Species-Specific Molecular Detection of the Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne luci
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nematode Isolates
2.2. Nematode Species Identification
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Analysis
2.5. Cloning and Sequencing RAPD Fragment
2.6. Primer Design and PCR for Sequence Characterized Amplified Region (SCAR)
3. Results
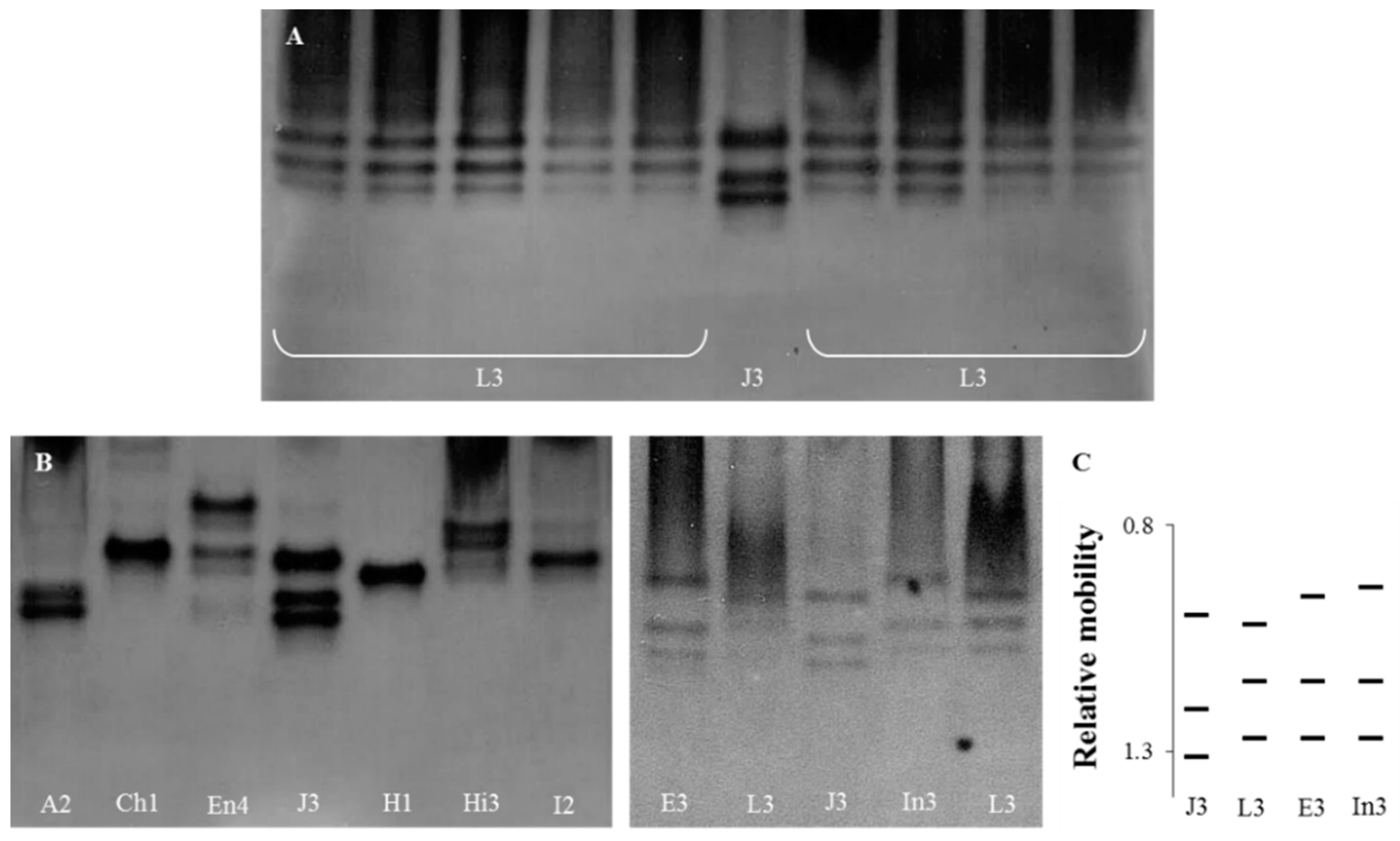
3.1. Esterase Phenotypes
3.2. Selection of Meloidogyne luci Specific RAPD Fragment
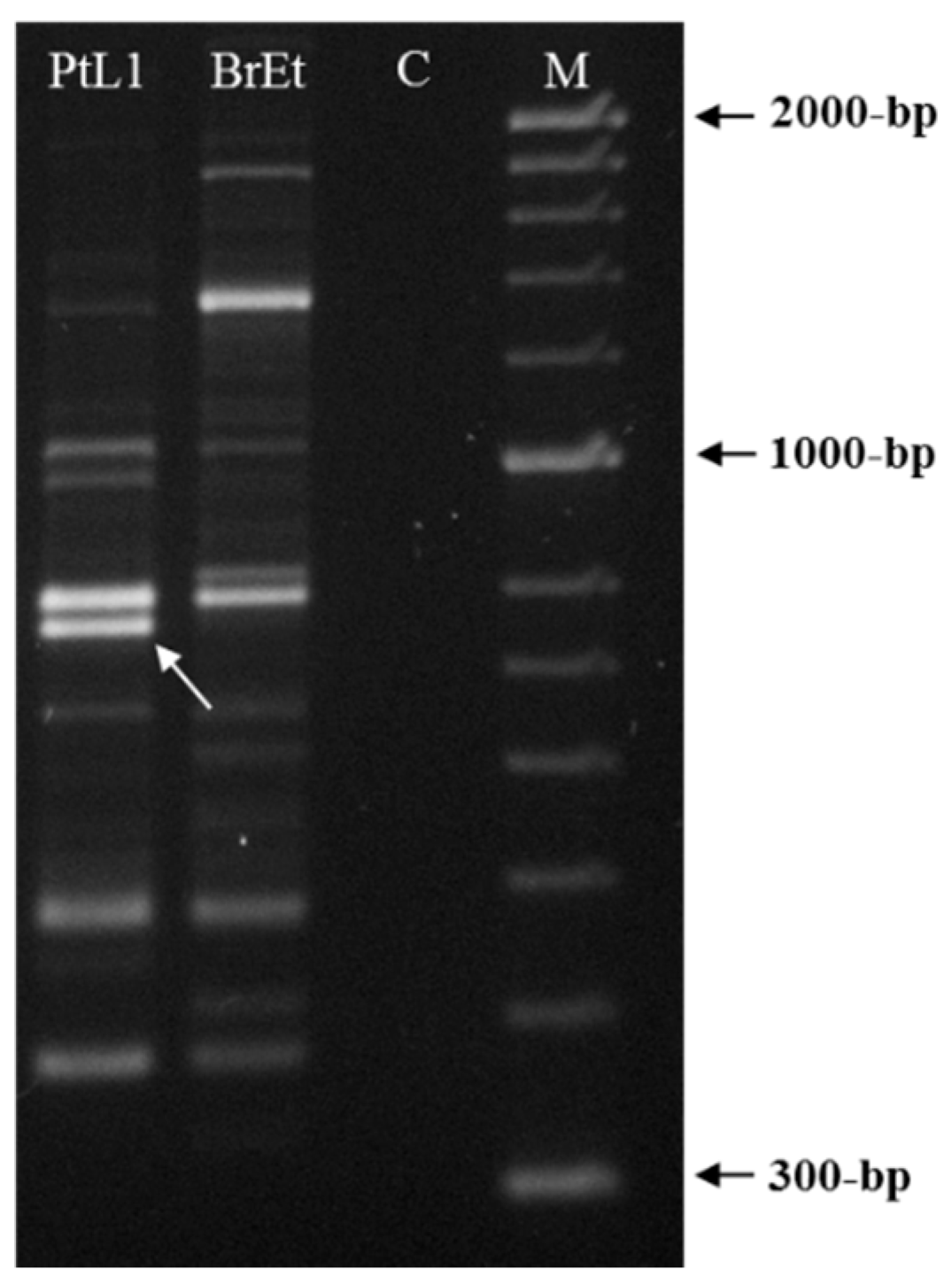
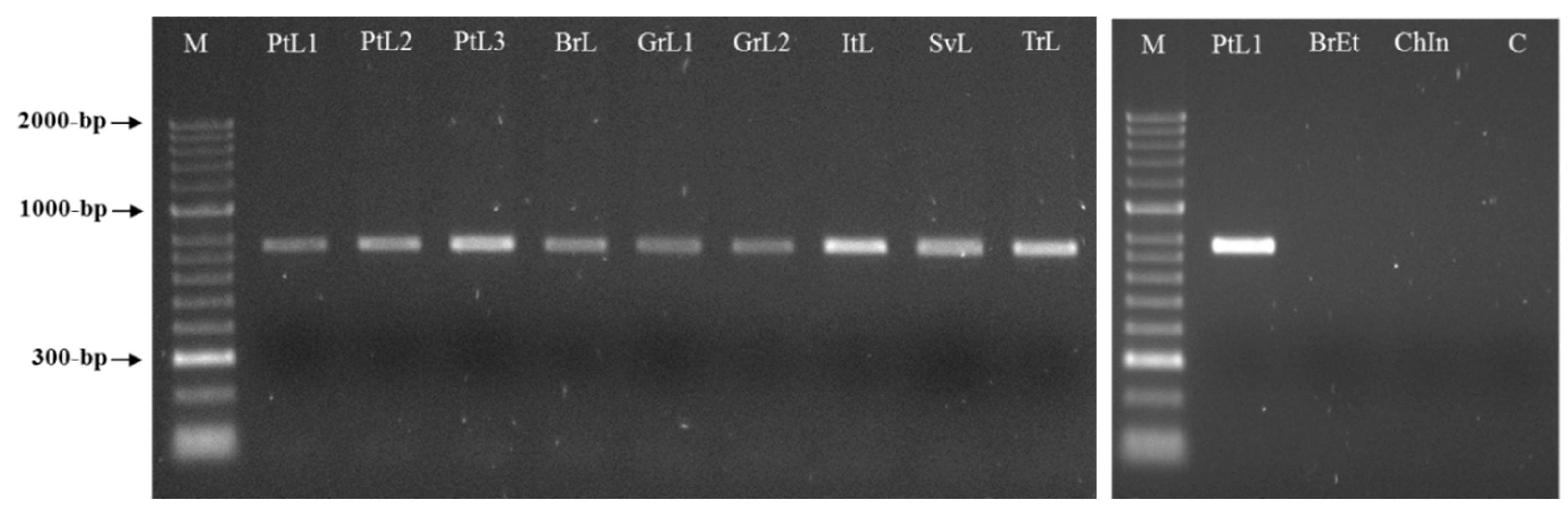
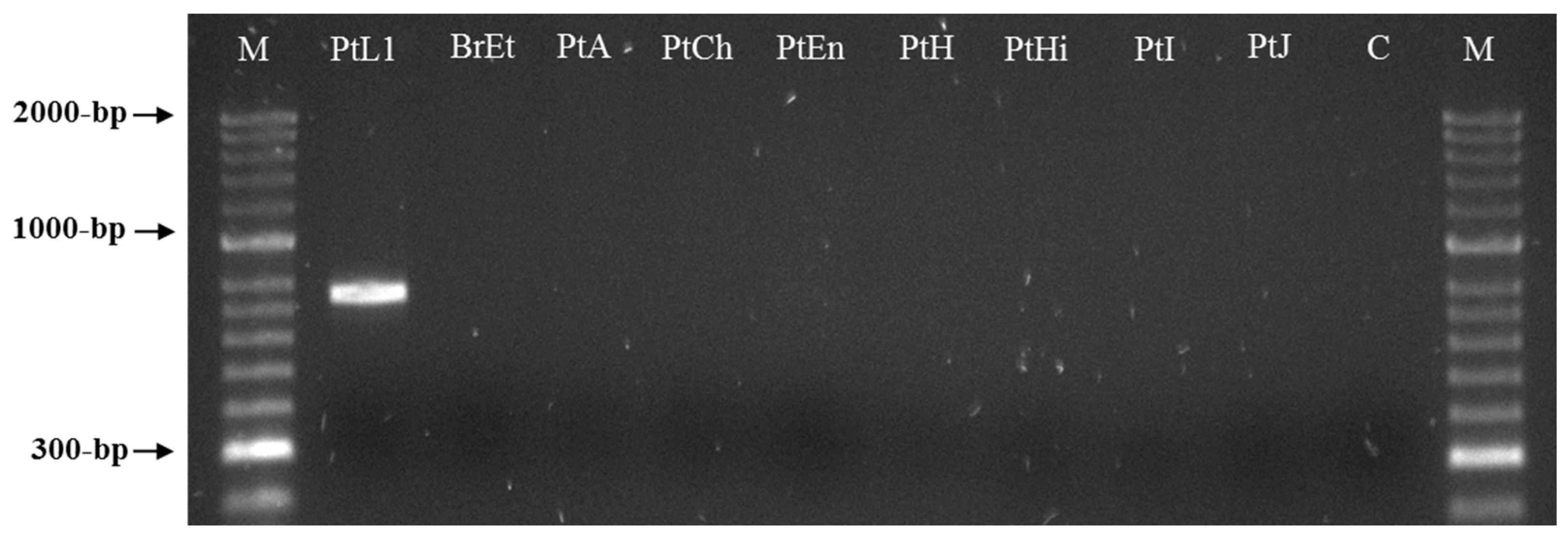
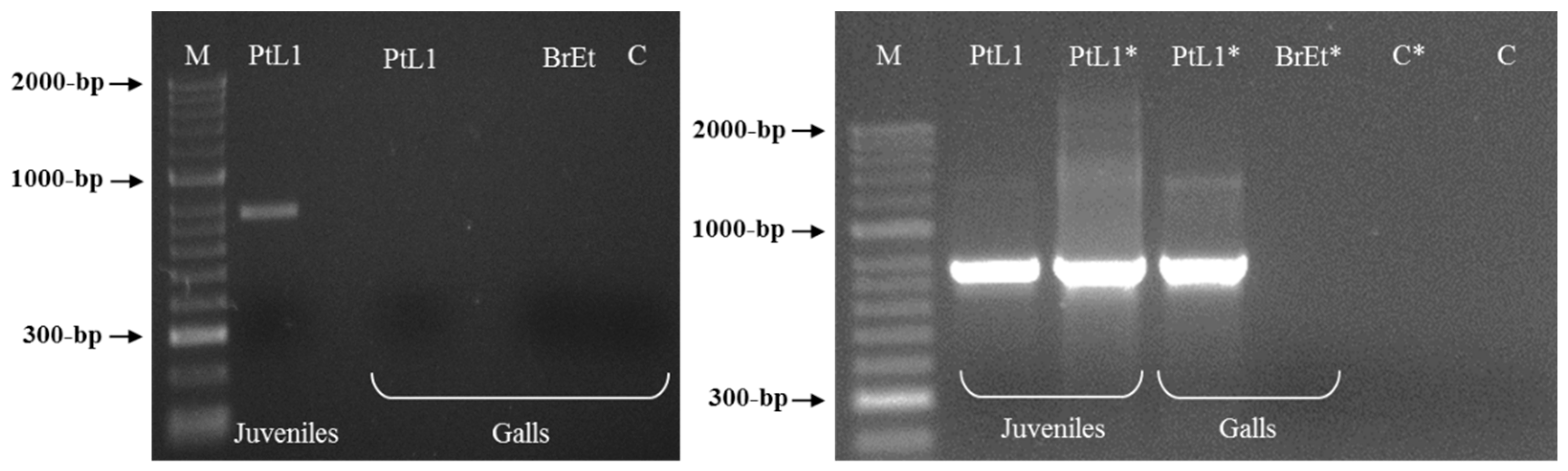
3.3. Meloidogyne luci SCAR Marker and Species-Specific Detection Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elling, A.A. Major emerging problems with minor Meloidogyne species. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 1092–10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.T.; Haegeman, A.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Gaur, H.S.; Helder, J.; Jones, M.G.K.; Kikuchi, T.; Manzanilla-López, R.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Wesemael, W.M.L. Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2013, 14, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderi, R.; Karssen, G. An updated checklist of Meloidogyne Göldi, 1887 species, with a diagnostic compendium for second-stage juveniles and males. J. Crop. Prot. 2020, 9, 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- EPPO. EPPO A2 List of Pests Recommended for Regulation as Quarantine Pests. 