2.6. Steroid Quantification
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
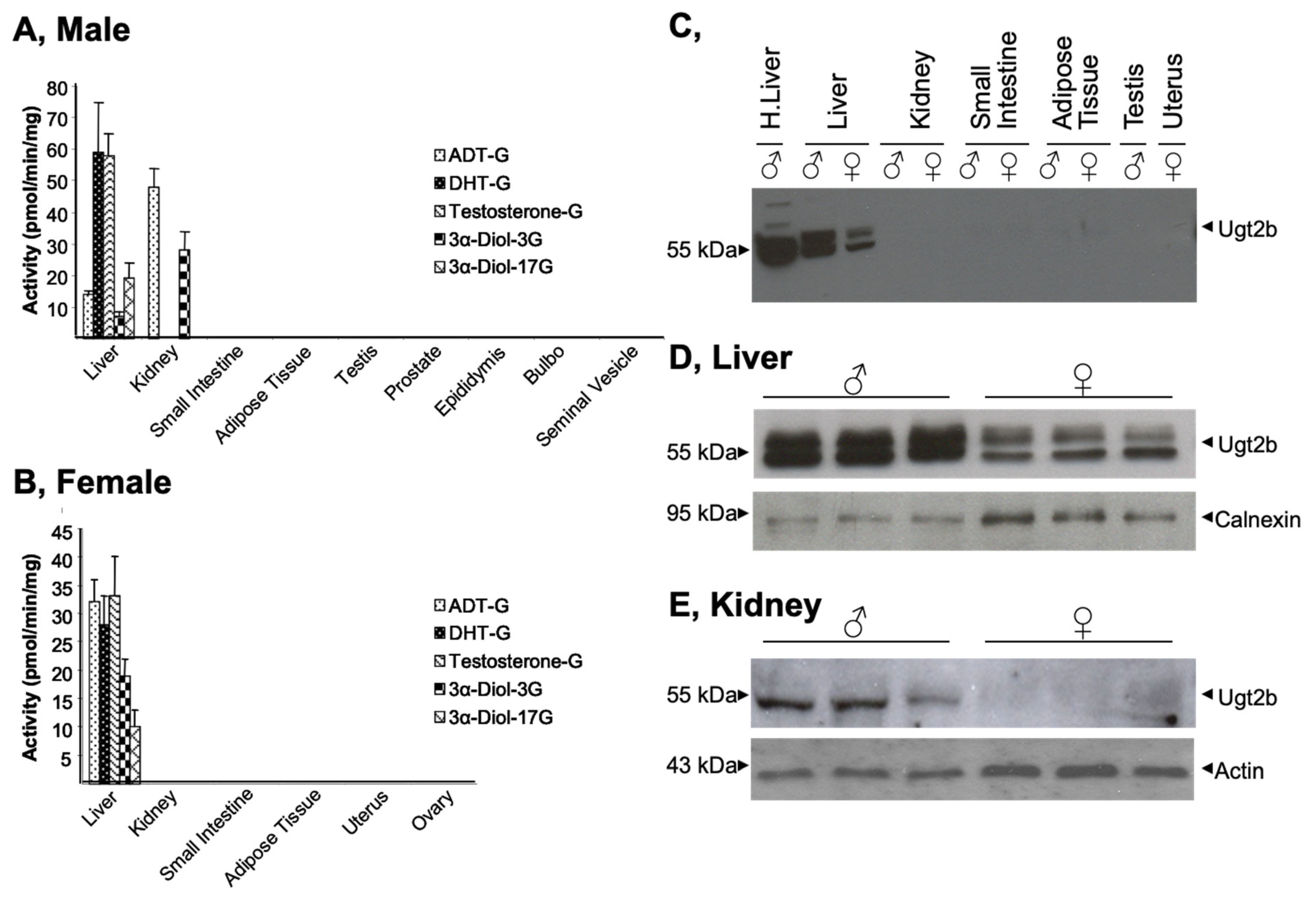
3.1. Gender- and Tissue-Specific Androgen Glucuronidation and Ugt2b Expression in Mice
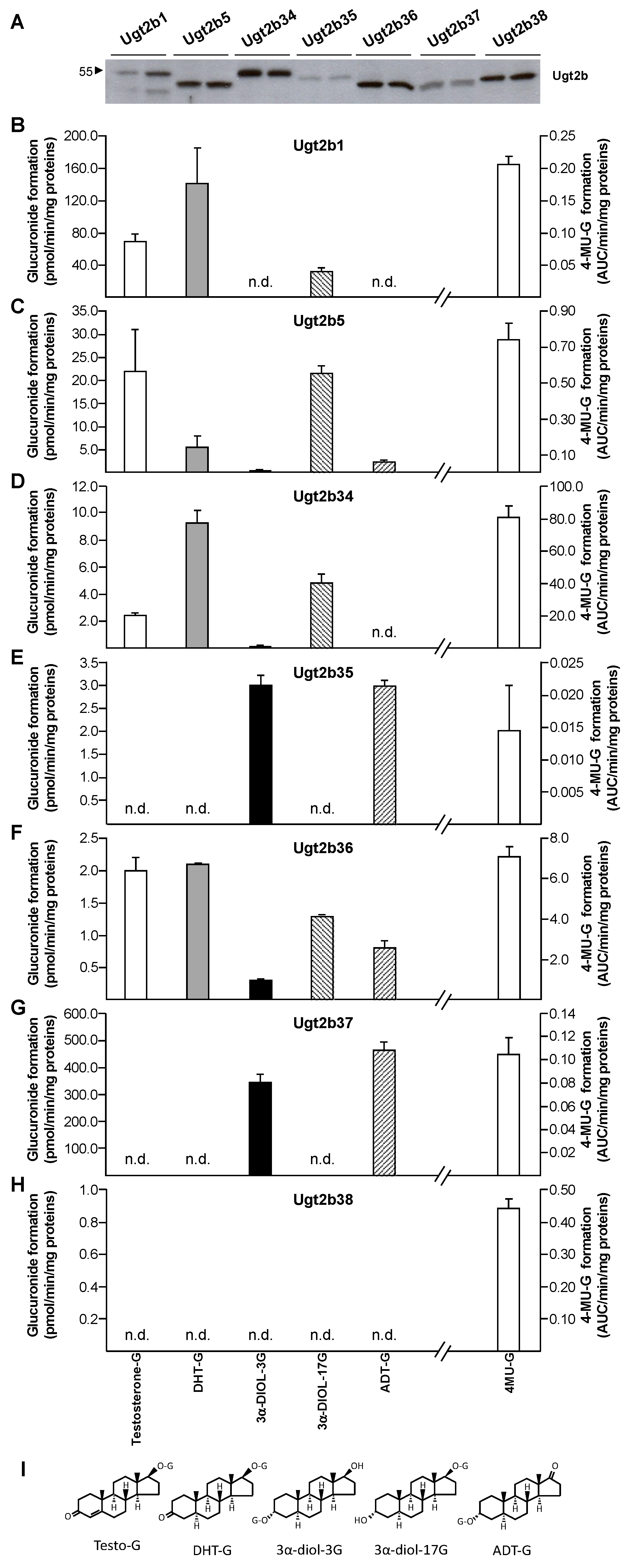
3.2. Androgen Selectivity of Murine Ugt2b Enzymes
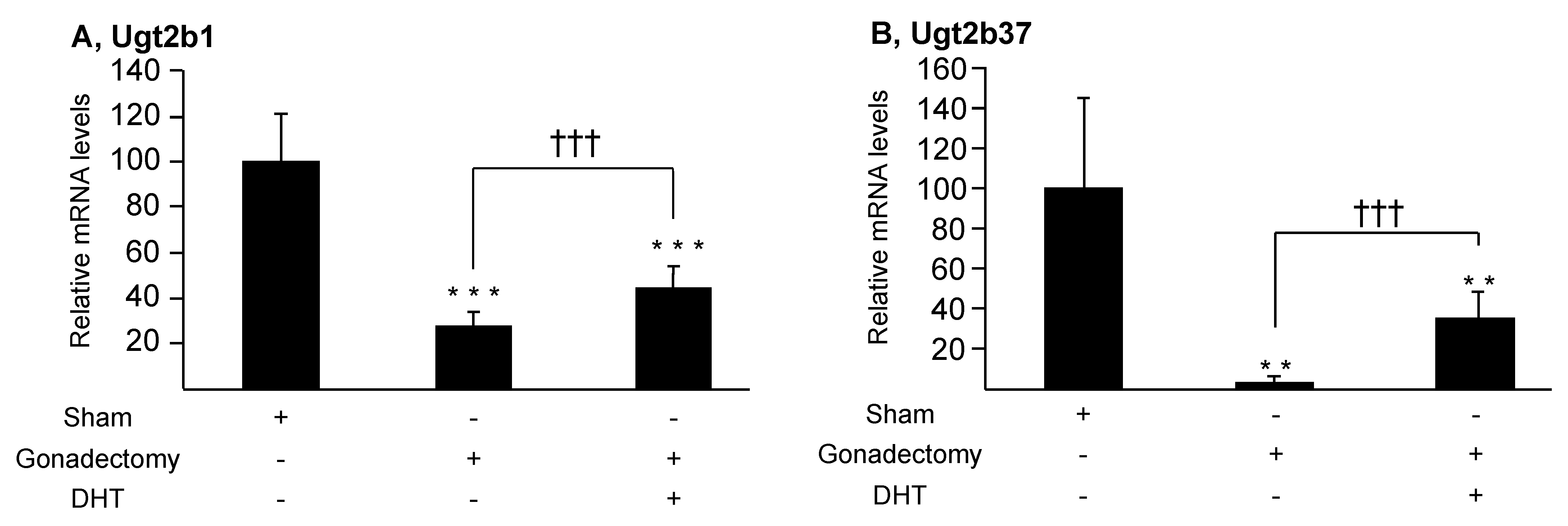
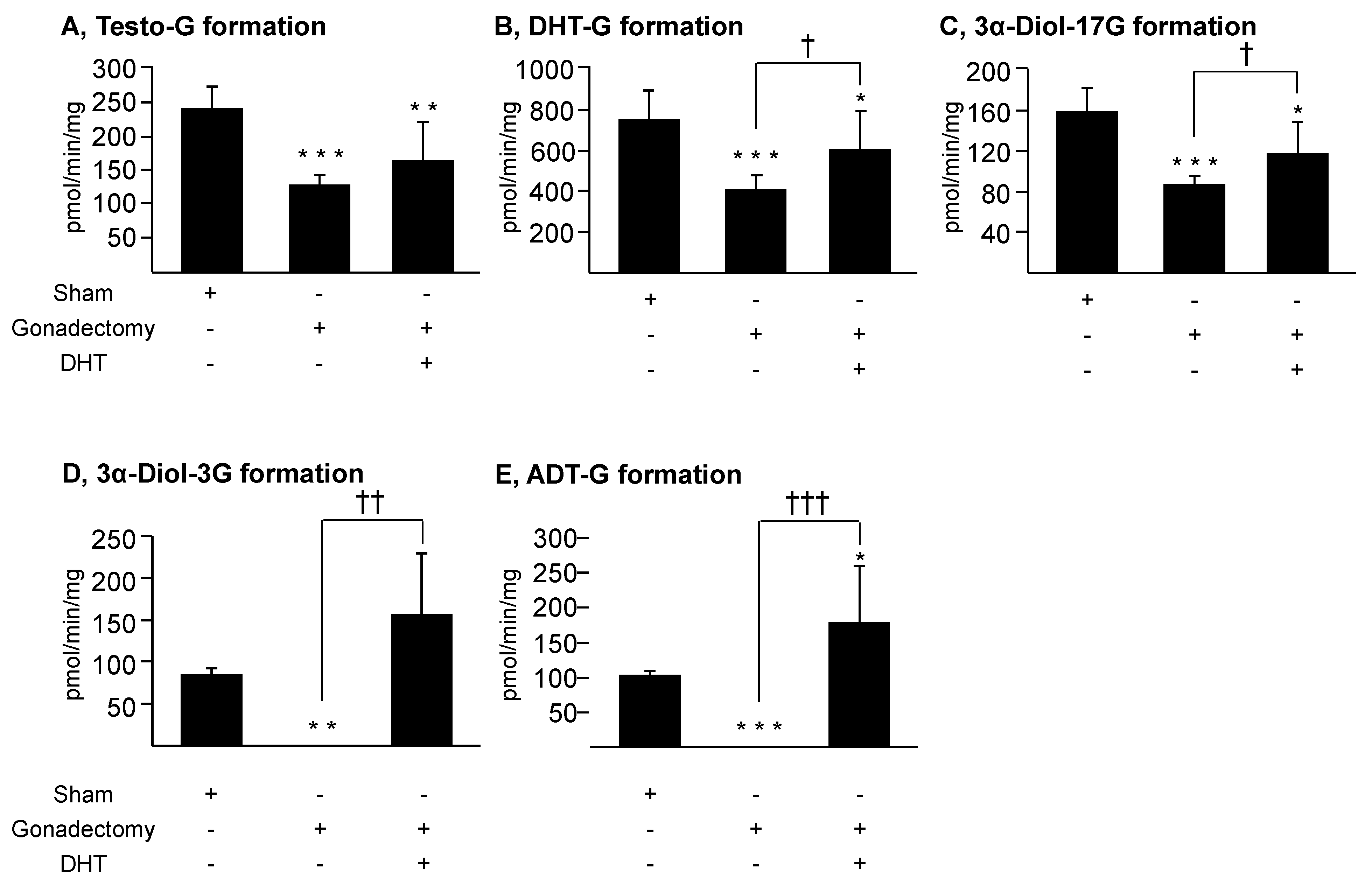
3.3. Androgens Control Their Own Glucuronidation in the Murine Liver and Kidney
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Tukey, R.H.; Strassburg, C.P. Human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: Metabolism, expression, and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 40, 581–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tephly, T.R.; Burchell, B. UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: A family of detoxifying enzymes. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1990, 11, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, D.; Carrier, J.S.; Levesque, E.; Hum, D.W.; Belanger, A. Relative enzymatic activity, protein stability, and tissue distribution of human steroid-metabolizing UGT2B subfamily members. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, P.I.; Bock, K.W.; Burchell, B.; Guillemette, C.; Ikushiro, S.; Iyanagi, T.; Miners, J.O.; Owens, I.S.; Nebert, D.W. Nomenclature update for the mammalian UDP glycosyltransferase (UGT) gene superfamily. Pharm. Genom. 2005, 15, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemette, C.; Levesque, E.; Harvey, M.; Bellemare, J.; Menard, V. UGT genomic diversity: Beyond gene duplication. Drug Metab. Rev. 2010, 42, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, D.B.; Klaassen, C.D. Tissue- and gender-specific mRNA expression of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) in mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, D.B.; Klaassen, C.D. Mechanism of gender-divergent UDP-glucuronosyltransferase mRNA expression in mouse liver and kidney. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, O.; Belanger, A. Inactivation of androgens by UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in the human prostate. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 22, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Basit, A.; Wolford, C.; Chen, K.F.; Gaedigk, A.; Lin, Y.S.; Leeder, J.S.; Prasad, B. Normalized Testosterone Glucuronide as a Potential Urinary Biomarker for Highly Variable UGT2B17 in Children 7–18 Years. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 107, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, E.; Labriet, A.; Hovington, H.; Allain, E.P.; Melo-Garcia, L.; Rouleau, M.; Brisson, H.; Turcotte, V.; Caron, P.; Villeneuve, L.; et al. Alternative promoters control UGT2B17-dependent androgen catabolism in prostate cancer and its influence on progression. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, L.; Roels, K.; Van Renterghem, P.; Van Eenoo, P.; Deventer, K. Steroid profiling in urine of intact glucuronidated and sulfated steroids using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1624, 461231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Gupta, A.; Gaborik, Z.; Kis, E.; Prasad, B. Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide-Mediated Hepatic Uptake of Glucuronide Metabolites of Androgens. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 98, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Hartmann, M.F.; Wudy, S.A. Targeted LC-MS/MS analysis of steroid glucuronides in human urine. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 205, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, B.M.; Howell, M.E.; Ma, L.; Enders, J.R.; Lehman, D.; Corey, E.; Barycki, J.J.; Simpson, M.A. Altered glucuronidation deregulates androgen dependent response profiles and signifies castration resistance in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1886–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, D.K.; Basit, A.; Zhang, H.; Gaedigk, A.; Lee, S.B.; Claw, K.G.; Mehrotra, A.; Chaudhry, A.S.; Pearce, R.E.; Gaedigk, R.; et al. Hepatic Abundance and Activity of Androgen- and Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme UGT2B17 Are Associated with Genotype, Age, and Sex. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemette, C.; Hum, D.W.; Belanger, A. Levels of plasma C19 steroids and 5 alpha-reduced C19 steroid glucuronides in primates, rodents, and domestic animals. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 271, E348–E353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Belanger, A.; Schroeder, P.; Chang, L.; Falk, R.T.; Fears, T.R. Reproducibility of serum sex steroid assays in men by RIA and mass spectrometry. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2007, 16, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sten, T.; Bichlmaier, I.; Kuuranne, T.; Leinonen, A.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Finel, M. UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) 2B7 and UGT2B17 display converse specificity in testosterone and epitestosterone glucuronidation, whereas UGT2A1 conjugates both androgens similarly. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, D.; Chouinard, S.; Belanger, P.; Picard, S.; Labbe, J.F.; Borgeat, P.; Belanger, A. Glucuronidation of arachidonic and linoleic acid metabolites by human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, M.; Levesque, E.; Hum, D.W.; Belanger, A. Isolation and characterization of a novel cDNA encoding a human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase active on C19 steroids. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22855–22862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, S.; Pelletier, G.; Belanger, A.; Barbier, O. Cellular specific expression of the androgen-conjugating enzymes UGT2B15 and UGT2B17 in the human prostate epithelium. Endocr. Res. 2004, 30, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque, E.; Beaulieu, M.; Green, M.D.; Tephly, T.R.; Belanger, A.; Hum, D.W. Isolation and characterization of UGT2B15(Y85): A UDP-glucuronosyltransferase encoded by a polymorphic gene. Pharmacogenetics 1997, 7, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouinard, S.; Pelletier, G.; Belanger, A.; Barbier, O. Isoform-specific regulation of uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase 2B enzymes in the human prostate: Differential consequences for androgen and bioactive lipid inactivation. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 5431–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Barbier, O.; Belanger, A. The cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis) is the best animal model for the study of steroid glucuronidation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 85, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, O.; Girard, C.; Breton, R.; Belanger, A.; Hum, D.W. N-glycosylation and residue 96 are involved in the functional properties of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 11540–11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier-Landry, L.; Belanger, A.; Barbier, O. Multiple roles for UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)2B15 and UGT2B17 enzymes in androgen metabolism and prostate cancer evolution. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 145, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard, S.; Barbier, O.; Belanger, A. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B15 (UGT2B15) and UGT2B17 enzymes are major determinants of the androgen response in prostate cancer LNCaP cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 33466–33474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Real-Time Pcr Primers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | Annealing Temperature | |
