Simple Summary
The iron uptake systems are associated with virulence in colistin-resistant high-risk clones of K. pneumoniae. The isolates belonging to high-risk clones of K. pneumoniae are resistant to phagocytosis by neutrophils and induce NET formation.
Abstract
We proposed the hypothesis that high-risk clones of colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae (ColR-Kp) possesses a high number of virulence factors and has enhanced survival capacity against the neutrophil activity. We studied virulence genes of ColR-Kp isolates and neutrophil response in 142 patients with invasive ColR-Kp infections. The ST101 and ST395 ColR-Kp infections had higher 30-day mortality (58%, p = 0.005 and 75%, p = 0.003). The presence of yersiniabactin biosynthesis gene (ybtS) and ferric uptake operon associated gene (kfu) were significantly higher in ST101 (99%, p ≤ 0.001) and ST395 (94%, p < 0.012). Being in ICU (OR: 7.9; CI: 1.43–55.98; p = 0.024), kfu (OR:27.0; CI: 5.67–179.65; p < 0.001) and ST101 (OR: 17.2; CI: 2.45–350.40; p = 0.01) were found to be predictors of 30-day mortality. Even the neutrophil uptake of kfu+-ybtS+ ColR-Kp was significantly higher than kfu--ybtS- ColR-Kp (phagocytosis rate: 78% vs. 65%, p < 0.001), and the kfu+-ybtS+ ColR-Kp survived more than kfu--ybtS- ColR-Kp (median survival index: 7.90 vs. 4.22; p = 0.001). The kfu+-ybtS+ ColR-Kp stimulated excessive NET formation. Iron uptake systems in high-risk clones of colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae enhance the success of survival against the neutrophil phagocytic defense and stimulate excessive NET formation. The drugs targeted to iron uptake systems would be a promising approach for the treatment of colistin-resistant high-risk clones of K. pneumoniae infections.
1. Introduction
Colistin resistance of Klebsiella pneumonia infections is one of the emerging threats in public health because of high fatality rates [1,2,3,4]. The ST101 and ST395 clones of K. pneumoniae are known as high-risk clones with high capacity of drug resistance acquisition and are reported to be significant predictors of the mortality [5,6,7,8,9]. The leading virulence factors of K. pneumoniae are mostly associated with capsular serotype, muco-viscosity, iron uptake systems, and allantoin metabolism [10,11,12]. Enhanced adhesion and attachment by fimbria and non-fimbrial structures promote pathogenicity of K. pneumoniae as well [10,13]. Iron uptake system is essential for survival and dissemination of pathogens during infections. These systems have a significant effect on host inflammatory response [14].
The neutrophils as the important cells of the immune defense, kill pathogens by engulfment or release of extracellular traps (NETs) [15]. The function of NETs is to trap bacteria and promote extracellular killing. This activity may either increase or minimize damage to host cells [15]. A previous study reported that low phagocytic activity of neutrophils contributes to the success of carbapenem-resistant ST258 clone [16]. However, our knowledge on immune escape mechanisms of colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae is very limited [11,12]. By this study, we aimed to identify major virulence factors of colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae in high-risk clones and show their interaction with the neutrophils. Our results provide an insight to depict the pathogenesis of the colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae infection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
The patients diagnosed with colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae infection between January 2015 and May 2018 from seven healthcare centers in Turkey were included in this study. A study protocol reviewing patient’s demographic data, underlying diseases, type of infection, isolation site, blood biochemical parameters, predisposing factors such as having operation within last 1-month, intensive care unit admission (ICU), type of antimicrobial agents used for empirical and agent-specific therapy, duration of colistin therapy before isolation of colistin-resistant isolates, and carbapenem resistance was used. The patients were followed-up for fatality within 30 days after hospital admission. Exclusion criteria were missing key data, subsequent episodes of the same patient.
2.2. Microbiological and Molecular Studies
Colistin resistance was studied by broth microdilution and the breakpoint for resistance was set to >2 mg/L [17]. Carbapenemase genes of OXA-48, NDM-1, and KPC were examined by multiplex-PCR, and amplicons were sequenced [18].
Genotyping of the isolates was carried out by MLST comparing seven housekeeping genes (phoE, gapA, rpoB, tonB, inf, mdh, and pgi) according to the protocol published on the Institute of Pasteur website (http://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/klebsiella/klebsiella.html/ (accessed on 7 January 2019)). ST types were determined using Applied Maths Bionumerics V7.6 software.
