Analysis of the Radiological Changes of the Sinus Membrane Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography and Its Relationship with Dental Treatments. A Retrospective Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Evaluation of Radiological Data
2.3. Whyte and Boeddinghaus Aetiological Classification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dental Factors
3.2. Iatrogenic Factors
3.3. Proximity of the Roots and Its Relationship with Dental Factors
3.4. Whyte and Boeddinghaus Classification
3.5. Thickening of the Sinus Membrane and Its Interrelation with Dental Factors and Iatrogenic Causes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Little, R.E.; Long, C.M.; Loehrl, T.A.; Poetker, D.M. Odontogenic sinusitis: A review of the current literature. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2018, 3, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkham-Ali, K.; La, M.; Sher, J.; Sholapurkar, A. Comparison of cone-beam computed tomography and panoramic imaging in assessing the relationship between posterior maxillary tooth roots and the maxillary sinus: A systematic review. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2019, 10, e12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Yokoi, H.; Kohno, N. Association between odontogenic infections and unilateral sinus opacification. Auris Nasus Larynx 2015, 42, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomeli, S.R.; Branstetter, B.F., 4th; Ferguson, B.J. Frequency of a dental source for acute maxillary sinusitis. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.H.L.; Pontual, M.L.A.; Pontual, A.A.; Freitas, D.Q.; Cruz Perez, D.E.; Ramos-Perez, F.M.M. Association between Odontogenic Conditions and Maxillary Sinus Disease: A Study Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, C.O.; Devito, K.L.; Baraky Vasconcelos, L.R.; Prado, M.D.; Campos, C.N. Correlation between Endodontic Infection and Periodontal Disease and Their Association with Chronic Sinusitis: A Clinical-tomographic Study. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1978–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñarrocha-Oltra, S.; Soto-Peñaloza, D.; Bagán-Debón, L.; Bagan, J.V.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D. Association between maxillary sinus pathology and odontogenic lesions in patients evaluated by conebeam computed tomography. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2020, 25, e34–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taschieri, S.; Torretta, S.; Corbella, S.; Del Fabbro, M.; Francetti, L.; Lolato, A.; Capaccio, P. Pathophysiology of sinusitis of odontogenic origin. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2017, 8, e12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persoon, I.F.; Özok, A.R. Definitions and Epidemiology of Endodontic Infections. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2017, 4, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaudin, R.A.; Hoehle, L.P.; Smeets, R.; Heiland, M.; Caradonna, D.S.; Gray, S.T.; Sedaghat, A.R. Impact of odontogenic chronic rhinosinusitis on general health-related quality of life. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J. Executive summary of EPOS 2020 including integrated care pathways. Rhinology 2020, 58, 82–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, P.H.; Chen, C.W.; Wu, C.C.; Fu, C.H.; Lee, T.J. The characteristics and new treatment paradigm of dental implant-related chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2013, 27, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Torradeflot, M.M.; Marti, C. Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Choi, B.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Li, J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.J. A retrospective study of the effects on sinus complications of exposing dental implants to the maxillary sinus cavity. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 103, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, A.; Favero, V.; Nocini, R.; Venco, J.; Nocini, P.F.; Trevisiol, L. Does Middle Meatal Antrostomy Prevent the Onset of Maxillary Sinusitis After Zygomatic Implant Placement? J Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, M.; Bowles, W.R.; McClanahan, S.L.; John, M.T.; Ahmad, M. Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of maxillary sinusitis. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, A.; Boeddinghaus, R. Imaging of odontogenic sinusitis. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorny, A.; Tataryn, R. Clinical and radiologic findings in a case series of maxillary sinusitis of dental origin. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestin Fredriksson, M.; Öhman, A.; Flygare, L.; Tano, K. When Maxillary Sinusitis Does Not Heal: Findings on CBCT Scans of the Sinuses With a Particular Focus on the Occurrence of Odontogenic Causes of Maxillary Sinusitis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2017, 2, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allevi, F.; Fadda, G.L.; Rosso, C.; Martino, F.; Pipolo, C.; Cavallo, G.; Felisati, G.; Saibene, A.M. Diagnostic Criteria for Odontogenic Sinusitis: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechien, J.R.; Filleul, O.; Costa de Araujo, P.; Hsieh, J.W.; Chantrain, G.; Saussez, S. Chronic maxillary rhinosinusitis of dental origin: A systematic review of 674 patient cases. Int. J. Otolaryngol. 2014, 2014, 465173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Craig, J.R.; Tataryn, R.W.; Cha, B.Y.; Bhargava, P.; Pokorny, A.; Gray, S.T.; Mattos, J.L.; Poetker, D.M. Diagnosing odontogenic sinusitis of endodontic origin: A multidisciplinary literature review. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajoria, A.A.; Sarkar, S.; Sinha, P. Evaluation of Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis with Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Retrospective Study with Review of Literature. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2019, 9, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turfe, Z.; Ahmad, A.; Peterson, E.I.; Craig, J.R. Odontogenic sinusitis is a common cause of unilateral sinus disease with maxillary sinus opacification. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saibene, A.M.; Pipolo, G.C.; Lozza, P.; Maccari, A.; Portaleone, S.M.; Scotti, A.; Borloni, R.; Messina, F.; Di Pasquale, D.; Felisati, G. Redefining boundaries in odontogenic sinusitis: A retrospective evaluation of extramaxillary involvement in 315 patients. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Irimia, O.; Barona-Dorado, C.; Santos-Marino, J.A.; Martínez-Rodriguez, N.; Martínez-González, J.M. Meta-analysis of the etiology of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2010, 15, e70–e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phothikhun, S.; Suphanantachat, S.; Chuenchompoonut, V.; Nisapakultorn, K. Cone-beam computed tomographic evidence of the association between periodontal bone loss and mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Pan, Y. Significance of maxillary sinus mucosal thickening in patients with periodontal disease. Int. Dent. J. 2015, 65, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, H.A.; Poetker, D.M. Odontogenic Sinusitis: Current Concepts in Diagnosis and Treatment. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2020, 40, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.C.; Lee, S.J. Clinical features and treatments of odontogenic sinusitis. Yonsei Med. J. 2010, 51, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longhini, A.B.; Ferguson, B.J. Clinical aspects of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis: A case series. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2011, 1, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskison, E.; Daniel, M.; Rowson, J.E.; Jones, N.S. Evidence of an increase in the incidence of odontogenic sinusitis over the last decade in the UK. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2012, 126, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crovetto-Martínez, R.; Martin-Arregui, F.J.; Zabala-López-de-Maturana, A.; Tudela-Cabello, K.; Crovetto-de la Torre, M.A. Frequency of the odontogenic maxillary sinusitis extended to the anterior ethmoid sinus and response to surgical treatment. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2014, 19, e409–e413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Nichols, B.G.; Poetker, D.M.; Loehrl, T.A. Odontogenic sinusitis: A case series studying diagnosis and management. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troeltzsch, M.; Pache, C.; Troeltzsch, M.; Kaeppler, G.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Otto, S.; Probst, F. Etiology and clinical characteristics of symptomatic unilateral maxillary sinusitis: A review of 174 cases. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirk, M.; Dreiseidler, T.; Pohl, M.; Rothamel, D.; Buller, J.; Peters, F.; Zöller, J.E.; Kreppel, M. Odontogenic sinusitis maxillaris: A retrospective study of 121 cases with surgical intervention. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, O.J.; Yafit, D.; Kleinman, S.; Raiser, V.; Safadi, A. Odontogenic sinusitis involving the frontal sinus: Is middle meatal antrostomy enough? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 2291–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.; Emanuelli, E.; Franz, L.; Tel, A.; Robiony, M. Single-step surgical treatment of odontogenic maxillary sinusitis: A retrospective study of 98 cases. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, J.R.; McHugh, C.I.; Griggs, Z.H.; Peterson, E.I. Optimal timing of endoscopic sinus surgery for odontogenic sinusitis. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safadi, A.; Kleinman, S.; Oz, I.; Wengier, A.; Mahameed, F.; Vainer, I.; Ungar, O.J. Questioning the Justification of Frontal Sinusotomy for Odontogenic Sinusitis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 78, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Mullol, J.; Bachert, C.; Alobid, I.; Baroody, F.; Cohen, N.; Cervin, A.; Douglas, R.; Gevaert, P.; et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology 2012, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pynnonen, M.A.; Kim, H.M.; Terrell, J.E. Validation of the Sino-Nasal Outcome Test 20 (SNOT-20) domains in nonsurgical patients. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2009, 23, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, I. Sinusitis of odontogenic origin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 135, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tataryn, R.W.; Lewis, M.J.; Horalek, A.L.; Thompson, C.G.; Cha, B.Y.; Pokorny, A.T. Maxillary Sinusitis of Endodontic Origin. American Association of Endodontists Position Statement; American Association of Endodontists: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–11. Available online: https://www.aae.org/specialty/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2018/04/AAE_PositionStatement_MaxillarySinusitis.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Whyte, A.; Boeddinghaus, R. The maxillary sinus: Physiology, development and imaging anatomy. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2019, 48, 20190205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liston, P.N.; Walters, R.F. Foreign bodies in the maxillary antrum: A case report. Aust. Dent. J. 2002, 47, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S173–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanbhag, S.; Karnik, P.; Shirke, P.; Shanbhag, V. Association between periapical lesions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: A retrospective cone-beam computed tomographic study. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian, M.; Vandewoude, C.; Wyatt, J.; Jacobs, R. Comparative assessment of periapical radiography and CBCT imaging for radiodiagnostics in the posterior maxilla. Odontology 2015, 103, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Q.; Duan, X.; Zheng, G.; Wang, H.; Huang, D. Associations between maxillary sinus mucosal thickening and apical periodontitis using cone-beam computed tomography scanning: A retrospective study. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goller-Bulut, D.; Sekerci, A.E.; Köse, E.; Sisman, Y. Cone beam computed tomographic analysis of maxillary premolars and molars to detect the relationship between periapical and marginal bone loss and mucosal thickness of maxillary sinus. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2015, 20, e572–e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, U.; Orhan, K. Association between odontogenic conditions and maxillary sinus mucosal thickening: A retrospective CBCT study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.T.; Hu, S.W.; Huang, J.Y.; Chang, Y.C. Assessment of relationship between maxillary sinus membrane thickening and the adjacent teeth health by cone-beam computed tomography. J. Dent. Sci. 2021, 16, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.A.; Guedes, O.A.; Alencar, A.H.; Peters, O.A.; Estrela, C.R.; Estrela, C. Evaluation of Periapical Lesions and Their Association with Maxillary Sinus Abnormalities on Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Images. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagassan-Berndt, D.C.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Lambrecht, J.T.; Weiger, R.; Walter, C. Is the Schneiderian membrane thickness affected by periodontal disease? A cone beam computed tomography-based extended case series. J. Int. Acad. Periodontol. 2013, 15, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Roque-Torres, G.D.; Ramirez-Sotelo, L.R.; de Acevedo Vaz, S.L.; de Almeida de Bóscolo, S.M.; Bóscolo, F.N. Association between maxillary sinus pathologies and healthy teeth. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhlaghi, F.; Esmaeelinejad, M.; Safai, P. Etiologies and Treatments of Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis: A Systematic Review. Iran Red Crescent Med. J. 2015, 17, e25536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco-Carro, B.; Barona-Dorado, C.; Martínez-González, M.J.S.; Rubio-Alonso, L.J.; Martínez-González, J.M. Meta-analytic study on the frequency and treatment of oral antral communications. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2011, 16, e682–e687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacic, B.; Todorovic, L.; Kokovic, V.; Danilovic, V.; Stojcev-Stajcic, L.; Drazic, R.; Markovic, A. The closure of oroantral communications with resorbable PLGA-coated beta-TCP root analogs, hemostatic gauze, or buccal flaps: A prospective study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 108, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, K.; Ito, K.; Kuroda, M.; Sugihara, N. Prevalence of vertical root fracture as the reason for tooth extraction in dental clinics. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, S.M.; Diaconu, O.A.; Scrieciu, M.; Marinescu, I.R.; Drăghici, E.C.; Truşcă, A.G.; Bănică, A.C.; Vătu, M.; Mercuţ, V. Root fractures: Epidemiological, clinical and radiographic aspects. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2017, 58, 501–506. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, C.H.; Park, Y.H.; Bae, J.H. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of dental implant-related paranasal sinusitis: A 2-year prospective observational study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, e100–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, L.; Agarwal, A.; Guirado, J.C.; Bali, P.; Poonia, N. Survival of Implants after Indirect Maxillary Sinus Elevation Procedure: A Two Years Longitudinal Study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2019, 20, 504–507. [Google Scholar]
