Comparison of the External Morphology of the Sternal Glands for Hornets in the Genus Vespa
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
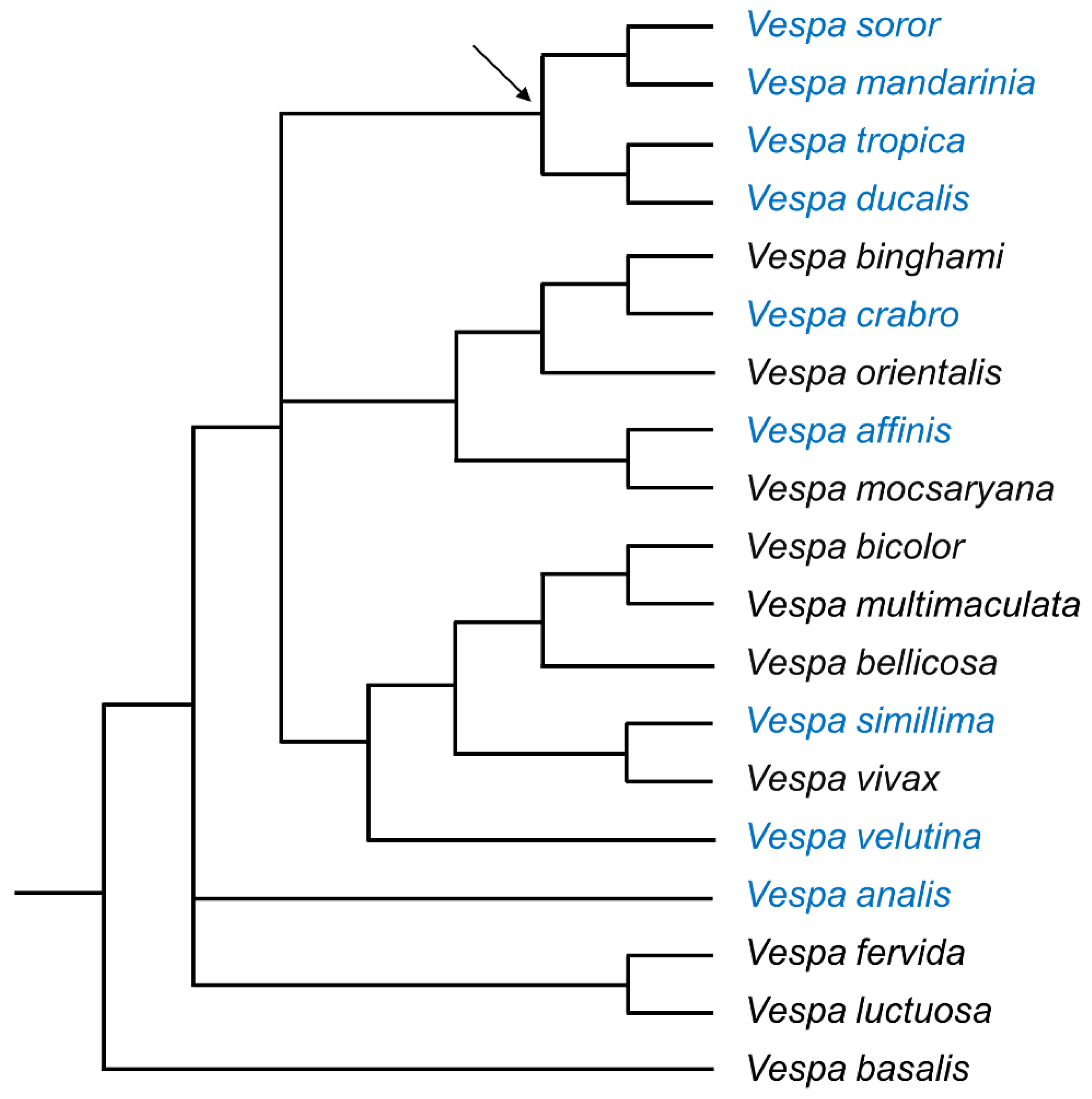
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Worker Specimens
2.2. SEM Imaging
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
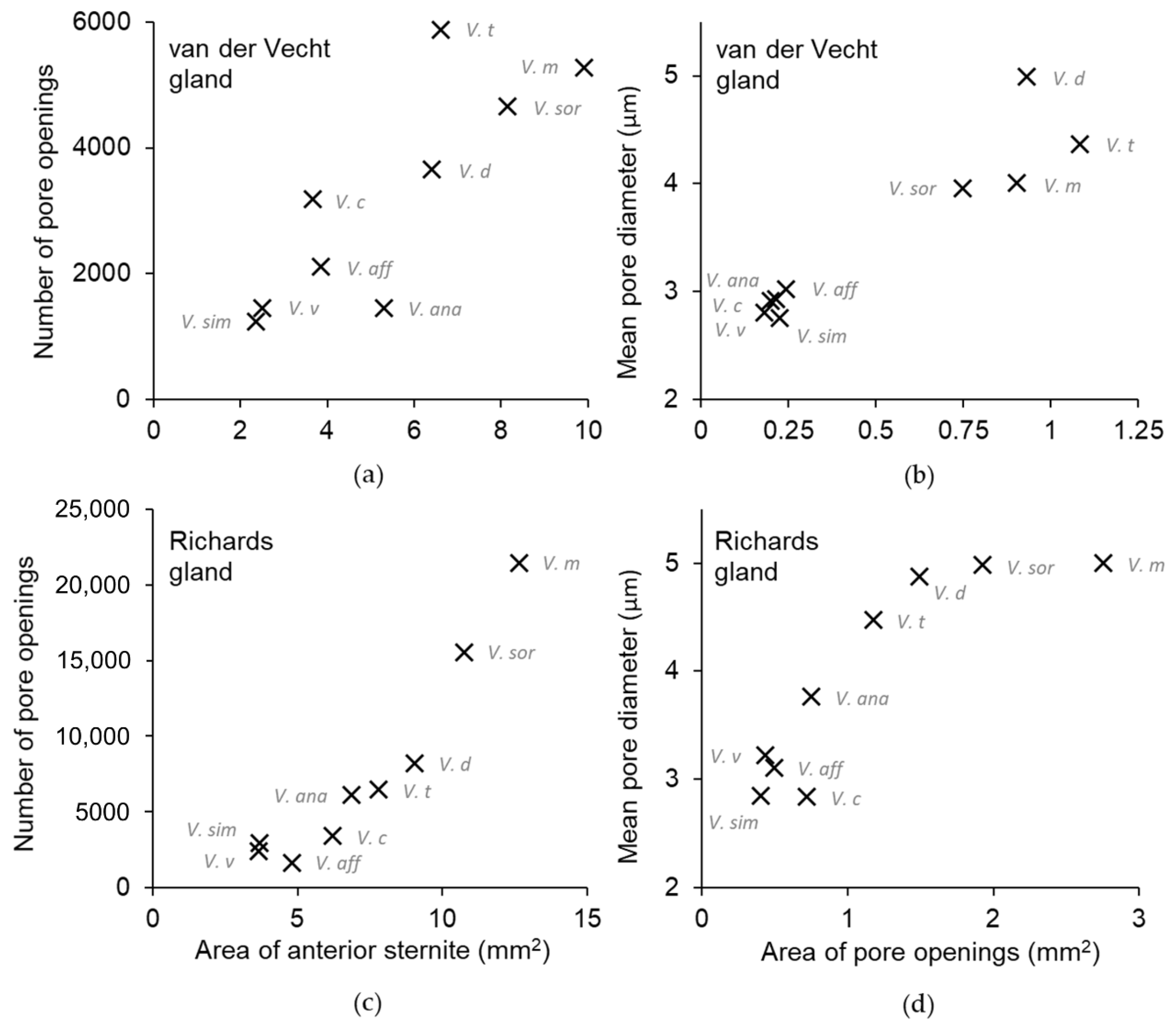
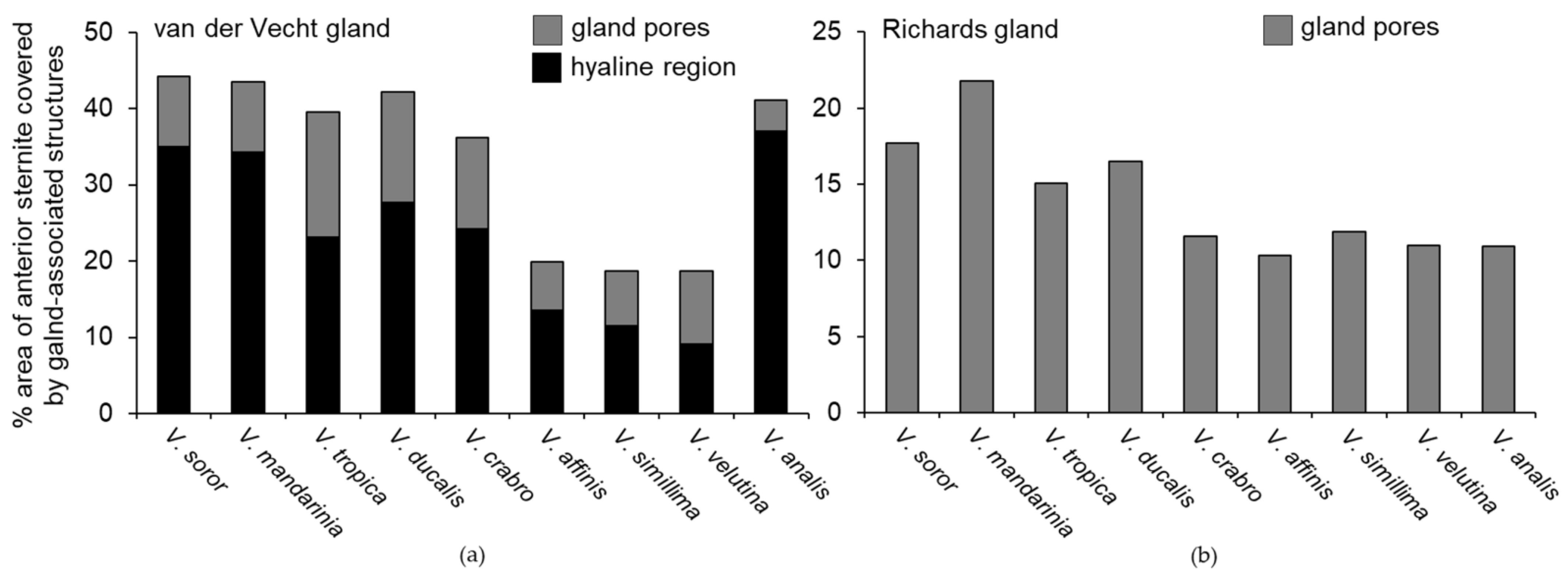
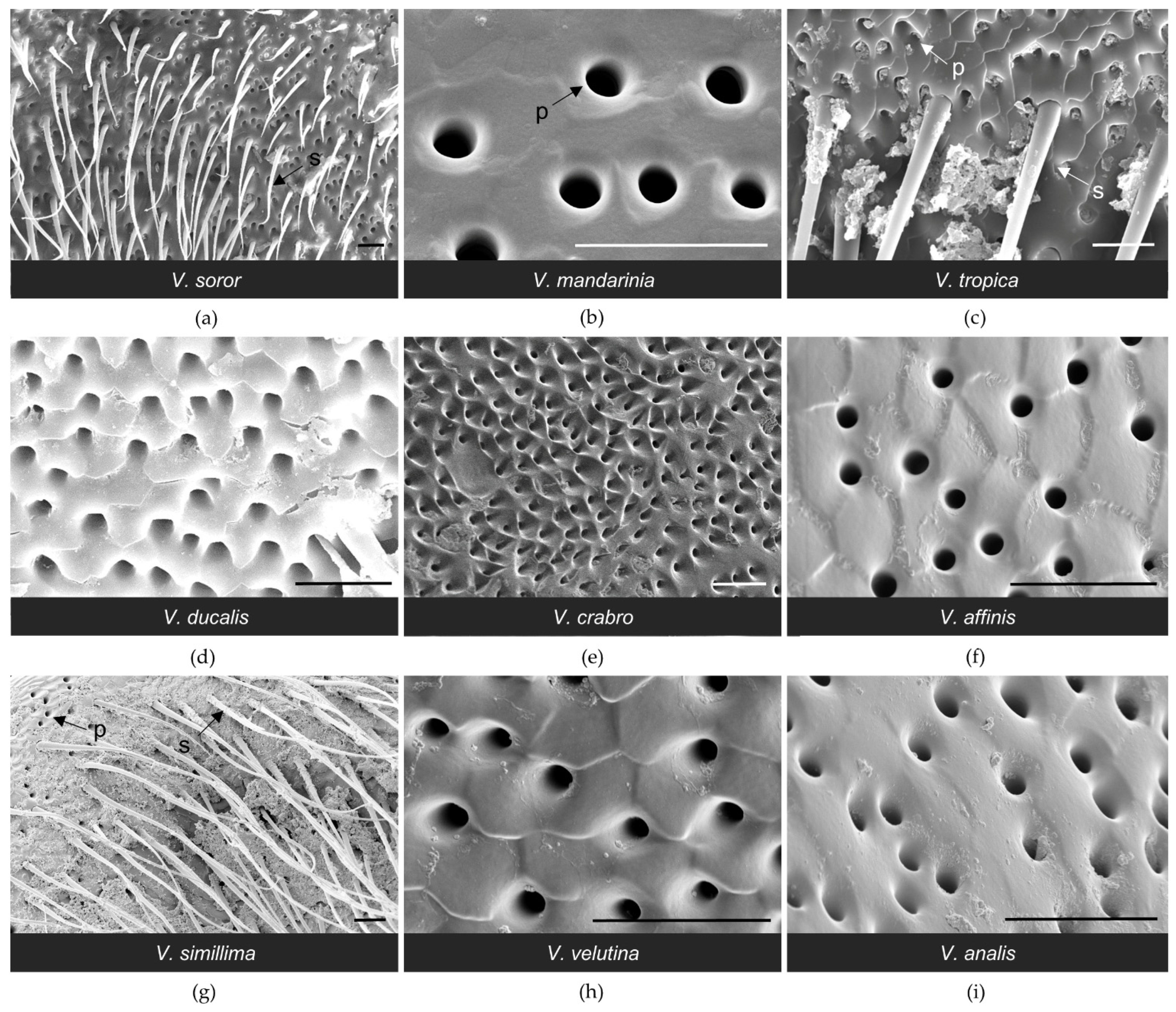
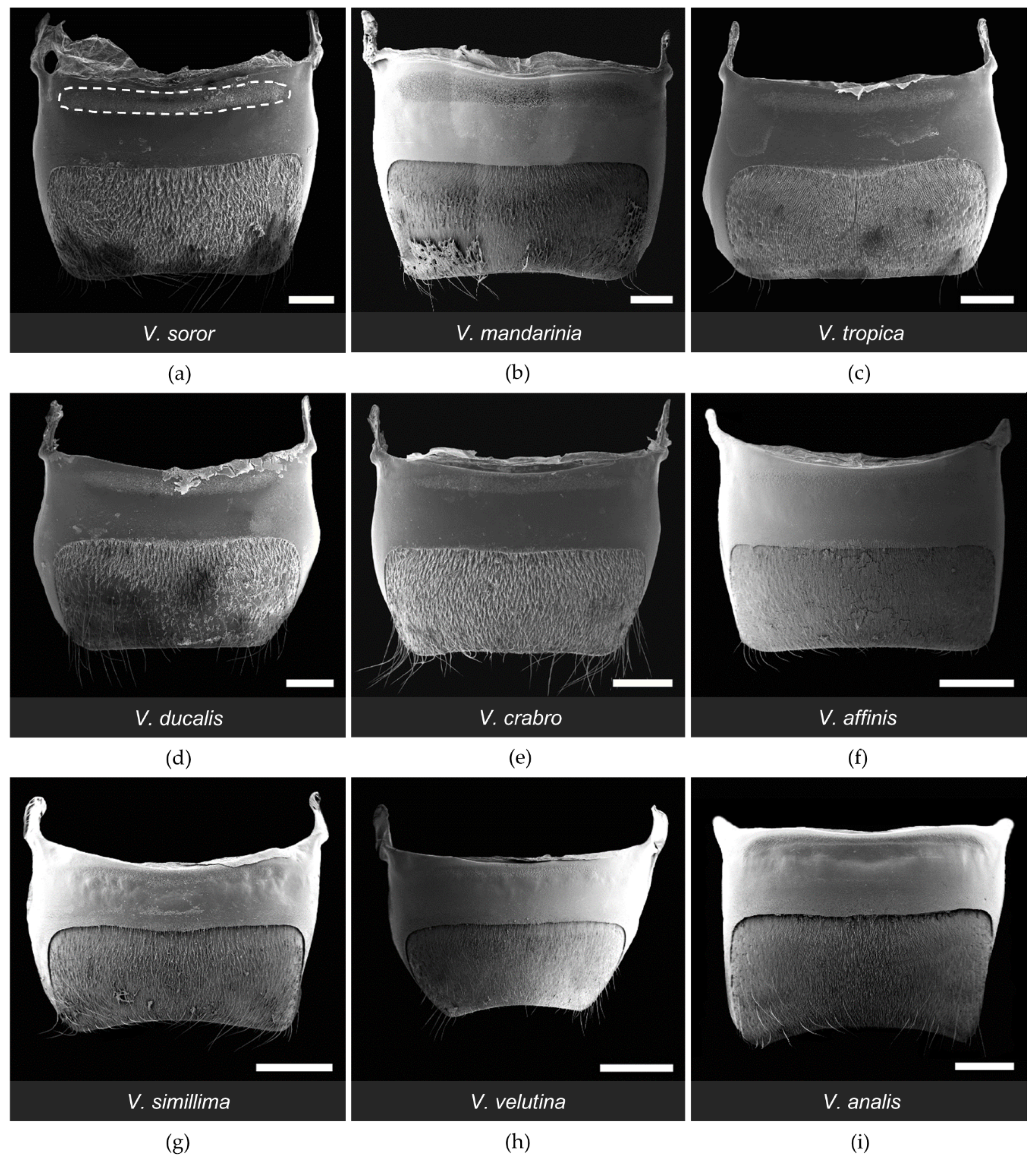
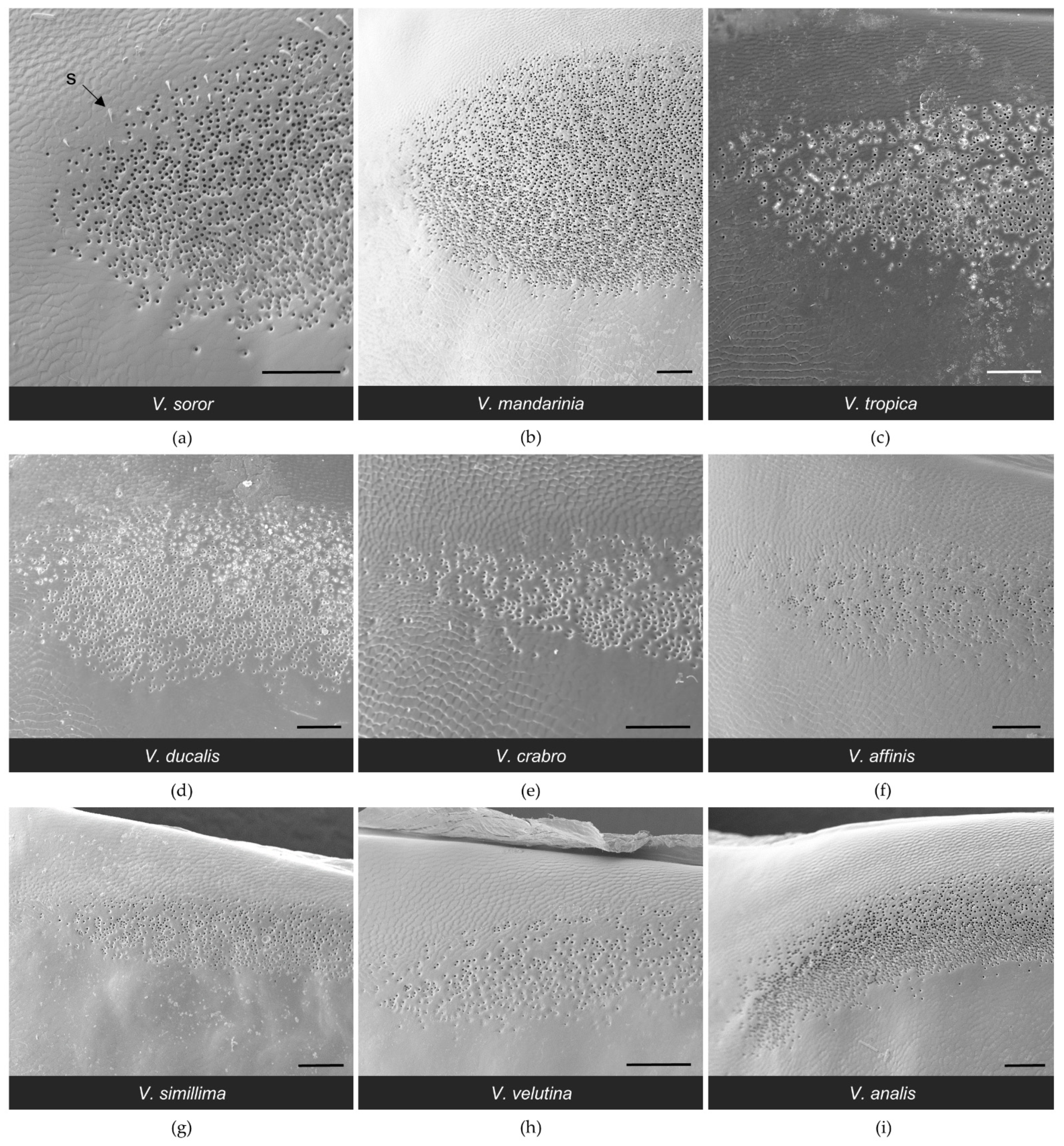
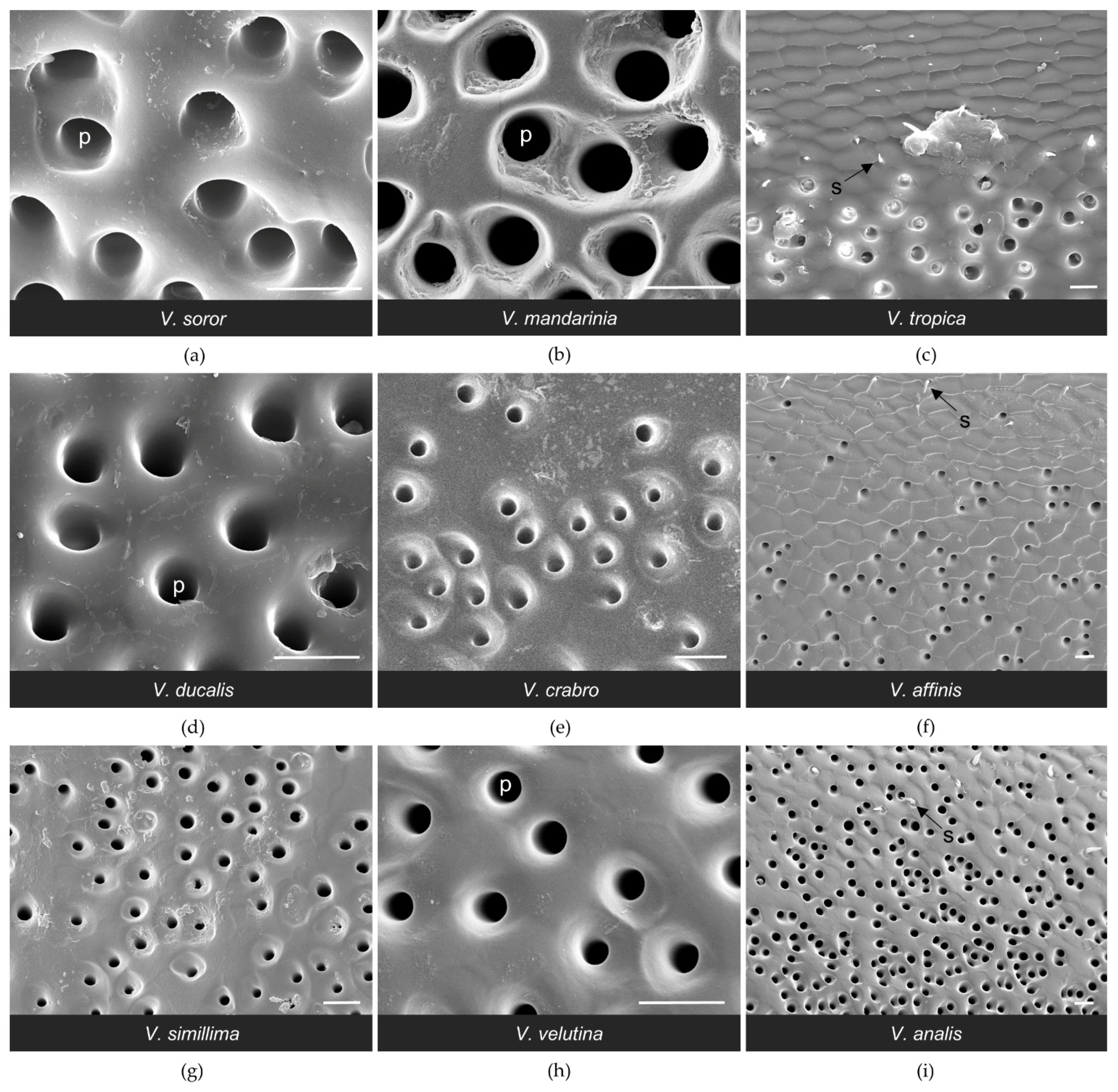
3.1. Structure of the van der Vecht Gland among Vespa Species
3.2. Structure of the Richards Gland among Vespa Species
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuura, M.; Yamane, S. Biology of the Vespine Wasps; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, M.E. Vespine Wasps of the World: Behaviour, Ecology and Taxonomy of the Vespinae; Siri Scientific Press: Manchester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Perrard, A.; Pickett, K.M.; Villemant, C.; Kojima, J.; Carpenter, J. Phylogeny of hornets: A total evidence approach (Hymenoptera, Vespidae, Vespinae, Vespa). J. Hymenopt. Res. 2013, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrard, A.; Lopez-Osorio, F.; Carpenter, J.M. Phylogeny, landmark analysis and the use of wing venation to study the evolution of social wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae: Vespinae). Cladistics 2016, 32, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Pardo, A.H.; Carpenter, J.M.; Kimsey, L. The diversity of hornets in the genus Vespa (Hymenoptera: Vespidae, Vespinae), their importance and interceptions in the United States. Insect Syst. Divers. 2020, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M. Vespa and Provespa. In The Social Biology of Wasps; Ross, K.G., Matthews, R.W., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 232–262. [Google Scholar]
- Brodmann, J.; Twele, R.; Francke, W.; Luo, Y.; Song, X.; Ayasse, M. Orchid mimics honey bee alarm pheromone in order to attract hornets for pollination. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Wu, H.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Lu, W.; Zheng, X. Diversity, daily activity patterns, and pollination effectiveness of the insects visiting Camellia osmantha, C. vietnamensis, and C. oleifera in South China. Insects 2019, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, M. Comparative biology of the five Japanese species of the genus Vespa (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Bull. Fac. Agric. Mie Univ. 1984, 69, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, M.; Sakagami, S.F. A bionomic sketch of the giant hornet, Vespa mandarinia, a serious pest for Japanese apiculture. J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ. Ser. VI Zool. 1973, 19, 125–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, M.; Igarashi, T.; Ohno, E.; Sasaki, M. Unusual thermal defence by a honeybee against mass attack by hornets. Nature 1995, 377, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.X.Q. A note on Vespa soror (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in Hong Kong. Hong Kong Entomol. Bull. 2009, 1, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mattila, H.R.; Otis, G.W.; Nguyen, L.T.P.; Pham, H.D.; Knight, O.M.; Phan, N.T. Honey bees (Apis cerana) use animal feces as a tool to defend colonies against group attack by giant hornets (Vespa soror). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, M.E. A phylogenetic study of the species of the genus Vespa (Hymenoptera: Vespinae). Entomol. Scand. 1993, 24, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, S.; Sann, M.; Mayer, C.; Meusemann, K.; Donath, A.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Kozlov, A.; Petersen, M.; Krogmann, L.; Meier, R.; et al. Transcriptome and target DNA enrichment sequence data provide new insights into the phylogeny of vespid wasps (Hymenoptera: Aculeata: Vespidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 116, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekarski, P.K.; Carpenter, J.M.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Sharanowski, B.J. Phylogenomic evidence overturns current conceptions of social evolution in wasps (Vespidae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 2097–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, H.A. The function and evolution of exocrine glands. In The Social Biology of Wasps; Ross, K.G., Matthews, R.W., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 540–569. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, M.; Noll, F.B.; Billen, J. Sternal exocrine glands in neotropical social wasps. In Neotropical Social Wasps; Prezoto, F., Nascimento, F.S., Barbosa, B.C., Somavilla, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 213–234. [Google Scholar]
- Noirot, C.; Quennedey, A. Fine structure of insect epidermal glands. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1974, 19, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noirot, C.; Quennedey, A. Glands, gland cells, glandular units: Some comments on terminology and classification. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 1991, 27, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Billen, J.; Šobotník, J. Insect exocrine glands. Arthropod Struct. Dev. 2015, 44, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, P.J.; Akre, R.D. Occurrence and location of exocrine glands in some social Vespidae (Hymenoptera). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1979, 72, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.C.; Jeanne, R.L. Morphology of the sternal glands of Polistes fuscatus and P. canadensis (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Psyche 1980, 87, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeanne, R.L.; Post, D.C. Richards’ gland and associated cuticular modifications in social wasps of the genus Polybia Lepeletier (Hymenoptera, Vespidae, Polistinae, Polybiini). Insectes Sociaux 1982, 29, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanne, R.L.; Downing, H.A.; Post, D.C. Morphology and function of sternal glands in polistine wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Zoomorphology 1983, 103, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.R.; O’Donnell, S.; Jeanne, R.L. Evolution of swarm communication in eusocial wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). J. Insect Behav. 