Proteomic Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Proboscis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drosophila Stocks and Sample Preparation
2.2. Mass Spectrometry Proteomic Analysis
2.3. Proteomic Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Broad Identification of Soluble Proteins from Drosophila melanogaster Proboscis
3.2. Identification of Proteins Involved in Transport and Detoxification Metabolism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raad, H.; Ferveur, J.-F.; Ledger, N.; Capovilla, M.; Robichon, A. Functional Gustatory Role of Chemoreceptors in Drosophila Wings. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 1442–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, R.F. The organization of the chemosensory system in Drosophila melanogaster: A rewiew. Cell Tissue Res 1994, 275, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vosshall, L.B.; Stocker, R.F. Molecular Architecture of Smell and Taste in Drosophila. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 505–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrein, H.; Thorne, N. Gustatory Perception and Behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, R673–R684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Gomez-Diaz, C.; Vosshall, L.B. Variant Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors as Chemosensory Receptors in Drosophila. Cell 2009, 136, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voets, T.; Talavera, K.; Owsianik, G.; Nilius, B. Sensing with TRP channels. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, K.; Seno, K.; Ozaki, M. A novel Takeout-like protein expressed in the taste and olfactory organs of the blowfly, Phormia regina. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 4311–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Guo, X.; Bu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, Y.; Yang, Q. Structural and biochemical insights into an insect gut-specific chitinase with antifungal activity. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 119, 103326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishiro, N.; Kijima, H. Impulse Frequency and Action Potential Amplitude in Labellar Chemosensory Neurones of Drosophila Melanogaster. J. Insect Physiol. 1984, 30, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, N.; Marion-Poll, F.; Rospars, J.