Simple Summary
Multi-strain probiotics are composed of more than one species or strains of bacteria and sometimes, including some fungal species with benefits to human and animals’ health. The mechanisms by which multi-strain probiotics exert their effects include cell–cell communications, interactions with the host tissues, and modulation of the immune systems. Multi-strain probiotics applications include alleviation of disease conditions, inhibition of pathogens, and restoration of the gastrointestinal microbiome. Despite all these benefits, the potential of using multi-strain probiotics is still not fully explored.
Abstract
The use of probiotics for health benefits is becoming popular because of the quest for safer products with protective and therapeutic effects against diseases and infectious agents. The emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance among pathogens had prompted restrictions over the non-therapeutic use of antibiotics for prophylaxis and growth promotion, especially in animal husbandry. While single-strain probiotics are beneficial to health, multi-strain probiotics might be more helpful because of synergy and additive effects among the individual isolates. This article documents the mechanisms by which multi-strain probiotics exert their effects in managing infectious and non-infectious diseases, inhibiting antibiotic-resistant pathogens and health improvement. The administration of multi-strain probiotics was revealed to effectively alleviate bowel tract conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome, inhibition of pathogens and modulation of the immune system and gut microbiota. Finally, while most of the current research focuses on comparing the effects of multi-strain and single-strain probiotics, there is a dearth of information on the molecular mechanisms of synergy among multi-strain probiotics isolates. This forms a basis for future research in the development of multi-strain probiotics for enhanced health benefits.
1. Introduction
The Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) working committee on probiotics defined probiotics as “live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer health benefits on the host” [1]. These microbial dietary preparations could exert valuable functions on man and animals’ physiology through modulation of systemic and mucosal immunity and restore the dietary and microbial balances within the gastrointestinal system [2,3]. The use of probiotics is increasing due to consideration as a suitable option following restrictions on antibiotics as growth promoters in the livestock industries by many countries [4]. Probiotics have gained several applications such as inhibition of pathogen [5], improvement of animals health and performance, and pond quality in aquaculture [6,7]. Previous studies revealed that some probiotics might affect health indexes, microbiome structure, and inhibit pathogenic microbes’ population within the gut [8,9,10]. The strains of microorganisms used as probiotics include members of the genus Bacillus, Enterococcus, Lactobacillus, Pedicoccus, Streptococcus, Propionibacterium, Bifidobacterium, Saccharomyces, Debaryomyces, Micrococcus, and Photobacterium among others [11]. Recently, different studies are also proposing the use of some commensal clostridial species as probiotics due to their spore formation [12] and stimulation of T-cell production [13].
There are different forms of probiotics preparations, and sometimes, their efficacy depends on whether they are single- or multi-strain preparations [14]. Compared to single-strain preparations, multi-strain probiotics contain more than one strain of the same species, genera, or multiple genera and sometimes including both bacteria and fungi (Saccharomyces species) [15]. Some single-strain probiotics are beneficial in alleviating gastrointestinal-tracts-associated diseases [16]. However, previous in-vitro studies showed that some multi-strain probiotics could exhibit better inhibitory effects on entero-pathogens, [17] and enhanced benefits by combining effects of different strains compared to their single-strain preparations [18]. Additionally, some multi-strain probiotics could reduce the absorption of harmful chemicals in humans and animals [19,20] due to their ability to absorb heavy metals within their cell walls [21]. Hence, prompting their application in biotechnology, detoxification therapy, and as dietary supplements [20,22]. The increased in the use of multi-strain probiotics has revealed optimal effects compared to single-strain probiotics [23]. However, despite the availability of multi-strain probiotics, not all had shown superior benefits [17], but overall, their effectiveness compared to single-strain probiotics are preferred [23]. Some multi-strain probiotics are more consistent in their actions than single-strain probiotics [15]. Therefore, this article discussed the mechanisms of synergy among constituent strains of multi-strain probiotics and their health benefits in humans and animals. However, very little data were found on the molecular mechanisms of cell-to-cell interactions among the isolates of multi-strain probiotics. Hence, the need for more robust and in-depth studies on this aspect.
2. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics
The mechanism of probiotics’ actions is the various means by which they exert their beneficial effects on the host, including immune modulation, stimulation/modulation of gut microbiota, stimulation of digestive enzymes, displacement of pathogens, and production of bioactive compounds [24,25,26]. The gut-associated actions are the principal effects of probiotics, also regarded as the basis of other health benefits [27] as summarized in Figure 1.
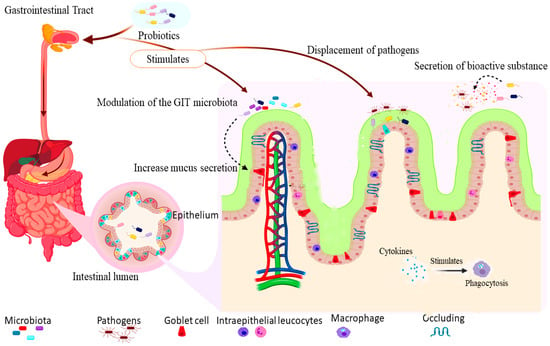
Figure 1.
(created with BioRender; https://app.biorender.com/illustrations/edit/6001622bd73fad00a4e81c08, accessed on 28 November 2020) shows the mechanism of actions of probiotics: the intake of probiotics stimulates an increase in the secretion of mucus by goblet cells, mobilization of intraepithelial leucocytes, and tightening of the tight junctions to protect against the invasion of pathogens. The increase in mucus secretion and improvement of gut microbiota enhances competitive displacement and inhibition of pathogens adhesion to the gut epithelial surface. Furthermore, the action of bioactive substances such as lysozyme and cytokines stimulate phagocytosis by macrophages.
2.1. Stimulation of Bowel Microbiota
The gastrointestinal tract (GIT) is home to an organized microbial community (microbiota) which partake in metabolic, nutritional, biochemical, and immunological processes within the body. Hence, cell-to-cell interactions exist to regulate microbial multiplication, and preserve the intestinal homeostasis, leading to a range of host responses against commensal and pathogenic organisms [28]. The microbiota is an active ecosystem which is affected by many factors such as genetics, metabolism, nutrition, geographical location, stress, and antimicrobial treatment [29]. Some probiotics stimulate the action of the bowel microbiota [30], while others like Bifidobacterium animalis alter the microbiota’s metabolic pathways to increase the metabolism of carbohydrate and nucleotide while decreasing the metabolism of lipids and amino acids [31]. Similarly, yoghurt starter cultures containing Streptococcus thermophilus MK-10 and Lactobacillus bulgaricus 151 alter the gut microbiota in rats by increasing the population and diversity of mucosal microbes including enterobacteria, enterococci, and yeast [28]. These organisms benefit the host through maintenance and modification of favorable microbial population in the gut [14,32], and also restore the gut microbiota disrupted by antibiotic treatment [33] (Figure 1).
2.2. Immune Modulation
One of the essential mechanism of probiotics’ action is immune stimulation and immunomodulation against pathogenic microbes in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) [34]. Probiotics influence the hosts’ immune system and have the ability to regulate inflammatory responses [35]. These effects were expressed in the intestine through the strengthening of the barrier protection resulting from the increased amounts of intra-epithelial leucocytes and goblet cells, and stimulation of the production of proinflammatory (tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and ILβ) and regulatory cytokines (TGFb, IL-10) for responses against pathogens, and the sustenance of mucosal integrity [36,37]. Multi-strain probiotics (containing Lactococcus lactis subspecies lactis CB460, L. lactis subspecies cremoris CB461, Streptococcus thermopilus, and Propionibacterium freudenreichii CB129) stimulates the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines; interleukin 10 and 12 (IL-10 and IL-12) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in-vitro [34]. Similarly, Pediococcus acidilactici and Saccharomyces cerevisiae subsp. boulardii mixture stimulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, and TNFα) in the ileum of pigs experimentally infected with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) F4 [38]. The lysozyme is an essential component of the innate immune system available in high quantity in the cytoplasmic granules of macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils [39]. Neveling, et al. [40] reported an increase in the serum concentration of lysozyme which stimulates the activity of macrophages for phagocytosis by the administration of a multi-strain probiotic (containing Lactobacillus crispatus, Lactobacillus salivarius, Lactobacillus gallinarum, Lactobacillus johnsonii, Enterococcus faecalis and Bifidobacterium amyloliquefaciens) in chickens (Figure 1). The synthesis of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) by natural killer cells and Th1-lymphocytes stimulates production of oxidants with antimicrobial properties, also known to be upregulated by Salmonellae infections due to inflammatory responses [41]. However, the administration of a multi-strain probiotic (containing Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus fermentum, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Enterococcus faecium) downregulates IFN-γ in chickens infected with Salmonella enterica [42]. Additional means by which probiotics modulate the immune system is through stimulation of mucus production and tightening of the intestinal tight junctions. Some strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium increase the expression of mucin on human intestinal cell lines and upregulate the tight junction protein (zona-occludens 1) which blocks pathogens from penetrating the lamina propria [27] (Figure 1).
