Simple Summary
In the class of insects, bees are advanced evolutionary groups that play a pivotal role in ecosystem balance, agriculture, and food security. Transposons are the driving factors of genome evolution and speciation, which shape the genomes of almost all organisms. Among them, the Tc1/mariner and pogo superfamily, as the most widely distributed transposons in nature, are widely reported in insects. However, in bees, the research on transposons has never been systematically reported. Therefore, this study focuses on annotating the transposons of the Tc1/mariner and pogo superfamily of bees that were sequenced, revealing the distribution, diversity, potential activities, evolutionary patterns, and structural characteristics of transposons in different bees.
Abstract
Bees (Apoidea), the largest and most crucial radiation of pollinators, play a vital role in the ecosystem balance. Transposons are widely distributed in nature and are important drivers of species diversity. However, transposons are rarely reported in important pollinators such as bees. Here, we surveyed 37 bee genomesin Apoidea, annotated the pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons in the genome of each species, and performed a phylogenetic analysis and determined their overall distribution. The pogo and Tc1/mariner families showed high diversity and low abundance in the 37 species, and their proportion was significantly higher in solitary bees than in social bees. DD34D/mariner was found to be distributed in almost all species and was found in Apis mellifera, Apis mellifera carnica, Apis mellifera caucasia, and Apis mellifera mellifera, and Euglossa dilemma may still be active. Using horizontal transfer analysis, we found that DD29-30D/Tigger may have experienced horizontal transfer (HT) events. The current study displayed the evolution profiles (including diversity, activity, and abundance) of the pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons across 37 species of Apoidea. Our data revealed their contributions to the genomic variations across these species and facilitated in understanding of the genome evolution of this lineage.
1. Introduction
Bees (Hymenoptera: Apoidea), which originated in the early to mid-cretaceous era [1], are the largest and most crucial radiation of pollinators with more than 20,000 described species [2]. Bees play a critical role in ecosystem balance, sustainable agriculture, and food security around the world [3,4]. Most bee species lead a solitary life; only ~10% of bee species are eusocial [3]. In the superfamily of Apoidea, seven extant families are recognized: Megachilidae and Apidae of the long-tongued families Andrenidae, Colletidae, Halictidae, and Melittidae, and Stenotritidae of the short-tongued families [1,5]. Apidae has the largest family size, with >5900 described species, followed by Halictidae and Megachilidae with >4000 species [2]. By contrast, Stenotritidae is the smallest family and includes just 21 recorded species [2]. Melittidae, with 204 known species, is viewed as the most basal bee family [1,6], although some earlier studies have argued that Colletidae is the sister group to the rest of the bees [7,8]. The emergence of different views relates to advances in molecular and genome research, which has substantially changed and continues to change the understanding of classifications and relationships in bees [3,9,10].
Transposons, also called jumping genes, were once considered junk sequences but were later confirmed to play an important role in genome evolution and size [11,12,13,14]. Transposons account for a significant sequence component of eukaryote genomes, in insects ranging from as little as 1% in the Antarctic midge [15] to as much as 65% in the migratory locust [16]. Transposons can move in the genome and make copies during this movement, and these processes facilitate the ability to invade the genome of almost all organisms and reshape the structure and phenotype of different lineages [17,18,19].
Transposons are usually divided into two types according to the structural organization and mechanism: Class I represents RNA transposons and Class II DNA transposons. DNA transposons have been widely reported and can be divided into three main types: cut-and-paste, peel-and-paste, and self-synthesizing transposons. Widely reported DNA transposons include: Tc1/mariner, pogo, hAT, PiggyBac, CACTA, Helitron, and PIF-Harbinger. The Tc1/mariner superfamily is a member of the cut-and-paste group that was first discovered in Drosophila mauritiana (transposon mariner) and Caenorhabditis elegans (transposon C. elegans number 1, Tc1). Generally, Tc1/mariner transposon usually has a single open reading frame (ORF) of about 340 amino acids (aa), flanked by two terminal inverted repeats (TIRs) and dinucleotide target site duplications (TSDs) of TA, and it may represent the most widely distributed transposon superfamily in nature [20,21,22]. The arthropods, particularly insects, are more susceptible to the invasion of DNA transposons including diverse Tc1/mariner families, and have been suggested as major reservoir hosts for DNA transposons and RNA viruses [21,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33].
Based on the phylogeny of the DDE-conserved catalytic motif, Tc1/mariner is classified into DD34E/Tc1 [34,35,36,37,38], DD34D/mariner [39,40,41,42], DD35E/TR [43], DD36E/IC [29], DD37D/maT [44,45], DD37E/TRT [46], DD39D/GT [31], and DD41D/VS [30]. The pogo transposon was first found in flies [47], then more pogo-like elements were detected, such as Tigger [48] was found in the human genome; Fot, Tan1, Pot1, Pot2, Flipper, and Aft1-transposons were found in the genome of fungi [49,50,51,52,53,54]; Lemi1 was found in the genome of plants [55]; and pogo-like elements were found in the teleost genome [56]. A previous study confirmed that pogo and Tc1/mariner are two distinct superfamilies [57], but represent a close phylogeny relationship.
The mariner element has been reported in studies of the annotation of honeybees and bumblebees [58,59]. However, comparative studies of transposons in the genome of Apoidea species are lacking. Here, we surveyed the genome of 37 bee species in Apoidea; annotated pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons in the genome of each species; and determined their phylogenetic positions, classification, overall distribution, and structural characteristics. We also investigated the evolutionary patterns of DD29-36D/Tigger and DD34D/mariner transposons. Our data reveal the evolutionary landscape of pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons in Apoidea and will add to the understanding of their contributions to the evolution of the Apoidea genomes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Distribution of pogo and Tc1/mariner within Apoidea
To survey the distribution and diversity of pogo and Tc1/mariner DNA transposons in 37 sequenced genomes of Apoidea (taxid:34735), we selected several representative transposase sequences from the well-defined families of pogo (DD35D/Passer, DD35D/Fot, DD29-42D/Lemi, DD29-59D/pogoR, DD36D/Mover, DD29-36D/Tigger) and Tc1/mariner (DD34E/Tc1, DD35E/TR, DD36E/IC, DD37E/TRT, DD38E/IT, DD34D/mariner, DD37D/maT, DD39D/Guest and DD41D/VS) superfamilies and subjected them to a TblastN search against the Apoidea genomes deposited in a whole-genome shotgun database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed on 22 June 2020) with default parameters (1e-10). The information of all genomes in this study is listed in Table S1. Significant hits (80% identity) were extracted with 2000-base pair (bp) flanking sequences, and the transposon boundaries (TIRs) were then determined manually by alignment using the BioEdit program. The copy number of transposon in each genome was estimated by using BLAST (40% coverage and 80% identity) with the obtained transposon sequence. The genomic transposons that contain putatively intact transposase (>300 aa) flanked with TIRs were designated as intact copies. In addition, transposons with very low copy numbers in the genome, which may be false-positive hits resulting from sequence contamination, were verified manually by checking the presence of the host genomic flank sequences of the transposon insertion.
