Role of Endocrine System in the Regulation of Female Insect Reproduction
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. 20-Hydroxyecdysone Regulated Reproduction in Insects
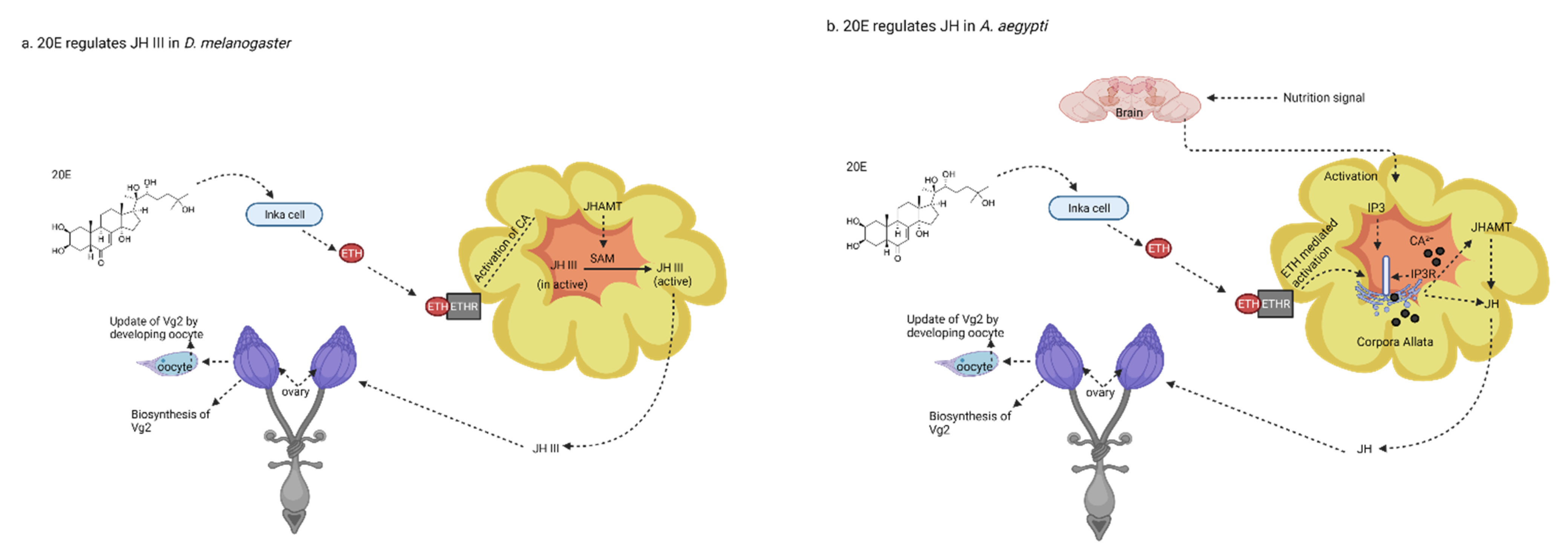
Interaction of 20E with JHs and Insulin Signaling Pathway
3. Juvenile Hormone Regulated Reproduction in Insects
Interaction of JHs with 20E and Insulin Signaling Pathway
4. Microbiomes and Endocrine System
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiang, R.G.; Chiang, J.A. Reproductive physiology in the blood feeding insect, Rhodnius prolixus, from copulation to the control of egg production. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 97, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelstrup, H.C.; Hartfelder, K.; Nascimento, F.S.; Riddiford, L.M. Reproductive status, endocrine physiology and chemical signaling in the Neotropical, swarm-founding eusocial wasp Polybia micans. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, R.; Niwa, Y.S. Enzymes for ecdysteroid biosynthesis: Their biological functions in insects and beyond. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentze, J.L.; Moeller, M.E.; Jørgensen, A.F.; Bengtsson, M.S.; Bordoy, A.M.; Warren, J.T.; Gilbert, L.I.; Andersen, O.; Rewitz, K.F. Accessory gland as a site for prothoracicotropic hormone controlled ecdysone synthesis in adult male insects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirth, C.K.; Tang, H.Y.; Makohon-Moore, S.C.; Salhadar, S.; Gokhale, R.H.; Warner, R.D.; Koyama, T.; Riddiford, L.M.; Shingleton, A.W. Juvenile hormone regulates body size and perturbs insulin signaling in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7018–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, H.; Kitamoto, T. The steroid molting hormone Ecdysone regulates sleep in adult Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2010, 185, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Deng, S.; Zhou, S. Krüppel-homolog 1 mediates juvenile hormone action to promote vitellogenesis and oocyte maturation in the migratory locust. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 52, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uryu, O.; Ou, Q.; Komura-Kawa, T.; Kamiyama, T.; Iga, M.; Syrzycka, M.; Hirota, K.; Kataoka, H.; Honda, B.M.; King-Jones, K. Cooperative control of ecdysone biosynthesis in Drosophila by transcription factors Séance, Ouija board, and Molting defective. Genetics 2018, 208, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-F.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, W. Ecdysone oxidase and 3-dehydroecdysone-3β-reductase contribute to the synthesis of ecdysone during early embryonic development of the silkworm. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonobe, H.; Yamada, R. Ecdysteroids during early embryonic development in silkworm Bombyx mori: Metabolism and functions. Zool. Sci. 2004, 21, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipper, L.; Jassmann, D.; Burgmer, S.; Görlich, B.; Reiff, T. Ecdysone steroid hormone remote controls intestinal stem cell fate decisions via the PPARγ-homolog Eip75B in Drosophila. elife 2020, 9, e55795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Saha, T.T.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. Regulatory pathways controlling female insect reproduction. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujar, H.; Palli, S.R. Juvenile hormone regulation of female reproduction in the common bed bug, Cimex lectularius. