Comparative Assessment of Medicinal Plant Utilization among Balti and Shina Communities in the Periphery of Deosai National Park, Pakistan
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- to record the phytonyms and traditional knowledge of medicinal plants gathered among the two linguistic communities;
- (b)
- to make a cross-cultural comparison of the gathered data between the two considered groups in order to understand the sociocultural adaptations that these groups have undergone;
- (c)
- to compare the gathered data with the existing Tibetan ethnomedicinal literature.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Targeted Communities
2.2. Field Study
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Medicinal Plants and Their Uses
3.2. Cross-Cultural Comparison
3.3. Comparison with Tibetan Ethnobotany
3.4. Novelty
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aziz, M.A.; Ullah, Z.; Pieroni, A. Wild Food Plant Gathering among Kalasha, Yidgha, Nuristani and Khowar Speakers in Chitral, NW Pakistan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua-Zambrana, N.Y.; Cámara-Leret, R.; Bussmann, R.W.; Macía, M.J. The influence of socioeconomic factors on traditional knowledge: A cross scale comparison of palm use in northwestern South America. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWF (World Wildlife Fund). “How Many Species are We Losing?” Our Work, How Much Is Being Lost? Available online: https://wwf.panda.org/our_work/biodiversity/biodiversity (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Maffi, L. Linguistic, cultural, and biological diversity. Annu. Rev. Anthr. 2005, 34, 599–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO-CBD. Joint Program between Biological and Cultural Diversity; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2010; Available online: http://www.unesco.org/new/en/natural-sciences/special-themes/biodiversity/biodiversity-culture/unesco-cbd-joint-programme (accessed on 9 March 2021).
- Hanspach, J.; Haider, L.J.; Oteros-Rozas, E.; Olafsson, A.S.; Gulsrud, N.M.; Raymond, C.M.; Torralba, M.; Martín-López, B.; Bieling, C.; García-Martín, M.; et al. Biocultural approaches to sustainability: A systematic review of the scientific literature. People Nat. 2020, 2, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Khan, S.M.; Alam, J.; Khan, S.W.; Abbasi, A.M. Medicinal plants used by inhabitants of the Shigar Valley, Baltistan region of Karakorum range-Pakistan. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2017, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, M.; Altaf, M.; Bussmann, R.W.; Abbasi, A.M. Ethnomedicinal uses of the local flora in Chenab riverine area, Punjab province Pakistan. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2019, 15, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Sultana, S.; Rashid, S.; Khan, M.A. Ethnomedicinal knowledge of the most commonly used plants from Deosai Plateau, Western Himalayas, Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.U.; Shah, M.; Ahmad, H.; Ashraf, M.; Rahman, I.U.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, S.M.; Majid, A. Investigation of traditional veterinary phytomedicines used in Deosai Plateau, Pakistan. Glob. Vet. 2015, 15, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Pieroni, A.; Giusti, M.E.; Quave, C.L. Cross-cultural ethnobiology in the western balkans: Medical ethnobotany and ethnozoology among albanians and serbs in the pešter plateau, sandžak, south-western serbia. Hum. Ecol. 2011, 39, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Bussmann, R.; Li, F.-F.; Li, J.-Q.; Hong, L.-Y.; Long, C.-L. Ethnobotanical approaches of traditional medicine studies in Southwest China: A literature review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 186, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.K.; Sharma, O.P.; Choubey, V.M.; Nagpaul, K.K. Past glacier (Würmian) ice thickness in the Karakoram and on the Deosai Plateau in the catchment area of the Indus River. Eiszeitalt. Ggw. 2004, 54, 95–123. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.K.; Sharma, O.P.; Choubey, V.M.; Nagpaul, K.K. Age of the Ladakh-Deosai granite batholith, Trans-Himalaya. Curr. Sci. 1981, 50, 819–821. [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich, M. Not only in the Caucasus: Ethno-linguistic Diversity on the Roof of the World. In Studies on Iran and the Caucasus; Bläsig, U., Arakelova, V., Weinreich, M., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Hook, P.E. Kesar of Layul: A Central Asian Epic in the Shina of Gultari. In Studies in Pakistani Popular Culture; Hanaway, W.L., Heston, W., Eds.; Sang-e-Meel and Lok Virsa Publications: Lahore, Paksitan, 1996; pp. 121–183. [Google Scholar]
- International Society of Ethnobiology (ISE). Code of Ethics. 2008. Available online: www.ethnobiology.net/whatwe-do/core-programs/ise-ethics-program/code-of-ethics (accessed on 9 March 2021).