-P.; Tanimura, T. Peripheral coding of bitter taste in Drosophila. J. Neurobiol. 2003, 56, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, S.R.; Singh, R.N. Functional implications of the projections of neurons from individual labellar sensillum of Drosophila melanogaster as revealed by neuronal-marker horseradish peroxidase. Cell Tissue Res. 1992, 267, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydel, J.-M.; Coetlho, A.; Thiebaud, N.; Legendre, A.; Le Bon, A.-M.; Faure, P.; Neiers, F.; Artur, Y.; Golebiowski, J.; Briand, L. Odorant-Binding Proteins and Xenobiotic Metabolizing Enzymes: Implications in Olfactory Perireceptor Events: Odorant-Binding Proteins and Metabolizing Enzymes. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P. Odorant-Binding Proteins. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1994, 29, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P. Diversity of Odorant-binding Proteins and Chemosensory Proteins in Insects. Chem. Senses 2005, 30 (Suppl. 1), i291–i292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, R.G.; Riddiford, L.M. Pheromone binding and inactivation by moth antennae. Nature 1981, 293, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, S.; Ceron, F.; Scaloni, A.; Monti, M.; Monteforti, G.; Minnocci, A.; Petacchi, R.; Pelosi, P. Purification, structural characterization, cloning and immunocytochemical localization of chemoreception proteins from Schistocerca gregaria. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 262, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, N.F.; Moreira, M.F.; Melo, A.C.A. A look inside odorant-binding proteins in insect chemoreception. J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 95, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihani, K.; Ferveur, J.-F.; Briand, L. The 40-Year Mystery of Insect Odorant-Binding Proteins. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Zhou, J.-J.; Ban, L.P.; Calvello, M. Soluble proteins in insect chemical communication. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollmann, S.M.; Mackay, T.F.C.; Anholt, R.R.H. Pinocchio, a novel protein expressed in the antenna, contributes to olfactory behavior in Drosophila melanogaster: Pinocchio Contributes to Olfaction. J. Neurobiol. 2005, 63, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, G.D.; Yi, X.; MacCoss, M.J.; Swanson, W.J. Proteomics Reveals Novel Drosophila Seminal Fluid Proteins Transferred at Mating. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemori, N.; Yamamoto, M.-T. Proteome mapping of the Drosophila melanogaster male reproductive system. Proteomics 2009, 9, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintapalli, V.R.; Wang, J.; Dow, J.A.T. Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-L.; Stern, U.; Yang, C.-H. Molecular control limiting sensitivity of sweet taste neurons in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 20158–20168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.; Rihani, K.; Neiers, F.; Poirier, N.; Fraichard, S.; Gotthard, G.; Chertemps, T.; Maïbèche, M.; Ferveur, J.-F.; Briand, L. The Drosophila odorant-binding protein 28a is involved in the detection of the floral odour ß-ionone. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 77, 2565–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrecht, R.A. Odorant-Binding Proteins: Expression and Function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 855, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmat-Scafe, D.S. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Odorant-Binding Protein Gene Family in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.T.; Shim, J.; Oh, S.R.; Yoon, H.I.; Kim, C.H.; Moon, S.J.; Montell, C. An Odorant-Binding Protein Required for Suppression of Sweet Taste by Bitter Chemicals. Neuron 2013, 79, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Sugaya, S.; Yasukawa, J.; Aigaki, T.; Fuyama, Y. Odorant-Binding Proteins OBP57d and OBP57e Affect Taste Perception and Host-Plant Preference in Drosophila sechellia. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihani, K.; Fraichard, S.; Chauvel, I.; Poirier, N.; Delompré, T.; Neiers, F.; Tanimura, T.; Ferveur, J.-F.; Briand, L. A conserved odorant binding protein is required for essential amino acid detection in Drosophila. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.S.; Larter, N.K.; Chahda, J.S.; Rioux, D.; Gumaste, A.; Carlson, J.R. Humidity response depends on the small soluble protein Obp59a in Drosophila. eLife 2018, 7, e39249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Atkinson, R.; Jones, D.N.M.; Smith, D.P. Drosophila OBP LUSH Is Required for Activity of Pheromone-Sensitive Neurons. Neuron 2005, 45, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant Reception in Insects: Roles of Receptors, Binding Proteins, and Degrading Enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouyssié, D.; Hesse, A.