Striated Muscle Evaluation Based on Velocity and Amortization Ratio of Mechanical Impulse Propagation in Simulated Microgravity Environment
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Dynamic stiffness characterizes resistance to a contraction or to an external force that deforms its initial shape;
- Oscillation frequency is an indicator of intrinsic tension of a muscle in passive state, without voluntary contraction;
- Logarithmic decrement is a parameter that indicates muscle-elasticity capabilities and mechanical energy dissipation after deformation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
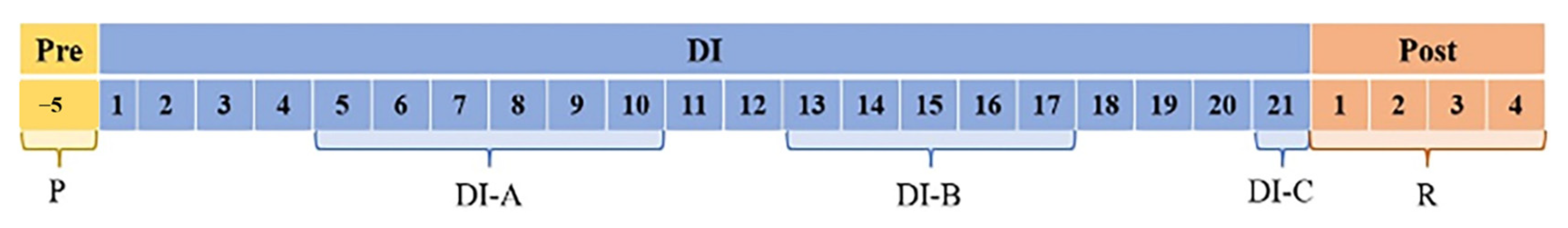
2.2. Study Procedure and Device Description
3. Results
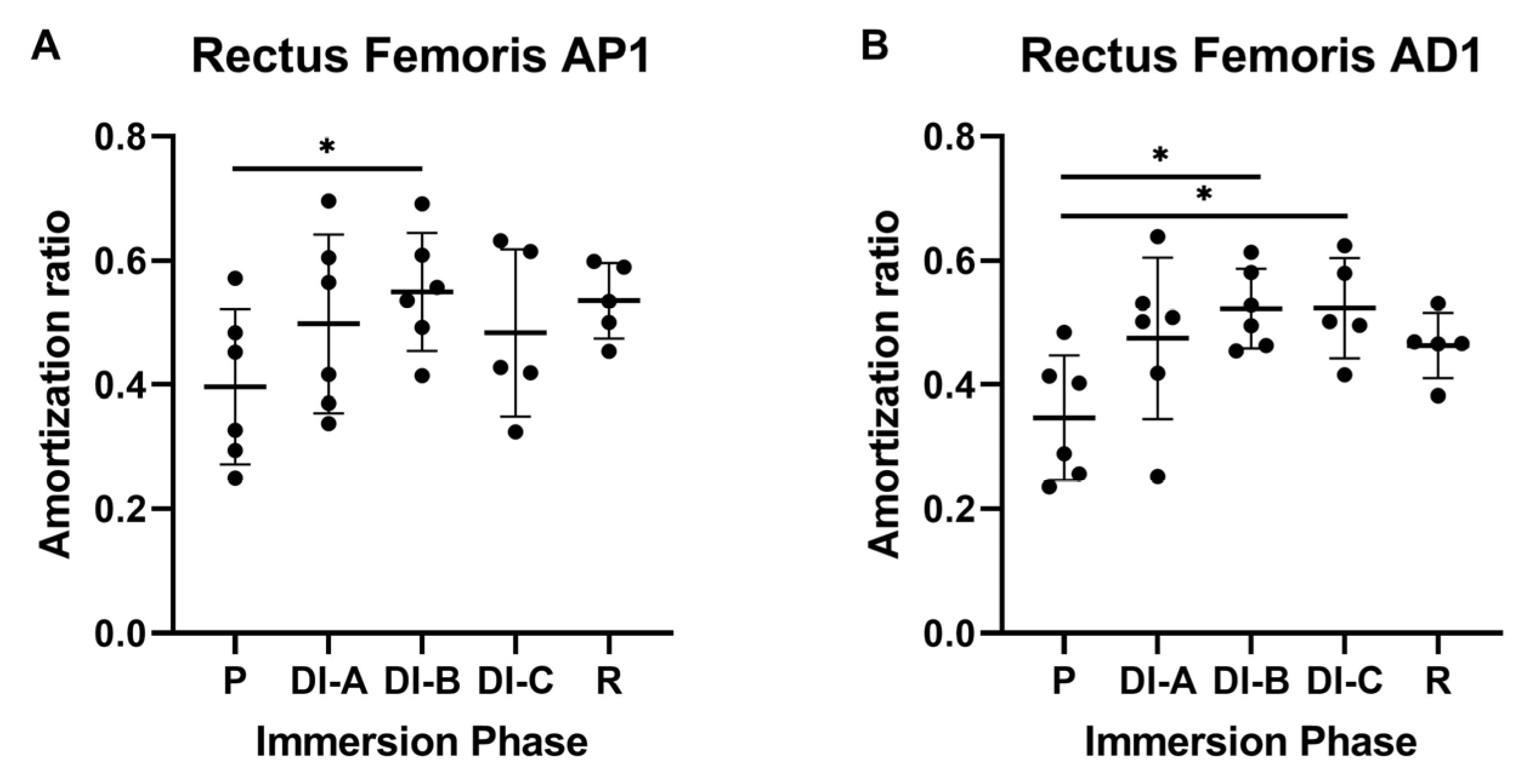
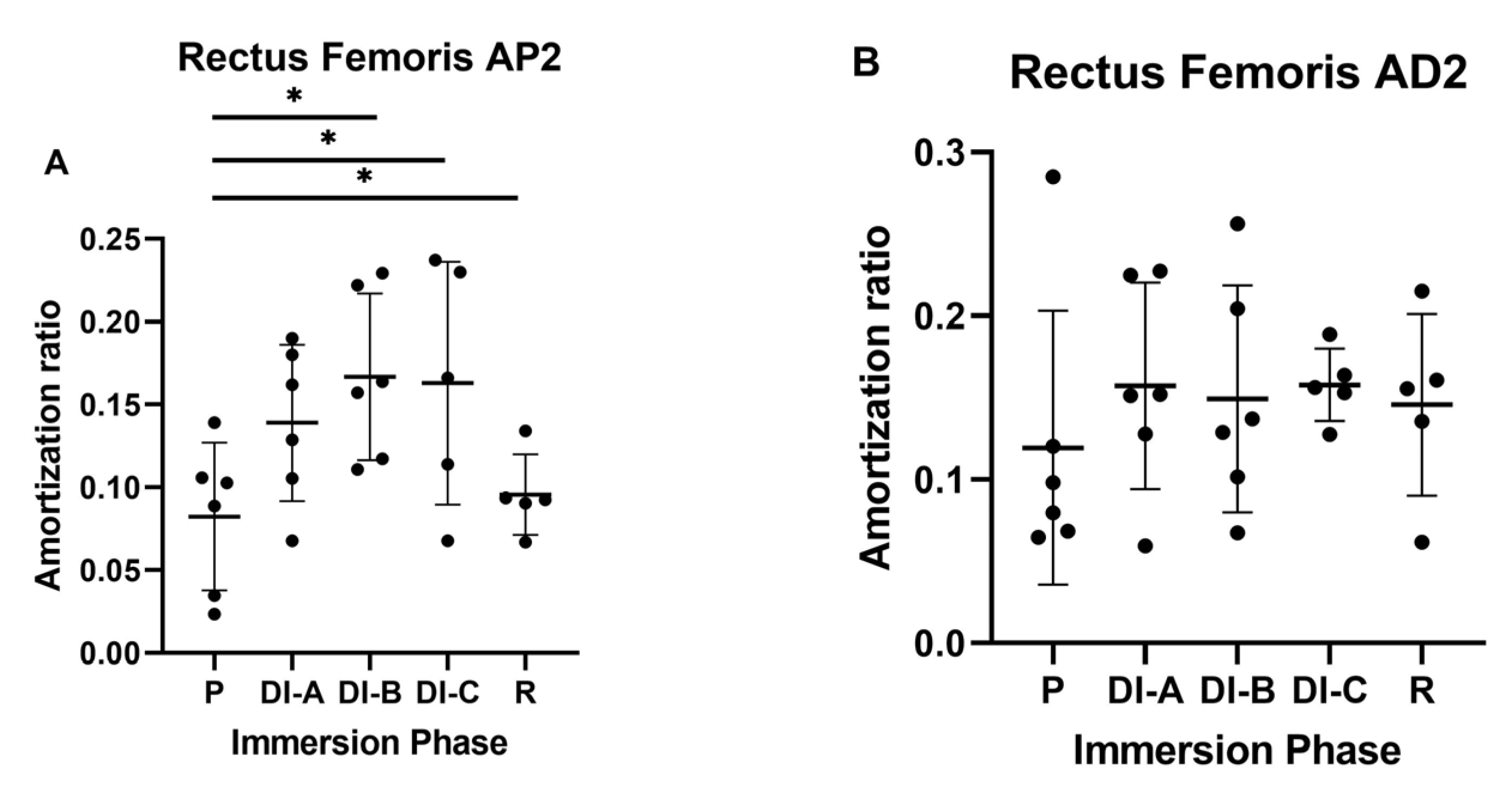
3.1. Amortization Ratio for Rectus Femoris Muscle (AR_RF)
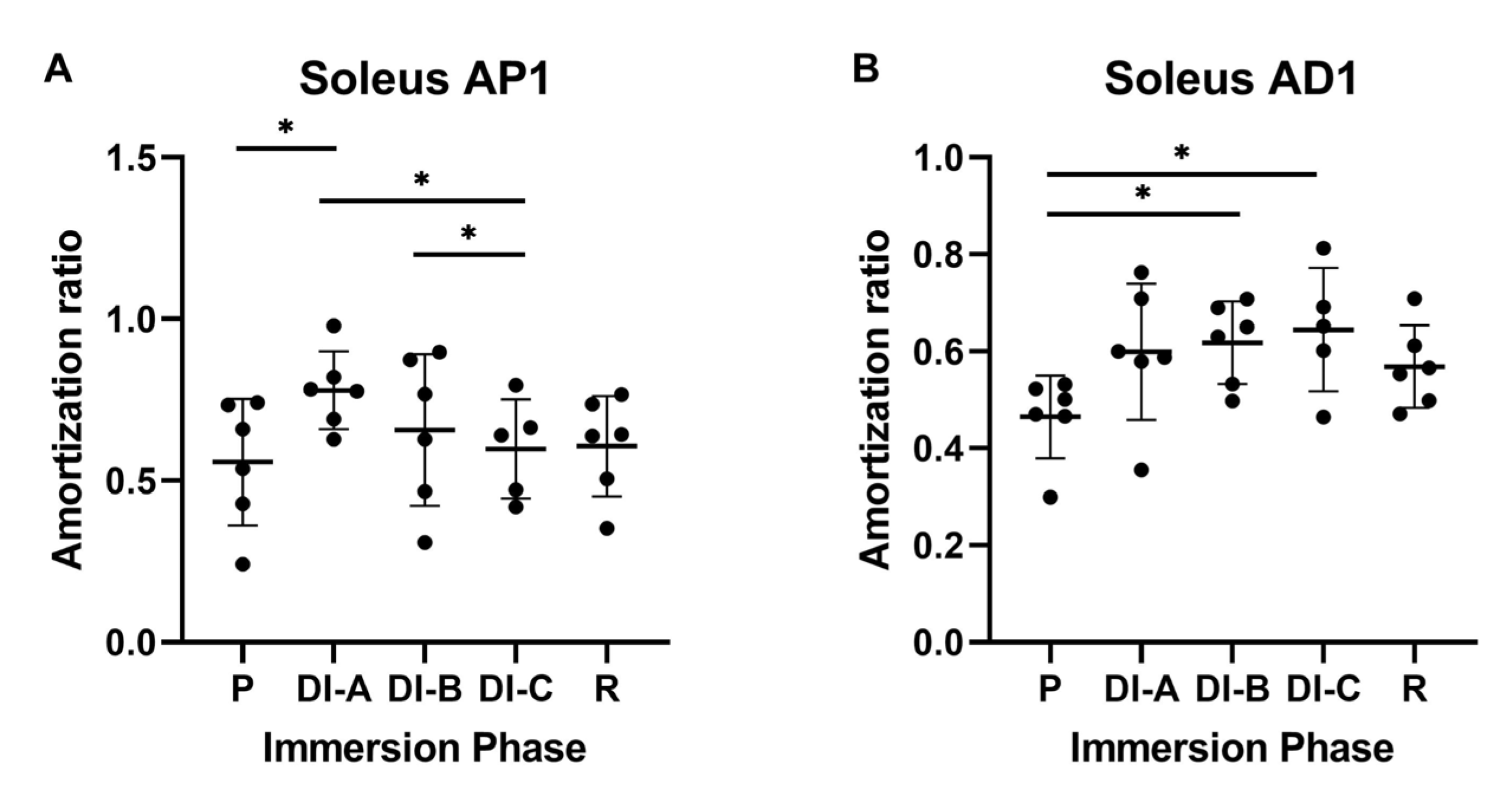
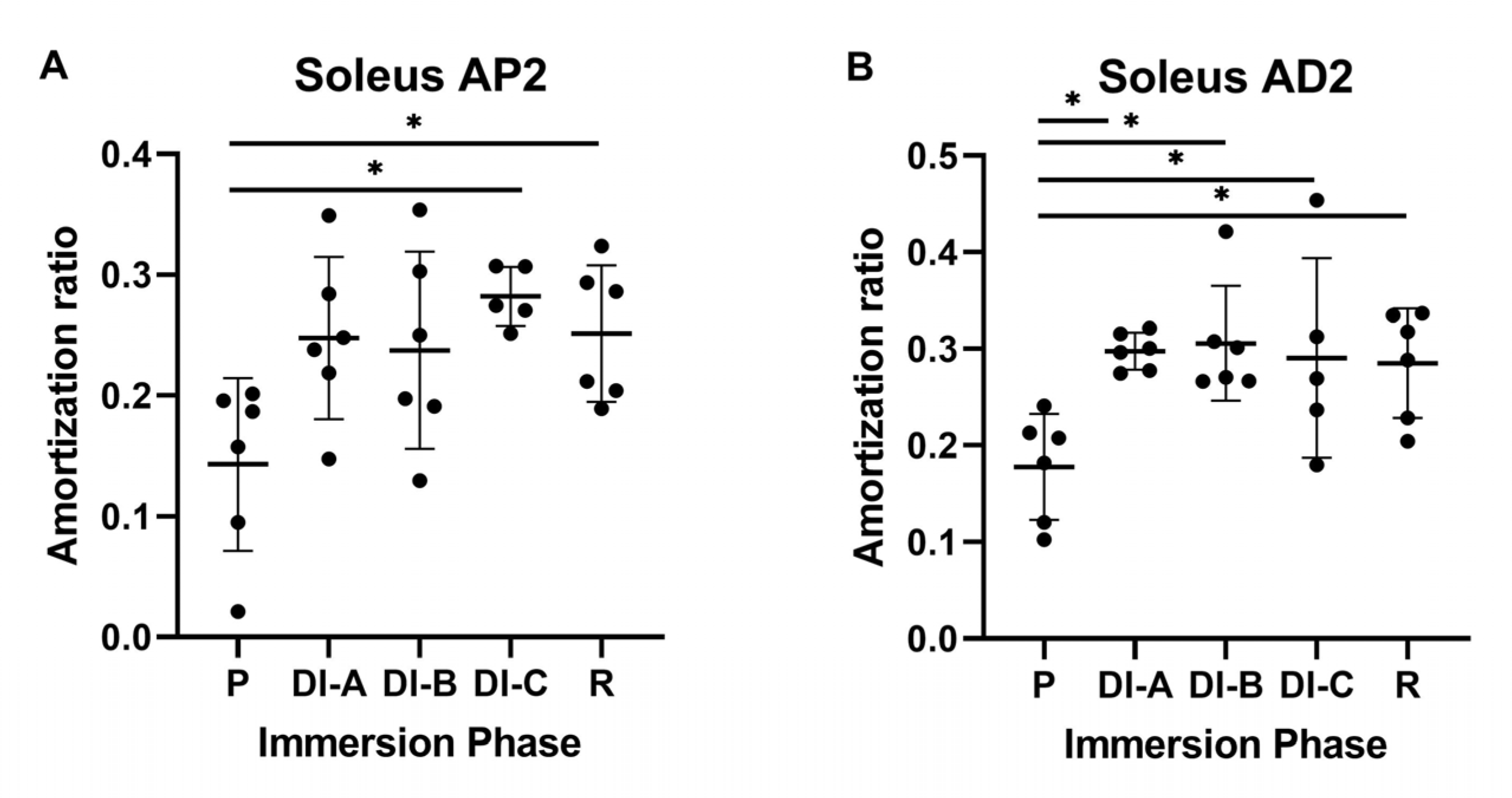
3.2. Amortization Ratio for Soleus Muscle (AR_Sol)
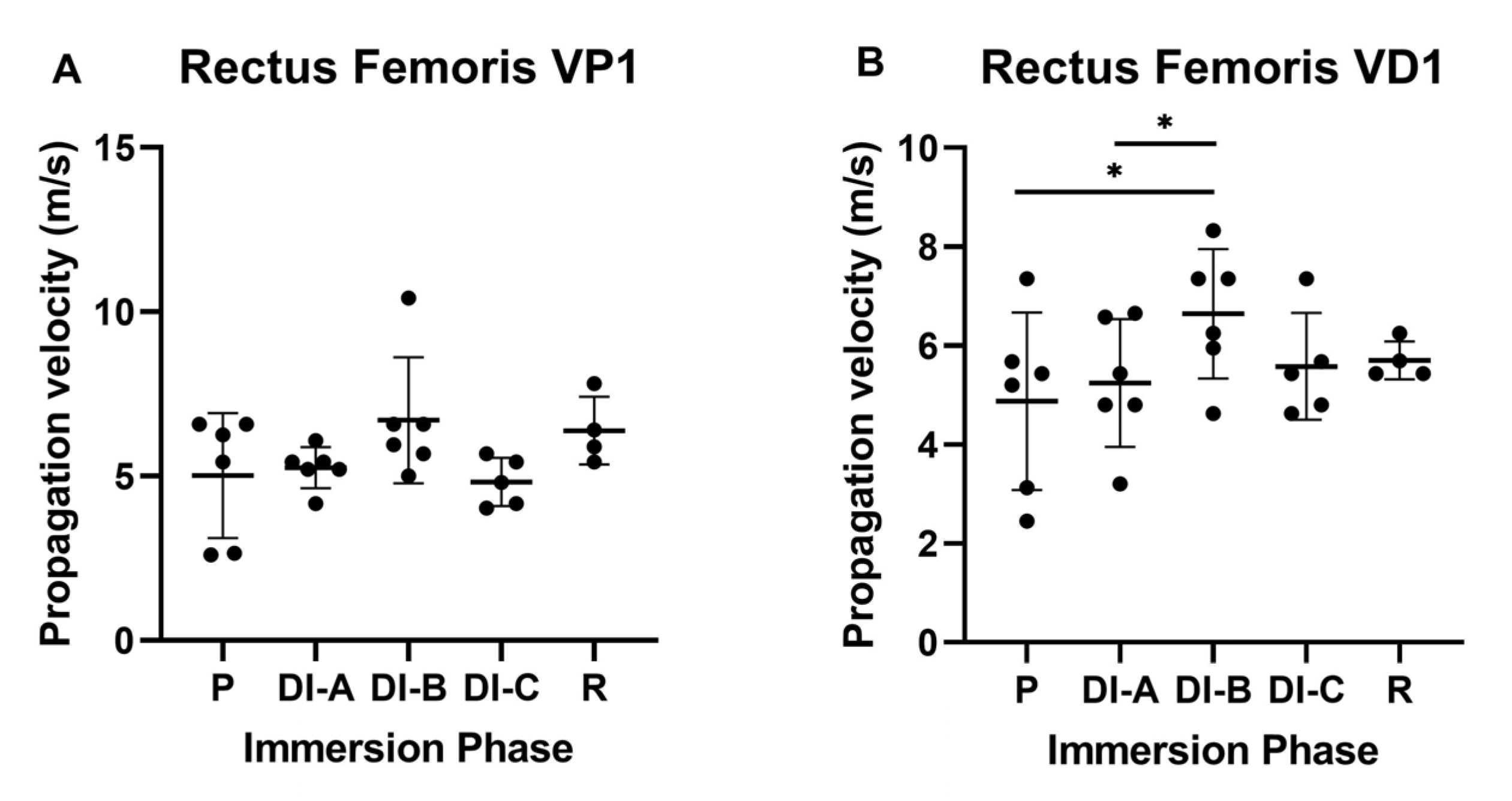
3.3. Propagation Velocity (V)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harris, B.A.; Stewart, D.F. Summary and Recommendations for Initial Exercise Prescription. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Exercise Long-Duration Space Flight Conference Proceedings, Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Texas 1986, NASA Conference Publication 3051. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19910001261 (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Letier, P.; Motard, E.; Luchsinger, R.; Kovacs, G.; Stauffer, Y.; Bertschi, M.; Evetts, S.; Waldie, J.; Ilzkovitz, M.; Gancet, J.; et al. Dynasuit, Intelligent Space Countermeasure Suit Concept Based on New Artificial Muscles Technologies and Biofeedback. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on artificial intelligence, robotics and automation in space, Turin, Italy, 4–6 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Trappe, S.; Costill, D.; Gallagher, P.; Creer, A.; Peters, J.R.; Evans, H.; Riley, D.A.; Fitts, R.H. Exercise in space: Human skeletal muscle after 6 months aboard the International Space Station. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richter, C.; Braunstein, B.; Winnard, A.; Nasser, M.; Weber, T. Human biomechanical and cardiopulmonary responses to partial gravity—A systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barratt, M.R.; Baker, E.S.; Pool, S.L. Principles of Clinical Medicine for Space Flight; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertz, D.; Pérot, C.; Kaspranski, R.; Goubel, F. Effects of long-term spaceflight on mechanical properties of muscles in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 90, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitts, R.H.; Riley, D.R.; Widrick, J.J. Physiology of a microgravity environment invited review: Microgravity and skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demangel, R.; Treffel, L.; Py, G.; Brioche, T.; Pagano, A.F.; Bareille, M.P.; Beck, A.; Pessemesse, L.; Candau, R.; Gharib, C.; et al. Early structural and functional signature of 3-day human skeletal muscle disuse using the dry immersion model. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holt, J.A.; Macias, B.R.; Schneider, S.M.; Watenpaugh, D.E.; Lee, S.M.C.; Chang, D.G. Hargens, A.R. WISE 2005: Aerobic and resistive countermeasures prevent paraspinal muscle deconditioning during 60-day bed rest in women. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 120, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, D.A.; Scott, J.P.R. Spinal health during unloading and reloading associated with spaceflight. Front. Physiol. 2018, 8, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amirova, L.E.; Saveko, A.A.; Rukavishnikov, I.V.; Nistorescu, A.; Dinculescu, A.; Valeanu, V.; Kozlovskaya, I.; Vizitiu, C.; Tomilovskaya, E.; Orlov, O.I. Effects Of 21-Day Support Unloading On Characteristics Of Transverse Stiffness Of Human Muscles. Aerosp. Environ. Med. 2020, 54, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomilovskaya, E.S.; Amirova, L.E.; Custaud, M.-A.; Kozlovskaya, I.B. Neuromuscular and cardiovascular alterations in orthostatic hypotension and postural instability induced by microgravity. In Proceedings of the 42nd Assembly Cospar, Pasadena, CA, USA, 14–22 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tomilovskaya, E.; Shigueva, T.; Sayenko, D.; Rukavishnikov, I.; Kozlovskaya, I. Dry immersion as a ground-based model of microgravity physiological effects. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEDES Dry Immersion Bathtubs. Available online: http://www.medes.fr/en/the-space-clinic/the-equipments/dry-immersion-bath.html (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- The European Space Agency Dry Immersion Infographic. Available online: https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2020/03/Dry_immersion_infographic (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- Navasiolava, N.M.; Custaud, M.A.; Tomilovskaya, E.S.; Larina, I.M.; Mano, T.; Gauquelin-Koch, G. Gharib, C.; Kozlovskaya, I.B. Long-term dry immersion: Review and prospects. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 111, 1235–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pechenkova, E.; Nosikova, I.N.; Rumshiskaya, A.D.; Litvinova, L.D.; Rukavishnikov, I.; Mershina, E.A.; Sinitsyn, V.; Van Ombergen, A.; Jeurissen, B.; Jillings, S.; et al. Alterations of functional brain connectivity after long-duration spaceflight as revealed by fMRI. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shenkman, B.S.; Kozlovskaya, I.B. Cellular responses of human postural muscle to dry immersion. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosikova, I.; Riabova, A.; Amirova, L.; Kitov, V.; Tomilovskaya, E. NAIAD-2020: Characteristics of Motor Evoked Potentials After 3-Day Exposure to Dry Immersion in Women. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomilovskaya, E.S.; Rukavishnikov, I.V.; Amirova, L.E.; Shigueva, T.A.; Saveko, A.A.; Kitov, V.V.; Vassilieva, G.Y.; Ponomarev, S.A..; Smirnova, T.A.; Kozlovskaya, I.B.; et al. 21-Day Dry Immersion: Schedule of Investigations and Major Results. Hum. Physiol. 2021, 47, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistorescu, A.; Dinculescu, A.; Vizitiu, C.; Marin, M.; Mandu, M. Soleus muscle assessment during 21 day dry immersion study using mustone device. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th E-Health and Bioengineering Conference, EHB, Lasi, Romania, 21–23 November 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, L.; Navasiolava, N.; Rukavishvikov, I.; Gauquelin-Koch, G.; Gharib, C.; Kozlovskaya, I.; Custaud, M.-A.; Tomilovskaya, E. Cardiovascular System Under Simulated Weightlessness: Head-Down Bed Rest vs. Dry Immersion. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technology–Myoton. Available online: https://www.myoton.com/technology/ (accessed on 18 March 2022).
- Wang, A.B.; Perreault, E.J.; Royston, T.J.; Lee, S.S.M. Changes in shear wave propagation within skeletal muscle during active and passive force generation. J. Biomech. 2019, 94, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomilovskaya, E.S.; Rukavishnikov, I.V.; Amirova, L.E.; Shigueva, T.A.; Saveko, A.A.; Kitov, V.V.; Vasilieva, G.; Ponomarev, S.; Smirnova, T.A.; Кozlovskaya, I.B.; et al. 21-day dry immersion: Design and primary results. Aviakosmicheskaya I Ekol. Meditsina 2020, 54, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleus, the Forgotten Muscle for Runners. Available online: https://www.shutterstock.com/ro/image-vector/medical-illustration-symptoms-calf-muscle-tear-1973677565/ (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Rectus Femoris Muscle. Available online: https://www.shutterstock.com/image-illustration/rectus-femoris-muscle-anatomy-3d-illustration-2101537804 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Rittweger, J.; Albracht, K.; Flück, M.; Ruoss, S.; Brocca, L.; Longa, E.; Moriggi, M.; Seynnes, O.; Di Giulio, I.; Tenori, L.; et al. Sarcolab pilot study into skeletal muscle’s adaptation to long-term spaceflight. Npj Microgravity 2018, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzawa, R.; Koike, H.; Manabe, I.; Oishi, Y. VDR regulates simulated microgravity-induced atrophy in C2C12 myotubes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.P.; Milne, K.J.; Hawke, T.J. Adiponectin—Consideration for its Role in Skeletal Muscle Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilchinskaya, N.A.; Krivoi, I.I.; Shenkman, B.S. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase as a Key Trigger for the Disuse-Induced Skeletal Muscle Remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilston, L.E.; Bolsterlee, B.; Nordez, A.; Sinha, S. Contemporary image-based methods for measuring passive mechanical properties of skeletal muscles in vivo. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, N.; Hirata, K.; Kanehisa, H.; Yoshitake, Y. Validity of Measurement of Shear Modulus by Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography in Human Pennate Muscle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikai, M.; Fukunaga, T. Calculation of muscle strength per unit cross-sectional area of human muscle by means of ultrasonic measurement. Int. Z. Fur Angew. Physiol. Einschl. Arb. 1968, 26, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
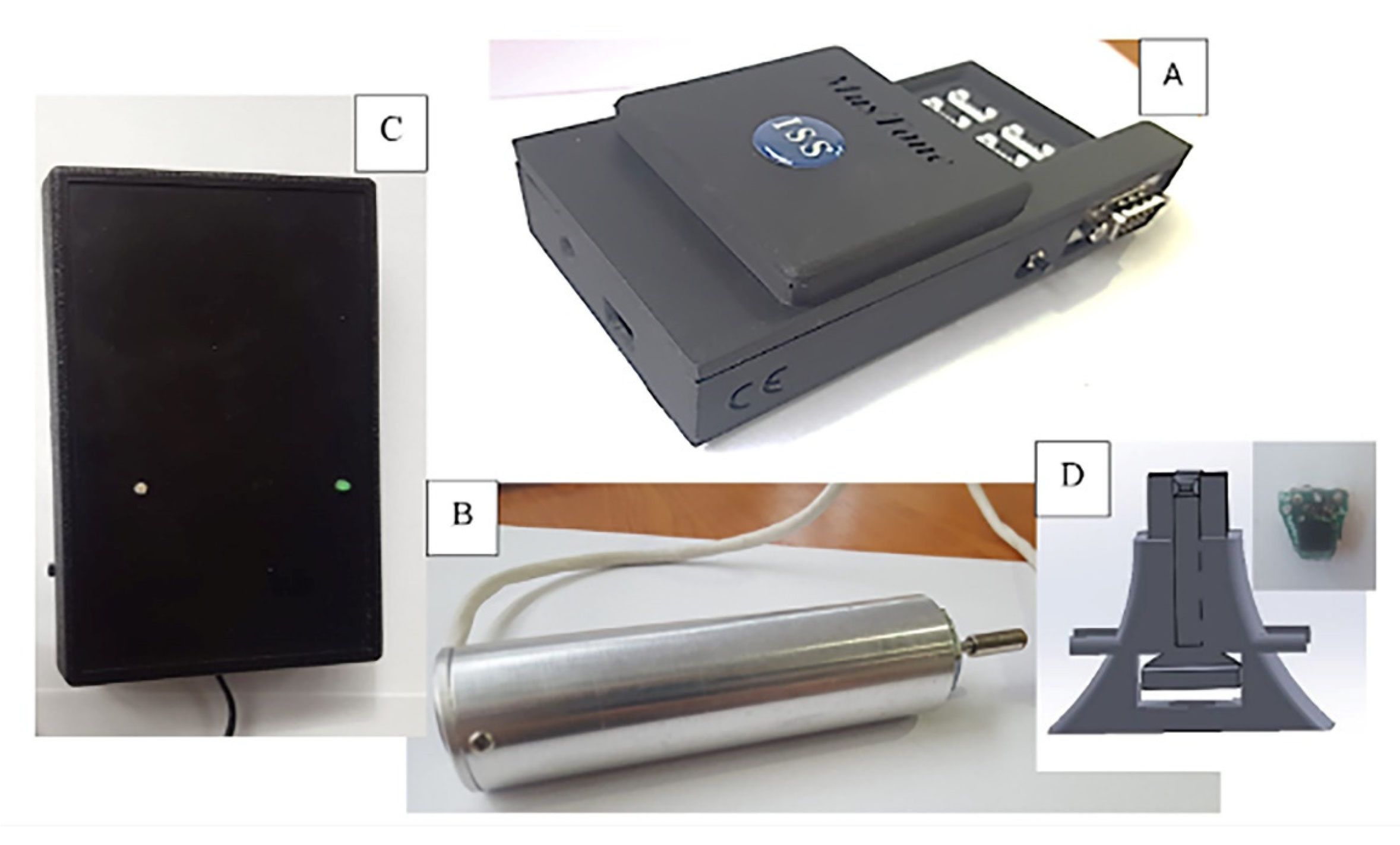
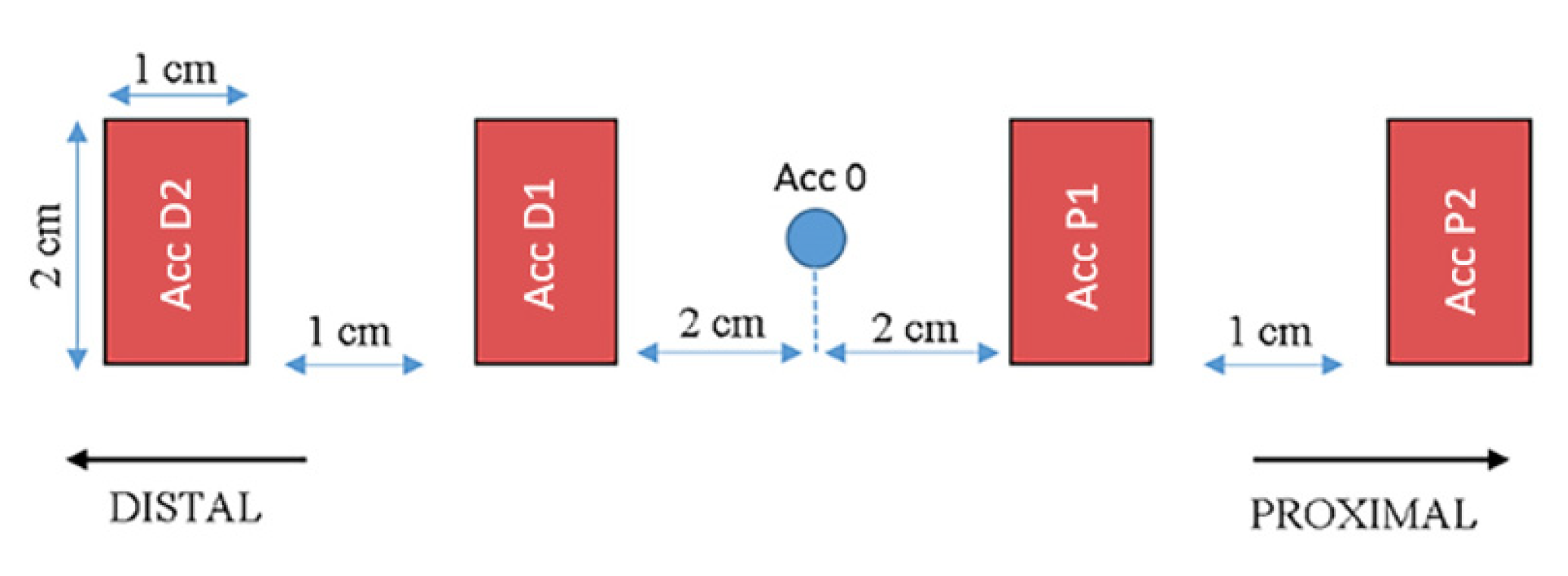
| Age | Height | Body Mass | Index of Body Mass | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 23 | 174 | 81.7 | 27.0 |
| S2 | 30 | 183 | 86.9 | 25.9 |
| S3 | 32 | 180.1 | 80.8 | 24.9 |
| S4 | 26 | 176.5 | 81 | 26.0 |
| S5 | 32 | 172 | 64.2 | 21.7 |
| S6 | 31 | 172.7 | 67.6 | 22.7 |
| Mean value | 29 | 176,383 | 77,033 | 24,700 |
| SD | 3.688 | 4.383 | 8.975 | 2.072 |
| SEM | 1.506 | 1.789 | 3.664 | 0.846 |
| Parameter | Set Value | Measurement Unit | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition step | 0.2 | ms | Values are recorded each 0.2 ms |
| Stimulus action time | 10 | ms | Time necessary for the percussion to be applied |
| Acquisition start | −5 | ms | If the value is negative, the acquisition starts before the impulse is applied |
| Acquisition time | 650 | ms | The duration of the recording |