2.3. Stimulation of the Digestive Enzymes
Some probiotics aid in the breakdown of complex macronutrients and provide the host with digestive enzymes and vitamins which enhance the absorption of nutrients [43,44]. Oak and Jha [27] showed the ability of some probiotics to lower lactose concentration in fermented food and increase the influx of lactase enzyme into the small intestine along with fermented food. The ability of probiotics to promote lactose fermentation has made them useful in treating lactose intolerance in humans [45]. Probiotics Bifidobacterium strains, such as B. longum and B. animalis, participate in the metabolism of oligosaccharides by secreting glycosyl hydrolases and stimulating beta-galactosidase activities [46]. Similarly, Lactobacillus species’ probiotic strains also exhibit high beta-galactosidase activities and increase insulin secretion, while S. boulardii expresses high disaccharidases alpha-glucosidases, alkaline phosphatases, and aminopeptidases activities [27].
Furthermore, feed supplementation with multi-strain probiotics (containing Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis and Lactobacillus strains) revealed increased lipase activities and amylase enzymes within the gastrointestinal tract of shrimps [30]. Similarly, feeding of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) with probiotics strains of B. subtilis, L. rhamnosus, and S. cerevisiae mixture also enhances amylase, lipase, and protease activities in the intestines [47]. The increase in digestive enzymes’ actions associated with some probiotics’ ingestion ultimately results in improved nutrients absorption, optimum feed utilization and growth performance [48]. In addition to the secretion of enzymes in the digestive tract, multi-strain probiotics containing B. subtilis, E. faecium, L. reuteri, and P. acidilactici, also enhances the intestinal surface area by increasing micro-villi density and heights, and immune integrity in tilapia fish [49]. The increase in villi heights was observed in heat-stressed broilers when fed with probiotics (containing strains of B. subtilis) [50]. Some probiotics were also found to stimulate the production of proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes helpful in the digestion of proteins and lipids, respectively [51].
2.4. Displacement of Possible Pathogens
One of the protective mechanisms of probiotics’ action is the competitive displacement of pathogens for adhesion and colonization of the mucosal surfaces [52] (Figure 1). Attachment to the intestinal mucosa is an essential factor associated with probiotics when there is intestinal inflammation [53]. Some probiotics microbes also share binding sites with some entero-pathogens and could hinder their attachment to the host’s cells by binding to the respective attachment sites [54]. Hence, justifying the rationale for using probiotics to protect against infections at early stages [52]. The adhesion of probiotics to the intestinal surface is necessary for the competitive displacement of pathogens and the modulation of immunological activities [55] (Figure 1). Additionally, the attachment of probiotics bacteria to the host’s mucosal surfaces increases the chance of host–probiotics interactions thereby resulting in temporary colonization and prolonging transit time within the intestine to cause their intended benefits [54].
2.5. Secretion of Bioactive Substances
The bioactive substances produced by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) include hydrogen peroxide, lactic acid, diacetyl, acetaldehyde, reuterin, and antimicrobial peptides [56] (Figure 1). For example, B. subtilis and B. licheniformis produce varieties of bioactive proteins, such as antibacterial peptides, chitinases, and dextranases which inhibits other pathogenic bacteria [57]. Antibacterial proteins were also isolated from LAB, among which bacteriocins constitute an essential group [58]. The bacteriocins are low-molecular-weight genetically encoded proteins synthesized in the ribosome and secreted outside the cell by some bacterial species [59]. These active peptides act by binding to surface receptors or invade host cells. Bacteriocins also act by pore formation on the target cells, cause cellular DNA degradation and inhibit the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan component of the bacterial cell wall [60]. The production of bacteriocin by LAB makes them inhibit pathogenic and food spoilage microbes, hence their potential for use as bio-preservatives [61]. Earlier research has revealed the presence of bacteriocin producing LAB strains from milk and cheese [62]. At a regulated pH (5.5), some produce gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) [63]; a neurotransmitter with antihypertensive activities [64]. Some probiotics can also stimulate the production of enzymes that hydrolyze bacterial toxins and modify toxin receptors in the host [65]. Different lactic acid bacteria species yield various bioactive substances that inhibit the proliferation of pathogenic microbes (Figure 1).
2.6. Mechanisms of Action of Multi-Strain Probiotics
Some multi-strain probiotics showed enhanced benefits due to the constituent strains’ synergy and additive effects resulting in high adhesion to the mucosae and pathogen inhibition within the digestive tract [66]. The genetics of the constituent species or strains of multi-microbial probiotics is vital for understanding the mechanisms by which they interact with each other, the intestinal microbiota, and the host. A comparative genomic analysis of the multi-strain probiotics VSL#3 by Douillard, et al. [67] revealed numerous genes that encode various bioactive substances associated with the probiotics’ health benefits. These include genes involved in lactose transport (lacF), peptidase activity, carbohydrate, metal, and amino acid transport. Some bacteria are endowed with extra-cellular structures known as fimbriae or pili that can adhere to the intestinal epithelium [68,69]. Two main types of pili are found in LAB and Bifidobacteria; the tight adherence pili (Tad pili) and the sortase-dependent pili where genes were found in some isolates of VSL#3 probiotics [67]. The Tad pilus gene clusters of B. breve (one of the VSL#3) strains are highly conserved and involved in gut colonization in mice [69]. All the isolates in VSL#3 also encoded cell-surface proteins carrying LPXTG motifs that enhance interactions with the host cells [67]. Several genes that encode fibronectin-binding region proteins, collagen adhesins, outer membrane proteins, fimbriae or pili were also identified in L. helveticus BD08, L. plantarum BP06, L. acidophilus BA05 and B. animalis subsp. lactis BL03 and BI04 with possible roles in host adherence [70]. Lactobacillus plantarum BP06 was shown to harbor the sortase-substrate, which were also present in L. plantarum WCFS1 in addition to a large mucus-binding protein that is O-glycosylated by N-acetyl-hexosamine [71]. These peptides are secreted in a glycosylated form and may have a host signaling function [72]. The presence of the genes encoding Tad pili, sortase-dependent pili, mucus binding proteins, some even glycosylated, and S-layer proteins involved in the interactions of probiotic isolates with one another, the host cells and the host’s microbiota showed that the combination of different species and strains might offer possible complementary, additive and synergistic effects in the gut [67]. Experimental assessment of the effects of single-strain probiotics of L. helveticus R0052, B. longum subsp. infantis R0033, and B. bifidum R0071 and the multi-strain preparation of all the three isolates revealed that the multi-strain synergistically influenced both T-helper type 1 (TH1) and T-helper type 2 (TH2) responses in Wistar rat models infected with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) and Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, respectively [73]. The mechanism by which the multi-strain probiotics exerts their effects was proposed to be through the downregulation of the nuclear factor-kappa-B (NFκB) pathway [74].
The other mechanism by which bacteria communicate and regulate several genes’ expression is through a cell–cell communication known as quorum sensing (QS). Quorum sensing is based on the production, secretion, and detection of small signaling molecules, whose concentration correlates with the organisms’ cell density secreting these molecules in the surrounding [75]. An example of QS signaling molecules in bacteria is linked to autoinducer-2 (AI-2) which is synthesized through LuxS enzyme action [76]. Notably, Gram-positive bacteria use autoinducing peptides (AIP or peptide pheromones) that act as species-specific communication signals [75]. The AIP gene regularly borders a two-component regulatory system (QSTCS) gene cassette [77] which comprises the membrane located histidine protein kinase (HPK) that monitors environmental factors, and the cytoplasmic response regulator (RR) that modulates some specific genes expressions [77]. L. plantarum WCFS1 genome contains relatively high amount of peptide-based QS-TCS and other putative QS genes [78]. In the past, it was shown that interactions with other lactobacilli influenced the metabolic traits of L. sanfranciscensis and L. plantarum strains through LuxS-mediated mechanisms of QS [79].