-M.; Mouton-Barbosa, E.; Rompais, M.; Macron, C.; Carapito, C.; de Peredo, A.G.; Couté, Y.; Dupierris, V.; Burel, A. Proline: An efficient and user-friendly software suite for large-scale proteomics. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Montellano, M.A.O. Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes; Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1995; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Willingham, A.T.; Keil, T. A tissue specific cytochrome P450 required for the structure and function of Drosophila sensory organs. Mech. Dev. 2004, 121, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegal, M.L.; Hartl, D.L. Oviposition-Site Preference in Drosophila Following Interspecific Gene Transfer of the Alcohol dehydrogenase Locus. Locus. Behav. Genet. 1999, 29, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.H.; Tu, C.P. Biochemical characterization of Drosophila glutathione S-transferases D1 and D21. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 27876–27884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonis, E.; Fraichard, S.; Chertemps, T.; Hecker, A.; Schwartz, M.; Canon, F.; Neiers, F. Expression Patterns of Drosophila Melanogaster Glutathione Transferases. Insects 2022, 13, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, Z.; Clark, A.G. Studies on the glutathione S-transferase proteome of adult Drosophila melanogaster: Responsiveness to chemical challenge. Proteomics 2007, 7, 3618–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, W.Y.; Feil, S.C.; Ng, H.L.; Gorman, M.A.; Morton, C.J.; Pyke, J.; McConville, M.J.; Bieri, M.; Mok, Y.-F.; Robin, C. Recognition and Detoxification of the Insecticide DDT by Drosophila melanogaster Glutathione S-Transferase D1. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 399, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anholt, R.R.H.; Williams, T.I. The Soluble Proteome of the Drosophila Antenna. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, K.; Smith, D.P. A Large Family of Divergent Drosophila Odorant-Binding Proteins Expressed in Gustatory and Olfactory Sensilla. Genetics 2001, 159, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbhag, S.; Park, S.