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Protein Domain Prediction
For phylogenetic analysis, the conserved DDE domains of the identified transposases were aligned to the representative families of the pogo and Tc1/mariner transposases separately using MAFFT (v.7.310). The phylogenetic trees were inferred based on the conserved DDE domain using the maximum-likelihood method in the IQ-TREE program. According to the Bayesian information criterion, the best-suited aa substitution model for these data was the LG + G4 model, which was selected by ModelFinder. The reliability of the maximum-likelihood trees was estimated using the ultrafast bootstrap approach with 1000 replicates [29,43]. Information for all representative sequences involved in constructing the phylogenetic tree is listed in Table S2. The phylogenetic tree of host was generated by Timetree (www.timetree.org, accessed on 12 September 2021).
Protein secondary structure predictions were performed using the PSIPRED program (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred, accessed on 1 March 2021). Putative nuclear localization signal (NLS) motifs were predicted using PSORT (https://www.genscript.com/psort.html?src=leftbar, accessed on 1 March 2021). The protein domains were identified using the profile hidden Markov models on the hmmscan online web server (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/hmmer/search/hmmscan, accessed on 3 March 2021).
2.3. Horizontal Transfer and Evolutionary Dynamics Analysis
The pairwise genetic distance between transpsons and the conserved host genes was applied to determine whether these species have experienced HT events. The coding sequences of 32 host genes, including elongation factor1 alpha (EF1-a), heat shock cognate 70 (Hsc70-4), tubulin beta-3 (tub3), and 29 Ribosomal proteins, were used for the comparison with transposon distance to test the HT hypothesis. The three genes (EF1-a, Hsc70-4, and tub3) were used as internal controls by other studies including HT analysis of transposons [60,61], while the 29 Ribosomal proteins are considered universally conserved in most species [62], and their accession numbers are listed in Table S3. Species that do not have a complete CDS region of the EF1-a, Hsc70-4, tub3, and 29 universally conserved genes in the US National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database were not included in these calculations. Multiple alignments of EF1-a, Hsc70-4, tub3, 29 universally conserved genes, and all transposons in Apoidea were created using MAFFT, and the pairwise distances were then calculated using MEGA software (v.7.2.06; pairwise deletion, maximum composite likelihood) based on two aligned files. The species divergence times were estimated using the online Timetree program (http://www.timetree.org, accessed on 12 June 2021). The bar chart was created by Graphpad 8, and then statistical differences were analyzed using a one-factor ANOVA test in SPSS (25.0). Significant differences were assessed at p < 0.05. The genomic copies of DD34D/mariner were annotated by using RepeatMasker (http://www.repeatmasker.org/RMDownload.html, accessed on 20 June 2021) with representative genome of each species, and then calculated the Kimura divergence parameter distance by using the calcDivergenceFromAlign.pl package from RepeatMasker. The Kimura two-parameter distance reflects the transpositional activity of DD34D/mariner on a relative time scale per genome [63], and it is generally believed that the younger transposons display lower Kimura divergences [64].
3. Results
3.1. Diversity and Distribution of pogo and Tc1/mariner Elements in the Apoidea Genomes
To determine the diversity and distribution of pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons in Apoidea (taxid:34735), we executed a Tblastn search using the NCBI whole-genome shotgun database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed on 22 June 2020) using 15 representative transposase sequences from different families of the pogo (DD35D/Passer, DD35D/Fot, DD29-42D/Lemi, DD29-59D/pogoR, DD36D/Mover, DD29-36D/Tigger) and Tc1/mariner (DD34E/Tc1, DD35E/TR, DD36E/IC, DD37E/TRT, DD38E/IT, DD34D/mariner, DD37D/maT, DD39D/Guest and DD41D/VS) superfamilies. We identified 164 unique elements in 37 species of Apoidea (Table S4). The phylogenetic tree was then used to define the evolutionary relationships of the pogo and Tc1/mariner elements in Apoidea that we identified. TP36_RB and Zator transposases, a clade of the ITm group [65], were used as the outgroup, and the incomplete DDE domains were excluded from this analysis. Based on the phylogenetic tree and distribution analysis, two families (DD29-36D/Tigger and DD35-36D/Fot) were classified as members of the pogo superfamily and seven families (DD34E/Tc1, DD36E/IC, DD38E/IT, DD34D/mariner, DD37D/maT, DD39D/Guest and DD41D/VS) classified as members of the Tc1/mariner superfamily were identified in 37 species of Apoidea (Figure 1 and Figure S4).
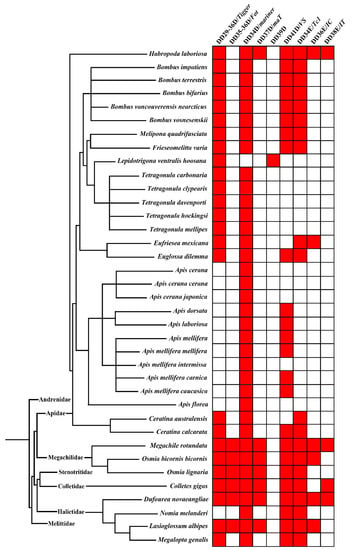
Figure 1.
Nine transposon families in various species of Apoidea. The tree on the left is the phylogenetic relationship between all species, generated by Timetree (www.timetree.org, accessed on 2 January 2021), and the block diagram on the right is generated by R studio 1.4.1106, and each red square represents a transposon hit.
Differential evolutionary profiles of these families were observed across the Apoidea superfamily in four bee families: Apidae, Megachilidae, Colletidae, and Halictidae (Figure 2 and Table S4). The Apidae family displayed high diversity of species (29 species) but represented a lower diversity of pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons than the other three families (Megachilidae, Colletidae, and Halictidae) of Apoidea, in which most species contained seven to eight transposon families. Most species of Apidae contained only two to four transposon families, particularly in the Apis genus, and most species exhibited only DD34D/mariner and DD41D/VS families. The exception was Habropoda laboriosa, which had one pogo family (Tigger), but variations of DDE domains (DD30D, DD33E, and DD36D) and six Tc1/mariner families (DD34D/mariner, DD37D/MaT, DD41D/VS, DD34E/Tc1, DD36E/IC and DD38E/IT). This species exhibited the highest diversity of pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons in Apoidea. Four transposon families (DD29-36D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner, DD41D/VS, and DD34E/Tc1) were detected in all bumblebees (five species), Melipona quadrifasciata and Frieseomelitta varia, whereas the five species of stingless bee (Tetragonula davenporti, Tetragonula hockingsi, Tetragonula carbonaria, Tetragonula clypearis and Tetragonula mellipes) exhibited only the DD29-36D/Tigger and DD34D/mariner transposon families. The DD29-36D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner, DD34E/Tc1, and DD36E/IC families were detected in Eufriesea mexicana, and DD29-36D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner, DD34E/Tc1, and DD41D/VS families in Euglossa dilemma. Moreover, families of DD29-36D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner, and DD34E/Tc1 were found in Ceratina australensis and Ceratina calcarata, and Ceratina calcarata also includes a DD41D/VS family (Figure 1 and Table S4).