Virulence genes of type-1 and type-3 adhesins (fimH-1 and mrkD), enterobactin biosynthesis (entB), aerobactin receptor (iutA), yersiniabactin receptor (fyuA), yersiniabactin biosynthesis (ybtS), ferric uptake operon associated gene (kfu), regulator of mucoid phenotype A (rmpA), capsule type 1 (magA), capsule type2 (K2Wzy), capsule type 5 (K5wzx), outer core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis (wabG), and allantoin metabolism (allS) were screened by PCR using primers described previously [19,20,21].
2.3. Phagocytosis Assays
For phagocytosis assays, 10 ybtS+-kfu+, 8 ybtS--kfu-, 2 ybtS--kfu+, and 1 ybtS+kfu- isolates were selected. Phagocytosis assays were performed with slight modifications described by Kobayashi et al. [16]. Colistin-sensitive standard strain K. pneumoniae ATCC 700,831 and Gram-positive standard S. epidermidis ATCC 35,984 were used as controls. Human neutrophils collected from heathy volunteers were separated from peripheral blood by density gradient centrifugation using Histopaque 1119 (Sigma–Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Neutrophil purity was determined by Flow Cytometry (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA)using mouse anti-human CD15-PE (Bechman-Coulter, USA, Indiana) antibody, and above 90% purity was achieved. K. pneumoniae isolates were stained with BacLight 488 (Thermo Scientific, Boston, MA, USA) with slight changes to manufacturer’s instructions. For phagocytosis, 2 × 107 neutrophils were incubated with bacterial suspension containing 3 × 108 bacteria for 30 min at 37 °C. Phagocytosis was stopped by adding 1 mL of ice-cold PBS into tubes. A portion of each sample was stained with Mouse-Anti Human CD15-PE (Beckman-Coulter, Indiana, IN, USA) and analyzed with BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer. The internalized and/or surface-attached bacteria were determined as CD15+BacLight 488+ cells, whereas free bacteria were determined as only BacLight 488+ Cells. Phagocytic Index (Ph Index) was calculated by the formula ((Initial bacterial count × Ph%)/100). For viability, neutrophils were lysed with dH2O for 20 min and cultured on tryptic soy agar by 10-fold dilutions. After overnight incubation, colonies were counted, and the survival index was calculated by ((Colony count per mL/Ph Index) × 100). Experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.4. Detection of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps
Two ybtS+-kfu+ and two ybtS--kfu- isolates were selected for observation of NET formation. Neutrophils (2 × 105 cells) were incubated for 1 h at 37 °C for attachment to the surface. After incubation, 6 × 106 bacteria were added on neutrophils and incubated 90 min at 37 °C for NET generation (1:30). A portion of each cell was fixed and permeabilized with 4% BSA and 0.2% Triton X-100. After blocking, the cells were stained with Mouse Anti-Human Myeloperoxidase (Santacruz, Heidelberg, Germany) and Rabbit Anti-Human Histone-H3 (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) antibodies for 1 h. Rabbit Anti-mouse Alexa-Fluor 594 (Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA) and Goat Anti-rabbit Alexa-Fluor 488 (Thermo Scientific, Massachusetts, MA, USA) were used as secondary antibodies. BSA 3% in PBS was used as blocking buffer. Fluoroshield medium with DAPI (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) was used for mounting, and analyses were performed under confocal microscope (Leica DMi8/SP8, Wetzlar, Germany). K. pneumoniae ATCC700831 was used as control. NETs were defined as cell-free filaments that were stained with both anti-Histone and anti-MPO antibody. For each slide, 10 microscopic areas were searched by experienced scientists. Degree of NETs formed was categorized into three groups: absence of NETs = 0% neutrophils forming NETs, moderate NET = weak and short NETs by a few neutrophiles, and strong NETs = multiple abundant and long NETs by many neutrophiles per microscopic field. The remaining part was assessed for the viability of the bacteria after NET formation. Cell suspensions were cultured on tryptic soy agar by 10-fold dilutions and colony count per milliliter was recorded.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the statistical software package R. In univariate analyses, Wilcoxon rank-sum test for continuous covariates, and Fisher’s exact test for discrete covariates were used. In multivariate analyses, logistic regression was performed using the variables that were detected to be significant in univariate analyses. p value below 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. All the results of statistical analysis are available at the Supplementary file https://midaslab.shinyapps.io/klebsiella_pneumoniae_virulence_analysis/ (accessed on 3 November 2020).
Koç University Institutional Review Board approved the study under the number 2015.048.IRB1.008.
3. Results
In this study, 142 adult patients with colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae infection were included. Overall, 84% (n = 119) of the patients stayed in ICU, bacteremia was detected among 43% (n = 61) of the patients, and 47% (n = 67) of them had ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). The median age of the patients was 61 years, and 58% (n = 82) of the patients were male. The 30-day mortality was 51% (n = 72). Results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the patients infected with colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae.