- Tongco, M.D.C. Purposive Sampling as a Tool for Informant Selection. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2007, 5, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertin, A.; Nair, P.K.R. Farmers’ Perspectives on the Role of Shade Trees in Coffee Production Systems: An Assessment from the Nicoya Peninsula, Costa Rica. Hum. Ecol. 2004, 32, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussmann, R.W.; Sharon, D. Traditional medicinal plant use in Northern Peru: Tracking two thousand years of healing culture. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2006, 2, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieroni, A.; Sõukand, R. Ethnic and religious affiliations affect traditional wild plant foraging in Central Azerbaijan. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2019, 66, 1495–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.I.; Qaiser, M. (Eds.) Flora of Pakistan; University of Karachi: Karachi, Pakistan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, R.R. The flora of Deosai plains. Pak. J. For. 1961, 11, 225–295. [Google Scholar]
- The Plant List, Version 1, Published on the Internet. Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/ (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Stevens, P.F. Angiosperm Phylogeny Website, Version 14. 2017. Available online: http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Tardío, J.; Pardo-De-Santayana, M.; Morales, R. Ethnobotanical review of wild edible plants in Spain. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 152, 27–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, Z.; Sultan, A. Ethnobotany of Palas valley, Pakistan. Ethnobot. Leafl. 2005, 1, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Shinwari, S.; Ahmad, M.; Luo, Y.; Zaman, W. Quantitative analyses of medicinal plants consumption among the inhabitants of Shangla-Kohistan areas in Northern-Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2017, 49, 725–734. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Khan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Jahan, S.; Sultana, S. Ethnopharmacological application of medicinal plants to cure skin diseases and in folk cosmetics among the tribal communities of North-West Frontier Province, Pakistan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 128, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Khan, S.M.; Alam, J.; Khan, S.W.; Abbasi, A.M. Herbal medicines used to cure various ailments by the inhabitants of Abbottabad district, North West Frontier Province, Pakistan. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2010, 9, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Khan, H.; Muhammad, N.; Sultana, S. Medicinal plants used for the treatment of jaundice and hepatitis based on socio-economic documentation. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, N.; Shah, M.H. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinally important wild edible fruits species used by tribal communities of Lesser Himalayas-Pakistan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.M.; Shah, M.H.; Li, T.; Xingbo, F.; Guo, R.; Liu, H. Ethnomedicinal values, phenolic contents and antioxidant properties of wild culinary vegetables. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 162, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, G.M.; Khan, M.A. Checklist of Medicinal Plants of Siran Valley, Mansehra, Pakistan. Ethnobot. Leafl. 2006, 2006, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, G.M.; Jamal, Z.; Hussain, M. Phytotherapy among the rural women of district Abbotabad. Pak. J. Bot. 2013, 45, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, G.M.; Abbasi, A.M.; Khan, N.; Guo, X.; Khan, M.A.; Hussain, M.; Bibi, S.; Nazir, A.; Tahir, A.A. Traditional uses of medicinal plants against malarial disease by the tribal communities of Lesser Himalayas–Pakistan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, A.; Amjad, M.S.; Ahmad, K.; Altaf, M.; Umair, M.; Abbasi, A.M. Ethnomedicinal knowledge of the rural communities of Dhirkot, Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2019, 15, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabh, B.; Chaurasia, O. Traditional medicinal plants of cold desert Ladakh—Used in treatment of cold, cough and fever. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 112, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabh, B.; Chaurasia, O.; Ahmed, Z.; Singh, S.B. Traditional medicinal plants of cold desert Ladakh—Used against kidney and urinary disorders. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabh, B. Medicinal plants of cold desert Ladakh used in the treatment of stomach disorders. Indian J. Tradit. Knowl. 2009, 8, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ballabh, B.; Chaurasia, O.P. Herbal Formulations from Cold Desert Plants Used For Gynecological Disorders. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2011, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Dias, M.I.; Lima, A.; Barros, L.; Rodrigues, M.E.; Ferreira, I.C.S.F.R.; Henriques, M. Satureja montana L. and Origanum majorana L. decoctions: Antimicrobial activity, mode of action and phenolic characterization. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, N.; Barros, L.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Henriques, M.; Silva, S.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Evaluation of bioactive properties and phenolic compounds in die rent extracts prepared from Salvia ocinalis L. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Khan, S.M.; Abbasi, A.M.; Pieroni, A.; Ullah, Z.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmad, Z. Ethnobotany of the Balti community, Tormik valley, Karakorum range, Baltistan, Pakistan. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2016, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, W.; Rahman, K.; Raja, N.I.; Qureshi, R.; Bussmann, R.W.; Mashwani, Z.-U.-R. A quantitative medico-botanical expedition of Fairy Meadows National Park, Diamir, Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2019, 18, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.W.; Khatoon, S. Ethnobotanical studies on some useful herbs of Haramosh and Bugrote valleys in Gilgit, northern areas of Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2008, 40, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, I.; Bano, A.; Ullah, F. Traditional drug therapies from various medicinal plants of central Karakoram national park, Gilgit-Baltistan Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Z.; Alam, J.; Muhammad, S.; Bussmann, R.W.; Khan, S.M.; Hussain, M. Phyto-cultural diversity of the Shigar valley (Central Karakorum) Baltistan, Northern Pakistan. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2019, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Ahmad, M.; Ben Hadda, T.; Saboor, A.; Sultana, S.; Zafar, M.; Khan, M.P.Z.; Arshad, M.; Ashraf, M.A. Quantitative ethnomedicinal study of plants used in the skardu valley at high altitude of Karakoram-Himalayan range, Pakistan. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2014, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, S. Story of the creation of Shigar. Cent. Asiat. J. 1978, 22, 102–120. [Google Scholar]
- Boesi, A. Plants in the Tibetan World: A Preliminary Study, in Tibetan Printing: Comparison, Continuities, and Change. In Tibetan Printing: Comparisons, Continuities and Change; Diemberger, H., Ehrhart, F.-K., Kornicki, P., Eds.; Brill’s Tibetan Studies Library: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 29, pp. 501–531. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhuo, J.; Liu, B.; Jarvis, D.; Long, C. Ethnobotanical study on wild plants used by Lhoba people in Milin County, Tibet. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2015, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, S.; Chaudhary, R.P.; Quave, C.L.; Taylor, R.S.L. The use of medicinal plants in the trans-himalayan arid zone of Mustang district, Nepal. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2010, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunwar, R.M.; Fadiman, M.; Cameron, M.; Bussmann, R.W.; Thapa-Magar, K.B.; Rimal, B.; Sapkota, P. Cross-cultural comparison of plant use knowledge in Baitadi and Darchula districts, Nepal Himalaya. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2018, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesi, A. Traditional knowledge of wild food plants in a few Tibetan communities. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2014, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Singh, C.; Chauhan, N.; Rani, A. A review: Ethnobotanical studiy on medicinal plants of Kargil district, Ladakh, India. J. Emerg. Technol. Innov. Res. 2018, 5, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
