MicroRNAs as Mediators of Adipose Thermogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Obesity
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MicroRNAs as Regulators of Adipose Thermogenesis
2.1. Positive Role of MicroRANs in Adipose Thermogenesis
2.1.1. miR-30b/c
2.1.2. miR-32
2.1.3. miR-455
2.1.4. miR-203
2.1.5. miR-182-5p
2.1.6. Other MicroRNAs as Positive Regulators of Adipose Thermogenesis
2.2. Negative Role of MicroRNAs in Adipose Thermogenesis
2.2.1. miR-133
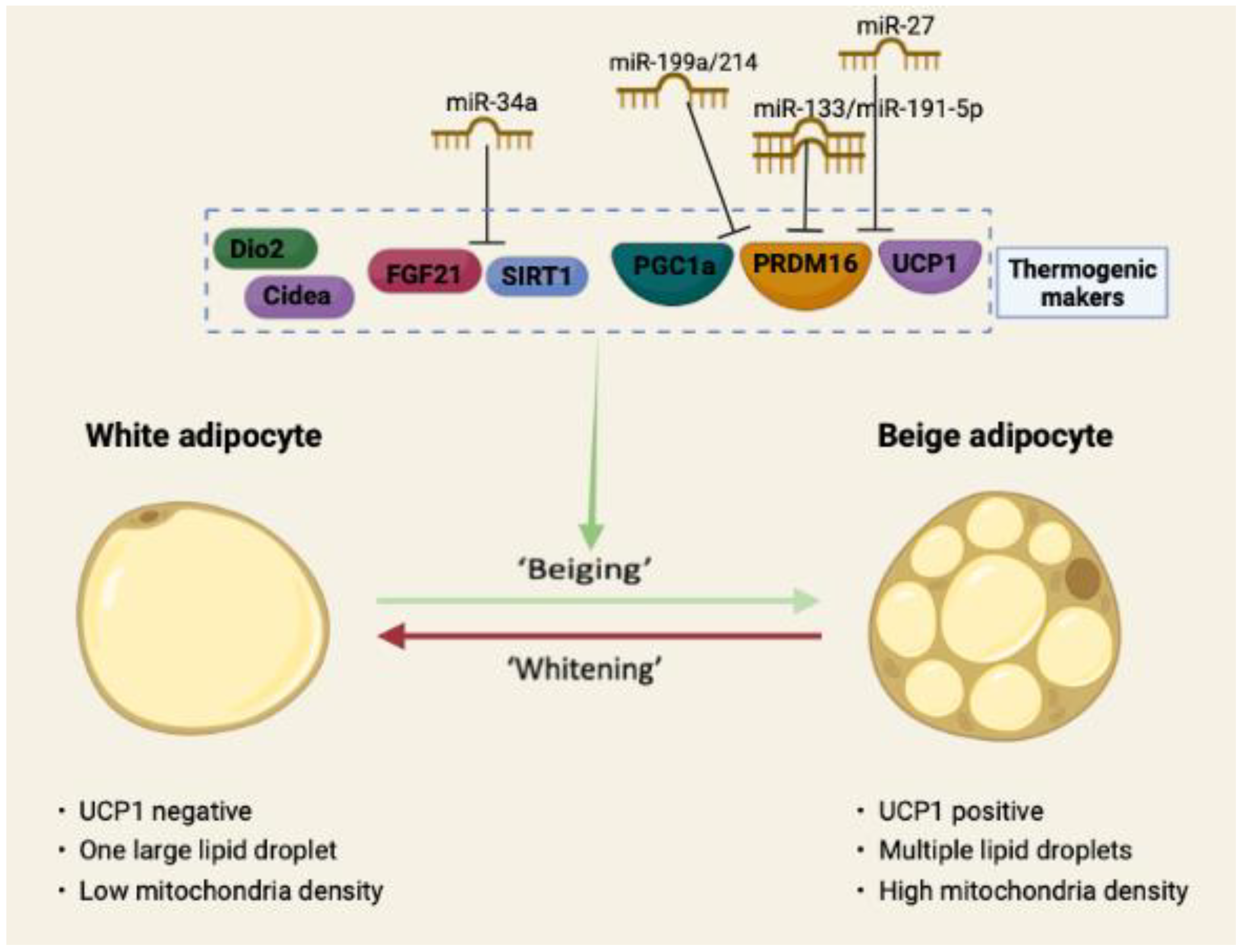
2.2.2. miR-34a
2.2.3. miR-27
2.2.4. miR-155
2.2.5. miR-327
2.2.6. miR-494-3p
2.2.7. miR-199a/214 Cluster
2.2.8. Other MicroRNAs as Negative Regulators of Adipose Thermogenesis
2.3. MicroRNAs with Controversial Functions in Adipose Thermogenesis
2.3.1. miR-22
2.3.2. miR-33
3. MicroRNAs as Therapeutic Targets for Obesity
3.1. MicroRNAs Associated with Obesity
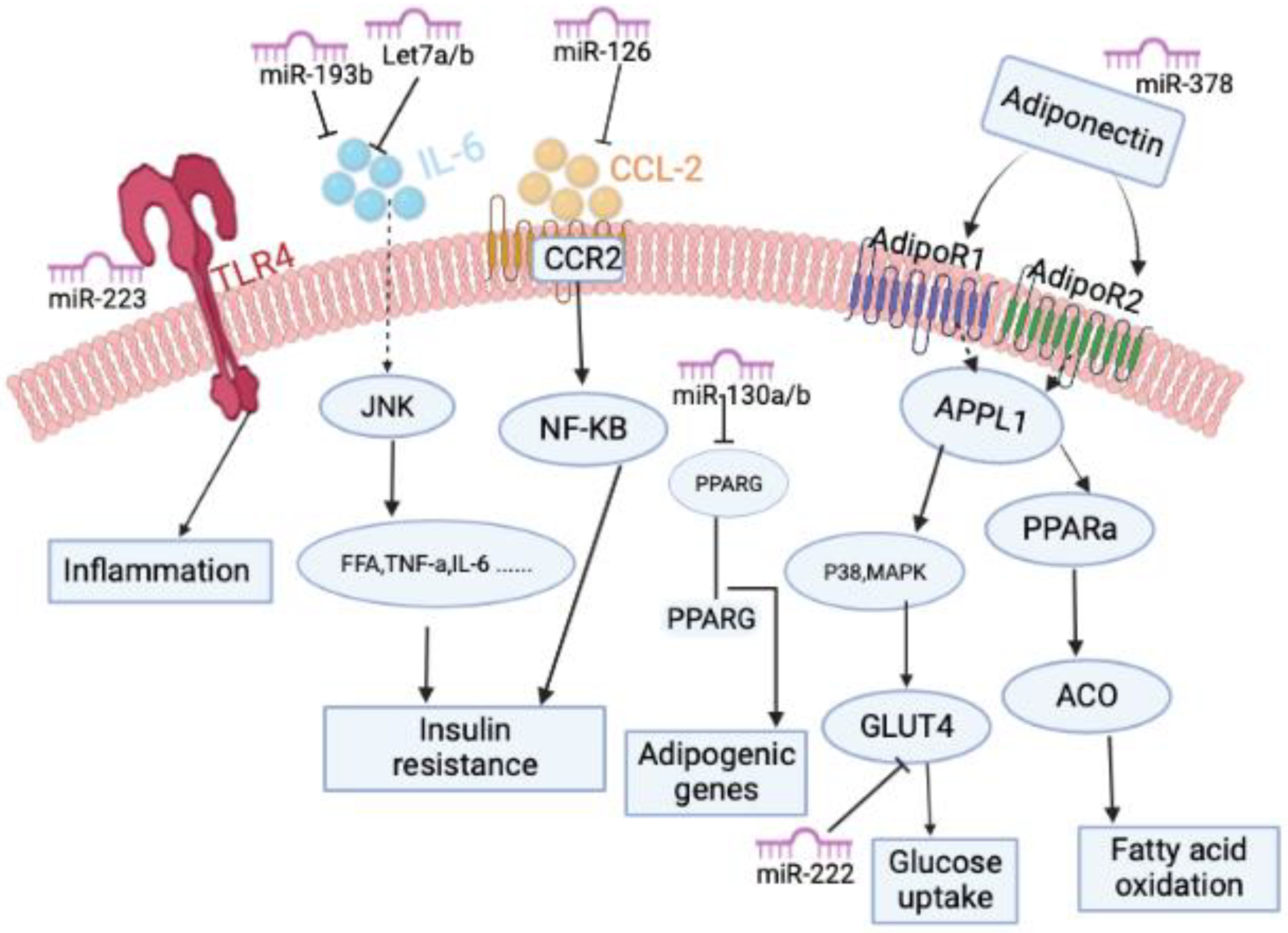
3.2. Adipokines Regulate miRNA Activity in Obesity
3.3. Influence of Obesity in the miRNome
3.4. Novel Approaches of MicroRNAs Delivery
4. Summary and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Gonzalez, A.B.; Hartge, P.; Cerhan, J.R.; Flint, A.J.; Hannan, L.; MacInnis, R.J.; Moore, S.C.; Tobias, G.S.; Anton-Culver, H.; Freeman, L.B.; et al. Body-Mass Index and Mortality among 1.46 Million White Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2211–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoldi, A.; Naffah de Souza, C.; Camara, N.O.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M. The Macrophage Switch in Obesity Development. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K.; International Agency for Research on Cancer Handbook Working Group. Body Fatness and Cancer--Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.O.; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrup, A.; Lundsgaard, C. What do pharmacological approaches to obesity management offer? Linking pharmacological mechanisms of obesity management agents to clinical practice. Exp. Clin. Endocr. Diabetes 1998, 106, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.W. Bone metabolism after bariatric surgery. J. Bone Min. Res. 2014, 29, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsa, J.A.; Botella-Carretero, J.I.; Peromingo, R.; Caballero, C.; Munoz-Malo, T.; Villafruela, J.J.; Arrieta, F.; Zamarron, I.; Vazquez, C. Chronic increase of bone turnover markers after biliopancreatic diversion is related to secondary hyperparathyroidism and weight loss. Relation with bone mineral density. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P.; Kajimura, S. The cellular and functional complexity of thermogenic fat. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, K.A.; Lidell, M.E.; Orava, J.; Heglind, M.; Westergren, R.; Niemi, T.; Taittonen, M.; Laine, J.; Savisto, N.J.; Enerback, S.; et al. Functional brown adipose tissue in healthy adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, J.; Bengtsson, T.; Cannon, B. Unexpected evidence for active brown adipose tissue in adult humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E444–E452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypess, A.M.; Lehman, S.; Williams, G.; Tal, I.; Rodman, D.; Goldfine, A.B.; Kuo, F.C.; Palmer, E.L.; Tseng, Y.H.; Doria, A.; et al. Identification and importance of brown adipose tissue in adult humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaisanlahti, A.; Glumoff, T. Browning of white fat: Agents and implications for beige adipose tissue to type 2 diabetes. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneshiro, T.; Aita, S.; Matsushita, M.; Kayahara, T.; Kameya, T.; Kawai, Y.; Iwanaga, T.; Saito, M. Recruited brown adipose tissue as an antiobesity agent in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3404–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondin, D.P.; Labbe, S.M.; Tingelstad, H.C.; Noll, C.; Kunach, M.; Phoenix, S.; Guerin, B.; Turcotte, E.E.; Carpentier, A.C.; Richard, D.; et al. Increased brown adipose tissue oxidative capacity in cold-acclimated humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E438–E446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenbelt, W.; Kingma, B.; van der Lans, A.; Schellen, L. Cold exposure—An approach to increasing energy expenditure in humans. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedergaard, J.; Cannon, B. The changed metabolic world with human brown adipose tissue: Therapeutic visions. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Seale, P. Control of brown and beige fat development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bostrom, P.; Sparks, L.M.; Ye, L.; Choi, J.H.; Giang, A.H.; Khandekar, M.; Virtanen, K.A.; Nuutila, P.; Schaart, G.; et al. Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human. Cell 2012, 150, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, H.M.; Golozoubova, V.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. UCP1 ablation induces obesity and abolishes diet-induced thermogenesis in mice exempt from thermal stress by living at thermoneutrality. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Mao, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, X. Molecular pathways regulating the formation of brown-like adipocytes in white adipose tissue. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahfeldt, T.; Schinzel, R.T.; Lee, Y.K.; Hendrickson, D.; Kaplan, A.; Lum, D.H.; Camahort, R.; Xia, F.; Shay, J.; Rhee, E.P.; et al. Programming human pluripotent stem cells into white and brown adipocytes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, M.J.; Ishibashi, J.; Wang, W.; Lim, H.W.; Goyama, S.; Sato, T.; Kurokawa, M.; Won, K.J.; Seale, P. Prdm16 is required for the maintenance of brown adipocyte identity and function in adult mice. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.M.; Staels, B. Review: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and adipose tissue—Understanding obesity-related changes in regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kursawe, R.; Narayan, D.; Cali, A.M.; Shaw, M.; Pierpont, B.; Shulman, G.I.; Caprio, S. Downregulation of ADIPOQ and PPARgamma2 gene expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese adolescents with hepatic steatosis. Obesity 2010, 18, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redonnet, A.; Bonilla, S.; Noel-Suberville, C.; Pallet, V.; Dabadie, H.; Gin, H.; Higueret, P. Relationship between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and retinoic acid receptor alpha gene expression in obese human adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, J.; Mi, S. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurylowicz, A. microRNAs in Human Adipose Tissue Physiology and Dysfunction. Cells 2021, 10, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragosi, L.E.; Wdziekonski, B.; Brigand, K.L.; Villageois, P.; Mari, B.; Waldmann, R.; Dani, C.; Barbry, P. Small RNA sequencing reveals miR-642a-3p as a novel adipocyte-specific microRNA and miR-30 as a key regulator of human adipogenesis. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wang, M.; Xiao, T.; Yin, B.; He, L.; Meng, W.; Dong, M.; Liu, F. miR-30 promotes thermogenesis and the development of beige fat by targeting RIP140. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2056–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, J.; Christian, M.; Parker, M.G. Distinct functions for RIP140 in development, inflammation, and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambs, S.; Prueitt, R.L.; Yi, M.; Hudson, R.S.; Howe, T.M.; Petrocca, F.; Wallace, T.A.; Liu, C.G.; Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; et al. Genomic profiling of microRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated microRNA expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6162–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zu, X.; Liu, J. Magic and mystery of microRNA-32. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 8588–8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Howng, S.Y.; Ptacek, L.J.; Fu, Y.H. miR-32 and its target SLC45A3 regulate the lipid metabolism of oligodendrocytes and myelin. Neuroscience 2012, 213, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.; Hussain, N.A.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, C.; Li, H.; Fu, Y.; Cao, L.; Han, W.; Stunkel, W.; Xu, F. miRNA-32 Drives Brown Fat Thermogenesis and Trans-activates Subcutaneous White Fat Browning in Mice. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1229–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.M.; Kleiner, S.; Douris, N.; Fox, E.C.; Mepani, R.J.; Verdeguer, F.; Wu, J.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Flier, J.S.; Maratos-Flier, E.; et al. FGF21 regulates PGC-1alpha and browning of white adipose tissues in adaptive thermogenesis. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guan, M.; Townsend, K.L.; Huang, T.L.; An, D.; Yan, X.; Xue, R.; Schulz, T.J.; Winnay, J.; Mori, M.; et al. MicroRNA-455 regulates brown adipogenesis via a novel HIF1an-AMPK-PGC1alpha signaling network. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1378–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Kokkotou, E.; Schulz, T.J.; Huang, T.L.; Winnay, J.N.; Taniguchi, C.M.; Tran, T.T.; Suzuki, R.; Espinoza, D.O.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. New role of bone morphogenetic protein 7 in brown adipogenesis and energy expenditure. Nature 2008, 454, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, T.J.; Huang, P.; Huang, T.L.; Xue, R.; McDougall, L.E.; Townsend, K.L.; Cypess, A.M.; Mishina, Y.; Gussoni, E.; Tseng, Y.H. Brown-fat paucity due to impaired BMP signalling induces compensatory browning of white fat. Nature 2013, 495, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Poy, M.N.; Stoffel, M.; Fuchs, E. A skin microRNA promotes differentiation by repressing ‘stemness’. Nature 2008, 452, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.J.; Perez de Castro, I.; Gomez de Cedron, M.; Santos, J.; Calin, G.A.; Cigudosa, J.C.; Croce, C.M.; Fernandez-Piqueras, J.; Malumbres, M. Genetic and epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 enhances ABL1 and BCR-ABL1 oncogene expression. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Cho, H.; Alexander, R.; Patterson, H.C.; Gu, M.; Lo, K.A.; Xu, D.; Goh, V.J.; Nguyen, L.N.; Chai, X.; et al. MicroRNAs are required for the feature maintenance and differentiation of brown adipocytes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 4045–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, T.; Lim, Y.C.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Yang, S.; Huang, C.; Xu, M.; Tao, L.; et al. cAMP-MicroRNA-203-IFNgamma network regulates subcutaneous white fat browning and glucose tolerance. Mol. Metab. 2019, 28, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Tang, M.; Xiao, T.; Liu, H.; Liu, W.; Li, G.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, F.; et al. Obesity-Associated miR-199a/214 Cluster Inhibits Adipose Browning via PRDM16-PGC-1alpha Transcriptional Network. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2585–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Xiao, T.; Liang, X.; Wen, J.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.; Liu, J.; Bialowas, C.; Luo, H.; et al. The miR-182-5p/FGF21/acetylcholine axis mediates the crosstalk between adipocytes and macrophages to promote beige fat thermogenesis. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e150249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonhogen, I.G.C.; El Azzouzi, H.; Olieslagers, S.; Vasilevich, A.; de Boer, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; da Costa Martins, P.A.; de Windt, L.J.; Murri, M. MiR-337-3p Promotes Adipocyte Browning by Inhibiting TWIST1. Cells 2020, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.J.; Gettys, T.W.; Chang, J.S. Transcriptional Activity of PGC-1alpha and NT-PGC-1alpha Is Differentially Regulated by Twist-1 in Brown Fat Metabolism. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012, 320454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dong, M.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Ye, R.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Jin, W. miR17-92 cluster drives white adipose tissue browning. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 65, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, B. Roles of miR-124-3p/Scd1 in urolithin A-induced brown adipocyte differentiation and succinate-dependent regulation of mitochondrial complex II. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 606, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walden, T.B.; Timmons, J.A.; Keller, P.; Nedergaard, J.; Cannon, B. Distinct expression of muscle-specific microRNAs (myomirs) in brown adipocytes. J. Cell Physiol. 2009, 218, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovski, M.; Ahmed, K.; Esau, C.C.; Stoffel, M. MyomiR-133 regulates brown fat differentiation through Prdm16. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Pasut, A.; Soleimani, V.D.; Bentzinger, C.F.; Antoun, G.; Thorn, S.; Seale, P.; Fernando, P.; van Ijcken, W.; Grosveld, F.; et al. MicroRNA-133 controls brown adipose determination in skeletal muscle satellite cells by targeting Prdm16. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Bi, P.; Shan, T.; Yang, X.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Liu, N.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Kuang, S. miR-133a regulates adipocyte browning in vivo. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.W.; Lee, M.G.; Nam, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Oh, H.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Yi, S.A.; Han, J.W. Reversine promotes browning of white adipocytes by suppressing miR-133a. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 3800–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Choi, S.E.; Kim, D.H.; Seok, S.; Suino-Powell, K.M.; Xu, H.E.; Kemper, J.K. Aberrantly elevated microRNA-34a in obesity attenuates hepatic responses to FGF19 by targeting a membrane coreceptor beta-Klotho. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16137–16142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.; Seok, S.; Choi, S.; Huang, Z.; Suino-Powell, K.; Xu, H.E.; Kemper, B.; Kemper, J.K. MicroRNA 34a inhibits beige and brown fat formation in obesity in part by suppressing adipocyte fibroblast growth factor 21 signaling and SIRT1 function. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 34, 4130–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Trajkovski, M. MiR-27 orchestrates the transcriptional regulation of brown adipogenesis. Metabolism 2014, 63, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Yu, J.; Bi, J.; Qi, H.; Di, W.; Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Zha, J.; Lv, S.; Zhang, F.; et al. Glucocorticoids transcriptionally regulate miR-27b expression promoting body fat accumulation via suppressing the browning of white adipose tissue. Diabetes 2015, 64, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alivernini, S.; Gremese, E.; McSharry, C.; Tolusso, B.; Ferraccioli, G.; McInnes, I.B.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M. MicroRNA-155-at the Critical Interface of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xu, Z.; Ding, T.; Kuang, D.M.; Zheng, L. MicroRNA-155 regulates inflammatory cytokine production in tumor-associated macrophages via targeting C/EBPbeta. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2009, 6, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worm, J.; Stenvang, J.; Petri, A.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Obad, S.; Elmen, J.; Hedtjarn, M.; Straarup, E.M.; Hansen, J.B.; Kauppinen, S. Silencing of microRNA-155 in mice during acute inflammatory response leads to derepression of c/ebp Beta and down-regulation of G-CSF. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 5784–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarn, M.; Namlos, H.M.; Noordhuis, P.; Wang, M.Y.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Myklebost, O. Adipocyte differentiation of human bone marrow-derived stromal cells is modulated by microRNA-155, microRNA-221, and microRNA-222. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Siegel, F.; Kipschull, S.; Haas, B.; Frohlich, H.; Meister, G.; Pfeifer, A. miR-155 regulates differentiation of brown and beige adipocytes via a bistable circuit. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloting, N.; Berthold, S.; Kovacs, P.; Schon, M.R.; Fasshauer, M.; Ruschke, K.; Stumvoll, M.; Bluher, M. MicroRNA expression in human omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.; Seki, T.; Lim, S.; Nakamura, M.; Andersson, P.; Yang, Y.; Honek, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, F.; et al. A miR-327-FGF10-FGFR2-mediated autocrine signaling mechanism controls white fat browning. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemecha, M.; Morino, K.; Imamura, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Ohashi, N.; Ida, S.; Sato, D.; Sekine, O.; Ugi, S.; Maegawa, H. MiR-494-3p regulates mitochondrial biogenesis and thermogenesis through PGC1-alpha signalling in beige adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zheng, S.; Garcia-Ruiz, D.; Hou, D.; Wei, Z.; Liao, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Zen, K.; et al. Fasting induces a subcutaneous-to-visceral fat switch mediated by microRNA-149-3p and suppression of PRDM16. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, L.; Ji, C.; Guo, X.; Chi, X. The role of microRNA-23b-5p in regulating brown adipogenesis and thermogenic program. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, W.; Amdanee, N.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y. Long-term exercise-secreted extracellular vesicles promote browning of white adipocytes by suppressing miR-191a-5p. Life Sci. 2020, 263, 118464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Bian, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, Y.; Li, H.; Han, Q.; Zhao, R.C. Upregulation of miR-22 promotes osteogenic differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by repressing HDAC6 protein expression. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, G.P.; Huang, Z.P.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Ding, J.; Fonseca, R.I.; Barreto-Chaves, M.L.; Donato, J., Jr.; Hu, X.; Wang, D.Z. Loss of microRNA-22 prevents high-fat diet induced dyslipidemia and increases energy expenditure without affecting cardiac hypertrophy. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2885–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, V.M.; Liu, J.; Brandao, B.B.; Lino, C.A.; Balbino Silva, C.S.; Ribeiro, M.A.C.; Oliveira, T.E.; Real, C.C.; de Paula Faria, D.; Cederquist, C.; et al. miRNA-22 deletion limits white adipose expansion and activates brown fat to attenuate high-fat diet-induced fat mass accumulation. Metabolism 2021, 117, 154723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, P.; Bi, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.; Kang, Q.; Lv, C.; Song, Y.; Xu, J.; Sheng, X.; Yang, X.; et al. MiR-22 modulates brown adipocyte thermogenesis by synergistically activating the glycolytic and mTORC1 signaling pathways. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3607–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakaran, D.; Thrush, A.B.; Nguyen, M.A.; Richards, L.; Geoffrion, M.; Singaravelu, R.; Ramphos, E.; Shangari, P.; Ouimet, M.; Pezacki, J.P.; et al. Macrophage Mitochondrial Energy Status Regulates Cholesterol Efflux and Is Enhanced by Anti-miR33 in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, M.S.; Verma, N.; van Solingen, C.; Cyr, Y.; Sharma, M.; Perie, L.; Corr, E.M.; Schlegel, M.; Shanley, L.C.; Peled, D.; et al. MicroRNA-33 Inhibits Adaptive Thermogenesis and Adipose Tissue Beiging. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1360–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, T.; Nakao, T.; Miyasaka, Y.; Nishino, T.; Matsumura, S.; Nakazeki, F.; Ide, Y.; Kimura, M.; Tsuji, S.; Rodriguez, R.R.; et al. microRNA-33 maintains adaptive thermogenesis via enhanced sympathetic nerve activity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiuliis, J.A.; Syed, R.; Duggineni, D.; Rutsky, J.; Rengasamy, P.