Genome-Wide Analysis of the Almond AP2/ERF Superfamily and Its Functional Prediction during Dormancy in Response to Freezing Stress
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening of AP2/ERF Gene Family Members
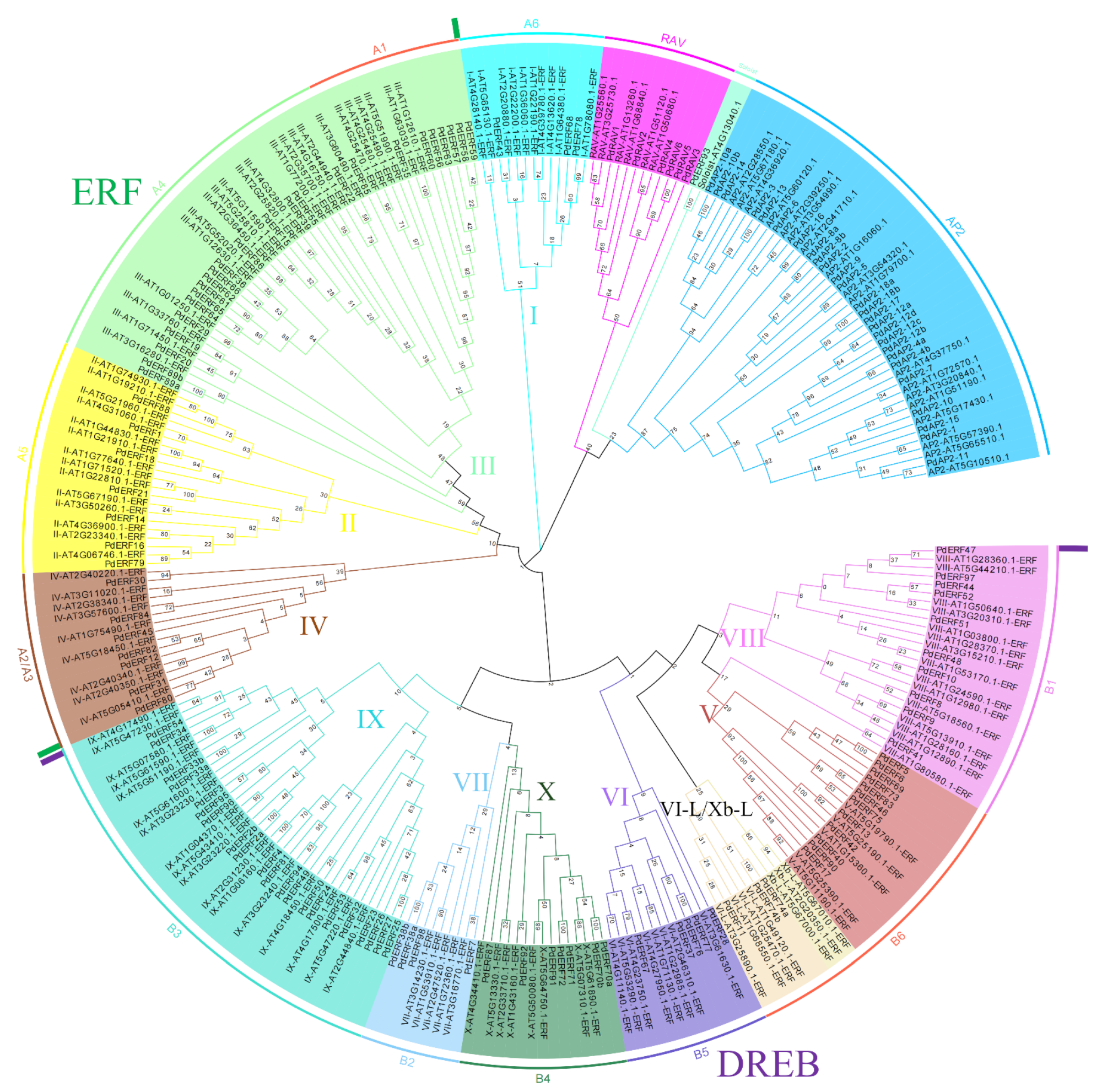
2.2. Phylogenetic Tree Construction and Classification
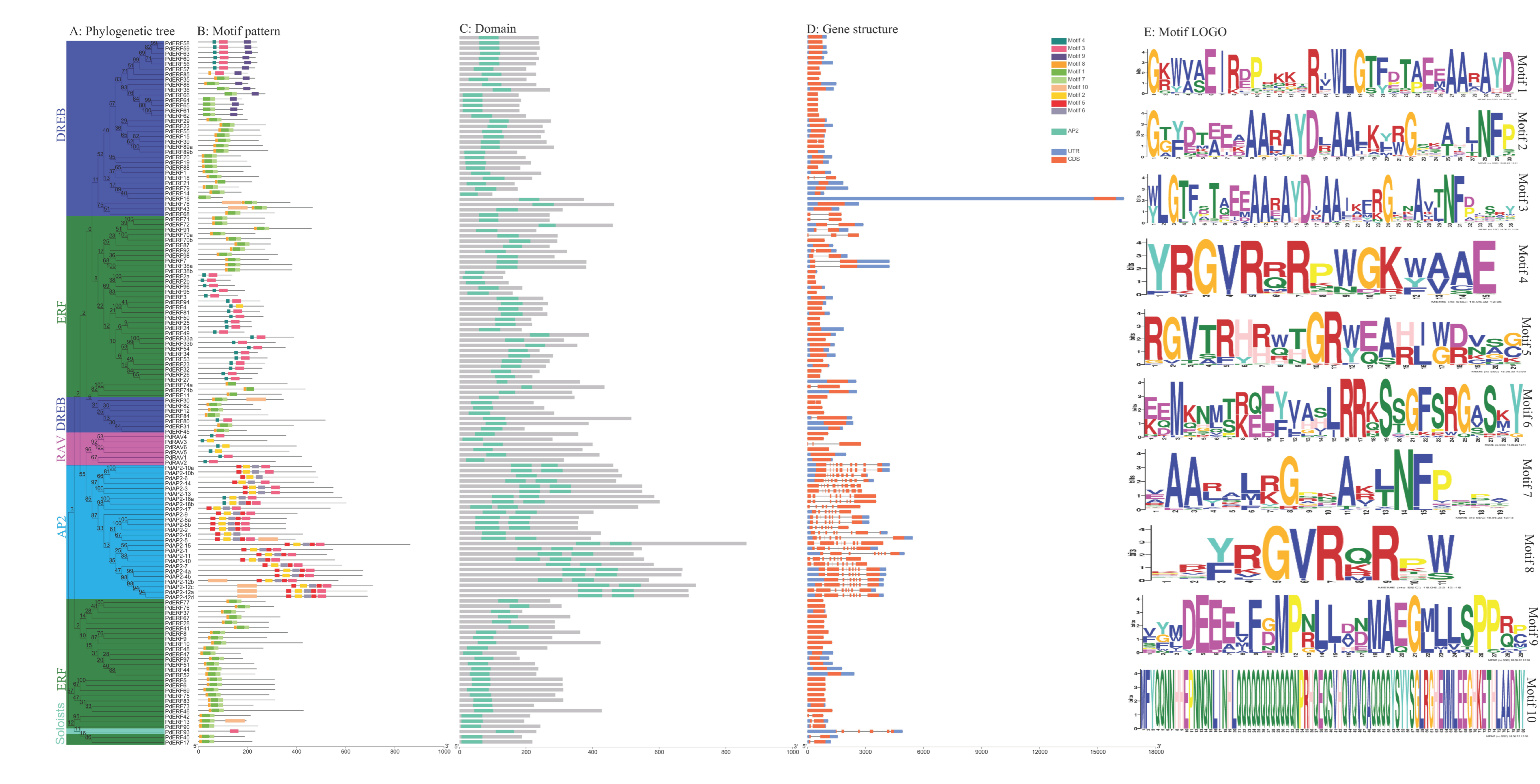
2.3. Analysis of the Motifs and Gene Structures of PdAP2/ERF Family Members
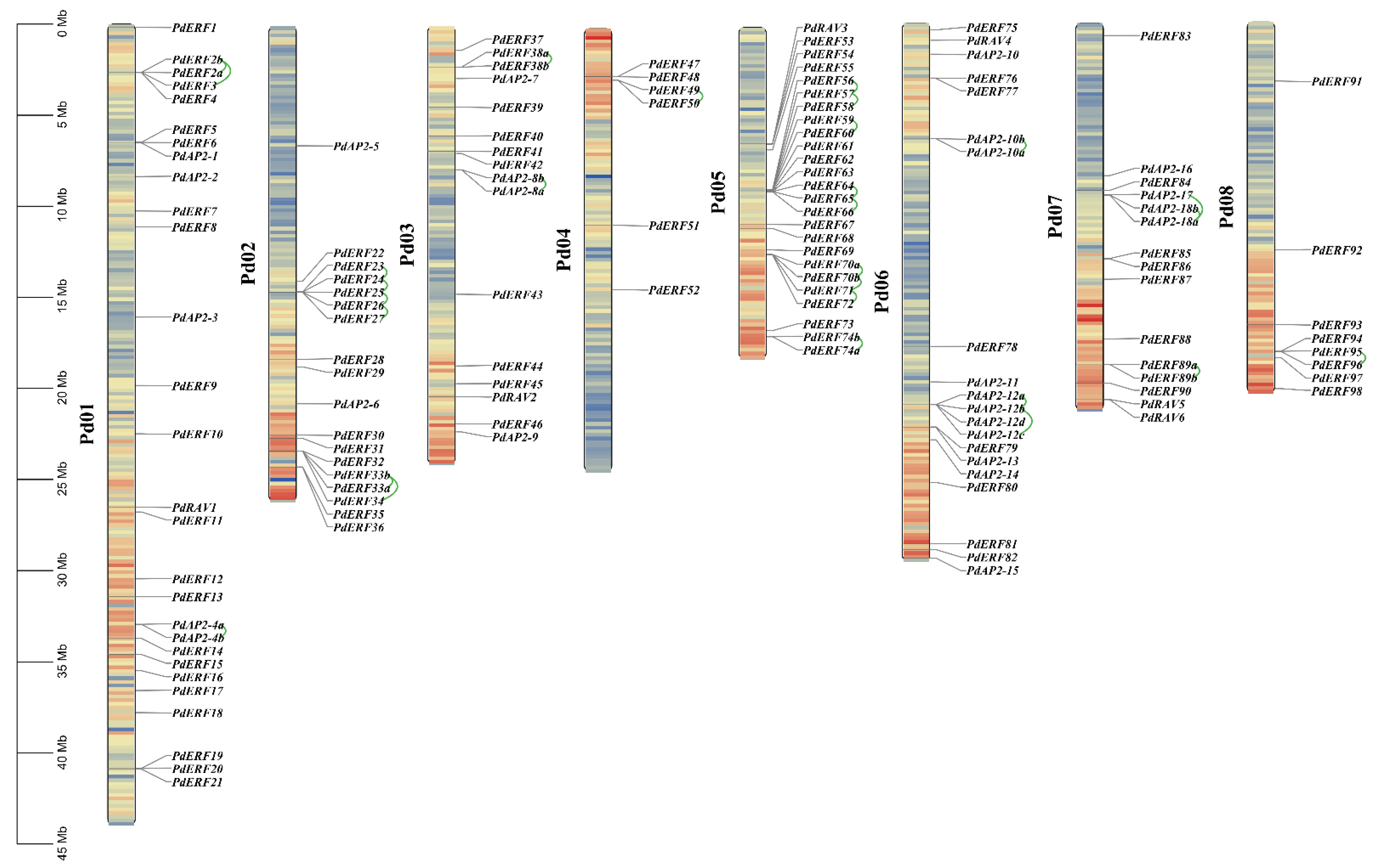
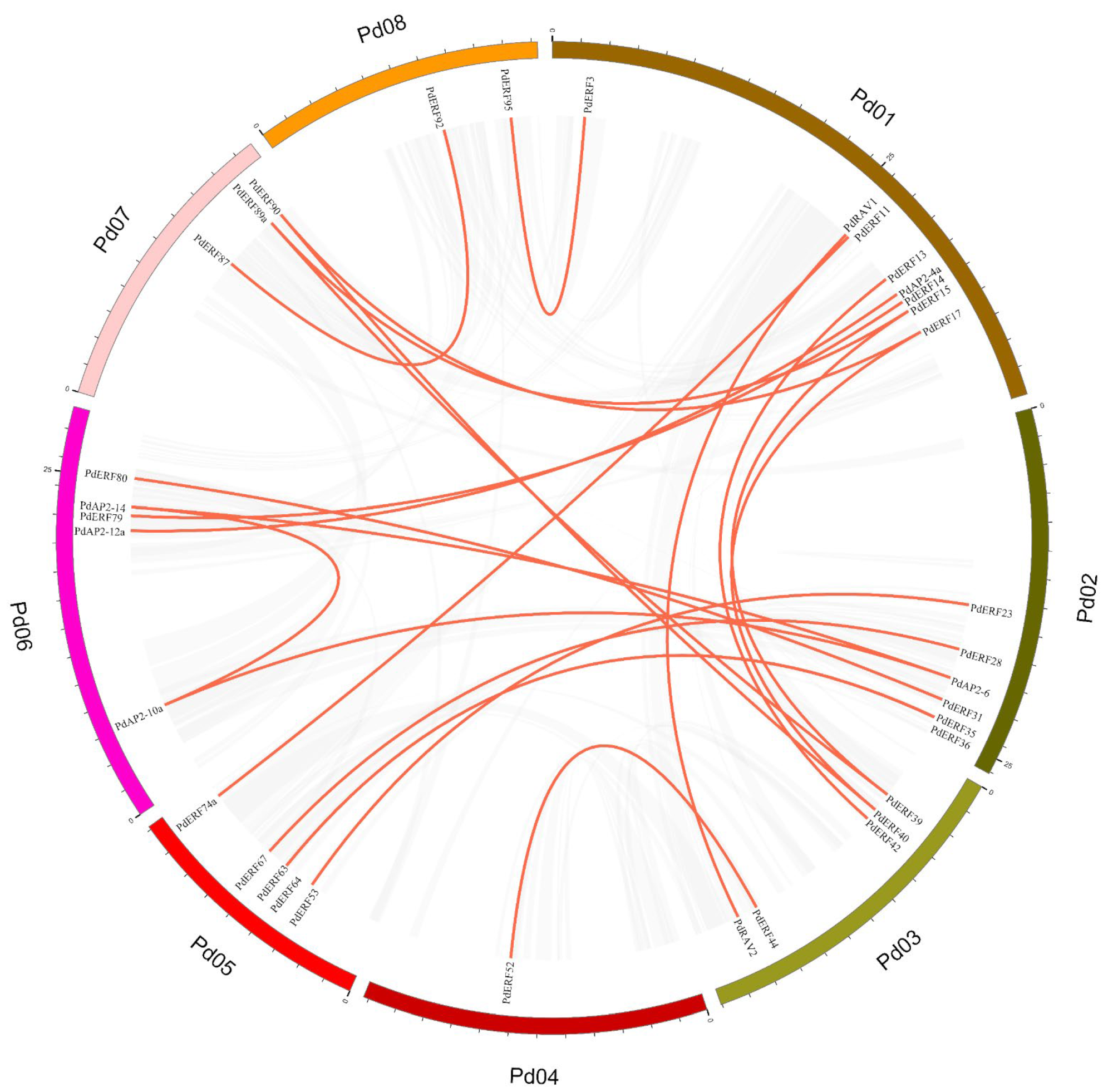
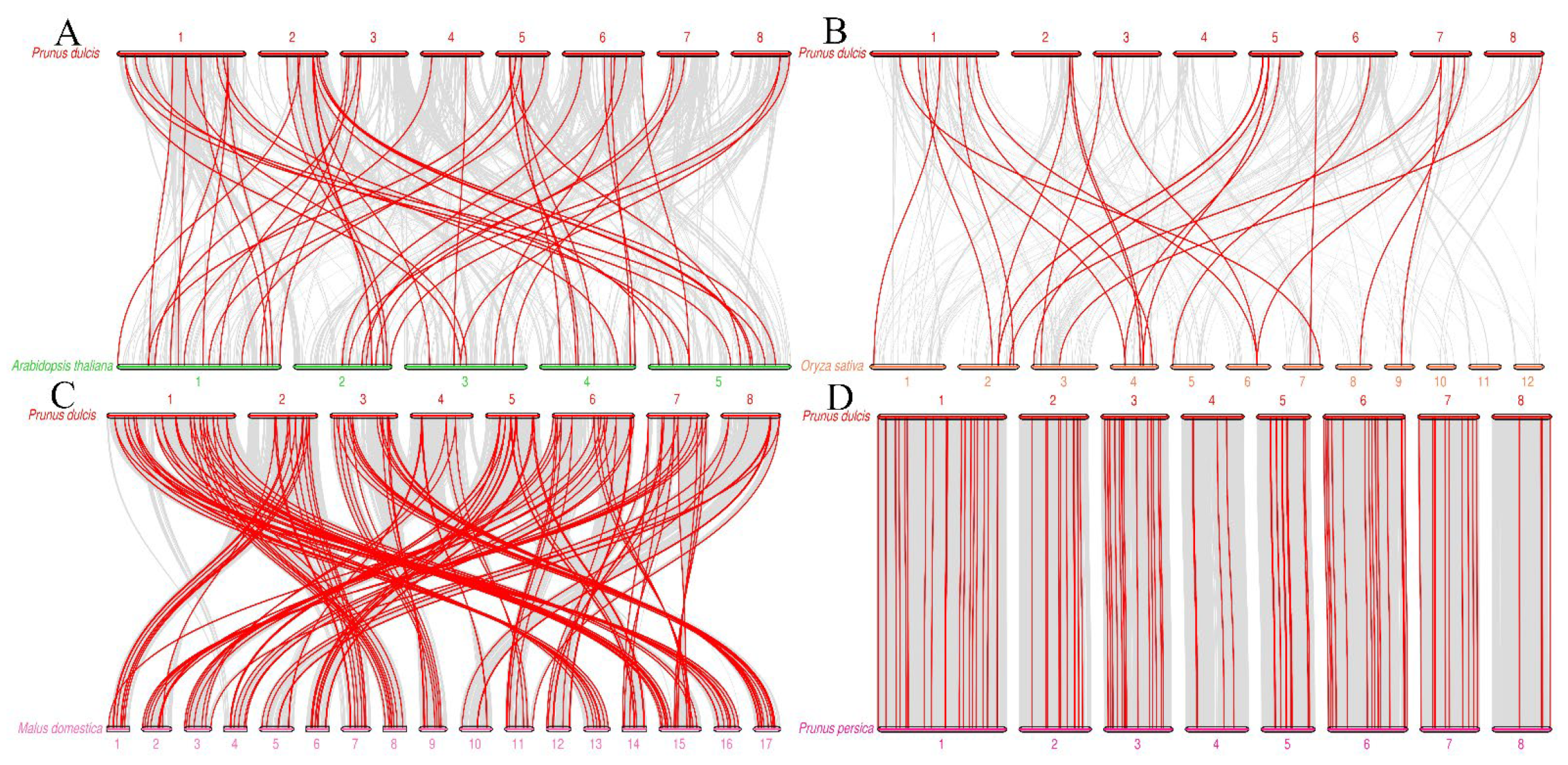
2.4. Chromosome Location, Collinearity, and Ka/Ks Value Analysis of the PdAP2/ERF Genes
2.5. Analysis of cis-Elements in PdAP2/ERF Genes
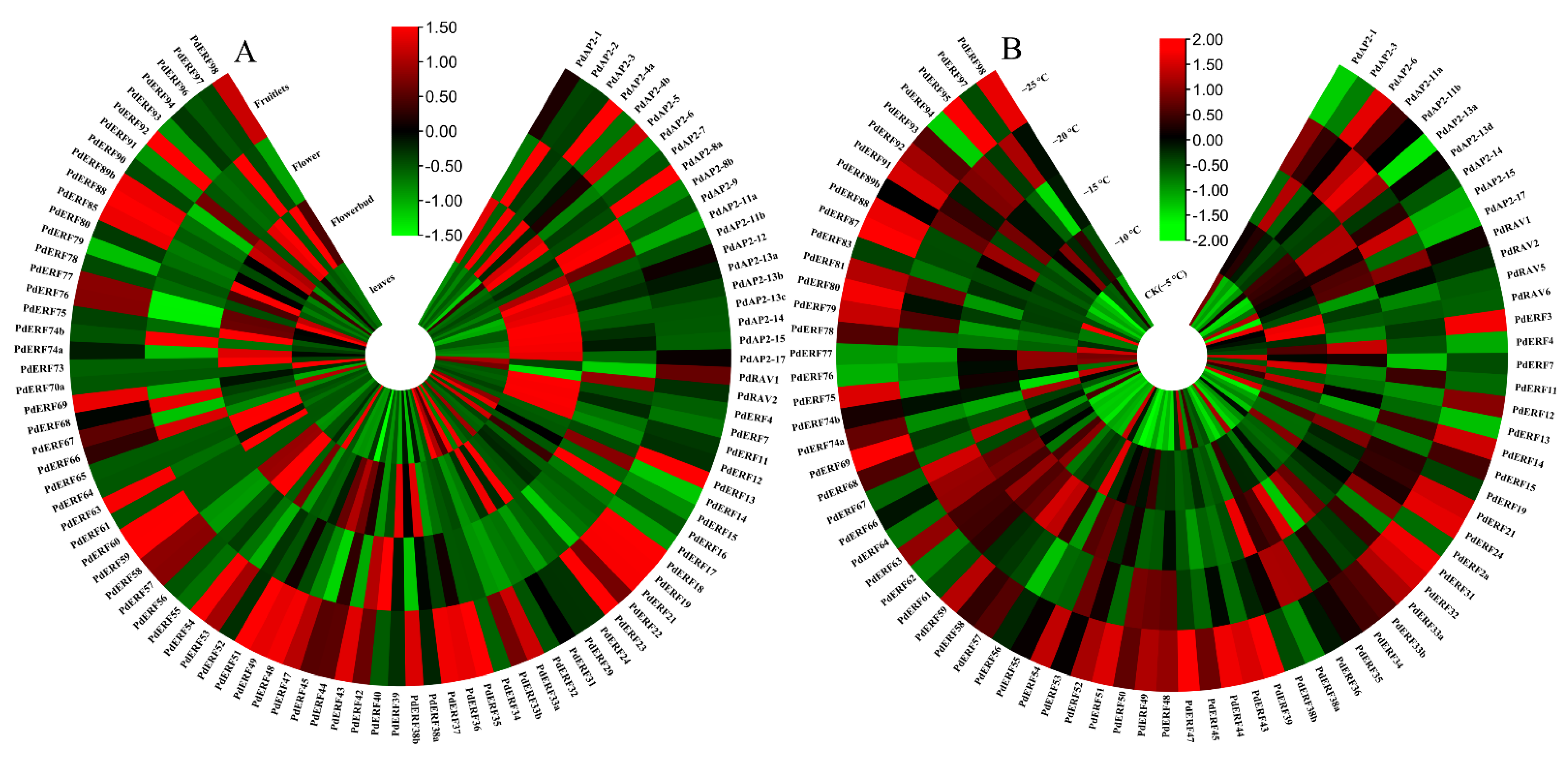
2.6. Expression Pattern Analysis
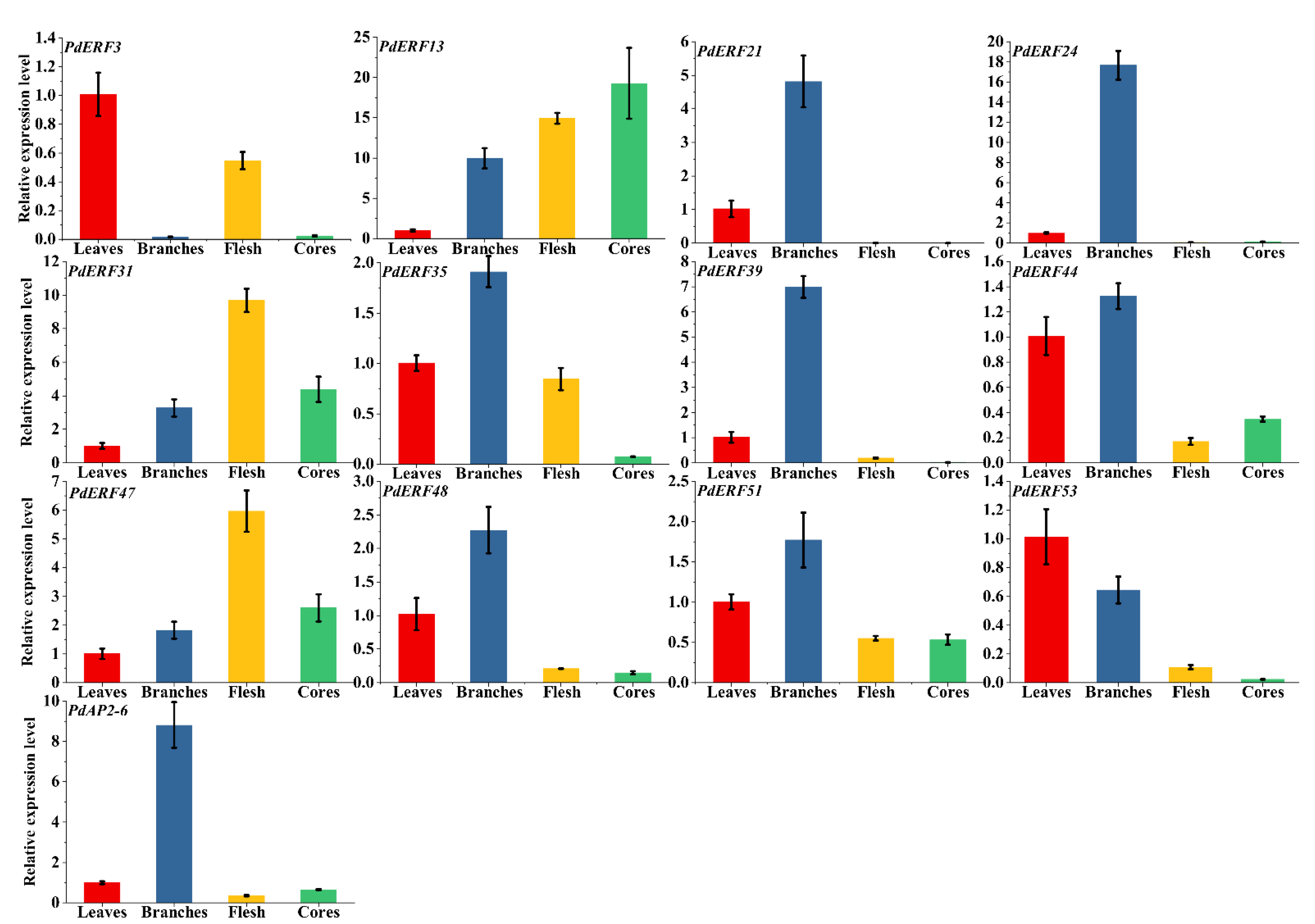
2.7. Material Handling and qRT–PCR Analysis
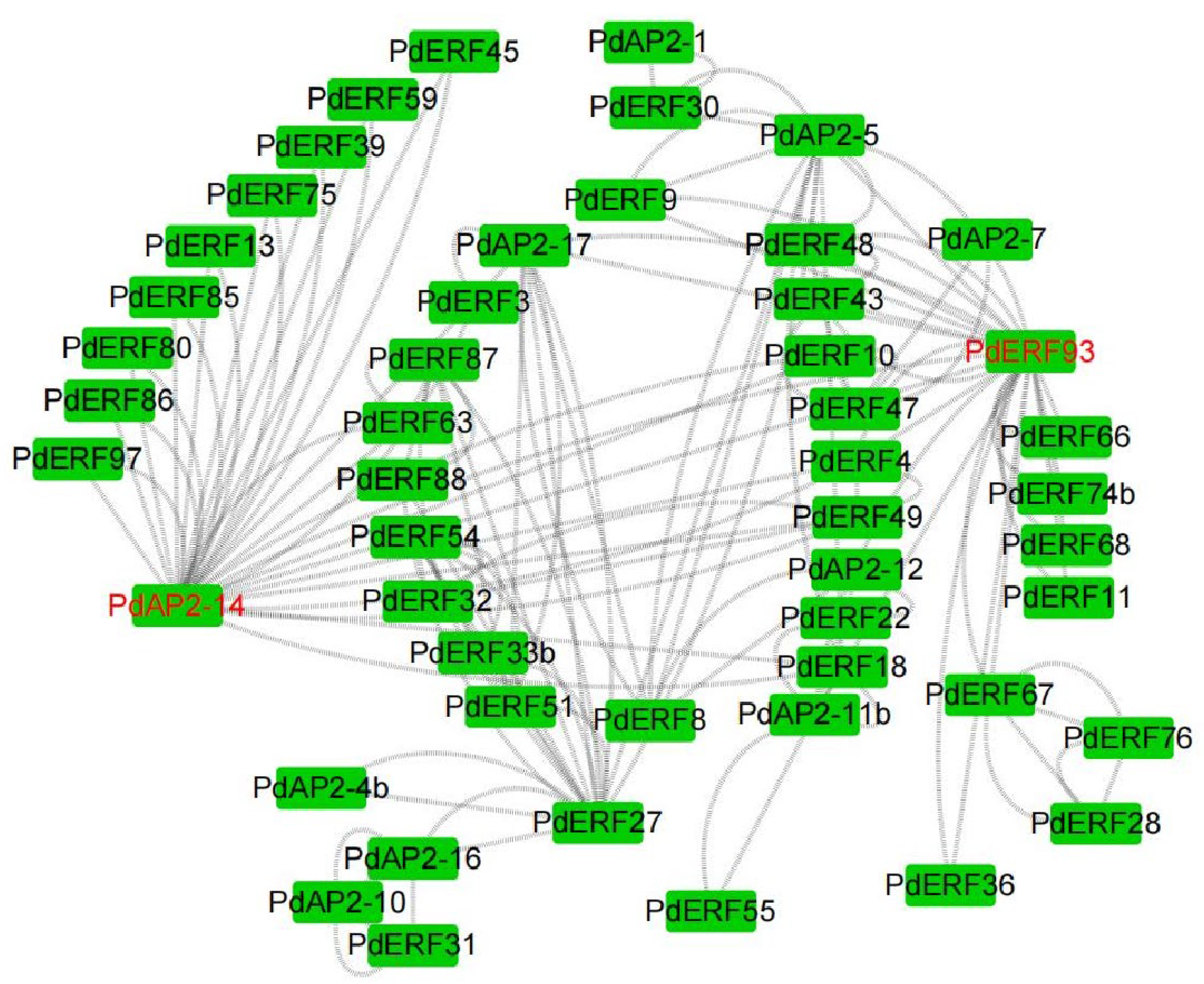
2.8. Construction of the PdAP2/ERF Protein Interaction Network
2.9. Identification and Annotation of Target Genes of PdAP2/ERF Genes
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Characteristics of PdAP2/ERF Family Members
3.2. Multiple Sequence Alignments and Phylogenetic Relationships of the PdAP2/ERF Family Members
3.3. Motif and Gene Structure Compositions of PdAP2/ERF Family Members
3.4. Gene Mapping, Collinearity, and Ka/Ks Values of PdAP2/ERF Family Members
3.5. Upstream cis-Regulatory Elements
3.6. Expression Pattern Analysis of the PdAP2/ERF Family Members
3.7. PdAP2/ERF Gene Quantitative qRT–PCR Analysis
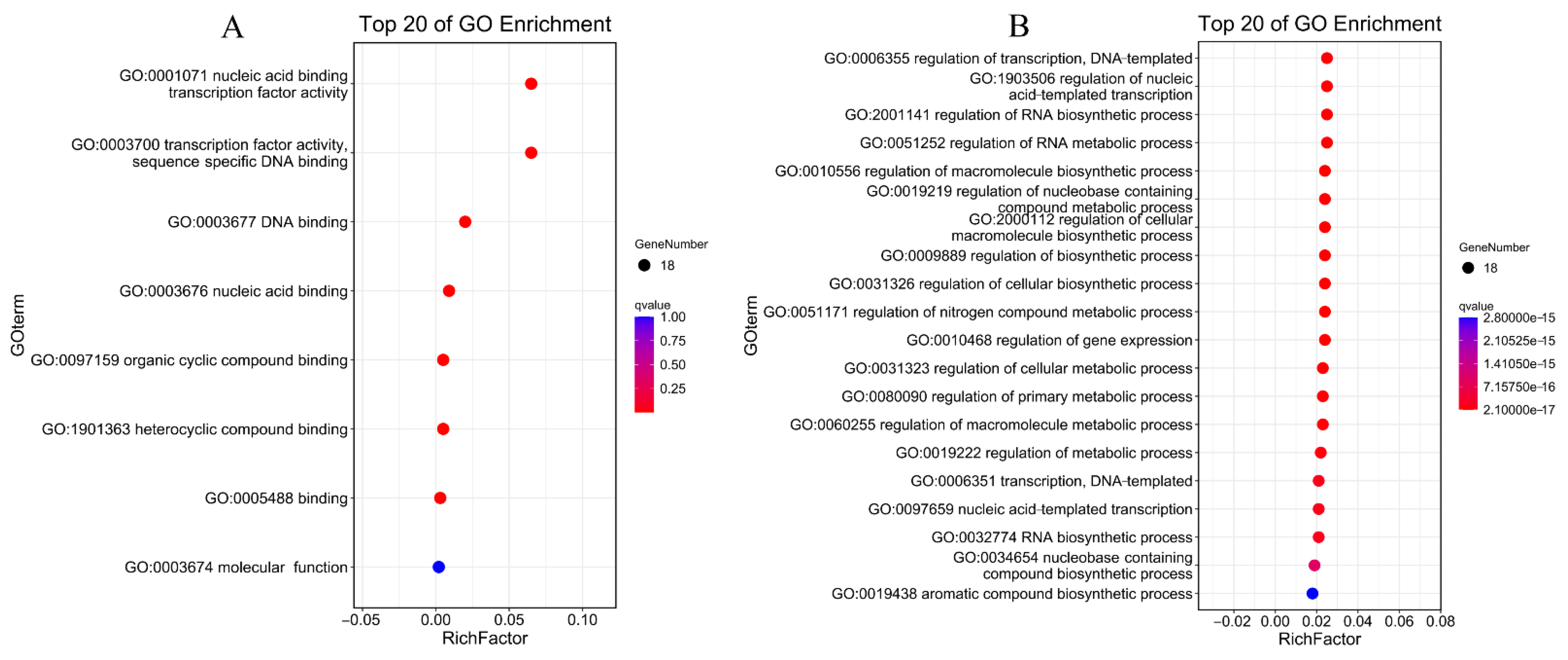
3.8. Protein Interactions and GO Annotations of PdAP2/ERF Members
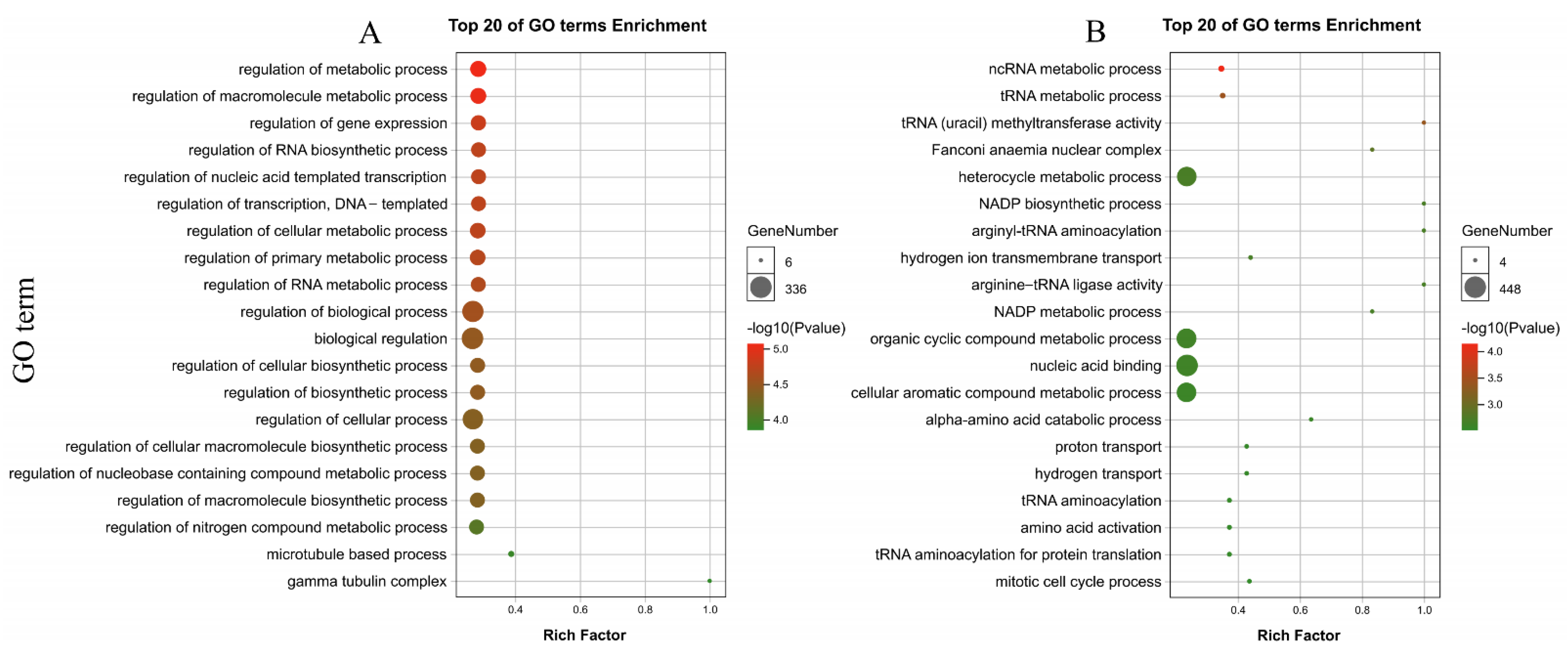