| Scale | ±4 g | m/s2 | Amplitude scale |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nistorescu, A.; Busnatu, S.S.; Dinculescu, A.; Olteanu, G.; Marin, M.; Jercalau, C.E.; Vizitiu, C.; Papacocea, I.R. Striated Muscle Evaluation Based on Velocity and Amortization Ratio of Mechanical Impulse Propagation in Simulated Microgravity Environment. Biology 2022, 11, 1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111677
Nistorescu A, Busnatu SS, Dinculescu A, Olteanu G, Marin M, Jercalau CE, Vizitiu C, Papacocea IR. Striated Muscle Evaluation Based on Velocity and Amortization Ratio of Mechanical Impulse Propagation in Simulated Microgravity Environment. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111677
Chicago/Turabian StyleNistorescu, Alexandru, Stefan Sebastian Busnatu, Adrian Dinculescu, Gabriel Olteanu, Mihaela Marin, Cosmina Elena Jercalau, Cristian Vizitiu, and Ioana Raluca Papacocea. 2022. "Striated Muscle Evaluation Based on Velocity and Amortization Ratio of Mechanical Impulse Propagation in Simulated Microgravity Environment" Biology 11, no. 11: 1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111677
APA StyleNistorescu, A., Busnatu, S. S., Dinculescu, A., Olteanu, G., Marin, M., Jercalau, C. E., Vizitiu, C., & Papacocea, I. R. (2022). Striated Muscle Evaluation Based on Velocity and Amortization Ratio of Mechanical Impulse Propagation in Simulated Microgravity Environment. Biology, 11(11), 1677. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111677








