Pb Induces MCP-1 in the Choroid Plexus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatment
2.2. Immunohistochemistry and Quantitation of Macrophage and MCP-1, Phosphorylated NF-kB p65- and p38-Positive CP Cells
2.3. Cultures of Choroidal Epithelial Z310 Cells
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. MCP-1 ELISA
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
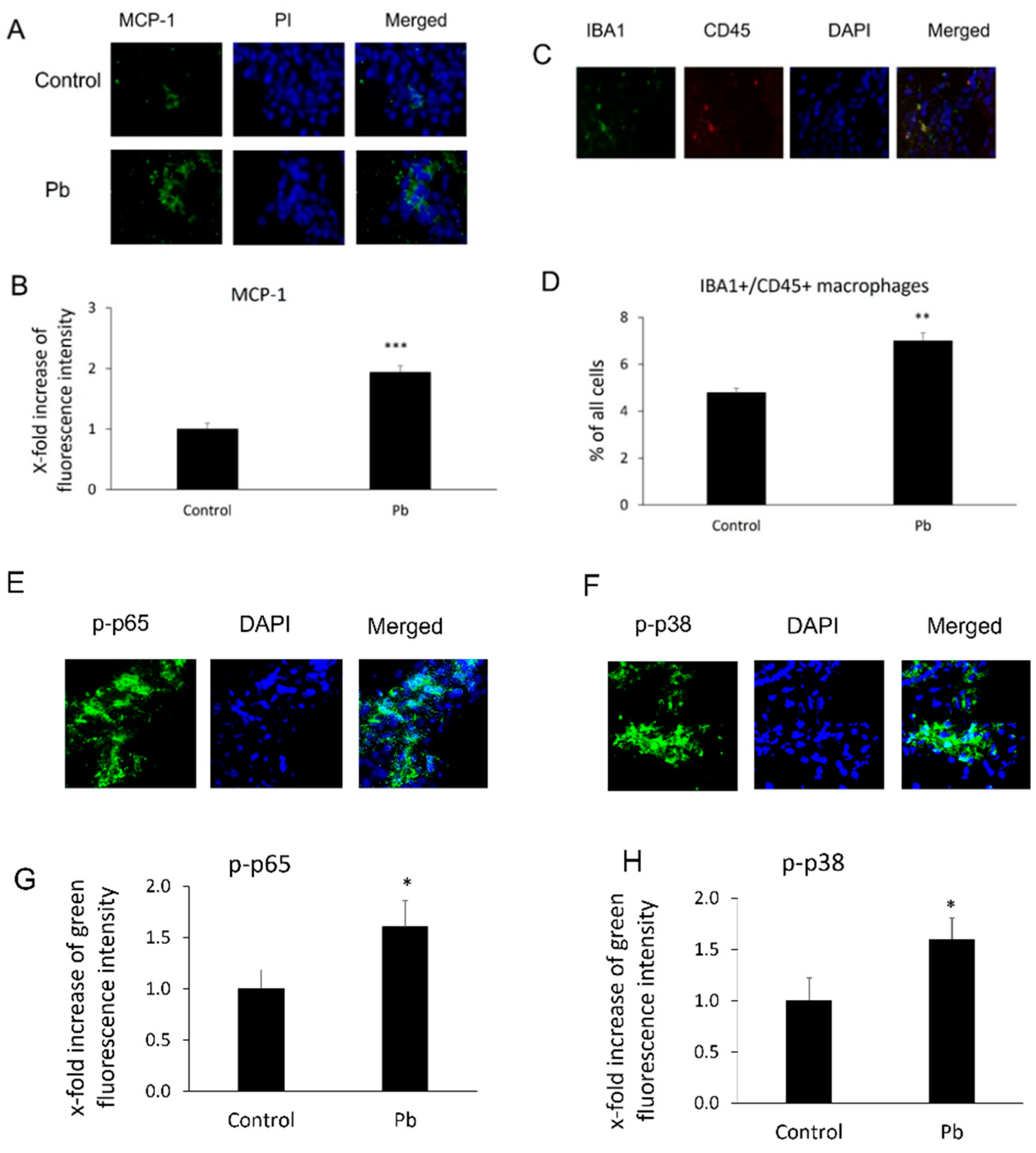
3.1. Pb Exposure Induced MCP-1 Expression and Enhanced Macrophage Infiltration in the CP Tissues
3.2. Pb Exposure Induced MCP-1 Expression in Rat Choroidal Epithelial Z310 Cells
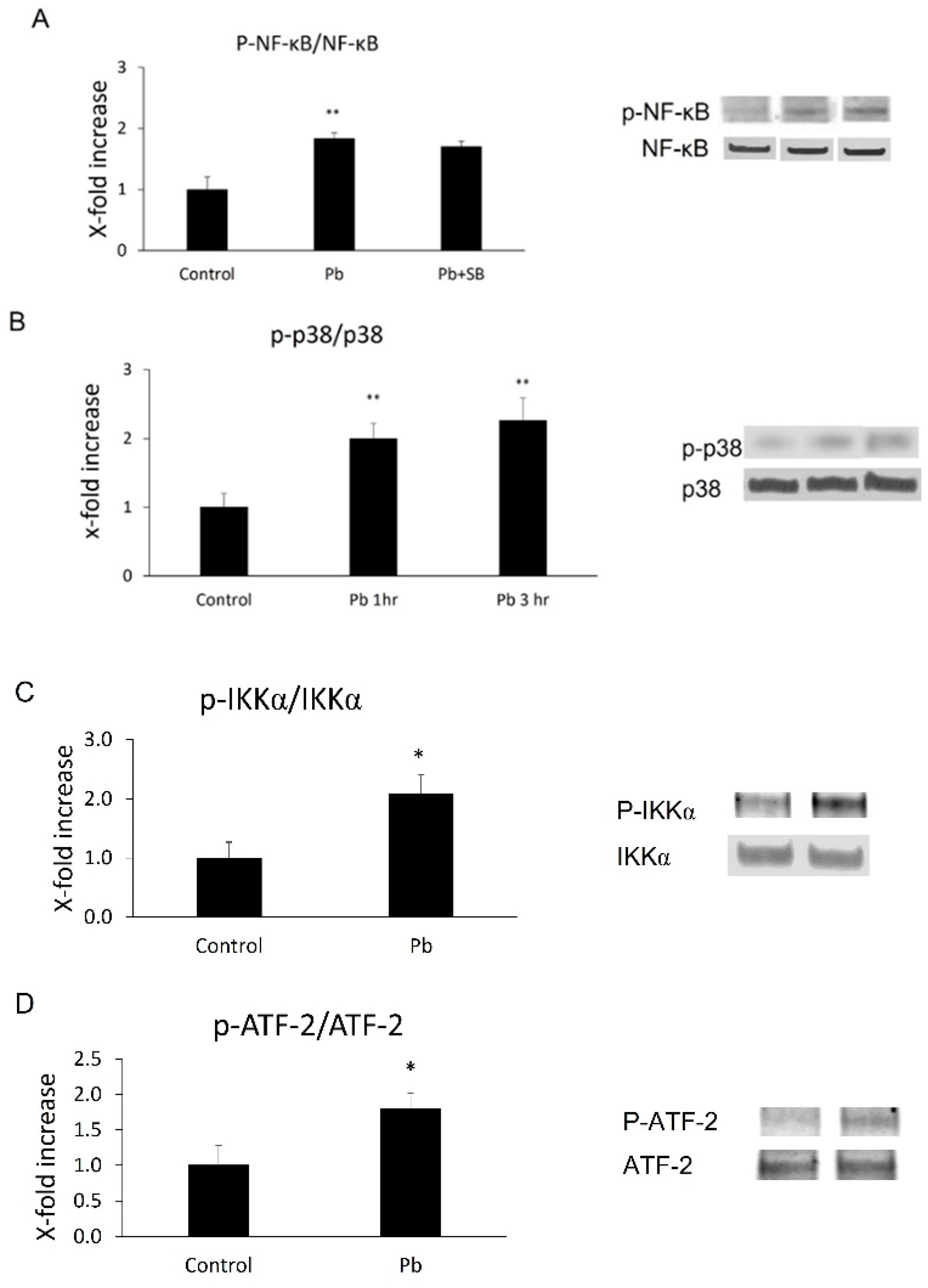
3.3. Both NF-κB p65 and p38 MAPkinase Were Activated in Z310 Cells by Pb
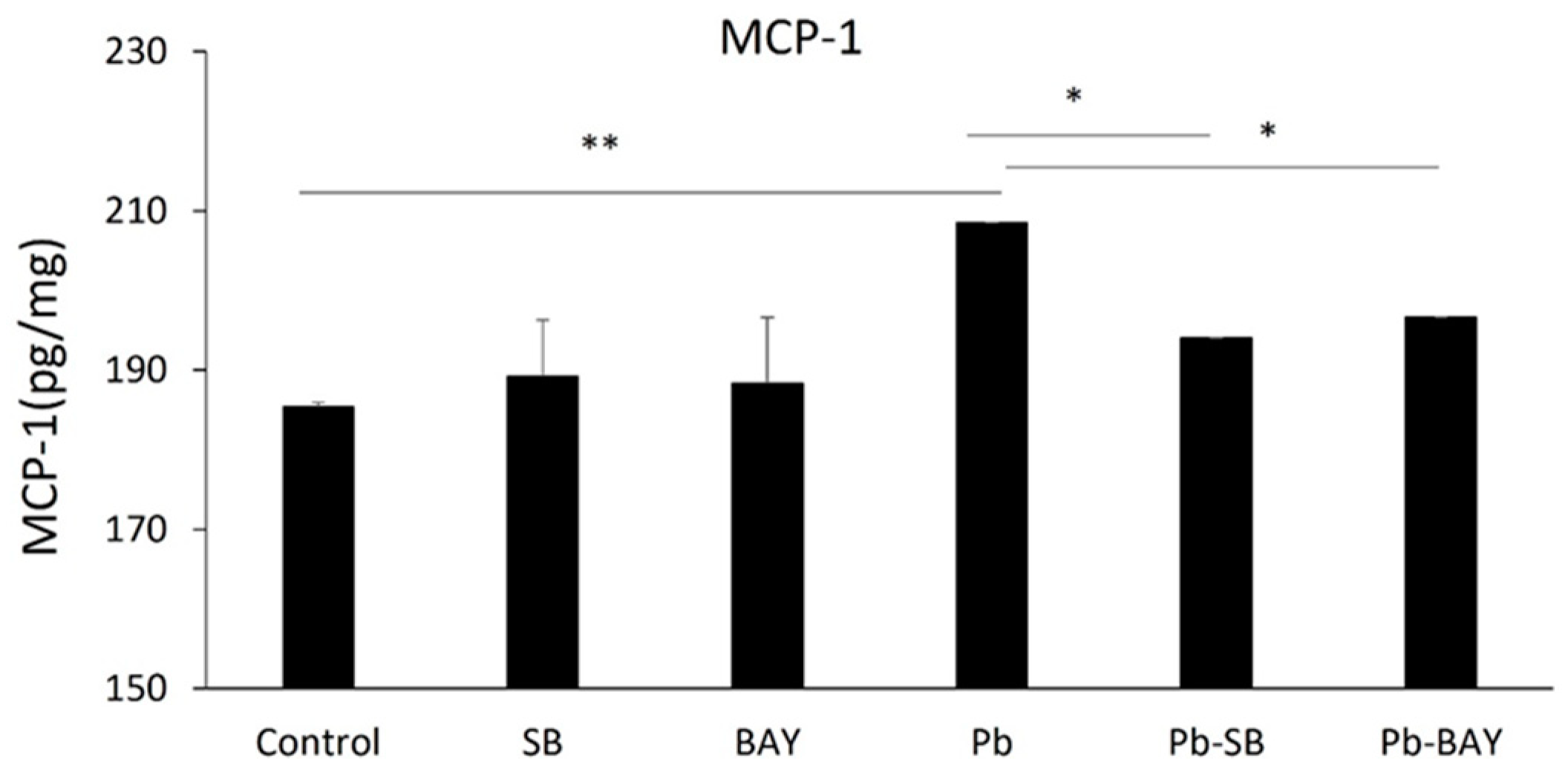
3.4. Both NF-κB and p38 MAPK Inhibitors Blocked Pb-Induced MCP-1 Expression
3.5. SB 253,580 Did Not Block NF-κB p65 Phosphorylation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, W.; Aschner, M.; Ghersi-Egea, J.F. Brain barrier systems: A new frontier in metal neurotoxicological research. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2003, 192, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakulski, K.M.; Rozek, L.S.; Dolinoy, D.C.; Paulson, H.L.; Hu, H. Alzheimer’s disease and environmental exposure to lead: The epidemiologic evidence and potential role of epigenetics. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, W.F.; Schwartz, B.S.; Simon, D.; Kelsey, K.; Todd, A.C. ApoE genotype, past adult lead exposure, and neurobehavioral function. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, W.F.; Schwartz, B.S.; Davatzikos, C.; Shen, D.; Liu, D.; Wu, X.; Todd, A.C.; Shi, W.; Bassett, S.; Youssem, D. Past adult lead exposure is linked to neurodegeneration measured by brain MRI. Neurology 2006, 66, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, B.S.; Caffo, B.; Stewart, W.F.; Hedlin, H.; James, B.D.; Yousem, D.; Davatzikos, C. Evaluation of cumulative lead dose and longitudinal changes in structural magnetic resonance imaging in former organolead workers. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 52, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, A.B.; van Duijn, C.M.; Chandra, V.; Fratiglioni, L.; Heyman, A.; Jorm, A.F.; Kokmen, E.; Kondo, K.; Mortimer, J.A.; Rocca, W.A.; et al. Occupational exposures to solvents and lead as risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease: A collaborative re-analysis of case-control studies. EURODEM Risk Factors Research Group. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1991, 20 (Suppl. 2), S58–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, T.; Ishizu, H.; Takehisa, Y.; Kawai, K.; Yokota, O.; Terada, S.; Tsuchiya, K.; Ikeda, K.; Morita, K.; Horike, T.; et al. Lead content of brain tissue in diffuse neurofibrillary tangles with calcification (DNTC): The possibility of lead neurotoxicity. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 3887–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, M.; Xia, W.; Hofmann, O.; Gregas, M.; Ho Sui, S.; Hide, W.; Yang, T.; Needleman, H.L.; Bellinger, D.C. Prenatal lead levels, plasma amyloid beta levels, and gene expression in young adulthood. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, M.R.; Murali, M.; Siddiqi, H.K.; Ghosal, K.; Siddiqi, O.K.; Lashuel, H.A.; Ge, Y.W.; Lahiri, D.K.; Zawia, N.H. Lead (Pb) exposure and its effect on APP proteolysis and Abeta aggregation. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 2083–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Robison, G.; Hong, L.; Barrea, R.; Wei, X.; Farlow, M.R.; Pushkar, Y.N.; Du, Y.; Zheng, W. Increased beta-amyloid deposition in Tg-SWDI transgenic mouse brain following in vivo lead exposure. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 213, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, T.; Zhao, F.; Yao, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, W.; Chen, J. The role of alpha-synuclein and tau hyperphosphorylation-mediated autophagy and apoptosis in lead-induced learning and memory injury. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bihaqi, S.W.; Bahmani, A.; Adem, A.; Zawia, N.H. Infantile postnatal exposure to lead (Pb) enhances tau expression in the cerebral cortex of aged mice: Relevance to AD. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juracek, K.E.; Ziegler, A.C. The legacy of leaded gasoline in bottom sediment of small rural reservoirs. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 2092–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, L.E.; Weuve, J.; Scherr, P.A.; Evans, D.A. Alzheimer disease in the United States (2010–2050) estimated using the 2010 census. Neurology 2013, 80, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Vadgama, J.V.; Wang, P. CCL2/CCR2 signaling in cancer pathogenesis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwandtner, M.; Derler, R.; Midwood, K.S. More than just Attractive: How CCL2 Influences Myeloid Cell Behavior Beyond Chemotaxis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.; Borsig, L.; Heikenwalder, M. CCL2-CCR2 Signaling in Disease Pathogenesis. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 15, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Yuzhalin, A.E.; Gordon-Weeks, A.N.; Muschel, R.J. Targeting the CCL2-CCR2 signaling axis in cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 28697–28710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettcher, B.M.; Neuhaus, J.; Wynn, M.J.; Elahi, F.M.; Casaletto, K.B.; Saloner, R.; Fitch, R.; Karydas, A.; Kramer, J.H. Increases in a Pro-inflammatory Chemokine, MCP-1, Are Related to Decreases in Memory Over Time. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banisadr, G.; Gosselin, R.D.; Mechighel, P.; Rostene, W.; Kitabgi, P.; Melik Parsadaniantz, S. Constitutive neuronal expression of CCR2 chemokine receptor and its colocalization with neurotransmitters in normal rat brain: Functional effect of MCP-1/CCL2 on calcium mobilization in primary cultured neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 492, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britschgi, M.; Wyss-Coray, T. Systemic and acquired immune responses in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 82, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, A.; Hill, M.D.; Rahimi, F.; Warden, L.A.; Halliday, G.M.; Shepherd, C.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 plays a dominant role in the chronic inflammation observed in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, D.; Fenoglio, C.; Lovati, C.; Venturelli, E.; Guidi, I.; Corra, B.; Scalabrini, D.; Clerici, F.; Mariani, C.; Bresolin, N.; et al. Serum MCP-1 levels are increased in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, D.; Schoonenboom, N.; Scheltens, P.; Fenoglio, C.; Bouwman, F.; Venturelli, E.; Guidi, I.