Revealing New Landscape of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Spleen Infected with Aeromonas salmonicida through Immune Related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Axis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Turbot Treatment and Sample Collection
2.2. Total RNA Isolation, Library Construction, and Sequencing
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Quality Control
2.3.2. RNA Identification and Annotation
2.3.3. Quantification of Gene Expression Levels
2.3.4. GO and KEGG Analyses
2.3.5. Co-Expression Network Analysis
2.3.6. Validation the Expression of RNAs with Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Analysis of circRNAs Data
3.2. Statistical Analysis of miRNAs Data
3.3. Statistical Analysis of mRNAs Data
3.4. Construction of the circRNA-miRNA Regulatory Network
3.5. Construction of the miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network
3.6. Construction of the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network
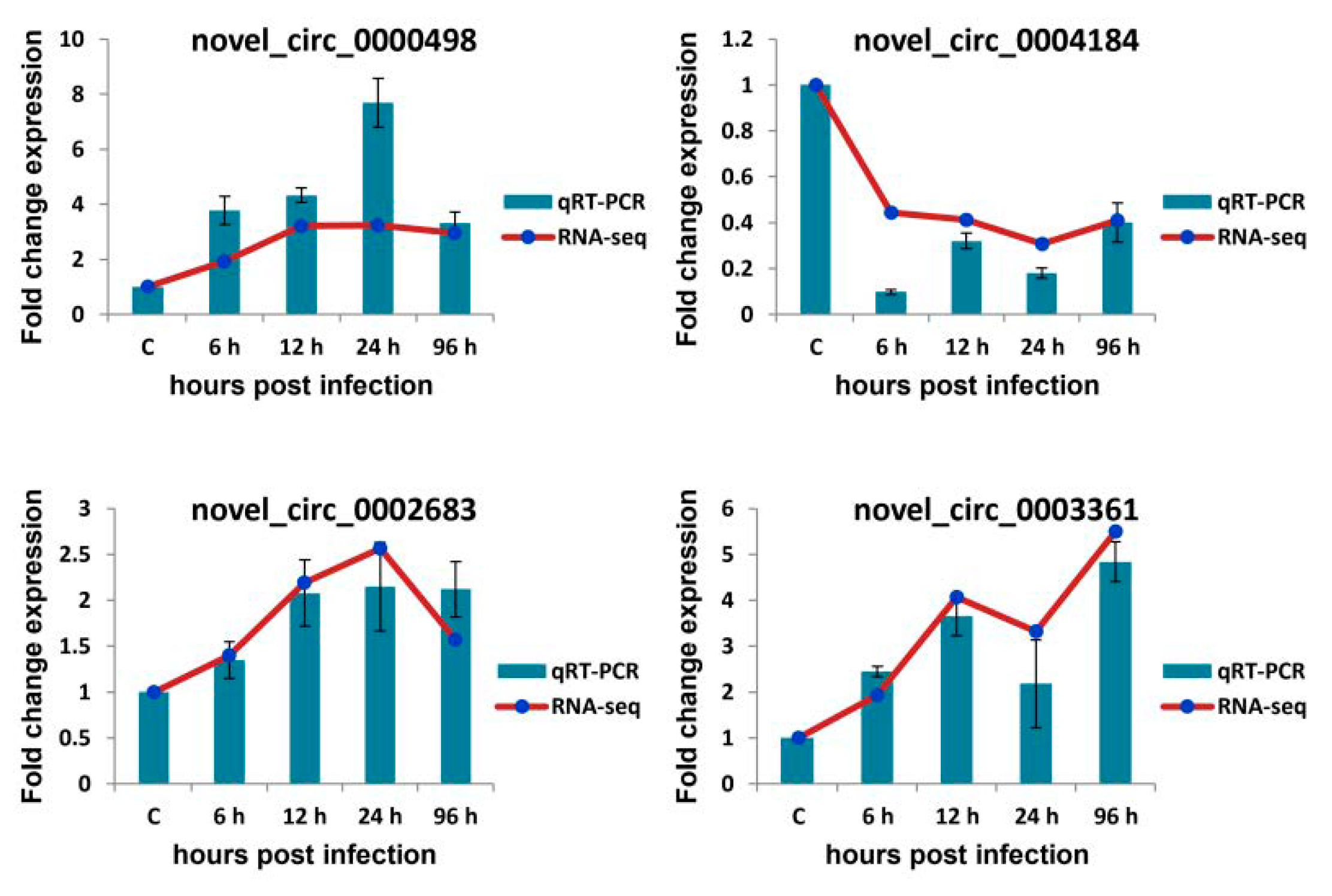
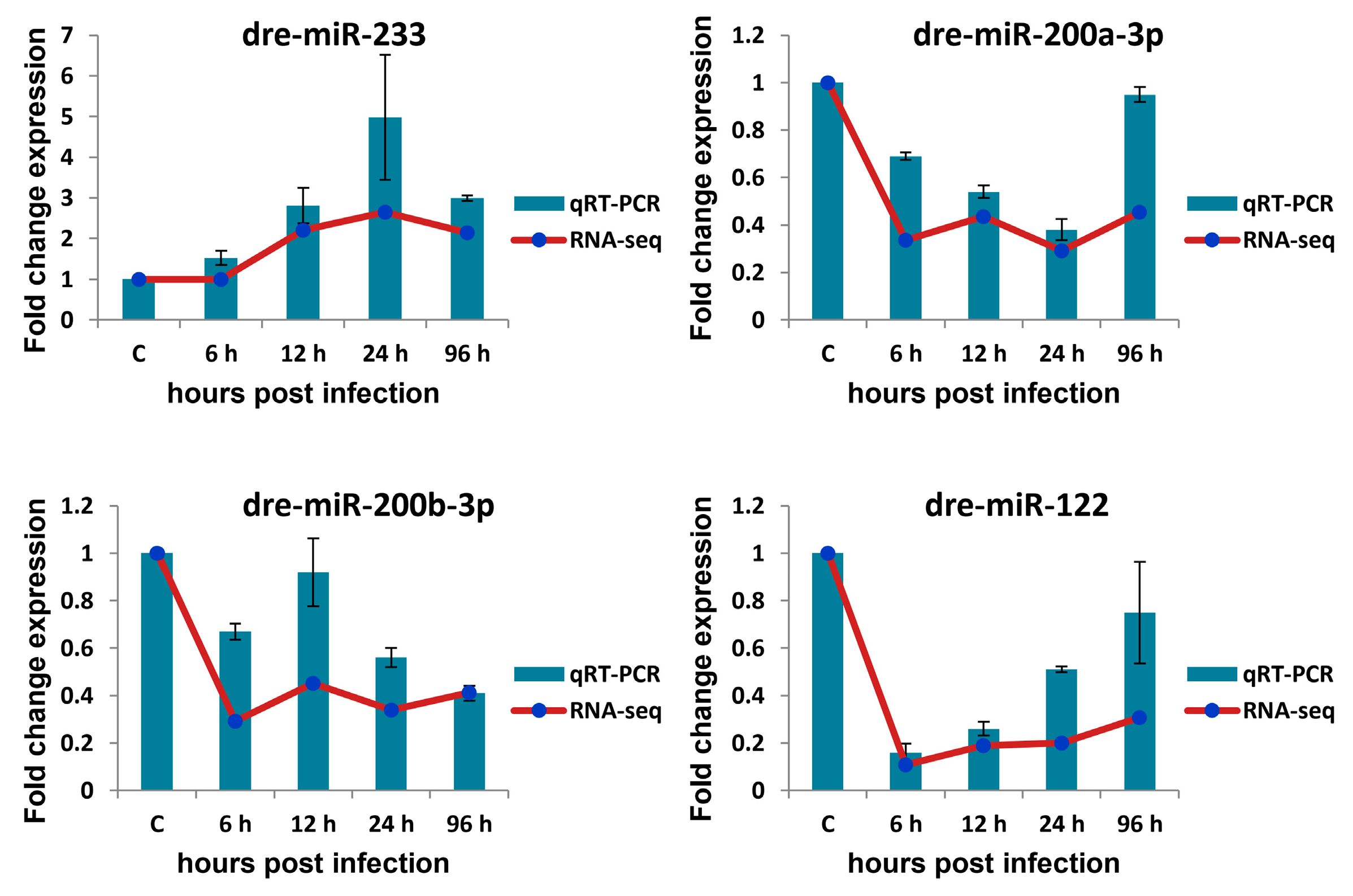
3.7. qRT-PCR Verification of Selected circRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, N.; Wang, B.; Yu, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, Q.; Cao, M.; Xue, T.; Ren, Y.; Tan, F.; Li, C. Characterization of a novel lncRNA (SETD3-OT) in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 102, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, E.N. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, M.-T.; Coca-Prados, M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature 1979, 280, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocquerelle, C.; Mascrez, B.; Hétuin, D.; Bailleul, B. Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nigro, J.M.; Cho, K.R.; Fearon, E.R.; Kern, S.E.; Ruppert, J.; Oliner, J.D.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Scrambled exons. Cell 1991, 64, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, K.; Lai, W.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Chu, S.; Wang, H.; Kang, C.; Qiu, Y. Comprehensive circular RNA profiles in plasma reveals that circular RNAs can be used as novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 480, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glažar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sai, L.; Li, L.; Hu, C.; Qu, B.; Guo, Q.