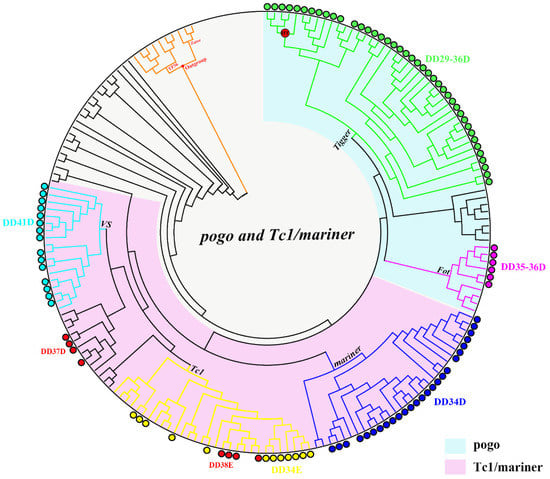
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree of all transposons. Each color represents a different family, and branches with horizontal transfer (HT) signals are represented by red circles. The transposons found in this study were labeled with circles, and the transposons absent of circle represent the reference sequences of each family.
Most species of Megachilidae, Colletidae, and Halictidae displayed high diversity of pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons, where seven to eight transposon families appeared within each species, except for Nomia melanderi and Megalopta genalis, where only three and four transposon families were detected, respectively. Eight families of pogo and Tc1/mariner were detected in Megachile rotundata (DD29-36D/Tigger, DD35-36D/Fot, DD34D/mariner, DD34E/Tc1, DD36E/IC, DD37D/maT, DD38E/IT and DD41D/VS) and Dufourea novaeangliae (DD29-36D/Tigger, DD35-36D/Fot, DD34D/mariner, DD34E/Tc1, DD36E/IC, DD37D/MaT, DD38E/IT and DD41D/VS), which represented the highest diversity across Apoidea species (Figure 1).
3.2. Invasions of pogo and Tc1/mariner in the Apoidea Genomes
For further analysis, we investigated the copy numbers of all transposons (Table 1 and Table S4). A copy was defined as Blast result coverage >40% and identity >80%. An intact copy was defined as a Blast result with the full-length of the transposon and the complete ORF encoded. Overall, a total of 164 transposon elements were found in 37 bee species. However, we found that most transposons had low copy numbers in the genome, ranging from 1 to 401 in 37 species, and 115 of 164 transposable elements had <10 copies (>80% identity and >40% coverage) in the host genomes. We found a total of 20 transposons in the bumble genus, of which 15 transposons had ≥15 copies and 14 had complete copies. Of the 14 transposons with complete copies, 11 transposons had only one copy (Table 1 and Table S4).

Table 1.
Copy number information for each transposon family.
With the exception of DD34D/mariner, all other transposon families had relatively low intact copy numbers. For example, neither DD39D/GT nor DD36E/IC contained an intact copy, whereas, in the DD35-36D/Fot, DD37D/maT, and DD38E/IT families, most transposons contained an intact copy. In addition, Colletes gigas had two intact copies in the DD35-36D/Fot family; Colletes gigas and Dufourea novaeangliae had two intact copies in DD37D/maT; and Habropoda laboriosa had two intact copies in DD38E/IT. All intact copies of DD29-36D/Tigger, DD41D/VS, and DD34E/Tc1 were ≤5 in hosts. In the DD34D/mariner family, we found five species with >10 intact copy numbers: Apis mellifera, Apis mellifera carnica, Apis mellifera caucasia, Apis mellifera mellifera, and Euglossa dilemma. The intact copy number for the Euglossa dilemma was the largest found in this study (Table 1 and Table S4).
To examine more comprehensively the evolutionary dynamics of transposons in the superfamily, we investigated the DD34D/mariner family of transposons, which are distributed in all bees except Lepidotrigona ventralis hoosana. Species that cannot be annotated with RepeatMasker were excluded from this analysis. Most transposons of several of the gregarious bee genera, including Bumble, Tetragonula and Apis, seem to have been very young at the time of invasion; some of these species displayed very recent activities (K < 10) (Figure 3), which suggests that these elements are highly active and may still be functional. We also found that the evolutionary dynamics of transposons in each genus are very similar, such as Bumble and Tetragonula, which means that they have the same accumulation pattern in this genus. However, among Apis genera, most European honeybees and Asian honeybees show different patterns of transposon accumulation. In contrast, some European honeybees appear to invade seats earlier than Asian honeybees (Figure 3).
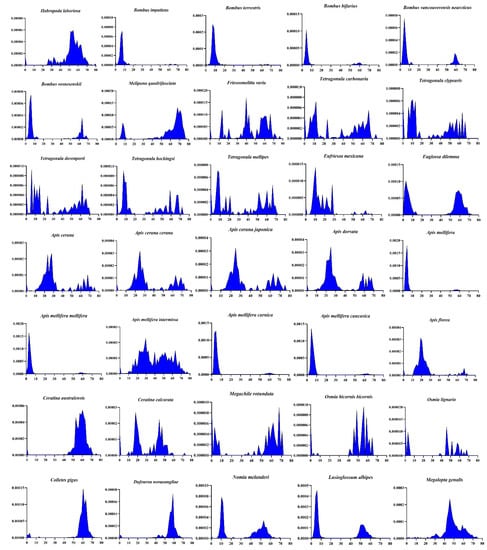
Figure 3.
Evolutionary dynamics analysis of DD34D/mariner transposons. Species that cannot be executed with RepeatMasker were excluded from this analysis. The y-axis represents the percentage of transposon elements in the genome and the x-axis indicates the Kimura divergence estimate.
3.3. Evolutionary Patterns of pogo and Tc1/mariner in Apoidea
HT is an important form of asexual transmission in nature, and there is increasing evidence that transposons are important participants in HT. Generally, HT events will follow three conditions: (1) high sequence similarity of TEs from divergent taxa; (2) incongruence between TE and host phylogeny; (3) a patchy TE distribution within a group of taxa [66]. In our analysis of four families of Apoidea, namely Apidae, Megachilidae, Colletidae, and Halictidae, the average divergence time was 110 million years ago. We found that Dufourea novaeangliae, Nomia melanderi, Lasioglossum albipes, and Megalopta genalis belong to the Halictidae family, but they had obvious irregular distribution of transposons, indicating putative HT events of these transposons across species within this lineage. By contrast, two very close species, Ceratina calcarata and Ceratina australensis, also had different distribution of transposons. Moreover, some relatively distantly related species on the phylogenetic tree were closer than closely-related species, for example, the DD29-30D/Tigger family in Dufourea novaeangliae and Megalopta genalis, which belong to Halictidae, but Dufourea novaeangliae was closer to the Osmia lignaria in the Megachilidae family on the clade than to Megalopta genalis, which is a more closely-related species of Nomia melanderi. Considering these findings, we speculate that some transposons might have been exposed to several episodes of HT.