The majority of ColR-Kp belonged to ST101 (56%, n = 80) and ST395(11%, n = 16) clones, and the others (%33, n = 46) distributed to various ST clones (minimum spanning tree in supplement). The patients infected with ST101 ColR-Kp had more VAP (n = 44.55%, p = 0.009) and had higher 30-day mortality rate (n = 46, 58% p = 0.005) than other clones. The mortality rate among ST395 type K. pneumoniae-infected patients was 75% (n = 12, p = 0.003) (Table 1). The MICs of colistin-resistant isolates were between 4 and 256 mg/L.
Among virulence factors, the presence of ferric uptake operon associated gene (kfu) and yersiniabactin (ybtS) components of iron uptake systems were found to be significantly higher in ST101 and ST395 ColR-Kp compared to the other clones. The ybtS and kfu positivity were 99% in ST101 (79/80, p ≤ 0.001) and 94% in ST395 clones (n = 15/16, p < 0.012). The mucoid type associated gene (rmpA) and fimH type adhesin were also significantly higher in ST101 with the percentage of 89% (n = 71/80, p = 0.005) and 99% (n = 79/80, p = 0.024), respectively.
The carriage of OXA-48 carbapenemase was significantly higher (n = 76/80, 95%) in ST101 than the other clones (76%), (p = 0.003). However, it was found to be significantly lower (n = 5/16, 31%) in ST395 clone than ST10, (p = 0.002). On the contrary, NDM-1 production was significantly higher in ST395 (n = 14/16, 88%, p < 0.001) and lower in ST101 (n = 3/80, 4%, p < 0.001) than the other clones (30%) (Table 2). Three ST395 strains were found to be positive for OXA-48 and NDM-1. None of the colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae isolates carried KPC-type carbapenemase.

Table 2.
The virulence factors and carbapenamase types in the colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae ST101 and ST395 clones.