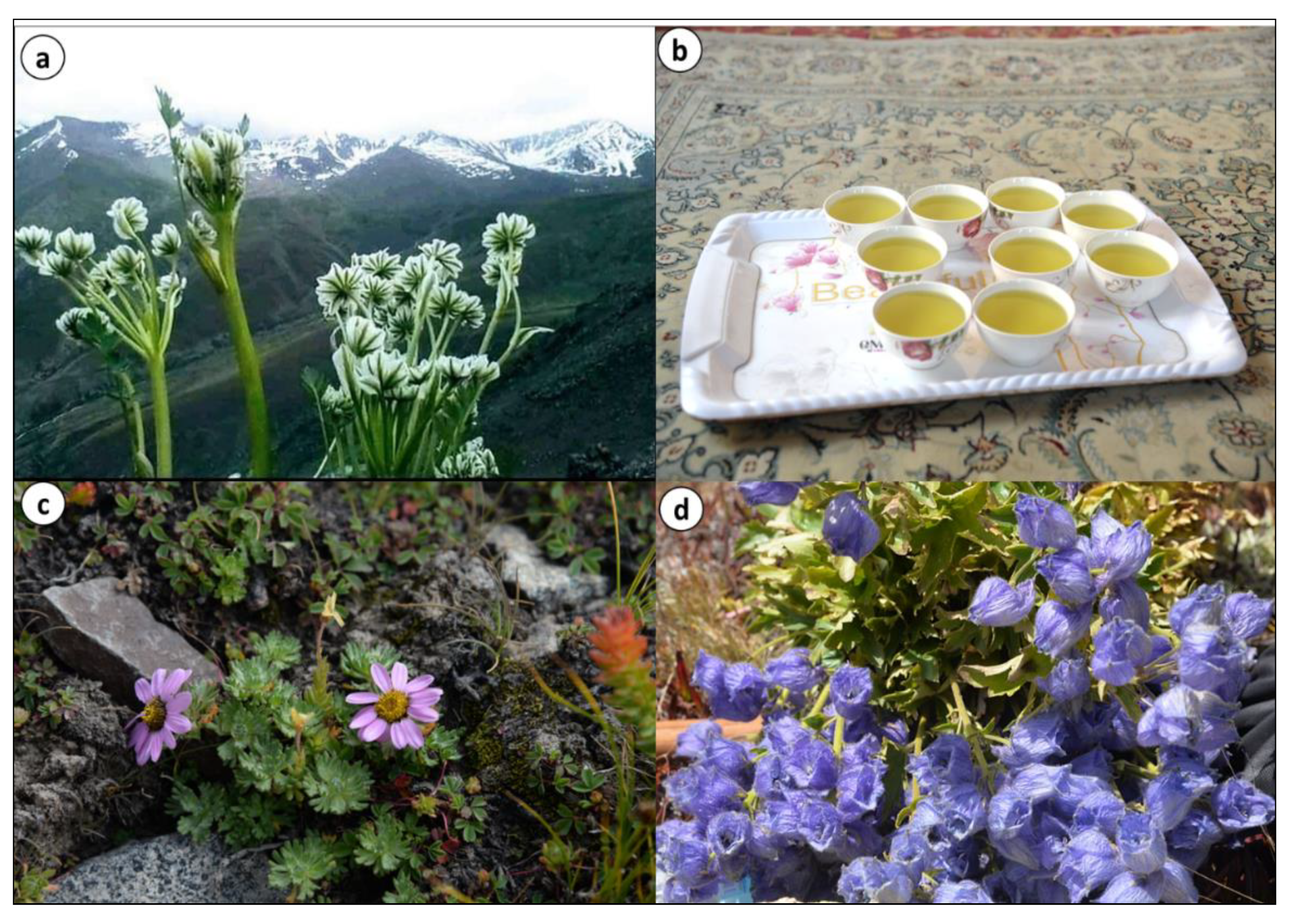
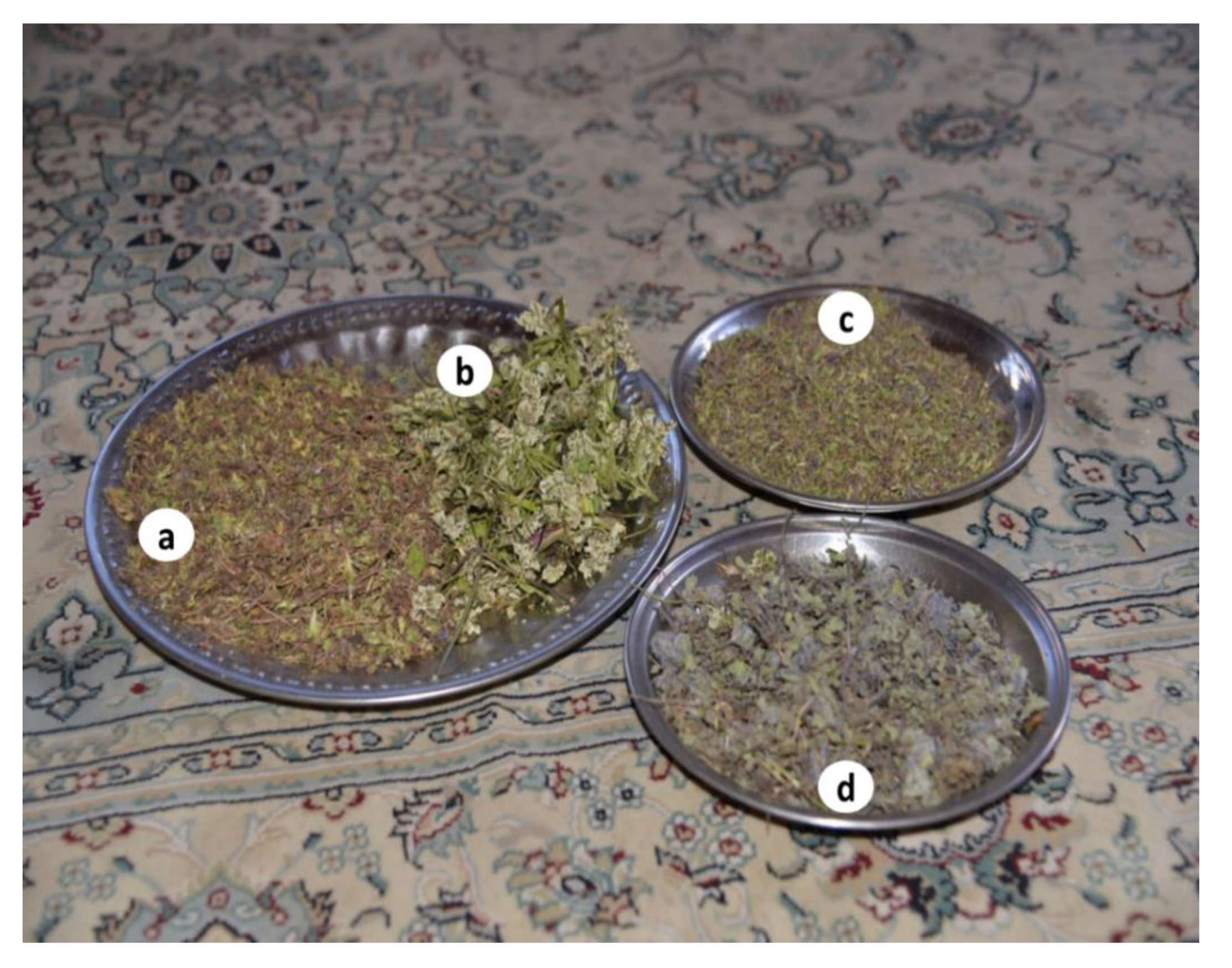
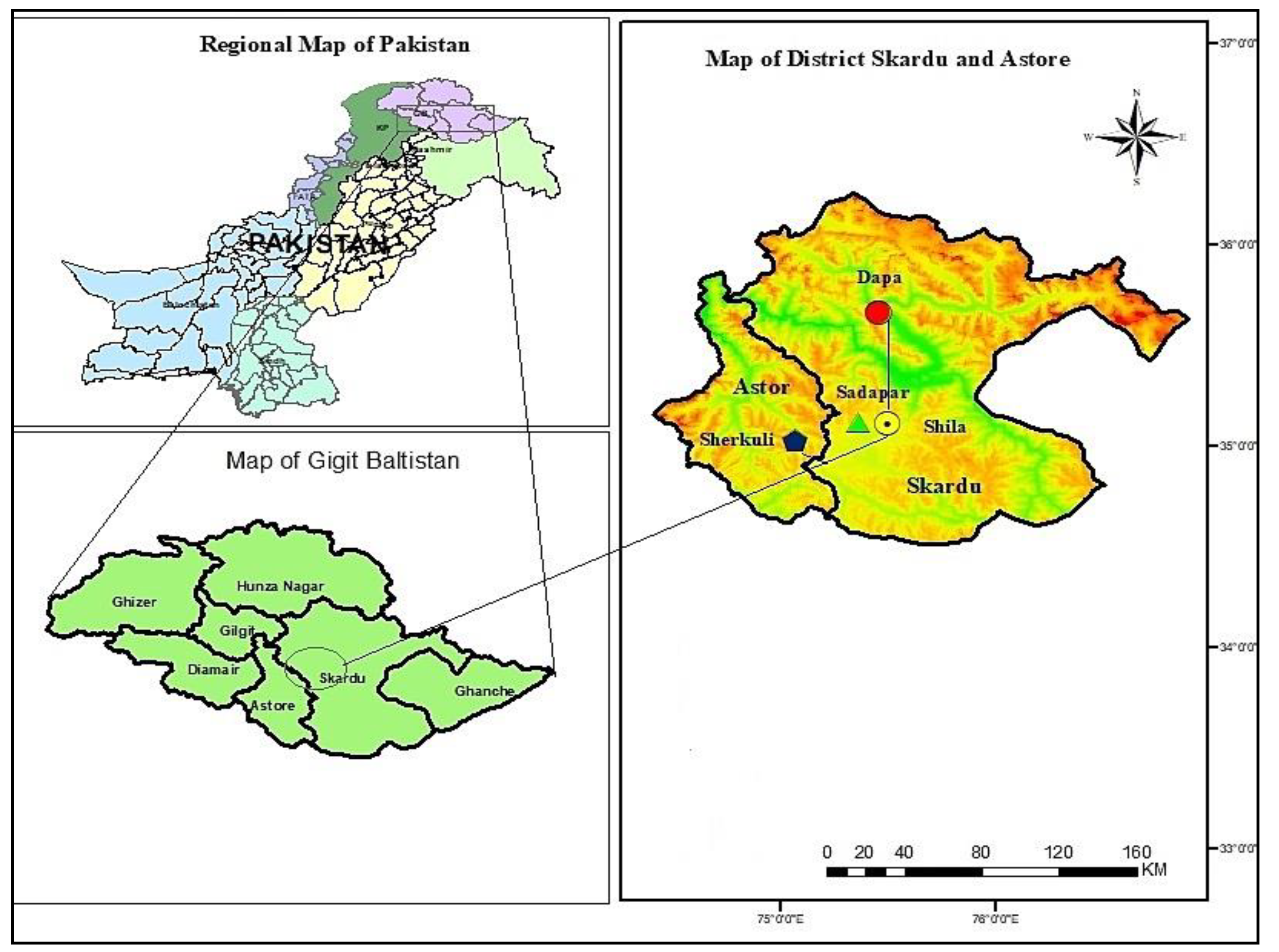




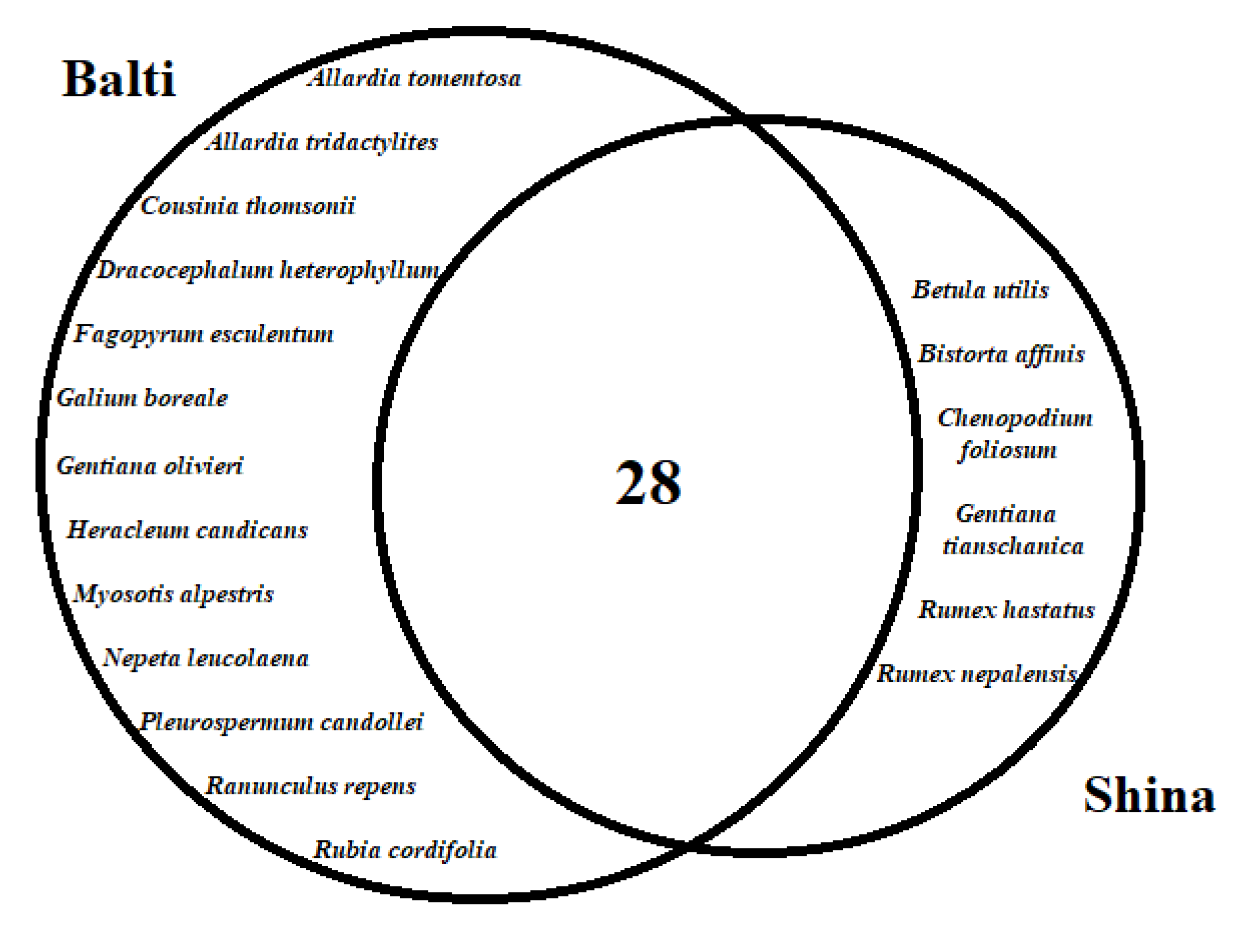
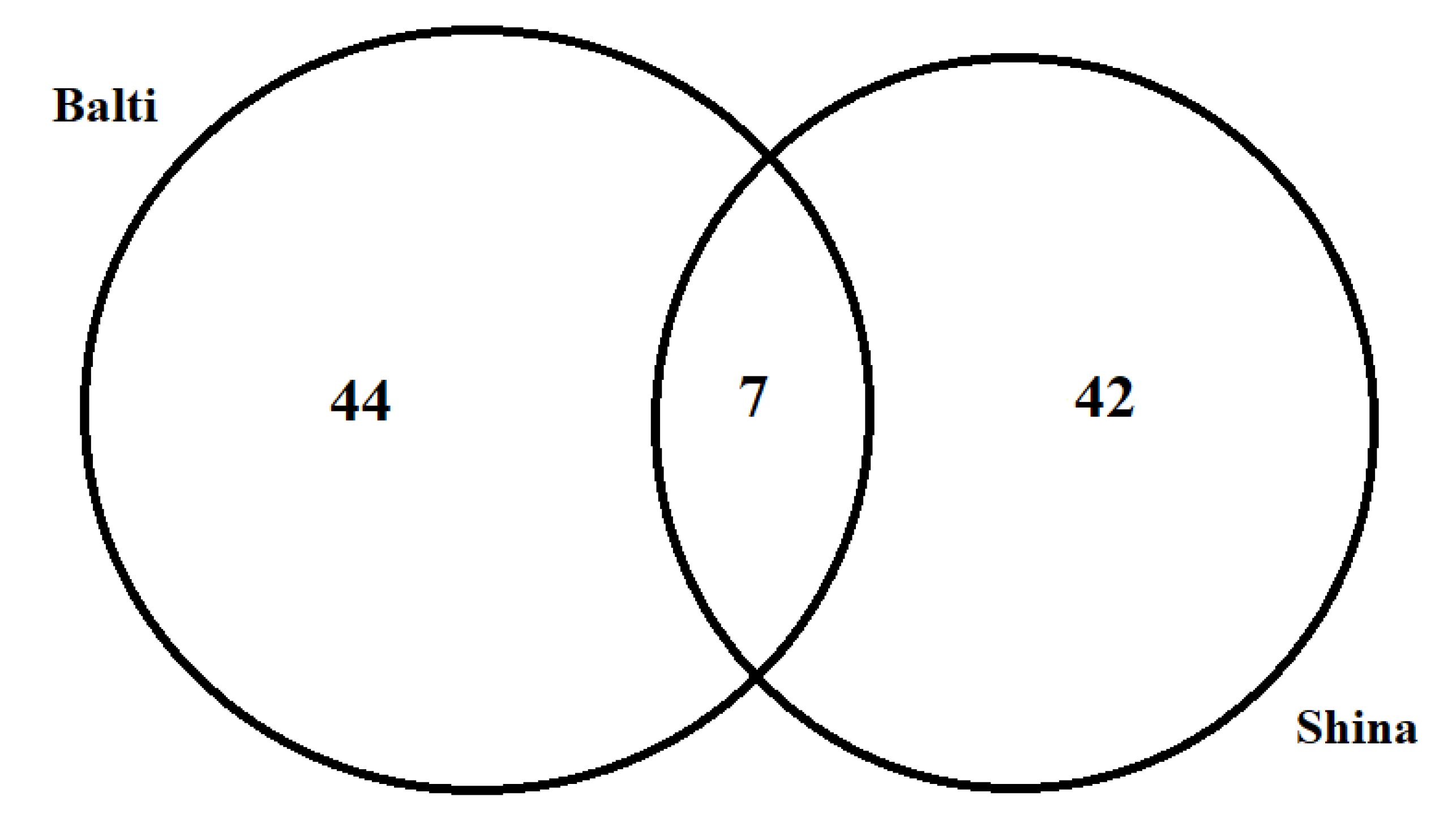
| Language | Village | Elevation (m.a.s.l.) | Number of Interviews | Number of Households | Religion (Faith) | Endogamic/Exogamic Rules | Arrival in the Area | Subsistence Activities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shina | Sherkuli | 3355 | 12 male/2 female | 150 | Shia | Endogamic (rarely exogamic) | 12th century | Horticulturists and pastoralists |
| Sadpara | 2350 | 8 male/2 female | 150 | |||||
| Balti | Dapa | 3886 | 10 male/2 female | 180 | Shia | Endogamic | Autochthonous | Horticulturists and pastoralists |
| Shila | 3252 | 6 male/4 female | 70 | Nurbakhshi |
| Name/Family/Voucher Number | Local Name | Habit | PU | DF | Ad | Disease(s) Treated | RSU | RFC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aconitum violaceum Jacquem. ex. Stapf./Ranunculaceae/DNP71 | Buma (B/S) | Herb | Root (B/S) | Decoction (B); Powder (S) | Oral (B); Oral and topical (S) | Abdominal pain, flatulence (B); Ringworm, typhoid (S) | No | 78.26 |
| Allardia tomentosa Decne./Asteraceae/DNP41 | Tarkhan (B) | Herb | Flowers (B) | Decoction (B) | Oral (B) | Menstrual cramps, abdominal pain (B) | No | 41.30 |
| Allardia tridactylites (Kar. and Kir.) Sch. Bip. /Asteraceae/DNP42 | Patkanstwa (B) | Herb | Whole plant (B) | Decoction (B) | Oral (B) | Food poisoning (B) | No | 28.26 |
| Allium carolinianum DC./Amaryllidaceae /DNP35 | Refor (B); Kachpauk (S) | Herb | Bulb (B); Leaves (S) | Infusion (B); Boiled leaves (S) | Oral (B/S) | Pharyngitis, bronchitis (B); Constipation (S) | Yes | 67.39 |
| Arnebia benthamii Wall. ex G. Don/Boraginaceae/DNP51 | Thang marsi (B); Kazaban(S) | Herb | Root (B/S) | Mixed with oil (B); Decoction (S) | Topical (B); Oral (S) | Hair tonic (B); Diabetes, pneumonia (S) | No | 43.47 |
| Artemisia brevifolia Wall./Asteraceae/DNP43 | Bursay (B); Zoon (S) | Herb | Aerial parts (B/S) | Decoction (B); Powder (S) | Oral (B/S) | Vermifuges (B); Hypertension (S) | Yes | 71.73 |
| Artemisia scoparia Waldst. and Kitam./Asteraceae/DNP45 | Khobursay (B); Zoon (S) | Herb | Flowers (B); Leaves (S) | Decoction (B); Paste (S) | Oral (B); Oral and topical (S) | Vermifuge, urethritis (B); Ring worm, indigestion (S) | Yes | 56.52 |
| Berberis pseudumbellata R. Parker/Berberidaceae/DNP48 | Skiurbu (B); Ishkeen (S) | Shrub | Root (B); Root, Leaves (S) | Decoction (B/S); Leaves eaten (S) | Oral (B/S) | Hepatitis, diabetes (B/S) | Yes | 32.60 |
| Bergenia stracheyi (Hook. f. and Thomson) Engl./Saxifragaceae/DNP76 | Shapur (B); Sansper (S) | Herb | Root (B/S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Stomach ulcer (B); Hepatitis, hypertension (S) | No | 60.86 |