2002, 15, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samacá, E.; Billen, J.; Sarmiento, C.E. Morphology of the fifth sternal glands of Neotropical social wasps (Hymenoptera, Vespidae, Polistinae). Invertebr. Biol. 2013, 132, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.R.; O’Donnell, S.; Jeanne, R.L. Correlated evolution of colony defence and social structure: A comparative analysis in eusocial wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Evol. Ecol. Res. 2001, 3, 331–344. [Google Scholar]
- Heselhaus, F. Die Hautdrüsen der Apiden und verwandter Formen. Zool. Jahrbücher Abt. Anat. Ontog. Tiere 1922, 43, 369–464. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Vecht, J. The terminal gastral sternite of female and worker social wasps (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. C 1968, 71, 411–422. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.J. Colony defence against ants in Vespa. Insectes Sociaux 1992, 39, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, H.R.; Shimano, S.; Otis, G.W.; Nguyen, L.T.P.; Maul, E.R.; Billen, J. Linking the morphology of sternal glands to rubbing behavior by Vespa soror (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) workers during recruitment for group predation. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2021, saab048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanne, R.L. Chemical defense of brood by a social wasp. Science 1970, 168, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, H.R.; Dirks, T.F. Sternal glands in polistine wasps: Morphology and associated behavior. J. Ga. Entomol. Soc. 1974, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Turillazzi, S.; Ugolini, A. Rubbing behaviour in some European Polistes (Hymenoptera Vespidae). Monit. Zool. Ital. 1979, 13, 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Post, D.C.; Jeanne, R.L. Colony defense against ants by Polistes fuscatus (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in Wisconsin. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 1981, 54, 599–615. [Google Scholar]
- Litte, M. Social biology of the Polistine wasp Mischocyttarus labiatus: Survival in a Colombian rain forest. Smithsonian Contrib. Zool. 1981, 327, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, J. Defense of the pre-emergence colony against ants by means of a chemical barrier in Ropalidia fasciata (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Jap. J. Ecol. 1983, 33, 213–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, J. The ant repellent function of the rubbing substance in an Old World polistine, Parapolybia indica (Hymenoptera Vespidae). Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 1992, 4, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeping, M.G. Rubbing behavior and morphology of van der Vecht’s gland in Belonogaster petiolata (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). J. Insect Behav. 1990, 3, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, F.R.; Cannoni, S.; Turillazzi, S.; Morgan, E.D. Ant repellent effect of the sternal gland secretion of Polistes dominulus (Christ) and P. sulcifer (Zimmermann) (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 1996, 22, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, S. Gastral rubbing on nest pedicel by the founding queen of the hornet Vespa analis (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Sociobiology 2010, 56, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanne, R.L. The evolution of exocrine gland function in wasps. In Natural History and the Evolution of Paper Wasps; Turillazzi, S., West-Eberhard, M.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 144–160. [Google Scholar]
- Dani, F.R.; Cervo, R.; Turillazzi, S. Abdomen stroking behaviour and its possible functions in Polistes dominulus (Christ) (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Behav. Process. 1992, 28, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapporto, L.; Santini, A.; Dani, F.R.; Turillazzi, S. Workers of a Polistes paper wasp detect the presence of their queen by chemical cues. Chem. Senses 2007, 32, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, M.G. Swarming behavior: Evidence for communication in social wasps. Science 1975, 189, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanne, R.L. Chemical communication during swarm emigration in the social wasp Polybia sericea (Olivier). Anim. Behav. 1981, 29, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Cheng, Y.-N.; Dong, S.-H.; Wang, Z.-W.; Tan, K.; Nieh, J.C. The sex pheromone of a globally invasive honey bee predator, the Asian eusocial hornet, Vespa velutina. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, O.W. The biology of the social wasps (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Biol. Rev. 1971, 46, 183–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turillazzi, S. Tegumental glands in the abdomen of some European Polistes (Hymenoptera Vespidae). Monit. Zool. Ital. 1979, 13, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, M.; Noll, F.B.; Billen, J. Morphology of Richards’ gland in the swarm-founding wasp Protonectarina sylveirae (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Acta Zool. 2015, 96, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, S.; Yamane, S.; Ban, T.; Kunou, I. The Japanese hornet Vespa simillima Smith, an important nuisance pest in urban areas (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Jap. J. Sanit. Zool. 1981, 32, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M. Ecological study on Vespine wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) attacking honeybee colonies: I. Seasonal changes in the frequency of visits to apiaries by vespine wasps and damage inflicted, especially in the absence of artificial protection. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1988, 23, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Terabe, H.; Hori, H.; Sasaki, M. Insect signalling: Components of giant hornet alarm pheromone. Nature 2003, 424, 637–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.B.; Martin, S.J.; Lee, J.W. Distribution, spread, and impact of the invasive hornet Vespa velutina in South Korea. J Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monceau, K.; Bonnard, O.; Thiéry, D. Vespa velutina: A new invasive predator of honeybees in Europe. J. Pest. Sci. 2014, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, A.; Cappa, F.; Petrocelli, I.; Pepiciello, I.; Bortolotti, L.; Cervo, R. Competition between the native and the introduced hornets Vespa crabro and Vespa velutina: A comparison of potentially relevant life-history traits. Ecol. Entomol. 2018, 43, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, E.; Gervasini, E.; De Jesus Cardoso, A.; La Notte, A.; Vallecillo Rodriguez, S.; Tsiamis, K.; Maes, J. Invasive Alien Species Impact on Ecosystem Services; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Barbet-Massin, M.; Salles, J.-M.; Courchamp, F. The economic cost of control of the invasive yellow-legged Asian hornet. NeoBiota 2020, 55, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanne, R.L. A latitudinal gradient in rates of ant predation. Ecology 1979, 60, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, J. A latitudinal gradient in intensity of applying ant-repellent substance to the nest petiole in paper wasps (Hymeno-ptera: Vespidae). Insectes Sociaux 1993, 40, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, M.E. Secondary nests of Vespa crabro L. (Hym., Vespidae). Entomol. Month. Mag. 1984, 120, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, M.E. Secondary nests of the hornet, Vespa crabro (L.) (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), produce queens. Proc. Trans. Br. Entomol. Nat. Hist. Soc. 1985, 18, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, M.E. Taxonomy, distribution and nesting biology of the Vespa bicolor group (Hym., Vespinae). Entomol. Month. Mag. 1994, 130, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, M.E. Taxonomy, distribution and nesting biology of species of the genera Provespa Ashmead and Vespa Linneaus (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Entomol. Month. Mag. 2008, 144, 69–101. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlyszyn, B. Nest relocation in the British hornet Vespa crabro gribodoi Bequaert (Hym., Vespidae). Entomol. Month. Mag. 1992, 128, 203–205. [Google Scholar]