2.7. Antagonisms among Multi-Strain Probiotics
Some probiotics and lactic acid bacterial strains produce antimicrobial substances ranging from organic acids to bacteriocins. Bacteriocins may be active against closely related strains, thereby suggesting the likelihood of antagonistic activities among closely related species or strains such as the lactic acid bacteria [66]. Previous studies have shown that the activation of some specific component regulatory systems such as plantaricin system regulated through the QS pathway by competing microorganisms could trigger microbial antagonism [80,81]. The growth of L. sanfranciscensis DPPMA174 and P. pentosaceus 2XA3 were shown to be inhibited when co-cultured with L. plantarum DC400 with an increased number of dead/damaged cells compared to their respective monocultures [80]. That was due to the biosynthesis of pheromone PlnA by L. plantarum DC400 either in a monoculture or co-culture conditions. The level of PlnA synthesis by L. plantarum DC400 is dependent on the co-cultivation microbe [82]. Hence, suggesting that co-culturing with L. plantarum DC400 might constitute stress to L. sanfranciscensis DPPMA174 and P. pentosaceus 2XA3. Another study by Di Cagno, et al. [75] showed that coculturing of L. sanfranciscensis CB1 and L. brevis CR13 or, L. plantarum DC400 constituted stress and inhibited L. sanfranciscensis CB1 with an increase in the number of dead/damaged cells and a decrease in the cultivable cell. This could have been due to several not easily definable conditions such as acid production, synthesis of antimicrobial compounds, ability to thrive in the medium, and competition for available nutrients.
3. Applications and Biological Functions of Multi-Strain Probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms with an expanded range of healthful activities, not just on the digestive tract but also on other body systems, including the urogenital and nervous systems [83]. There is increasing evidence in the biological applications of probiotics for the maintenance and improvement of gut health [34], inhibition of microbial pathogens and biofilms [84], improvement of human health through ingestion of fermented food products [85], and enhancement of growth and productivity in animals [86]. These and many other beneficial effects of probiotics made it necessary to review the different multi-strain probiotics applications, such as treating non-infectious diseases, inhibiting pathogens, and improving human and animal health.
3.1. Treatment of Diseases
Different randomized control clinical trials revealed that some specific probiotics are useful in the therapeutic management of gastrointestinal (GI) illnesses like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [34], irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and pouchitis [87,88]. The administration of multi-strain probiotics containing different Lactobacilli species, Streptococcus and Bifidobacterium to patients who have systemic sclerosis alleviates the symptoms of gastrointestinal reflux and increased microbial alpha diversity group [88] (Table 1). Frech, et al. [89], suggested the intake of multi-strain probiotics in the amelioration of systemic sclerosis due to the association of the GI microbiome imbalance with the pathogenesis of the disease. Evaluating the functions of multi-strain probiotics containing a mixture of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, and Streptococcus probiotics strains significantly alleviate the indicators of IBS including abdominal ache/distress and bloating and improved the compositions of intestinal microbiota in the treated patients [90]. Yoon, et al. [90] further proposed that these benefits were due to synergy between the different strains in the probiotic preparation since the action of probiotics is strain- and disease-specific.

Table 1.
The use of multi-strain probiotics in disease treatment.
Similarly, a multi-strain probiotic containing S. boulardii, B. lactis, L. acidophilus, and L. plantarum alleviated the signs of constipation, diarrhea, and modulates the microbial community in the small intestine of IBS patients [91]. The evidence of the existing relationship between alteration in the intestinal microbiome and cognitive behavioral changes is also increasing the application of probiotics [92]. In line with this, multi-strains probiotics consisting of L. acidophilus, L. casei, B. bifidum, and L. fermentum improve cognitive behavior in patients with Alzheimer’s disease [93]. Some multi-strain probiotics could significantly lower the level of circulating bacterial endotoxin in type-II diabetes mellitus patients [94]. Ingestion of multi-strain probiotics by pregnant women and their infants decreases food allergens’ sensitivity and the incidence of atopic eczema [95]. Consumption of yoghurt starter culture of L. bulgaricus 151 and S. thermophilus MK-10 mixture also relieves the symptoms of colitis in rats by increasing the colon length and the amount of mucosa-associated microbiota [28]. A decrease in the level of putrefactive short-chain fatty acid in the cecum contents of dextran sodium-sulphate salt-induced colitis in BALB/c rats was previously reported by Wasilewska, et al. [28]. A similar study also revealed the improvement of the same condition by a probiotic Dahi (made up of L. acidophilus LaVK2 and B. bifidum Bbvk3 mixture) through a reduction in myeloperoxidase action and level of TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ in mice [96]. These studies showed the applications of multi-strain probiotics in alleviating inflammatory responses within the digestive tract, which might be useful in the treatment of different conditions, as shown in Table 1.
3.2. Inhibition of Pathogens
Recently, there is a rising concern over the high prevalence and spread of antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) pathogens worldwide. This global challenge is multifactorial and linked to selective pressure due to the frequent, prolonged, and irrational use of antibiotics in humans and animals [97]. The prolonged antimicrobial intake depletes the gut microbial populations thereby allowing the proliferation of pathogenic AMR pathogens like toxigenic Clostridium difficile, extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing Enterobacteria, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus species and other multi-drug resistant bacteria [98]. Patients on prolonged treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics are at high risk of antibiotics-associated diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis caused by antibiotic-resistant C. difficile and other pathogenic bacteria [99,100]. Some probiotics’ ability to modulate the intestinal microbiome is one of the mechanisms by which they prevent antibiotics-associated diarrhea and decrease the spread of AMR bacteria [101]. Lakhtin, et al. [102] reported that multi-strain probiotics consisting of L. acidophilus (strains NK1, K3III24, 100 ash), Bifidobacterium adolescentis MC 42, B. bifidum, and B. gallinarum GB synergistically produced lectins with antimicrobial activity against clinical strains of nystatin-resistant Candida albicans, S. aureus, and their biofilms. Experimental administration of probiotics to mice showed the inhibition of C. difficile by a multi-strain probiotic containing four strains of E. faecalis [103] (Table 1). Very similar work by Kondepudi, et al. [99] also showed the inhibition of C. difficile by the administration of multi-strain probiotics containing L. plantarum F44, L. paracasei F8, B. breve 46, and B. lactis to mice experimentally infected with C. difficile. The minimal side effects associated with the intake of probiotics for treatment coupled with the high incidence of reoccurrence of infections such as UTI [104] is also increasing the use of probiotics as a suitable alternative or adjunct therapeutic plan to conventional antimicrobials [33]. Probiotics do not leave residues or facilitate the development of resistance to antibiotics because they are preparations of live organisms [105].
Certain probiotics can modify or alter pathogenic microbial colonization in humans and animals [108]. Different multi-strain probiotics preparations significantly inhibit pathogenic bacteria such as Vibrio cholerae (in-vitro) [2], S. aureus, S. epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, Propionibacterium acnes, Moraxella catarrhalis [109], and Proteus mirabilis [84]. Similarly, cell-free supernatants of Lactobacilli inhibit non-Albicans Candida species biofilm formation and suggest its use for adjunctive treatment of oral candida infection [110]. These authors further suggested that some of these probiotic bacteria’s anti-biofilm activities are due to subtilisin and subtilin production, which are active antimicrobial molecules. Multi-strain probiotics containing a culture of L. rhamnosus and L. reuteri modify the vaginal microbial flora to decrease the vaginal coliforms and yeast in patients with bacterial vaginosis [104]. However, oral administration of multi-strain probiotics comprising L. rhamnosus GR-1 and L. reuteri RC-14 showed inactivity on the microbiome of the lower urinary system, rather an increase in the population of urinary pathogens was observed [108], thus, emphasizing the administration route as an essential factor for consideration to achieving the desired benefits.
