Acute Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Contralateral Plantar Flexor Neuromuscular Function
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Approach
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.3.1. Torque Recordings
2.3.2. EMG Recordings
2.3.3. Tibial Nerve Stimulation
2.3.4. NMES
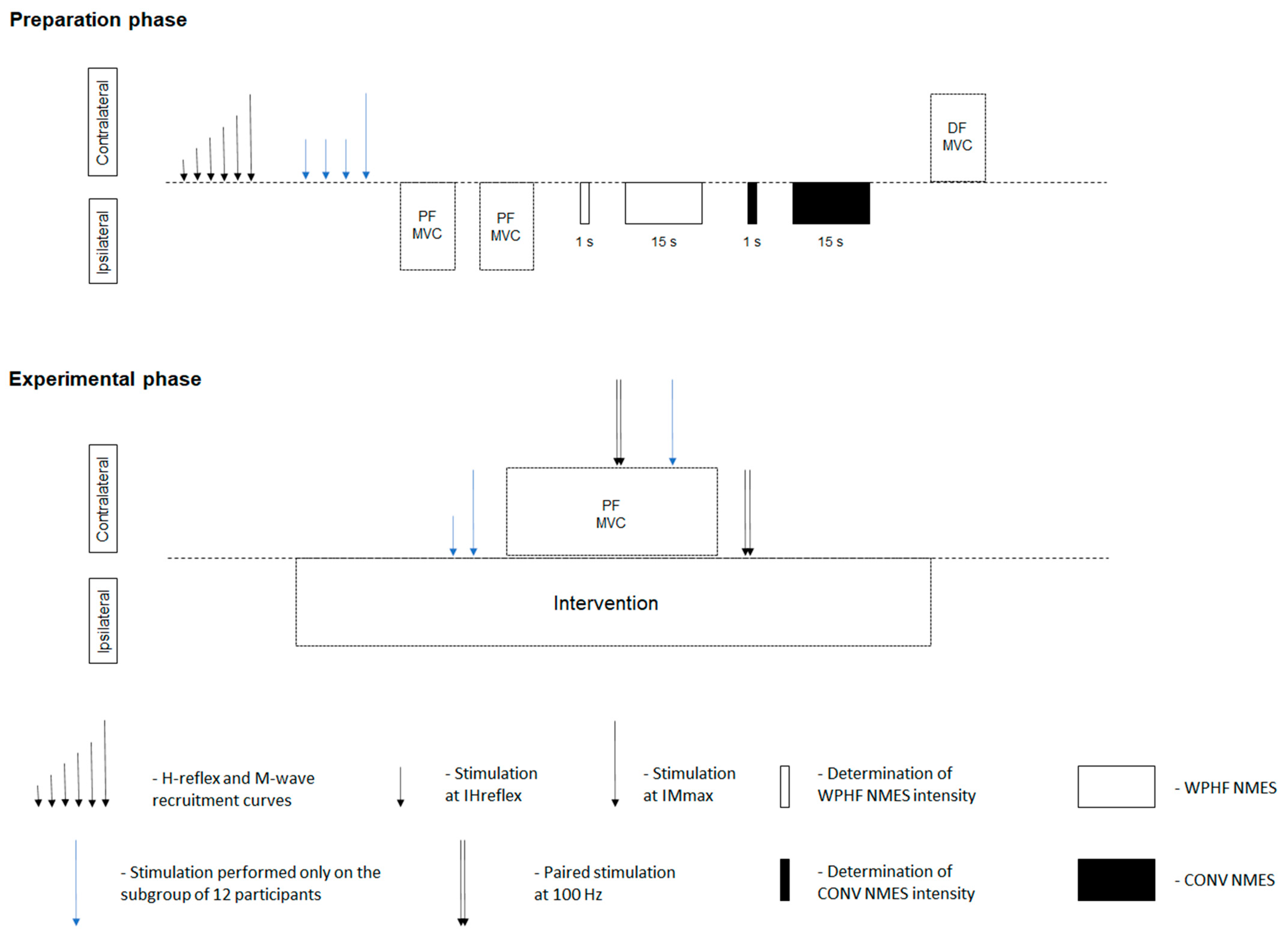
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.4.1. Preparation Phase
2.4.2. Experimental Phase
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
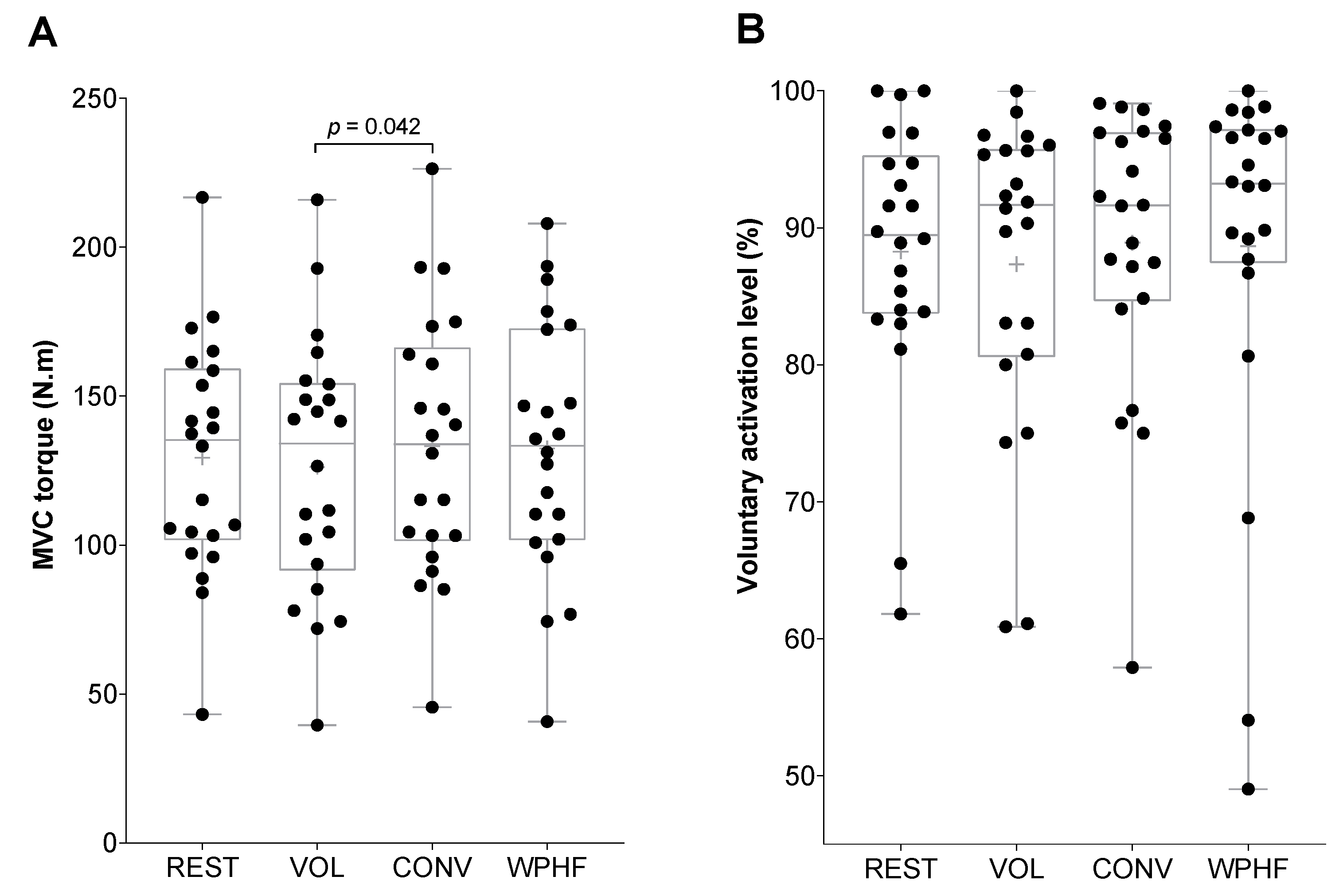
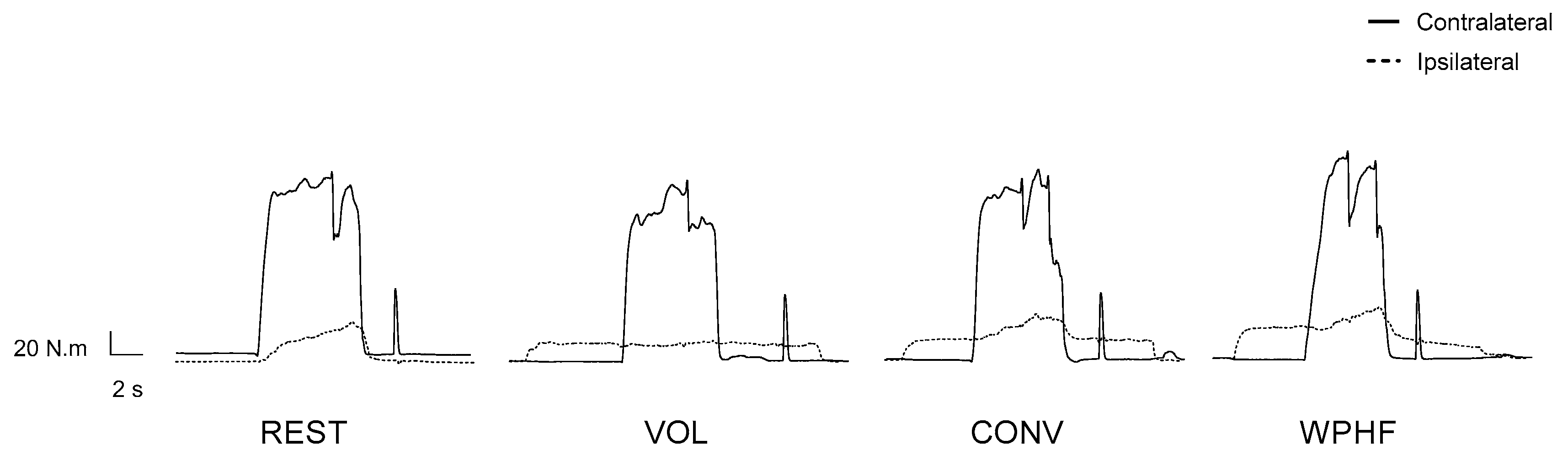
3. Results
3.1. Contralateral Side
3.2. Ipsilateral Side
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hultman, E.; Sjoholm, H.; Jaderholm-Ek, I.; Krynicki, J. Evaluation of methods for electrical stimulation of human skeletal muscle in situ. Pflug. Arch. 1983, 398, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.D.; Enoka, R.M. Maximum bilateral contractions are modified by neurally mediated interlimb effects. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 70, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattagni, T.; Lepers, R.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on contralateral quadriceps function. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 38, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minetto, M.A.; Botter, A.; Gamerro, G.; Varvello, I.; Massazza, G.; Bellomo, R.G.; Maffiuletti, N.A.; Saggini, R. Contralateral effect of short-duration unilateral neuromuscular electrical stimulation and focal vibration in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 54, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weavil, J.C.; Sidhu, S.K.; Mangum, T.S.; Richardson, R.S.; Amann, M. Intensity-dependent alterations in the excitability of cortical and spinal projections to the knee extensors during isometric and locomotor exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 308, R998–R1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, B.; Ashby, P. Corticospinal projections to lower limb motoneurons in man. Exp. Brain Res. 1992, 89, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oya, T.; Hoffman, B.W.; Cresswell, A.G. Corticospinal-evoked responses in lower limb muscles during voluntary contractions at varying strengths. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, E.R.; Klakowicz, P.M.; Collins, D.F. Wide-pulse-width, high-frequency neuromuscular stimulation: Implications for functional electrical stimulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 101, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.F. Central contributions to contractions evoked by tetanic neuromuscular electrical stimulation. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2007, 35, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.; Stegmuller, J.; Blazevich, A.J.; Crettaz von Roten, F.; Kayser, B.; Neyroud, D.; Place, N. Modulation of torque evoked by wide-pulse, high-frequency neuromuscular electrical stimulation and the potential implications for rehabilitation and training. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, C.J.; Butler, J.E.; Taylor, J.L.; Gandevia, S.C. Testing the excitability of human motoneurons. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyroud, D.; Grospretre, S.; Gondin, J.; Kayser, B.; Place, N. Test-retest reliability of wide-pulse high-frequency neuromuscular electrical stimulation evoked force. Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, E70–E77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyroud, D.; Gonzalez, M.; Mueller, S.; Agostino, D.; Grospretre, S.; Maffiuletti, N.A.; Kayser, B.; Place, N. Neuromuscular adaptations to wide-pulse high-frequency neuromuscular electrical stimulation training. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermens, H.J.; Freriks, B.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Rau, G. Development of recommendations for SEMG sensors and sensor placement procedures. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2000, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegrzyk, J.; Foure, A.; Vilmen, C.; Ghattas, B.; Maffiuletti, N.A.; Mattei, J.P.; Place, N.; Bendahan, D.; Gondin, J. Extra Forces induced by wide-pulse, high-frequency electrical stimulation: Occurrence, magnitude, variability and underlying mechanisms. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeit, L.; Rozand, V.; Millet, G.Y.; Gondin, J.; Maffiuletti, N.A.; Lapole, T. Influence of wide-pulse neuromuscular electrical stimulation frequency and superimposed tendon vibration on occurrence and magnitude of extra torque. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 131, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strojnik, V.; Komi, P.V. Fatigue after submaximal intensive stretch-shortening cycle exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, N.; Duclay, J.; Lepers, R.; Martin, A. Unchanged H-reflex during a sustained isometric submaximal plantar flexion performed with an EMG biofeedback. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19, e395–e402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellis, E.; Baltzopoulos, V. The effects of normalization method on antagonistic activity patterns during eccentric and concentric isokinetic knee extension and flexion. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1996, 6, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, C.S.; Gregory, C.M.; Dean, J.C. Motor unit recruitment during neuromuscular electrical stimulation: A critical appraisal. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderthommen, M.; Duteil, S.; Wary, C.; Raynaud, J.S.; Leroy-Willig, A.; Crielaard, J.M.; Carlier, P.G. A comparison of voluntary and electrically induced contractions by interleaved 1H- and 31P-NMRS in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theurel, J.; Lepers, R.; Pardon, L.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Differences in cardiorespiratory and neuromuscular responses between voluntary and stimulated contractions of the quadriceps femoris muscle. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2007, 157, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubeau, M.; Yann, L.E.F.; Duhamel, G.; Wegrzyk, J.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Vilmen, C.; Cozzone, P.J.; Mattei, J.P.; Bendahan, D.; Gondin, J. Localized metabolic and t2 changes induced by voluntary and evoked contractions. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, A.J.; Clair, J.M.; Lagerquist, O.; Mang, C.S.; Okuma, Y.; Collins, D.F. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation: Implications of the electrically evoked sensory volley. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 2409–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dideriksen, J.L.; Muceli, S.; Dosen, S.; Laine, C.M.; Farina, D. Physiological recruitment of motor units by high-frequency electrical stimulation of afferent pathways. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, D.F.; Burke, D.; Gandevia, S.C. Large involuntary forces consistent with plateau-like behavior of human motoneurons. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 4059–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.F.; Burke, D.; Gandevia, S.C. Sustained contractions produced by plateau-like behaviour in human motoneurones. J. Physiol. 