Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria from the National Parks of Thailand and Larvicidal Property of Symbiotic Bacteria against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
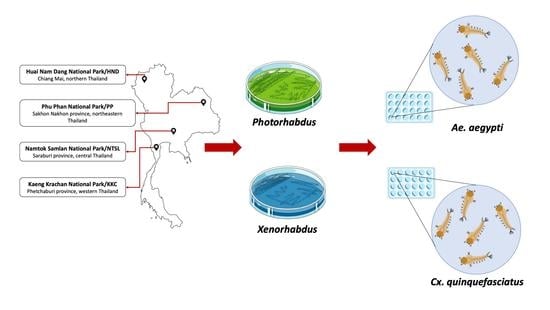
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Collection of Soil Samples
2.3. Isolation of EPNs from Soil Samples
2.4. Species Identification of EPNs
2.5. Species Identification of Symbiotic Bacteria
2.6. Analysis of the ITS, 28S rDNA, and recA Sequences
2.7. Bioassay for Larvicidal Property against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Recovery of EPNs
3.2. Identification and Phylogeny of EPNs
3.3. Identification and Phylogeny of Symbiotic Bacteria
3.4. Whole Cell Suspension of Symbiotic Bacteria against the Larvae of Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Travassos, L. Uma nova Cappillaria parasite de peixes be agua doce: Capillaria sentinosa n. sp. Boletim Biologico. 1927, 10, 215–217. [Google Scholar]
- Poinar, G.O., Jr. Description and biology of a new insect parasitic rhabditoid, Heterorhabditis bacteriophora n. gen. n. sp. (Rhabditida; Heterorhabditidae n. fam.). Nematologica 1976, 21, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.B.; Smart, G.C., Jr. Neosteinernema longicurvicauda n. gen., n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), a parasite of the termite Reticulitermes flavipes (Koller). J. Nematol. 1994, 26, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smart, G.C. Entomopathogenic nematodes for the biological control of insects. J. Nematol. 1995, 27, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Divya, K.; Sankar, M. Entomopathogenic nematodes in pest management. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2009, 2, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowds, B.C.A.; Peters, A. Virulence mechanisms. In Entomopathogenic Nematology; Gaugler, R., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Alotaibi, S.S.; Darwish, H.; Zaynab, M.; Alharthi, S.; Alghamdi, A.; Al-Barty, A.; Asif, M.; Wahdan, R.H.; Baazeem, A.; Noureldeen, A. Isolation, identification, and biocontrol potential of entomopathogenic nematodes and associated bacteria against Virachola livia (Lepidoptera: Lycaenidae) and Ectomyelois ceratoniae (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Biology 2022, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaxter, M.L.; De Ley, P.; Garey, J.R.; Lui, L.X.; Scheldeman, P.; Vierstraete, J.R.; Thomas, W.K. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature 1998, 392, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.P.; Campbell, J.F.; Nadler, S.A. Phylogeny of Steinernema Travassos 1927 (Cephalobina: Steinernematidae) inferred from ribosomal DNA sequences and morphological characters. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hominick, W.M.; Briscoe, B.R.; del Pino, F.G.; Heng, J.; Hunt, D.J.; Kozodoy, E.; Mracek, Z.; Nguyen, K.B.; Reid, A.P.; Spiridonov, S.; et al. Biosystematics of entomopathogenic nematodes: Current status, protocols and definitions. J. Helminthol. 1997, 71, 271–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Le Saux, M.; Viallard, V.; Brunel, B.; Normand, P.; Boemare, N.E. Polyphasic classification of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of new taxa: P. luminescens subsp. luminescens subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. akhurstii subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. laumondii subsp. nov., P. temperata sp. nov., P. temperata subsp. temperata subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Akhurst, R.J.; Boemare, N.E.; Janssen, P.H.; Peel, M.M.; Alfredson, D.A.; Beard, C.E. Taxonomy of Australian clinical isolates of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of Photorhabdus asymbiotica subsp. asymbiotica subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica subsp. australis subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tailliez, P.; Laroui, C.; Ginibre, N.; Paule, A.; Pages, S.; Boemare, N. Phylogeny of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus based on universally conserved protein-coding sequences and implications for the taxonomy of these two genera. Proposal of new taxa: X. vietnamensis sp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. caribbeanensis subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. hainanensis subsp. nov., P. temperata subsp. khanii subsp. nov., P. temperate subsp. tasmaniensis subsp. nov., and the reclassification of P. luminescens subsp. thracensis as P. temperate subsp. thracensis. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1921–1937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tangchitsomkid, N.; Sontirat, S. Occurrence of entomopathogenic nematode in Thailand. Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.). 1998, 32, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Thanwisai, A.; Tandhavanant, S.; Saiprom, N.; Waterfield, N.R.; Phan, K.L.; Bode, H.B.; Peacock, S.J.; Chantratita, N. Diversity of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus spp. and their symbiotic entomopathogenic nematodes from Thailand. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vitta, A.; Yimthin, T.; Fukruksa, C.; Wongpeera, W.; Yotpanya, W.; Polseela, R.; Thanwisai, A. Distribution of entomopathogenic nematodes in lower northern Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2015, 46, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vitta, A.; Fukruksa, C.; Yimthin, T.; Deelue, K.; Sarai, C.; Polseela, R.; Thanwisai, A. Preliminary survey of entomopathogenic nematodes in upper northern Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 48, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Muangpat, P.; Yooyangket, T.; Fukruksa, C.; Suwannaroj, M.; Yimthin, T.; Sitthisak, S.; Chantratita, N.; Vitta, A.; Tobias, N.J.; Bode, H.B.; et al. Identification and characterization of the antimicrobial activity against drug resistant bacteria of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus associated with entomopathogenic nematodes from Mae Wong National Park, Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yooyangket, T.; Muangpat, P.; Polseela, R.; Tandhavanant, S.; Thanwisai, A.; Vitta, A. Identification of entomopathogenic nematodes and symbiotic bacteria from Nam Nao National Park in Thailand and larvicidal activity of symbiotic bacteria against Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanwisai, A.; Muangpat, P.; Dumidae, A.; Subkrasae, C.; Ardpairin, J.; Tandhavanant, S.; Vitta, A. Identification of entomopathogenic nematodes and their symbiotic bacteria in national parks of Thailand, and mosquitocidal activity of Xenorhabdus griffiniae against Aedes aegypti larvae. Nematology 2021, 24, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, L.K.; Subbotin, S.A.; Waeyenberge, L.; Moens, M. A new entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema robustispiculum n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), from Chumomray National Park in Vietnam. Syst. Parasitol. 2005, 60, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.L.; Mráček, Z.; Půža, V.; Nermut, J.; Jarošová, A. Steinernema huense sp. n., a new entomopathogenic nematode (Nematoda: Steinernematidae) from Vietnam. Nematology 2014, 16, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casida, J.E.; Quistad, G.B. Golden age of insecticide research: Past, present, or future? Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hemingway, J.; Ranson, H. Insecticide resistance in insect vectors of human disease. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 371–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beding, R.A.; Akhurst, R.J. A simple technique for the determination of insect parasitic Rhabditid nematodes in soil. Nematologica 1975, 21, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.F. A method for obtaining infective nematode larvae from cultures. Science 1927, 66, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcu, B.; Cimen, H.; Raja, R.K.; Hazir, S. Entomopathogenic nematodes and their mutualistic bacteria: Their ecology and application as microbial control agents. Biopestic. Int. 2017, 13, 79–112. [Google Scholar]
- Fukruksa, C.; Yimthin, T.; Suwannaroj, M.; Muangpat, P.; Tandhavanant, S.; Thanwisai, A.; Vitta, A. Isolation and identification of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus bacteria associated with entomopathogenic nematodes and their larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti. Parasite Vectors 2017, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Steche, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, Y.K.; Lee, K.Y. Oral toxicity of Photorhabdus culture media on gene expression of the adult sweet potato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 109, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.H.; Chaubey, A.K.; Askary, T.H. Global distribution of entomopathogenic nematodes, Steinernema and Heterorhabditis. