Identification and Characterization of a Rhodopsin Kinase Gene in the Suckers of Octopus vulgaris: Looking around Using Arms?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
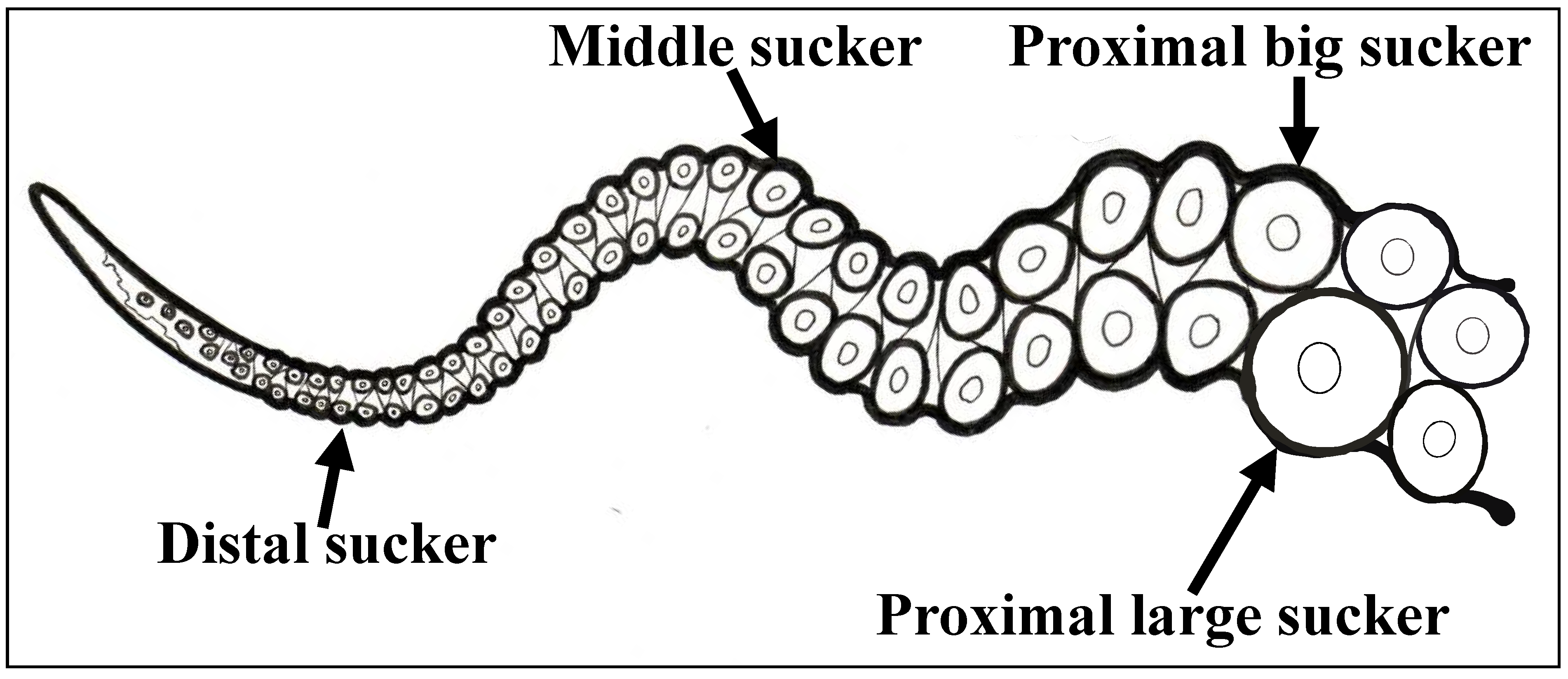
2.2. Tissue Collection and Fixation
2.3. Expression Analysis of Rhodopsin Kinase in Different Tissues and Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Methods
2.5. Sucker Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization
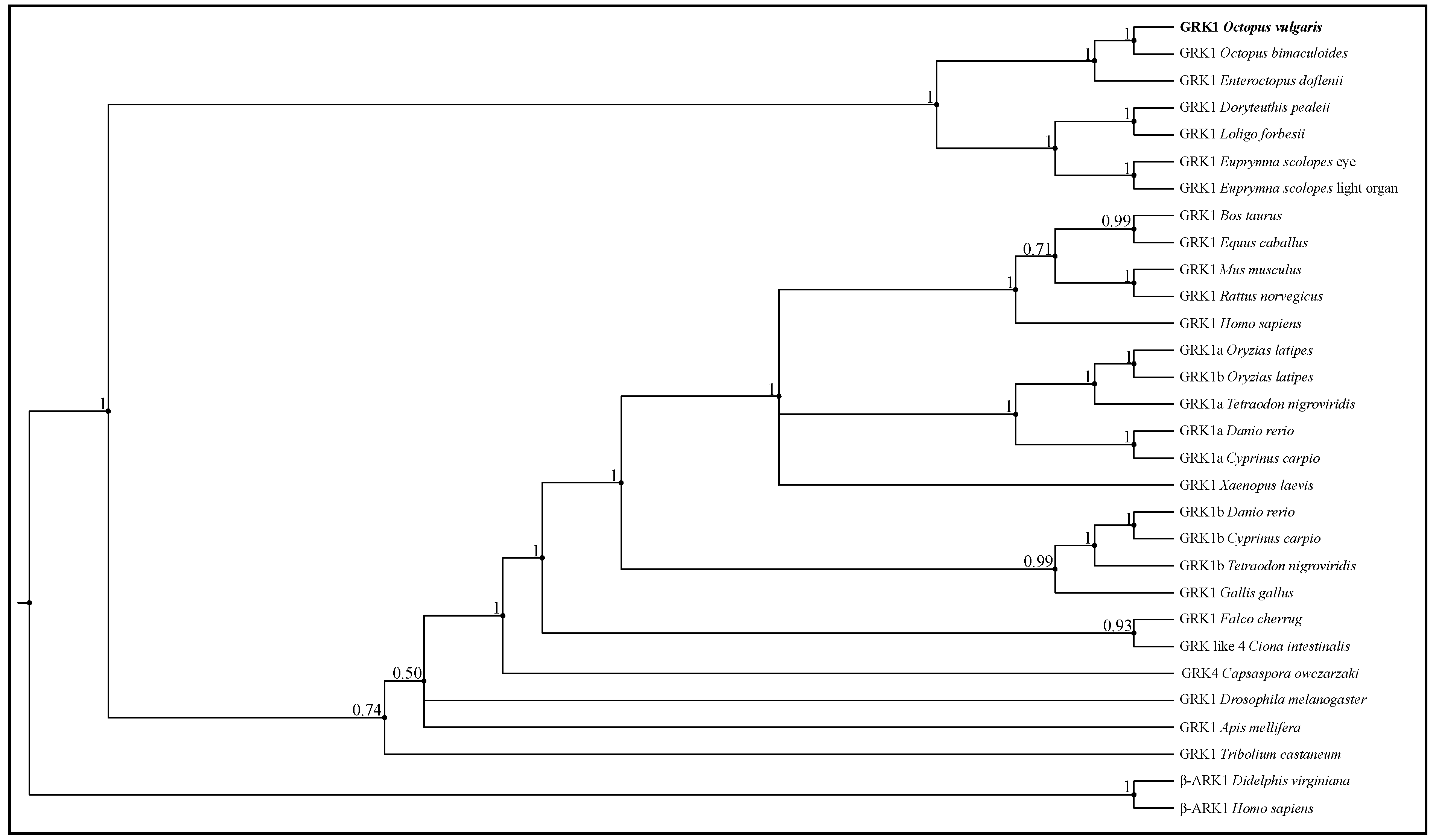
2.6. Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
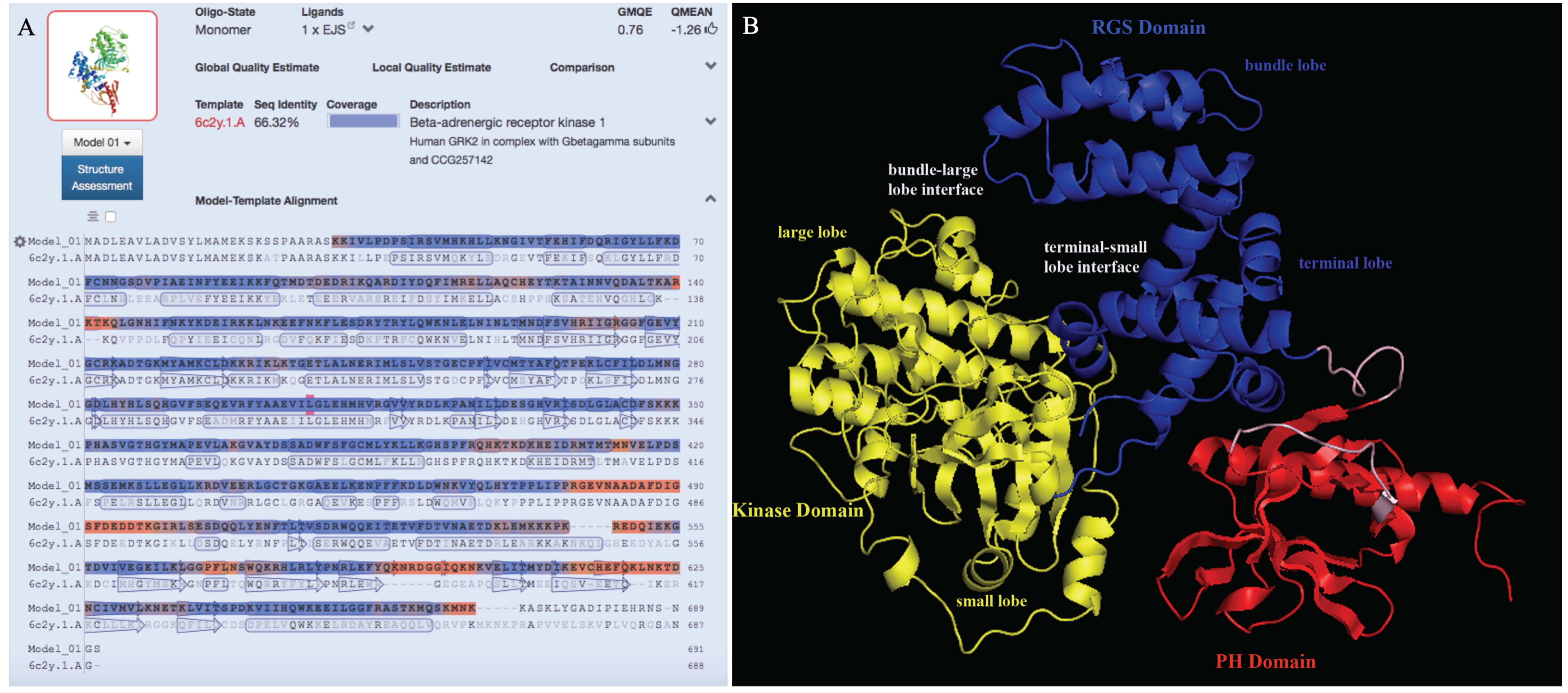
2.7. Prediction of 3D Structure Model
3. Results
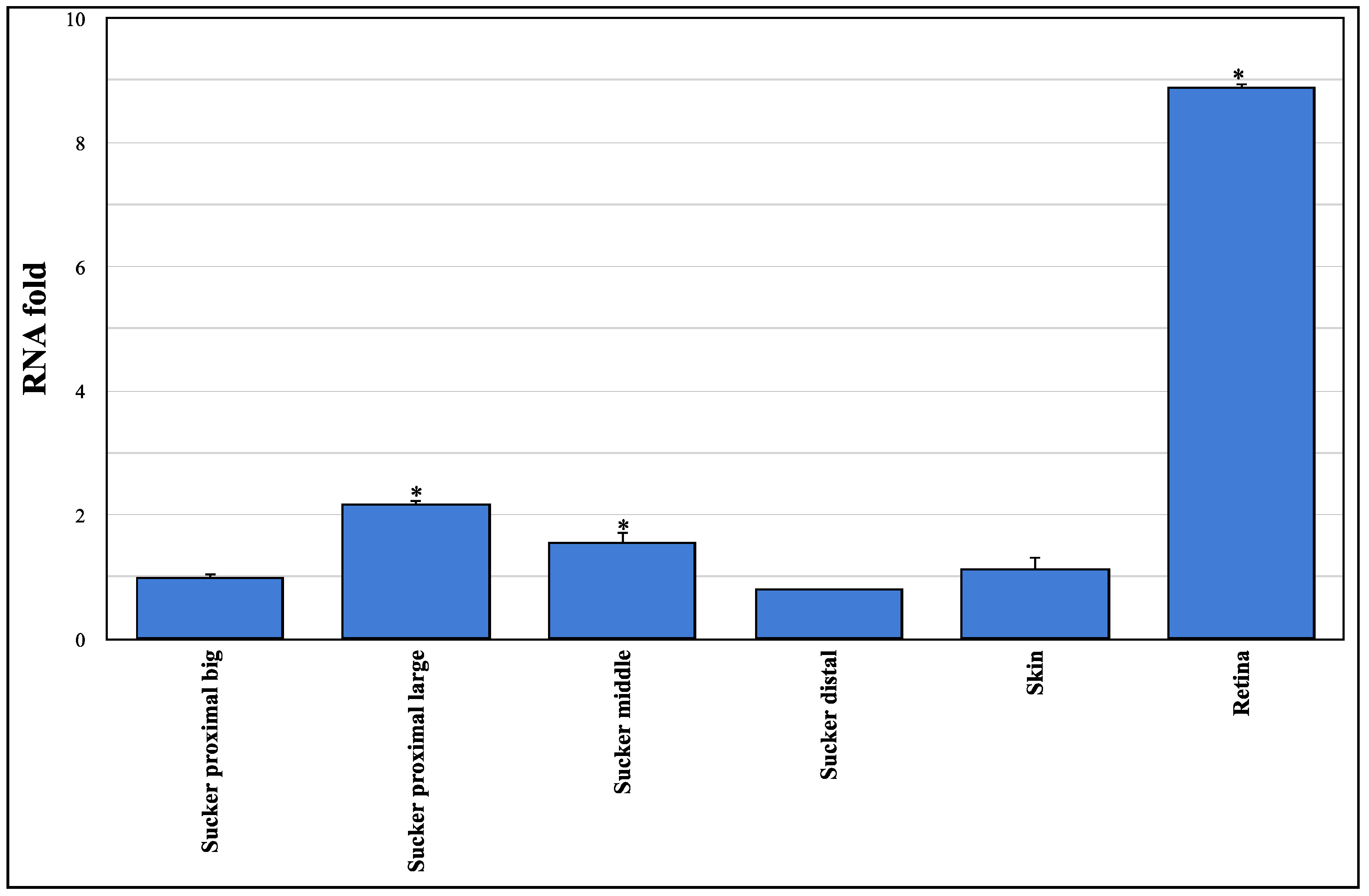
3.1. Sequencing and Expression Analysis of Ov-GRK1 Gene
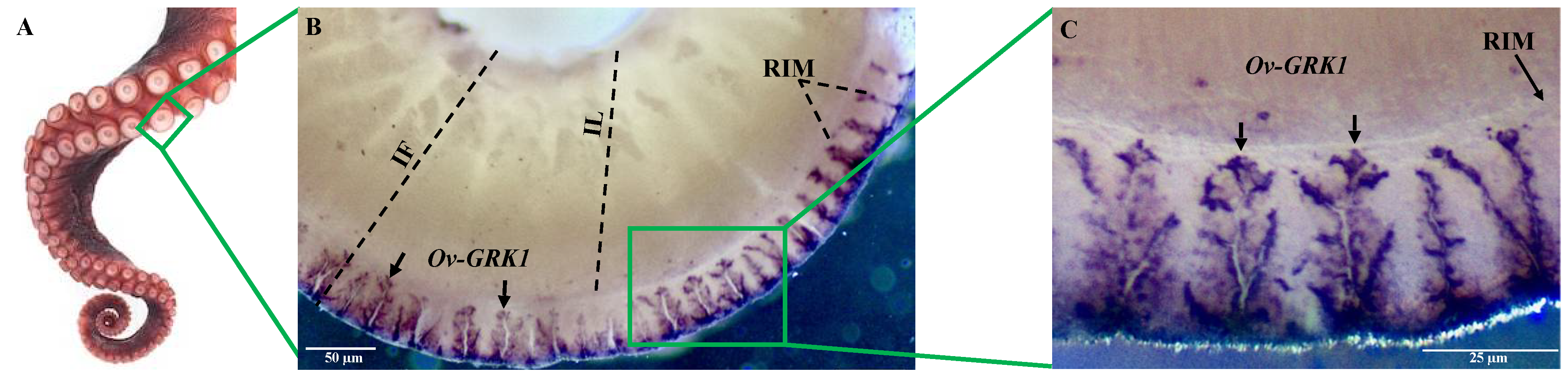
3.2. Localization of Ov-GRK1 Transcript in the Sucker of O. vulgaris
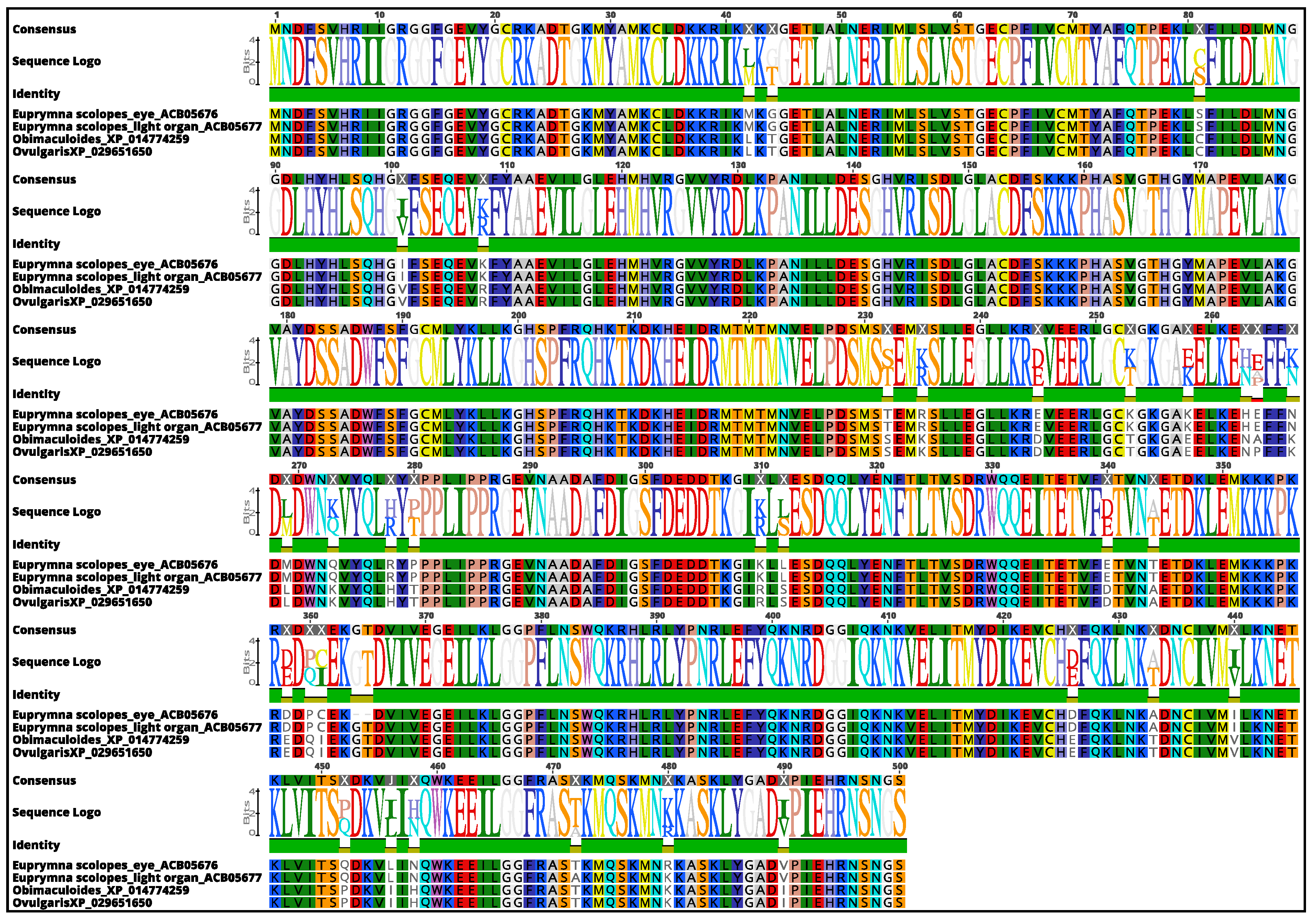
3.3. Molecular Phylogenetic Construction
3.4. Prediction of the 3D Structure Model for Ov-GRK1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanlon, R.; Messenger, J. Adaptive coloration in young cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis L.): The morphology and development of body patterns and their relation to behavior. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1988, 320, 437–487. [Google Scholar]
- Chiao, C.-C.; Chubb, C.; Buresch, K.C.; Barbosa, A.; Allen, J.J.; Mäthger, L.M.; Hanlon, R.T. Mottle camouflage patterns in cuttlefish: Quantitative characterization and visual background stimuli that evoke them. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloney, R.; Brocco, S. Chromatophore organs, reflector cells, iridocytes and leucophores in cephalopods. Am. Zool. 1983, 23, 581–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.J.; Mäthger, L.M.; Barbosa, A.; Hanlon, R.T. Cuttlefish use visual cues to control three-dimensional skin papillae for camouflage. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2009, 195, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagny, S.; Darmaillacq, A.S.; Guibé, M.; Bellanger, C.; Dickel, L. Feel, smell and see in an egg: Emergence of perception and learning in an immature invertebrate, the cuttlefish embryo. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 4125–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, J.B. The peduncle lobe: A visuo-motor centre in octopus. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1967, 167, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.Z. The organization of a cephalopod ganglion. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 1972, 263, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Hara, R. Distribution of rhodopsin and retinochrome in the squid retina. J. Gen. Physiol. 1976, 67, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, T.; Hara, R. Retinochrome and rhodopsin in the extraocular photoreceptor of the squid, Todarodes. J. Gen. Physiol. 1980, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, A.; Sten-Knudsen, O.V.E. Light-evoked Impulses from Extra-ocular Photoreceptors in the Squid Todarodes. Nature 1972, 237, 342–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, D.; Rozas, N.S.; Oakley, T.H.; Mitchell, J.; Colley, N.J.; McFall-Ngai, M.J. Evidence for light perception in a bioluminescent organ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathger, L.M.; Chiao, C.C.; Barbosa, A.; Hanlon, R.T. Color matching on natural substrates in cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2008, 194, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäthger, L.M.; Roberts, S.B.; Hanlon, R.T. Evidence for distributed light sensing in the skin of cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, A.C.N.; Kuzirian, A.M.; Hanlon, R.T.; Cronin, T.W. Visual phototransduction components in cephalopod chromatophores suggest dermal photoreception. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messenger, J.B.; Sanders, G.D. Visual preference and two-cue discrimination learning in octopus. Anim. Behav. 1972, 20, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.D.; Oakley, T.H. Eye-independent, light-activated chromatophore expansion (LACE) and expression of phototransduction genes in the skin of Octopus bimaculoides. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, A.C.N.; Wardill, T.J.; Hanlon, R.T.; Cronin, T.W. An Unexpected Diversity of Photoreceptor Classes in the Longfin Squid, Doryteuthis pealeii. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, I.; Shomrat, T.; Nesher, N. Feel the light-sight independent negative phototactic response in octopus’ arms. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb.237529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, A. The skin of cephalopods (Coleoids): General and special adaptations. In The Mollusca, Form and Function; Trueman, E.R., Clarke, M.R., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1988; Volume 11, pp. 37–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kuba, M.J.; Byrne, R.A.; Meisel, D.V.; Mather, J.A. Exploration and habituation in intact free moving Octopus vulgaris. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2006, 19, 426–438. [Google Scholar]
- Kuba, M.J.; Byrne, R.A.; Meisel, D.V.; Mather, J.A. When do octopuses play? Effects of repeated testing, object type, age, and food deprivation on object play in Octopus vulgaris. J. Comp. Psychol. 2006, 120, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziadei, P. Receptors in the Suckers of Octopus. Nature 1962, 195, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.J. Octopus. Physiology and Behaviour of an Advanced Invertebrate; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziadei, P.P.C.; Gagne, H.T. Sensory innervation in the rim of the octopus sucker. J. Morphol. 1976, 150, 639–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Giesen, L.; Kilian, P.B.; Allard, C.A.H.; Bellono, N.W. Molecular Basis of Chemotactile Sensation in Octopus. Cell 2020, 183, 594–604.e514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuda, R.; Hamilton, S.C.; McInerney, J.O.; Pisani, D. Metazoan opsin evolution reveals a simple route to animal vision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18868–18872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, M.L.; Blasic, J.R.; Bok, M.J.; Cameron, E.G.; Pringle, T.; Cronin, T.W.; Robinson, P.R. Shedding new light on opsin evolution. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.D.; Pairett, A.N.; Pankey, M.S.; Serb, J.M.; Speiser, D.I.; Swafford, A.J.; Oakley, T.H. The Last Common Ancestor of Most Bilaterian Animals Possessed at Least Nine Opsins. Genome. Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3640–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertin, C.B.; Simakov, O.; Mitros, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Pungor, J.R.; Edsinger-Gonzales, E.; Brenner, S.; Ragsdale, C.W.; Rokhsar, D.S. The octopus genome and the evolution of cephalopod neural and morphological novelties. Nature 2015, 524, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfinito, E.; Reggiani, L. Mechanisms responsible for the photocurrent in bacteriorhodopsin. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft. Matter. Phys. 2015, 91, 032702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Kouyama, T. Crystal structure of squid rhodopsin. Nature 2008, 453, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukolyukov, S. Digitonin and sodium dodecylsulfate-solubilized frog rho-dopsin: Behavior under native and denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Adv. Biol. Chem. 2012, 2, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maselli, V.; Al-Soudy, A.S.; Buglione, M.; Aria, M.; Polese, G.; Di Cosmo, A. Sensorial Hierarchy in Octopus vulgaris’s Food Choice: Chemical vs. Visual. Animals 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polese, G.; Winlow, W.; Di Cosmo, A. Dose-dependent effects of the clinical anesthetic isoflurane on Octopus vulgaris: A contribution to cephalopod welfare. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2014, 26, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Muscle: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest 3: Fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1164–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöver, B.C.; Müller, K.F. TreeGraph 2: Combining and visualizing evidence from different phylogenetic analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2--a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C.; Schwede, T. Automated comparative protein structure modeling with SWISS-MODEL and Swiss-PdbViewer: A historical perspective. Electrophoresis 2009, 30 (Suppl. 