TLR7 Activation of Macrophages by Imiquimod Inhibits HIV Infection through Modulation of Viral Entry Cellular Factors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Virus and Reagents
2.3. Preparation of Virus Stocks
2.4. MTS Assay
2.5. Imiquimod Treatment and HIV Infection
2.6. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Detection of HIV Strong-Stop DNA
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Measurement of Green Fluorescence
2.11. ELISA
2.12. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
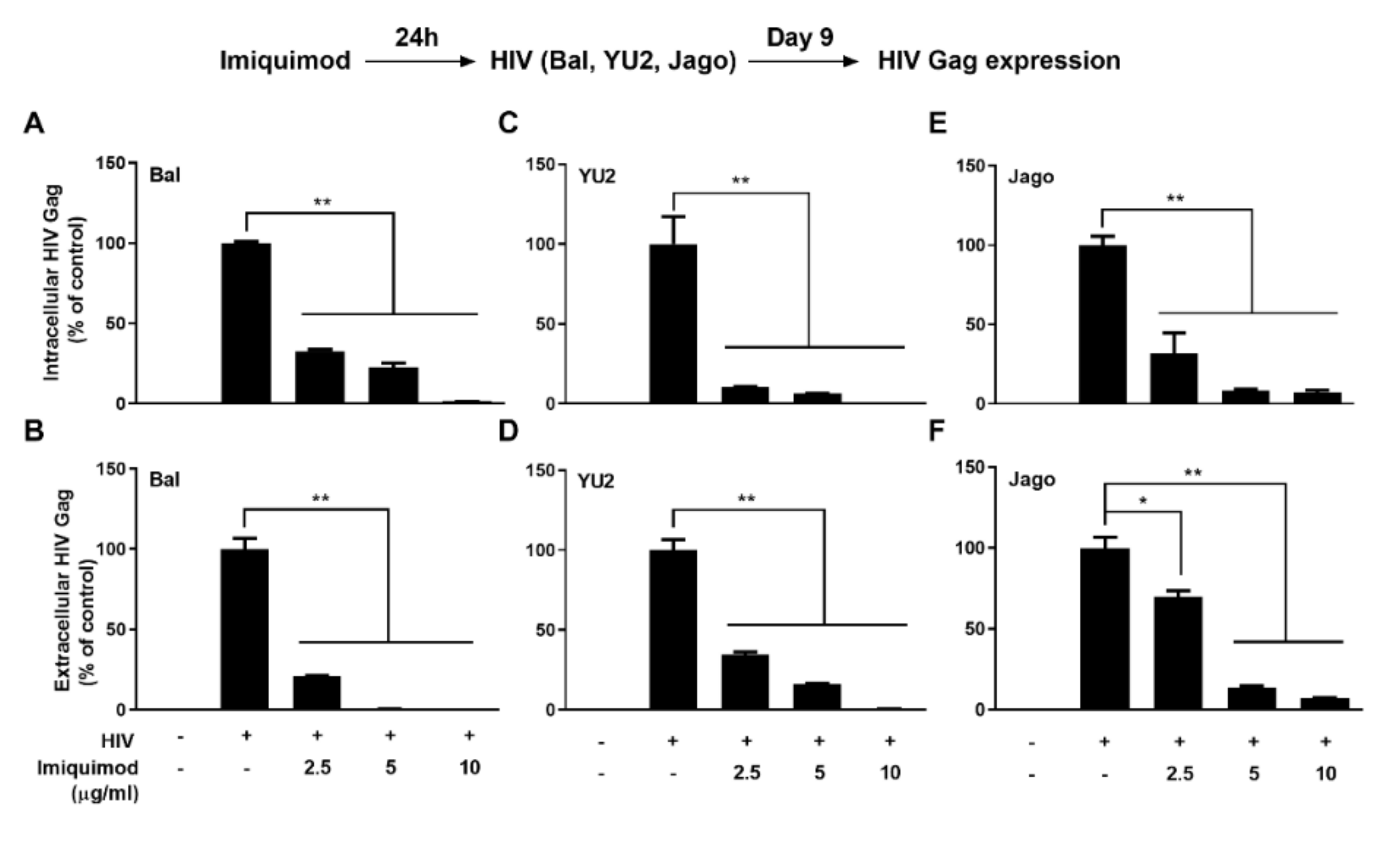
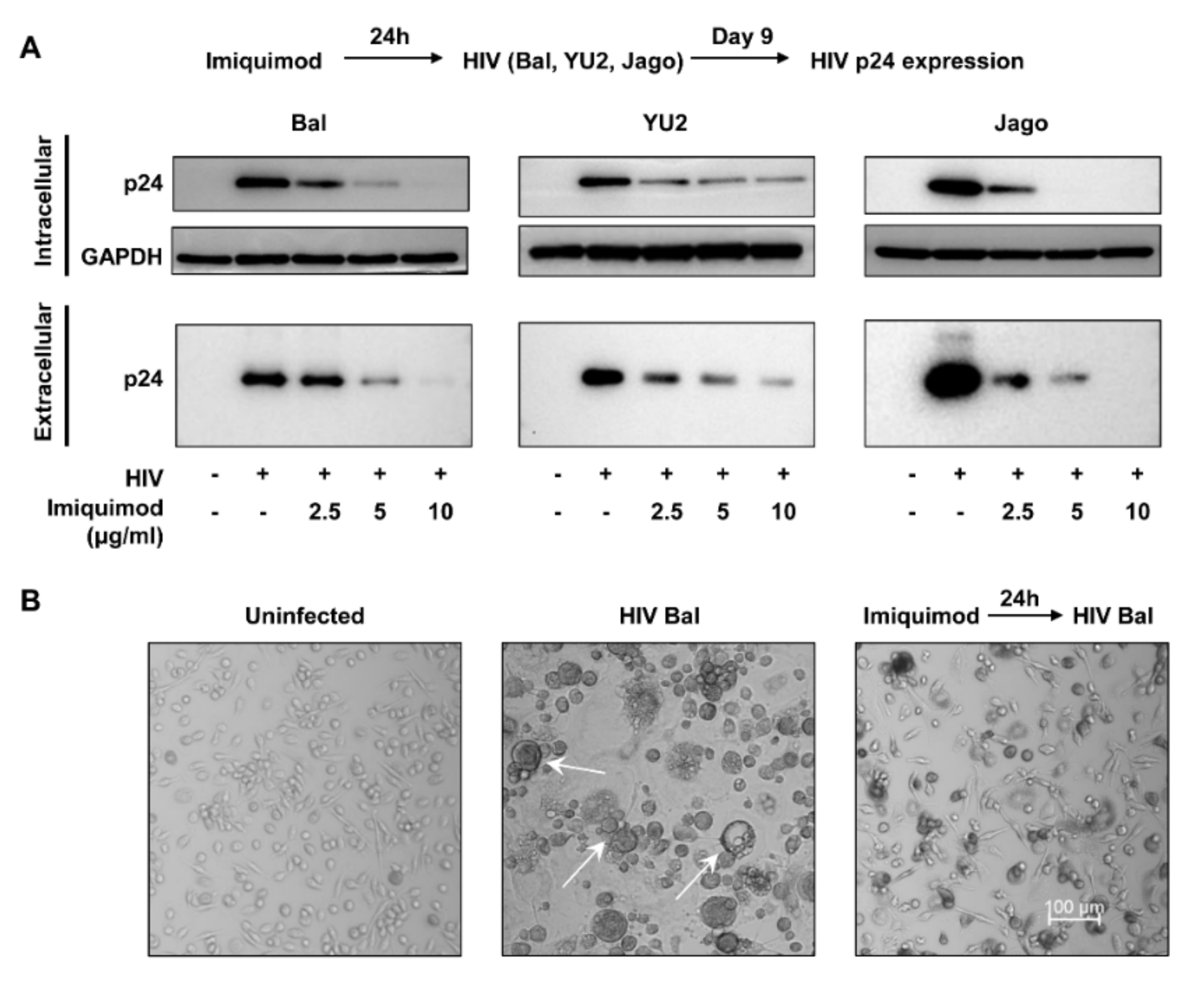
3.1. Imiquimod Inhibits HIV Infection of Macrophages
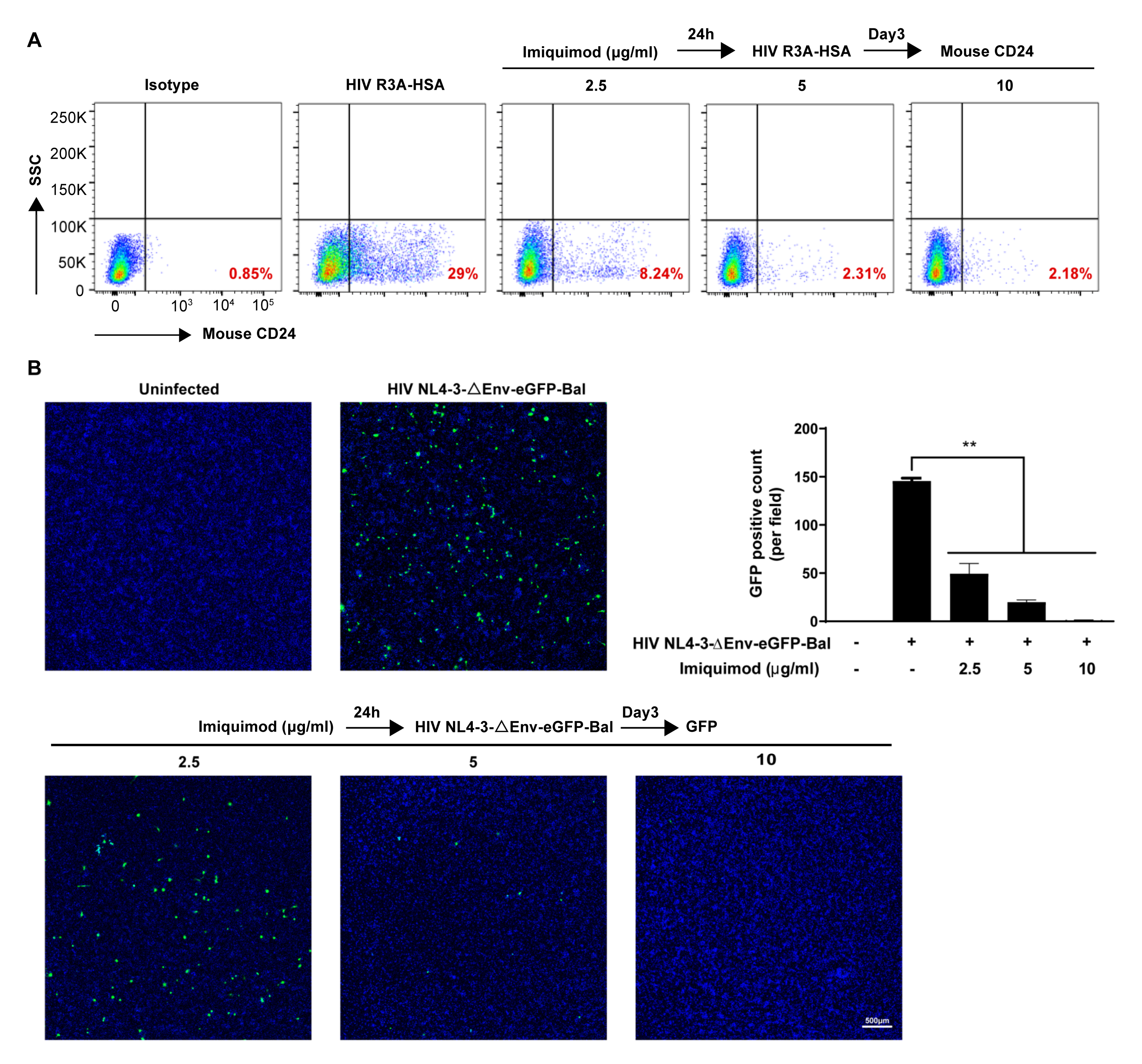
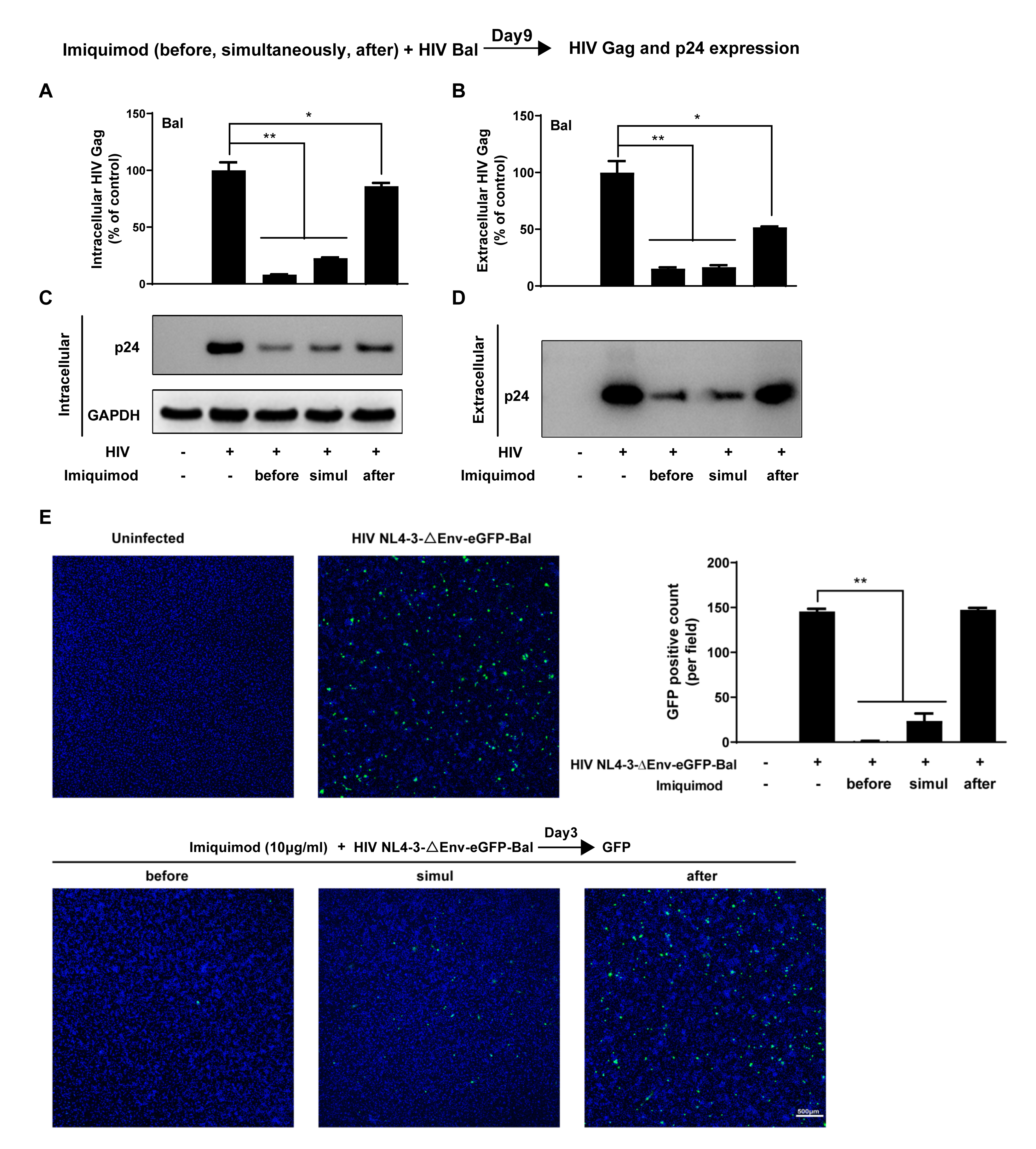
3.2. Imiquimod Blocks HIV Entry into Macrophages
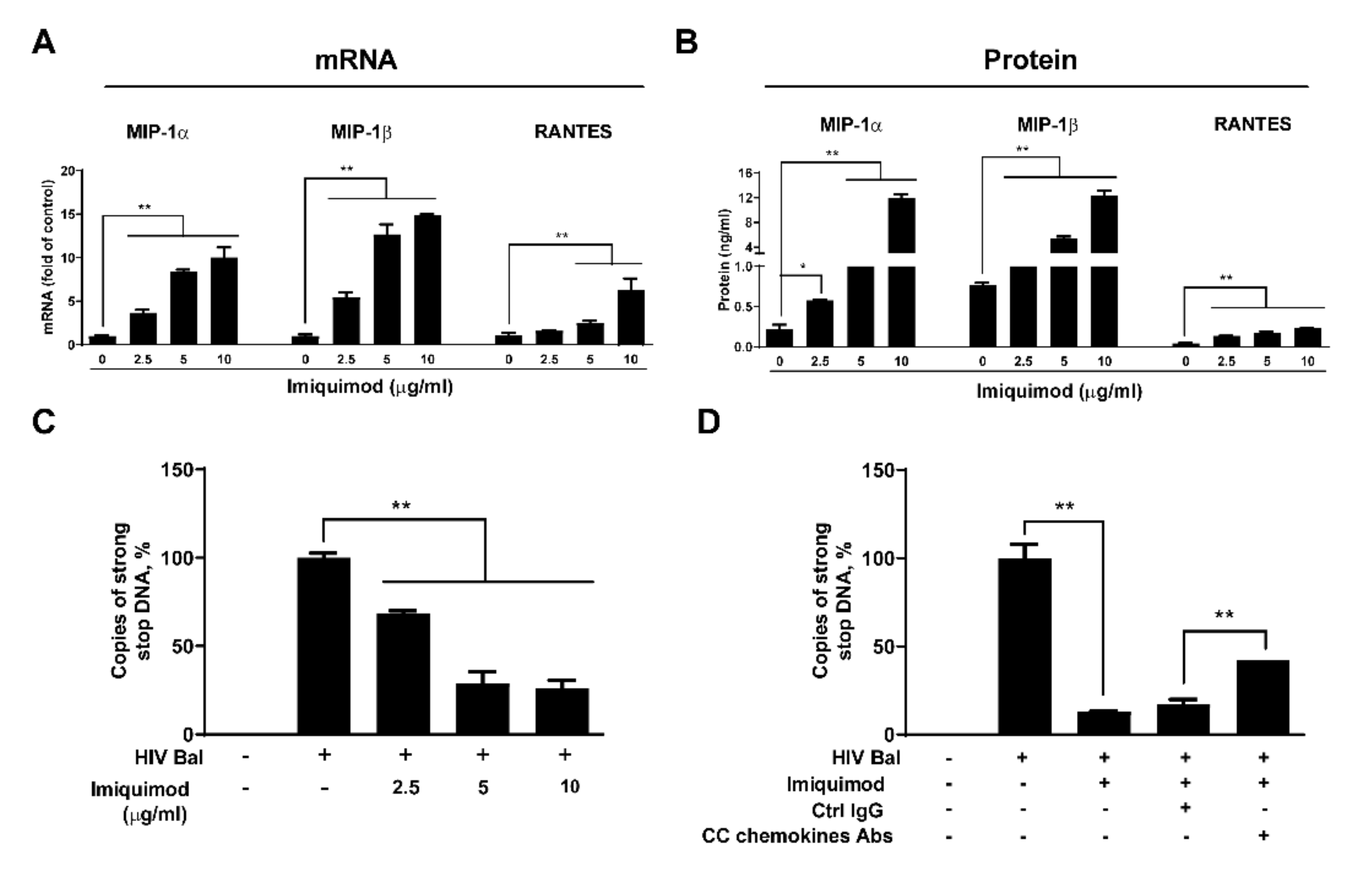
3.3. Imiquimod Induces CC Chemokines
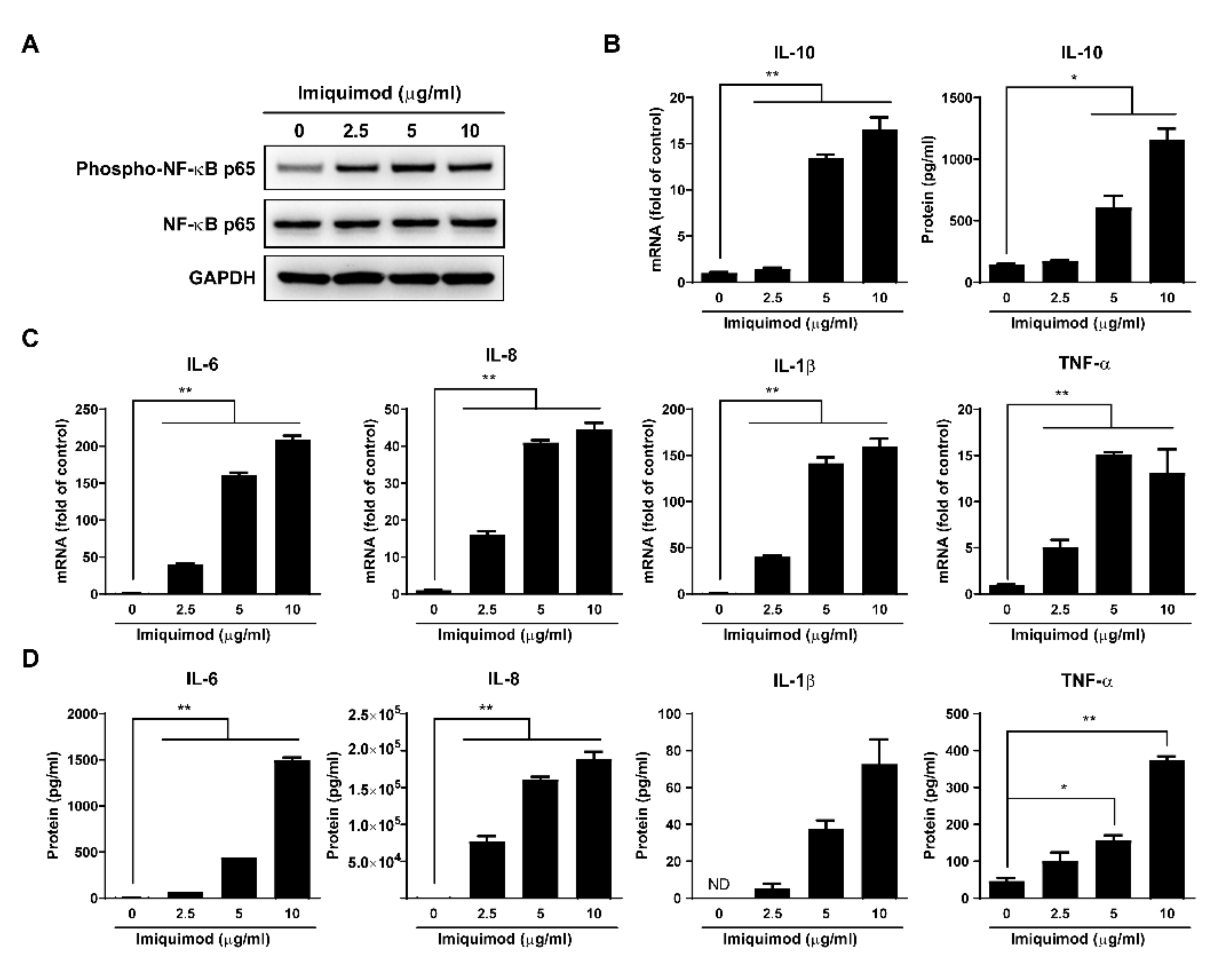
3.4. Imiquimod Induces Inflammatory Cytokines
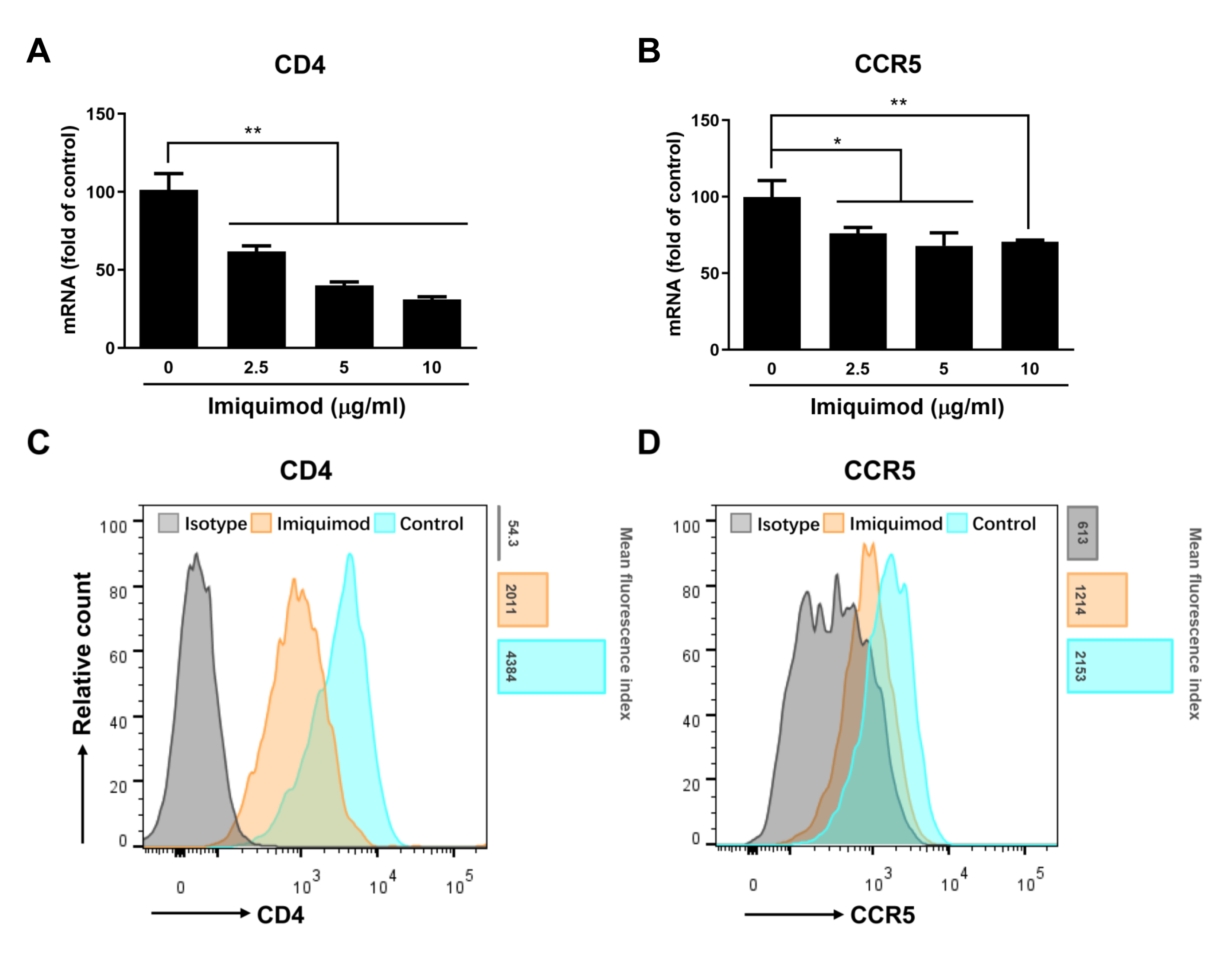
3.5. Imiquimod Suppresses CD4 and CCR5 Expression
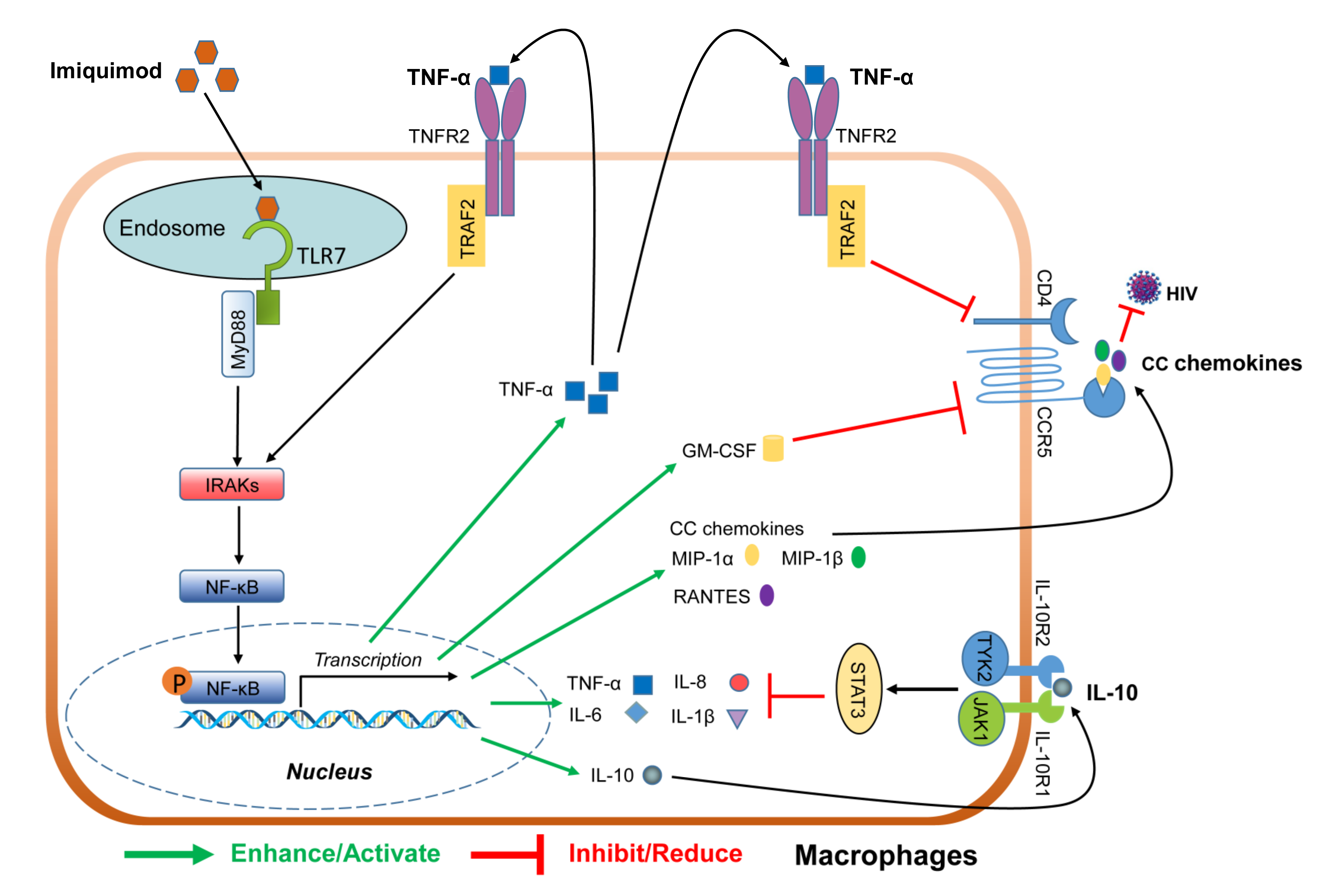
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carty, M.; Guy, C.; Bowie, A.G. Detection of Viral Infections by Innate Immunity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 183, 114316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, K.L.; Garcia, J.V.; Clements, J.E.; Walker, B.D. HIV Infection of Macrophages: Implications for Pathogenesis and Cure. Pathog. Immun. 2017, 2, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruize, Z.; Kootstra, N.A. The Role of Macrophages in HIV-1 Persistence and Pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, S.; Gendelman, H.E.; Orenstein, J.M.; Canto, M.C.D.; Pezeshkpour, G.H.; Yungbluth, M.; Janotta, F.; Aksamit, A.; Martin, M.A.; Fauci, A.S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science 1986, 233, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, N.; The Swiss HIV Cohort Study; von Siebenthal, C.; Vongrad, V.; Turk, T.; Neumann, K.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Bogojeska, J.; Fellay, J.; Roth, V.; et al. Determinants of HIV-1 reservoir size and long-term dynamics during suppressive ART. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.E.; Jaworowski, A.; Hearps, A.C. The HIV Reservoir in Monocytes and Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Pang, K.C.; Masters, S.L. Intercellular communication for innate immunity. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 86, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like Receptors and Their Crosstalk with Other Innate Receptors in Infection and Immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asami, J.; Shimizu, T. Structural and functional understanding of the toll-like receptors. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasius, A.L.; Beutler, B. Intracellular Toll-like Receptors. Immunity 2010, 32, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, H.; Vanwalscappel, B.; Bloch, N.; Landau, N.R. TLR7/8 agonist induces a post-entry SAMHD1-independent block to HIV-1 infection of monocytes. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitendijk, M.; Eszterhas, S.K.; Howell, A.L. Gardiquimod: A Toll-Like Receptor-7 Agonist That Inhibits HIV Type 1 Infection of Human Macrophages and Activated T Cells. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2013, 29, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bam, R.A.; Hansen, D.; Irrinki, A.; Mulato, A.; Jones, G.S.; Hesselgesser, J.; Frey, C.R.; Cihlar, T.; Yant, S.R. TLR7 Agonist GS-9620 Is a Potent Inhibitor of Acute HIV-1 Infection in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chuang, T.-H.; Redecke, V.; She, L.; Pitha, P.M.; Carson, D.A.; Raz, E.; Cottam, H.B. Molecular basis for the immunostimulatory activity of guanine nucleoside analogs: Activation of Toll-like receptor 7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6646–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, C.J.; Jenski, L.; Voychehovski, T.; Bernstein, D. Modification of immunological responses and clinical disease during topical R-837 treatment of genital HSV-2 infection. Antivir. Res. 1988, 10, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megyeri, K.; Au, W.C.; Rosztoczy, I.; Raj, N.B.; Miller, R.L.; Tomai, M.A.; Pitha, P.M. Stimulation of interferon and cytokine gene expression by imiquimod and stimulation by Sendai virus utilize similar signal transduction pathways. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengge, U.R.; Cusini, M. Topical immunomodulators for the treatment of external genital warts, cutaneous warts and molluscum contagiosum. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 149 (Suppl. 66), 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, E.E.; Erlich, J.; Liong, F.; Luong, R.; Liong, S.; Bozinovski, S.; Seow, H.; O’Leary, J.J.; Brooks, D.A.; Vlahos, R.; et al. Intranasal and epicutaneous administration of Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) agonists provides protection against influenza A virus-induced morbidity in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, A.; Alexandris, N.; Konstantinou, E.; Mesiakaris, K.; Zanidis, C.; Farsalinos, K.; Poulas, K. Imiquimod—A toll like receptor 7 agonist—Is an ideal option for management of COVID 19. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiag, P.; Bauhofer, A.; Bouscarat, F.; Aquilina, C.; Ortonne, J.P.; Dupin, N.; Mougin, C. Imiquimod 5% cream for external genital or perianal warts in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy: An open-label, noncomparative study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanclemente, G.; Herrera, S.; Tyring, S.; Rady, P.; Zuleta-Tobón, J.J.; Correa, L.-A.; He, Q.; Wolff, J.-C. Human papillomavirus (HPV) viral load and HPV type in the clinical outcome of HIV-positive patients treated with imiquimod for anogenital warts and anal intraepithelial neoplasia. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2007, 21, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, A.; Potthoff, A.; Brockmeyer, N.H.; Gambichler, T.; Stücker, M.; Altmeyer, P.; Swoboda, J.; Pfister, H.; Wieland, U. Imiquimod Leads to a Decrease of Human Papillomavirus DNA and to a Sustained Clearance of Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia in HIV-Infected Men. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2078–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, M.A. Immunomodulatory therapy in the management of viral infections in patients with HIV infection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 43, S27–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, L.; Qin, H.; Muldowney, M.T.; Yanagisawa, L.L.; Kutsch, O.; Clements, J.E.; Benveniste, E.N. Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 Inhibits Antiviral IFN-β Signaling To Enhance HIV-1 Replication in Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.L.; Wilson, H.D.; Iyer, S.S.; Coss, K.; Doores, K.; Smith, S.; Kellam, P.; Finzi, A.; Borrow, P.; Hahn, B.; et al. Resistance of Transmitted Founder HIV-1 to IFITM-Mediated Restriction. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, A.N.; Lai, J.; Turville, S.; Samarajiwa, S.; Gray, L.; Marsden, V.; Mercier, S.K.; Jones, K.; Nasr, N.; Rustagi, A.; et al. HIV infection of dendritic cells subverts the IFN induction pathway via IRF-1 and inhibits type 1 IFN production. Blood 2011, 118, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, A.; Alce, T.; Lubyova, B.; Ezelle, H.; Strebel, K.; Pitha, P.M. HIV-1 accessory proteins VPR and Vif modulate antiviral response by targeting IRF-3 for degradation. Virology 2008, 373, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehle, B.P.; Hladik, F.; McNevin, J.P.; McElrath, M.J.; Gale, M. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Mediates Global Disruption of Innate Antiviral Signaling and Immune Defenses within Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10395–10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, R.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.; Ho, W. HIV infection suppresses TLR3 activation-mediated antiviral immunity in microglia and macrophages. Immunology 2020, 160, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.-Q.; Hu, Q.; Song, L.; Ye, L.; Zhou, D.; Ho, W. A critical function of toll-like receptor-3 in the induction of anti-human immunodeficiency virus activities in macrophages. Immunology 2010, 131, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, L.; Zhou, Y.; Persidsky, Y.; Ho, W. Immune activation of human brain microvascular endothelial cells inhibits HIV replication in macrophages. Blood 2013, 121, 2934–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.A.; Doms, R.W.; Fenyö, E.