2020. Available online: https://www.eppo.int/ACTIVITIES/plant_quarantine/A2_list (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Carneiro, R.M.D.G.; Almeida, M.R.A.; Quénéhervé, T.P. Enzyme phenotypes of Meloidogyne spp. populations. Nematology 2000, 2, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, V.C.; Powers, T.O. Biochemical and molecular identification. In Root Knot Nematodes, 1st ed.; Perry, R.N., Moens, M., Star, J., Eds.; CABI International: London, UK, 2009; pp. 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, T.O.; Harris, T.S. A polymerase chain reaction method for identification of five major Meloidogyne species. J. Nematol. 1993, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra, C.; Donkers-Venne, D.T.H.M.; Fargette, M. Identification of Meloidogyne incognita, M. javanica and M. arenaria using sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) based PCR assays. Nematology 2000, 2, 847–853. [Google Scholar]
- Randig, O.; Bongiovanni, M.; Carneiro, R.M.D.G.; Castagnone-Sereno, P. Genetic diversity of root-knot nematodes from Brazil and development of SCAR markers specific for the coffee-damaging species. Genome 2002, 45, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, C.; van Hoof, R.; Donkers-Venne, D. A PCR test to detect the cereal root-knot nematode Meloidogyne naasi. Eur. J. Plant. Pathol. 2004, 110, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, P.; Meng, Q.; Long, H. Characterisation of Meloidogyne species from China using isozyme phenotypes and amplified mitochondrial DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism. Eur. J. Plant. Pathol. 2004, 110, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.A.M.; Phillips, M.S.; Blok, V.C. Molecular diagnostic key for identification of single juveniles of seven common and economically important species of root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.). Plant. Pathol. 