1), S162–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thal, D.M.; Homan, K.T.; Chen, J.; Wu, E.K.; Hinkle, P.M.; Huang, Z.M.; Chuprun, J.K.; Song, J.; Gao, E.; Cheung, J.Y.; et al. Paroxetine is a direct inhibitor of g protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and increases myocardial contractility. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdita, M.; von den Driesch, L.; Galiez, C.; Martin, M.J.; Söding, J.; Steinegger, M. Uniclust databases of clustered and deeply annotated protein sequences and alignments. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2017, 45, D170–D176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinegger, M.; Meier, M.; Mirdita, M.; Vöhringer, H.; Haunsberger, S.J.; Söding, J. HH-suite3 for fast remote homology detection and deep protein annotation. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, G.; Rempfer, C.; Waterhouse, A.M.; Gumienny, R.; Haas, J.; Schwede, T. Qmeand is co-distance constraints applied on model quality estimation. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siderovski, D.P.; Hessel, A.; Chung, S.; Mak, T.W.; Tyers, M. A new family of regulators of G-protein-coupled receptors? Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodowski, D.T.; Barnhill, J.F.; Pyskadlo, R.M.; Ghirlando, R.; Sterne-Marr, R.; Tesmer, J.J. The role of G beta gamma and domain interfaces in the activation of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 6958–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benovic, J.L.; Mayor, F., Jr.; Staniszewski, C.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Caron, M.G. Purification and characterization of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9026–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, T.H.; Speiser, D.I. How complexity originates: The evolution of animal eyes. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2015, 46, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichida, Y.; Imai, H. Visual pigment: G-protein-coupled receptor for light signals. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1998, 54, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, E.; Kasai, A.; Sato, M.; Yokozeki, A.; Hisatomi, O.; Oshima, N. The signaling pathway in photoresponses that may be mediated by visual pigments in erythrophores of Nile tilapia. Pigm. Cell Res. 2005, 18, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, A.; Oshima, N. Light-sensitive motile iridophores and visual pigments in the neon tetra, Paracheirodon innesi. Zool. Sci. 2006, 23, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Shi, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, Y. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of NDUFS4 gene in m. longissimus dorsi of Laiwu pig (Sus scrofa). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-C.; Robertson, R.M.; Hawryshyn, C.W. Possible Involvement of Cone Opsins in Distinct Photoresponses of Intrinsically Photosensitive Dermal Chromatophores in Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Graziadei, P.P.C.; Gagne, H.T. Neural components in octopus sucker. J. Cell Biol. 1973, 59, A21–A121. [Google Scholar]
- Dickens, J.C.; Eaton, J.L. Fine structure of ocelli in sphinx moths. Tissue Cell 1974, 6, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho-Uehara, M.; Francis, W.R.; Haddock, S.H.D. Biochemical characterization of diverse deep-sea anthozoan bioluminescence systems. Mar. Biol. 2020, 167, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, P.J. Bioluminescence in decapod Crustacea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1976, 56, 1029–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgione, D.; Buglione, M.; Rippa, D.; Trapanese, M.; Petrelli, S.; Monti, D.M.; Aria, M.; Del Giudice, R.; Maselli, V. Selection for background matching drives sympatric speciation in Wall Gecko. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.; Lown, A.E.; Wood, L.E. Color change and camouflage in juvenile shore crabs Carcinus maenas. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zylinski, S.; Osorio, D.; Shohet, A.J. Perception of edges and visual texture in the camouflage of the common cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, G.; Mallick, S.; Kodandaramaiah, U. Background complexity and optimal background matching camouflage. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2021, 75, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgione, D.; Trapanese, M.; Maselli, V.; Rippa, D.; Itri, F.; Avallone, B.; Van Damme, R.; Monti, D.M.; Raia, P. Seeing through the skin: Dermal light sensitivity provides cryptism in moorish gecko. J. Zool. 2014, 294, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrella, I.; Herten, K.; Maes, G.E.; Tai, S.; Yang, M.; Seuntjens, E.; Ritschard, E.A.; Zach, M.; Styfhals, R.; Sanges, R.; et al. The survey and reference assisted assembly of the Octopus vulgaris genome. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.M.; Kang, S.; Ahn, D.H.; Jung, S.H.; Rhee, H.; Yoo, J.S.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.; Han, Y.H.; Ryu, K.B.; et al. The genome of common long-arm octopus Octopus minor. Gigascience 2018, 7, giy119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Bian, L.; Ge, J.; Han, F.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Shi, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the East Asian common octopus (Octopus sinensis) using PacBio sequencing and Hi-C technology. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1572–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benovic, J.L.; Strasser, R.H.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: Identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 2797–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, K.; Kameyama, K.; Haga, T. Synergistic activation of a G protein-coupled receptor kinase by G protein beta gamma subunits and mastoparan or related peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 12594–12599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, R.J. G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Cell 1993, 74, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Hirata, H.; Tsuda, T. Interaction of rhodopsin, G-protein and kinase in octopus photoreceptors. Photochem. Photobiol. 1992, 56, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, M. Photoreception and phototransduction in invertebrate photoreceptors. Photochem. Photobiol. 1987, 45, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.K.; Woodruff, M.L.; Fain, G.L. Rhodopsin kinase and recoverin modulate phosphodiesterase during mouse photoreceptor light adaptation. J. Gen. Physiol. 