A multi-strain probiotic containing different Lactobacillus strains hinders the adhesion of E. coli and E. faecalis to the bladder cell-lines, unlike the single-probiotics preparations [33] (Table 2). Likewise, the addition of feed-supplement fermented with a mixed culture of S. cerevisiae, E. faecium, L. acidophilus, and B. subtilis resulted in significant increase in serum immunoglobulin-M (IgM) level and inhibit the multiplication of E. coli in broilers [111]. Prophylactic and therapeutic administration of multi-strain probiotics of L. acidophilus (LA-5) and B. animalis subsp. Lactis (Bb12) mixture proved useful in preventing scar formation in the kidney of E. coli-induced pyelonephritis in a rat model [112]. Pre-treatment of chicks with certain multi-strain probiotics before exposure to pathogenic S. Enteritidis A9 inhibits the pathogens from colonizing the birds [40] (Table 2). Similarly, the administration of multi-strain probiotics and a recombinant attenuated Salmonella vaccine confers protection against avian pathogenic E. coli and Salmonella Kentucky in White Leghorn chicks [113]. The in-vitro study of a multi-strain probiotic containing L. plantarum (strain L21 and strain L80) and L. paraplantarum (strain L103) revealed the inhibition of E. coli, Salmonella groups B and D in a co-culture tested using agar-spot assay [114]. Multi-strain probiotics mixture of L. casei and E. faecium also showed significant inhibition of Entamoeba invadens (the causative agent of traveler’s diarrhea in humans) [115].

Table 2.
Multi-strains probiotics against pathogenic microbes.
3.3. Improvement of Human Health
The health effects of probiotics are necessitating its commercial development due to their worldwide consumption [85]. The benefits accrued to ingestion of fermented milk containing probiotic bacteria include decreased total cholesterol, enhanced immunity by facilitating resistance to infection and bacterial inhibition and preventing oxidative stress during exhaustive bodily activities [119]. Ingestion of probiotics is known to improve gut health in humans and animals [120]. In humans, probiotics have beneficial effects on the nervous [93], gastrointestinal [121], and immune systems [122]. Some probiotics alleviate various gastrointestinal ailments like irritable bowel disease (IBD) and systemic sclerosis in humans [89]. Multi-strain probiotics had proved beneficial for the treatment of dysentery in addition to the standard regimen with a marked reduction in the extent of bloody stooling, and a decreased average length of hospital stay [123]. These effects were a result of the alteration of the microbial and metabolic activities within the gut, and which are enough to modify the disease process and pathological conditions [124].
3.4. Multi-Strains Probiotics in Animal Husbandry
The increase in the demand for animal proteins due to the global population’s rise is overstretching the livestock industry, leading to the use of antibiotics as growth promoters and prophylaxis against infectious agents [125]. However, this strategy is not sustainable because of the growing concerns about antibiotic resistance among microbial pathogens [126]. Hence, resulting in restrictions on the non-therapeutic administration of antibiotics to animals [125] in different regions of the world. Therefore, probiotics may be a potential alternative for improving gastrointestinal health and growth promotion in different animal species [86]. Based on these, the roles of probiotics in the various livestock sub-sectors, including poultry, aquaculture, piggery, and ruminant nutrition were discussed as follows.
3.5. Poultry Farming
In poultry, the addition of probiotics derived from Lactobacillus, Bacillus [127], and Clostridium species to feed has a positive impact on the growth yield, feed digestion [128], immunity [129], meat quality [130], and coliforms bacterial count [86,131]. The administration of multi-strain probiotics (comprising of L. acidophilus LAP5, L. fermentum P2, P. acidophilus LS, and L. casei L21) to specific-pathogen-free (SPF) chicks infected with Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica decreases the abundance of proteobacteria of which Salmonella is a member [9]. Likewise, multi-strain probiotics containing L. acidophilus, B. subtilis DSM 17299, and Clostridium butyricum increases the serum level of IgA and IgM with a decline in the count of E. coli in the feces of broiler chickens [86]. Furthermore, supplementing poultry feed with multi-strain probiotics was reported to result in a rise in villus length and the number of goblet cells in the jejunum, and villus height to crypt ratio in the ileum of chickens [132]. Feeding of chickens with citrus-Junos by-product fermented with multi-strain probiotics (containing S. cerevisiae, E. faecium, L. acidophilus and B. subtilis) also increases the weight gain and mean daily feed consumption [111]. Multi-strain probiotics of B. subtilis (B. subtilis 1781 plus B. subtilis 747 or B. subtilis 1104 plus B. subtilis 747) boost the bowel immunity and strengthen the veracity of the gut barrier by stiffening the gut tight junctions in chickens [133]. In laying chickens, administration of multi-strain probiotics reduces feed conversion ratio and percentage of damaged eggs [134]. These studies are advocating probiotics to chickens feed to promote growth performance and health through enhancement of digestive function and regulation of intestinal microbiome [129,135]. However, several works have also reported a little or no improvement in the total increase of weight in chickens administered with probiotic (including multi-strain) supplemented feed [136]. These differences could be a result of variations in the strains or species used in the formulation of the probiotics, preparation techniques, the dosage administered, age of the birds and general level of sanitation [86,128].
3.6. Aquaculture
The use of probiotics for health improvement has also found application in aquaculture. The addition of multi-strain probiotics in the feed of rohu (Labeo rohita) was revealed to stimulate cellulolytic and amylolytic enzymes secretions with improved the growth output [137]. The multi-strain culture of B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, and lactobacilli probiotics significantly improves pacific white shrimps’ growth (Litopenaeus vannamei) and enhances non-specific immunity and the abundance of Bacillus to influence the intestinal microbiota [30]. Similarly, a cocktail of Lactobacillus pentosus BD6, L. fermentum LW2, B. subtilis E20, and S. cerevisiae P13 probiotics enhanced the health and growth output of white shrimp (L. vannamei) compared to single-strain probiotics [6]. These works positioned that the improved growth noted from the administration of the multi-strain probiotic is due to a synergy or additive effects observed by the individual strains in the preparation resulting in enhanced enzyme activity during digestion and better feed conversion [138]. Multi-strain probiotics (containing B. subtilis, E. faecium, L. reuteri, and P. acidilactici) also results in improved growth yield, and bowel immunity through the elevation of proinflammatory cytokines (TNFα and ILβ) in the intestines of tilapia fish [139]. Unlike the previously cited works, multi-strain probiotics decrease the growth rate in mud-crabs when fed with B. subtilis E20 and L. plantarum 7–40 combination supplemented feed due to antagonism [140]. These studies’ findings imply a careful selection of strains for inclusion in multi-strain preparations [6].
3.7. Swine Production/Piggery
The weaning period in piggery coupled with diets changes from simply digestible (milk) to solid feeds may result in intestinal perturbation, thereby causing diarrhea and slow growth rate [141,142,143]. The stress of post-weaning alongside the alteration in the gut microbiota results in post-weaning diarrhea; a severe health challenge characterized by diarrhea, death in severe cases, and substantial monetary implications in piggery [38]. Post-weaning diarrhea may result from the rapid multiplication of enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) and primarily affects piglets two weeks after weaning [144]. The treatment of this economic disease is by using antibiotics; however, the current surge of AMR bacteria had necessitated the demand for farmers to look for an alternative treatment to prevent and control diseases in their livestock [38]. Probiotics may serve as viable options to antibiotics in piggery, especially for non-therapeutic usage and growth enhancement [145]. The ingestion of probiotic bacteria (like P. acidilactici) and yeast (S. cerevisiae boulardii) protect from microbial infection by enhancing intestinal defenses and performance in different monogastric animals [146]. In line with this, piglets fed with multi-strain probiotics consisting of L. reuteri (strains VB4 and ZJ625), Streptococcus salivarius NBCR 13956, and L. salivarius ZJ614 have better mean regular weight increase and feed utilization, unlike the single-strain and control groups [141].