To further illustrate the evolutionary patterns of pogo and Tc1/mariner in the bee genome, clusters that are inconsistent with the host phylogeny and have an identity of each cluster of the phylogenetic tree close to or greater than 80%, which may experience HT events, are selected. We detected the presence of HT signs in the four clusters (DD29-30D/Tigger, DD33D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner-cluster 1, and DD34D/mariner-cluster 2). Then, the pairwise genetic distances between the four host-conserved genes (EF1-a, Hsc70-4, tub3 and RPL3) and these transposons were calculated and compared. we found that the average distance is smaller for DD29-30D/Tigger, DD33D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner-cluster 1, and DD34D/mariner-cluster 2 than for the four host genes (Table S5 and Figure S2). However, our data revealed that with the exception of DD29-30D/Tigger, the genetic distances of the other three clusters are close to the host genes, indicating that HT events of these transposons are not well-supported (Table S5). In the cluster of DD29-30D/Tigger, we found that the genetic distance is much lower than the host genes and may be exposed to HT events (Table S5). Whereas, the genetic distances varied significantly across host genes and the control gene selection may influence the deduction of HT events. In order to find more evidences to support the HT events of this cluster, we added 29 ribosomal proteins including RPL3, which were suggested as universally conserved host genes [62], as controls for further analysis. By calculating the genetic distance of 29 control genes, we found that the average distance was significantly smaller (p < 0.05) for DD29-30D/Tigger than for almost all host genes, except for EF1-a, RPL2, RPL18, RPL23, RPS8, and RPS9 (Figure 4A, Tables S5 and S6). Moreover, the four transposon ORFs of DD29-30D/Tigger showed very high overall average sequence identity (91.00% ± 6.00%) across these species (Figure 4B), while their average divergence time was >100 million years ago (Table S5). Additionally, the host phylogeny, by using Timetree and the rebuilt phylogenetic tree of the DD29-30D/Tigger cluster, is not consistent (Figure 4C). Overall, these data suggest a possibility of HT of DD29-30D/Tigger transposons.
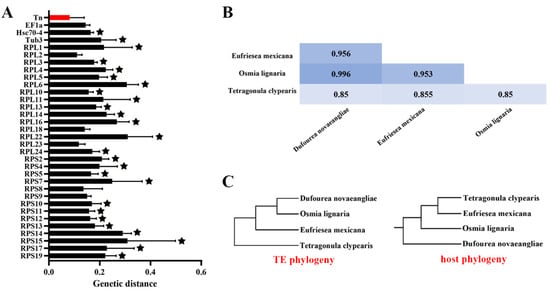
Figure 4.
HT analysis of DD29-30D/Tigger in Apoidea. (A) genetic distance and significance analysis. The x-axis represents the paired genetic distance between every two species, and the y-axis is the DD29-30D/Tigger transposon, EF1-a, Hsc70-4, tub3, and 29 universally conserved ribosomal protein genes. The stars that appear above each bar chart represent a significant difference. (B) Sequence identities of DD29-30D/Tigger family. The sequence identities were measured by pairwise comparisons of full-length transposases. (C) Transposon phylogenetic tree and host phylogenetic tree. The host phylogenetic tree is created by using Timetree (http://timetree.org, accessed on 12 September 2021).
In addition, we did not find HT signals in most other species, which suggests that most of these elements that differ between bee species were not obtained by HT. Overall, these data suggest that the pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons in bees were obtained by both HT and vertical transfer.
3.4. Structural Organization of the Detected pogo and Tc1/mariner Transposons
Previous studies have shown that the pogo and Tc1/mariner protein structure is highly conserved along with the transposons, as summarized in Figure 5. The transposase of Tigger comprises a CENP-B protein and helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain at the N-terminus and a catalytic domain at the C-terminus. The N-terminal of Fot-like transposase comprises HTH and DNA-binding domain regions, and the C-terminal is a catalytic domain. The Tc1/mariner transposase contains an HTH domain at the N-terminus and a catalytic domain at the C-terminus. The DD29-36D/Tigger transposons invaded almost all species except the Apis genus, among which 26 species contain 58 transposons, representing a high diversity of transposons. The length of all transposons ranged from 907 bp to 4213 bp, and the length of the TIR was 10–33 bp. The overall copy number content was very low, but most transposons included an intact copy. Generally speaking, the last aa of the DD/D catalytic domain of the pogo transposon was ‘D’, but we found an exception in this study. DD33D and DD33E are similar in structure and have a very close phylogenetic relationship. Considering their phylogenetic location and all species that appear in stingless bees, DD33E may have been caused by the DD33D mutation at some stage. DD34D/mariner was found to be the most widely distributed transposon in this study. Almost all bees except Lepidotrigona ventralis hoosana have the DD34D/mariner transposon and it appears to represent a very young transposon family in Apoidea. We found that all DD34D/mariner transposons were around 1200 bp in length and that 24 transposons contained complete transposase. However, among the six Apis genomes studied (Apis cerana, Apis cerana cerana, Apis cerana japonica, Apis dorsata, Apis florea, and Apis mellifera intermissa), we could identify only complete ORFs but could not determine the boundary. DD34E/Tc1 is considered to be the origin of many Tc1/mariner transposons and was found to be a very widely distributed transposon in this analysis. All DD34E/Tc1 transposons were 952–1805 bp in length, and the TIRs were 24–221 bp in length. We also found six Fot-like transposons, namely DD35-36D/Fot in Colletes gigas, Lasioglossum albipes, Megachile rotundata, Osmia bicornis bicornis, Osmia lignaria, and Dufourea novaeangliae. Six transposons were found in DD36E/IC, but they all lost the function of encoding complete transposase. The first five base changes seem to be typical characteristics of some subfamilies. All DD37D/maT started with CAGGG, and DD38E/IT started with CACTA and CACTG. Lepidotrigona ventralis hoosana had an incomplete DD39D/GT transposase with a total length of 2381 bp, which retains the typical characteristics of DD39D/GT transposon beginning with CTCCC. In addition, the recently well-defined DD41D/VS family was also found in this study. Eleven of the 24 transposons had complete ORFs and were 1024–2258 bp in length. All of the bumblebee catalytic domains changed from DD41D to DD40D.
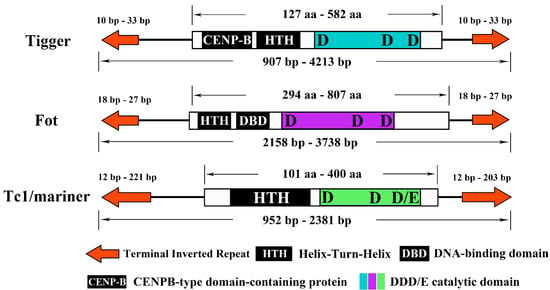
Figure 5.
The structure of the two subfamilies of the pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons. (1) terminal inverted repeats (TIRs) are represented by orange arrows; (2) different protein elements in the DNA-binding domain are represented by black rectangles, each with its name; (3) catalytic domains of the three types of transposons are shown in blue, purple, and green. Amino acid length range, full-length nucleotide length range, and TIR length range are indicated.