-K.; Pikielny, C.; Steinbrecht, R. Gustatory organs of Drosophila melanogaster: Fine structure and expression of the putative odorant-binding protein PBPRP2. Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 304, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, F.W.; Sirot, L.K.; LaFlamme, B.A.; Rubinstein, C.D.; Wolfner, M.F. Insect Seminal Fluid Proteins: Identification and Function. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepil, I.; Hopkins, B.R.; Dean, R.; Thézénas, M.-L.; Charles, P.D.; Konietzny, R.; Fischer, R.; Kessler, B.; Wigby, S. Quantitative Proteomics Identification of Seminal Fluid Proteins in Male Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, S46–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfner, M.F. The gifts that keep on giving: Physiological functions and evolutionary dynamics of male seminal proteins in Drosophila. Heredity 2002, 88, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaille, F.; Hiroi, M.; Twele, R.; Inoshita, T.; Umemoto, D.; Manière, G.; Marion-Poll, F.; Ozaki, M.; Francke, W.; Cobb, M. An Inhibitory Sex Pheromone Tastes Bitter for Drosophila Males. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Vosshall, L.B. An essential role for a CD36-related receptor in pheromone detection in Drosophila. Nature 2007, 450, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.E.; Steinbrecht, R.A.; Vogt, R.G. Expression of SNMP-1 in olfactory neurons and sensilla of male and female antennae of the silkmoth Antheraea polyphemus. Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 303, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Repp, A.; Smith, D.P. LUSH Odorant-Binding Protein Mediates Chemosensory Responses to Alcohols in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1998, 150, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, T.A.; Morinaga, S.; Ihara, S.; Touhara, K.; Marks, D.S.; Benton, R. Amino acid coevolution reveals three-dimensional structure and functional domains of insect odorant receptors. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younus, F.; Chertemps, T.; Pearce, S.L.; Pandey, G.; Bozzolan, F.; Coppin, C.W.; Russell, R.J.; Maïbche-Coisne, M.; Oakeshott, J.G. Identification of candidate odorant degrading gene/enzyme systems in the antennal transcriptome of Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 53, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
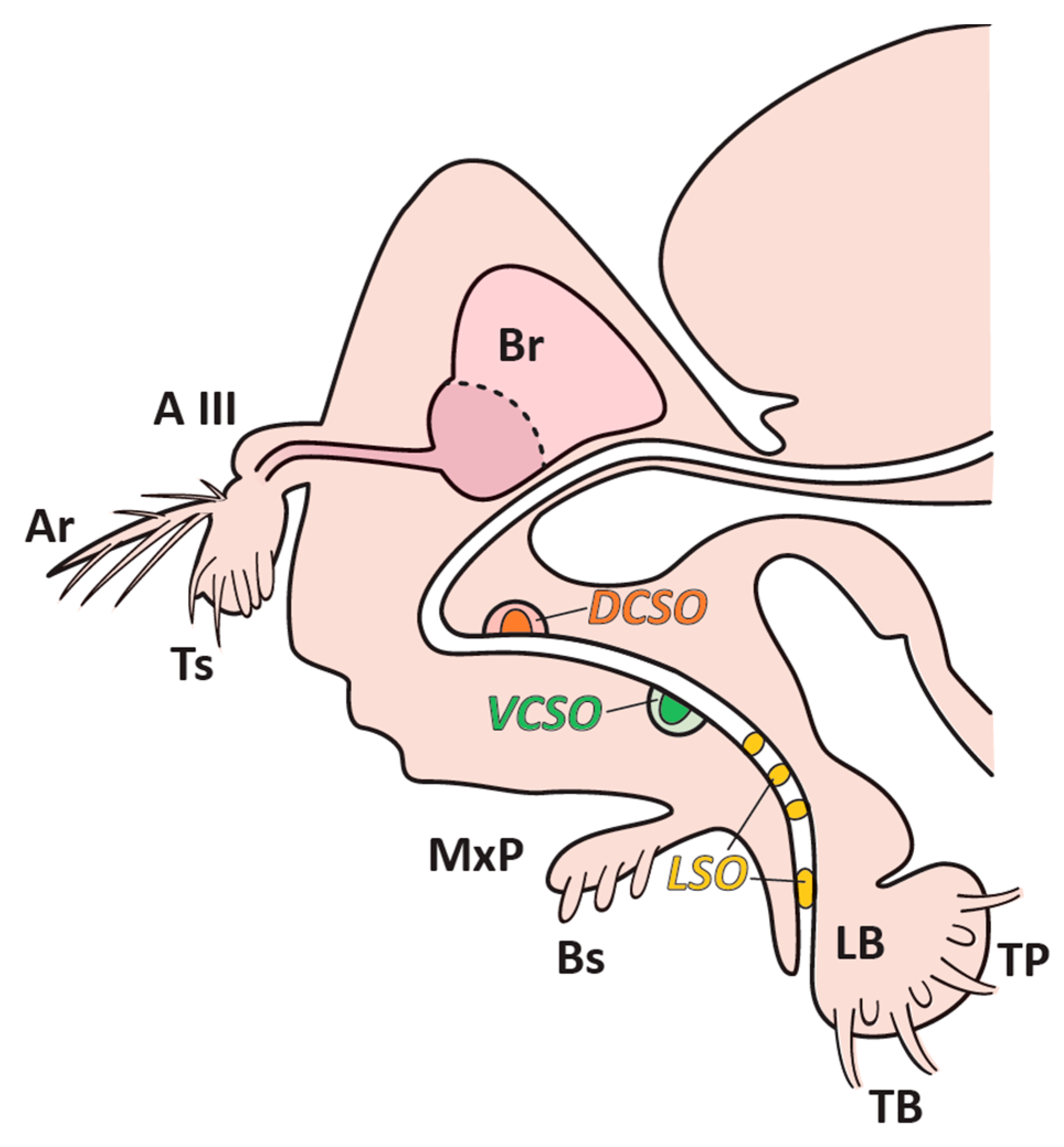
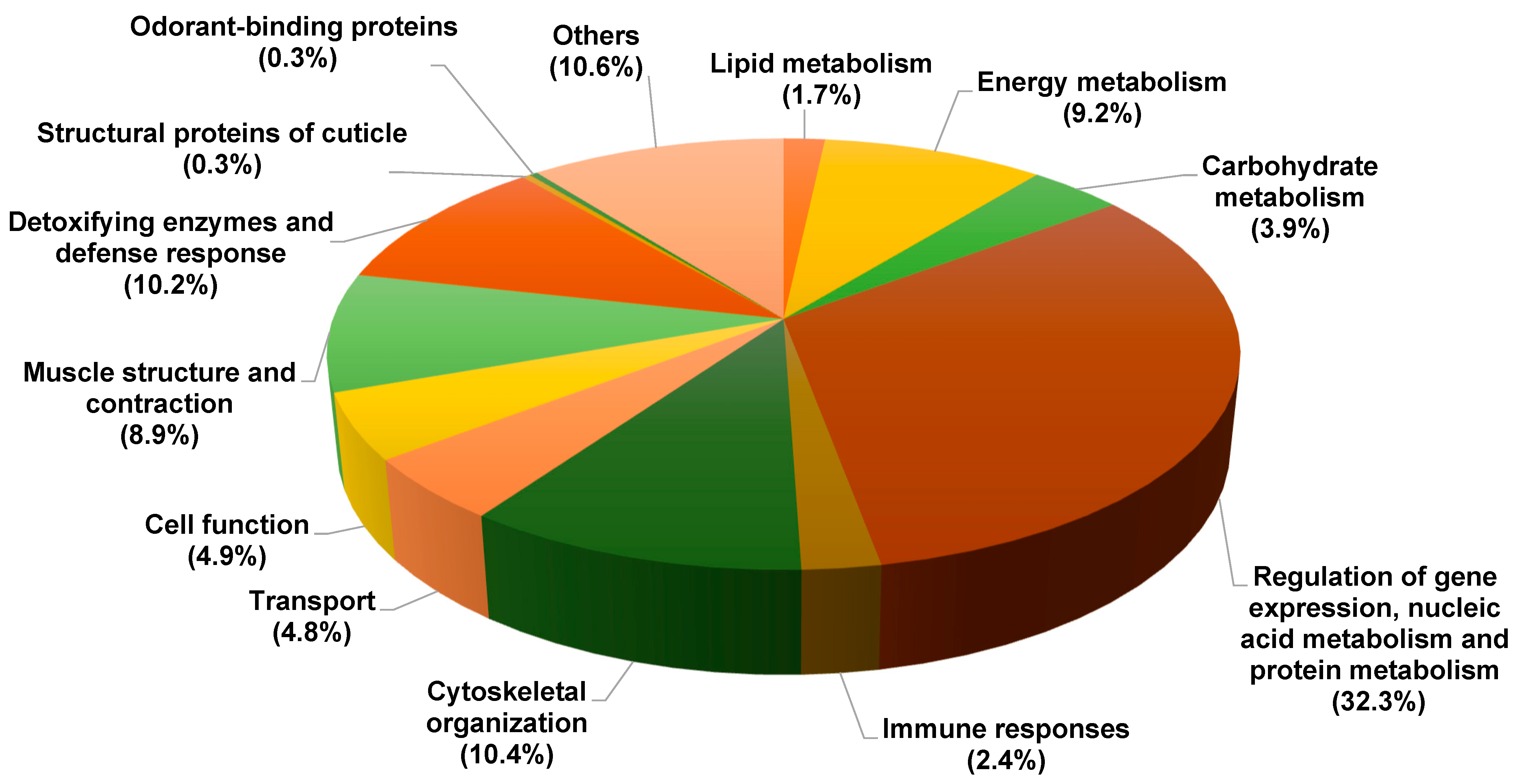