-M.; Korber, B.; Littman, D.R.; Moore, J.P.; Sattentau, Q.J.; Schuitemaker, H.; Sodroski, J.; Weiss, R.A. A new classification for HIV-1. Nature 1998, 391, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Li, G.; Jeffrey, J.; Kovalev, G.; Su, L. Efficient infection, activation, and impairment of pDCs in the BM and peripheral lymphoid organs during early HIV-1 infection in humanized rag2−/−γ C−/− mice in vivo. Blood 2011, 117, 6184–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, B.D.; Zack, J.A. In Vivo Pathogenesis of a Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Reporter Virus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6520–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.N.; Aldrovandi, G.M.; Kutsch, O.; Shaw, G.M. Dynamics of HIV-1 recombination in its natural target cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4204–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Balakrishnan, M.; Gorelick, R.J.; Bambara, R.A. A Succession of Mechanisms Stimulate Efficient Reconstituted HIV-1 Minus Strand Strong Stop DNA Transfer. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Basu, V.P.; Song, M.; Gao, L.; Rigby, S.T.; Hanson, M.N.; Bambara, R.A. Strand transfer events during HIV-1 reverse transcription. Virus Res. 2008, 134, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinkovich, A.; Weisman, Z.; Bentwich, Z. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Role in HIV infection. Immunol. Lett. 1999, 68, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmi, H.; Kaisho, T.; Takeuchi, O.; Sato, S.; Sanjo, H.; Hoshino, K.; Horiuchi, T.; Tomizawa, H.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88–dependent signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, F.; Yamauchi, K.; Murat, M.; Bernasconi, M.; Yamanaka, N.; Speck, R.; Nadal, D. Activation of NF- B via Endosomal Toll-Like Receptor 7 (TLR7) or TLR9 Suppresses Murine Herpesvirus 68 Reactivation. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10002–10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petes, C.; Odoardi, N.; Gee, K. The Toll for Trafficking: Toll-Like Receptor 7 Delivery to the Endosome. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, J.; Cagnard, N.; Woollard, K.; Patey, N.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Senechal, B.; Puel, A.; Biswas, S.K.; Moshous, D.; Picard, C.; et al. Human CD14dim Monocytes Patrol and Sense Nucleic Acids and Viruses via TLR7 and TLR8 Receptors. Immunity 2010, 33, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patinote, C.; Karroum, N.B.; Moarbess, G.; Cirnat, N.; Kassab, I.; Bonnet, P.