2007, 56, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, V.R.; Mattos, V.S.; Almeida, M.R.A.; Santos, M.F.A.; Tigano, M.S.; Castagnone-Sereno, P.; Carneiro, R.M.D.G. Genetic diversity of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne ethiopica and development of a species-specific SCAR marker for its diagnosis. Plant. Pathol. 2014, 63, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssen, T.; Karssen, G.; Verhaeven, M.; Coyne, D.; Bert, W. Mitochondrial coding genome analysis of tropical root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne) supports haplotype based diagnostics and reveals evidence of recent reticulate evolution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerič Stare, B.; Strajnar, P.; Susic, N.; Urek, G.; Širca, S. Reported populations of Meloidogyne ethiopica in Europe identified as Meloidogyne luci. Plant. Dis. 2017, 101, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerič Stare, B.; Aydınlı, G.; Devran, Z.; Mennan, S.; Strajnar, P.; Urek, G.; Širca, S. Recognition of species belonging to Meloidogyne ethiopica group and development of a diagnostic method for its detection. Eur. J. Plant. Pathol. 2019, 154, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carneiro, R.M.D.G.; Correa, V.R.; Almeida, M.R.A.; Gomes, A.C.M.M.; Deimi, A.M.; Castagnone-Sereno, P.; Karssen, G. Meloidogyne luci n. sp. (Nematoda: Meloidogynidae), a root-knot nematode parasitising different crops in Brazil, Chile and Iran. Nematology 2014, 16, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Širca, S.; Urek, G.; Karssen, G. First report of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne ethiopica on tomato in Slovenia. Plant. Dis. 2004, 88, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strajnar, P.; Širca, S.; Gerič Stare, B.; Urek, G. Characterization of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne ethiopica Whitehead, 1968, from Slovenia. Russ. J. Nematol. 