Furthermore, the administration of some certain multi-strain probiotics to pigs results in weight gain [125] and inhibits the attachment of Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) F4 to ileal mucosa of piglets [38]. This finding was supported by the discoveries of the modulatory effects of P. acidilactici and S. cerevisiae boulardii either as mixed or single preparations on establishing microbial population such as members of the family Bifidobacteriaceae and Lactobacillaceae in the porcine bowel [147]. These are therefore advised for a careful screening and inclusion of probiotics microbes with proven properties to play vital roles in the improvement of growths of piglets, primarily through the post-weaning period. Similarly, multi-strain probiotics stimulate a rise in the level of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β) and antibodies in the colostrum of sows when administered during pregnancy and lactation, hence offering protection to both the dam and neonates through stimulation of cellular immunity [148].
3.8. Ruminants Nutrition and Production
Some probiotics are suitable supplements in livestock feeds and may improve the rumen’s microbial ecosystem, enhance feed digestion, and restores gut microflora in diarrhea in ruminants [149]. The administration of lactobacilli probiotics enhances calves’ overall health status [150]. Consequently, a probiotic mix (containing E. faecium, B. bifidum, P. acidilactici, L. acidophilus, L. casei, peptide extract, an enzyme blend and killed yeast extract) significantly shortens the duration of diarrhea in dairy calves at the onset of diarrhea [151]. Additionally, several studies reported using probiotics to control diarrhea, improve average daily weight gain, and feed efficiency in calves [151,152,153]. The administration of multi-strain probiotics (made up of Lactobacillus sakei FUA3089 and P. acidilactici FUA3138 and FUA3140) modulates specific serum metabolites, milk components, and increased milk production in dairy cows [154]. Similarly, feeding of dairy cows with pasture from paddocks treated with multi-strain probiotics (containing L. parafarraginis, L. buchneri, L. rapi, L. zeae, Acetobacter fabarum and Candida ethanolica) showed a higher volume of milk and protein content in the treatment group compared to the control group [155].
3.9. Synbiosis of Multi-Strain Probiotics with Other Biologically Active Molecules
Some probiotics are prepared as synbiotics (prebiotics) along with other active substances for maximum physiological effects. Ingestion of synbiotics made of multi-strain probiotics (containing L. acidophilus strain T16, L. casei strain T2 and B. bifidum strain T1) and 800 mg inulin (HPX) by gravid women with gestational diabetes mellitus decrease the rate of caesarean section and hyperbilirubinemia and hospitalization of newborns [156]. Administration of synbiotics (containing multi-strain probiotics and prebiotics) may alleviate some digestive system conditions, sepsis, and death in preterm babies [157] (Table 3). Treatment of vaginal candidiasis in patients is enhanced by administering azoles alongside multi-strain probiotics comprising L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, S. thermophilus, and L. delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus [158] (Table 3). This study further reiterates the potentials of multi-strain probiotics combination for treatment and deterrence of recurrence of vaginal candidiasis, especially in cases of azole-resistant mycosis. In poultry, co-administration of a specific multi-strain probiotic mixture and zinc to broiler increases the final body weight, feed efficiency, total goblet cells, and ileal villus height unlike in the control group [159]. Similarly, short-term administration of multi-strain probiotic-synbiotics to laying chickens infected with Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) positively modulated the caecal microbiota but had no marked effect on shedding of S. typhimurium [65] (Table 3).

Table 3.
Use of multi-strain probiotics along with other substances.
4. Conclusion and Future Consideration
Several studies suggest using multi-strains probiotics to prevent and treat different kinds of conditions from non-infectious to infectious diseases. Most of these studies emphasized probiotics in diets and have shown several derived benefits from such administrations. The potential of individual probiotic organisms to act in synergy or additively when in a mixture, holds a grand promise for future use in treating various diseases. Based on this review, probiotic organisms could secrete various substances that can inhibit the multiplication of pathogenic microbes, which is vital for future considerations because of the safety in its consumption and the associated health benefits. The current global challenges associated with the rise and spread of antimicrobial resistance by several pathogens had provoked the need for suitable alternatives to the current antibiotics, thus, indicating the need for further development of probiotics because of its potential in producing several bioactive compounds like lectins, bacteriocins, bioactive proteins, and antibacterial peptides that are inhibitory to pathogenic antibiotic-resistant bacteria and some fungi. The production of these essential bioactive peptides could be harnessed for further development into bio-additives to be used instead of the whole-cell probiotics formulations. In animals, feed supplementation with probiotics has proven helpful by improving growth performance and weight gain, meat quality, and humoral immunity and decreasing pathogenic microbes’ shedding. The use of probiotics could gradually outshine the prophylactic applications of antimicrobial drugs for growth enhancement in animals, thereby decreasing the spread of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens. Furthermore, this review had also shown that probiotics could be used in combination with prebiotics as symbiotics to give maximum benefits for better physiological effects. Therapeutic use of probiotics in a mixture with other compounds such as zinc and some antimycotic agents could exert more effects compared to the usage of those substances alone.
Finally, to maximize all the benefits associated with probiotics consumption, research should determine the specific mechanisms of actions of probiotics microbes for more specific applications in respective disease conditions. There is also the need to study and understand each probiotics strain’s best combination because some bacteria act synergistically, some additively, and some antagonistically. Additionally, the bioactive substances produced by some probiotics could be extracted to formulate supplements for use in specific conditions where individuals showed some reactions to the consumption of the whole-cells preparations. The harvesting and harnessing of the bioactive substances produced by individual constituents of mixed probiotics could also solve the challenges associated with the inconsistency of viable cells when live microbes are used. That will also enable large-scale production for commercialization. Finally, further studies in this direction could be an essential factor in the future research and development of multi-strain probiotics.
Author Contributions
M.A.A., O.A.A., M.O. and I.D.K. designed and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the South Africa Agricultural research Council- Animal Production Parliamentary Grant (Cost center: P02000032) and the article processing charges (APC) was paid by the College of Agriculture, Engineering and Sciences, University of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors duly acknowledged the College of Agriculture, Engineering and Sciences, the University of KwaZulu-Natal for granting I.D.K full tuition fees remission. The authors also acknowledge Biorender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VidyaLaxme, B.; Rovetto, A.; Grau, R.; Agrawal, R. Synergistic effects of probiotic Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Bacillus subtilis in malted ragi (Eleucine corocana) food for antagonistic activity against V. cholerae and other beneficial properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 3072–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bravo, J.A.; Julio-Pieper, M.; Forsythe, P.; Kunze, W.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Communication between gastrointestinal bacteria and the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagawany, M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Farag, M.R.; Sachan, S.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K. The use of probiotics as eco-friendly alternatives for antibiotics in poultry nutrition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10611–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.-F.; Chiu, C.-H.; Shiu, Y.-L.; Cheng, W.; Liu, C.-H. Effects of the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis E20, on the survival, development, stress tolerance, and immune status of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei larvae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 28, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Hu, S.-Y.; Chiu, C.-S.; Liu, C.-H. Multiple-strain probiotics appear to be more effective in improving the growth performance and health status of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, than single probiotic strains. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Durand, H. Probiotics in animal nutrition and health. Benef. Microbes 2010, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abudabos, A.; Al-Batshan, H.; Murshed, M. Effects of prebiotics and probiotics on the performance and bacterial colonization of broiler chickens. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 45, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Teng, P.Y.; Lee, T.T.; Yu, B. The effects of the supplementation of multi-strain probiotics on intestinal microbiota, metabolites and inflammation of young SPF chickens challenged with Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Behare, P.V.; Jain, S.; Yadav, H. Probiotics, their health benefits and applications for developing healthier foods: A review. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 334, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babot, J.; Argañaraz-Martínez, E.; Saavedra, L.; Apella, M.; Chaia, A.P. Compatibility and safety of five lectin-binding putative probiotic strains for the development of a multi-strain protective culture for poultry. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartman, S.T. Time to consider Clostridium probiotics? Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 969–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narushima, S.; Sugiura, Y.; Oshima, K.; Atarashi, K.; Hattori, M.; Suematsu, M.; Honda, K. Characterization of the 17 strains of regulatory T cell-inducing human-derived Clostridia. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalaei, M.; Khatibjoo, A.; Zaghari, M.; Taherpour, K.; Akbari Gharaei, M.; Soltani, M. Comparison of single- and multi-strain probiotics effects on broiler breeder performance, egg production, egg quality and hatchability. Br. Poult. Sci. 2018, 59, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, H.; Koning, C.; Mulder, L.; Rombouts, F.; Beynen, A. Monostrain, multistrain and multispecies probiotics—A comparison of functionality and efficacy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 96, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, T.; Sequoia, J. Probiotics for gastrointestinal conditions: A summary of the evidence. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chapman, C.; Gibson, G.; Todd, S.; Rowland, I. Comparative in vitro inhibition of urinary tract pathogens by single-and multi-strain probiotics. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamberg, S.; Sumeri, I.; Uusna, R.; Ambalam, P.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Adamberg, K.; Wadström, T.; Ljungh, Å. Survival and synergistic growth of mixed cultures of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli combined with prebiotic oligosaccharides in a gastrointestinal tract simulator. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2014, 25, 23062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinder, M.; Bisanz, J.; Burton, J.; Reid, G. Probiotic lactobacilli: A potential prophylactic treatment for reducing pesticide absorption in humans and wildlife. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, M.L.; Protano, C.; Schiavi, E.; Marconi, E.; Capobianco, D.; Massimi, L.; Ristorini, M.; Baldassarre, M.E.; Laforgia, N.; Vitali, M. A prophylactic multi-strain probiotic treatment to reduce the absorption of toxic elements: In-vitro study and biomonitoring of breast milk and infant stools. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H. Biosorption of Heavy Metals by Lactic Acid Bacteria for Detoxification. In Lactic Acid Bacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 145–157. [Google Scholar]
- Daisley, B.A.; Monachese, M.; Trinder, M.; Bisanz, J.E.; Chmiel, J.A.; Burton, J.P.; Reid, G. Immobilization of cadmium and lead by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 mitigates apical-to-basolateral heavy metal translocation in a Caco-2 model of the intestinal epithelium. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredua-Agyeman, M.; Stapleton, P.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Microcalorimetric evaluation of a multi-strain probiotic: Interspecies inhibition between probiotic strains. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Shukla, P. An overview of advanced technologies for selection of probiotics and their expediency: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogucka, J.; Ribeiro, D.M.; Bogusławska-Tryk, M.; Dankowiakowska, A.; da Costa, R.P.R.; Bednarczyk, M. Microstructure of the small intestine in broiler chickens fed a diet with probiotic or synbiotic supplementation. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, B.K.; Razdan, K.; Claes, I.J.; Lebeer, S. Probiotic Attributes of the Newly Isolated Lactic Acid Bacteria from Infants’gut. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2020, 2020, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Oak, S.J.; Jha, R. The effects of probiotics in lactose intolerance: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, E.; Zlotkowska, D.; Wroblewska, B. Yogurt starter cultures of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus ameliorate symptoms and modulate the immune response in a mouse model of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago, L.; Toscano, M.; Rodighiero, V.; De Vecchi, E.; Mogna, G. Cultivable and pyrosequenced fecal microflora in centenarians and young subjects. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, S81–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.-J.; Liu, Q.-Q.; Liao, S.; Fang, H.-H.; Yin, P.; Xie, S.-W.; Tian, L.-X.; Liu, Y.-J.; Niu, J. Effects of dietary mixed probiotics on growth, non-specific immunity, intestinal morphology and microbiota of juvenile pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 90, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNulty, N.P.; Yatsunenko, T.; Hsiao, A.; Faith, J.J.; Muegge, B.D.; Goodman, A.L.; Henrissat, B.; Oozeer, R.; Cools-Portier, S.; Gobert, G. The impact of a consortium of fermented milk strains on the gut microbiome of gnotobiotic mice and monozygotic twins. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 106ra106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, C.; Acuti, G.; Manuali, E.; Casagrande Proietti, P.; Pavone, S.; Trabalza-Marinucci, M.; Moscati, L.; Onofri, A.; Lorenzetti, C.; Franciosini, M. Effects of two different probiotics on microflora, morphology, and morphometry of gut in organic laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2528–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.; Gibson, G.; Rowland, I. Effects of single-and multi-strain probiotics on biofilm formation and in vitro adhesion to bladder cells by urinary tract pathogens. Anaerobe 2014, 27, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foligné, B.; Parayre, S.; Cheddani, R.; Famelart, M.-H.; Madec, M.-N.; Plé, C.; Breton, J.; Dewulf, J.; Jan, G.; Deutsch, S.-M. Immunomodulation properties of multi-species fermented milks. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wróblewska, B.; Kaliszewska, A.; Kołakowski, P.; Pawlikowska, K.; Troszyńska, A. Impact of transglutaminase reaction on the immunoreactive and sensory quality of yoghurt starter. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standen, B.; Rawling, M.; Davies, S.; Castex, M.; Foey, A.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O.; Merrifield, D. Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici modulates both localised intestinal-and peripheral-immunity in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamil, L.; Reyes, C.; Martínez-Silva, M. In vivo and in vitro assessment of Lactobacillus acidophilus as probiotic for tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, Perciformes: Cichlidae) culture improvement. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daudelin, J.-F.; Lessard, M.; Beaudoin, F.; Nadeau, É.; Bissonnette, N.; Boutin, Y.; Brousseau, J.-P.; Lauzon, K.; Fairbrother, J.M. Administration of probiotics influences F4 (K88)-positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli attachment and intestinal cytokine expression in weaned pigs. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragland, S.A.; Criss, A.K. From bacterial killing to immune modulation: Recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neveling, D.P.; van Emmenes, L.; Ahire, J.J.; Pieterse, E.; Smith, C.; Dicks, L. Effect of a Multi-Species Probiotic on the Colonisation of Salmonella in Broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasina, Y.; Holt, P.; Moran, E.; Moore, R.; Conner, D.; McKee, S. Intestinal cytokine response of commercial source broiler chicks to Salmonella typhimurium infection. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Tsen, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-L.; Yu, B.; Chen, C.-S. Oral administration of a combination of select lactic acid bacteria strains to reduce the Salmonella invasion and inflammation of broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Ghosh, K.; Ringø, E. Enzyme-producing bacteria isolated from fish gut: A review. Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhama, K.; Latheef, S.K.; Munjal, A.K.; Khandia, R.; Samad, H.A.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Joshi, S.K. Probiotics in curing allergic and inflammatory conditions-research progress and futuristic vision. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2016, 10, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Huang, C.; He, T.; Harmsen, H. Effect of probiotics and yogurt on colonic microflora in subjects with lactose intolerance. J. Hyg. Res. 2006, 35, 587–591. [Google Scholar]
- Essa, M.A.; El-Serafy, S.; El-Ezabi, M.M.; Daboor, S.M.; Esmael, N.A.; Lall, S.P. Effect of different dietary probiotics on growth, feed utilization and digestive enzymes activities of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. Arab. Aquac. Soc. 2010, 5, 143–162. [Google Scholar]