| PPIA | 5′-TCCTGGCATCTTGTCCATG-3′ | 5′-CATCCAGCCATTCAGTCTTG-3′ | 54 °C |
| Ugt2b1 | 5′-TATGTTGCAGGTGTTGCT-3′ | 5′-GTCCCAGAAGGTTCGAAC-3′ | 60 °C |
| Ugt2b5 | 5′-GGGACTCATTTTACAGTGAG-3′ | 5′-CATGTTACTAACCATTGACC-3′ | 56 °C |
| Ugt2b34 | 5′-AGCCCCTGCCTAAGGAAATA-3′ | 5′-GAGTGTTGGAGCCCAATGTC-3′ | 60 °C |
| Ugt2b35 | 5′CCAGACATTTACAGAGAAGG-3′ | 5′CTGTCATGTTACTGACCATC-3′ | 60 °C |
| Ugt2b36 | 5′-TTGTTCAGAGCTCTGGAGAG-3′ | 5′-GATGACCAAGAAGATCATTT-3′ | 56 °C |
| Ugt2b37 | 5′-ATTTGGAGTTTCCTCACCCGA-3′ | 5′-TAGATTGCCTCATAGACACTG-3′ | 60 °C |
| Ugt2b38 | 5′-GCAACTTTAGGACACAATACG-3′ | 5′-ACTTCCTCCAGTGCATTGAGT-3′ | 60 °C |
| Primer | Sequence | RefSeq | Full Length cDNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ugt2b1 NheI Forward | 5′-CTAGGCTAGCATCTAGTCAGTGATGTGGTTAGAAG | AC119816.5 | 2560 bp |
| Ugt2b1 XhoI Reverse | 5′-TCGACTCGAGCAGGACTCTCTGCTTCAGCCTTCAT | ||
| Ugt2b5 NheI Forward | 5′-CTAGGCTAGCAGCAAATGGACTGTGAGAGAAGGAT | NM_009467.3 | 1901 bp |
| Ugt2b5 XhoI Reverse | 5′-TCGACTCGAGAGGCTGAAAGTTTGTTCATGTAGTT | ||
| Ugt2b34 NheI Forward | 5′-CTAGGCTAGCGCCTGAAGTTAACCAA | NM_153598.2 | 3048 bp |
| Ugt2b34 XhoI Reverse | 5′-TCGACTCGAGTGAAGGACCCTAAATCATTGCCTCC | ||
| Ugt2b35 NheI Forward | 5′-CTAGGCTAGCGTTAACAGAAGCCCTTTGAC | NM_172881.3 | 3358 bp |
| Ugt2b35 XhoI Reverse | 5′-TCGACTCGAGTTCTTCCTTTTCTTTGCC | ||
| Ugt2b36 NheI Forward | 5′-CTAGGCTAGCACTCTGAAGAGAAGAACA | NM_001029867.1 | 1888 bp |
| Ugt2b36 XhoI Reverse | 5′-TCGACTCGAGATGCATTATCAATGAGT | ||
| Ugt2b37 NheI Forward | 5′-CTAGGCTAGCGCAAATGAACTGTGAAGAGAAGGAT | AC100269.7 | 1879 bp |
| Ugt2b37 XhoI Reverse | 5′-TCGACTCGAGAAATAGATGGGATTTTTGAAAATGC | ||
| Ugt2b38 NheI Forward | 5′-CTAGGCTAGCCCCACGCGTCCGGGATT | NM_133894.2 | 1894 bp |