2009, 17, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Strajnar, P.; Širca, S.; Knapič, M.; Urek, G. Effect of Slovenian climatic conditions on the development and survival of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne ethiopica. Eur. J. Plant. Pathol. 2011, 129, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, I.L.; Tzortzakakis, E.A.; Gomes, P.; Abrantes, I.; da Cunha, M.J. Detection of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne ethiopica in Greece. Eur. J. Plant. Pathol. 2012, 134, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleita, C.M.; Simões, M.J.; Egas, C.; Curtis, R.H.C.; de O. Abrantes, I.M. Biometrical, biochemical, and molecular diagnosis of Portuguese Meloidogyne hispanica isolates. Plant. Dis. 2012, 96, 865–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydınlı, G.; Mennan, S.; Devran, Z.; Širca, S.; Urek, G. First report of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne ethiopica on tomato and cucumber in Turkey. Plant. Dis. 2013, 97, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellé, C.; Brum, D.; Groth, M.Z.; Barros, D.R.; Kaspary, T.E.; Schafer, J.T.; Gomes, C.B. First report of Meloidogyne luci parasitizing Glycine max in Brazil. Plant. Dis. 2016, 100, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.C.Z.; Dorigo, O.F.; Carneiro, R.M.D.G.; Araújo, J.V.F. Meloidogyne luci, a new infecting nematode species on common bean fields at Paraná State, Brazil. Helminthologia 2016, 53, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerič Stare, B.; Strajnar, P.; Širca, S.; Susic, N.; Urek, G. Record of a new location for tropical root knot nematode Meloidogyne luci in Slovenia. EPPO Bull. 2018, 48, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maleita, C.; Esteves, I.; Cardoso, J.M.S.; Cunha, M.J.; Carneiro, R.M.D.G.; Abrantes, I. Meloidogyne luci, a new root-knot nematode parasitizing potato in Portugal. Plant. Pathol. 2018, 67, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellé, C.; Balardin, R.R.; Ramos, R.F.; Sobucki, L.; Gabriel, M.; Antoniolli, Z.I. First report of Meloidogyne luci (Nematoda: Meloidogynidae) parasitizing Luffa cylindrica in Brazil. Plant. Dis. 2019, 103, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellé, C.; Ramos, R.F.; Balardin, R.R.; Nora, D.D.; Gabriel, M.; Antoniolli, Z.I. Reproduction of the root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne ethiopica and Meloidogyne luci, on common bean cultivars. Revista de Ciências Agrárias 2019, 42, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Correia, A.; Abrantes, I.; Maleita, C. New hosts and records in Portugal for the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne luci. J. Nematol. 2019, 51, e2019-03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, A.R.; Conceição, I.L.; Kormpi, M.; Tzortzakakis, E.A. Lavandula angustifolia and Oxalis pes-caprae, hosts of Meloidogyne hapla and Meloidogyne javanica—A note for Meloidogyne luci in Greece. Hell. Plant. Prot. J. 2020, 13, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susič, N.; Širca, S.; Urek, G.; Gerič Stare, B. Senecio vulgaris L. recorded as a new host plant for the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne luci. Acta Agric. Slov. 2020, 115, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinque, L.; Nóbrega, F.; Cordeiro, L.; Serra, C.; Inácio, M.L. First detection of Meloidogyne luci (Nematoda: Meloidogynidae) parasitizing potato in the Azores, Portugal. Plants 2021, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žibrat, U.; Gerič Stare, B.; Knapič, M.; Susič, N.; Lapajne, J.; Širca, S. Detection of root-knot nematode Meloidogyne luci infestation of potato tubers using hyperspectral remote sensing and real-time PCR molecular methods. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Conceição, I.L.; da Cunha, M.J.; Feio, G.; Correia, M.; dos Santos, M.C.V.; Isabel, M.D.O.; Santos, M.S.D.A. Root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne spp., on potato in Portugal. Nematology 2009, 11, 311–313. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, D.; Abrantes, I.; Maleita, C. The quarantine root knot nematode Meloidogyne enterolobii—A potential threat to Portugal and Europe. Plant. Pathol. 2019, 68, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, R.M.D.G.; Gomes, C.B.; Almeida, M.R.A.; Gomes, A.C.M.M.; Martins, I. Primeiro registro de Meloidogyne ethiopica, Whitehead, 1968 em plantas de quivi no Brasil e reação de diferentes plantas cultivadas. Nematol. Bras. 2003, 27, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Abrantes, I.D.O.; dos Santos, M.V.; da Conceição, I.L.P.M.; Santos, M.D.A.; Vovlas, N. Root-knot and other plant parasitic nematodes associated with fig trees in Portugal. Nematol. Mediterr. 2008, 36, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EPPO. 2016. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/reporting/article-5957 (accessed on 4 July 2021).
- EPPO. 2017. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/reporting/article-6186 (accessed on 4 July 2021).