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Bo, C.; Li, X.; Shao, H.; et al. Identification of circular RNAs and their alterations involved in developing male Xenopus laevis chronically exposed to atrazine. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, S.; Diao, J.; Liu, H.; Su, B.; Li, C. Identification of Potential Immune-Related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Intestine of Paralichthys olivaceus During Edwardsiella tarda Infection. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulcheski, F.R.; Christoff, A.P.; Margis, R. Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of biomarker. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 238, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezikov, E. Evolution of microRNA diversity and regulation in animals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, A.C. Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1087, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhao, J.; Huo, T.; Zhang, M.; Wu, X. Effects of CircRNA-ITCH on proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. BUON 2020, 25, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Cheng, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Z. The comprehensive detection of miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA in regulation of mouse melanocyte and skin development. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, C.; Yuan, W.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Sun, Z. Roles of circRNAs in the tumour microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, P.; Zhang, B.; Huang, J.; Xing, C.; Liu, W.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Yao, S.; Ruan, W.; Ning, G.; et al. Identification of a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network to explore the effects of circRNAs on pathogenesis and treatment of spinal cord injury. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.-H. Role of non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of depression. Gene 2020, 735, 144276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Chen, Y.G. Circular RNAs in Immune Response and Viral Infection. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, B.; Huang, S.; Zhao, L. Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Shao, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Lu, J.; Li, W. The circRNA_102911/miR-129-5p/SOX6 axis is involved with T lymphocyte immune function in elderly patients with laparoscopic left hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.-Y.; Zhu, M.-X.; Lu, N.-H.; Liu, J.-Q.; Yang, Y.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.-D.; Feng, Z.-H.; Li, J.-X.; Qi, F.-Z.; et al. Circular RNA circ_0020710 drives tumor progression and immune evasion by regulating the miR-370-3p/CXCL12 axis in melanoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-S.; Huang, X.Y.; Yu, H.Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhu, P.L. Corrigendum to first author affiliations of circular RNA circ-RELL1 regulates inflammatory response by miR-6873-3p/MyD88/NF-kB axis in endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 532, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, A.; Xiong, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Z. Deep Circular RNA Sequencing Provides Insights into the Mechanism Underlying Grass Carp Reovirus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, H.; Chu, Q.; Zheng, W.; Chang, R.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, T. Circular RNA circPIKfyve acts as a sponge of miR-21-3p to enhance antiviral immunity through regulating MAVS in teleost fish. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Zheng, W.; Su, H.; Zhang, L.; Chang, R.; Gao, W.; Xu, T. A Highly Conserved Circular RNA circRasGEF1B Enhances Antiviral Immunity by Regulating miR-21-3p/MITA Pathway in Lower Vertebrates. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. The Biogenesis, Functions, and Challenges of Circular RNAs. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G. The circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Tang, M. Identification of potential circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks in response to graphene quantum dots in microglia by microarray analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, F.W.; Cao, D.; Tang, Y.F.; Shu, L.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, L.Y. Identification of CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Lv, X. Revealing new landscape of cardiovascular disease through circular RNA-miRNA-mRNA axis. Genomics 2020, 112, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Yan, X.; Su, B.; Yang, N.; Fu, Q.; Xue, T.; Song, L.; Li, Q.; Li, C. Integrated Analysis of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Networks in the Intestine of Sebastes schlegelii Following Edwardsiella tarda Challenge. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 618687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liang, W.; Lin, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Feng, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H. Single molecule real-time sequencing and RNA-seq unravel the role of long non-coding and circular RNA in the regulatory network during Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) infection with Streptococcus agalactiae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coscelli, G.; Bermúdez, R.; Ronza, P.; Losada, A.P.; Quiroga, M.I.; García, A.P.L. Immunohistochemical study of inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumour necrosis factor alpha response in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) experimentally infected with Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 56, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F. Circular RNA identification based on multiple seed matching. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Shen, Y.; Shi, S.; Tang, T. MiREvo: An integrative microRNA evolutionary analysis platform for next-generation sequencing experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedländer, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. MiRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, A.J.; John, B.; Gaul, U.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol. 2003, 5, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; et al. Integrated profiling of microRNAs and mRNAs: microRNAs located on Xq27.3 associate with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, G.; Morris, J.H.; Demchak, B.; Bader, G.D. Biological network exploration with Cytoscape 3. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 47, 8.13.1–8.13.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Rexroad, C.E.; Thorgaard, G.H.; Yao, J.; Salem, M. Characterization of the rainbow trout spleen transcriptome and identification of immune-related genes. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Díaz-Rosales, P.; Tafalla, C. Systemic and Mucosal B and T Cell Responses Upon Mucosal Vaccination of Teleost Fish. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 622377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, J.; Mitra, S. (Eds.) Chapter 1—Introduction. In Cancer and Noncoding RNAs; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hombach, S.; Kretz, M. Non-coding RNAs: Classification, Biology and Functioning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 937, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, C.-J.; Zhai, Z.-S.; Zhang, X.; Qin, T.; Zhang, H.-W. Single-Cell Non-coding RNA in Embryonic Development. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1068, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, S.U.; Grote, P.; Herrmann, B.G. Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2491–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Bobryshev, Y.V. The role of miR-126 in embryonic angiogenesis, adult vascular homeostasis, and vascular repair and its alterations in atherosclerotic disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 97, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ouyang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, L.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, W.; Li, S.; Peng, D. CircRNA_28313/miR-195a/CSF1 axis modulates osteoclast differentiation to affect OVX-induced bone absorption in mice. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cheng, M.; Gu, B.; Wang, J.; Yan, S.; Xu, D. CircRNA_09505 aggravates inflammation and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis mice via miR-6089/AKT1/NF-κB axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Xiao, W.; Gao, Y.; Liang, Q.; Luo, F.; Lu, W.; et al. Hsa_circ_0060450 Negatively Regulates Type I Interferon-Induced Inflammation by Serving as miR-199a-5p Sponge in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 576903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, T.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. Characterization of three connexin32 genes and their role in inflammation-induced ATP release in the Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, B.; Wolf, M.; Walz, A.; Loetscher, P. Chemokines: Multiple levels of leukocyte migration control. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, K.J.; Secombes, C.J. Chemokines. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Hu, K.; Huang, L.; Lu, M.; Hu, Q. CCL19 and CCR7 Expression, Signaling Pathways, and Adjuvant Functions in Viral Infection and Prevention. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, W.; Xie, L.; Lv, J.; Li, H.; Yang, S. MiR-325-3p inhibits renal inflammation and fibrosis by targeting CCL19 in diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lu, X.-J.; Nie, L.; Ning, Y.-J.; Chen, J. Molecular characterization of a CC motif chemokine 19-like gene in ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis) and its role in leukocyte trafficking. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepahi, A.; Tacchi, L.; Casadei, E.; Takizawa, F.; LaPatra, S.E.; Salinas, I. CK12a, a CCL19-like Chemokine That Orchestrates both Nasal and Systemic Antiviral Immune Responses in Rainbow Trout. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3900–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Y.-H.; Xiao, Z.-Z.; Sun, L. SmCCL19, a CC chemokine of turbot Scophthalmus maximus, induces leukocyte trafficking and promotes anti-viral and anti-bacterial defense. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
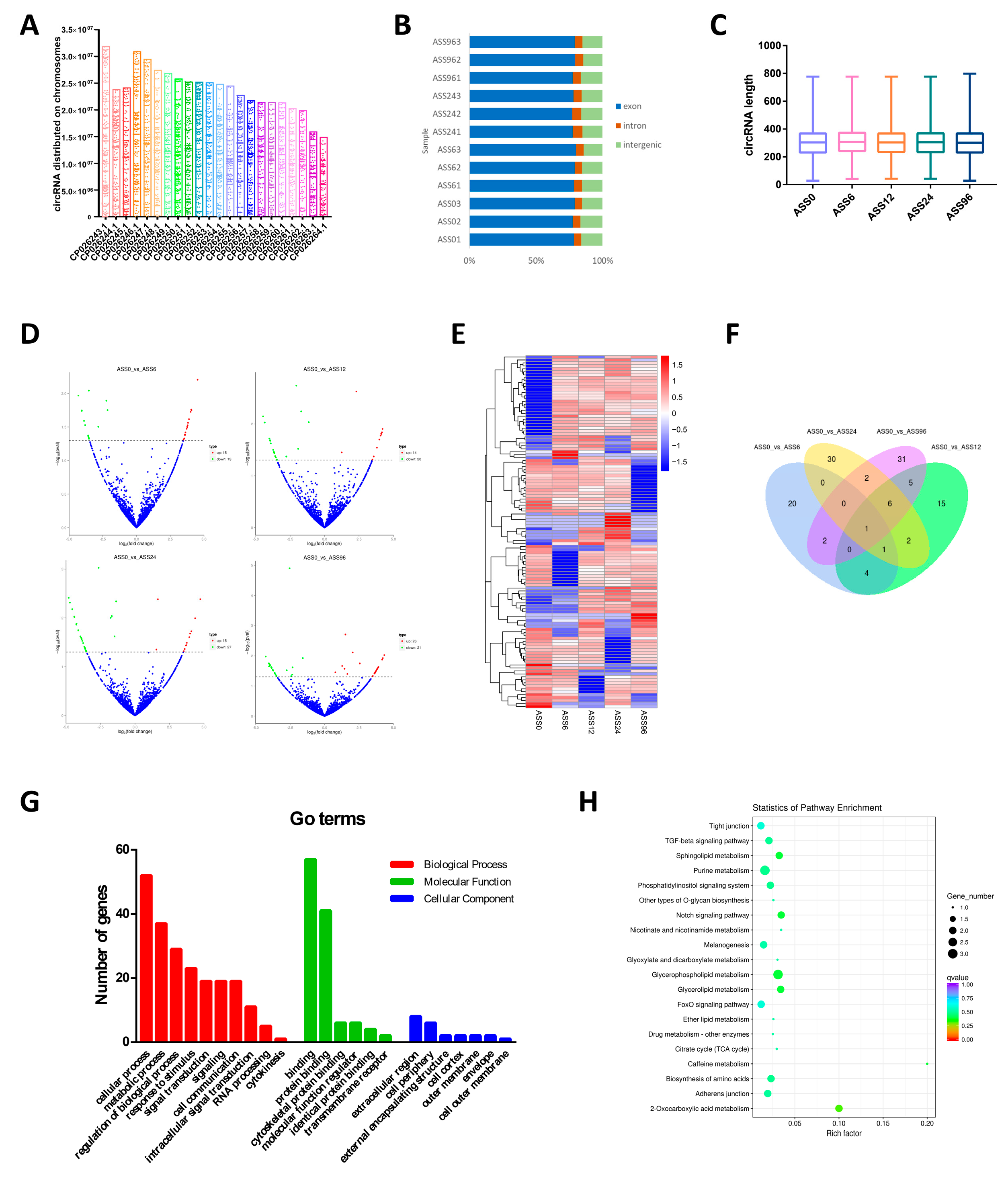
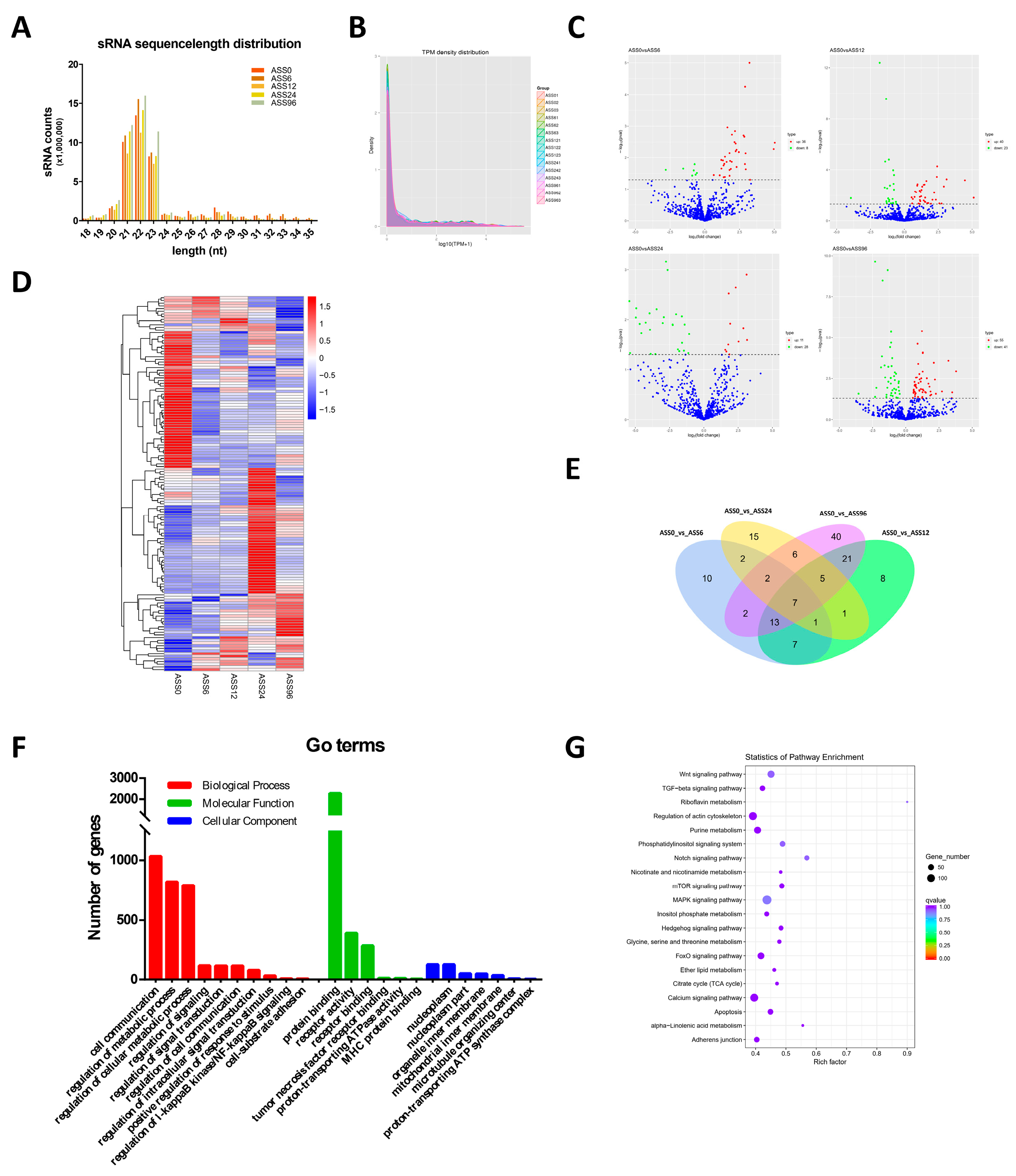
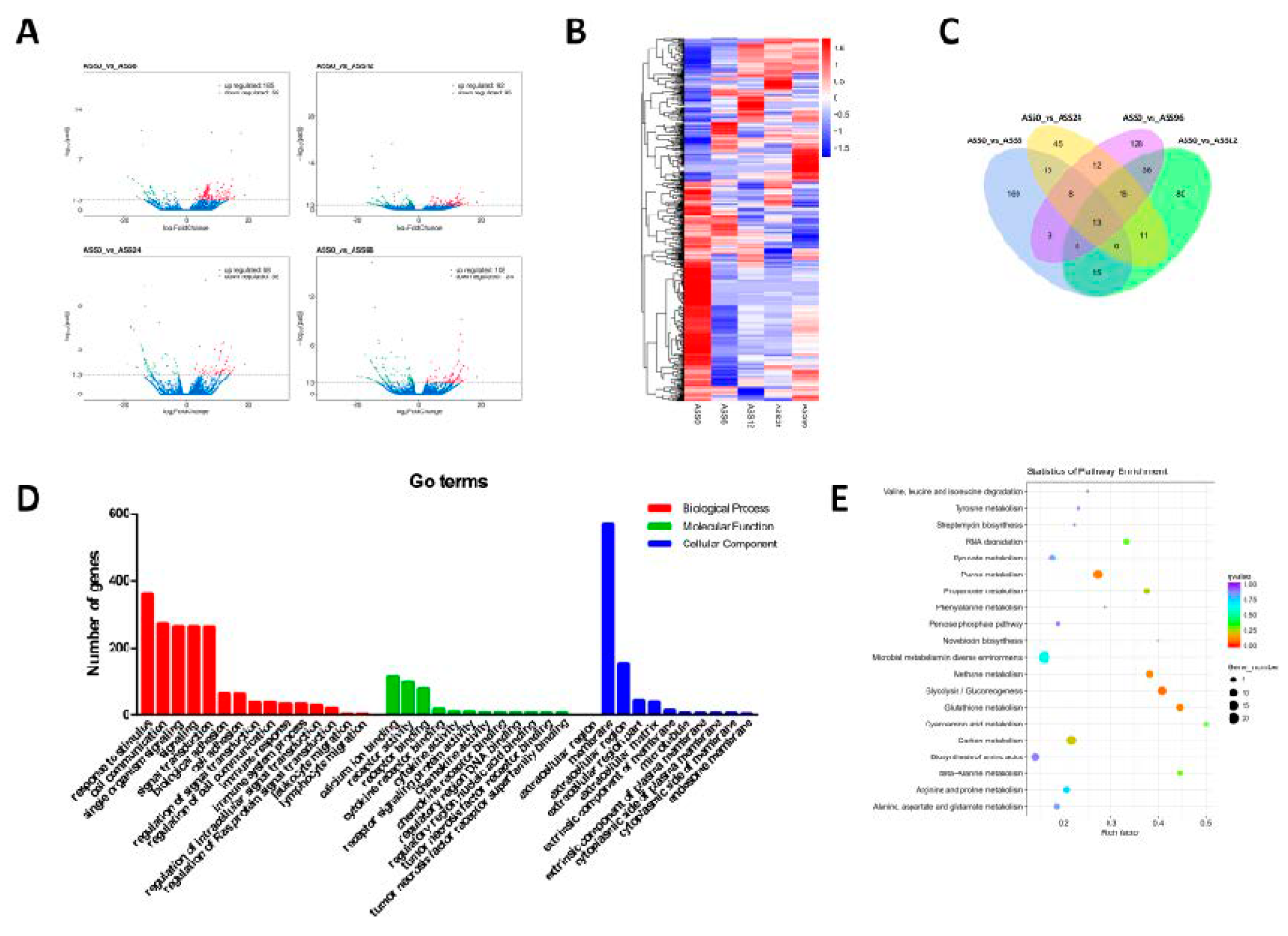
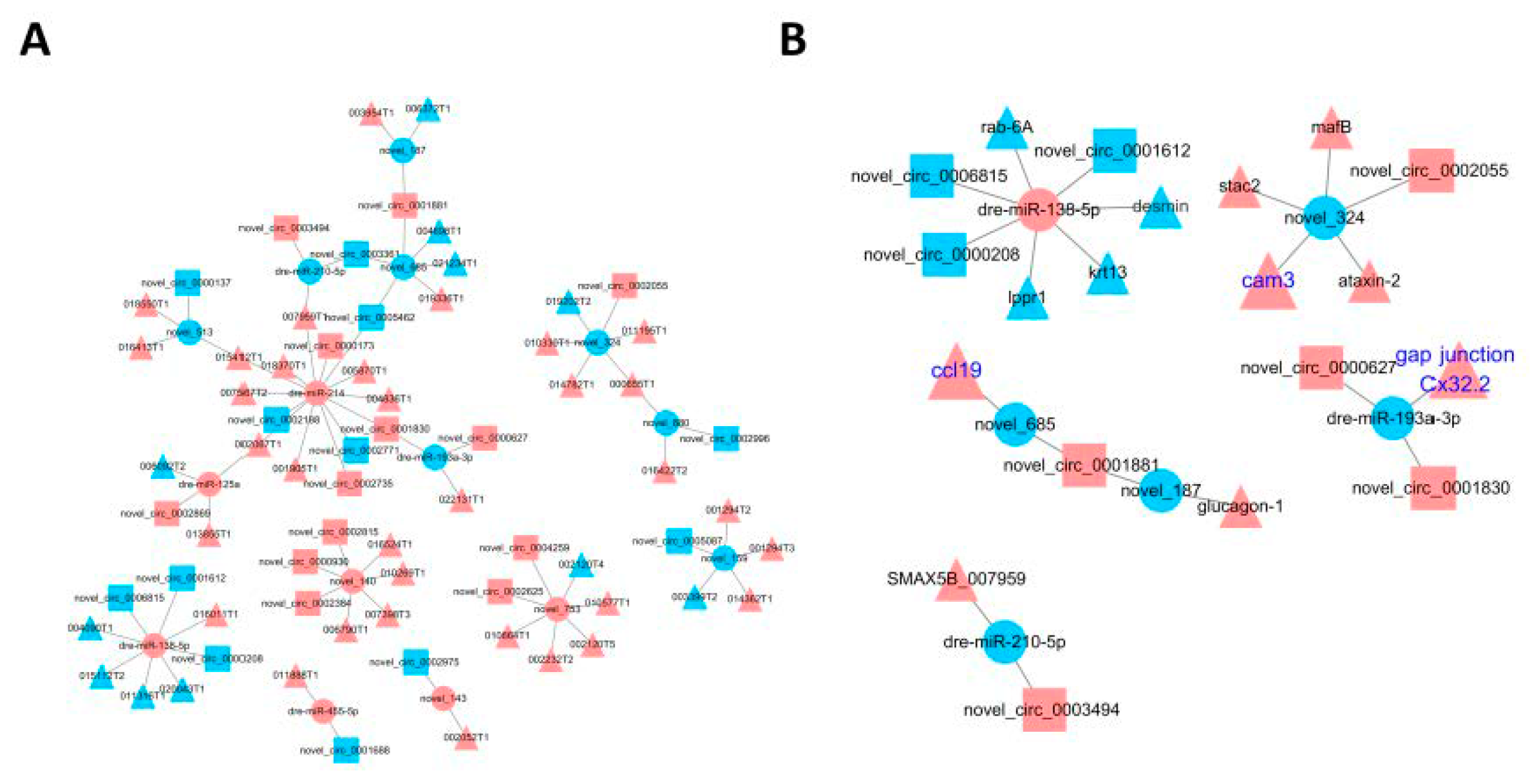

| Sample_Name | Raw_Reads | Clean_Reads | Clean_Bases (Gb) | Error Rate (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC_Content (%) | Mapped to Genome (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASS01 | 89,427,870 | 87,674,318 | 13.15 | 0.03 | 97.22 | 92.58 | 54.11 | 89.81 |
| ASS02 | 88,835,296 | 86,925,034 | 13.04 | 0.03 | 97.32 | 92.84 | 51.33 | 90.62 |
| ASS03 | 91,281,976 | 87,308,908 | 13.10 | 0.03 | 97.01 | 92.23 | 53.22 | 86.94 |
| ASS61 | 84,909,274 | 78,465,246 | 11.77 | 0.03 | 96.81 | 92.12 | 55.28 | 90.44 |
| ASS62 | 95,743,386 | 93,531,870 | 14.03 | 0.03 | 97.37 | 92.93 | 52.17 | 87.85 |
| ASS63 | 89,110,602 | 87,785,728 | 13.17 | 0.03 | 97.51 | 93.21 | 52.94 | 90.53 |
| ASS121 | 97,847,968 | 96,072,446 | 14.41 | 0.03 | 97.42 | 92.93 | 53.21 | 85.35 |
| ASS122 | 107,925,458 | 106,515,648 | 15.98 | 0.03 | 97.26 | 92.60 | 53.04 | 87.26 |
| ASS123 | 88,551,056 | 86,735,528 | 13.01 | 0.03 | 97.24 | 92.61 | 52.54 | 90.15 |
| ASS241 | 108,968,470 | 107,506,050 | 16.13 | 0.03 | 97.26 | 92.67 | 55.74 | 80.36 |
