Egg-Laying Behavior of Cataglyphis niger Ants Is Influenced More Strongly by Temperature Than Daylength
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment 1: The Effect of Temperature and Daylength on Oviposition and Development
2.2. Experiment 2: The Effect of Temperature on the Fate of Oviposited Eggs
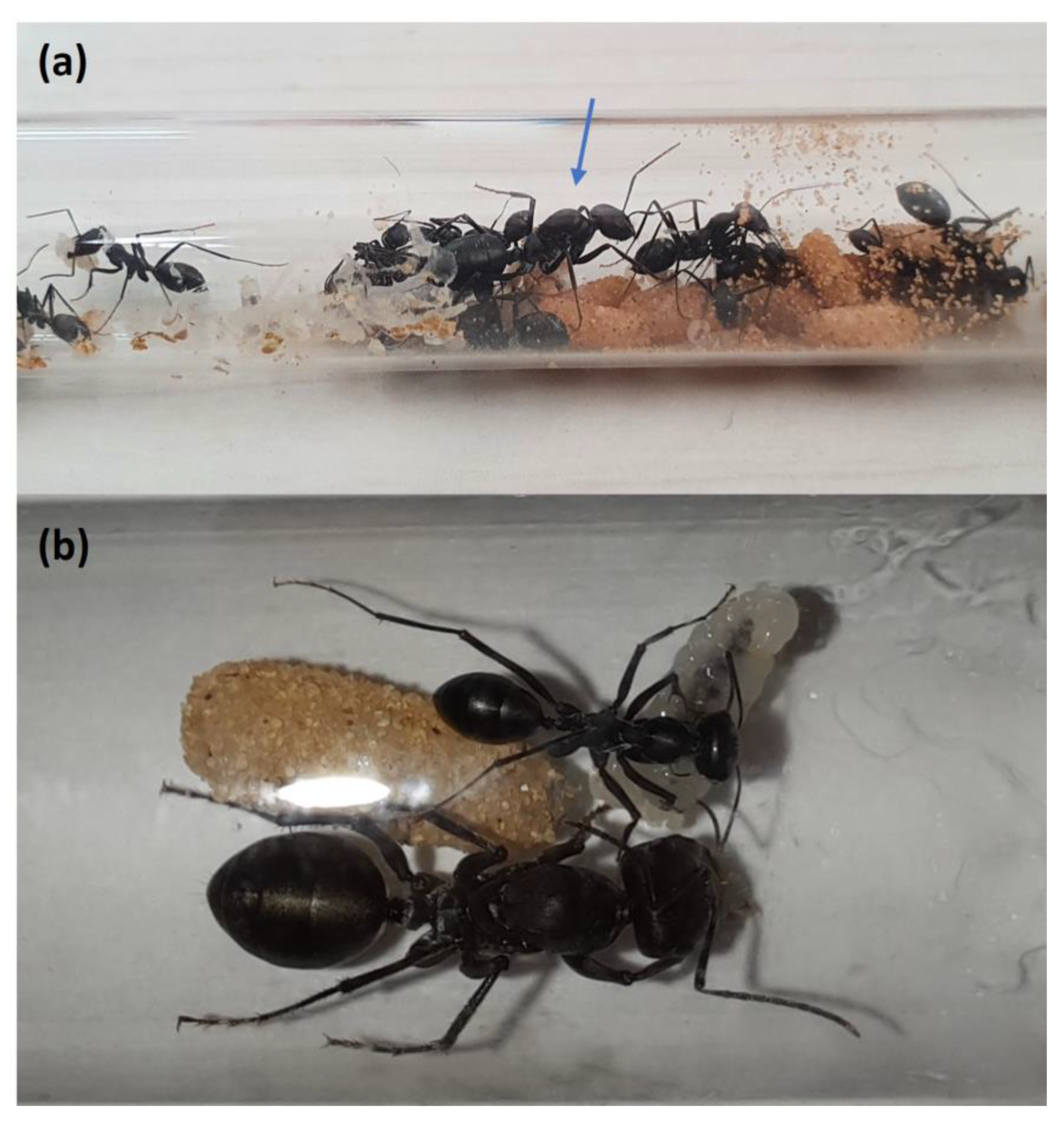
3. Results
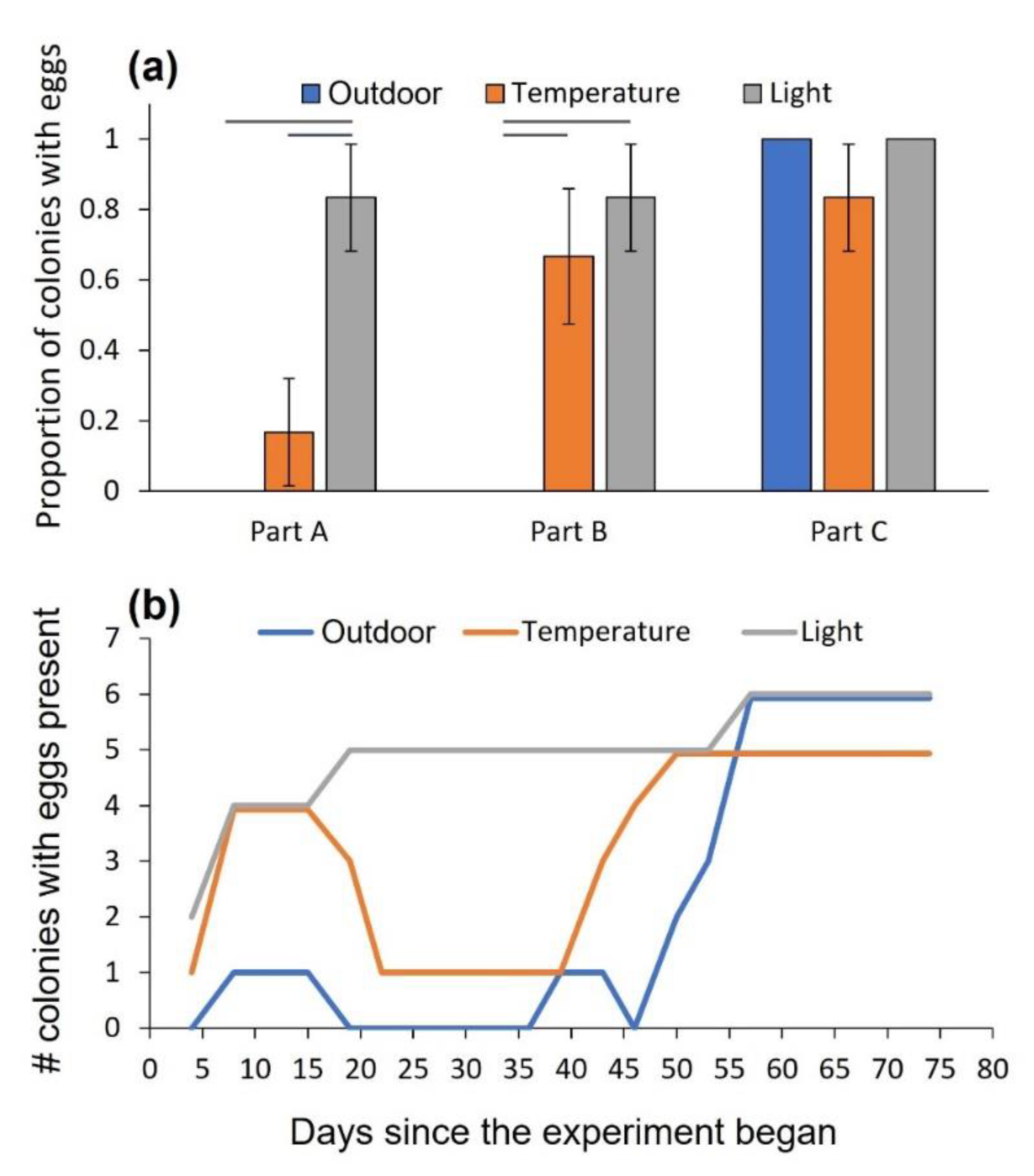
3.1. Experiment 1: The Effect of Temperature and Daylength on Oviposition and Development
3.2. Experiment 2: The Effect of Temperature on the Fate of Oviposited Eggs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dingle, H. Migration strategies of insects: Migration is an environmentally modified physiological syndrome adapted for dispersal and colonization. Science 1972, 175, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, D.S. The temperature-compensated photoperiodic clock ‘programming’ development and pupal diapause in the flesh-fly, Sarcophaga argyrostoma. J. Insect Physiol. 1971, 17, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutcherov, D.A.; Lopatina, E.B. Photoperiodic insensitivity of temperature-dependent development in some chrysomeloid beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae, Megalopodidae). Entomol. Rev. 2022, 102, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, H.; Arbiv, A.; Gersani, M.; Ovadia, O.; Novoplansky, A. The effects of nutrient dynamics on root patch choice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwick, E.E.; Heldmaier, G. Temperature control in honey bee colonies. Bioscience 1987, 37, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traniello, J.F.; Fujita, M.S.; Bowen, R.V. Ant foraging behavior: Ambient temperature influences prey selection. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1984, 15, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, F.; Tinaut, A.; Soler, A.J.J. High surface temperatures select for individual foraging in ants. Behav. Ecol. 2000, 11, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril, S.; Oliveras, J.; Gómez, C. Effect of temperature on the oviposition rate of Argentine ant queens (Linepithema humile Mayr) under monogynous and polygynous experimental conditions. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril, S.; Oliveras, J.; Gómez, C. Effect of temperature on the development and survival of the Argentine ant, Linepithema humile. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasei, J.N.; Aupinel, P. Effect of photoperiodic regimes on the oviposition of artificially overwintered Bombus terrestris L. queens and the production of sexuals. J. Apic. Res. 1994, 33, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipyatkov, V.E.; Lopatina, E.B. Seasonal cycle and winter diapause induction in ants of the genus Myrmica in the Polar Circle region. Proc. Int. Colloq. Soc. Insects 1997, 3, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Foitzik, S.; Heinze, J. Intraspecific parasitism and split sex ratios in a monogynous and monandrous ant (Leptothorax nylanderi). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2000, 47, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipyatkov, V.E. Seasonal life cycles and the forms of dormancy in ants (Hymenoptera: Formicoidea). Acta Soc. Zool. Bohem. 2001, 65, 211–238. [Google Scholar]