In univariate analysis, being in ICU (OR: 4.3; CI: 1.42–16.04; p = 0.005), presence of ybtS (OR: 3.0; CI: 1.01–10.02; p = 0.034) and kfu (OR: 3.9; CI: 1.27–14.63; p = 0.009) were found to be associated with 30-day mortality. In multivariate analysis, being in ICU (OR: 7.9; CI: 1.43–55.98; p = 0.024), kfu (OR: 27.0; CI: 5.67–179.65; p < 0.001) and ST101 (OR: 17.2; CI: 2.45–350.40; p = 0.01) were found to be the predictors of 30-day fatality (supplement).
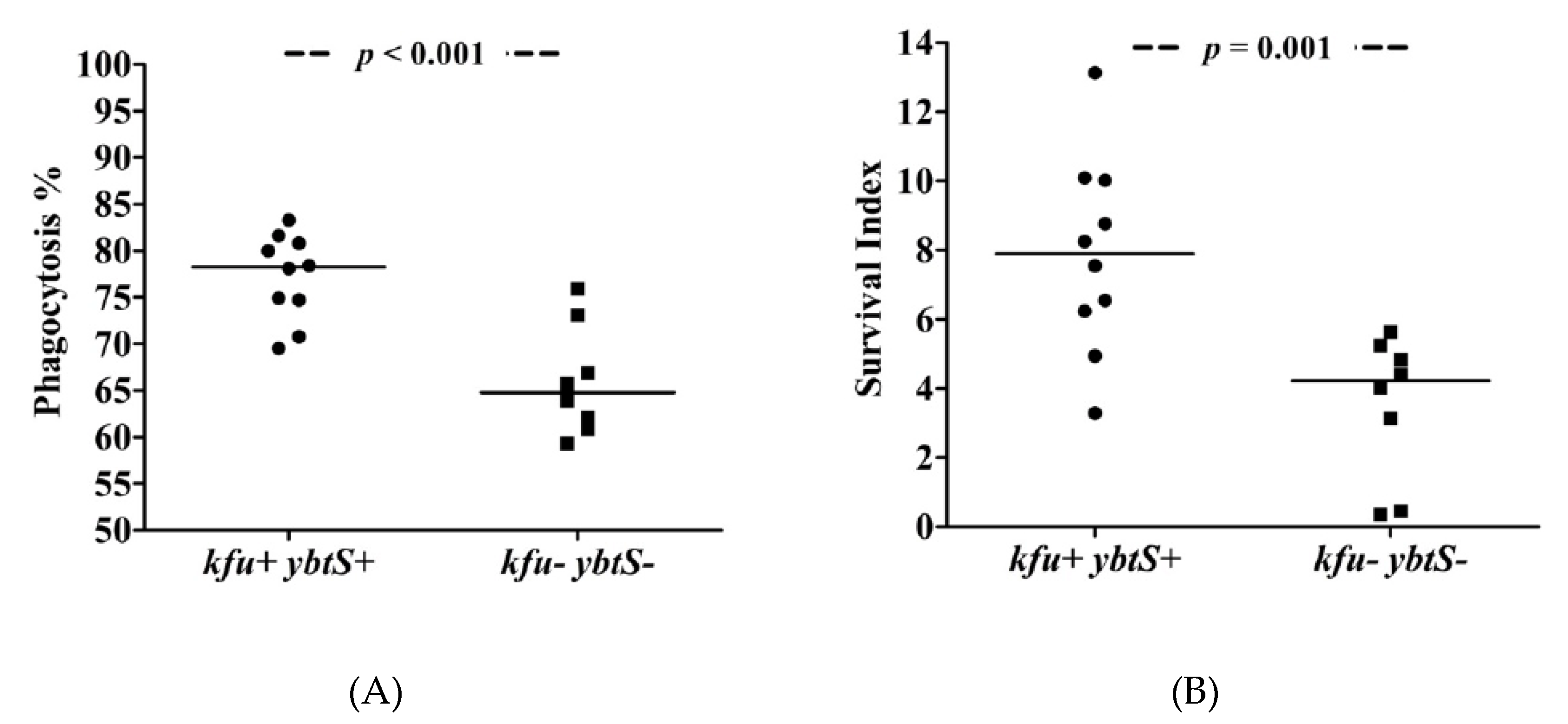
The phagocytosis experiments showed that ybtS- and kfu-positive ColR-Kp were internalized at higher rates (median = 78%), while negative isolates exhibited low phagocytosis rates (median = 65%) after 30 min of interaction with neutrophils (p < 0.001, Figure 1). The phagocytosis rates of S. epidermidis and K. pneumoniae ATCC controls were 89% and 73%, respectively. Survival of kfu+-ybtS+ positive ColR-Kp was significantly higher than negative isolates with median survival index of 7.90 (range: 3.29–13.13) vs. 4.22 (range: 0.36–5.64), respectively (p = 0.001). The survival index of S. epidermidis was detected as 0.64, and it was 1.89 for K. pneumoniae (Figure 2). The survival index of two ybtS--kfu+ isolates were 12.04 and 12.13, and it was 5.13 in one ybtS+-kfu- isolate. Among all isolates studied by phagocytosis assay, four was in ST101 clone. The median phagocytosis rate was found to be 80%, and the survival index was 8.51.
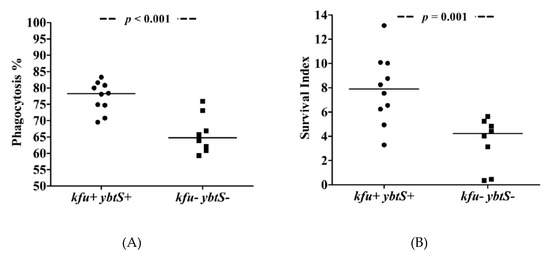
Figure 1.
The phagocytosis of ColR-Kp by neutrophils. Phagocytosis rate of kfu+-ybtS+ and kfu--ybtS- isolates (A) and survival of kfu+-ybtS+ and kfu--ybtS- isolates after being phagocytosed by neutrophils (B).