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuart, R.J.; Barbercheck, M.E.; Grewal, P.S. Entomopathogenic nematodes in the soil environment: Distributions, interactions and the influence of biotic and abiotic factors. In Nematode Pathogenesis of Insects and Other Pests. Sustainability in Plant and Crop Protection; Campos-Herrera, R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.J. Nematology monographs and perspectives. In Advances in Entomopathogenic Nematodes Taxonomy and Phylogeny; Hunt, D.J., Nguyen, K.B., Eds.; Bill: Lieden, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, S.P.; Somsook, V.; Reid, A.P. Steinernema siamkayai n. sp. (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae), an entomopathogenic nematode from Thailand. Syst. Parasitol. 1998, 41, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneesakorn, P.; Grewal, P.S.; Chandrapatya, A. Steinernema minutum sp. nov. (Rhabditida: Steinernema): A new entomopathogenic from Thailand. Int. J. Nematol. 2010, 20, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Maneesakorn, P.; An, R.; Daneshvar, H.; Taylor, K.; Bai, X.; Adams, B.J.; Grewal, P.S.; Chandrapatya, A. Phylogenetic and cophylogenetic relationships of entomopathogenic nematodes (Heterorhabditis: Rhabditida) and their symbiotic bacteria (Photorhabdus: Enterobacteriaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 59, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannaroj, M.; Yimthin, T.; Fukruksa, C.; Muangpat, P.; Yooyangket, T.; Tandhavanant, S.; Thanwisai, A.; Vitta, A. Survey of entomopathogenic nematodes and associate bacteria in Thailand and their potential to control Aedes aegypti. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 144, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardpairin, J.; Muangpat, P.; Sonpom, S.; Dumidae, A.; Subkrasae, C.; Tandhavanant, S.; Thanwisai, A.; Vitta, A. A survey of entomopathogenic nematodes and their symbiotic bacteria in agricultural areas of northern Thailand. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimthin, T.; Fukruksa, C.; Muangpat, P.; Dumidae, A.; Wattanachaiyingcharoen, W.; Vitta, A.; Thanwisai, A. A study on Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus isolates from Northeastern Thailand: Identification, antibacterial activity, and association with entomopathogenic nematode hosts. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subkrasae, C.; Ardpairin, J.; Dumidae, A.; Janthu, P.; Meesil, W.; Muangpat, P.; Tandhavanant, S.; Thanwisai, A.; Vitta, A. Molecular identification and phylogeny of Steinernema and Heterorhabditis nematodes and their efficacy in controlling the larvae of Aedes aegypti, a major vector of the dengue virus. Acta Trop. 2022, 228, 106318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Grewal, P.S. Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kleinii subsp. nov. (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae). Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, S.P.; Tobias, N.J.; Thanwisai, A.; Chantratita, N.; Bode, H.B.; Kämpfer, P. Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. namnaonensis subsp. nov., isolated from Heterorhabditis baujardi nematodes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.; Muller, A.; Ghazal, S.M.; Thanwisai, A.; Pagès, S.; Bode, H.B.; Hussein, M.A.; Khalil, K.M.; Tisa, L.S. Photorhabdus heterorhabditis subsp. aluminescens subsp. nov., Photorhabdus heterorhabditis subsp. heterorhabditis subsp. nov., Photorhabdus australis subsp. thailandensis subsp. nov., Photorhabdus australis subsp. australis subsp. nov., and Photorhabdus aegyptia sp. nov. isolated from Heterorhabditis entomopathogenic nematodes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tailliez, P.; Pagès, S.; Ginibre, N.; Boemare, N. New insight into diversity in the genus Xenorhabdus, including the description of ten novel species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2805–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer-Le Saux, M.; Maule´on, H.; Constant, P.; Brunel, B.; Boemare, N. PCR-ribotyping of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus isolates from the Caribbean region in relation to the taxonomy and geographic distribution of their nematode hosts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4246–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalia, V.; Sharma, G.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Ganguly, S. Biocontrol potential of Steinernema thermophilum and its symbiont Xenorhabdus indica against lepidopteran pests: Virulence to egg and larval stages. J. Nematol. 