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution, Diversity and Copy Number in Apoidea
Transposons can generate new genes through genome rearrangement and overexpression, which play a role in the behavioral diversification of Apis dorsata from other honeybees [67]. Given their transposable properties, TEs can accumulate a large number of copies in the host genome, and evidence suggests that transposons are the main cause of differences in genome size between some species [13,14]. The genome of the North African honeybee Apis mellifera intermissa contains 5.16% TEs with low diversity, most of which comprise simple repeat sequences [68]. In the European honeybee Apis mellifera genome, the percentage of TEs is close to 8% [69]. DNA transposons are the major repeat sequence, and mariner transposons are the most common element within this class [70]. A recent study reported that TEs in the genome of the Asian honeybee Apis cerana accounted for 9.15% and simple repeats accounted for most TEs [71]. The DNA transposons constitute 0.11% (247 kb) of the Apis cerana genome and 0.57% (1.34 Mb) of the Apis mellifera genome. The TEs are significantly smaller in Apis cerana than in Apis mellifera [72]. In a study of bumblebees, TEs accounted for 14.8% and 17.9% in Bombus terrestris and Bombus impatiens, respectively, and most of them were retrotransposons, of which Gypsy was the most common element. The main types of DNA transposons are TIRs of mariner, which account for 1.6% and 2.7%, and their abundance is higher than that of Apis cerana and Apis mellifera [73]. In addition, compared with other Hymenoptera, the abundance of TEs is low in honeybees, and the lack of TEs is one of the main genomic characteristics of these species [74,75,76,77]. Overall, these data suggest that TEs occupy <10% of genomic sequences in honeybees but >10% in bumblebees.
As expected, in our analysis, the transposon diversity was also higher for bumblebees than honeybees. We detected at least seven families of Tc1/mariner and two families of pogo, which suggests that the genome of some bees represents high diversity of Tc1/mariner and pogo transposons. In our study, the genomes of 37 bee genomes were rich in pogo and Tc1/mariner transposons, and included nine different transposon families: DD29-36D/Tigger, DD35-36D/Fot, DD34D/mariner, DD34E/Tc1, DD36E/IC, DD37D/maT, DD38E/IT, DD39D/GT, and DD41D/VS. Among all transposon families discovered to date, DD34D/mariner is the most widely distributed and appears in almost all bee genomes. In addition, DD34D/mariner is also widely distributed in nature and has been reported in all species [39,78,79,80,81,82]. The distribution of transposons differs between species, but the distribution of transposons is similar in sister species, which suggests that transposons invade the host’s genome before species divergence.
It is generally believed that the copy number is related to transposon activity and that a genome with more intact transposon copies, which include the full-length transposase (no frameshift mutation) and the flanking TIRs with very high identity, usually reflects a recent invasion activity, suggesting that some copies may be still active [83]. We examined the copy numbers for all transposons included in this study and found that most families of transposons had only one or few copies, which suggests that most Tc1/mariner and pogo transposons do not display significant amplification in these lineages. This is consistent with previous findings that most Tc1/mariner is detected with low genomic coverage [68,71]. In addition, we found >10 intact copies of DD34D/mariner in the genomes of Apis mellifera, Apis mellifera carnica, Apis mellifera caucasia, Apis mellifera mellifera, and Euglossa dilemma. The evolutionary dynamics analysis showed that the DD34D/mariner elements of these five genomes are very young, and we speculate that these elements may remain active in the genomes of some species. The European honeybee is an important economic animal introduced into China in the last century, where there is a considerable amount of breeding. Active transposon elements may play an important role in the genome evolution and subspecies differentiation of European honeybees, and their existence raises the possibility of molecular operations on honeybees. In addition, the number of newly discovered families of the pogo and Tc1/mariner superfamily continues to increase as more genomic sequencing data are obtained, and this trend indicates that the diversity of the pogo and Tc1/mariner superfamilies may be much larger than the currently known families.
4.2. Differential Susceptibility of Apoidea Species to DNA Transposons
In this analysis, we detected a total of nine families of Tc1/mariner and pogo transposons in 37 species, for a total of 164 transposons. Interestingly, we found that the genomes of some solitary bees were rich in DNA transposons. For example, Habropoda laboriosa exhibited DD29-36D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner, DD37D/MaT, DD41D/VS, DD34E/Tc1, DD36E/IC and DD38E/IT transposons; Dufourea novaeangliae exhibited DD29-36D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner, DD35-36D/Fot, DD34E/Tc1, DD36E/IC, DD37D/MaT, DD38E/IT and DD41D/VS transposons; and Colletes gigas exhibited DD29-36D/Tigger, DD35-36D/Fot, DD34D/mariner, DD34E/Tc1, DD36E/IC, DD37D/maT, DD38E/IT, and DD41D/VS transposons. Social bees exhibited significantly fewer transposons than solitary bees. For example, the Tetragonula genus exhibited only two transposon subfamilies, DD29-36D/Tigger and DD34D/mariner. In Apis genus, there are also two families of transposons (DD34D/mariner and DD41D/VS) that appear in the genome of honeybees. This seems to be related to the living environment. Solitary bees act alone and their long-term migration and living environment are more complicated and unstable, whereas social bees live in a group involving social activities and their living environment is more stable [84]. On further analysis, the Bombus genus exhibited four families, DD29-36D/Tigger, DD34D/mariner, DD41D/VS, and DD34E/Tc1. Interestingly, Bombus genus are a group that once transformed from solitary bees to social bees, which seems to further verify that the content of transposon may be related to the living environment.
We also found another interesting phenomenon. Apis mellifera, Apis mellifera carnica, Apis mellifera caucasia, and Apis mellifera mellifera exhibited a complete DD34D/mariner element (full-length and complete ORF). However, only the complete ORF of DD34D/mariner was exhibited by Apis cerana, Apis cerana cerana, Apis cerana japonica, Apis dorsata, Apis florea, and Apis mellifera intermissa, and the boundary could not be determined. Compared with its close relative, the European honeybee, the Asian honeybee seems to have a stronger selection of transposons in the genome. It is possible that the drones that develop from unfertilized eggs and carry haploid chromosomes experience strong selective pressure on some active elements [85]. In our further analysis of DD41D/VS, we only found that Apis mellifera, Apis mellifera carnica, Apis mellifera caucasia, Apis mellifera mellifera, and Apis dorsata have the complete full-length transposon sequence, but no complete ORF was found. Moreover, Apis cerana, Apis cerana cerana, and Apis cerana japonica did not exhibit any DD41D/VS transposon elements. It seems that DD41D/VS may be an ancient invasion and that, during long-term genome evolution, European honeybees gradually lost their complete copy and Asian honeybees completely lost the entire transposon. Finally, some studies have noted that a host contains an endogenous enzyme system that can silence the transposon or some virus expression, such as RNA interference [86]. However, the mechanism responsible for the interaction between the disappearance of transposon copies and the host in the honeybee genome requires further research.