| ASS242 | 93,831,136 | 92,152,780 | 13.82 | 0.03 | 97.41 | 92.96 | 51.69 | 85.96 |
| ASS243 | 86,686,374 | 84,702,798 | 12.71 | 0.03 | 97.29 | 92.76 | 53.08 | 88.55 |
| ASS961 | 100,039,326 | 98,296,586 | 14.74 | 0.03 | 97.68 | 93.61 | 54.47 | 88.51 |
| ASS962 | 87,993,170 | 83,798,128 | 12.57 | 0.03 | 96.98 | 92.24 | 53.90 | 84.57 |
| ASS963 | 104,529,398 | 102,835,526 | 15.43 | 0.03 | 97.62 | 93.43 | 53.81 | 84.48 |
| Sample | Total_Reads | Clean Reads | Error Rate (%) | GC Content (%) | Mapped sRNA (%) | Uniq Reads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASS01 | 16,992,257 | 16,776,891 | 0.01 | 48.91 | 94.56 | 225,970 |
| ASS02 | 13,585,729 | 13,445,193 | 0.01 | 49.72 | 91.22 | 256,756 |
| ASS03 | 14,090,926 | 13,924,028 | 0.01 | 49.17 | 93.82 | 233,122 |
| ASS61 | 16,759,631 | 16,480,923 | 0.01 | 48.43 | 94.80 | 292,697 |
| ASS62 | 14,970,408 | 14,487,862 | 0.01 | 49.27 | 90.79 | 297,090 |
| ASS63 | 17,691,027 | 17,287,838 | 0.01 | 48.97 | 93.65 | 380,538 |
| ASS121 | 15,944,207 | 15,759,031 | 0.01 | 48.90 | 95.73 | 280,956 |
| ASS122 | 14,993,055 | 14,650,290 | 0.01 | 49.43 | 92.89 | 331,440 |
| ASS123 | 14,495,408 | 10,351,418 | 0.01 | 51.08 | 89.65 | 172,990 |
| ASS241 | 19,726,929 | 19,222,454 | 0.01 | 48.95 | 95.82 | 276,881 |
| ASS242 | 13,696,253 | 12,062,266 | 0.01 | 54.28 | 66.84 | 301,900 |
| ASS243 | 15,432,974 | 15,212,095 | 0.01 | 48.60 | 95.28 | 305,646 |
| ASS961 | 16,295,413 | 16,051,491 | 0.01 | 48.70 | 95.38 | 326,589 |
| ASS962 | 18,209,628 | 17,873,027 | 0.01 | 48.35 | 94.96 | 376,083 |
| ASS963 | 17,714,908 | 17,364,745 | 0.01 | 49.44 | 93.82 | 319,525 |
| Types | Known miRNA | New miRNA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mapped Mature | Mapped Hairpin | Mapped Uniq sRNA | Mapped Total sRNA | Mapped Mature | Mapped Star | Mapped Hairpin | Mapped Uniq sRNA | Mapped Total sRNA | |
| ASS01 | 214 | 258 | 2539 | 10,109,019 | 354 | 159 | 422 | 1721 | 849,828 |
| ASS02 | 206 | 255 | 2394 | 7,201,071 | 330 | 143 | 400 | 1504 | 486,725 |
| ASS03 | 212 | 257 | 2559 | 8,142,478 | 355 | 173 | 432 | 1714 | 577,499 |
| ASS121 | 218 | 263 | 2643 | 10,991,726 | 389 | 180 | 464 | 1910 | 721,131 |
| ASS122 | 210 | 257 | 2468 | 8,730,453 | 344 | 167 | 404 | 1690 | 641,866 |
| ASS123 | 202 | 237 | 1834 | 3,157,360 | 234 | 112 | 305 | 1036 | 234,731 |