- Chiapasco, M.; Felisati, G.; Zaniboni, M.; Pipolo, C.; Borloni, R.; Lozza, P. The treatment of sinusitis following maxillary sinus grafting with the association of functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) and an intra-oral approach. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibene, A.M.; Pipolo, C.; Maccari, A.; Lozza, P.; Chiapasco, M.; Scotti, A.; Borloni, R.; Felisati, G. One-Step Maxillary Sinus Augmentation in Association with Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: Case Series and Review of the Literature. Implant. Dent. 2016, 25, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manor, Y.; Mardinger, O.; Bietlitum, I.; Nashef, A.; Nissan, J.; Chaushu, G. Late signs and symptoms of maxillary sinusitis after sinus augmentation. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 110, e1–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirilă, L.; Rotaru, C.; Filipov, I.; Săndulescu, M. Management of acute maxillary sinusitis after sinus bone grafting procedures with simultaneous dental implants placement—A retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16 (Suppl. 1), 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molteni, M.; Bulfamante, A.M.; Pipolo, C.; Lozza, P.; Allevi, F.; Pisani, A.; Chiapasco, M.; Portaleone, S.M.; Scotti, A.; Maccari, A.; et al. Odontogenic sinusitis and sinonasal complications of dental treatments: A retrospective case series of 480 patients with critical assessment of the current classification. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2020, 40, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.; Browne, J.P.; Slack, R.; Lund, V.; Brown, P. The Lund-Mackay staging system for chronic rhinosinusitis: How is it used and what does it predict? Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 137, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
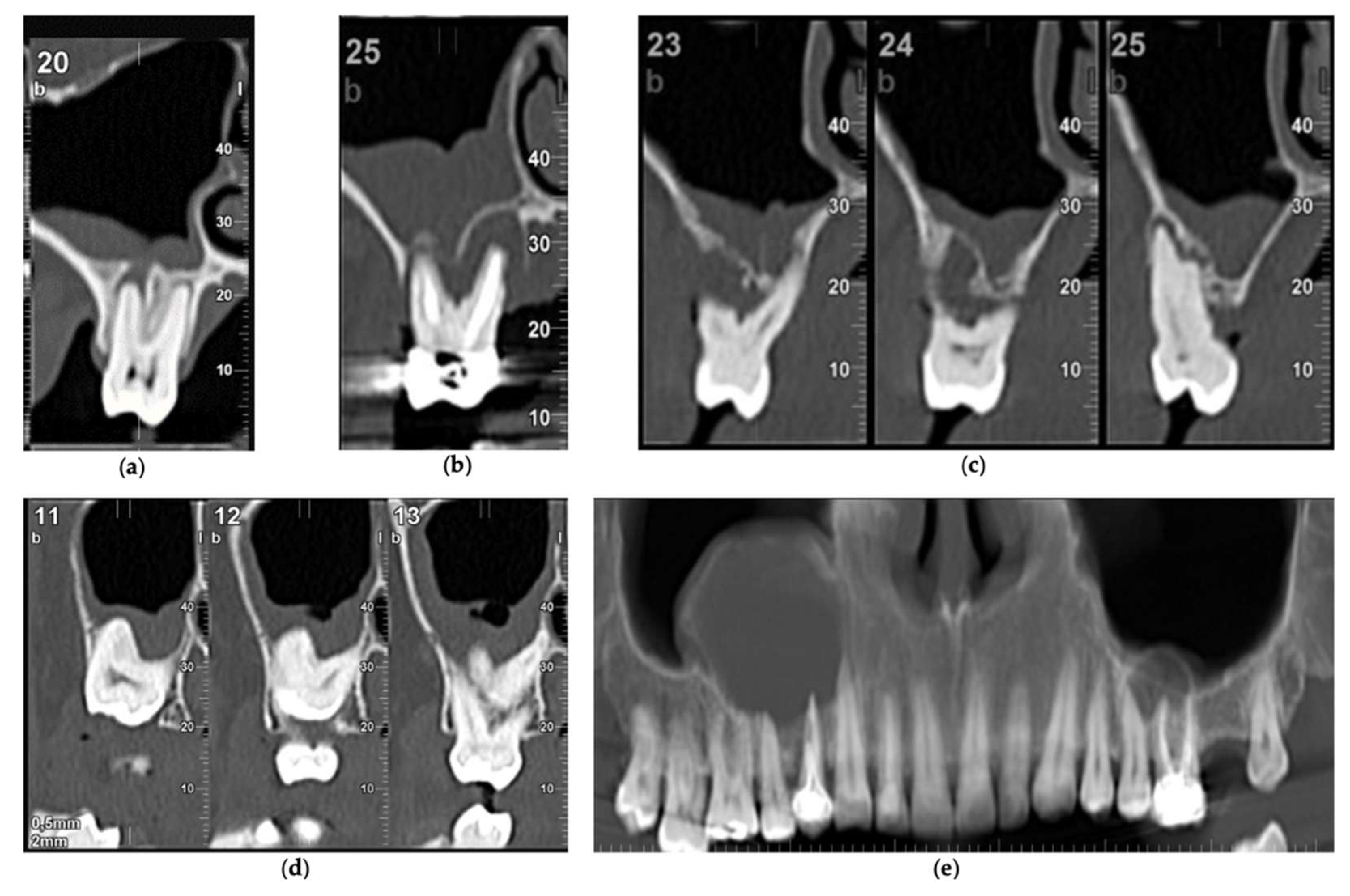

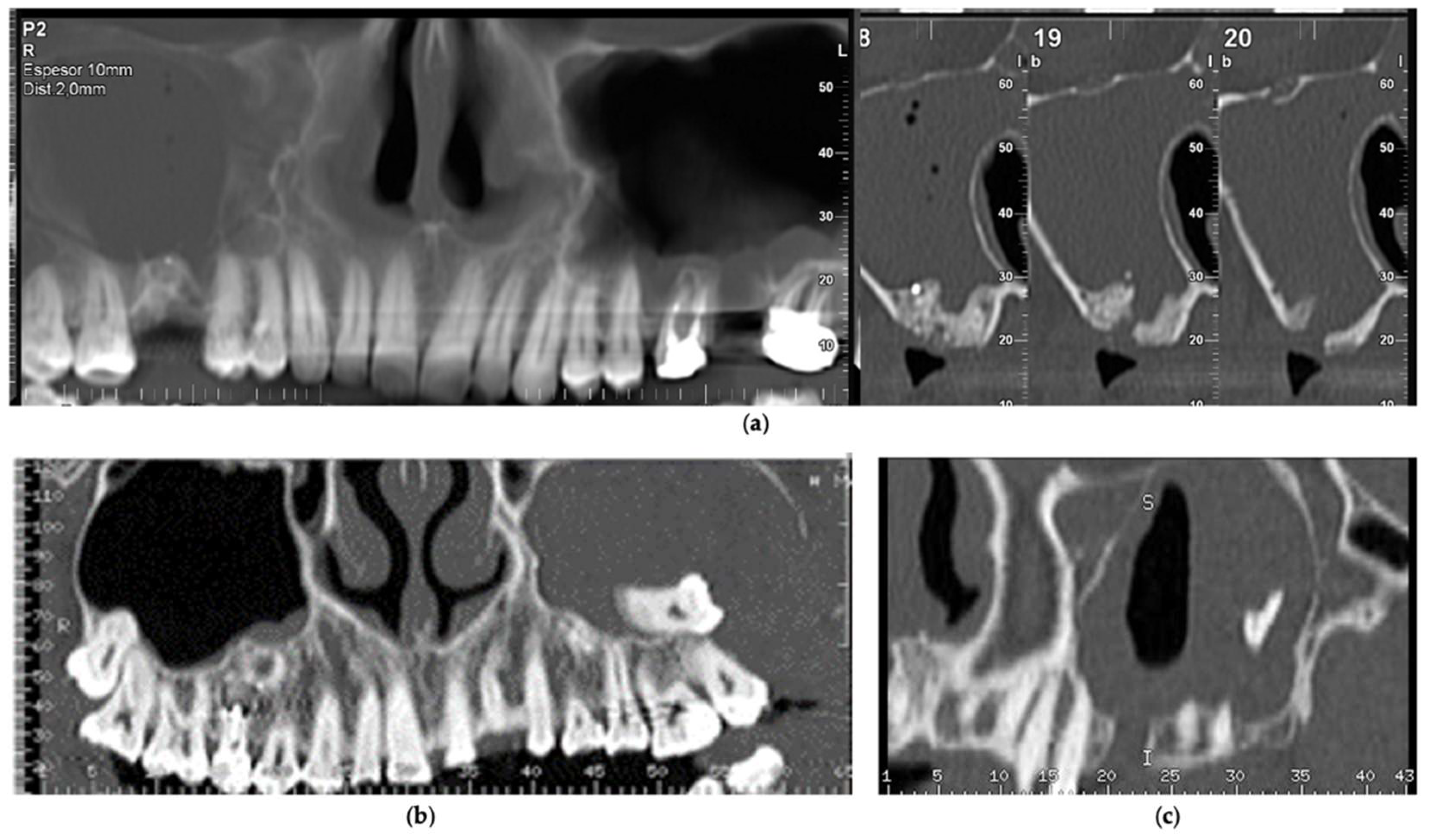
| Dental Factors | RMS | LMS | Both | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Cases | % | No. Cases | % | No. Cases | % | No. Cases | % | |
| Periapical pathology | 31 | 11.2 | 28 | 10.1 | 6 | 2.1 | 65 | 23.5 |
| Endodontic treatments | 32 | 11.5 | 28 | 10.1 | 7 | 2.5 | 64 | 23.1 |
| Periodontitis | 49 | 17.7 | 50 | 18.1 | 31 | 11.2 | 130 | 47.1 |
| Impacted teeth | 10 | 3.6 | 8 | 2.8 | 5 | 1.8 | 23 | 8.3 |
| Radicular cysts | 3 | 1.1 | 3 | 1.1 | 1 | 0.3 | 7 | 2.5 |
| RMS | LMS | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implant treatments | No. cases | % | No. cases | % | No. cases | % |
| Implants | 14 | 5.1 | 13 | 4.7 | 27 | 9.8 |
| Sinus elevations | 6 | 2.2 | 11 | 4.0 | 17 | 6.2 |
| Peri-implantitis | 1 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.4 | 2 | 0.8 |
| Oroantral communications | No. cases | % | No. cases | % | No. cases | % |
| Extractions | 9 | 3.2 | 5 | 1.8 | 14 | 5.0 |
| Root displacements | 1 | 0.4 | 4 | 1.4 | 5 | 1.8 |
| Third molar displacements | 1 | 0.4 | 3 | 1.1 | 4 | 1.5 |
| Proximity of the Roots | RMS | LMS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Cases | % | No. Cases | % | |
| (0) Within | 30 | 10.9 | 34 | 12.3 |
| (1) Protruding | 70 | 25.4 | 76 | 27.5 |
| (2) Contact | 88 | 31.9 | 97 | 35.1 |
| (3) 0.1–1 mm | 31 | 11.2 | 27 | 9.8 |
