Test-Retest Reliability of Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST) in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
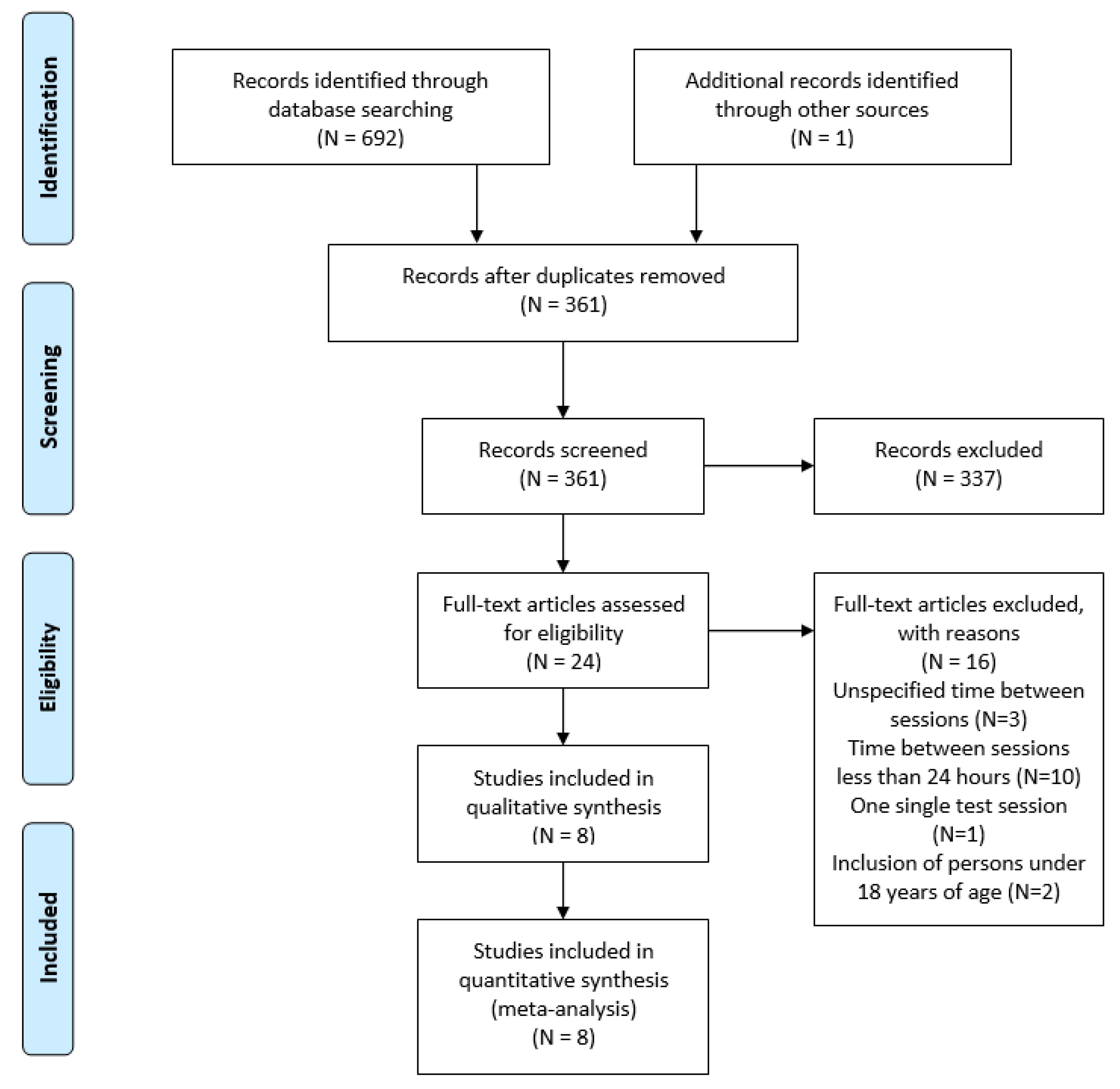
3.1. Search Strategy
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.3. Meta-Analysis
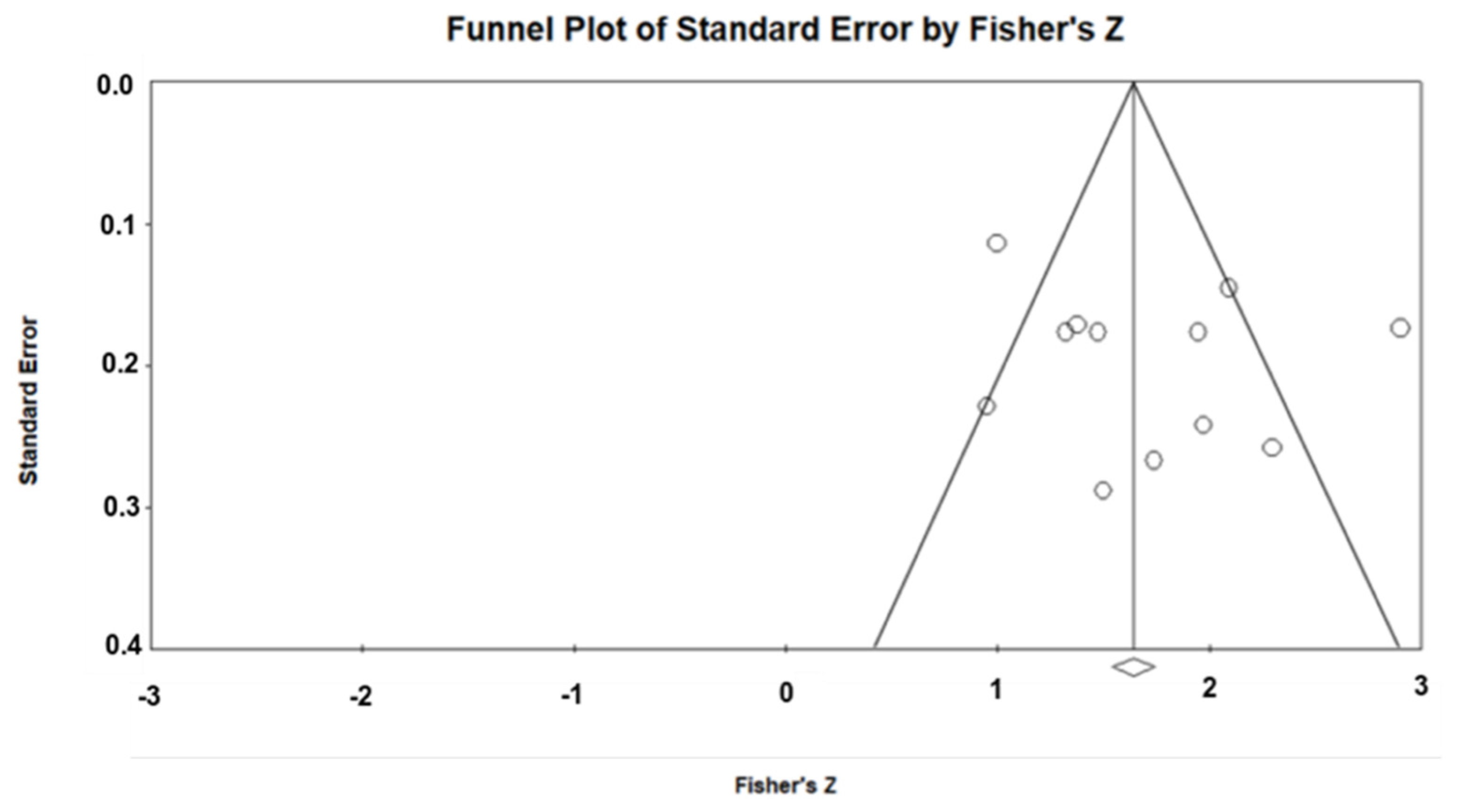
Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samson, M.M.; Meeuwsen, I.B.; Crowe, A.; Dessens, J.A.; Duursma, S.A.; Verhaar, H.J. Relationships between physical performance measures, age, height and body weight in healthy adults. Age Ageing 2000, 29, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakola, L.; Komulainen, P.; Hassinen, M.; Savonen, K.; Litmanen, H.; Lakka, T.A.; Rauramaa, R. Cardiorespiratory fitness in aging men and women: The DR’s EXTRA study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2011, 21, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yümin, E.T.; Şimşek, T.T.; Sertel, M.; Öztürk, A.; Yümin, M. The effect of functional mobility and balance on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among elderly people living at home and those living in nursing home. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2011, 52, e180–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, G.E.; Shardell, M.; Alley, D.E.; Miller, R.R.; Bandinelli, S.; Guralnik, J.; Lauretani, F.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L. Absolute strength and loss of strength as predictors of mobility decline in older adults: The InCHIANTI study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med Sci. 2012, 67, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makizako, H.; Shimada, H.; Doi, T.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Lee, S.; Suzuki, T. Onset of Disability According to Mild Cognitive Impairment Subtype in Community-Dwelling Older Adults in Japan. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2015, 63, 1959–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.A.; Hagaman, A.K.; Reinders, I.; Steeves, J.A.; Newman, A.B.; Rubin, S.M.; Satterfield, S.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Yaffe, K.; Ayonayon, H.N. Depressive trajectories and risk of disability and mortality in older adults: Longitudinal findings from the health, aging, and body composition study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biomed. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, J.; Neyens, J.C.; van Rossum, E.; Spreeuwenberg, M.D.; de Witte, L.P. Predicting ADL disability in community-dwelling elderly people using physical frailty indicators: A systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2011, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadore, E.L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Sinclair, A.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of different exercise interventions on risk of falls, gait ability, and balance in physically frail older adults: A systematic review. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, A.; Gray, C.; Culham, E.; Durward, B.R.; Langhorne, P. Interventions for improving sit-to-stand ability following stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, Cd007232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuna, L.; Thaweewannakij, T.; Wattanapan, P.; Amatachaya, P.; Amatachaya, S. Five times sit-to-stand test for ambulatory individuals with spinal cord injury: A psychometric study on the effects of arm placements. Spinal Cord 2020, 58, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, W.G.; Bussmann, H.B.; Stam, H.J. Determinants of the sit-to-stand movement: A review. Phys. Ther. 2002, 82, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, A.; Chavis, M.; Watkins, J.; Wilson, T. The five-times-sit-to-stand test: Validity, reliability and detectable change in older females. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 24, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Bubela, D.J.; Magasi, S.R.; Wang, Y.C.; Gershon, R.C. Sit-to-stand test: Performance and determinants across the age-span. Isokinet. Exerc. Sci. 2010, 18, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Shove, M.E.; Barreca, S.R.; Masters, L.M.; Sigouin, C.S. Five-repetition sit-to-stand test performance by community-dwelling adults: A preliminary investigation of times, determinants, and relationship with self-reported physical performance. Isokinet. Exerc. Sci. 2007, 15, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W. Test-retest reliability of the five-repetition sit-to-stand test: A systematic review of the literature involving adults. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 3205–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, S.R.; Murray, S.M.; Chapman, K.; Munro, B.; Tiedemann, A. Sit-to-stand performance depends on sensation, speed, balance, and psychological status in addition to strength in older people. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2002, 57, M539–M543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kamide, N.; Kitai, Y.; Ando, M.; Sato, H.; Yoshitaka, S.; Sakamoto, M. Absolute reliability of measurements of muscle strength and physical performance measures in older people with high functional capacities. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2019, 10, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.E.; Kon, S.S.; Canavan, J.L.; Patel, M.S.; Clark, A.L.; Nolan, C.M.; Polkey, M.I.; Man, W.D. The five-repetition sit-to-stand test as a functional outcome measure in COPD. Thorax 2013, 68, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buatois, S.; Perret-Guillaume, C.; Gueguen, R.; Miget, P.; Vançon, G.; Perrin, P.; Benetos, A. A simple clinical scale to stratify risk of recurrent falls in community-dwelling adults aged 65 years and older. Phys. Ther. 2010, 90, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, S.L.; Wrisley, D.M.; Marchetti, G.F.; Gee, M.A.; Redfern, M.S.; Furman, J.M. Clinical measurement of sit-to-stand performance in people with balance disorders: Validity of data for the Five-Times-Sit-to-Stand Test. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, L.; Bourke, G.J. Interpretation and Uses of Medical Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dutil, É.; Bottari, C.; Auger, C. Test-retest reliability of a measure of independence in everyday activities: The ADL profile. Occup. Ther. Int. 2017, 2017, 3014579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruton, A.; Conway, J.H.; Holgate, S.T. Reliability: What is it, and how is it measured? Physiotherapy 2000, 86, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, G.; Nevill, A.M. Statistical methods for assessing measurement error (reliability) in variables relevant to sports medicine. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvir, Z. Isokinetic muscle testing: Reflections on future venues. Hong Kong Physiother. J. 2000, 18, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.S.; Feinstein, A.R. Clinical biostatistics: LIV. The biostatistics of concordance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 29, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.P. Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Schuck, P.; Zwingmann, C. The ‘smallest real difference’as a measure of sensitivity to change: A critical analysis. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2003, 26, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, W.G. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954, 10, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northgraves, M.J.; Hayes, S.C.; Marshall, P.; Madden, L.A.; Vince, R.V. The test-retest reliability of four functional mobility tests in apparently healthy adults. Isokinet. Exerc. Sci. 2016, 24, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Regterschot, G.R.; Schaabova, H.; Baldus, H.; Zijlstra, W. Test-retest reliability of a pendant-worn sensor device in measuring chair rise performance in older persons. Sensors 2014, 14, 8705–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, T.; Magnusson, S.P.; Kjaer, M.; Beyer, N. Intra-rater reliability and agreement of muscle strength, power and functional performance measures in patients with hip osteoarthritis. J. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 46, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.P.; Leddy, A.L.; Earhart, G.M. Five times sit-to-stand test performance in Parkinson’s disease. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2011, 92, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, C.; Steffen, T.; Paly, E.; Dvorak, L.; Nelson, R. Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change for Sit-to-Stand Tests and the Functional Gait Assessment for Individuals With Parkinson Disease. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2001 2017, 40, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mong, Y.; Teo, T.W.; Ng, S.S. 5-repetition sit-to-stand test in subjects with chronic stroke: Reliability and validity. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, K.B.; Addison, O.; Kim, H.S.; Dibble, L.E. Testing balance and fall risk in persons with Parkinson disease, an argument for ecologically valid testing. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leddy, A.L.; Crowner, B.E.; Earhart, G.M. Functional gait assessment and balance evaluation system test: Reliability, validity, sensitivity, and specificity for identifying individuals with Parkinson disease who fall. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meretta, B.M.; Whitney, S.L.; Marchetti, G.F.; Sparto, P.J.; Muirhead, R.J. The five times sit to stand test: Responsiveness to change and concurrent validity in adults undergoing vestibular rehabilitation. J. Vestib. Res. Equilib. Orientat. 2006, 16, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Mentiplay, B.F.; Clark, R.A.; Bower, K.J.; Williams, G.; Pua, Y.-H. Five times sit-to-stand following stroke: Relationship with strength and balance. Gait Posture 2020, 78, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Demura, S. Relationships between ground reaction force parameters during a sit-to-stand movement and physical activity and falling risk of the elderly and a comparison of the movement characteristics between the young and the elderly. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2009, 48, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaton, D.E. Understanding the relevance of measured change through studies of responsiveness. Spine 2000, 25, 3192–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Fernández, R.; Gasca-Salas, C.; Sánchez-Ferro, Á.; Obeso, J.Á. Actualización en la enfermedad de Parkinson. Rev. Médica Clínica Condes 2016, 27, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkster, L.M.; Eng, J.J. Postural control during a sit-to-stand task in individuals with mild Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Brain Res. 2004, 154, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study, Year | Sample | Age (Years) | Time of Rest | Session 1 (Seconds) | Session 2 (Seconds) | ICC (95% CI) | SEM | SEM % | MDC | MDC % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Type | ||||||||||
| Bieler et al. 2014 | 37 | HOA | 68 (4) | 1 wk | 10.14 (2.63) | 9.34 (2.61) | 0.880 | 0.91 | 10.7 | 2.11 | - |
| 35 | 68 (6) | 2 wk | 11.37 (3.02) | 10.49 (2.70) | 0.867 | 0.99 | 11 | 2.31 | - | ||
| 15 | 71 (5) | 2.5 wk | 9.99 (2.12) | 9.38 (1.94) | 0.905 | 0.63 | 7.7 | 1.47 | - | ||
| Duncan et al. 2011 | 80 | PD | 67 (9.0) | 7 d | 20.25 (14.12) | - | 0.76 | - | - | - | - |
| Jones et al. 2013 | 50 | COPD | 69 (10) | 24–48 h | 14.1 (11.5) | 12.4 (10.2) | 0.97 (0.95–0.99) | - | - | - | - |
| Khuna et al. 2019 | 20 | SCI | 51.1 (13.4) | 7 d | 16.2 (5.97) | 15.2 (4.95) | 0.962 (0.905–0.985) | 1.05 | - | 2.93 | - |
| Mong et al. 2010 | 36 | CS | 60.0 (4.8) | 7 d | 17.1 (7.5) | - | 0.989–0.999 | - | - | - | - |
| Northgrave et al. 2016 | 35 | H | 54.6 (12.1) | 4 wk | T (n = 35): 11.40 (2.89) | T: 10.96 (2.79) | T: 0.96 (0.91–0.98) | T: 0.58 | T: 5.19 | T: 1.60 | T: 16.09 |