2002, 538, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, M.; Masugi, Y.; Sasaki, A.; Sayenko, D.G.; Nakazawa, K. On the reflex mechanisms of cervical transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation in human subjects. J. Neurophysiol. 2019, 121, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Sasaki, A.; Yokoyama, H.; Milosevic, M.; Nakazawa, K. Effects of neuromuscular electrical stimulation and voluntary commands on the spinal reflex excitability of remote limb muscles. Exp. Brain Res. 2019, 237, 3195–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonca, G.V.; Vila-Cha, C.; Teodosio, C.; Goncalves, A.D.; Freitas, S.R.; Mil-Homens, P.; Pezarat-Correia, P. Contralateral training effects of low-intensity blood-flow restricted and high-intensity unilateral resistance training. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 2305–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.C.; Yates, L.M.; Collins, D.F. Turning on the central contribution to contractions evoked by neuromuscular electrical stimulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 103, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cresswell, A.G.; Loscher, W.N.; Thorstensson, A. Influence of gastrocnemius muscle length on triceps surae torque development and electromyographic activity in man. Exp. Brain Res. 1995, 105, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donnelly, C.; Popesco, T.; Rossé, J.; Kayser, B.; Maffiuletti, N.A.; Place, N. Acute Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Contralateral Plantar Flexor Neuromuscular Function. Biology 2022, 11, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111655
Donnelly C, Popesco T, Rossé J, Kayser B, Maffiuletti NA, Place N. Acute Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Contralateral Plantar Flexor Neuromuscular Function. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111655
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonnelly, Chris, Timothée Popesco, Julie Rossé, Bengt Kayser, Nicola A. Maffiuletti, and Nicolas Place. 2022. "Acute Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Contralateral Plantar Flexor Neuromuscular Function" Biology 11, no. 11: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111655
APA StyleDonnelly, C., Popesco, T., Rossé, J., Kayser, B., Maffiuletti, N. A., & Place, N. (2022). Acute Effects of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Contralateral Plantar Flexor Neuromuscular Function. Biology, 11(11), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111655