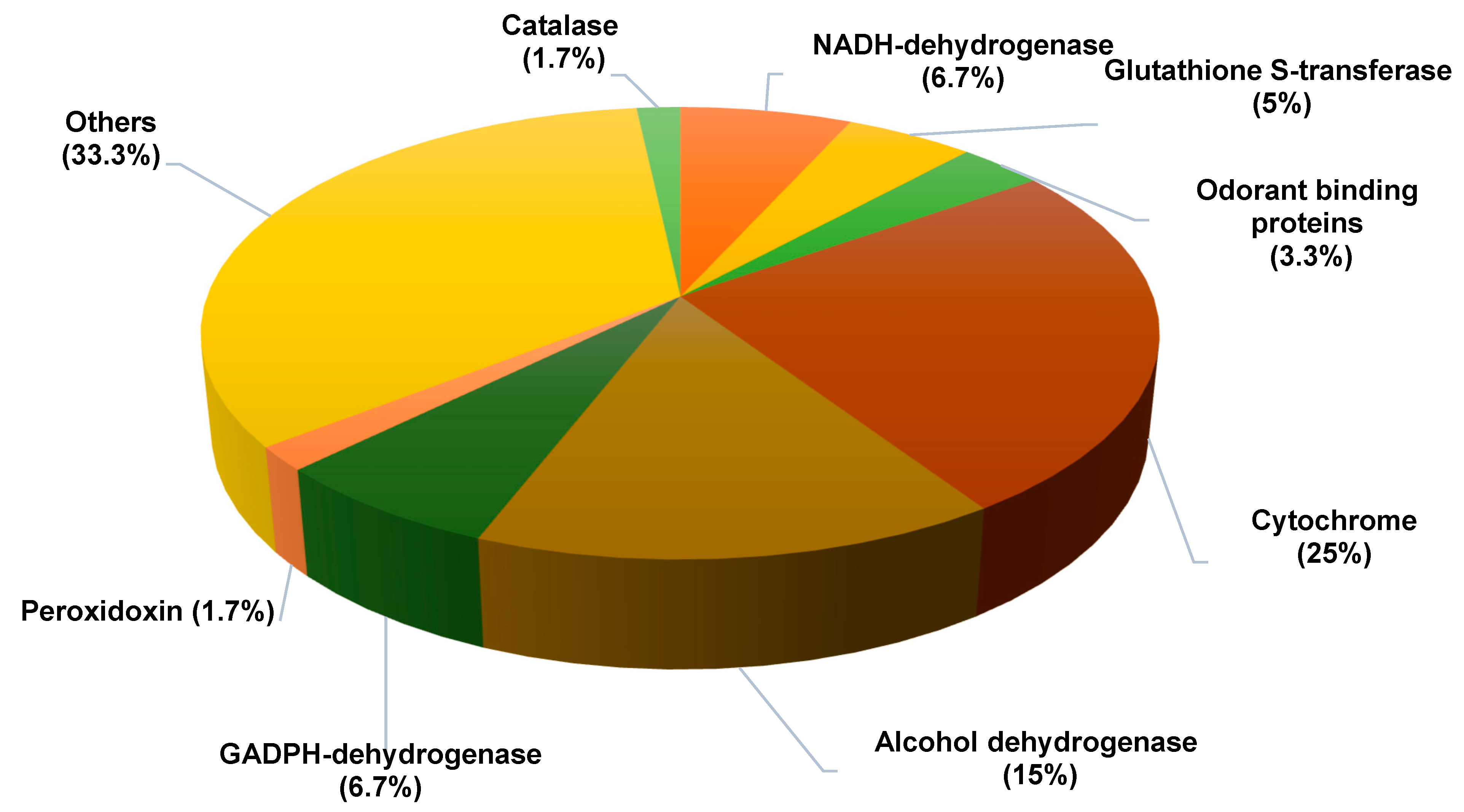
| Accession Number | Protein Identification | Female Mean | Male Mean |
|---|---|---|---|
| sp|Q8SY61|OB56D_DROME | General odorant-binding protein 56d | 5.09 × 106 | 6.41 × 105 |
| sp|P54192|OB19D_DROME | General odorant-binding protein 19d | 9.86 × 106 | 7.10 × 106 |
| sp|Q95RA9|GILT1_DROME | GILT-like protein 1 | 1.38 × 107 | 3.45 × 106 |
| sp|Q9V521|PPO2_DROME | Phenoloxidase 2 | 6.06 × 107 | 2.79 × 107 |
| sp|Q9V3Z2|SER7_DROME | Serine protease 7 | 6.70 × 105 | 4.15 × 105 |
| sp|Q9V3D2|HEM6_DROME | Oxygen-coproporphyrinogen-III oxidase | 3.29 × 106 | 1.26 × 106 |
| sp|Q9W265|HOT_DROME | Hydroxyacid-oxoacid transhydrogenase | 1.81 × 106 | |
| sp|O18404|HCD2_DROME | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 4.94 × 107 | 1.90 × 107 |
| sp|Q04499|PROD_DROME | Proline dehydrogenase 1 | 2.68 × 106 | 1.71 × 106 |
| sp|Q6AWN0|MTND_DROME | Acireductone dioxygenase | 7.14 × 105 | 1.71 × 105 |
| sp|P36951|HYI_DROME | Putative hydroxypyruvate isomerase | 3.57 × 106 | 1.67 × 106 |
| sp|O77458|TPIS_DROYA | Triosephosphate isomerase | 5.76 × 107 | 2.27 × 107 |
| sp|B3M098|MTNA_DROAN | Methylthioribose-1-phosphate isomerase | 1.05 × 106 | 4.21 × 105 |
| sp|Q7KML2|ACOX1_DROME | Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1 | 4.97 × 107 | 2.41 × 107 |
| sp|Q9V6U9|MECR_DROME | 2-enoyl thioester reductase | 2.36 × 107 | 4.40 × 106 |
| sp|Q01597|G3P_DROHY | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 2.23 × 108 | 8.95 × 107 |
| sp|P07487|G3P2_DROME | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 | 3.49 × 108 | 1.50 × 108 |
| sp|P07486|G3P1_DROME | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1 | 2.91 × 108 | 1.30 × 108 |
| sp|O44104|G3P2_DROPS | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 | 3.70 × 108 | 1.63 × 108 |
| sp|P13706|GPDA_DROME | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1.32 × 108 | 6.49 × 107 |
| sp|O02373|UGDH_DROME | UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase | 7.76 × 105 | 3.19 × 105 |
| sp|P54399|PDI_DROME | Protein disulfide-isomerase | 9.64 × 107 | 4.18 × 107 |
| sp|Q9V429|THIO2_DROME | Thioredoxin-2 | 3.41 × 106 | 2.07 × 106 |
| sp|Q9VSA3|ACADM_DROME | Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 9.71 × 107 | 4.54 × 107 |
| sp|Q9VWH4|IDH3A_DROME | Isocitrate dehydrogenase | 6.06 × 107 | 5.34 × 107 |