| M (n = 18): 10.96 (2.86) | M: 10.61 (2.94) | M: 0.98 (0.94–0.99) | M: 0.43 | M: 3.94 | M: 1.18 | M: 10.92 | |||||
| F (n = 17): 11.87 (2.94) | F: 11.33 (2.67) | F: 0.94 (0.82–0.98) | F: 0.71 | F: 6.12 | F: 1.96 | F: 16.92 | |||||
| Petersen et al. 2017 | 22 | PD | 71.5 (8.5) | 6–8 d | 12.7 (7.3) | 14.1 (15.2) | 0.74 | - | - | 10.3 | - |
| Zhang et al. 2014 | 35 | H | 81.9 (5.5) | 3–8 d | 17.36 (4.87) | 16.29 (4.68) | 0.90 | - | 9.0 | - | - |
| Study | Sample Size | Correlation Coefficient | 95% IC | z | p | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||||
| Bieler et al. 2014 (a) | 37 | 0.880 | 0.778 to 0.937 | 8.10 | 7.37 | ||
| Bieler et al. 2014 (b) | 35 | 0.867 | 0.751 to 0.931 | 7.62 | 7.34 | ||
| Bieler et al. 2014 (c) | 15 | 0.905 | 0.732 to 0.968 | 2.86 | 6.44 | ||
| Duncan et al. 2011 | 80 | 0.760 | 0.649 to 0.840 | 18.33 | 7.71 | ||
| Jones et al. 2013 | 50 | 0.970 | 0.947 to 0.983 | 11.19 | 7.54 | ||
| Khuna et al. 2019 | 20 | 0.962 | 0.905 to 0.985 | 4.05 | 6.83 | ||
| Mong et al. 2010 | 36 | 0.995 | 0.990 to 0.997 | 7.86 | 7.36 | ||
| Northgrave et al. 2016 (a) | 35 | 0.960 | 0.922 to 0.980 | 7.62 | 7.34 | ||
| Northgrave et al. 2016 (b) | 18 | 0.980 | 0.946 to 0.993 | 3.57 | 6.70 | ||
| Northgrave et al. 2016 (c) | 17 | 0.940 | 0.838 to 0.979 | 3.33 | 6.62 | ||
| Petersen et al. 2017 | 22 | 0.740 | 0.463 to 0.885 | 4.52 | 6.94 | ||
| Zhang et al. 2014 | 35 | 0.900 | 0.810 to 0.949 | 7.62 | 7.34 | ||
| Total (fixed effects) | 400 | 0.928 | 0.912 to 0.941 | 31.325 | <0.001 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 400 | 0.937 | 0.877 to 0.968 | 9.572 | <0.001 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Bermejo, L.; Adsuar, J.C.; Mendoza-Muñoz, M.; Barrios-Fernández, S.; Garcia-Gordillo, M.A.; Pérez-Gómez, J.; Carlos-Vivas, J. Test-Retest Reliability of Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST) in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060510
Muñoz-Bermejo L, Adsuar JC, Mendoza-Muñoz M, Barrios-Fernández S, Garcia-Gordillo MA, Pérez-Gómez J, Carlos-Vivas J. Test-Retest Reliability of Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST) in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology. 2021; 10(6):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060510
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Bermejo, Laura, José Carmelo Adsuar, María Mendoza-Muñoz, Sabina Barrios-Fernández, Miguel A. Garcia-Gordillo, Jorge Pérez-Gómez, and Jorge Carlos-Vivas. 2021. "Test-Retest Reliability of Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST) in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Biology 10, no. 6: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060510
APA StyleMuñoz-Bermejo, L., Adsuar, J. C., Mendoza-Muñoz, M., Barrios-Fernández, S., Garcia-Gordillo, M. A., Pérez-Gómez, J., & Carlos-Vivas, J. (2021). Test-Retest Reliability of Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST) in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology, 10(6), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10060510