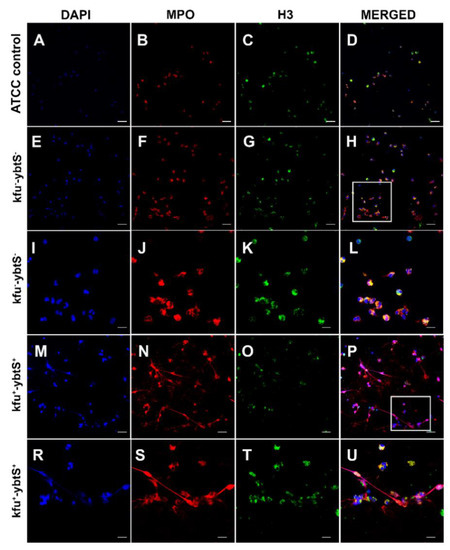
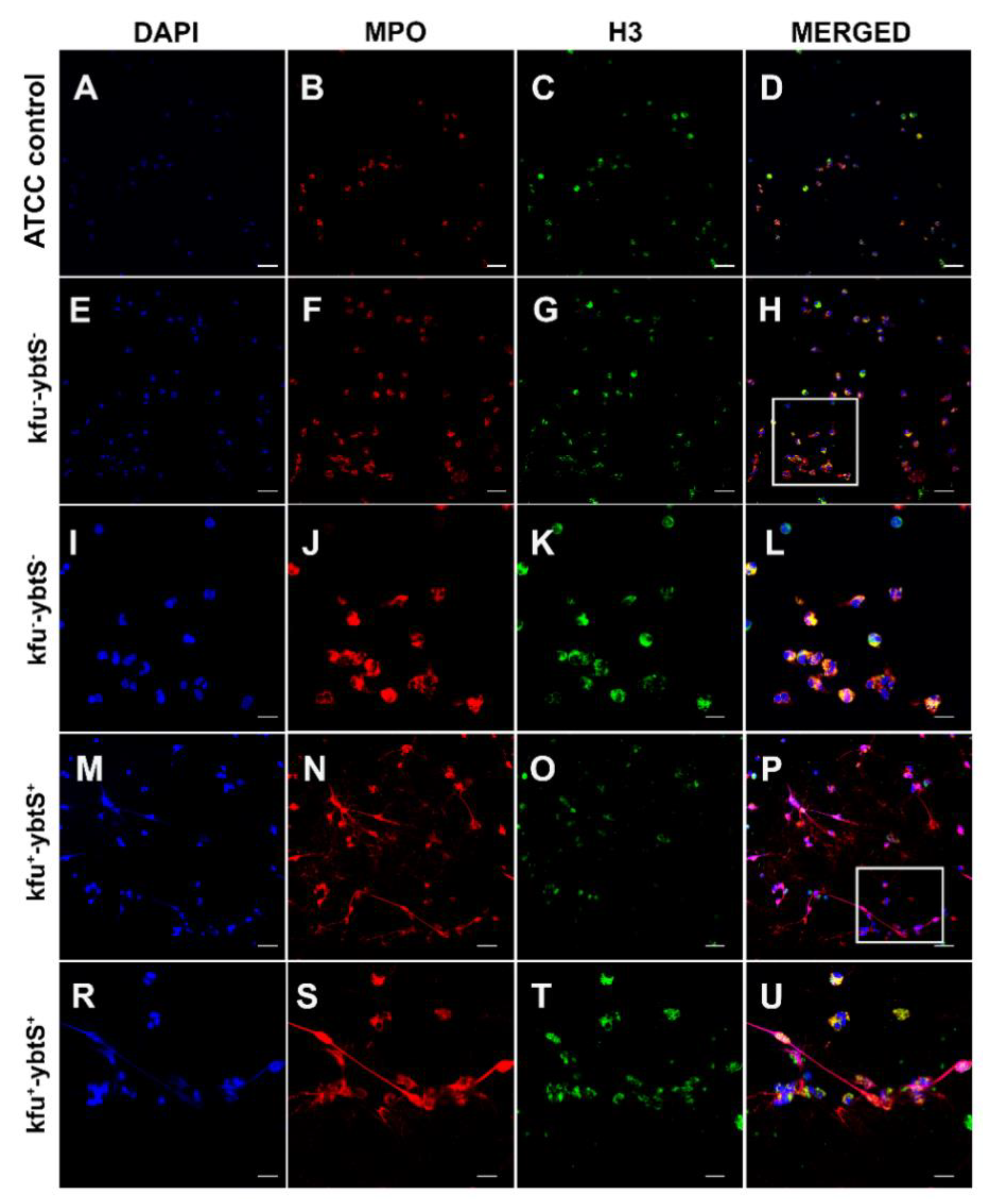
Figure 2.
Confocal microscopic images of NETs. The samples were stained consecutively with myeloperoxidase (MPO, red) and histone 3 (H3, green). The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Neutrophils were seen intact with K. pneumonia ATCC 700,831 control (A–D). The kfu- -ybtS- isolates depicted rare and weak NET formation (E–L). The rectangular area in image H was magnified in images I–L. The kfu+ -ybtS+ isolates showed abundant NET formation with excessive histone and MPO release in extracellular matrix (M–U). The rectangular area in image p was magnified in images R–U. Bars: A–H, M-p = 25 μm; I–L, R–U = 10 μm.
After NET formation, the mean colony count of two kfu+-ybtS+ isolates was 5.50 × 106, and it was 4.05 × 106 for kfu--ybtS- strains, while the colony count of ATCC K. pneumoniae was 4.3 × 106. Confocal microscopy images showed that the kfu+-ybtS+ isolate stimulated strong NET formation with excessive release of chromatin granular content to the extracellular area in each microscopic field. However, the kfu--ybtS-negative ColR-Kp caused moderate NETs seen only in a few areas. NETs were absent on the slide of control ATCC strain (Figure 2).