| Ugt2b38 XhoI Reverse | 5′-TCGACTCGAGATGGATCAGTATCCACAGATTTAC |
| Androgen-Glucuronide | Tissue/Enzyme | Vmaxapp (pmol/min/mg Proteins) | KM (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone-G | Liver | 1611.3 ± 56.1 | 29.2 ± 1.7 |
| Ugt2b1 | 51.2 ± 1.5 | 20.3 ± 0.7 | |
| Ugt2b5 | 186.5 ± 1.0 | 65.5 ± 8.6 | |
| DHT-G | Liver | 3987.0 ± 95.5 | 24.1 ± 1.0 |
| Ugt2b1 | 238.5 ± 0.3 | 17.8 ± 0.7 | |
| Ugt2b5 | 50.5 ± 2.1 | 35.6 ± 11.5 | |
| Ugt2b34 | 43.1 ± 1.7 | 54.9 ± 2.9 | |
| 3α-Diol-17G | Liver | 485.3 ± 24.5 | 19.3 ± 2.0 |
| Ugt2b1 | 34.8 ± 1.7 | 11.7 ± 2.0 | |
| Ugt2b5 | 115.2 ± 12.4 | 22.7 ± 5.1 | |
| Ugt2b34 | 8.5 ± 0.6 | 16.3 ± 4.8 | |
| 3α-Diol-3G | Kidney | 215.9 ± 2.9 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| Ugt2b37 | 1774.1 ± 51.6 | 3.9 ± 1.5 | |
| ADT-G | Kidney | 262.8 ± 2.2 | 2.3 ± 0.8 |
| Ugt2b37 | 2091.0 ± 50.8 | 3.6 ± 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grosse, L.; Chouinard, S.; Pâquet, S.; Verreault, M.; Trottier, J.; Bélanger, A.; Barbier, O. Androgen Glucuronidation in Mice: When, Where, and How. Biology 2022, 11, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030403
Grosse L, Chouinard S, Pâquet S, Verreault M, Trottier J, Bélanger A, Barbier O. Androgen Glucuronidation in Mice: When, Where, and How. Biology. 2022; 11(3):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030403
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrosse, Laurent, Sarah Chouinard, Sophie Pâquet, Mélanie Verreault, Jocelyn Trottier, Alain Bélanger, and Olivier Barbier. 2022. "Androgen Glucuronidation in Mice: When, Where, and How" Biology 11, no. 3: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030403
APA StyleGrosse, L., Chouinard, S., Pâquet, S., Verreault, M., Trottier, J., Bélanger, A., & Barbier, O. (2022). Androgen Glucuronidation in Mice: When, Where, and How. Biology, 11(3), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11030403





