Neurophysiological Response of Adults with Cerebral Palsy during Inclusive Dance with Wheelchair
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
- (1)
- At baseline for two minutes with open eyes.
- (2)
- While performing inclusive dance choreography with an occupational therapist and a kinesiologist. Under this condition, the specialist was next to the chair, in parallel and facing the front, so that constant visual contact was established with the patients. The specialists moved the chair, accompanying them in a dance that includes linear movements and turns. In addition, a ribbon tied to the chair was included for certain moments of the dance in which the professionals moved away from the chairs and later pulled it to continue with spins.
- (3)
- While listening to music for two minutes. The selected songs in both conditions (under choreography and listening to music conditions) were not the same in order to avoid mental associations with the choreography. Nevertheless, a song of the same artist was selected to maintain the tone and style (114 beats per minutes for the choreographed song and 104 beats per minutes for the music condition). The order of inclusive dance and listening to music was randomized. All participants underwent the same choreography and listened to the same music.
2.3. Tests and Instruments
2.4. Statistical Analysis
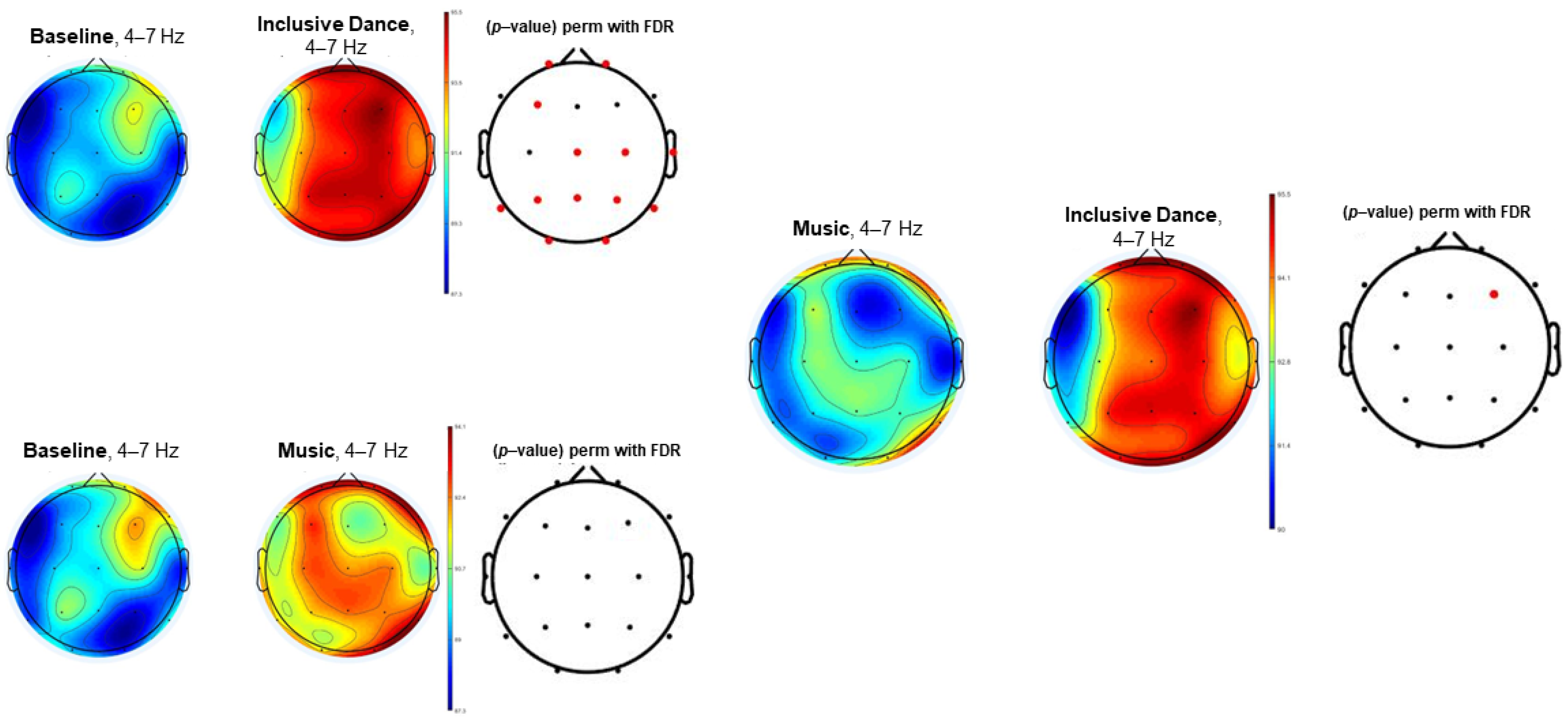
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bax, M.; Goldstein, M.; Rosenbaum, P.; Leviton, A.; Paneth, N.; Dan, B.; Jacobsson, B.; Damiano, D. Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2005, 47, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Guo, C.; Zheng, X. Children with motor impairment related to cerebral palsy: Prevalence, severity and concurrent impairments in China. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2017, 53, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odding, E.; Roebroeck, M.E.; Stam, H.J. The epidemiology of cerebral palsy: Incidence, impairments and risk factors. Disabil. Rehabil. 2006, 28, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.M.; Meehan, E.M.; Arnup, S.J.; Reddihough, D.S. Intellectual disability in cerebral palsy: A population-based retrospective study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, R.C.; Becher, J.G.; Ketelaar, M.; Smits, D.-W.; Voorman, J.M.; Tan, S.S.; Reinders-Messelink, H.A.; Dallmeijer, A.J. Developmental trajectories of daily activities in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e915–e923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, L.B.; Rose, S.E.; Boyd, R.N. Rehabilitation and neuroplasticity in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Hallett, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Safety of TMS Consensus Group. Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 2008–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jochumsen, M.; Shafique, M.; Hassan, A.; Niazi, I.K. Movement intention detection in adolescents with cerebral palsy from single-trial EEG. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 066030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matusz, P.J.; Key, A.P.; Gogliotti, S.; Pearson, J.; Auld, M.L.; Murray, M.M.; Maitre, N.L. Somatosensory plasticity in pediatric cerebral palsy following constraint-induced movement therapy. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 1891978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Ortiz, C.; Gladden, K.; Deon, L.; Schmidt, J.; Girolami, G.; Gaebler-Spira, D. Dance program for physical rehabilitation and participation in children with cerebral palsy. Arts Health 2012, 4, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Machado, L.; Azevedo-Santos, I.; DeSantana, J.M. Dance improves functionality and psychosocial adjustment in cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Pazi, H.; Aran, A.; Pandyan, A.; Gelkop, N.; Ginsberg, G.; Pollak, Y.; Elnatan, D. Auditory stimulation improves motor function and caretaker burden in children with cerebral palsy-a randomized double blind study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, C.M.; Baker, F.A. The role of music therapy in physical rehabilitation: A systematic literature review. Nord. J. Music. Ther. 2011, 20, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bläsing, B.; Calvo-Merino, B.; Cross, E.S.; Jola, C.; Honisch, J.; Stevens, C.J. Neurocognitive control in dance perception and performance. Acta Psychol. 