| ASS241 | 216 | 245 | 2906 | 12,630,412 | 393 | 185 | 479 | 2055 | 974,386 |
| ASS242 | 179 | 223 | 1272 | 1,934,747 | 207 | 117 | 282 | 810 | 154,078 |
| ASS243 | 211 | 258 | 2573 | 10,726,049 | 397 | 174 | 474 | 1935 | 776,575 |
| ASS61 | 208 | 271 | 2446 | 10,849,391 | 396 | 168 | 462 | 1829 | 779,494 |
| ASS62 | 203 | 249 | 2401 | 7,794,581 | 318 | 151 | 392 | 1613 | 356,696 |
| ASS63 | 211 | 256 | 2559 | 11,483,832 | 399 | 167 | 470 | 1867 | 693,347 |
| ASS961 | 211 | 241 | 2690 | 10,345,787 | 395 | 186 | 464 | 2005 | 880,402 |
| ASS962 | 212 | 259 | 2602 | 12,439,717 | 415 | 198 | 493 | 2073 | 983,840 |
| ASS963 | 214 | 256 | 2720 | 10,828,035 | 394 | 178 | 472 | 1941 | 845,700 |
| Total | 252 | 286 | 65,488 | 245,032,276 | 668 | 442 | 726 | 45,784 | 16,824,392 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, T.; Liu, Y.; Cao, M.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, C. Revealing New Landscape of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Spleen Infected with Aeromonas salmonicida through Immune Related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Axis. Biology 2021, 10, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070626
Xue T, Liu Y, Cao M, Tian M, Zhang L, Wang B, Liu X, Li C. Revealing New Landscape of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Spleen Infected with Aeromonas salmonicida through Immune Related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Axis. Biology. 2021; 10(7):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070626
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Ting, Yiping Liu, Min Cao, Mengyu Tian, Lu Zhang, Beibei Wang, Xiaoli Liu, and Chao Li. 2021. "Revealing New Landscape of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Spleen Infected with Aeromonas salmonicida through Immune Related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Axis" Biology 10, no. 7: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070626
APA StyleXue, T., Liu, Y., Cao, M., Tian, M., Zhang, L., Wang, B., Liu, X., & Li, C. (2021). Revealing New Landscape of Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Spleen Infected with Aeromonas salmonicida through Immune Related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Axis. Biology, 10(7), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070626