3.9. Identification and Annotation of PdAP2/ERF Target Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.-S.; Chen, M.; Li, L.-C.; Ma, Y.-Z. Functions and Application of the AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family in Crop ImprovementF. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-H.; Peng, T.; Dai, W. Critical cis-Acting Elements and Interacting Transcription Factors: Key Players Associated with Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, P.J.; Park, M.-J.; Park, C.-M. Alternative splicing of transcription factors in plant responses to low temperature stress: Mechanisms and functions. Planta 2013, 237, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, R.; Song, J.; Lv, Z.; Qi, X.; Han, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Jian, Z.; Hu, Q.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Comprehensive Analysis of the AP2/ERF Gene Family in Pomegranate Fruit Development and Postharvest Preservation. Genes 2022, 13, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, F.; Feng, J.; Zhou, Y. Characterization of the AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family and Expression Profiling of DREB Subfamily under Cold and Osmotic Stresses in Ammopiptanthus nanus. Plants 2020, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-J.; Li, X.-H.; Liu, Z.-W.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhuang, J. Transcriptome-based discovery of AP2/ERF transcription factors related to temperature stress in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2015, 15, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-X.; Chen, S.-K.; Wang, P.-D.; Peng, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.-F.; Feng, C.-Z. Genome-Wide Analysis of the RAV Gene Family in Wheat and Functional Identification of TaRAV1 in Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Deng, Z.; Liang, C.; Sun, H.; Li, D.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R. Genome-Wide Analysis of RAV Transcription Factors and Functional Characterization of Anthocyanin-Biosynthesis-Related RAV Genes in Pear. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Ma, C.