- Lopatina, E. Structure, diversity and adaptive traits of seasonal cycles and strategies in ants (ch. 2). In The Complex World of Ants; Shields, V.D.C., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, A.A.; Busch, T.M.; Vinson, S.B. Factors affecting brood cannibalism in laboratory colonies of the imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 1983, 56, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Masuko, K. Larval oophagy in the ant Amblyopone silvestrii (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Insectes Sociaux 2003, 50, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüppell, O.; Kirkman, R.W. Extraordinary starvation resistance in Temnothorax rugatulus (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) colonies: Demography and adaptive behavior. Insectes Sociaux 2005, 52, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hesse, L.; Falk, J.; Koch, K. Inflexible versus flexible: The influence of temperature and photoperiod on pre- and post-eyespot development time in Libellulidae (Odonata). Physiol. Entomol. 2016, 41, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, A.; Aron, S.; Cerdá, X.; Hefetz, A. Cataglyphis desert ants: A good model for evolutionary biology in Darwin’s s anniversary year: A review. Isr. J. Entomol. 2009, 39, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Boulay, R.; Aron, S.; Cerdá, X.; Doums, C.; Graham, P.; Hefetz, A.; Monnin, T. Social life in arid environments: The case study of Cataglyphis ants. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, W.J.; Wehner, R. Heat shock protein synthesis and thermotolerance in Cataglyphis, an ant from the Sahara desert. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2994–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.; de Souza Araujo, N.; Defrance, M.; Aron, S. Molecular adaptations to heat stress in the thermophilic ant genus Cataglyphis. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 5503–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razin, N.; Eckmann, J.P.; Feinerman, O. Desert ants achieve reliable recruitment across noisy interactions. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bega, D.; Samocha, Y.; Yitzhak, N.; Saar, M.; Subach, A.; Scharf, I. Non-spatial information on the presence of food elevates search intensity in ant workers, leading to faster maze solving in a process parallel to spatial learning. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Wehner, R. The hidden spiral: Systematic search and path integration in desert ants, Cataglyphis fortis. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1994, 175, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiélin-Bescond, M.; Beugnon, G. Vision-independent odometry in the ant Cataglyphis cursor. Naturwissenschaften 2005, 92, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, R.; Müller, M. The significance of direct sunlight and polarized skylight in the ant’s celestial system of navigation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12575–12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chameron, S.; Schatz, B.; Pastergue-Ruiz, I.; Beugnon, G.; Collett, T.S. The learning of a sequence of visual patterns by the ant Cataglyphis cursor. Proc. R. Soc. B 1998, 265, 2309–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wystrach, A.; Buehlmann, C.; Schwarz, S.; Cheng, K.; Graham, P. Rapid aversive and memory trace learning during route navigation in desert ants. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar, A.; Marom, C.; Zorin, N.; Gilad, T.; Subach, A.; Foitzik, S.; Scharf, I. Desert ants learn to avoid pitfall traps while foraging. Biology 2022, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdá, X.; Retana, J.; De Haro, A. Social carrying between nests in polycalic colonies of the monogynous ant Cataglyphis iberica (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Sociobiology 1994, 23, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Darras, H.; Kuhn, A.; Aron, S. Genetic determination of female castes in a hybridogenetic desert ant. J. Evol. Biol. 2014, 27, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodetzki, T.R.; Inbar, S.; Cohen, P.; Aron, S.; Privman, E.; Hefetz, A. The Interplay between Incipient species and social polymorphism in the Desert Ant Cataglyphis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subach, A.; Avidov, B.; Dorfman, A.; Bega, D.; Gilad, T.; Kvetny, M.; Reshef, M.H.; Foitzik, S.; Scharf, I. The value of spatial experience and group size for ant colonies in direct competition. Insect Sci. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saar, M.; Subach, A.; Reato, I.; Liber, T.; Pruitt, J.N.; Scharf, I. Consistent differences in foraging behavior in 2 sympatric harvester ant species may facilitate coexistence. Curr. Zool. 2018, 64, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Fujiyama, M.; Ohta, K. Effect of temperature on queen oviposition and seasonal colony development in Lasius japonicus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2017, 52, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, W.E.; Holzapfel, C.M. Evolution of animal photoperiodism. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2007, 38, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, R.; Wehner, S. Parallel evolution of thermophilia: Daily and seasonal foraging patterns of heat-adapted desert ants: Cataglyphis and Ocymyrmex species. Physiol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, D.; Walters, R.; Gotthard, K. What limits insect fecundity? Body size-and temperature-dependent egg maturation and oviposition in a butterfly. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Escudero, I.F.; Tinaut, A.; Ruano, F. Ovarian maturation under cold winter conditions in a high-mountain ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Environ. Entomol. 1997, 26, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doblas-Miranda, E.; Sánchez-Piñero, F.; González-Megías, A. Soil macroinvertebrate fauna of a Mediterranean arid system: Composition and temporal changes in the assemblage. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, I.; Martin, O.Y. Same-sex sexual behavior in insects and arachnids: Prevalence, causes, and consequences. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2013, 67, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, N.; Baracchi, D.; Giurfa, M.; d’Ettorre, P. Pheromone-induced accuracy of nestmate recognition in carpenter ants: Simultaneous decrease in type I and type II errors. Am. Nat. 2019, 193, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modlmeier, A.P.; Foitzik, S.; Scharf, I. Starvation endurance in the ant Temnothorax nylanderi depends on group size, body size and access to larvae. Physiol. Entomol. 2013, 38, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, A.F. Queen behaviour, reproduction and egg cannibalism in multiple-queen colonies of the ant Leptothorax acervorum. Anim. Behav. 1991, 42, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, J.; Trunzer, B.; Oliveira, P.S.; Hölldobler, B. Regulation of reproduction in the neotropical ponerine ant, Pachycondyla villosa. J. Insect Behav. 1996, 9, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnin, T.; Peeters, C. Cannibalism of subordinates’ eggs in the monogynous queenless ant Dinoponera quadriceps. Naturwissenschaften 1997, 84, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonacs, P. Less growth with more food: How insect-prey availability changes colony demographics in the ant, Camponotus floridanus. J. Insect Physiol. 1991, 37, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspari, M.; Vargo, E.L. Colony size as a buffer against seasonality: Bergmann’s rule in social insects. Am. Nat. 1995, 145, 610–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bar, A.; Shalev, L.; Scharf, I. Egg-Laying Behavior of Cataglyphis niger Ants Is Influenced More Strongly by Temperature Than Daylength. Biology 2022, 11, 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121714
Bar A, Shalev L, Scharf I. Egg-Laying Behavior of Cataglyphis niger Ants Is Influenced More Strongly by Temperature Than Daylength. Biology. 2022; 11(12):1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121714
Chicago/Turabian StyleBar, Adi, Lior Shalev, and Inon Scharf. 2022. "Egg-Laying Behavior of Cataglyphis niger Ants Is Influenced More Strongly by Temperature Than Daylength" Biology 11, no. 12: 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121714
APA StyleBar, A., Shalev, L., & Scharf, I. (2022). Egg-Laying Behavior of Cataglyphis niger Ants Is Influenced More Strongly by Temperature Than Daylength. Biology, 11(12), 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121714