4.3. HT Events in Apoidea
Transposons are parasitic DNAs whose only role is to replicate and propagate. When a transposon invades a host, the germline genome must be colonized to ensure that it remains in the population. This then increases the copy number [87], and the transposon remains in the genome until, through vertical inhibition, all copies of the transposon become inactive and remain as fossils only [88]. Through genetic drift, these inactive elements can even vanish [88]. To evade this cycle, a transposon must invade a new species or spread to multiple species. That is, to guarantee its longevity, the transposon must transfer to a new genome through HT to start its life cycle again. Although the molecular mechanism responsible for HT is uncertain, studies have provided evidence that HT is the main reason why transposons are widely distributed in nature. Instances include the exchange across marine crustaceans [89], among insects of various orders [90,91], and even between species of different phylae as diverse as the human and parasitic nematode [92].
In this study, although most transposons did not show obvious HT signs, the potential HT traces were detected for DD29-30D/Tigger. To find the HT origin of the DD29-30D/Tigger transposon, we performed Blast searching of this transposase in Dufourea novaeangliae in the NCBI nucleotide collection (nr/nt) database. The complete DDD spacing (DD30D) catalytic domains were detected in Nosema bombycis, Strongyloides stercoralis, and Ctenocephalides felis. Interestingly, these three creatures have parasitic abilities: Nosema bombycis is a parasite of silkworm, Strongyloides stercoralis is parasitic in humans, and the host of Ctenocephalides felis is the cat. These species may serve as potential vectors for Tigger transposons that have invaded the bee genome at a certain time; if so, this strongly suggests the existence of a host–parasitic relationship in bees. These findings suggest that the host–parasitic mode may also be the primary mode of HT of Tigger transposon.
5. Conclusions
Our research provides, for the first time, information about the distribution of pogo and Tc1/mariner family transposons in 37 sequenced Apoidea genomes. In general, pogo and Tc1/mariner show high diversity in most species, except for a few honeybees, but have a low abundance. In addition, only DD34D/mariner has a high copy number in several species, appears as a complete structure, and may have potential activity. Finally, our results also show that DD29-30D/Tigger may experience HT events, and we speculate that they may have invaded their common ancestor before some species formed.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology10090940/s1, Figure S1: phylogenetic tree of TEs based on the alignment of the DDE domains, Figure S2: HT analysis in Apoidea, Table S1: Genome assembly information for all species, Table S2: The access number of reference pogo and Tc1/mariner elements, Table S3: EF1-a Hsc70-4 tub3 and Ribosomal protein Accession Number, Table S4: Taxonomic distribution of Apoidea, Table S5: distance of TEs, EF1-a, Hsc70-4, tub3, 29 Ribosomal proteins and Divergence time, Table S6: Significance analysis data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L., W.Z., Z.L., B.G., T.J. and C.S.; methodology, Y.L., W.Z., S.W. and C.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L., W.Z., M.D., Z.L. and C.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.L., W.Z., B.G. and C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the National Genetically Modified Organisms Breeding Major Projects program (2018ZX08010-08B), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671313), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and the High-end Talent Support Program of Yangzhou University to Chengyi Song.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Yang and Chen for help in bioinformatics analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Danforth, B.N.; Sipes, S.; Fang, J.; Brady, S.G. The history of early bee diversification based on five genes plus morphology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15118–15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascher, J.S.; Pickering, J. Discover Life Bee Species Guide and World Checklist (Hymenoptera:Apoidea:Anthophila). Available online: https://bugguide.net/node/view/468583 (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Danforth, B.N.; Cardinal, S.; Praz, C.; Almeida, E.A.B.; Michez, D. The impact of molecular data on our understanding of bee phylogeny and evolution. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, S.G.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, V.; Ngo, H.T.; Aizen, M.A.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Breeze, T.D.; Dicks, L.V.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Hill, R.; Settele, J.; et al. Safeguarding pollinators and their values to human well-being. Nature 2016, 540, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepburn, H.R. The Bees of the World. Afr. Zool. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danforth, B.N.; Fang, J.; Sipes, S. Analysis of family-level relationships in bees (Hymenoptera: Apiformes) using 28S and two previously unexplored nuclear genes: CAD and RNA polymerase II. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 39, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.B. Genesis of the Hymenoptera and the Phases of Their Evolution. Bull. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1969, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Engel, M.S. A monograph of the baltic amber bees and evolution of the apoidea (Hymenoptera). Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2001, 259, 1–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyasov, R.A.; Poskryakov, A.V.; Nikolenko, A.G. Modern methods of assessing the taxonomic affiliation of honeybee colonies. Ecol. Genet. 2017, 15, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, J.; Parejo, M.; Nielsen, R.O.; Langa, J.; Montes, I.; Papoutsis, L.; Farajzadeh, L.; Bendixen, C.; Căuia, E.; Charrière, J.D.; et al. Authoritative subspecies diagnosis tool for European honey bees based on ancestry informative SNPs. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgel, L.E.; Crick, F.H.C. Selfish DNA: The ultimate parasite. Nature 1980, 284, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, K.R.; Greene, W.K. Transposable elements and viruses as factors in adaptation and evolution: An expansion and strengthening of the TE-Thrust hypothesis. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 2912–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenaillon, M.I.; Hollister, J.D.; Gaut, B.S. A triptych of the evolution of plant transposable elements. Trends Plant. Sci. 2010, 15, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Shen, D.; Xue, S.; Chen, C.; Cui, H.; Song, C. The contribution of transposable elements to size variations between four teleost genomes. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, J.L.; Peyton, J.T.; Fiston-Lavier, A.S.; Teets, N.M.; Yee, M.C.; Johnston, J.S.; Bustamante, C.D.; Lee, R.E.; Denlinger, D.L. Compact genome of the Antarctic midge is likely an adaptation to an extreme environment. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, X.; Yang, P.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, D.; Li, B.; Cui, F.; Wei, J.; Ma, C.; et al. The locust genome provides insight into swarm formation and long-distance flight. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chénais, B.; Caruso, A.; Hiard, S.; Casse, N. The impact of transposable elements on eukaryotic genomes: From genome size increase to genetic adaptation to stressful environments. Gene 2012, 509, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Mager, D.L. Transposable elements: Not as quiet as a mouse. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feschotte, C.; Pritham, E.J. DNA transposons and the evolution of eukaryotic genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2007, 41, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicker, T.; Sabot, F.; Hua-Van, A.