- Álvarez-Ortega, S.; Brito, J.A.; Subbotin, S.A. Multigene phylogeny of root-knot nematodes and molecular characterization of Meloidogyne nataliei Golden, Rose & Bird, 1981 (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 11788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Susič, N.; Koutsovoulos, G.D.; Riccio, C.; Danchin, E.; Blaxter, M.L.; Lunt, D.H.; Strajnar, P.; Širca, S.; Urek, G.; Stare, B.G. Genome sequence of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne luci. J. Nematol. 2020, 52, e2020-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carneiro, R.; Karssen, G.; Gomes, A.C.; de Lourdes Mendes, M.; Almeida, M.R.; dos Santos, M. Additional information on Meloidogyne inornata Lordello, 1956 (Tylenchida: Meloidogynidae) and its characterisation as a valid species. Nematology 2008, 10, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, G.R.; Carvalho, A.H.O.; Teixeira, A.G.; Ferreira, M.L.S.M.; Oliveira, F.L.; de Moraes, W.B.; Alves, F.R. First report of Meloidogyne inornata on Smallanthus sonchifolius in Brazil. Plant. Dis. 2020, 104, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species (Isolate Code) a | Host Plant | Geographic Origin | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| M. luci(PtL1) | Solanum tuberosum L. | Coimbra | [27] |
| (PtL2) | Oxalis corniculata L. | Montemor-o-Velho | [30] |
| (PtL3) | Cordyline australis (Forst f.) Hook. F | Figueira da Foz | [30] |
| (BrL) | Phaseolus vulgaris L. | Paraná State | [25] |
| (GrL1) | Zea mays L. | Kavalla | [15,21] |
| (GrL2) | Actinidia sp. | Kavalla | [15,21] |
| (ItL) | S. lycopersicum L. | Pontecagnano | [15,22] |
| (SvL) | S. lycopersicum L. | Dornberk | [15,18] |
| (TrL) | Cucumis sativus L. | Çarsamba | [15,23] |
| M. arenaria (PtA) | Crassula multicava Lem. | Coimbra | — |
| M. chitwoodi (PtCh) | S. tuberosum L. | Porto | [35] |
| M. enterolobii (PtEn) | Cereus hildmannianus K. Schum. | Montemor-o-Velho | [36] |
| M. ethiopica (BrEt) | Actinidia deliciosa (Chevalier) Liang & Ferguson | Rio Grande do Sul State | [37] |
| M. hapla (PtHa) | S. lycopersicum L. | Montemor-o-Velho | — |
| M. hispanica (PtHi) | Ficus carica L. | Setúbal | [38] |
| M. incognita (PtI) | Cucumis melo L. | Azores | [22] |
| M. inornata (ChIn) b | S. lycopersicum L. | Chile | — |
| M. javanica (PtJ) | S. tuberosum L. | Guarda | [22] |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| OPA-06 | GGTCCCTGAC |
| OPA-08 | GTGACGTAGG |
| OPA-09 | GGGTAACGCC |
| OPA-17 | GACCGCTTGT |
| OPAB-05 | CCCGAAGCGA |
| OPAS-09 | TGGAGTCCCC |
| OPB-01 | GTTTCGCTCC |
| OPB-14 | TCCGCTCTGG |
| OPC-06 | GAACGGACTC |
| OPC-08 | TGGACCGGTG |
| OPD-01 | ACCGCGAAGG |
| OPE-06 | AAGACCCCTC |
| OPE-07 | AGATGCAGCC |
| OPF-07 | CCGATATCCC |
| OPG-04 | AGCGTGTCTG |
| OPK-02 | GTCTCCGCAA |
| OPM-01 | GTTGGTGGCT |
| OPN-11 | CTCACGTTGG |
| OPO-06 | CCACGGGAAG |
| OPR-09 | TGAGCACGAG |
| OPY-11 | AGACGATGGG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maleita, C.; Cardoso, J.M.S.; Rusinque, L.; Esteves, I.; Abrantes, I. Species-Specific Molecular Detection of the Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne luci. Biology 2021, 10, 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080775
Maleita C, Cardoso JMS, Rusinque L, Esteves I, Abrantes I. Species-Specific Molecular Detection of the Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne luci. Biology. 2021; 10(8):775. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080775
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaleita, Carla, Joana M. S. Cardoso, Leidy Rusinque, Ivânia Esteves, and Isabel Abrantes. 2021. "Species-Specific Molecular Detection of the Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne luci" Biology 10, no. 8: 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080775
APA StyleMaleita, C., Cardoso, J. M. S., Rusinque, L., Esteves, I., & Abrantes, I. (2021). Species-Specific Molecular Detection of the Root Knot Nematode Meloidogyne luci. Biology, 10(8), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080775