- Rome, Q.; Muller, F.J.; Touret-Alby, A.; Darrouzet, E.; Perrard, A.; Villemant, C. Caste differentiation and seasonal changes in Vespa velutina (Hym.: Vespidae) colonies in its introduced range. J. Appl. Entomol. 2015, 139, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimsey, L.S.; Carpenter, J.M. The Vespinae of North America (Vespidae, Hymenoptera). J. Hymenopt. Res. 2012, 28, 37–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, P.; Otis, G.W. New honey bee pests in North America: A guide to Asian hornets that affect honey bees. Bee Cult. 2020, 148, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Billen, J. Exocrine glands and their key function in the communication system of social insects. Formos. Entomol. 2011, 31, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dapporto, L.; Petrocelli, I.; Turillazzi, S. Incipient morphological castes in Polistes gallicus. Zoomorphology 2011, 130, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrocelli, I.; Turillazzi, S. Comparative morphology of Van der Vecht’s organ in Polistes social parasites: Host ecology and adaptation of the parasite. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 109, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrocelli, I.; Turillazzi, S. The morphology of Van der Vecht’s organ as a tool to measure caste dimorphism in Polistes paper wasps: A comparative approach. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2013, 51, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, A.R.; Petrocelli, I.; Lino-Neto, J.; Santos, E.F.; Noll, F.B.; Turillazzi, S. Ontogenic caste differences in the Van der Vecht organ of primitively eusocial neotropical paper wasps. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, A.R.; Baptista, C.F.; Lino-Neto, J. The sternal brush of the Van der Vecht organ scales isometrically with body size: Implications for the study of incipient morphological castes in primitively eusocial wasps. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 29, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M. Colony defence strategies of social wasps and bees. Ecology of social wasps and bees. Insectarium 1983, 20, 254–260. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, M. Social Wasps of Japan in Color; Hokkaido University Press: Sapporo, Japan, 1995; (In Japanese with English Summary). [Google Scholar]
- Van der Vecht, J. The Vespinae of the Indo-Malayan and Papuan areas (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Zool. Verh. 1957, 34, 1–83. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, M.E. Taxonomy and bionomics of the Vespa tropica group (Hym., Vespinae). Entomol. Month. Mag. 1991, 127, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, M.E. Taxonomy, distribution and nesting biology of Vespa affinis (L.) and Vespa mocsaryana du Buysson (Hym., Vespinae). Entomol. Month. Mag. 1997, 133, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yamane, S.; Makino, S. Bionomics of Vespa analis insularis and V. mandarinia latilineata in Hokkaido, northern Japan, with notes on vespine embryo nests (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Insecta Matsumurana 1977, 12, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Starr, C.K.; Jacobson, R.S. Nest structure in Philippine hornets (Hymenoptera, Vespidae, Vespa spp.). Jap. J. Entomol. 