Contiguity and Structural Impacts of a Non-Myosin Protein within the Thick Filament Myosin Layers
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
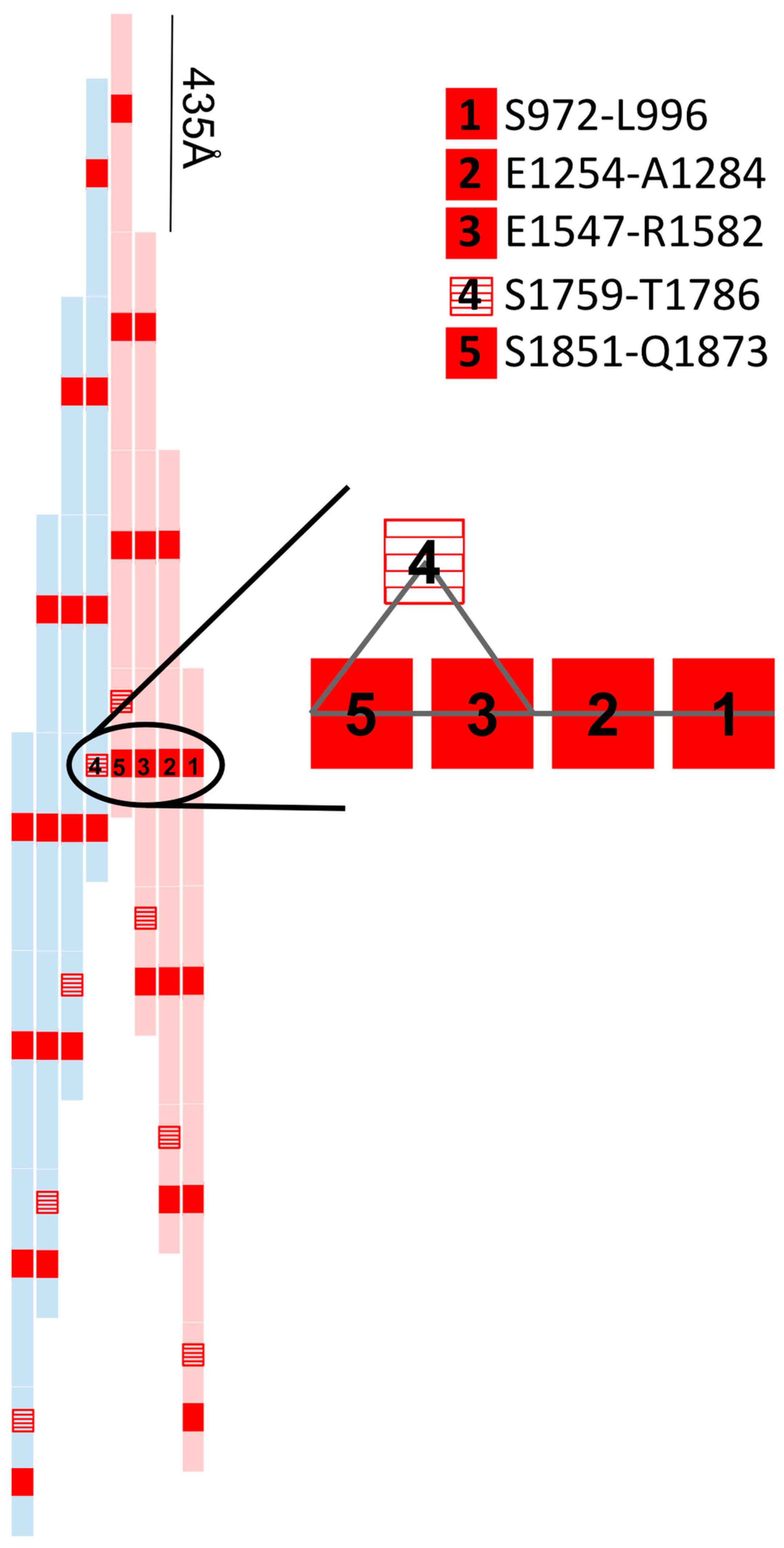
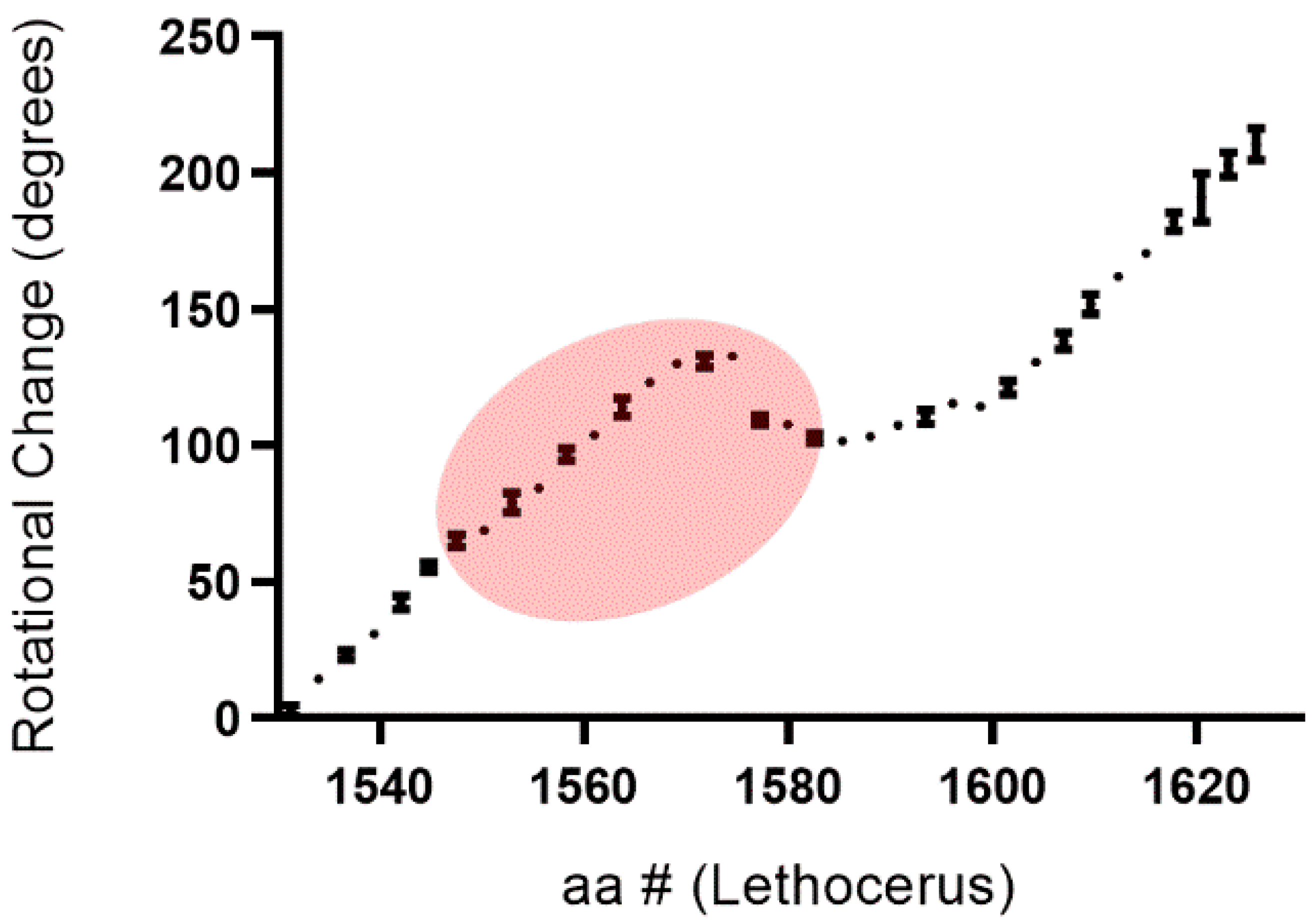
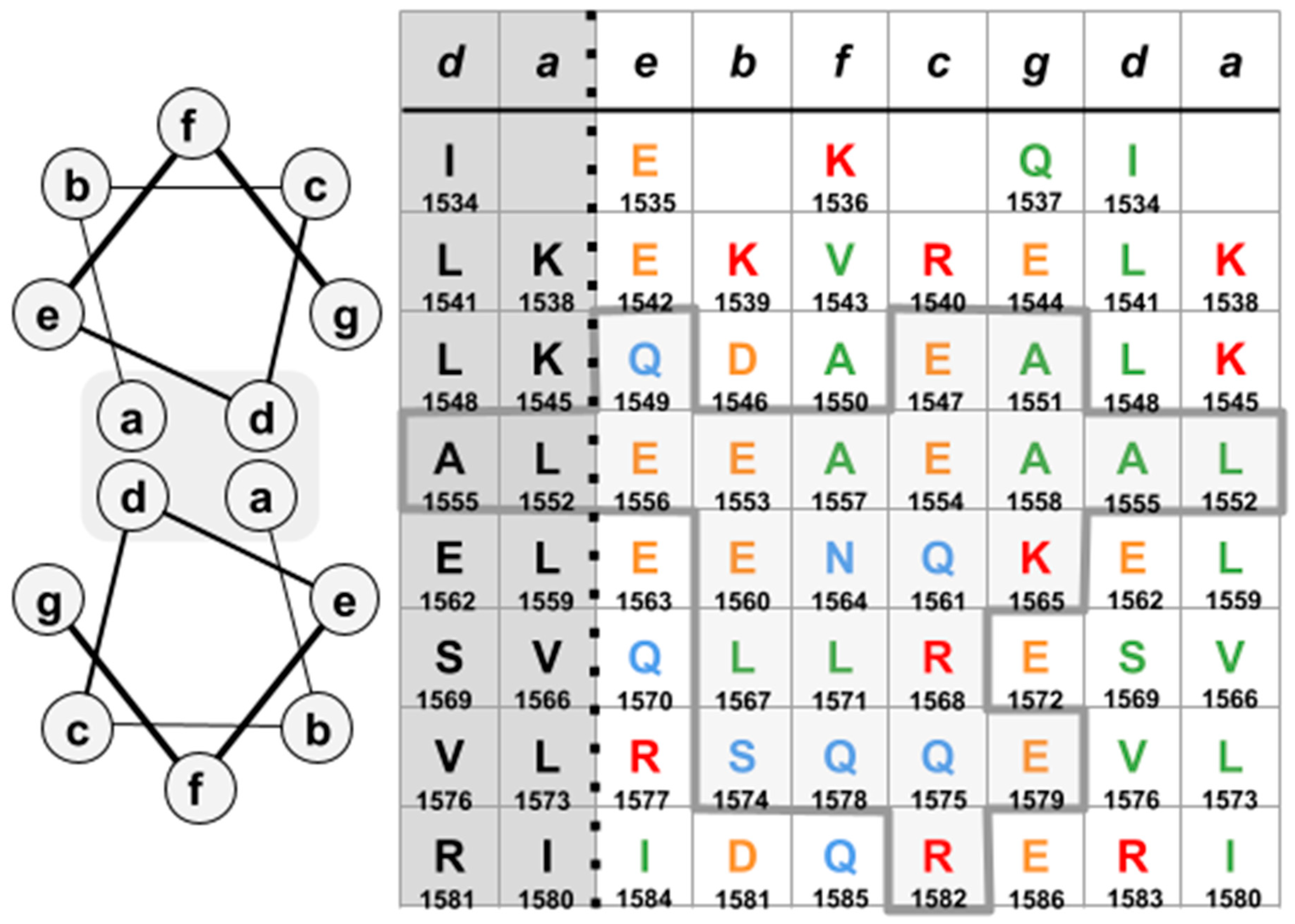
2. Materials, Methods and Results
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Squire, J.M. Muscle myosin filaments: Cores, crowns and couplings. Biophys. Rev. 2009, 1, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Taylor, D.W.; Reedy, M.K.; Edwards, R.J.; Taylor, K.A. Structure of myosin filaments from relaxed Lethocerus flight muscle by cryo-EM at 6 A resolution. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigoreaux, J.; Saide, J.D.; Valgeirsdottir, K.; Pardue, M.L. Flightin, a novel myofibrillar protein of Drosophila stretch-activated muscles. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 121, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Brendel, S.; Cunha, P.M.F.; Astola, N.; Song, B.; Furlong, E.; Leonard, K.R.; Bullard, B. Myofilin, a protein in the thick filaments of insect muscle. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118 Pt 7, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reedy, M.C.; Bullard, B.; Vigoreaux, J.O. Flightin is essential for thick filament assembly and sarcomere stability in Drosophila flight muscles. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 1483–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayer, G.; Vigoreaux, J.O. Flightin is a myosin rod binding protein. Cell Biophys. 2003, 38, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronert, W.A.; O’Donnell, P.T.; Fieck, A.; Lawn, A.; Vigoreaux, J.O.; Sparrow, J.C.; Bernstein, S.I. Defects in the Drosophila myosin rod permit sarcomere assembly but cause flight muscle degeneration. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 249, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, C.; Lakey, A.; Hutchings, A.; Butcher, G.; Leonard, K.; Bullard, B. Cytoskeletal proteins of insect muscle: Location of zeelins in Lethocerus flight and leg muscle. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 107, 1115–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangxu Technology (HK) CO.; ApowerEdit. Apowersoft 2017. Available online: https://www.apowersoft.com/ (accessed on 20 December 2017).
- TGD. GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP). 2017. Available online: https://www.gimp.org (accessed on 20 December 2017).