| Betula utilis D. Don/Betulaceae/DNP49 | Jongi (S) | Tree | Bark (S) | Powder (S) | Oral and topical (S) | Back ache, leg pain (S) | Yes | 34.78 |
| Bistorta affinis (D. Don) Greene/Polygonaceae/DNP67 | Chomoi (S) | Herb | Rhizome (S) | Powder | Oral (S) | Diarrhoea, fever (S) | No | 54.34 |
| Carum bulbocastanum (L.) Koch/Apiaceae/DNP39 | Karpho thalay (B); Hayyo (S) | Herb | Seeds (B/S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Gastric ulcer (B); Abdominal pain (S) | Yes | 43.47 |
| Carum carvi L./Apiaceae/DNP38 | Naqpo thalay (B); Hayyo (S) | Herb | Seeds (B/S) | Decoction (B); Seeds eaten (S) | Oral (B/S) | Gastric ulcer, gastric trouble (B); Abdominal pain (S) | No | 60.80 |
| Chenopodium foliosum Asch/Chenopodiaceae/DNP52 | Suyaro (S) | Herb | Leaves (S) | Paste (S) | Oral (S) | Oedema, diabetes (C) | No | 13.04 |
| Codonopsis clematidea (Schrenk) C.B. Clarke/Campanulaceae | Bajo mindoq (B); Tumtaq (S) | Herb | Flowers (B/S) | Infusion (B/S) | Oral (B, S) | Stress relief (B); Male sexual tonic (S) | No | 39.13 |
| Cousinia thomsonii C.B. Clarke./Asteraceae/DNP40 | Charchu (B) | Herb | Flowers (B) | Powder (B) | Topical (B); Oral (S) | Pimples, boils, pustules (B); Constipation (S) | No | 43.47 |
| Delphinium brunonianum Royle/Ranunculaceae | Makhoting (B); Mahoti (S) | Herb | Flowers (B); Whole plant (S) | Powder + oil (B); Decoction (S) | Topical (B); Oral (S) | Hair tonic (B); Asthma, pneumonia, hair tonic (S) | No | 78.26 |
| Dracocephalum heterophyllum Benth./Lamiaceae/DNP61 | Triba (B) | Herb | Flowers (B) | Decoction (B) | Oral (B) | Abdominal pain, flatulence (B) | Yes | 60.86 |
| Ephedra gerardiana Wall. ex Stapf/Ephedraceae/DNP55 | Chay (B); Soom (S) | Shrub | Fruit, Root (B/S) | Juice, Root paste (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Tonic and eye pain (B); Asthma, bronchitis (S) | No | 52.17 |
| Fagopyrum esculentum Moench/Polygonaceae /DNP65 | Bro (B) | Herb | Seeds (B) | Powder (B) | Oral (B) | Diabetes, stomach ulcer (B) | Yes | 26.08 |
| Galium boreale L./Rubiaceae/DNP73 | Shatong (B) | Herb | Fruits (B) | Powder (B) | Oral (B) | Hepatitis (B) | No | 60.86 |
| Gentiana olivieri Griseb/Gentianaceae/DNP57 | Tikta (B) | Herb | Flowers (B) | Powder (B) | Oral (B) | Diabetes (B) | Yes | 45.34 |
| Gentiana tianschanica Rupr. ex Kusn./Gentianceae/DNP59 | Palmat (S) | Herb | Flowers, Leaves (S) | Powder (S) | Oral (B) | Blood tonic, hemorrhoids (B) | Yes | 43.47 |
| Heracleum candicans Wall. ex DC./Apiaceae/DNP37 | Ghang (B) | Herb | Root | Powder (B) | Topical (B) | Boils, pimples, pustules (B) | Yes | 39.13 |
| Hippophae rhamnoides L./Elaeagnaceae/DNP54 | Karsokh (B); Buru (S) | Shrub | Fruits (B); Fruits, Seeds (S) | Jam, Powder (B); Paste (S) | Oral and topical (B/S) | Cancer, diabetes, dermatitis (B); Pertussis, cutaneous eruptions (S) | Yes | 56.52 |