1990, 58, 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Archer, M.E. Taxonomy, distribution and nesting biology of the Vespa mandarinia group (Hym., Vespinae). Entomol. Month. Mag. 1995, 131, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Jeanne, R.L. The adaptiveness of social wasp nest architecture. Quart. Rev. Biol. 1975, 50, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arca, M.; Mougel, F.; Guillemaud, T.; Dupas, S.; Rome, Q.; Perrard, A.; Muller, F.; Fossoud, A.; Capdevielle-Dulac, C.; Torres-Leguizamon, M.; et al. Reconstructing the invasion and the demographic history of the yellow-legged hornet, Vespa velutina, in Europe. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, S.F.; Fukushima, K. Some biological observations on a hornet, Vespa tropica var. pulchra (Du Buysson), with special reference to its dependence on Polistes wasps (Hymenoptera). Treubia 1957, 24, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Seeley, T.D.; Seeley, R.H.; Akratanakul, A. Colony defense strategies of the honeybees of Thailand. Ecol. Monogr. 1982, 52, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

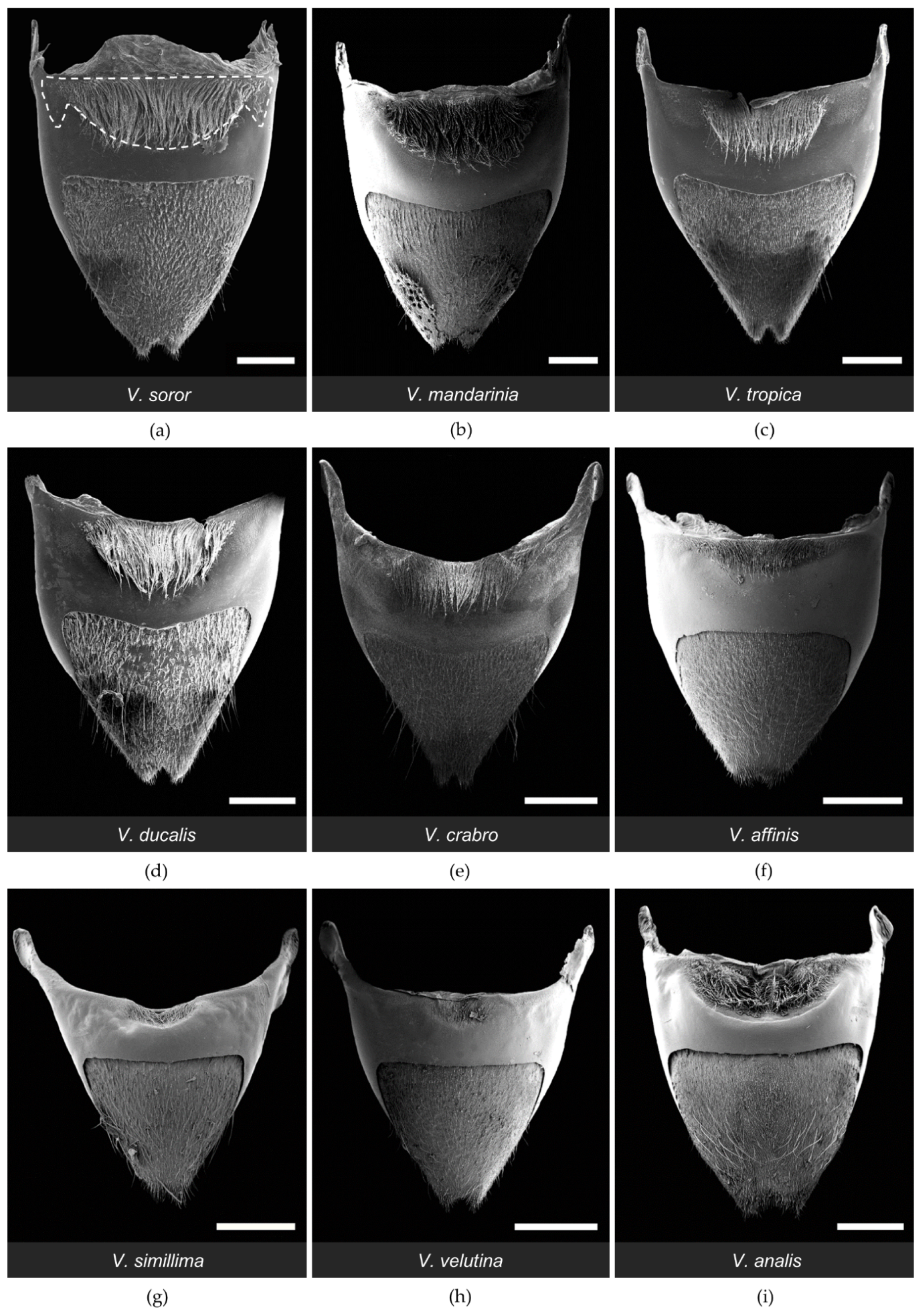
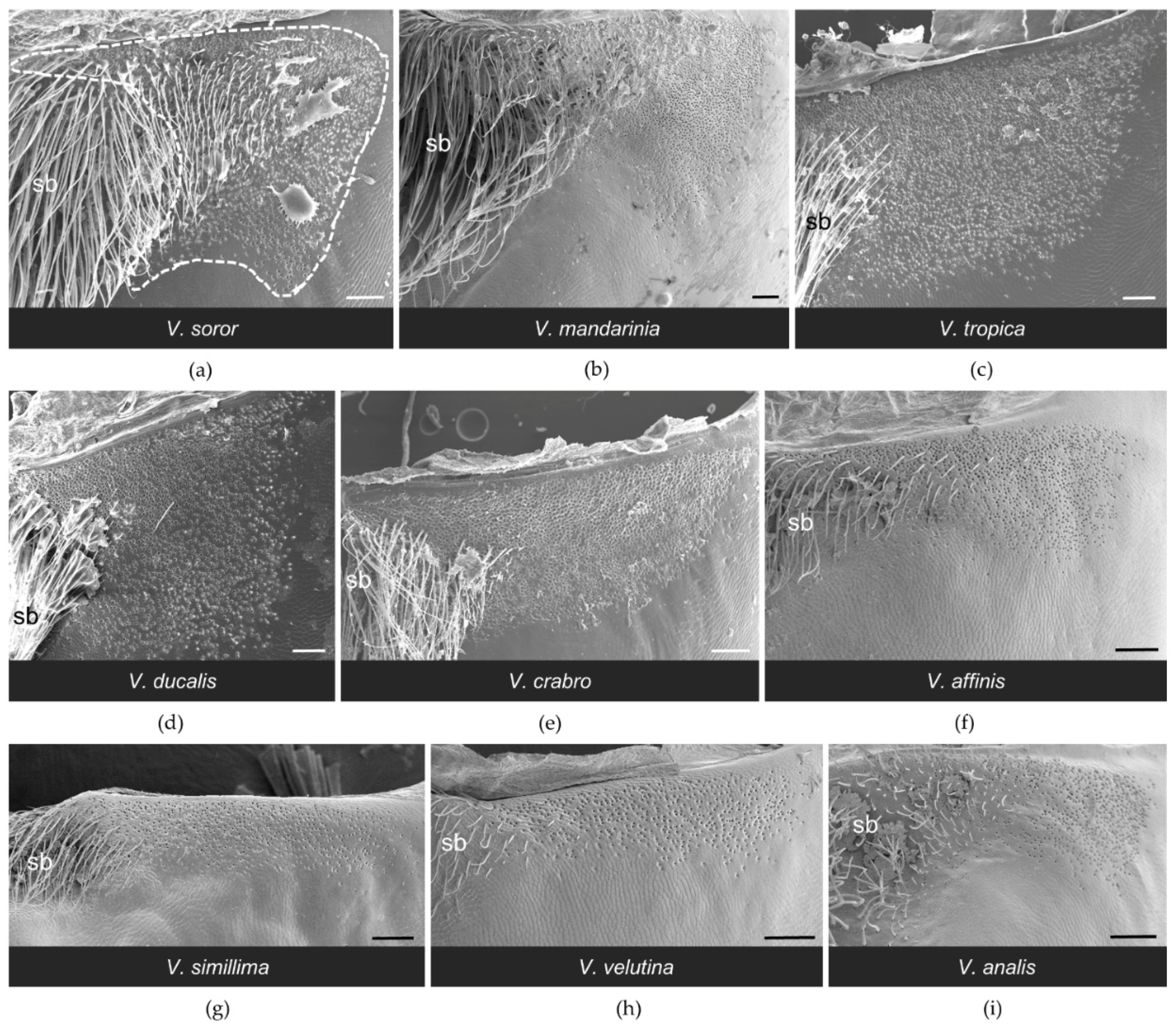
| Species | n | Location | Coordinates | Date | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V. soror du Buysson, 1905 | 3 | Da Chong, Ba Vi district, Hanoi Prov., Vietnam | 21.118° N, 105.335° E | September 2013 | G.W. Otis, pers. coll. |
| 2 | Muong Leo, Sop Cop district, Son La Prov., Vietnam | 20.836° N, 103.308° E | October 2020 | L.T.P. Nguyen, pers. coll. | |
| V. mandarinia Smith, 1852 | 1 | Tamugawa-gakuen, Machida City, Tokyo, Japan | 35.56° N, 139.46° E | September 2019 | M. Ono, Tamagawa Univ. |
| 1 | Lianhuachi Nursery, Nantou County, Taiwan | 23.922° N, 120.886° E | August 2015 | J.-T. Chao, Taiwan Forestry Res. Inst. | |
| V. tropica (Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 | Da Chong, Ba Vi district, Hanoi Prov., Vietnam | 21.118° N, 105.335° E | September 2013 | G.W. Otis, pers. coll. |
| V. ducalis Smith 1852 | 2 | Ngoc Dong, Yen Lap district, Phu Tho Prov., Vietnam | 21.242° N, 105.150° E | August 2013 | G.W. Otis, pers. coll. |
| V. crabro Linnaeus, 1758 | 1 | Plougras, Brittany, France | 49.498° N, 3.546° E | September 2018 | S. Paiero, Univ. Guelph Insect Coll. |
| 3 | Leuven, Belgium | 50.876° N, 4.701° E | September 2020 | J. Billen, pers. coll. | |
| 1 | Oakville, Ontario, Canada | 43.466° N, 79.785°W | September 2013 | S. Paiero, Univ. Guelph Insect Coll. | |
| V. affinis (Linnaeus, 1764) | 1 | Da Chong, Ba Vi district, Hanoi Prov., Vietnam | 21.118° N, 105.335° E | September 2013 | G.W. Otis, pers. coll. |
| V. simillima Smith, 1868 | 1 | Tsukuba Bot. Garden, Akakubo, Tsukuba, Ibaraki Pref., Japan | 36.103° N, 140.113° E | July 2020 | S. Nomura, Nat. Mus. Nature and Science |
| V. velutina Lepeletier, 1836 | 1 | Taipei Feitsui Reservoir, Taiwan | 24.905° N, 121.562° E | June 2020 | J.-T. Chao, Taiwan Forestry Res. Inst. |