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, J. Genome-Wide Screening of AP2 Transcription Factors Involving in Fruit Color and Aroma Regulation of Cultivated Strawberry. Genes 2021, 12, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, K.H.; Lee, S.C.; Jung, H.W.; Hong, J.K.; Hwang, B.K. Expression and functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced transcription factor RAV1 in bacterial disease resistance, and drought and salt stress tolerance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 61, 897–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yarra, R. Genome-Wide identification and characterization of AP2/ERF transcription factor family genes in oil palm under abiotic stress conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhai, H.; Zhao, N.; He, S. An AP2/ERF gene, IbRAP2-12, from sweetpotato is involved in salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2019, 281, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.; Jung, I.; Shin, S.-J.; Park, J.; Rhee, S.; Kim, J.-K.; Jung, W.; Kwon, H.-B.; Kim, S. Transcriptional Network Analysis Reveals Drought Resistance Mechanisms of AP2/ERF Transgenic Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challam, C.; Ghosh, T.; Rai, M.; Tyagi, W. Allele mining across DREB1A and DREB1B in diverse rice genotypes suggest a highly conserved pathway inducible by low temperature. J. Genet. 2015, 94, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukura, S.; Mizoi, J.; Yoshida, T.; Todaka, D.; Ito, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Comprehensive analysis of rice DREB2-type genes that encode transcription factors involved in the expression of abiotic stress-responsive genes. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2010, 283, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Chen, C. Colinearity and Similar Expression Pattern of Rice DREB1s Reveal Their Functional Conservation in the Cold-Responsive Pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.; Chu, C. Overexpression of a rice OsDREB1F gene increases salt, drought, and low temperature tolerance in both Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 67, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, E.M.; Prudencio, S.; Ortega, E. Protein Profiling of Pollen–Pistil Interactions in Almond (Prunus dulcis) and Identification of a Transcription Regulator Presumably Involved in Self-Incompatibility. Agronomy 2022, 12, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alioto, T.; Alexiou, K.G.; Bardil, A.; Barteri, F.; Castanera, R.; Cruz, F.; Dhingra, A.; Duval, H.; Fernández i Martí, Á.; Frias, L.; et al. Transposons played a major role in the diversification between the closely related almond and peach genomes: Results from the almond genome sequence. Plant J. 2020, 101, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnhammer, E.L.; Eddy, S.R.; Birney, E.; Bateman, A.; Durbin, R. Pfam: Multiple sequence alignments and HMM-profiles of protein domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39 (Suppl. 2), W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zeng, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Ma, X. Characterization of the WRKY gene family reveals its contribution to the adaptability of almond (Prunus dulcis). PeerJ 2022, 10, e13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico-Willman, K.M.; Niederhuth, C.E.; Willman, M.R.; Gradziel, T.M.; Ouma, W.Z.; Meulia, T.; Fresnedo-Ramírez, J. Integrated analysis of the methylome and transcriptome of twin almonds (Prunus dulcis [Mill.] D.A.Webb) reveals genomic features associated with non-infectious bud failure. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico-Willman, K.M.; Ouma, W.Z.; Meulia, T.; Sideli, G.M.; Gradziel, T.M.; Fresnedo-Ramírez, J. Whole-genome sequence and methylome profiling of the almond [Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A. Webb] cultivar ‘Nonpareil’. G3 2022, 12, jkac065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudencio Ángela, S.; Hoeberichts Frank, A.; Dicenta, F.; Martínez-Gómez, P.; Sánchez-Pérez, R. Identification of early and late flowering time candidate genes in endodormant and ecodormant almond flower buds. Tree Physiol. 2021, 41, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Wei, Y.; Yang, B.; Ayup, M.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Liao, K.; Wang, H. Developmental transcriptome profiling uncovered carbon signaling genes associated with almond fruit drop. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Fornés, O.; Stigliani, A.; Gheorghe, M.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Van Der Lee, R.; Bessy, A.; Chèneby, J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Tan, G.; et al. JASPAR 2018: Update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles and its web framework. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D260–D266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-Wide Analysis of the ERF Gene Family in Arabidopsis and Rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chai, Z.; Lin, P.; Huang, C.; Huang, G.; Xu, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors in sugarcane (Saccharum spontaneum L.). Bmc Genom. 2020, 21, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, S.; Filiz, E.; Kazemitabar, S.K.; Vannozzi, A.; Palumbo, F.; Barcaccia, G.; Heidari, P. The AP2/ERF Gene Family in Triticum durum: Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis under Drought and Salinity Stresses. Genes 2020, 11, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Chen, J.; Yao, Q.; Xiong, F.; Sun, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, A. Discovery and expression profile analysis of AP2/ERF family genes from Triticum aestivum. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-X.; Wu, Y.