| Juniperus excelsa M. Bieb./Cupressaceae/DNP53 | Shukpa (B); Chilli (S) | Tree | Fruits (B/S) | Decoction (B); Dry eaten (S) | Oral (B/S) | Stomach ulcer, fever, diabetes (B); Kidney stones, diabetes (S) | Yes | 23.91 |
| Jurinea dolomiaea Boiss. /Asteraceae/DNP46 | Sathing (B);Gogal Dhoop (S) | Herb | Root (B); Leaves (S) | Paste (B/S) | Topical (B/S) | Fever, cold (B); Wounds, cutaneous eruptions (S) | Yes | 52.17 |
| Mentha royleana Wall. ex Benth./Lamiaceae /DNP63 | Foling (B); Phileel (S) | Herb | Leaves (B/S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Hypertension, abdominal pain, obesity (B/S) | Yes | 78.26 |
| Myosotis alpestris F.W. Schmid/Boraginaceae/DNP50 | Mandaqskor (B) | Herb | Flowers (B) | Decoction (B) | Oral (B) | Abdominal pain, fever (B) | Yes | 34.78 |
| Nepeta leucolaena Benth. ex Hook. f./Lamiaceae/DNP62 | Azoomal (B) | Herb | Flowers, Leaves (B) | Decoction (B) | Oral (B) | Gastric ulcer (B) | No | 39.13 |
| Pleurospermum candollei Benth. ex C.B. Clarke in Hook.f./Apiaceae/DNP36 | Shamdun (B) | Herb | Flowers (B) | Decoction (B) | Oral (B) | Stomatitis, constipation, abdominal ache (B) | Yes | 41.30 |
| Ranunculus repens L./Ranunculaceae/DNP70 | Khser mandoq (B) | Herb | Flowers, Leaves (B) | Paste mix with oil (B) | Topical (B) | Pimples, pustules (B) | Yes | 21.37 |
| Rheum australe D./Polygonaceae/DNP66 | Lachu (B); Chontal (S) | Herb | Root (B); Root, Leaves (S) | Powder (B); Decoction (S) | Oral (B/S) | Stomach ulcer (B); Laxative, dyspepsia (S) | Yes | 69.56 |
| Ribes alpestre Wall. ex Decne./Glossulariaceae/DNP60 | Askuta (B); Churkani (S) | Shrub | Fruits (B) Leaves (S) | Eaten fresh, Paste (B/S) | Oral and topical (B/S) | Ringworm, blood tonic (B/S) | No | 84.78 |
| Rosa webbiana Wall.ex Royle/Rosaceae/DNP72 | Siya marfo (B); Shighaye (S) | Shrub | Leaves, Root, Seeds (B/S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Jaundice, anemia, tonic (S/B) | No | 58.69 |
| Rubia cordifolia L./Rubiaceae/DNP74 | Zghinoq (B) | Herb | Root (B) | Powder (B) | Oral (B) | Skin inflammation, joint pain (B) | No | 32.60 |
| Rumex hastatus D. Don./Polygonaceae/DNP68 | Churki (S) | Herb | Root (S) | Powder | Topical (S) | Closed bone fractures (S) | No | 39.13 |
| Rumex nepalensis Spreng./Polygonaceae/DNP69 | Hubable (S) | Herb | Root (S) | Powder | Oral and topical (S) | Backache, abdominal pain (S) | Yes | 36.95 |
| Solanum nigrum L./Solanaceae/DNP77 | Drumba Shoghlo (B); Gabeeli (S) | Herb | Seeds (B/S) | Roasted seeds (B/S) | Topical (B/S) | Toothache (B/S) | Yes | 52.17 |
| Swertia petiolata D. Don./Gentianaceae/DNP58 | Brama (B); Mumiri (S) | Herb | Leaves (B); Root (S) | Decoction, Paste, Powder (B/S) | Oral (B); Topical (S) | Hepatitis, pneumonia, dysentery (B); Conjunctivitis (S) | No | 71.73 |