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Bresolin, N.; Scarpini, E. Intrathecal chemokine synthesis in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Liao, Y.C.; Wang, Y.F.; Lin, I.F.; Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L. Plasma MCP-1 and Cognitive Decline in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Two-year Follow-up Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westin, K.; Buchhave, P.; Nielsen, H.; Minthon, L.; Janciauskiene, S.; Hansson, O. CCL2 is associated with a faster rate of cognitive decline during early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melah, K.E.; Lu, S.Y.; Hoscheidt, S.M.; Alexander, A.L.; Adluru, N.; Destiche, D.J.; Carlsson, C.M.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Okonkwo, O.C.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology and Microglial Activation are Associated with Altered White Matter Microstructure in Asymptomatic Adults at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 50, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettcher, B.M.; Johnson, S.C.; Fitch, R.; Casaletto, K.B.; Heffernan, K.S.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Carlsson, C.M.; Neuhaus, J.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Plasma Levels of Inflammation Differentially Relate to CNS Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology and Neuronal Damage. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, S.M.; Zhao, N. The Potential Roles of Blood-Brain Barrier and Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barrier in Maintaining Brain Manganese Homeostasis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Xia, L.; Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; Shannahan, J.; Du, Y.; Zheng, W. Altered clearance of beta-amyloid from the cerebrospinal fluid following subchronic lead exposure in rats: Roles of RAGE and LRP1 in the choroid plexus. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 61, 126520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Xu, H.; Lehtinen, M.K. Macrophages on the margin: Choroid plexus immune responses. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, K.; Yang, H.Y.; Berk, J.D.; Tran, J.H.; Iadarola, M.J. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the choroid plexus: A potential link between vascular pro-inflammatory mediators and the CNS during peripheral tissue inflammation. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, V.; Chauveau, F.; Dumot, C.; Ong, E.; Berner, L.P.; Canet-Soulas, E.; Ghersi-Egea, J.F.; Wiart, M. Clinical Imaging of Choroid Plexus in Health and in Brain Disorders: A Mini-Review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Kotter, H.U.; Moller, H.J. Blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier dysfunction for high molecular weight proteins in Alzheimer disease and major depression: Indication for disease subsets. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1997, 11, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, A.A.; Kaing, S.; Ten Brink, J.B.; Netherlands Brain, B.; Gorgels, T.G.; Janssen, S.F. Gene expression and functional annotation of human choroid plexus epithelium failure in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha-Chowdhury, R.; Henderson, J.W.; Raha, A.A.; Vuono, R.; Bickerton, A.; Jones, E.; Fincham, R.; Allinson, K.; Holland, A.; Zaman, S.H. Choroid Plexus Acts as Gatekeeper for TREM2, Abnormal Accumulation of ApoE, and Fibrillary Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease and in Down Syndrome Dementia. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 69, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadayon, E.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Press, D.; Santarnecchi, E. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Choroid plexus volume is associated with levels of CSF proteins: Relevance for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 89, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedheim, E.; Corvi, C.; Graziano, J.; Donnelli, T.; Breslin, D. Choroid plexus as a protective sink for heavy metals? Lancet 1983, 1, 981–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Territo, P.R.; Persohn, S.A.; Bedwell, A.A.; Eldridge, K.; Speedy, R.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, W.; Du, Y. Evaluation of chronic lead effects in the blood brain barrier system by DCE-CT. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 62, 126648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, Q. Establishment and characterization of an immortalized Z310 choroidal epithelial cell line from murine choroid plexus. Brain Res. 2002, 958, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zhong, Z.; Jiang, W.; Du, E.; Dodel, R.; Farlow, M.R.; Zheng, W.; Du, Y. The role of choroid plexus