| 1 | Son Tho, Vu Quang district, Ha Tinh Prov., Vietnam | 18.414° N, 105.443° E | May 2012 | G.W. Otis, pers. coll. | |
| 2 | Sergeac, Aquitaine Region, south France | 45.0° N, 1.1° E | 2010 | A. Perrard, Inst. Ecol. Envir. Sci., Univ. Paris | |
| V. analis Fabricius, 1775 | 1 | Tsukuba Bot. Garden, Akakubo, Tsukuba, Ibaraki Pref., Japan | 36.103° N, 140.113° E | July 2020 | S. Nomura, Nat. Mus. Nature and Science |
| Species | Number of Pores | Pore Area (mm2) | Hyaline Area (mm2) | Total Area (mm2) | Sternite Area (mm2) | Pore Diameter (μm ± SD) | % Length of Setae Relative to Sternite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V. soror | 4700 | 0.76 | 2.85 | 3.61 | 8.14 | 3.8 ± 0.5 a | 69.3 |
| V. mandarinia | 5300 | 0.90 | 3.39 | 4.29 | 9.91 | 4.1 ± 0.8 a | 62.9 |
| V. tropica | 5900 | 1.08 | 1.53 | 2.61 | 6.62 | 4.4 ± 0.7 b | 58.7 |
| V. ducalis | 3700 | 0.93 | 1.77 | 2.70 | 6.41 | 5.0 ± 0.7 c | 58.7 |
| V. crabro | 3200 | 0.20 | 0.87 | 1.07 | 3.67 | 2.9 ± 0.4 d | 56.2 |
| V. affinis | 2100 | 0.24 | 0.52 | 0.76 | 3.85 | 3.0 ± 0.5 d | 29.4 |
| V. simillima | 1200 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 2.36 | 2.8 ± 0.6 d | 34.3 |
| V. velutina | 1500 | 0.18 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 2.51 | 2.8 ± 0.4 d | 30.9 |
| V. analis | 1500 | 0.22 | 1.96 | 2.18 | 5.30 | 2.9 ± 0.5 d | 38.9 |
| Species | Number of Pores | Pore Area (mm2) | Sternite Area (mm2) | Pore Diameter (μm ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V. soror | 15,500 | 1.92 | 10.75 | 5.0 ± 0.5 a |
| V. mandarinia | 21,500 | 2.76 | 12.65 | 5.0 ± 0.6 a |
| V. tropica | 6500 | 1.18 | 7.80 | 4.5 ± 0.6 b |
| V. ducalis | 8200 | 1.49 | 9.04 | 4.9 ± 0.6 a |
| V. crabro | 3400 | 0.72 | 6.22 | 2.8 ± 0.6 e |
| V. affinis | 1600 | 0.50 | 4.80 | 3.1 ± 0.4 d |
| V. simillima | 3000 | 0.41 | 3.69 | 2.9 ± 0.5 e |
| V. velutina | 2400 | 0.44 | 3.65 | 3.7 ± 0.8 d |
| V. analis | 6100 | 0.75 | 6.87 | 3.8 ± 0.4 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mattila, H.R.; Otis, G.W.; Billen, J.; Nguyen, L.T.P.; Shimano, S. Comparison of the External Morphology of the Sternal Glands for Hornets in the Genus Vespa. Biology 2022, 11, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020245
Mattila HR, Otis GW, Billen J, Nguyen LTP, Shimano S. Comparison of the External Morphology of the Sternal Glands for Hornets in the Genus Vespa. Biology. 2022; 11(2):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020245
Chicago/Turabian StyleMattila, Heather R., Gard W. Otis, Johan Billen, Lien T. P. Nguyen, and Satoshi Shimano. 2022. "Comparison of the External Morphology of the Sternal Glands for Hornets in the Genus Vespa" Biology 11, no. 2: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020245
APA StyleMattila, H. R., Otis, G. W., Billen, J., Nguyen, L. T. P., & Shimano, S. (2022). Comparison of the External Morphology of the Sternal Glands for Hornets in the Genus Vespa. Biology, 11(2), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020245