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Capy, P.; Chalhoub, B.; Flavell, A.; Leroy, P.; Morgante, M.; Panaud, O.; et al. A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.W.; Medhora, M.M.; Hartl, D.L. Molecular structure of a somatically unstable transposable element in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8684–8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmons, S.W.; Yesner, L.; Ruan, K.s.; Katzenberg, D. Evidence for a transposon in caenorhabditis elegans. Cell 1983, 32, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomeque, T.; Sanllorente, O.; Maside, X.; Vela, J.; Mora, P.; Torres, M.I.; Periquet, G.; Lorite, P. Evolutionary history of the Azteca-like mariner transposons and their host ants. Sci. Nat. 2015, 102, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coy, M.R.; Tu, Z. Gambol and Tc1 are two distinct families of DD34E transposons: Analysis of the Anopheles gambiae genome expands the diversity of the IS630-Tc1-mariner superfamily. Insect Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Hernandez, E.M.; Fernández-Medina, R.D.; Navarro-Escalante, L.; Nuñez, J.; Benavides-Machado, P.; Carareto, C.M.A. Genome-wide analysis of transposable elements in the coffee berry borer Hypothenemus hampei (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): Description of novel families. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2017, 292, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, E.S.; Wallau, G.L. Mosquito genomes are frequently invaded by transposable elements through horizontal transfer. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, R.A.; Akala, O.O.; Adejinmi, J.O.; O’Brochta, D.A. Topi, an IS630/Tc1/mariner-type transposable element in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Gene 2008, 423, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zong, W.; Miskey, C.; Ullah, N.; Diaby, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Ivics, Z.; Song, C. Intruder (DD38E), a recently evolved sibling family of DD34E/Tc1 transposons in animals. Mob. DNA 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Gao, B.; Diaby, M.; Zong, W.; Chen, C.; Shen, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ivics, Z.; Song, C. Incomer, a DD36E family of Tc1/mariner transposons newly discovered in animals. Mob. DNA 2019, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Gao, B.; Miskey, C.; Chen, C.; Sang, Y.; Zong, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ivics, Z.; et al. Multiple invasions of visitor, a DD41D family of tc1/mariner transposons, throughout the evolution of vertebrates. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 1060–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Diaby, M.; Puzakov, M.; Ullah, N.; Wang, Y.; Danley, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Gao, B.; Song, C. Divergent evolution profiles of DD37D and DD39D families of Tc1/mariner transposons in eukaryotes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2021, 161, 107143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Tu, Z. Expanding the diversity of the IS630-Tc1-mariner superfamily: Discovery of a unique DD37E transposon and reclassification of the DD37D and DD39D transposons. Genetics 2001, 159, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Shi, M.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Kang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J.; Qin, X.C.; Xu, J.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Unprecedented genomic diversity of RNA viruses in arthropods reveals the ancestry of negative-sense RNA viruses. eLife 2015, 29, e05378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, J.C.; van Luenen, H.G.; Plasterk, R.H. Characterization of the Caenorhabditis elegans Tc1 transposase in vivo and in vitro. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radice, A.D.; Bugaj, B.; Fitch, D.H.A.; Emmons, S.W. Widespread occurrence of the Tc1 transposon family: Tc1-like transposons from teleost fish. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994, 244, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.L.; Seo, P.; Robison, K.; Virk, S.; Gilbert, W. Discovery of amphibian Tc1-like transposon families. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 257, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivics, Z.; Hackett, P.B.; Plasterk, R.H.; Izsvák, Z. Molecular Reconstruction of Sleeping Beauty, a Tc1-like Transposon from Fish, and Its Transposition in Human Cells. Cell 1997, 91, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinzelle, L.; Pollet, N.; Bigot, Y.; Mazabraud, A. Characterization of multiple lineages of Tc1-like elements within the genome of the amphibian Xenopus tropicalis. Gene 2005, 349, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, H.M. The mariner transposable element is widespread in insects. Nature 1993, 362, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasterk, R.H.A.; Izsvák, Z.; Ivics, Z. Resident aliens the Tc1/mariner superfamily of transposable elements. Trends Genet. 1999, 15, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhipova, I.R.; Meselson, M. Diverse DNA transposons in rotifers of the class Bdelloidea. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11781–11786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Hermann, D.; Caruso, A.; Tastard, E.; Marchand, J.; Rouault, J.D.; Denis, F.; Thiriet-Rupert, S.; Casse, N.; Morant-Manceau, A. First Evidence of Mariner-like Transposons in the Genome of the Marine Microalga Amphora acutiuscula (Bacillariophyta). Protist 2014, 165, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, W.; Gao, B.; Diaby, M.; Shen, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Song, C. Traveler, a new DD35E family of Tc1/mariner transposons, invaded vertebrates very recently. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, H.M.; Asplund, M.L. Bmmar1: A basal lineage of the Mariner family of transposable elements in the silkworm moth, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 26, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, A.S.; Shearman, D.C.A.; Frommer, M.; Raphael, K.A.; Deshpande, N.P.; Wilkins, M.R.; Sherwin, W.B.; Sved, J.A. The draft genome of the pest tephritid fruit fly Bactrocera tryoni: Resources for the genomic analysis of hybridising species. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Li, G.Y.; Xiong, X.M.; Han, M.J.; Dai, F.Y. TRT, a Vertebrate and Protozoan Tc1-Like Transposon: Current Activity and Horizontal Transfer. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 2994–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, M.; Lobocka, M.; Goodell, M.; Pettitt, J.; O’Hare, K. The pogo transposable element family of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1992, 232, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Riggs, A.D. Tiggers and other DNA transposon fossils in the human genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, M.; Lespinet, O.; Daboussi, M.J.; Hua-Van, A. Genome-wide comparative analysis of pogo-like transposable elements in different Fusarium species. J. Mol. Evol. 2011, 73, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, P.; Robson, G.; Birch, M.; Bromley, M. Characterisation of Aft1 a Fot1/Pogo type transposon of Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2008, 45, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyyssönen, E.; Amutan, M.; Enfield, L.; Stubbs, J.; Dunn-Coleman, N.S. The transposable element Tan1 of Aspergillus niger var. awamori, a new member of the Fot1 family. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1996, 253, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levis, C.; Fortini, D.; Brygoo, Y. Flipper, a mobile Fot1-like transposable element in Botrytis cinerea. MGG Mol. Gen. Genet. 1997, 254, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachroo, P.; Leong, S.A.; Chattoo, B.B. Pot2, an inverted repeat transposon from the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. MGG Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994, 245, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daboussi, M.J.; Langin, T.; Brygoo, Y. Fot1, a new family of fungal transposable elements. MGG Mol. Gen. Genet. 1992, 232, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feschotte, C.; Mouchès, C. Evidence that a family of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) from the Arabidopsis thaliana genome has arisen from a pogo- like DNA transposon. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Chen, W.; Shen, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Song, C. Characterization of autonomous families of Tc1/mariner transposons in neoteleost genomes. Mar. Genom. 