| (4) >1 mm | 57 | 20.7 | 42 | 15.2 |
| Dental Factors | Proximity of Roots to RMS | Proximity of Roots to LMS | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (0) | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | p | (0) | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | p | |
| Periapical pathology | 0.0 | 21.4 | 9.1 | 19.4 | 14.0 | 0.028 | 8.8 | 18.4 | 11.3 | 14.8 | 4.8 | 0.243 |
| Endodontic treatment | 26.7 | 14.3 | 13.6 | 16.1 | 7.0 | 0.172 | 2.9 | 18.4 | 12.4 | 11.1 | 11.9 | 0.261 |
| Periodontitis | 16.7 | 22.9 | 38.6 | 38.7 | 22.8 | 0.041 | 8.8 | 23.7 | 36.1 | 44.4 | 31.0 | 0.010 |
| Radicular cysts | 3.3 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 0.338 | 8.8 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.004 |
| Whyte and Boeddinghaus Classification | RMS | LMS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Cases | % | No. Cases | % | |
| Without pathology | 72 | 26.1 | 73 | 26.4 |
| 1. Periapical pathology (non-vital tooth) | 37 | 13.4 | 34 | 12.3 |
| 2. Periodontitis | 80 | 28.9 | 81 | 29.3 |
| 3. Endo-periodontal pathology (1 + 2) | 39 | 14.1 | 35 | 12.6 |
| 4. Post-exo communication/fistula | 9 | 3.2 | 14 | 5.0 |
| 5. Sinus elevation | 6 | 2.2 | 11 | 3.9 |
| 6. Foreign bodies | 16 | 5.7 | 23 | 8.3 |
| Dental Factors | RMS Thickening | LMS Thickening | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | p | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | p | |
| Periapical pathology | 27.0 | 37.8 | 21.6 | 13.5 | 0.021 | 20.6 | 47.1 | 17.6 | 14.7 | 0.106 |
| Endodontic treatment | 41.0 | 33.3 | 5.1 | 20.5 | 0.111 | 34.3 | 42.9 | 17.1 | 5.7 | 0.540 |
| Periodontitis | 31.3 | 47.5 | 12.5 | 8.8 | 0.014 | 27.2 | 44.4 | 16.0 | 12.3 | 0.054 |
| Radicular cysts | 50.0 | 0.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 0.349 | 0.0 | 50.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 0.361 |
| Iatrogenic Factors | RMS Thickening | LMS Thickening | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implant treatments | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | p | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | p |
| Implants | 28.6 | 64.3 | 7.1 | 0.0 | 0.110 | 23.1 | 69.2 | 0.0 | 7.7 | 0.111 |
| Sinus elevation | 0.0 | 50.0 | 0.0 | 50.0 | 0.004 | 9.1 | 63.6 | 0.0 | 27.3 | 0.026 |
| Peri-implantitis | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.001 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.001 |
| Oroantral communications | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | p | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | p |
| Exodontia | 0.0 | 42.9 | 0.0 | 57.1 | 0.014 | 0.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 0.001 |
| Root displacements | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.014 | 0.0 | 25.0 | 50.0 | 25.0 | 0.001 |
| Third molar displacements | 0.0 | 100.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.014 | 0.0 | 33.3 | 0.0 | 66.7 | 0.001 |
| Authors | Study Design | No. Cases | Average Age | Gender | Unilateral | Dental Factors | Iatrogenic Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lee and Lee [30], 2010 | Retrospective | 27 | 43 | Male: 56% Female: 44% | Almost all | 33% | 67% |