-A.; Deleuze-Masquéfa, C. Agonist and antagonist ligands of toll-like receptors 7 and 8: Ingenious tools for therapeutic purposes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 193, 112238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahama, S.; Yamamoto, T. Pattern Recognition Receptor Ligands as an Emerging Therapeutic Agent for Latent HIV-1 Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, M. Recent trends in the development of Toll-like receptor 7/8-targeting therapeutics. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzierska, K.; Rainbird, M.A.; Lopez, A.F.; Crowe, S.M. Effect of GM-CSF on HIV-1 replication in monocytes/macrophages in vivo and in vitro: A review. Veter. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 63, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, C.E.; Gibson, S.J. Induction of Interferon and Other Cytokines by Imiquimod and Its Hydroxylated Metabolite R-842 in Human Blood Cells In Vitro. J. Interf. Res. 1994, 14, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, S.J.; Imbertson, L.M.; Wagner, T.L.; Testerman, T.; Reiter, M.J.; Miller, R.L.; Tomai, M.A. Cellular Requirements for Cytokine Production in Response to the Immunomodulators Imiquimod and S-27609. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 1995, 15, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, T.L.; Horton, V.L.; Carlson, G.L.; Myhre, P.E.; Gibson, S.J.; Imbertson, L.M.; Tomai, M.A. Induction of cytokines in cynomolgus monkeys by the immune response modifiers, imiquimod, S-27609 and S-28463. Cytokine 1997, 9, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testerman, T.L.; Gerster, J.F.; Imbertson, L.M.; Reiter, M.J.; Miller, R.L.; Gibson, S.J.; Wagner, T.L.; Tomai, M.A. Cytokine induction by the immunomodulators imiquimod and S-27609. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1995, 58, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Samani, D.; Nain, S.; Dhole, T.N. Interleukin-10 polymorphisms and susceptibility to ARV associated hepatotoxicity. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 133, 103544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbein, G.; Montaner, L.J.; Gordon, S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits entry of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 into primary human macrophages: A selective role for the 75-kilodalton receptor. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7388–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbein, G.; Doyle, A.G.; Montaner, L.J.; Gordon, S. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) down-regulates CD4 expression in primary human macrophages through induction of endogenous tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-1β. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1995, 102, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzio, P.; Tse, J.; Landau, N.R. Chemokine Receptor Regulation and HIV Type 1 Tropism in Monocyte-Macrophages. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1998, 14, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, B.R.; Markovitz, D.M.; Woodford, N.L.; Rochford, R.; Strieter, R.M.; Coffey, M.J. TNF-alpha inhibits HIV-1 replication in peripheral blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages by inducing the production of RANTES and decreasing C-C chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) expression. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar]
- McManus, C.M.; Brosnan, C.F.; Berman, J.W. Cytokine induction of MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta in human fetal microglia. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Primer | Accession No. | Orientation | Sequences | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | NM_002046 | Sense Antisense | 5′-GGTGGTCTCCTCTGACTTCAACA-3′ 5′-GTTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGTTGT-3′ | 127 |
| GAG | NC_001802.1 | Sense Antisense | 5′-ATAATCCACCTATCCCAGTAGGAGAAA-3′ 5′-TTTGGTCCTTGTCTTATGTCCAGAATGC-3′ | 115 |
| CD4 | NM_001382706.1 | Sense Antisense | 5′-AGTCCCTTTTAGGCACTTGC-3′ 5′-GATCATTCAGCTTGGATGG-3′ | 224 |
| CCR5 | NM_001100168.2 | Sense Antisense | 5′-CAAGTGTCAAGTCCAATCTA-3′ 5′-ACCAAAGATGAACACCAGTG-3′ | 123 |
| MIP-1α | NM_021006.5 | Sense Antisense | 5′-GCTGACTACTTTGAGACGAGC-3′ 5′-CCAGTCCATAGAAGAGGTAGC-3′ | 252 |
| MIP-1β | NM_002984.4 | Sense Antisense | 5′- CCAAACCAAAAGAAGCAAGC -3′ 5′- AGAAACAGTGACAGTGGACC -3′ | 314 |