4. Discussion
Infections with high-risk clones of K. pneumoniae are usually fatal since therapeutic options are limited due to extensive drug resistance and successful immune escape mechanisms of these pathogens. Alternative approaches are urgently needed in order to prevent and treat infections. Likewise, one of the most promising strategies is inhibition of virulence factors of the bacterium. Here, we revealed the major virulence factors of K. pneumoniae high-risk clones ST101 and ST395 and found an enhanced neutrophil activity against the isolates carrying iron uptake system-related genes.
In this study, a significantly higher presence of iron uptake associated gene (kfu) and yersiniabactin (ybtS) positivity were observed in ST101 (99%) and ST395 (94%) isolates (p < 0.001 and p = 0.012, respectively). Holden et al. demonstrated that during pneumonia, siderophores stabilizes hypoxia inducible factor (HIF-1alpha), which controls vascular permeability and increases bacterial dissemination to the spleen [14]. Yersiniabactin and iron uptake genes were found to be associated with high mortality and dissemination of infections [22,23].
The kfu gene is also associated with higher virulence in bacterial infection murine model [24]. In our study, multivariate analysis showed that kfu predicts 30-day mortality (OR: 27; CI: 5.67–179.56; p < 0.001) and is a predictor of belonging ST101 clone (OD:20.3; CI: 2.17–484.56; p = 0.018). Lawlor et al. reported that the acquisition of yersiniabactin is an important step in the evolution of virulent K. pneumoniae [2]. Therefore, we postulated that iron uptake systems in high ST101 and ST395 risk clones of K. pneumoniae could be responsible of high mortality rates of infections caused by these clones.
Another important disease strategy of hypervirulent clones is immune evasion from the innate response [25,26]. Interaction of siderophores with host cells promotes pathogenicity of K. pneumoniae by induction of proinflammatory cytokines [23]. Proinflammatory cytokines have a protective effect against K. pneumoniae by recruitment of neutrophils to the infection site. However, studies pointed out the evasion strategy of virulent K. pneumoniae through yersiniabactin secretion [16,23,24,27,28]. One important effect of yersiniabactin is evasion from innate immune protein Lipocalin 2, which is produced by neutrophils or mucosal surfaces [24]. The other effect of yersiniabactin is the enhancement of bacterial survival in phagocytic cells by reduction in the oxidative stress response [27]. We proposed that although neutrophils could intake the kfu+-ybtS+ producing ColR-Kp, the high survival rates of bacteria were probably due to bacterial resistance to intracellular killing processes of neutrophils. Capsular polysaccharides of ST258 clone of K. pneumoniae were reported to have an inhibition on phagocytosis activity of neutrophils [16]. In this study, we did not find a difference in capsule types of high-risk clones and others.
Another significant finding of our study was NET release from neutrophils after encountering kfu+ybtS+ ColR-Kp (Figure 2). We observed the extensive spread of myeloperoxidase and histone in the extracellular space of neutrophils. The role of NETs in the infection pathogenesis is still under debate. While some pathogens are killed by NETs, others may survive or even benefit from NETs [29]. Phagocytosis is a critical event of decisions to form NETs, and if the bacterium is killed by phagocytosis, only a few azurophilic granules may leak into extracellular space with no NET formation [30]. Similarly, the kfu--ybtS- isolates of our study induced very rare NETs with a low amount of myeloperoxidase and histones in extracellular space (Figure 2). As a control of our experiment, we studied K. pneumoniae ATCC strain and we did not observe NET formation. Branzk et al. reported that virulent bacteria may circumvent phagocytosis by the formation of large aggregates and trigger NET formation [30]. The successful survival of kfu+-ybtS+ isolates (median survival index 7.9) from phagocytosis with induction of extensive formation of NETs suggested us that the protective function of iron uptake systems from being killed by neutrophils might be one of the reasons for mortality of the patients through increased inflammation.