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, R.; Sheng, Z.; Sun, Z.; Palli, S.R. Ecdysteroid regulation of ovarian growth and oocyte maturation in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; He, Q.; Zhou, S. Regulatory Mechanisms of Vitellogenesis in Insects. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Lucas, K.J.; Roy, S.; Ha, J.; Raikhel, A.S. Mosquito-specific microRNA-1174 targets serine hydroxymethyltransferase to control key functions in the gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14460–14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedes, C.C.; Carney, G.E. Ecdysone signaling in adult Drosophila melanogaster. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenaerts, C.; Marchal, E.; Peeters, P.; Broeck, J.V. The ecdysone receptor complex is essential for the reproductive success in the female desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauhar, Z.; Sun, L.V.; Hua, S.; Mason, C.E.; Fuchs, F.; Li, T.-R.; Boutros, M.; White, K.P. Genomic mapping of binding regions for the Ecdysone receptor protein complex. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.J.; Billas, I.M.; Bonneton, F.; Graham, L.D.; Lawrence, M.C. Ecdysone receptors: From the Ashburner model to structural biology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King-Jones, K.; Thummel, C.S. Nuclear receptors—A perspective from Drosophila. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazina, M.Y.; Kocheryzhkina, E.; Nikolenko, J.; Krasnov, A.; Georgieva, S.; Vorobyeva, N. Nuclear receptors EcR, Usp, E75, DHR3, and ERR regulate transcription of ecdysone cascade genes. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 473, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-J.; Chen, E.-H.; Song, Z.-H.; He, W.; Liu, S.-H.; Dou, W.; Wang, J.-J. Molecular Characterization and Expression Profiling of Nuclear Receptor Gene Families in Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera Dorsalis (Hendel). Insects 2020, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchal, E.; Verlinden, H.; Badisco, L.; Van Wielendaele, P.; Broeck, J.V. RNAi-mediated knockdown of Shade negatively affects ecdysone-20-hydroxylation in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchal, E.; Badisco, L.; Verlinden, H.; Vandersmissen, T.; Van Soest, S.; Van Wielendaele, P.; Broeck, J.V. Role of the Halloween genes, Spook and Phantom in ecdysteroidogenesis in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, D.; Kasahara, R.; Matsuno, K.; Aoki, F.; Suzuki, M.G. Involvement of Ecdysone Signaling in the Expression of the doublesex Gene during Embryonic Development in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori. Sex. Dev. 2019, 13, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Rewitz, K.F.; Shinoda, T.; Itoyama, K.; Petryk, A.; Rybczynski, R.; Jarcho, M.; Warren, J.T.; Marqués, G.; Shimell, M.J. Spook and Spookier code for stage-specific components of the ecdysone biosynthetic pathway in Diptera. Dev. Biol. 2006, 298, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.J.; Brown, M.R.; Strand, M.R. Ovary ecdysteroidogenic hormone requires a receptor tyrosine kinase to activate egg formation in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5057–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, L.X.; Spradling, A.C. Steroid signaling within Drosophila ovarian epithelial cells sex-specifically modulates early germ cell development and meiotic entry. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ables, E.T.; Bois, K.E.; Garcia, C.A.; Drummond-Barbosa, D. Ecdysone response gene E78 controls ovarian germline stem cell niche formation and follicle survival in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2015, 400, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Cherry, C.M.; Matunis, E.L. Steroid signaling promotes stem cell maintenance in the Drosophila testis. Dev. Biol. 2014, 394, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, P.; Kakani, E.G.; Mitchell, S.N.; Mameli, E.; Want, E.J.; Anton, A.M.; Serrao, A.; Baldini, F.; Catteruccia, F. Sexual transfer of the steroid hormone 20E induces the postmating switch in Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16353–16358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, C.; Yan, B.; Yu, X.; Yang, M. Delayed mating with multiple partners decreases indexes of mating in female and male Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ. Entomol. 2020, 49, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Song, X.-Q.; Yu, H.; Fu, D.-Y.; Xu, J.; Ye, H. Mating-Induced Differential Expression in Genes Related to Reproduction and Immunity in Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Female Moths. J. Insect Sci. 2020, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Shen, C.P. The effects of exogenous 20-hydroxyecdysone on the feeding, development, and reproduction of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Fla. Entomol. 2015, 98, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schwenke, R.A.; Lazzaro, B.P.; Wolfner, M.F. Reproduction–immunity trade-offs in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, I.A.; Attardo, G.M.; Rodriguez, S.D.; Drake, L.L. Four-way regulation of mosquito yolk protein precursor genes by juvenile hormone-, ecdysone-, nutrient-, and insulin-like peptide signaling pathways. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Tian, Z.; Wu, Q.-W.; King-Jones, K.; Liu, W.; Zhu, F.; Wang, X.-P. Steroid hormone ecdysone deficiency stimulates preparation for photoperiodic reproductive diapause. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiselman, M.; Lee, S.S.; Tran, R.-T.; Dai, H.; Ding, Y.; Rivera-Perez, C.; Wijesekera, T.P.; Dauwalder, B.; Noriega, F.G.; Adams, M.E. Endocrine network essential for reproductive success in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3849–E3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, T.-Y.; Jiang, H.-B.; Liu, X.-Q.; Dou, W.; Park, Y.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.-J. The ecdysis triggering hormone system, via ETH/ETHR-B, is essential for successful reproduction of a major pest insect, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, R.; Niimi, T.; Honda, N.; Yoshiyama, M.; Itoyama, K.; Kataoka, H.; Shinoda, T. Juvenile hormone acid O-methyltransferase in Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashima, J.; Bownes, M. E75A and E75B have opposite effects on the apoptosis/development choice of the Drosophila egg chamber. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, M.H.; Spradling, A.C. Steroid signaling establishes a female metabolic state and regulates SREBP to control oocyte lipid accumulation. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulos, P.; Alexandratos, A.; Nellas, I.; Dedos, S.G. Refining a steroidogenic model: An analysis of RNA-seq datasets from insect prothoracic glands. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areiza, M.; Nouzova, M.; Rivera-Perez, C.; Noriega, F.G. Ecdysis triggering hormone ensures proper timing of juvenile hormone biosynthesis in pharate adult mosquitoes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 54, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamruzzaman, A.; Mikani, A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Elgendy, A.M.; Takeda, M. Crosstalk among Indoleamines, Neuropeptides and JH/20E in Regulation of Reproduction in the American Cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Insects 2020, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.-H.; Lin, J.-L.; Lin, P.-L.; Chen, C.-H. Insulin stimulates ecdysteroidogenesis by prothoracic glands in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Song, J.; Kang, L.; Zhou, S. An isoform of Taiman that contains a PRD-repeat motif is indispensable for transducing the vitellogenic juvenile hormone signal in Locusta migratoria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 82, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wen, D.; Jia, Q.; Cui, C.; Wang, J.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S. Heat shock protein 83 (Hsp83) facilitates methoprene-tolerant (Met) nuclear import to modulate juvenile hormone signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27874–27885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Dong, W.; Li, S.; Wu, R. Nucleoporin Nup358 facilitates nuclear import of Methoprene-tolerant (Met) in an importin β-and Hsp83-dependent manner. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 81, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-H.; Lozano, J.; Belles, X. Broad-complex functions in postembryonic development of the cockroach Blattella germanica shed new light on the evolution of insect metamorphosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Yang, R.-L.; Wang, W.-P.; Zhou, Q.-H.; Chen, E.-H.; Yuan, G.-R.; Wang, J.-J.; Dou, W. Involvement of Met and Kr-h1 in JH-mediated reproduction of female Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel). Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, R.; Sun, Z.; Bai, H.; Palli, S.R. Juvenile hormone regulation of vitellogenin synthesis in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, B. Methoprene-tolerant (Met) and Krüpple-homologue 1 (Kr-h1) are required for ovariole development and egg maturation in the brown plant hopper. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ojani, R.; Fu, X.; Ahmed, T.; Liu, P.; Zhu, J. Krüppel homologue 1 acts as a repressor and an activator in the transcriptional response to juvenile hormone in adult mosquitoes. Insect Mol. Biol. 2018, 27, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smykal, V.; Bajgar, A.; Provaznik, J.; Fexova, S.; Buricova, M.; Takaki, K.; Hodkova, M.; Jindra, M.; Dolezel, D. Juvenile hormone signaling during reproduction and development of the linden bug, Pyrrhocoris apterus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 45, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijbels, M.; Lenaerts, C.; Broeck, J.V.; Marchal, E. Juvenile Hormone receptor Met is essential for ovarian maturation in the Desert Locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Saha, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Raikhel, A.S. Juvenile hormone and its receptor methoprene-tolerant promote ribosomal biogenesis and vitellogenesis in the Aedes aegypti mosquito. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10306–10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchal, E.; Hult, E.F.; Huang, J.; Pang, Z.; Stay, B.; Tobe, S.S. Methoprene-tolerant (Met) knockdown in the adult female cockroach, Diploptera punctata completely inhibits ovarian development. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos-Sambucaro, M.J.; Riccillo, F.L.; Calderón-Fernández, G.M.; Sterkel, M.; Diambra, L.A.; Ronderos, J.R. Genomic and functional characterization of a methoprene-tolerant gene in the kissing-bug Rhodnius prolixus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 216, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiki, R.; Gotoh, H.; Toga, K.; Miura, T.; Maekawa, K. High juvenile hormone titre and abdominal activation of JH signalling may induce reproduction of termite neotenics. Insect Mol. Biol. 2015, 24, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilen, J.; Atallah, J.; Azanchi, R.; Levine, J.D.; Riddiford, L.M. Regulation of onset of female mating and sex pheromone production by juvenile hormone in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18321–18326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Saha, T.T.; Roy, S.; Shin, S.W.; Backman, T.W.; Girke, T.; White, K.P.; Raikhel, A.S. Juvenile hormone and its receptor, methoprene-tolerant, control the dynamics of mosquito gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2173–E2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.N.; Ma, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Xiao, H.J.; Liang, G.M. Dissecting the role of Krüppel homolog 1 in the metamorphosis and female reproduction of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Mol. Biol. 2018, 27, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; An, Y.; Fang, H.; Michaud, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. Molecular characterization of primary juvenile hormone responders Methoprene-tolerant (Met) and Krüppel homolog 1 (Kr-h1) in Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) with clarification of their roles in metamorphosis and reproduction. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oi, C.A.; Ferreira, H.M.; da Silva, R.C.; Bienstman, A.; Nascimento, F.S.d.; Wenseleers, T. Effects of juvenile hormone in fertility and fertility-signaling in workers of the common wasp Vespula vulgaris. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brent, C.; Peeters, C.; Dietmann, V.; Crewe, R.; Vargo, E. Hormonal correlates of reproductive status in the queenless ponerine ant, Streblognathus peetersi. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2006, 192, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuvillier-Hot, V.; Lenoir, A.; Peeters, C. Reproductive monopoly enforced by sterile police workers in a queenless ant. Behav. Ecol. 2004, 15, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.-Z.; Ye, G.-Y.; Guo, J.-Y.; Hu, C. Roles of ecdysteroid and juvenile hormone in vitellogenesis in an endoparasitic wasp, Pteromalus puparum (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swevers, L. An update on ecdysone signaling during insect oogenesis. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 31, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.G.; Humann, F.C.; Hartfelder, K. Juvenile hormone signaling in insect oogenesis. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 31, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayukawa, T.; Jouraku, A.; Ito, Y.; Shinoda, T. Molecular mechanism underlying juvenile hormone-mediated repression of precocious larval–adult metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Z.; Xu, J.; Bai, H.; Zhu, F.; Palli, S.R. Juvenile hormone regulates vitellogenin gene expression through insulin-like peptide signaling pathway in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41924–41936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruntenko, N.; Rauschenbach, I.Y. Interplay of JH, 20E and biogenic amines under normal and stress conditions and its effect on reproduction. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Raikhel, A.S. Posttranscriptional control of the competence factor βFTZ-F1 by juvenile hormone in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13338–13343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrisqueta, M.; Süren-Castillo, S.; Maestro, J.L. Insulin receptor-mediated nutritional signalling regulates juvenile hormone biosynthesis and vitellogenin production in the German cockroach. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Jia, Q.; Yuan, D.; Ren, C.; Li, K.; Liu, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, H.; Cao, Y. The genomic and functional landscapes of developmental plasticity in the American cockroach. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, M.; Gálvez-Ontiveros, Y.; Rivas, A. Endobolome, a New Concept for Determining the Influence of Microbiota Disrupting Chemicals (MDC) in Relation to Specific Endocrine Pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 578007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.; Veerus, L.; Trosvik, P.; Buckling, A.; Pizzari, T. The reproductive microbiome: An emerging driver of sexual selection, sexual conflict, mating systems, and reproductive isolation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otti, O. Genitalia-associated microbes in insects. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganley, J.G.; Pandey, A.; Sylvester, K.; Lu, K.-Y.; Toro-Moreno, M.; Rütschlin, S.; Bradford, J.M.; Champion, C.J.; Böttcher, T.; Xu, J. A Systematic Analysis of Mosquito-Microbiome Biosynthetic Gene Clusters Reveals Antimalarial Siderophores that Reduce Mosquito Reproduction Capacity. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 817–826.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Yosef, M.; Pasternak, Z.; Jurkevitch, E.; Yuval, B. Symbiotic bacteria enable olive flies (Bactrocera oleae) to exploit intractable sources of nitrogen. J. Evol. Biol. 2014, 27, 2695–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malacrinò, A.; Campolo, O.; Medina, R.F.; Palmeri, V. Instar-and host-associated differentiation of bacterial communities in the Mediterranean fruit fly Ceratitis capitata. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, J.; Freed, S.; Khan, B.A.; Farooq, M. Effectiveness of Beauveria bassiana against cotton whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius)(Aleyrodidae: Homoptera) on different host plants. Pak. J. Zool. 2016, 48, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, J.; Shoukat, R.F.; Zhang, Y.; Freed, S.; Xu, X.; Jin, F. Metarhizium Anisopliae Challenges Immunity and Demography of Plutella xylostella. Insects 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäpers, A.; Petrén, H.; Wheat, C.W.; Wiklund, C.; Friberg, M. Female fecundity variation affects reproducibility of experiments on host plant preference and acceptance in a phytophagous insect. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20162643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Shabbir, R.; Ali, A.; Afzal, I.; Zaheer, U.; Gao, S.-J. Transcription factors in plant stress responses: Challenges and potential for sugarcane improvement. Plants 2020, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, R.; Javed, T.; Afzal, I.; Sabagh, A.E.; Ali, A.; Vicente, O.; Chen, P. Modern Biotechnologies: Innovative and Sustainable Approaches for the Improvement of Sugarcane Tolerance to Environmental Stresses. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piesik, D.; Rochat, D.; Bocianowski, J.; Marion-Poll, F. Repellent activity of plants from the genus Chenopodium to Ostrinia nubilalis larvae. Plant Prot. Sci. 2018, 54, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Ajaha, A.; Bouayad, N.; Aarab, A.; Rharrabe, K. Effect of 20-hydroxyecdysone, a phytoecdysteroid, on development, digestive, and detoxification enzyme activities of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Stilling, R.M.; Kennedy, P.J.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Minireview: Gut microbiota: The neglected endocrine organ. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsuka, J.; Nakai, M.; Shinoda, T. A virus carries a gene encoding juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase, a key regulatory enzyme in insect metamorphosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
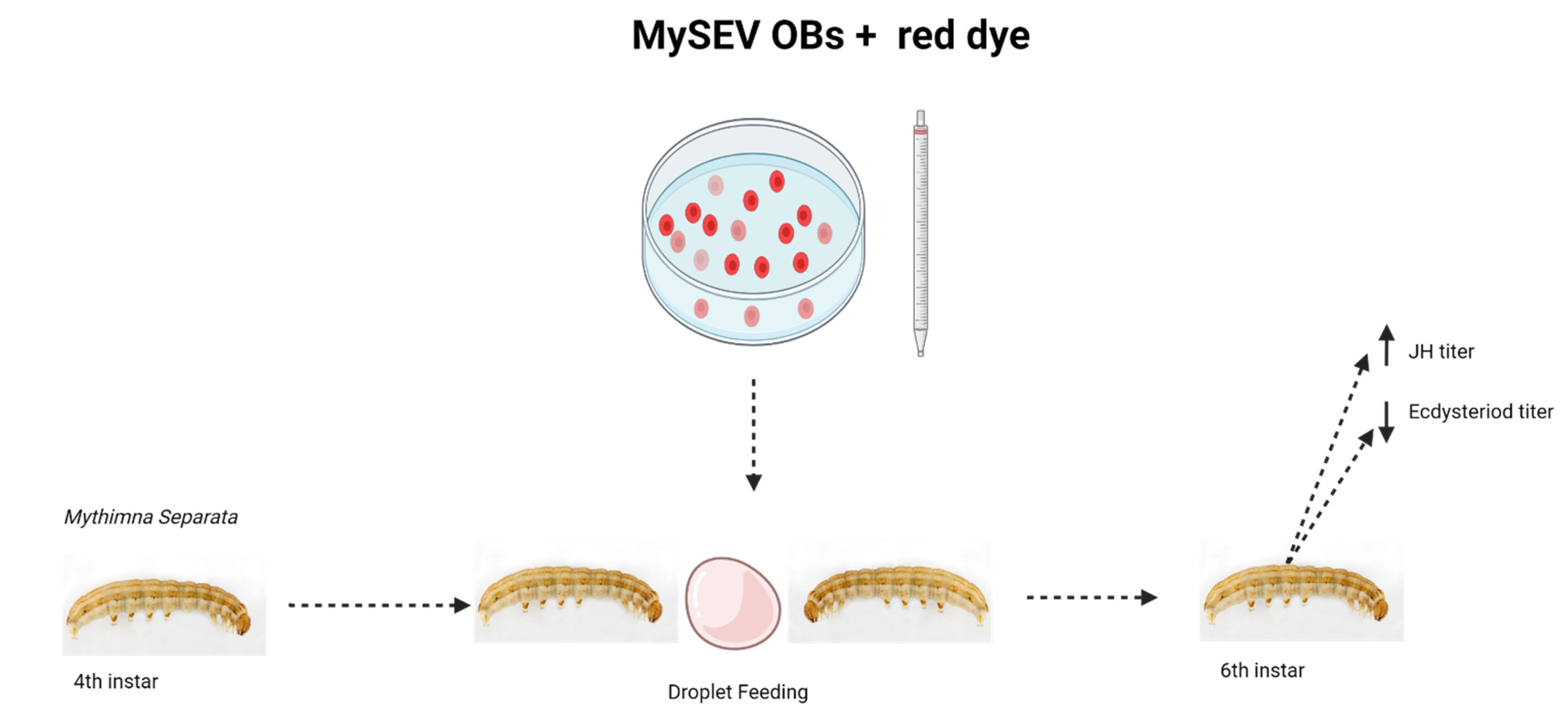
- Nakai, M.; Kinjo, H.; Takatsuka, J.; Shiotsuki, T.; Kamita, S.G.; Kunimi, Y. Entomopoxvirus infection induces changes in both juvenile hormone and ecdysteroid levels in larval Mythimna separata. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Down, R.E.; Bell, H.A.; Bryning, G.; Kirkbride-Smith, A.E.; Edwards, J.P.; Weaver, R.J. Infection by the microsporidium Vairimorpha necatrix (Microspora: Microsporidia) elevates juvenile hormone titres in larvae of the tomato moth, Lacanobia oleracea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 97, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.L.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Tubbs, C.W.; Bisesi, J.H., Jr. Regulation of endocrine systems by the microbiome: Perspectives from comparative animal models. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 292, 113437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prindle, A.; Liu, J.; Asally, M.; Ly, S.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Süel, G.M. Ion channels enable electrical communication in bacterial communities. Nature 2015, 527, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freestone, P.P.; Sandrini, S.M.; Haigh, R.D.; Lyte, M. Microbial endocrinology: How stress influences susceptibility to infection. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neish, A.S. Mucosal immunity and the microbiome. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, S28–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trompette, A.; Gollwitzer, E.S.; Yadava, K.; Sichelstiel, A.K.; Sprenger, N.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Blanchard, C.; Junt, T.; Nicod, L.P.; Harris, N.L. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalid, M.Z.; Ahmad, S.; Ngegba, P.M.; Zhong, G. Role of Endocrine System in the Regulation of Female Insect Reproduction. Biology 2021, 10, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070614
Khalid MZ, Ahmad S, Ngegba PM, Zhong G. Role of Endocrine System in the Regulation of Female Insect Reproduction. Biology. 2021; 10(7):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070614
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalid, Muhammad Zaryab, Sajjad Ahmad, Patrick Maada Ngegba, and Guohua Zhong. 2021. "Role of Endocrine System in the Regulation of Female Insect Reproduction" Biology 10, no. 7: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070614
APA StyleKhalid, M. Z., Ahmad, S., Ngegba, P. M., & Zhong, G. (2021). Role of Endocrine System in the Regulation of Female Insect Reproduction. Biology, 10(7), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070614