| Tanacetum falconeri Hook. f./Asteraceae /DNP44 | Tyalo (B); Flagyl(S) | Herb | Flower (B/S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Body ache, fever (B); Diarrhea, dysentery, abdominal pain (S) | Yes | 67.39 |
| Taraxacum officinale (L.) Weber ex F.H. Wigg/Asteraceae/DNP47 | Khoshmas (B); Guleikasidi (S) | Herb | Whole plant (B); Leaves (S) | Boiled leaves (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Diabetes, constipation (B/S) | No | 43.47 |
| Thymus linearis Benth./Lamiaceae/DNP64 | Tumburuk (B); Tumuro (S) | Herb | Whole plant (B/S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Flatulence, abdominal pain (B); Cough, asthma (S) | Yes | 60.86 |
| Trifolium repens L./Fabaceae/DNP56 | Skabuksuk (B); Chapati (S) | Herb | Flowers (B/S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Pneumonia (B); Bronchitis (S) | Yes | 56.52 |
| Urtica dioica L./Urticaceae/DNP78 | Khashoshing (B); Jhoomi (S) | Herb | Aerial parts (B/S) | Boiled leaves (B/S) | Oral (B); Topical (B) | Constipation (B); Pustule, cutaneous eruptions (S) | Yes | 43.47 |
| Verbascum thapsus L./Scrophulariaceae /DNP75 | Apo Tambaku (B); Tamakush (S) | Herb | Flowers, Seeds (B); Leaves, Flowers (S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Tonic, labor pain (B); Bronchitis, tuberculosis (S) | No | 56.52 |
| Viola serpens Wall.ex Ging./Violaceae/DNP79 | Skor mindoq (B); Lelo (S) | Herb | Flowers (B/S) | Decoction (B/S) | Oral (B/S) | Abdominal pain, flatulence (B); Bronchitis (S) | No | 56.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, Z.; Kousar, S.; Aziz, M.A.; Pieroni, A.; Aldosari, A.A.; Bussmann, R.W.; Raza, G.; Abbasi, A.M. Comparative Assessment of Medicinal Plant Utilization among Balti and Shina Communities in the Periphery of Deosai National Park, Pakistan. Biology 2021, 10, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050434
Abbas Z, Kousar S, Aziz MA, Pieroni A, Aldosari AA, Bussmann RW, Raza G, Abbasi AM. Comparative Assessment of Medicinal Plant Utilization among Balti and Shina Communities in the Periphery of Deosai National Park, Pakistan. Biology. 2021; 10(5):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050434
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Zaheer, Shazia Kousar, Muhammad Abdul Aziz, Andrea Pieroni, Ali Abdullah Aldosari, Rainer W. Bussmann, Ghulam Raza, and Arshad Mehmood Abbasi. 2021. "Comparative Assessment of Medicinal Plant Utilization among Balti and Shina Communities in the Periphery of Deosai National Park, Pakistan" Biology 10, no. 5: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050434
APA StyleAbbas, Z., Kousar, S., Aziz, M. A., Pieroni, A., Aldosari, A. A., Bussmann, R. W., Raza, G., & Abbasi, A. M. (2021). Comparative Assessment of Medicinal Plant Utilization among Balti and Shina Communities in the Periphery of Deosai National Park, Pakistan. Biology, 10(5), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10050434