| sp|P32748|PYRD_DROME | Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase | 2.65 × 105 | 1.70 × 105 |
| sp|Q9VXJ0|DHB4_DROME | Peroxisomal multifunctional enzyme type 2 | 1.86 × 107 | 1.14 × 107 |
| sp|Q9V3P0|PRDX1_DROME | Peroxiredoxin 1 | 4.19 × 107 | 1.84 × 107 |
| sp|P17336|CATA_DROME | Catalase | 1.05 × 108 | 4.20 × 107 |
| sp|Q9VG97|GSTD3_DROME | Glutathione S-transferase D3 | 6.02 × 105 | 2.29 × 105 |
| sp|P20432|GSTD1_DROME | Glutathione S-transferase D1 | 8.75 × 107 | 4.04 × 107 |
| sp|P41043|GSTS1_DROME | Glutathione S-transferase S1 | 2.18 × 106 | 9.93 × 105 |
| sp|Q9VZU4|NDUS3_DROME | NADH dehydrogenase | 7.11 × 106 | 4.10 × 106 |
| sp|Q27597|NCPR_DROME | NADPH--cytochrome P450 reductase | 1.31 × 106 | 1.27 × 106 |
| sp|P07705|NU3M_DROYA | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 3 | 6.85 × 105 | 4.46 × 105 |
| sp|P91929|NDUAA_DROME | NADH dehydrogenase | 5.74 × 106 | 2.43 × 106 |
| sp|Q05114|ADH_DROWI | Alcohol dehydrogenase | 4.37 × 106 | 1.82 × 106 |
| sp|B4M8Y0|ADH_DROVI | Alcohol dehydrogenase | 7.10 × 106 | 2.22 × 106 |
| sp|P46415|ADHX_DROME | Alcohol dehydrogenase class-3 | 5.37 × 106 | 2.56 × 106 |
| sp|P48584|ADH_DROBO | Alcohol dehydrogenase | 2.85 × 107 | 1.90 × 107 |
| sp|P09369|ADH2_DROMO | Alcohol dehydrogenase 2 | 5.41 × 107 | 3.36 × 107 |
| sp|P07161|ADH1_DROMU | Alcohol dehydrogenase 1 | 5.41 × 107 | 3.36 × 107 |
| sp|P00334|ADH_DROME | Alcohol dehydrogenase | 1.92 × 108 | 1.30 × 108 |
| sp|P07159|ADH_DROOR | Alcohol dehydrogenase | 1.85 × 108 | 1.25 × 108 |
| sp|P10807|ADH_DROLE | Alcohol dehydrogenase | 7.30 × 107 | 4.76 × 107 |
| sp|Q9W5N0|COA7_DROME | Cytochrome c oxidase | 5.51 × 105 | 2.14 × 105 |
| sp|Q9V9L1|CP6W1_DROME | Cytochrome P450 6w1 | 7.56 × 105 | 7.89 × 105 |
| sp|Q9V558|CP4P1_DROME | Cytochrome P450 4p1 | 3.71 × 105 | 2.80 × 105 |
| sp|Q9V4N3|CYB5_DROME | Cytochrome b5 | 1.96 × 106 | 1.86 × 106 |
| sp|P19967|CYB5R_DROME | Cytochrome b5 | 1.71 × 105 | 3.67 × 105 |
| sp|Q9VFP1|CP6D5_DROME | Cytochrome P450 6d5 | 8.61 × 106 | 1.08 × 107 |
| sp|Q9VE01|C12A5_DROME | Cytochrome P450 12a5 | 1.80 × 106 | 1.85 × 106 |
| sp|P33270|CP6A2_DROME | Cytochrome P450 6a2 | 3.40 × 106 | 3.50 × 106 |
| sp|Q9VCW1|CP6D4_DROME | Cytochrome P450 6d4 | 1.05 × 106 | 5.61 × 105 |
| sp|Q27606|CP4E2_DROME | Cytochrome P450 4e2 | 1.90 × 105 | 2.16 × 105 |
| sp|Q9VFJ0|CA131_DROME | Cytochrome P450 313a1 | 5.47 × 106 | 3.35 × 107 |