2015, 145, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, K.; Chen, J.; Khani, S.C.; Kefalov, V.J. Regulation of mammalian cone phototransduction by recoverin and rhodopsin kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 9239–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikkawa, S.; Yoshida, N.; Nakagawa, M.; Iwasa, T.; Tsuda, M. A novel rhodopsin kinase in octopus photoreceptor possesses a pleckstrin homology domain and is activated by G protein betagamma-subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7441–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer Pairs Used in RT-PCR | Primer Sequences (5′→3′) |
| Ov-GRK1 F | CCGCCTCTCATTCCTCCAAG |
| Ov-GRK1 R | AGATCTCTCCTTCCACAATCACA |
| Ubiquitin_ F | TCAAAACCGCCAACTTAACC |
| Ubiquitin_ R | CCTTCATTTGGTCCTTCGTC |
| For WM-ISH probe | Primer sequences (5′→3′) |
| Ov-GRK1 F | CCGCCTCTCATTCCTCCAAG |
| Ov-GRK1 R + T7 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGAGA AGATCTCTCCTTCCACAATCAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Soudy, A.-S.; Maselli, V.; Galdiero, S.; Kuba, M.J.; Polese, G.; Di Cosmo, A. Identification and Characterization of a Rhodopsin Kinase Gene in the Suckers of Octopus vulgaris: Looking around Using Arms? Biology 2021, 10, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090936
Al-Soudy A-S, Maselli V, Galdiero S, Kuba MJ, Polese G, Di Cosmo A. Identification and Characterization of a Rhodopsin Kinase Gene in the Suckers of Octopus vulgaris: Looking around Using Arms? Biology. 2021; 10(9):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090936
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Soudy, Al-Sayed, Valeria Maselli, Stefania Galdiero, Michael J. Kuba, Gianluca Polese, and Anna Di Cosmo. 2021. "Identification and Characterization of a Rhodopsin Kinase Gene in the Suckers of Octopus vulgaris: Looking around Using Arms?" Biology 10, no. 9: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090936
APA StyleAl-Soudy, A.-S., Maselli, V., Galdiero, S., Kuba, M. J., Polese, G., & Di Cosmo, A. (2021). Identification and Characterization of a Rhodopsin Kinase Gene in the Suckers of Octopus vulgaris: Looking around Using Arms? Biology, 10(9), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10090936