| Longhini and Ferguson [31], 2011 | Retrospective | 21 | 53 | Male: 48% Female: 52% | 57% | 100% | |
| Hoskison et al. [32], 2012 | Retrospective | 26 | 46 | Male: 65% Female: 35% | Not reported | 73% | 27% |
| Pokorny and Tataryn [18], 2013 | Retrospective | 31 | 48 | Male: 35% Female: 65% | 94% | 100% | |
| Crovetto-Martínez et al. [33], 2014 | Retrospective | 55 | 48 | Male: 60% Female: 40% | 100% | 69% | 31% |
| Wang et al. [34], 2015 | Retrospective | 55 | 55 | Male: 40% Female: 60% | 84% | 58% | 42% |
| Troeltzsch et al. [35], 2015 | Retrospective | 130 | 53 | Male: 59% Female: 41% | 100% | 28% | 68% |
| Zirk et al. [36], 2017 | Retrospective | 121 | 57 | Male: 44% Female: 56% | 92% | 34% | 66% |
| Ungar et al. [37], 2018 | Prospective | 25 | 49 | Male: 36% Female: 64% | Not reported | 16% | 84% |
| Costa et al. [38], 2019 | Retrospective | 98 | 52 | Male: 51% Female: 49% | 100% | 39% | 61% |
| Craig et al. [39], 2019 | Prospective | 37 | 53 | Male: 65% Female: 35% | 89% | 68% | 32% |
| Turfe et al. [24], 2019 | Prospective | 60 | 55 | Male: 58% Female: 42% | 100% | 70% | 30% |
| Safadi et al. [40], 2020 | Prospective | 45 | 58 | Male: 51% Female: 49% | Not reported | 38% | 62% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rey-Martínez, M.H.; Ruiz-Sáenz, P.L.; Martínez-Rodríguez, N.; Barona-Dorado, C.; Meniz-García, C.; Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann, J.; Suárez-Quintanilla, J.A.; Martínez-González, J.M. Analysis of the Radiological Changes of the Sinus Membrane Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography and Its Relationship with Dental Treatments. A Retrospective Study. Biology 2022, 11, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020165
Rey-Martínez MH, Ruiz-Sáenz PL, Martínez-Rodríguez N, Barona-Dorado C, Meniz-García C, Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann J, Suárez-Quintanilla JA, Martínez-González JM. Analysis of the Radiological Changes of the Sinus Membrane Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography and Its Relationship with Dental Treatments. A Retrospective Study. Biology. 2022; 11(2):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleRey-Martínez, María Helena, Pedro Luis Ruiz-Sáenz, Natalia Martínez-Rodríguez, Cristina Barona-Dorado, Cristina Meniz-García, Jorge Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann, Juan Antonio Suárez-Quintanilla, and José María Martínez-González. 2022. "Analysis of the Radiological Changes of the Sinus Membrane Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography and Its Relationship with Dental Treatments. A Retrospective Study" Biology 11, no. 2: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020165
APA StyleRey-Martínez, M. H., Ruiz-Sáenz, P. L., Martínez-Rodríguez, N., Barona-Dorado, C., Meniz-García, C., Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann, J., Suárez-Quintanilla, J. A., & Martínez-González, J. M. (2022). Analysis of the Radiological Changes of the Sinus Membrane Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography and Its Relationship with Dental Treatments. A Retrospective Study. Biology, 11(2), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020165