| RANTES | NM_002985.3 | Sense Antisense | 5′- CTGCATCTGCCTCCCCATA -3′ 5′- GCGGGCAATGTAGGCAAA -3′ | 62 |
| HIV-1 LTR RU/5 | NC_001802.1 | Sense Antisense | 5′-TCTCTCTGGTTAGACCAGATCTG-3′ 5′-ACTGCTAGAGATTTTCCACACTG-3′ | 180 |
| IL-6 | NM_001371096 | Sense Antisense | 5′-AGGAGACTTGCCTGGTGAAA-3′ 5′-CAGGGGTGGTTATTGCATCT-3′ | 180 |
| IL-8 | NM_000584 | Sense Antisense | 5′-ATGACTTCCAAGCTGGCCGTGGCT-3′ 5′-TCTCAGCCCTCTTCAAAAACTTCTC-3′ | 292 |
| IL-1β | NM_000576 | Sense Antisense | 5′-AGGTGCATCGTGCACATAAG-3′ 5′-AAGCTGATGGCCCTAAACAG-3′ | 281 |
| TNF-α | NM_000594 | Sense Antisense | 5′-CGAGTGACAAGCCTGTAGC-3′ 5′-GGTGTGGGTGAGGAGCACAT-3′ | 215 |
| IL-10 | NM_001382624 | Sense Antisense | 5′-CTTTAATAAGCTCCAAGAGAAAGGC-3′ 5′-CAGATCCGATTTTGGAGACC-3′ | 167 |
| IFN-α | NM_002169.3 | Sense Antisense | 5′-TTTCTCCTGCCTGAAGAACAG-3′ 5′-GCTCATGATTTCTGCTCTGACA-3′ | 373 |
| IFN-β | NM_002176.4 | Sense Antisense | 5′-GCCGCATTGACCATCTATGAGA-3′ 5′-GAGATCTTCAGTTTCGGAGGTAAC-3′ | 346 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, F.-Z.; Liu, J.-B.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Hu, W.-H.; Hou, W.; Ho, W.-Z. TLR7 Activation of Macrophages by Imiquimod Inhibits HIV Infection through Modulation of Viral Entry Cellular Factors. Biology 2021, 10, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070661
Meng F-Z, Liu J-B, Wang X, Wang P, Hu W-H, Hou W, Ho W-Z. TLR7 Activation of Macrophages by Imiquimod Inhibits HIV Infection through Modulation of Viral Entry Cellular Factors. Biology. 2021; 10(7):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070661
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Feng-Zhen, Jin-Biao Liu, Xu Wang, Peng Wang, Wen-Hui Hu, Wei Hou, and Wen-Zhe Ho. 2021. "TLR7 Activation of Macrophages by Imiquimod Inhibits HIV Infection through Modulation of Viral Entry Cellular Factors" Biology 10, no. 7: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070661
APA StyleMeng, F.-Z., Liu, J.-B., Wang, X., Wang, P., Hu, W.-H., Hou, W., & Ho, W.-Z. (2021). TLR7 Activation of Macrophages by Imiquimod Inhibits HIV Infection through Modulation of Viral Entry Cellular Factors. Biology, 10(7), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070661