| sp|Q9VLZ7|C4D21_DROME | Cytochrome P450 4d21 | 1.36 × 105 | 3.54 × 106 |
| sp|Q9XY35|QCR9_DROME | Cytochrome b-c1 | 1.25 × 107 | 9.11 × 106 |
| sp|Q9VHS2|COX7A_DROME | Cytochrome c oxidase | 6.20 × 106 | 3.43 × 106 |
| sp|P84029|CYC2_DROME | Cytochrome c-2 | 7.44 × 107 | 3.46 × 107 |
| Accession Number | Protein Identification | Protein Mass (kDa) |
|---|---|---|
| sp|Q9V3P0|PRDX1_DROME | Peroxiredoxin 1 | 21.738 |
| sp|P17336|CATA_DROME | Catalase | 57.15 |
| sp|Q8SY61|OB56D_DROME | Odorant-binding protein 56d | 14.119 |
| sp|P54192|OB19D_DROME | Odorant-binding protein 19d | 16.782 |
| sp|Q9VFP1|CP6D5_DROME | Cytochrome P450 6d5 | 57.384 |
| sp|Q9VE01|C12A5_DROME | Cytochrome P450 12a5 | 61.355 |
| sp|Q9VCW1|CP6D4_DROME | Cytochrome P450 6d4 | 59.182 |
| sp|Q9VFJ0|CA131_DROME | Cytochrome P450 313a1 | 56.534 |
| sp|Q9V4N3|CYB5_DROME | Cytochrome b5 | 15.206 |
| sp|Q9W5N0|COA7_DROME | Cytochrome c oxidase | 29.64 |
| sp|P84029|CYC2_DROME | Cytochrome c-2 (Cytochrome c-proximal) | 11.735 |
| sp|Q9VHS2|COX7A_DROME | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A | 9.902 |
| sp|Q9V558|CP4P1_DROME | Cytochrome P450 4p1 | 59.433 |
| sp|P20432|GSTD1_DROME | Glutathione S-transferase D1 | 23.866 |
| sp|B4M8Y0|ADH_DROVI | Alcohol dehydrogenase | 27.608 |
| sp|P09369|ADH2_DROMO | Alcohol dehydrogenase 2 | 27.605 |
| sp|P07161|ADH1_DROMU | Alcohol dehydrogenase 1 | 27.495 |
| sp|P00334|ADH_DROME | Alcohol dehydrogenase | 27.761 |
| sp|P46415|ADHX_DROME | Alcohol dehydrogenase 3 | 40.389 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aruçi, E.; Saliou, J.-M.; Ferveur, J.-F.; Briand, L. Proteomic Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Proboscis. Biology 2022, 11, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111687
Aruçi E, Saliou J-M, Ferveur J-F, Briand L. Proteomic Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Proboscis. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111687
Chicago/Turabian StyleAruçi, Enisa, Jean-Michel Saliou, Jean-François Ferveur, and Loïc Briand. 2022. "Proteomic Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Proboscis" Biology 11, no. 11: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111687
APA StyleAruçi, E., Saliou, J.-M., Ferveur, J.-F., & Briand, L. (2022). Proteomic Characterization of Drosophila melanogaster Proboscis. Biology, 11(11), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111687