Overall, the 30-day mortality was 51% and being in ICU was found to be significantly associated with the 30-day mortality. Bacteremia was detected among 43% of the patients and 47% of them had ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). K. pneumoniae ST101 is known as hypervirulent clone mostly responsible for pneumonia and bacteremia in intensive care units. [7,8]. This clone was also presented as dual-risk clone because of carriage of antibiotic resistance genes and several known virulence factors. In a recent study, the ST101 genetic repertoire was defined as a “perfect storm” allowing for newly emerging resistance and virulence genes [31]. In this study, ColR-Kp ST101 isolates were found to be associated with VAP infections (p = 0.009). The ST395 clone is known as a potentially high-risk clone [4], and recent studies pointed out the emergence of carbapenem-resistant ST395 in France and Italy [32,33]. KPC-2 producing ST101 K. pneumoniae was shown to have the highest number of virulence genes associated with capsule type, attachment and iron uptake compared to other epidemic clones of K. pneumoniae [11]. Similarly, we observed higher presence of virulence genes for iron uptake system, attachment and mucoid phenotype among isolates belonged to ST101 and ST395 than other clones (heatmap, supplement).
The weak part of the study is, we did not confirm the correlation of iron uptake gene positivity and neutrophil response by further genetic studies. Our data represent the results of observational analyses. Our novel findings in depiction of pathogenesis of strains that are referred as high-risk clones should be supported by the animal studies.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, iron uptake systems have a significant contribution to the pathogenesis hypervirulent K. pneumoniae ST101 and ST395 infections. These systems contribute to successful survival of K. pneumoniae against neutrophil phagocytic defense and stimulate NET formation. The drugs targeted to ferric uptake systems would be a promising approach for treatment of hypervirulent K. pneumoniae infections.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology10050436/s1, Figure S1: Heatmap analysis, Table S1: Summary Table
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.D. and F.C.; methodology, O.D., C.V., N.A., O.A., S.K., O.E.S., B.K.K., A.D., F.C.; software, M.G.; validation, F.C., O.E., and M.G.; formal analysis, M.G.; investigation, C.V., N.A., and O.D.; writing—original draft preparation, O.D., C.V., O.A., and F.C.; writing—review and editing, F.C. and O.D.; visualization, F.C.; supervision, F.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Koc University under the number 2015.048.IRB1.008E.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available at https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/677492v1.full.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2021).
Acknowledgments
M.G. was supported by the Turkish Academy of Sciences (TÜBA-GEBİP; The Young Scientist Award Program) and the Science Academy of Turkey (BAGEP; The Young Scientist Award Program). The authors gratefully acknowledge use of the services and facilities of the Koç University Research Center for Translational Medicine (KUTTAM), funded by the Presidency of Turkey, Presidency of Strategy and Budget. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Presidency of Strategy and Budget.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial Resistance of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Hypervirulence-Associated Determinants, and Resistance Mechanisms. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, M.S.; O’Connor, C.; Miller, V.L. Yersiniabactin is a virulence factor for Klebsiella pneumoniae during pulmonary infection. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tella, D.; Tamburro, M.; Guerrizio, G.; Fanelli, I.; Sammarco, M.L.; Ripabelli, G. Molecular Epidemiological Insights into Colistin-Resistant and Carbapenemases-Producing Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3783–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Kondratyeva, K.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammina, C.; Bonura, C.; Aleo, A.; Fasciana, T.; Brunelli, T.; Pesavento, G.; Degl’Innocenti, R.; Nastasi, A. Sequence type 101 (ST101) as the predominant carbapenem-non-susceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae clone in an acute general hospital in Italy. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Franco, M.; Paone, L.; Novati, R.; Giacomazzi, C.G.; Bagattini, M.; Galotto, C.; Montanera, P.G.; Triassi, M.; Zarrilli, R. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Valle d’Aosta region, Italy, shows the emergence of KPC-2 producing Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal complex 101 (ST101 and ST1789). BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, F.; Menekse, S.; Ispir, P.; Atac, N.; Albayrak, O.; Demir, T.; Karaaslan, D.C.; Karahan, S.N.; Kapmaz, M.; Kurt Azap, O.; et al. Impact of the ST101 clone on fatality among patients with colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgoulea, K.; Di Pilato, V.; Zarkotou, O.; Sennati, S.; Politi, L.; Cannatelli, A.; Themeli-Digalaki, K.; Giani, T.; Tsakris, A.; Rossolini, G.M.; et al. Characterization of Extensively Drug-Resistant or Pandrug-Resistant Sequence Type 147 and 101 OXA-48-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Causing Bloodstream Infections in Patients in an Intensive Care Unit. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Ergonul, O.; Azap, A.; Bilgin, H.; Aydin, G.; Cavus, S.A.; Demiroglu, Y.Z.; Aliskan, H.E.; Memikoglu, O.; Menekse, S.; et al. Rapid emergence of colistin resistance and its impact on fatality among healthcare-associated infections. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 98, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteo, J.; Perez-Vazquez, M.; Bautista, V.; Ortega, A.; Zamarron, P.; Saez, D.; Fernandez-Romero, S.; Lara, N.; Ramiro, R.; Aracil, B.; et al. The spread of KPC-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Spain: WGS analysis of the emerging high-risk clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11/KPC-2, ST101/KPC-2 and ST512/KPC-3. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3392–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wand, M.E.; Bock, L.J.; Sutton, J.M. Retention of virulence following colistin adaptation in Klebsiella pneumoniae is strain-dependent rather than associated with specific mutations. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouvelekis, L.S.; Miriagou, V.; Kotsakis, S.D.; Spyridopoulou, K.; Athanasiou, E.; Karagouni, E.; Tzelepi, E.; Daikos, G.L. KPC-producing, multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 258 as a typical opportunistic pathogen. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5144–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, V.I.; Breen, P.; Houle, S.; Dozois, C.M.; Bachman, M.A. Klebsiella pneumoniae Siderophores Induce Inflammation, Bacterial Dissemination, and HIF-1alpha Stabilization during Pneumonia. MBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.J.; Radic, M. Neutrophil extracellular traps: Double-edged swords of innate immunity. J. Immun. Mol. 2012, 189, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.D.; Porter, A.R.; Dorward, D.W.; Brinkworth, A.J.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; DeLeo, F.R. Phagocytosis and Killing of Carbapenem-Resistant ST258 Klebsiella pneumoniae by Human Neutrophils. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twentieth Informationtional Supplement; CLSI Document M100-S20; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2010; ISBN 1-56238-716-2. [Google Scholar]
- Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Cuvillier, V.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for detection of acquired carbapenemase genes. Diagn Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compain, F.; Babosan, A.; Brisse, S.; Genel, N.; Audo, J.; Ailloud, F.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Arlet, G.; Decre, D. Multiplex PCR for detection of seven virulence factors and K1/K2 capsular serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4377–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, J.F.; Perry, C.; Elgohari, S.; Hampton, C.V. PCR characterization and typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae using capsular type-specific, variable number tandem repeat and virulence gene targets. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.L.; Ko, W.C.; Cheng, K.C.; Lee, H.C.; Ke, D.S.; Lee, C.C.; Fung, C.P.; Chuang, Y.C. Association between rmpA and magA genes and clinical syndromes caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniel, E. The Yersinia high-pathogenicity island: An iron-uptake island. Microbes. Infect. 2001, 3, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnsen, J.; Raffatellu, M. Siderophores: More than Stealing Iron. MBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, M.A.; Oyler, J.E.; Burns, S.H.; Caza, M.; Lepine, F.; Dozois, C.M.; Weiser, J.N. Klebsiella pneumoniae Yersiniabactin Promotes Respiratory Tract Infection through Evasion of Lipocalin 2. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3309–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Simmonds, A.; Uhlemann, A.C. Clinical Implications of Genomic Adaptation and Evolution of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, S18–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, A.S.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: The next superbug? Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paauw, A.; Leverstein-van Hall, M.A.; van Kessel, K.P.; Verhoef, J.; Fluit, A.C. Yersiniabactin reduces the respiratory oxidative stress response of innate immune cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, K.S.; Hung, C.S.; Giblin, D.E.; Urushidani, S.; Austin, A.M.; Dinauer, M.C.; Henderson, J.P. Cupric yersiniabactin is a virulence-associated superoxide dismutase mimic. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegazzi, R.; Decleva, E.; Dri, P. Killing by neutrophil extracellular traps: Fact or folklore? Blood 2012, 119, 1214–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branzk, N.; Lubojemska, A.; Hardison, S.E.; Wang, Q.; Gutierrez, M.G.; Brown, G.D.; Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophils sense microbe size and selectively release neutrophil extracellular traps in response to large pathogens. Nat. Immun. Mol. 2014, 15, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, C.C.; Vazquez, A.J.; Esposito, E.P.; Zarrilli, R.; Sahl, J.W. Diversity, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance in Isolates from the Newly Emerging Klebsiella pneumoniae ST101 Lineage. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggeo, A.; Guillard, T.; Klein, F.; Reffuveille, F.; Francois, C.; Babosan, A.; Bajolet, O.; Bertrand, X.; de Champs, C.; Grp, C. Spread of Klebsiella pneumoniae ST395 non-susceptible to carbapenems and resistant to fluoroquinolones in North-Eastern France. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Res. 2018, 13, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maida, C.M.; Bonura, C.; Geraci, D.M.; Graziano, G.; Carattoli, A.; Rizzo, A.; Torregrossa, M.V.; Vecchio, D.; Giuffre, M. Outbreak of ST395 KPC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in Palermo, Italy. Infect. Cont. Hosp. Ep. 2018, 39, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).