-M. Genome-Wide Analysis of AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family in Zea Mays. Curr. Bioinform. 2012, 7, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Argout, X.; Gébelin, V.; Summo, M.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Leclercq, J.; Kuswanhadi, N.; Piyatrakul, P.; Pirrello, J.; Rio, M.; et al. Identification of the Hevea brasiliensisAP2/ERF superfamily by RNA sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Cai, B.; Peng, R.; Zhu, B.; Jin, X.; Xue, Y.; Gao, F.; Fu, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, W.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2008, 371, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shangguan, L.; Ma, R.; Sun, X.; Tao, R.; Guo, L.; Korir, N.; Yu, M. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in peach (Prunus persica). Genet. Mol. Res. 2012, 11, 4789–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Liu, S. Genome-wide identification and phylogenetic analysis of the ERF gene family in cucumbers. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2011, 34, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Wang, H.; Guo, C.; Zhang, N.; Zeng, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, H.; Qi, J. Widespread Whole Genome Duplications Contribute to Genome Complexity and Species Diversity in Angiosperms. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Hao, R.; Cheng, T.; Pan, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. Genome-Wide Analysis of the AP2/ERF Gene Family in Prunus mume. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 31, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, C.L.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Cero, J.D.; Nobile, P.M.; Laurens, F.; Bouzayen, M.; Quecini, V. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in apple and transcriptional evidence of ERF involvement in scab pathogenesis. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 151, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, R.; Kong, H.; Zhang, N.; Ma, H. Resolution of deep angiosperm phylogeny using conserved nuclear genes and estimates of early divergence times. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, F.; Sun, Z.; Ni, Z.; Iqbal, S.; Xu, W.; Gao, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Tufail, M.A.; Jahan, M.S.; Khan, U.; et al. Exogenous Melatonin Improves Cold Tolerance of Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) through Modulation of DREB/CBF-COR Pathway and Antioxidant Defense System. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dang, P.; Liu, L.; He, C. Cold acclimation by the CBF–COR pathway in a changing climate: Lessons from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshu, Y.; Eliu, Y.; Ezhang, J.; Esong, L.; Eguo, C. Genome-Wide Analysis of the AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes and their Responses to Abiotic Stress in Medicago truncatula. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.; Catalá, R.; Salinas, J. The CBFs: Three arabidopsis transcription factors to cold acclimate. Plant Sci. 2011, 180, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.; Barah, P.; Suarez-Rodriguez, M.C.; Bressendorff, S.; Friis, P.; Costantino, P.; Bones, A.M.; Nielsen, H.B.; Mundy, J. Transcriptome Responses to Combinations of Stresses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ye, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, Y.; Pei, H.; Duan, F.; et al. A transcriptional regulator that boosts grain yields and shortens the growth duration of rice. Science 2022, 377, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Guo, Y.; Du, C.; Yu, H.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, S. BnERF114.A1, a Rapeseed Gene Encoding APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR, Regulates Plant Architecture through Auxin Accumulation in the Apex in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, H.