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; Dezonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigoreaux, J.; Hernandez, C.; Moore, J.; Ayer, G.; Maughan, D. A genetic deficiency that spans the flightin gene of Drosophila melanogaster affects the ultrastructure and function of the flight muscles. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, S.M.; Elber, R. Coiled-coil response to mechanical force: Global stability and local cracking. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, D.D.; Yadavalli, V.K.; Forbes, J.G.; Wang, K. Coiled-coil nanomechanics and uncoiling and unfolding of the superhelix and alpha-helices of myosin. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 2852–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taylor, K.C.; Buvoli, M.; Korkmaz, E.N.; Buvoli, A.; Zheng, Y.; Heinze, N.T.; Cui, Q.; Leinwand, L.A.; Rayment, I. Skip residues modulate the structural properties of the myosin rod and guide thick filament assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3806–E3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H.; Cohen, C.; Parry, D.A. Heptad breaks in alpha-helical coiled coils: Stutters and stammers. Proteins 1996, 26, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupas, A.N.; Bassler, J.; Dunin-Horkawicz, S. The structure and topology of α-helical coiled coils. In Fibrous Proteins: Structures and Mechanisms; Parry, D.A.D., Squire, J.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 95–129. [Google Scholar]
- Korkmaz, E.N.; Taylor, K.C.; Andreas, M.P.; Ajay, G.; Heinze, N.T.; Cui, Q.; Rayment, I. A composite approach towards a complete model of the myosin rod. Proteins 2016, 84, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkin, J.A.; Maughan, D.W.; Vigoreaux, J.O. Mutations that affect flightin expression in Drosophila alter the viscoelastic properties of flight muscle fibers. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 286, C65–C72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasek, N.S.; Nyland, L.R.; Vigoreaux, J.O. The contributions of the amino and carboxy terminal domains of flightin to the biomechanical properties of drosophila flight muscle thick filaments. Biology 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, S.; Tanner, B.; Foelber, V.L.; Vu, H.; Rosenthal, M.; Ruiz, T.; Vigoreaux, J.O. Flightin maintains myofilament lattice organization required for optimal flight power and courtship song quality in Drosophila. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2017, 284, 20170431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, B.C.W.; Miller, M.S.; Miller, B.M.; Lekkas, P.; Irving, T.C.; Maughan, D.W.; Vigoreaux, J.O. COOH-terminal truncation of flightin decreases myofilament lattice organization, cross-bridge binding, and power output in Drosophila indirect flight muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2011, 301, C383–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Adames, F.N.; Alvarez-Ortiz, P.; Vigoreaux, J.O. An evolutionary analysis of flightin reveals a conserved motif unique and widespread in Pancrustacea. J. Mol. Evol. 2013, 78, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemas, D.; Lekkas, P.; Ballif, B.A.; Vigoreaux, J.O. Intrinsic disorder and multiple phosphorylations constrain the evolution of the flightin N-terminal region. J. Proteom. 2016, 135, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermann, W.M.; Gautel, M.; Weber, K.; Fürst, D.O. Molecular structure of the sarcomeric M band: Mapping of titin and myosin binding domains in myomesin and the identification of a potential regulatory phosphorylation site in myomesin. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermann, W.M.J.; Van Der Ven, P.F.M.; Steiner, F.; Weber, K.; Fürst, D.O. Mapping of a myosin-binding domain and a regulatory phosphorylation site in M-protein, a structural protein of the sarcomeric M band. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flashman, E.; Watkins, H.; Redwood, C. Localization of the binding site of the C-terminal domain of cardiac myosin-binding protein-C on the myosin rod. Biochem. J. 2007, 401, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyland, L.R.; Palmer, B.M.; Chen, Z.; Maughan, D.W.; Seidman, C.E.; Seidman, J.; Kreplak, L.; Vigoreaux, J.O. Cardiac myosin binding protein-C is essential for thick-filament stability and flexural rigidity. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, 3273–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, L.; Nyland, L.; Vigoreaux, J. The structural and biomechanical properties of insect thick filaments expressing flightin and cardiac myosin binding protein-C. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 80–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menard, L.M.; Wood, N.B.; Vigoreaux, J.O. Contiguity and Structural Impacts of a Non-Myosin Protein within the Thick Filament Myosin Layers. Biology 2021, 10, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070613
Menard LM, Wood NB, Vigoreaux JO. Contiguity and Structural Impacts of a Non-Myosin Protein within the Thick Filament Myosin Layers. Biology. 2021; 10(7):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070613
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenard, Lynda M., Neil B. Wood, and Jim O. Vigoreaux. 2021. "Contiguity and Structural Impacts of a Non-Myosin Protein within the Thick Filament Myosin Layers" Biology 10, no. 7: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070613
APA StyleMenard, L. M., Wood, N. B., & Vigoreaux, J. O. (2021). Contiguity and Structural Impacts of a Non-Myosin Protein within the Thick Filament Myosin Layers. Biology, 10(7), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070613