2014, 46, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manachini, B.; Schillaci, D.; Arizza, V. Biological responses of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) to Steinernema carpocapsae (Nematoda: Steinernematidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, O.S.; Prado, G.R.; Da Silva, J.L.R.; Silva, C.E.; Da Costa, M.; Heermann, R. Oral toxicity of Photorhabdus luminescens and Xenorhabdus nematophila (Enterobacteriaceae) against Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol Res. 2013, 112, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.J.; Pilz-Júnior, H.L.; Heermann, R.; Da Silva, O.S. The great potential of entomopathogenic bacteria Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus for mosquito control: A review. Parasit Vectors 2020, 13, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitta, A.; Thimpoo, P.; Meesil, W.; Yimthin, T.; Fukruksa, C.; Polseela, R.; Mangkit, B.; Tandhavanant, S.; Thanwisai, A. Larvicidal activity of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus bacteria against Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2018, 8, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilipkumar, A.; Raja Ramalingam, K.; Chinnaperumal, K.; Govindasamy, B.; Paramasivam, D.; Dhayalan, A.; Pachiappan, P. Isolation and growth inhibition potential of entomopathogenic nematodes against three public health important mosquito vectors. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 197, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.; Almeida, A.M.; Dolinski, C.; Souza, R.M. Efficacy of Heterorhabdits indica LPP35 against Aedes aegypti in domiciliary oviposition sites. J. Nematol. 2019, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.T.; Chen, T.L.; Hou, R.F.; Chen, C.C.; Tu, W.C. The invasion and encapsulation of the entomopathogenic nematode, Steinernema abbasi, in Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. Insects 2020, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, Y.K.; Jang, E.K.; Yu, Y.S.; Kwon, M.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, K.Y. Oral toxicity of symbiotic bacteria Photorhabdus spp. against immature stages of insects. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2011, 14, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Yang, E.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Koo, K.B.; Song, K.S.; Lee, K.Y. Mosquitocidal activity of anthraquinones isolated from symbiotic bacteria Photorhabdus of entomopathogenic nematode. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2013, 16, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahantarig, A.; Chantawat, N.; Waterfield, N.R.; Ffrench-Constant, R.; Kittayapong, P. PirAB toxin from Photorhabdus asymbiotica as a larvicide against dengue vectors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4627–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McInerney, B.V.; Gregson, R.P.; Lacey, M.J.; Akhurst, R.J.; Lyons, G.R.; Rhodes, S.H.; Smith, D.R.; Engelhardt, L.M.; White, A.H. Biologically active metabolites from Xenorhabdus spp. part 1 dithiolopyrrolone derivatives with antibiotic activity. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hu, K.; Webster, J.M. Antibiotics from Xenorhabdus spp. and Photorhabdus spp. (enterobacteriaceae): (Review). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 1998, 34, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, B.V.; Gregson, R.P.; Lacey, M.J.; Akhurst, R.J.; Taylor, W.C. Biologically active metabolites from Xenorhabdus spp. part 2. Benzopyran-1-one derivatives with gastroprotective activity. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Yi, Y.; Kang, G.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, P.; Baek, N.I.; Kim, Y. Identification of an antibacterial compound, benzylideneacetone, from Xenorhabdus nematophila against major plant-pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 239, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furgani, G.; Böszörményi, E.; Fodor, A.; Máthé-Fodor, A.; Forst, S.; Hogan, J.S.; Katona, Z.; Klein, M.G.; Stackebrandt, E.; Szentirmai, A.; et al. Xenorhabdus antibiotics: A comparative analysis and potential utility for controlling mastitis caused by bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, H.B. Entomopathogenic bacteria as a source of secondary metabolites. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2009, 13, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaston, J.M.; Suen, G.; Tucker, S.L.; Andersen, A.W.; Bhasin, A.; Bode, E.; Bode, H.B.; Brachmann, A.O.; Cowles, C.E.; Cowles, K.N.; et al. The entomopathogenic bacterial endosymbionts Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus: Convergent lifestyles from divergent genomes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiswarya, D.; Raja, R.K.; Kamaraj, C.; Balasubramani, G.; Deepak, P.; Arul, D.; Amutha, V.; Sankaranarayanan, C.; Hazir, S.; Perumal, P. Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles from the symbiotic bacterium, Photorhabdus luminescens of entomopathogenic nematode: Larvicidal properties against three mosquitoes and Galleria mellonella larvae. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y. Entomopathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila and Photorhabdus luminescens, enhances Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxicity against yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2015, 18, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| National Park/Code | Province/Region of Thailand | No. of Soil Site | No. of Soil Samples (No. of Soil Sample with EPN) | No. of Positive with Molecular Sequences (Isolate) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbiotic Bacteria | EPNs | ||||||
| Xenorhabdus | Photorhabdus | Steinernema | Hetorhabditis | ||||
| Huai Nam Dang National Park/HND | Chiang Mai/Northern | 40 | 200 (6) | 6 | - | - | - |
| Kaeng Krachan National Park/KKC | Phetchaburi/ Western | 40 | 200 (23) | 8 | 12 | 4 | 4 |
| Namtok Samlan National Park/NTSL | Saraburi/ Central | 48 | 240 (24) | 2 | 12 | 4 | 8 |
| Phu Phan National Park/PP | Sakhon Nakhon/ Northeastern | 40 | 200 (27) | 8 | 17 | 7 | 6 |
| Total | 168 | 840 (80) | 24 | 41 | 12 | 18 | |
| National Parks/Code | Mean ± SD of Soil pH (Minimum–Maximum) | Mean ± SD of Soil Temperature (Minimum–Maximum) | Mean ± SD of Soil Moisture (Minimum–Maximum) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With EPN | Without EPN | All | With EPN | Without EPN | All | With EPN | Without EPN | All | |
| Huai Nam Dang National Park/HND (n = 6 for with EPN, n = 194 for without EPN, n = 200 for all) | 6.9 ± 0.11 (6.8–7.0) | 6.87 ± 0.20 (5.8–7.0) | 6.87 ± 0.19 (5.8–7.0) | 21.17 ± 0.98 (20–23) | 20.67 ± 1.08 (19–23) | 20.68 ± 1.07 (19–23) | 1.0 ± 0.00 (1.00) | 1.12 ± 0.49 (1.0–5.0) | 1.11 ± 0.48 (1.0–5.0) |
| Kaeng Krachan National Park/KKC (n = 23 for with EPN, n = 177 for without EPN, n = 200 for all) | 6.75 ± 0.40 (5.6–7.0) | 6.61 ± 0.58 (4.4–9.0) | 6.62 ± 0.56 (4.4–9.0) | 23.0 ± 1.00 (22–25) | 22.79 ± 0.82 (22–26) | 22.81 ± 0.83 (22–26) | 1.87 ± 1.56 (1.0–7.0) | 2.38 ± 2.04 (1.0–8.0) | 2.31 ± 1.99 (1.0–8.0) |
| Namtok Samlan National Park/NTSL (n = 24 for with EPN, n = 216 for without EPN, n = 240 for all) | 6.68 ± 0.21 (6.2–7.0) | 6.62 ± 0.41 (4.2–7.0) | 6.63 ± 0.39 (4.2–7.0) | 26.21 ± 1.18 (24–28) | 25.99 ± 1.03 (24–28) | 26.0 ± 1.04 (24–28) | 1.38 ± 0.58 (1.0–3.0) | 1.40 ± 1.00 (1.0–8.0) | 1.39 ± 0.96 (1.0–8.0) |
| Phu Phan National Park/PP (n = 27 for with EPN, n = 173 for without EPN, n = 200 for all) | 6.61± 0.47 (5.0–7.0) | 6.78 ± 0.38 (4.0–8.0) | 6.75 ± 0.39 (4.0–7.0) | 26.07 ± 0.87 (25–29) | 26.43 ± 1.14 (20–30) | 26.38 ± 1.11 (20–30) | 1.98 ± 1.92 (1.0–7.0) | 1.50 ± 1.33 (1.0–8.0) | 1.56 ± 1.42 (1.0–8.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thanwisai, A.; Muangpat, P.; Meesil, W.; Janthu, P.; Dumidae, A.; Subkrasae, C.; Ardpairin, J.; Tandhavanant, S.; Yoshino, T.P.; Vitta, A. Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria from the National Parks of Thailand and Larvicidal Property of Symbiotic Bacteria against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus. Biology 2022, 11, 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111658
Thanwisai A, Muangpat P, Meesil W, Janthu P, Dumidae A, Subkrasae C, Ardpairin J, Tandhavanant S, Yoshino TP, Vitta A. Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria from the National Parks of Thailand and Larvicidal Property of Symbiotic Bacteria against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111658
Chicago/Turabian StyleThanwisai, Aunchalee, Paramaporn Muangpat, Wipanee Meesil, Pichamon Janthu, Abdulhakam Dumidae, Chanakan Subkrasae, Jiranun Ardpairin, Sarunporn Tandhavanant, Timothy P. Yoshino, and Apichat Vitta. 2022. "Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria from the National Parks of Thailand and Larvicidal Property of Symbiotic Bacteria against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus" Biology 11, no. 11: 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111658
APA StyleThanwisai, A., Muangpat, P., Meesil, W., Janthu, P., Dumidae, A., Subkrasae, C., Ardpairin, J., Tandhavanant, S., Yoshino, T. P., & Vitta, A. (2022). Entomopathogenic Nematodes and Their Symbiotic Bacteria from the National Parks of Thailand and Larvicidal Property of Symbiotic Bacteria against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus. Biology, 11(11), 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111658