-Y.; Ha, J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Bae, H.; Moon, Y.-H. Two Alternative Splicing Variants of AtERF73/HRE1, HRE1α and HRE1β, Have Differential Transactivation Activities in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh Tuan, P.; Bai, S.; Saito, T.; Imai, T.; Ito, A.; Moriguchi, T. Involvement of EARLY BUD-BREAK, an AP2/ERF tran-scription factor gene, in bud break in Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) lateral flower buds: Expression, histone modifica-tions and possible target genes. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016, 57, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Zeng, B.; Gao, W.; He, Y.; Qin, H.; Ma, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Almond AP2/ERF Superfamily and Its Functional Prediction during Dormancy in Response to Freezing Stress. Biology 2022, 11, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101520
Yu Z, Zhang D, Hu S, Liu X, Zeng B, Gao W, He Y, Qin H, Ma X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Almond AP2/ERF Superfamily and Its Functional Prediction during Dormancy in Response to Freezing Stress. Biology. 2022; 11(10):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101520
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhenfan, Dongdong Zhang, Shaobo Hu, Xingyue Liu, Bin Zeng, Wenwen Gao, Yawen He, Huanxue Qin, and Xintong Ma. 2022. "Genome-Wide Analysis of the Almond AP2/ERF Superfamily and Its Functional Prediction during Dormancy in Response to Freezing Stress" Biology 11, no. 10: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101520
APA StyleYu, Z., Zhang, D., Hu, S., Liu, X., Zeng, B., Gao, W., He, Y., Qin, H., & Ma, X. (2022). Genome-Wide Analysis of the Almond AP2/ERF Superfamily and Its Functional Prediction during Dormancy in Response to Freezing Stress. Biology, 11(10), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101520