2012, 139, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, K.; Satonaka, A.; Terada, Y.; Suzuki, N. Training effects of wheelchair dance on aerobic fitness in bedridden individuals with severe athetospastic cerebral palsy rated to GMFCS level V. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaronnik, N. Musical Chairs: Using Wheelchair Ballroom Dance in Disability Education. JAMA 2018, 320, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J. Dancing wheelchairs: An innovative way to teach medical students about disability. Am. J. Med. 2011, 124, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palisano, R.; Rosenbaum, P.; Walter, S.; Russell, D.; Wood, E.; Galuppi, B. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1997, 39, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.J.; Rosenbaum, P.; Wright, M.; Avery, L.M. Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM-66 & GMFM-88) Users Manual; Mac Keith Press: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, W. Sensory Profile; Psychological Corporation San Antonio: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1999; Volume 555. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, D.N.; Miller, L.J.; Shyu, V.; Dunn, W. Development and validation of the short sensory profile. Sens. Profile Man. 1999, 62, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Haley, S.M.; New England Medical Center Hospital, P.R.G. Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory (PEDI): Development, Standardization and Administration Manual; New England Medical Center Hospital, PEDI Research Group: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Collado-Mateo, D.; Adsuar, J.C.; Olivares, P.R.; Cano-Plasencia, R.; Gusi, N. Using a dry electrode EEG device during balance tasks in healthy young-adult males: Test-retest reliability analysis. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2015, 32, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Palmer, J.; Onton, J.; Oostenveld, R.; Makeig, S. Independent EEG sources are dipolar. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pion-Tonachini, L.; Kreutz-Delgado, K.; Makeig, S. The ICLabel dataset of electroencephalographic (EEG) independent component (IC) features. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, C.M.R. Nonparametric vs parametric tests of location in biomedical research. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 147, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López-Ortiz, C.; Gaebler-Spira, D.J.; McKeeman, S.N.; McNish, R.N.; Green, D. Dance and rehabilitation in cerebral palsy: A systematic search and review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulak, W.; Sobaniec, W. Quantitative EEG analysis in children with hemiparetic cerebral palsy. NeuroRehabilitation 2005, 20, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesný, I. EEG study in different forms of cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1963, 5, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sulaiman, A. Electroencephalographic findings in children with cerebral palsy: A study of 151 patients. Funct. Neurol. 2001, 16, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, L.J.; Harrison, L.M.; Evans, A.L.; Stephens, J.A. Patterns of central motor reorganization in hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Brain A J. Neurol. 1993, 116, 1223–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebl, J.; Brücke, C.; Merkl, A.; Bajbouj, M.; Schneider, G.