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Needleman, B.; Mikami, D.; Perry, K.; et al. Visceral Adipose MicroRNA 223 Is Upregulated in Human and Murine Obesity and Modulates the Inflammatory Phenotype of Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Xiao, X.; Wu, C.; Gao, R.; Peng, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Du, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. miR-1934, downregulated in obesity, protects against low-grade inflammation in adipocytes. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 428, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerson, A.; Traurig, M.; Ossowski, V.; Fleming, J.M.; Mullins, M.; Baier, L.J. Human adipose microRNA-221 is upregulated in obesity and affects fat metabolism downstream of leptin and TNF-alpha. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, E.; Mejhert, N.; Kulyte, A.; Balwierz, P.J.; Pachkov, M.; Cormont, M.; Lorente-Cebrian, S.; Ehrlund, A.; Laurencikiene, J.; Heden, P.; et al. Adipose tissue microRNAs as regulators of CCL2 production in human obesity. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1986–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, H.M.; Miller, N.; McAnena, O.J.; O’Brien, T.; Kerin, M.J. Differential miRNA expression in omental adipose tissue and in the circulation of obese patients identifies novel metabolic biomarkers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E846–E850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, R.; Nardelli, C.; Pilone, V.; Buonomo, T.; Liguori, R.; Castano, I.; Buono, P.; Masone, S.; Persico, G.; Forestieri, P.; et al. miR-519d overexpression is associated with human obesity. Obesity 2010, 18, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.J.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Pardo, G.; Sabater, M.; Hummel, M.; Ferrer, A.; Rodriguez-Hermosa, J.I.; Ruiz, B.; Ricart, W.; Peral, B.; et al. MiRNA expression profile of human subcutaneous adipose and during adipocyte differentiation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Shimabukuro, M.; Yagi, S.; Nishimoto, S.; Kozuka, C.; Fukuda, D.; Soeki, T.; Masuzaki, H.; Tsutsui, M.; Sata, M. MicroRNA-378 regulates adiponectin expression in adipose tissue: A new plausible mechanism. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulyte, A.; Belarbi, Y.; Lorente-Cebrian, S.; Bambace, C.; Arner, E.; Daub, C.O.; Heden, P.; Ryden, M.; Mejhert, N.; Arner, P. Additive effects of microRNAs and transcription factors on CCL2 production in human white adipose tissue. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, S.M.; Saltiel, A.R. Adapting to obesity with adipose tissue inflammation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belarbi, Y.; Mejhert, N.; Lorente-Cebrian, S.; Dahlman, I.; Arner, P.; Ryden, M.; Kulyte, A. MicroRNA-193b Controls Adiponectin Production in Human White Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1084–E1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.K.; Lee, M.J.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Kim, W.; Kim, M.M.; Srikantan, S.; Martindale, J.L.; Hutchison, E.R.; Kim, H.H.; Marasa, B.S.; et al. miR-130 suppresses adipogenesis by inhibiting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Favelyukis, S.; Nguyen, A.K.; Reichart, D.; Scott, P.A.; Jenn, A.; Liu-Bryan, R.; Glass, C.K.; Neels, J.G.; Olefsky, J.M. A subpopulation of macrophages infiltrates hypertrophic adipose tissue and is activated by free fatty acids via Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 and JNK-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35279–35292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitseva, O.I.; Tanriverdi, K.; Tchkonia, T.T.; Kirkland, J.L.; McDonnell, M.E.; Apovian, C.M.; Freedman, J.; Gokce, N. Inducible Toll-like receptor and NF-kappaB regulatory pathway expression in human adipose tissue. Obesity 2008, 16, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadashiv; Tiwari, S.; Paul, B.N.; Kumar, S.; Chandra, A.; Dhananjai, S.; Negi, M.P. Over expression of resistin in adipose tissue of the obese induces insulin resistance. World J. Diabetes 2012, 3, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.; Danielson, K.M.; Benton, M.C.; Ziegler, O.; Shah, R.; Stubbs, R.S.; Das, S.; Macartney-Coxson, D. miRNA Signatures of Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Obesity 2017, 25, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santovito, D.; De Nardis, V.; Marcantonio, P.; Mandolini, C.; Paganelli, C.; Vitale, E.; Buttitta, F.; Bucci, M.; Mezzetti, A.; Consoli, A.; et al. Plasma exosome microRNA profiling unravels a new potential modulator of adiponectin pathway in diabetes: Effect of glycemic control. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1681–E1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, S.Y.; Liao, C.H.; Wu, H.P.; Hsiao, W.C.; Wu, I.H.; Jinpu; Yu; Lin, S.H.; Hsieh, C.L. Loss of let-7 microRNA upregulates IL-6 in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells triggering a reactive stromal response to prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, M.; James, R.; Marks, J.; Zhao, S.; Szabo, A.; Kidambi, S. Adiposity distribution influences circulating adiponectin levels. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lihn, A.S.; Bruun, J.M.; He, G.; Pedersen, S.B.; Jensen, P.F.; Richelsen, B. Lower expression of adiponectin mRNA in visceral adipose tissue in lean and obese subjects. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2004, 219, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, J.J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.B. Adiponectin increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle cells by sequential activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, V.; Nagaev, I.; Smith, U. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and is, like IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, overexpressed in human fat cells from insulin-resistant subjects. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45777–45784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda-Rodriguez, A.; Assmann, T.S.; Alonso-Pedrero, L.; Azcona-Sanjulian, M.C.; Milagro, F.I.; Marti, A. Circulating miRNAs in girls with abdominal obesity: miR-221-3p as a biomarker of response to weight loss interventions. Pediatr. Obes. 2022, 17, e12910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.J.; Moreno, M.; Mercader, J.M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Fuentes-Batllevell, N.; Sabater, M.; Ricart, W.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Inflammation triggers specific microRNA profiles in human adipocytes and macrophages and in their supernatants. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Puig, A.; Ortega, F.J.; Mercader, J.M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Moreno, M.; Bonet, N.; Ricart, W.; Lopez-Bermejo, A.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Changes in circulating microRNAs are associated with childhood obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1655–E1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.J.; Mercader, J.M.; Catalan, V.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Pueyo, N.; Sabater, M.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Anglada, R.; Fernandez-Formoso, J.A.; Ricart, W.; et al. Targeting the circulating microRNA signature of obesity. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, S.B.; Dewhurst, T.; Hammond, C.; Topham, C.H. MiRNAs as Novel Adipokines: Obesity-Related Circulating MiRNAs Influence Chemosensitivity in Cancer Patients. Noncoding RNA 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.T.; Tsai, P.C.; Liao, Y.C.; Hsu, C.Y.; Juo, S.H. Circulating microRNAs have a sex-specific association with metabolic syndrome. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouidhi, S.; Berrhouma, R.; Rouissi, K.; Jarboui, S.; Clerget-Froidevaux, M.S.; Seugnet, I.; Bchir, F.; Demeneix, B.; Guissouma, H.; Elgaaied, A.B. Human subcutaneous adipose tissue Glut 4 mRNA expression in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhao, C.; Guo, X.; Ding, H.; Cui, Y.; Shen, R.; Liu, J. Differential expression of microRNAs in omental adipose tissue from gestational diabetes mellitus subjects reveals miR-222 as a regulator of ERalpha expression in estrogen-induced insulin resistance. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Song, T.; Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Peng, J. miR-221 negatively regulates inflammation and insulin sensitivity in white adipose tissue by repression of sirtuin-1 (SIRT1). J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 6418–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, Y.; Barhod, E.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Gordin, R.; Shomron, N.; Baruch-Umansky, K.; Hemi, R.; Karasik, A.; Kanety, H. RNA-binding protein PTB and microRNA-221 coregulate AdipoR1 translation and adiponectin signaling. Diabetes 2014, 63, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Lim, B.; Lodish, H.F. MicroRNAs induced during adipogenesis that accelerate fat cell development are downregulated in obesity. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattikota, S.G.; Rathjen, T.; McAnulty, S.J.; Wessels, H.H.; Akerman, I.; van de Bunt, M.; Hausser, J.; Esguerra, J.L.; Musahl, A.; Pandey, A.K.; et al. Argonaute2 mediates compensatory expansion of the pancreatic beta cell. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viesti, A.C.R.; Salgado, W., Jr.; Pretti da Cunha Tirapelli, D.; dos Santos, J.S. The expression of LEP, LEPR, IGF1 and IL10 in obesity and the relationship with microRNAs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.J.; Yang, M.H.; Cao, G.; Lu, J.T.; Luo, J.; Dai, L.J.; Huang, K.M.; Zhang, L.I. Protective effect of microRNA-138 against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, A.; Kim, M.J.; Nepal, S.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, J.A.; Sohn, D.H.; Song, K.; Lee, S.H.; Park, W.S.; Jeong, B.S.; et al. Globular adiponectin modulates expression of programmed cell death 4 and miR-21 in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.M.; Pang, L.X.; Ji, C.B.; Wang, J.Q.; Lin, N.; Chen, J.T.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Huang, F.Y.; Zhou, Y.H.; et al. Obesity-associated miR-148a is regulated by cytokines and adipokines via a transcriptional mechanism. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 5707–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rius, B.; Titos, E.; Moran-Salvador, E.; Lopez-Vicario, C.; Garcia-Alonso, V.; Gonzalez-Periz, A.; Arroyo, V.; Claria, J. Resolvin D1 primes the resolution process initiated by calorie restriction in obesity-induced steatohepatitis. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Gu, N.; Chen, L.; Zhu, L.; Yang, L.; Pang, L.; Guo, X.; Ji, C.; et al. IL-6 and TNF-alpha induced obesity-related inflammatory response through transcriptional regulation of miR-146b. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nteeba, J.; Ortinau, L.C.; Perfield, J.W.; Keating, A.F. Diet-Induced Obesity Alters Immune Cell Infiltration and Expression of Inflammatory Cytokine Genes in Mouse Ovarian and Peri-Ovarian Adipose Depot Tissues. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Bartolini, D.; Mensa, E.; Torquato, P.; Albertini, M.C.; Olivieri, F.; Testa, R.; Rossi, S.; Piroddi, M.; Cruciani, G.; et al. Physical Activity Modulates the Overexpression of the Inflammatory miR-146a-5p in Obese Patients. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Jimenez-Vacas, J.M.; Saez-Martinez, P.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Lopez-Canovas, J.L.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Herrera-Martinez, A.D.; Garcia-Bermejo, L.; Macias-Gonzalez, M.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; et al. Influence of Obesity in the miRNome: miR-4454, a Key Regulator of Insulin Response Via Splicing Modulation in Prostate. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e469–e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurylowicz, A.; Wicik, Z.; Owczarz, M.; Jonas, M.I.; Kotlarek, M.; Swierniak, M.; Lisik, W.; Jonas, M.; Noszczyk, B.; Puzianowska-Kuznicka, M. NGS Reveals Molecular Pathways Affected by Obesity and Weight Loss-Related Changes in miRNA Levels in Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oger, F.; Gheeraert, C.; Mogilenko, D.; Benomar, Y.; Molendi-Coste, O.; Bouchaert, E.; Caron, S.; Dombrowicz, D.; Pattou, F.; Duez, H.; et al. Cell-specific dysregulation of microRNA expression in obese white adipose tissue. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 2821–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, I.; Chatterjee, A. Recent Advances in miRNA Delivery Systems. Methods Protoc. 2021, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasar, S.; Salerno, E.; Yuan, Y.; Underbayev, C.; Vollenweider, D.; Laurindo, M.F.; Fernandes, H.; Bonci, D.; Addario, A.; Mazzella, F.; et al. Systemic in vivo lentiviral delivery of miR-15a/16 reduces malignancy in the NZB de novo mouse model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourshafie, N.; Lee, P.R.; Chen, K.L.; Harmison, G.G.; Bott, L.C.; Fischbeck, K.H.; Rinaldi, C. Systemic Delivery of MicroRNA Using Recombinant Adeno-associated Virus Serotype 9 to Treat Neuromuscular Diseases in Rodents. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 138, e55724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gemeinhart, R.A. Progress in microRNA delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 962–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Liao, J.Z.; Xiang, G.Y.; Zhao, P.X.; Ye, F.; Zhao, Q.; He, X.X. MiR-101 and doxorubicin codelivered by liposomes suppressing malignant properties of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecot, C.V.; Rupaimoole, R.; Yang, D.; Akbani, R.; Ivan, C.; Lu, C.; Wu, S.; Han, H.D.; Shah, M.Y.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; et al. Tumour angiogenesis regulation by the miR-200 family. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, L.; Zhang, M.; Datta, J.; Xie, X.; Su, T.; Li, H.; Teknos, T.N.; Pan, Q. Lipid-based nanoparticle delivery of Pre-miR-107 inhibits the tumorigenicity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; Manicardi, A.; Casnati, A.; Corradini, R.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A.; Sansone, F. Efficient cell penetration and delivery of peptide nucleic acids by an argininocalix[4]arene. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparello, J.; Lomazzi, M.; Papi, C.; D’Aversa, E.; Sansone, F.; Casnati, A.; Donofrio, G.; Gambari, R.; Finotti, A. Efficient Delivery of MicroRNA and AntimiRNA Molecules Using an Argininocalix[4]arene Macrocycle. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Sanchez, C.; Martinez-Navarrete, G.; Humphreys, L.; Puras, G.; Zarate, J.; Pedraz, J.L.; Fernandez, E. Enduring high-efficiency in vivo transfection of neurons with non-viral magnetoparticles in the rat visual cortex for optogenetic applications. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titze de Almeida, S.S.; Horst, C.H.; Soto-Sanchez, C.; Fernandez, E.; Titze de Almeida, R. Delivery of miRNA-Targeted Oligonucleotides in the Rat Striatum by Magnetofection with Neuromag®. Molecules 2018, 23, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ding, F.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Su, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C. Nanobody-guided targeted delivery of microRNA via nucleic acid nanogel to inhibit the tumor growth. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Tay, C.Y.; Setyawati, M.I.; Chia, S.L.; Lee, D.S.; Leong, D.T. Protecting microRNAs from RNase degradation with steric DNA nanostructures. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Ghosh, A.; Subudhi, U.; Maiti, S. Enhanced and synergistic downregulation of oncogenic miRNAs by self-assembled branched DNA. Nanoscale 2017, 10, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Guo, T.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Kang, J.; Ma, W.; Nian, Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. Bacteria-derived outer membrane vesicles engineered with over-expressed pre-miRNA as delivery nanocarriers for cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2022, 45, 102585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, J. Exosome based miRNA delivery strategy for disease treatment. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginter, E.; Simko, V. Brown fat tissue—A potential target to combat obesity. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2012, 113, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Levy, J.D.; Zhang, Y.; Frontini, A.; Kolodin, D.P.; Svensson, K.J.; Lo, J.C.; Zeng, X.; Ye, L.; Khandekar, M.J.; et al. Ablation of PRDM16 and beige adipose causes metabolic dysfunction and a subcutaneous to visceral fat switch. Cell 2014, 156, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goody, D.; Pfeifer, A. MicroRNAs in brown and beige fat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Ikeda, K.; Tanabe, Y.; Thomson, E.A.; Yoneshiro, T.; Oguri, Y.; Ferro, M.D.; Poon, A.S.Y.; Kajimura, S. Wireless optogenetics protects against obesity via stimulation of non-canonical fat thermogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazak, L.; Chouchani, E.T.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Erickson, B.K.; Shinoda, K.; Cohen, P.; Vetrivelan, R.; Lu, G.Z.; Laznik-Bogoslavski, D.; Hasenfuss, S.C.; et al. A creatine-driven substrate cycle enhances energy expenditure and thermogenesis in beige fat. Cell 2015, 163, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanelli, S.M.; MacDougald, O.A. Viral and Nonviral Transfer of Genetic Materials to Adipose Tissues: Toward a Gold Standard Approach. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2581–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Buyel, J.J.; Hanssen, M.J.; Siegel, F.; Pan, R.; Naumann, J.; Schell, M.; van der Lans, A.; Schlein, C.; Froehlich, H.; et al. Exosomal microRNA miR-92a concentration in serum reflects human brown fat activity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomou, T.; Mori, M.A.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Konishi, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Wolfrum, C.; Rao, T.N.; Winnay, J.N.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Grinspoon, S.K.; et al. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature 2017, 542, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| microRNA | Cell/Tissue | Effect of Thermogenesis | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-30b/c | WAT/primary adipocytes | Positive | [29,30] |
| miR-32 | BAT | Positive | [34] |
| miR-203 | WAT/brown adipocytes | Positive | [41,42] |
| miR-337-3p | BAT/brown adipocytes | Positive | [45] |
| miR17-92 | BAT | Positive | [47] |
| miR-124-3p | Brown adipocytes | Positive | [48] |
| miR-182-5p | WAT/primary adipocytes | Positive | [43,44] |
| miR-455 | WAT/primary adipocytes | Positive | [36] |
| miR-133 | BAT/WAT | Negative | [50,52,53] |
| miR-327 | WAT | Negative | [64] |
| miR-149-3p | WAT | Negative | [66] |
| miR-199a/214 | Primary adipocytes | Negative | [43] |
| miR-494-3p | WAT/primary adipocytes | Negative | [65] |
| miR-191-5p | WAT | Negative | [68] |
| miR-27 | BAT/WAT | Negative | [56,57] |
| miR-155 | WAT/primary adipocytes | Negative | [59,60,61,62] |
| miR-34a | BAT/WAT | Negative | [55] |
| miR-23b-5p | Brown adipocytes | Negative | [67] |
| miR-22 | BAT/WAT/adipocytes | Controversial | [70,71,72] |
| miR-33 | BAT/WAT | Controversial | [74,75] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Gilani, A.; Yi, Q.; Tang, L. MicroRNAs as Mediators of Adipose Thermogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Obesity. Biology 2022, 11, 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111657
Ma L, Gilani A, Yi Q, Tang L. MicroRNAs as Mediators of Adipose Thermogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Obesity. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111657
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Lunkun, Ankit Gilani, Qian Yi, and Liling Tang. 2022. "MicroRNAs as Mediators of Adipose Thermogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Obesity" Biology 11, no. 11: 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111657
APA StyleMa, L., Gilani, A., Yi, Q., & Tang, L. (2022). MicroRNAs as Mediators of Adipose Thermogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Obesity. Biology, 11(11), 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111657