2017, 34, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Wang, Y.; Diaby, M.; Zong, W.; Shen, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Evolution of pogo, a separate superfamily of IS630-Tc1-mariner transposons, revealing recurrent domestication events in vertebrates. Mob. DNA 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitani, M.; Lee, J.M.; Hatakeyama, M.; Oishi, K. Cloning and characterization of Acmar1, a mariner-like element in the Asiatic honey bee, Apis cerana japonica (Hymenoptera, Apocrita). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2002, 50, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouleux-Bonnin, F.; Petit, A.; Demattei, M.V.; Bigot, Y. Evolution of full-length and deleted forms of the Mariner-like element, Botmar1, in the genome of the bumble bee, Bombus terrestris (hymenoptera: Apidae). J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 60, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Li, G.Y.; Xiong, X.M.; Han, M.J.; Dai, F.Y. Horizontal transfer of a novel Helentron in insects. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2017, 292, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Xu, H.E.; Shen, Y.H.; Han, M.J.; Zhang, Z. The origin and evolution of six miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements in Bombyx mori and Rhodnius prolixus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.K.; Kelley, S.T.; Spiegelman, G.B.; Pace, N.R. The genetic core of the universal ancestor. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunemann, S.M.; Wasmuth, J.D. Horizontal transfer of a retrotransposon between parasitic nematodes and the common shrew. Mob. DNA 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.; Jurka, M.G.; Kapitonov, V.V.; Jurka, J. New superfamilies of eukaryotic DNA tyransposons and their internal divisions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, K.; Zhang, X.; Han, M.; Zhang, Z. Repeated horizontal transfers of four DNA transposons in invertebrates and bats. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheim, S.; Cao, X.; Rueppel, O.; Krongdang, S.; Phokasem, P.; Desalle, R.; Goodwin, S.; Xing, J.; Chantawannakul, P.; Rosenfeld, J.A. Whole Genome Sequencing and Assembly of the Asian Honey Bee Apis dorsata. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 3677–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.J.; Adjlane, N.; Saini, D.; Menon, A.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Jonklaas, D.; Tomkins, J.P.; Loucif-Ayad, W.; Horth, L. Whole-genome sequencing of north African honey bee Apis mellifera intermissa to assess its beneficial traits. Entomol. Res. 2018, 48, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallberg, A.; Bunikis, I.; Pettersson, O.V.; Mosbech, M.B.; Childers, A.K.; Evans, J.D.; Mikheyev, A.S.; Robertson, H.M.; Robinson, G.E.; Webster, M.T. A hybrid de novo genome assembly of the honeybee, Apis mellifera, with chromosome-length scaffolds. BMC Genom. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsik, C.G.; Worley, K.C.; Bennett, A.K.; Beye, M.; Camara, F.; Childers, C.P.; de Graaf, D.C.; Debyser, G.; Deng, J.; Devreese, B.; et al. Finding the missing honey bee genes: Lessons learned from a genome upgrade. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Yan, Q.; Yan, W.Y.; Zheng, H.J.; Zeng, Z.J. A Chromosome-Scale Assembly of the Asian Honeybee Apis cerana Genome. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Jung, W.W.; Choi, B.S.; Jayakodi, M.; Lee, J.; Lim, J.; Yu, Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, M.L.; Park, Y.; et al. Uncovering the novel characteristics of Asian honey bee, Apis cerana, by whole genome sequencing. BMC Genom. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadd, B.; Barribeau, S.; Bloch, G.; de Graaf, D.; Dearden, P.; Elsik, C.; Gadau, J.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.; Hasselmann, M.; Lozier, J.; et al. The genomes of two key bumblebee species with primitive eusocial organization. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminker, J.S.; Bergman, C.M.; Kronmiller, B.; Carlson, J.; Svirskas, R.; Patel, S.; Frise, E.; Wheeler, D.A.; Lewis, S.E.; Rubin, G.M.; et al. The transposable elements of the Drosophila melanogaster euchromatin: A genomics perspective. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suen, G.; Teiling, C.; Li, L.; Holt, C.; Abouheif, E.; Bornberg-Bauer, E.; Bouffard, P.; Caldera, E.J.; Cash, E.; Cavanaugh, A.; et al. The genome sequence of the leaf-cutter ant Atta cephalotes reveals insights into its obligate symbiotic lifestyle. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werren, J.H.; Richards, S.; Desjardins, C.A.; Niehuis, O.; Gadau, J.; Colbourne, J.K.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Desplan, C.; Elsik, C.G.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P.; et al. Functional and evolutionary insights from the genomes of three parasitoid nasonia species. Science 2010, 327, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Gibbs, R.A.; Gerardo, N.M.; Moran, N.; Nakabachi, A.; Stern, D.; Tagu, D.; Wilson, A.C.C.; Muzny, D.; Kovar, C.; et al. Genome sequence of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.C.; Bastida, F.; Bidwell, S.L.; Johnson, P.J.; Carlton, J.M. A potentially functional mariner transposable element in the protist Trichomonas vaginalis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langin, T.; Capy, P.; Daboussi, M.J. The transposable element impala, a fungal member of the Tc1-mariner superfamily. MGG Mol. Gen. Genet. 1995, 246, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halaimia-Toumi, N.; Casse, N.; Demattei, M.V.; Renault, S.; Pradier, E.; Bigot, Y.; Laulier, M. The GC-rich transposon Bytmar1 from the deep-sea hydrothermal crab, Bythograea thermydron, may encode three transposase isoforms from a single ORF. J. Mol. Evol. 2004, 59, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auge-Gouillou, C.; Bigot, Y.; Pollet, N.; Hamelin, M.H.; Meunier-Rotival, M.; Periquet, G. Human and other mammalian genomes contain transposons of the mariner family. FEBS Lett. 1995, 368, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvik, T.; Lark, K.G. Characterization of Soymar1, a mariner element in soybean. Genetics 1998, 149, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujolar, J.M.; Astolfi, L.; Boscari, E.; Vidotto, M.; Barbisan, F.; Bruson, A.; Congiu, L. Tana1, a new putatively active Tc1-like transposable element in the genome of sturgeons. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 66, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, J.D.; Paulus, H.F. Evolution and phylogeny of bees—Review and cladistic analysis in light of morphological evidence (Hymenoptera, Apoidea). Zoologica 2016, 161, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock, G.M.; Robinson, G.E.; Gibbs, R.A.; Worley, K.C.; Evans, J.D.; Maleszka, R.; Robertson, H.M.; Weaver, D.B.; Beye, M.; Bork, P.; et al. Insights into social insects from the genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nature 2006, 443, 931–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, P.M.; Wang, M.B.; Lough, T. Gene silencing as an adaptive defence against viruses. Nature 2001, 411, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, D.L.; Lohe, A.R.; Lozovskaya, E.R. Modern thoughts on an ancyent marinere: Function, evolution, regulation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1997, 31, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-López, M.; Garcia-Pérez, J.L. DNA transposons: Nature and applications in genomics. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casse, N.; Bui, Q.T.; Nicolas, V.; Renault, S.; Bigot, Y.; Laulier, M. Species sympatry and horizontal transfers of Mariner transposons in marine crustacean genomes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, H.M.; Lampe, D.J. Recent horizontal transfer of a mariner transposable element among and between Diptera and Neuroptera. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1995, 12, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, D.J. Recent Horizontal Transfer of Mellifera Subfamily Mariner Transposons into Insect Lineages Representing Four Different Orders Shows that Selection Acts Only During Horizontal Transfer. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, T.; Loukas, A.; Wattanasatitarpa, S.; Somprakhon, J.; Kewgrai, N.; Sithithaworn, P.; Kaewkes, S.; Mitreva, M.; Brindley, P.J. The bandit, a new DNA transposon from a hookworm possible horizontal genetic transfer between host and parasite. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2007, 1, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).