-H.; Kühn, A.A. Processing of emotional stimuli is reflected by modulations of beta band activity in the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex in patients with treatment resistant depression. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2016, 11, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, M.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, S.; Hyun, M.H.; Lee, S.-H. An integrated model of emotional problems, beta power of electroencephalography, and low frequency of heart rate variability after childhood trauma in a non-clinical sample: A path analysis study. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soukhtanlou, M.; Rostami, R.; Salehinejad, M.A.; Lavasani, M.G.; Sharifi, A.; Hekmatmanesh, A. Electrophysiological processing of happiness during conscious and sub-conscious awareness in depression. Neurol. Psychiatry Brain Res. 2019, 33, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherriere, C.; Martel, M.; Sarrasin, A.; Ballaz, L.; Tallet, J.; Lemay, M. Benefits of a Dance Intervention on Balance in Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatrics 2020, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stribling, K.; Christy, J. Creative dance practice improves postural control in a child with cerebral palsy. Pediatric Phys. Ther. 2017, 29, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joung, H.J.; Park, J.; Ahn, J.; Park, M.S.; Lee, Y. Effects of creative dance-based exercise on gait performance in adolescents with cerebral palsy. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2020, 16, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherriere, C.; Robert, M.; Fung, K.; Tremblay Racine, F.; Tallet, J.; Lemay, M. Is there evidence of benefits associated with dancing in children and adults with cerebral palsy? A scoping review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 42, 3395–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimi, N.S.; Mountstephens, J.; Teo, J. EEG-Based Emotion Recognition: A State-of-the-Art Review of Current Trends and Opportunities. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameera, A.; Saidatul, A.; Ibrahim, Z. Analysis of EEG Spectrum Bands Using Power Spectral Density for Pleasure and Displeasure State; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; p. 012030. [Google Scholar]


| Variable | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 37.50 (7.78) |
| PEDI | 69.68 (51.01) |
| SSP | 148.87 (7.69) |
| GMFM-88 | 39.19 (25.96) |
| GMFCS levels | N (Percentage) |
| Level I | 0 (0%) |
| Level II | 9 (56.25%) |
| Level III | 0 (0%) |
| Level IV | 3 (18.75%) |
| Level V | 4 (25%) |
| Sex, N (%) | Females: 11 (68.75%) |
| Males: 5 (31.25%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza-Sánchez, S.; Murillo-Garcia, A.; Leon-Llamas, J.L.; Sánchez-Gómez, J.; Gusi, N.; Villafaina, S. Neurophysiological Response of Adults with Cerebral Palsy during Inclusive Dance with Wheelchair. Biology 2022, 11, 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111546
Mendoza-Sánchez S, Murillo-Garcia A, Leon-Llamas JL, Sánchez-Gómez J, Gusi N, Villafaina S. Neurophysiological Response of Adults with Cerebral Palsy during Inclusive Dance with Wheelchair. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111546
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza-Sánchez, Sandra, Alvaro Murillo-Garcia, Juan Luis Leon-Llamas, Jesús Sánchez-Gómez, Narcis Gusi, and Santos Villafaina. 2022. "Neurophysiological Response of Adults with Cerebral Palsy during Inclusive Dance with Wheelchair" Biology 11, no. 11: 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111546
APA StyleMendoza-Sánchez, S., Murillo-Garcia, A., Leon-Llamas, J. L., Sánchez-Gómez, J., Gusi, N., & Villafaina, S. (2022). Neurophysiological Response of Adults with Cerebral Palsy during Inclusive Dance with Wheelchair. Biology, 11(11), 1546. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111546