in IVIG-induced beta-amyloid clearance. Neuroscience 2014, 270, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, Z. Curcumin inhibits ox-LDL-induced MCP-1 expression by suppressing the p38MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Inflamm. Res. 2012, 61, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebeler, M.; Gillitzer, R.; Kilian, K.; Utzel, K.; Brocker, E.B.; Rapp, U.R.; Ludwig, S. Multiple signaling pathways regulate NF-kappaB-dependent transcription of the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene in primary endothelial cells. Blood 2001, 97, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Stopa, E.G.; Johanson, C.E.; Baird, A.; Silverberg, G.D. Choroid plexus genes for CSF production and brain homeostasis are altered in Alzheimer’s disease. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, B.D.; Bye, N.; Rancan, M.; Ziebell, J.M.; Morganti-Kossmann, M.C. Role of CCL2 (MCP-1) in traumatic brain injury (TBI): Evidence from severe TBI patients and CCL2-/- mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwarha, G.; Ghribi, O. Nuclear Factor Kappa-light-chain-enhancer of Activated B Cells (NF-kappaB)—A Friend, a Foe, or a Bystander—In the Neurodegenerative Cascade and Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 1050–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Kim, N.J. Recent Advances in the Inhibition of p38 MAPK as a Potential Strategy for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2017, 22, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, H.; Xu, Y.; Du, N.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Du, Y. Pb Induces MCP-1 in the Choroid Plexus. Biology 2022, 11, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020308
Gu H, Xu Y, Du N, Yu Y, Zheng W, Du Y. Pb Induces MCP-1 in the Choroid Plexus. Biology. 2022; 11(2):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020308
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Huiying, Yundan Xu, Nicole Du, Yongqi Yu, Wei Zheng, and Yansheng Du. 2022. "Pb Induces MCP-1 in the Choroid Plexus" Biology 11, no. 2: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020308
APA StyleGu, H., Xu, Y., Du, N., Yu, Y., Zheng, W., & Du, Y. (2022). Pb Induces MCP-1 in the Choroid Plexus. Biology, 11(2), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020308