- Emami, N.K.; Samie, A.; Rahmani, H.; Ruiz-Feria, C. The effect of peppermint essential oil and fructooligosaccharides, as alternatives to virginiamycin, on growth performance, digestibility, gut morphology and immune response of male broilers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 175, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standen, B.; Rodiles, A.; Peggs, D.; Davies, S.; Santos, G.; Merrifield, D. Modulation of the intestinal microbiota and morphology of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, following the application of a multi-species probiotic. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8403–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fataftah, A.-R.; Abdelqader, A. Effects of dietary Bacillus subtilis on heat-stressed broilers performance, intestinal morphology and microflora composition. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 198, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgain, J.; Scher, J.; Francius, G.; Borges, F.; Corgneau, M.; Revol-Junelles, A.; Cailliez-Grimal, C.; Gaiani, C. Lactic acid bacteria in dairy food: Surface characterization and interactions with food matrix components. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 213, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueimonde, M.; Jalonen, L.; He, F.; Hiramatsu, M.; Salminen, S. Adhesion and competitive inhibition and displacement of human enteropathogens by selected lactobacilli. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagliuolo, I.; Galeazzi, F.; Ferrari, S.; Elli, M.; Brun, P.; Cavaggioni, A.; Tormen, D.; Sturniolo, G.C.; Morelli, L.; Palù, G. Beneficial effect of auto-aggregating Lactobacillus crispatus on experimentally induced colitis in mice. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Rastall, R.A.; Gibson, G.R.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Chatzifragkou, A. Adhesion mechanisms mediated by probiotics and prebiotics and their potential impact on human health. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 6463–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Puong, K.-Y. Competition for adhesion between probiotics and human gastrointestinal pathogens in the presence of carbohydrate. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, S101–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ołdak, A.; Zielińska, D.; Łepecka, A.; Długosz, E.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from Polish regional cheeses exhibit anti-staphylococcal activity and selected probiotic properties. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, D.; Lu, W.; Piao, X.; Chen, X. Screening of Bacillus strains as potential probiotics and subsequent confirmation of the in vivo effectiveness of Bacillus subtilis MA139 in pigs. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2006, 90, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Sieiro, P.; Montalbán-López, M.; Mu, D.; Kuipers, O.P. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria: Extending the family. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2939–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli, V.; Camargo, A.; Todorov, S.; Nero, L. Novel bacteriocinogenic Enterococcus hirae and Pediococcus pentosaceus strains with antilisterial activity isolated from Brazilian artisanal cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2526–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heu, S.; Oh, J.; Kang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Cho, S.K.; Cho, Y.; Cho, M. gly gene cloning and expression and purification of glycinecin A, a bacteriocin produced by Xanthomonas campestris pv. glycines 8ra. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4105–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deegan, L.H.; Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, P. Bacteriocins: Biological tools for bio-preservation and shelf-life extension. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich dos Santos, K.M.; Silva Vieira, A.D.; Salles, H.O.; Oliveira, J.d.S.; Costa Rocha, C.R.; Borges, M.d.F.; Bruno, L.M.; de Melo Franco, B.D.G.; Todorov, S.D. Safety, beneficial and technological properties of Enterococcus faecium isolated from Brazilian cheeses. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnentis, H.; Nurmiati, N.; Marlida, Y.; Adzitey, F.; Huda, N. γ-Aminobutyric acid production by selected lactic acid bacteria isolate of an Indonesian indigenous fermented buffalo milk (dadih) origin. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, R.; Bajpai, V.K.; Baek, K.-H. Production of GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) by microorganisms: A review. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Chousalkar, K.K. Short-term feeding of probiotics and synbiotics modulates caecal microbiota during Salmonella Typhimurium infection but does not reduce shedding and invasion in chickens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, L.V. Efficacy of Single-Strain Probiotics Versus Multi-Strain Mixtures: Systematic Review of Strain and Disease Specificity. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douillard, F.P.; Mora, D.; Eijlander, R.T.; Wels, M.; De Vos, W.M. Comparative genomic analysis of the multispecies probiotic-marketed product VSL# 3. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192452. [Google Scholar]
- Kankainen, M.; Paulin, L.; Tynkkynen, S.; von Ossowski, I.; Reunanen, J.; Partanen, P.; Satokari, R.; Vesterlund, S.; Hendrickx, A.P.; Lebeer, S. Comparative genomic analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reveals pili containing a human-mucus binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17193–17198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motherway, M.O.C.; Zomer, A.; Leahy, S.C.; Reunanen, J.; Bottacini, F.; Claesson, M.J.; O’Brien, F.; Flynn, K.; Casey, P.G.; Munoz, J.A.M. Functional genome analysis of Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003 reveals type IVb tight adherence (Tad) pili as an essential and conserved host-colonization factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11217–11222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, R.; Altermann, E.; Anderson, R.C.; McNabb, W.C.; Moughan, P.J.; Roy, N.C. The role of cell surface architecture of lactobacilli in host-microbe interactions in the gastrointestinal tract. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 237921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksen, L.; Moen, A.; Adzhubei, A.A.; Mathiesen, G.; Eijsink, V.G.; Egge-Jacobsen, W. Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 O-linked protein glycosylation: An extended spectrum of target proteins and modification sites detected by mass spectrometry. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytgat, H.L.; De Vos, W.M. Sugar coating the envelope: Glycoconjugates for microbe–host crosstalk. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzola, M.; Tompkins, T.A.; Matera, M.G. Immunomodulatory impact of a synbiotic in Th1 and Th2 models of infection. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2010, 4, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, M.-T.; Girardin, S.E.; Regnault, B.; Le Bourhis, L.; Dillies, M.-A.; Coppée, J.-Y.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Pédron, T. Anti-inflammatory effect of Lactobacillus casei on Shigella-infected human intestinal epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; De Angelis, M.; Limitone, A.; Minervini, F.; Simonetti, M.C.; Buchin, S.; Gobbetti, M. Cell–cell communication in sourdough lactic acid bacteria: A proteomic study in Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis CB1. Proteomics 2007, 7, 2430–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, K.B.; Bassler, B.L. LuxS quorum sensing: More than just a numbers game. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J.; Cao, Y.; Horii, T.; Sakuda, S.; Akkermans, A.D.; De Vos, W.M.; Nagasawa, H. Gelatinase biosynthesis-activating pheromone: A peptide lactone that mediates a quorum sensing in Enterococcus faecalis. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturme, M.H.; Francke, C.; Siezen, R.J.; de Vos, W.M.; Kleerebezem, M. Making sense of quorum sensing in lactobacilli: A special focus on Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3939–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cagno, R.; De Angelis, M.; Coda, R.; Minervini, F.; Gobbetti, M. Molecular adaptation of sourdough Lactobacillus plantarum DC400 under co-cultivation with other lactobacilli. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diep, D.; Mathiesen, G.; Eijsink, V.; Nes, I. Use of lactobacilli and their pheromone-based regulatory mechanism in gene expression and drug delivery. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, A.; Ruiz-Barba, J.L.; Jiménez-Díaz, R. Production of plantaricin NC8 by Lactobacillus plantarum NC8 is induced in the presence of different types of gram-positive bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2004, 181, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; De Angelis, M.; Calasso, M.; Vincentini, O.; Vernocchi, P.; Ndagijimana, M.; De Vincenzi, M.; Dessì, M.R.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Gobbetti, M. Quorum sensing in sourdough Lactobacillus plantarum DC400: Induction of plantaricin A (PlnA) under co-cultivation with other lactic acid bacteria and effect of PlnA on bacterial and Caco-2 cells. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Hu, J. Positive effect of probiotics on constipation in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of six randomized controlled trials. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algburi, A.; Alazzawi, S.A.; Al-Ezzy, A.I.A.; Weeks, R.; Chistyakov, V.; Chikindas, M.L. Potential Probiotics Bacillus subtilis KATMIRA1933 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B-1895 Co-Aggregate with Clinical Isolates of Proteus mirabilis and Prevent Biofilm Formation. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, E.A.; Roy, T.; D’Adamo, C.R.; Wieland, L.S. Probiotics and gastrointestinal conditions: An overview of evidence from the Cochrane Collaboration. Nutrition 2018, 45, 125–134.e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kim, I. Effects of multistrain probiotics on growth performance, apparent ileal nutrient digestibility, blood characteristics, cecal microbial shedding, and excreta odor contents in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, C.N. Antibiotics, probiotics and prebiotics in IBD. In Nutrition, Gut Microbiota and Immunity: Therapeutic Targets for IBD; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 79, pp. 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hajela, N.; Ramakrishna, B.; Nair, G.B.; Abraham, P.; Gopalan, S.; Ganguly, N.K. Gut microbiome, gut function, and probiotics: Implications for health. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 34, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frech, T.M.; Khanna, D.; Maranian, P.; Frech, E.J.; Sawitzke, A.D.; Murtaugh, M.A. Probiotics for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated gastrointestinal bloating/distention. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, S22. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.S.; Sohn, W.; Lee, O.Y.; Lee, S.P.; Lee, K.N.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, H.L.; Yoon, B.C.; Choi, H.S.; Chung, W.S. Effect of multispecies probiotics on irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventogiannis, K.; Gkolfakis, P.; Spithakis, G.; Tsatali, A.; Pistiki, A.; Sioulas, A.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Triantafyllou, K. Effect of a preparation of four probiotics on symptoms of patients with irritable bowel syndrome: Association with intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareau, M.G. Microbiota-gut-brain axis and cognitive function. In Microbial Endocrinology: The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Health and Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 357–371. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, E.; Asemi, Z.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Bahmani, F.; Kouchaki, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Hamidi, G.A.; Salami, M. Effect of probiotic supplementation on cognitive function and metabolic status in Alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, double-blind and controlled trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabico, S.; Al-Mashharawi, A.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Wani, K.; Amer, O.E.; Hussain, D.S.; Ansari, M.G.A.; Masoud, M.S.; Alokail, M.S.; McTernan, P.G. Effects of a 6-month multi-strain probiotics supplementation in endotoxemic, inflammatory and cardiometabolic status of T2DM patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Jordan, S.; Storey, M.; Thornton, C.A.; Gravenor, M.B.; Garaiova, I.; Plummer, S.F.; Wang, D.; Morgan, G. Probiotics in the prevention of eczema: A randomised controlled trial. Arch. Dis. Child. 2014, 99, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.R.; Shandilya, U.K.; Kansal, V.K. Immunoprotective effect of probiotic dahi containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum on dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2012, 4, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Schwack, W. High-performance thin-layer chromatography screening of multi class antibiotics in animal food by bioluminescent bioautography and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1356, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambalam, P.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Balusupati, P.; Nilsson, I.; Wadström, T.; Ljungh, Å. Prebiotic preferences of human lactobacilli strains in co-culture with bifidobacteria and antimicrobial activity against Clostridium difficile. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondepudi, K.K.; Ambalam, P.; Karagin, P.H.; Nilsson, I.; Wadström, T.; Ljungh, Å. A novel multi-strain probiotic and synbiotic supplement for prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in a murine model. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, S.; Pardi, D.S. Clostridium difficile infection: Management strategies for a difficult disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Forssten, S.; Hibberd, A.A.; Lyra, A.; Stahl, B. Probiotic approach to prevent antibiotic resistance. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhtin, M.; Alyoshkin, V.; Lakhtin, V.; Afanasyev, S.; Pozhalostina, L.; Pospelova, V. Probiotic lactobacillus and bifidobacterial lectins against Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus clinical strains: New class of the pathogen biofilm destructors. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2010, 2, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, N.M.; Elkhatib, W.F.; Aboshanab, K.M.; Bahr, M.M. Inhibition of Clostridium difficile in mice using a mixture of potential probiotic strains Enterococcus faecalis NM815, E. faecalis NM915, and E. faecium NM1015: Novel candidates to control C. difficile infection (CDI). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Bruce, A.W. Selection of Lactobacillus strains for urogenital probiotic applications. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, S77–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Zhang, F.; Peng, Y.; Ji, Z.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, J. Mixed culture of probiotics on a solid-state medium: An efficient method to produce an affordable probiotic feed additive. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2017, 22, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, G.; Jamaluddin, R.; Mohtarrudin, N.; Ahmad, Z.; Khazaai, H.; Parvaneh, M. Single-species versus dual-species probiotic supplementation as an emerging therapeutic strategy for obesity. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Huo, Y.; Su, B.; Li, X. Effects of a probiotic intervention on Escherichia coli and high-fat diet-induced intestinal microbiota imbalance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, B.J.; Price, T.K.; Joyce, C.J.; Wolfe, A.J.; Mueller, E.R. Oral probiotics and the female urinary microbiome: A double-blinded randomized placebo-controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidossi, A.; De Grandi, R.; Toscano, M.; Bottagisio, M.; De Vecchi, E.; Gelardi, M.; Drago, L. Probiotics Streptococcus salivarius 24SMB and Streptococcus oralis 89a interfere with biofilm formation of pathogens of the upper respiratory tract. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Leonhard, M.; Moser, D.; Ma, S.; Schneider-Stickler, B. Inhibitory effect of probiotic lactobacilli supernatants on single and mixed non-albicans Candida species biofilm. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 85, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Mun, H.-S.; Islam, M.; Kim, S.-S.; Hwang, J.-A.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yang, C.-J. Effects of Citrus junos by-products fermented with multistrain probiotics on growth performance, immunity, caecal microbiology and meat oxidative stability in broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2014, 55, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetkish, N.; Sabetkish, S.; Mohseni, M.J.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M. Prevention of renal scarring in acute pyelonephritis by probiotic therapy: An experimental study. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redweik, G.A.; Stromberg, Z.R.; Van Goor, A.; Mellata, M. Protection against avian pathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella Kentucky exhibited in chickens given both probiotics and live Salmonella vaccine. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyadeatsoontorn, S.; Taharnklaew, R.; Upathanpreecha, T.; Sornplang, P. Encapsulating viability of multi-strain Lactobacilli as potential probiotic in pigs. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarjapuram, N.; Mekala, N.; Singh, M.; Tatu, U. The potential of Lactobacillus casei and Entercoccus faecium combination as a preventive probiotic against Entamoeba. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambori, C.; Morvay, A.A.; Sala, C.; Licker, M.; Gurban, C.; Tanasie, G.; Tîrziu, E. Antimicrobial effect of probiotics on bacterial species from dental plaque. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.T.; Hoon, J.; Mun, H.-S.; Yang, C.-J. Evaluation of Lactobacillus and Bacillus-based probiotics as alternatives to antibiotics in enteric microbial challenged weaned piglets. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tejero-Sariñena, S.; Barlow, J.; Costabile, A.; Gibson, G.R.; Rowland, I. Antipathogenic activity of probiotics against Salmonella Typhimurium and Clostridium difficile in anaerobic batch culture systems: Is it due to synergies in probiotic mixtures or the specificity of single strains? Anaerobe 2013, 24, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lollo, P.C.B.; de Moura, C.S.; Morato, P.N.; Cruz, A.G.; de Freitas Castro, W.; Betim, C.B.; Nisishima, L.; José de Assis, F.F.; Junior, M.M.; Fernandes, C.O. Probiotic yogurt offers higher immune-protection than probiotic whey beverage. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, B.M.S.; Borgonovi, T.F.; Casarotti, S.N.; Todorov, S.D.; Penna, A.L.B. Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus fermentum strains isolated from mozzarella cheese: Probiotic potential, safety, acidifying kinetic parameters and viability under gastrointestinal tract conditions. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawłowska, J.; Klewicka, E.; Czubkowski, P.; Motyl, I.; Jankowska, I.; Libudzisz, Z.; Teisseyre, M.; Gliwicz, D.; Cukrowska, B. Effect of Lactobacillus casei DN-114001 application on the activity of fecal enzymes in children after liver transplantation. In Transplantation Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 3219–3221. [Google Scholar]
- Schwenger, E.M.; Tejani, A.M.; Loewen, P.S. Probiotics for preventing urinary tract infections in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, A.; Kashani, H.H.; Nasri, E.; Soleimani, Z.; Sharif, M.R. The role of probiotics in the treatment of dysentery: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.-R. Gut flora in health and disease. Lancet 2003, 361, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Lee, S.; Kim, I. Effects of multistrain probiotics on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood profiles, faecal microbial shedding, faecal score and noxious gas emission in weaning pigs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 100, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Masani, K.; Sato, C.; Hiki, M.; Usui, M.; Baba, K.; Ozawa, M.; Harada, K.; Aoki, H.; Sawada, T. Phylogenetic groups and cephalosporin resistance genes of Escherichia coli from diseased food-producing animals in Japan. Acta Vet. Scand. 2011, 53, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, G.; Orman, A.; Cetinkaya, F.; Gencoglu, H.; Meral, Y.; Turkmen, I. Effects of probiotic (Bacillus subtilis DSM 17299) supplementation on the caecal microflora and performance in broiler chickens. Rev. Méd. Vét. 2011, 162, 538–545. [Google Scholar]
- Mountzouris, K.; Tsirtsikos, P.; Kalamara, E.; Nitsch, S.; Schatzmayr, G.; Fegeros, K. Evaluation of the efficacy of a probiotic containing Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Enterococcus, and Pediococcus strains in promoting broiler performance and modulating cecal microflora composition and metabolic activities. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cao, G.; Ferket, P.; Liu, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, A. Effects of probiotic, Clostridium butyricum, on growth performance, immune function, and cecal microflora in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, P.; Sahoo, J.; Panda, P. Effect of probiotic (Lacto-Sacc) feeding, packaging methods and seasons on the microbial and organoleptic qualities of chicken meat balls during refrigerated storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. (Mysore) 2000, 37, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Siragusa, G.R. Direct-fed microbials and their impact on the intestinal microflora and immune system of chickens. J. Poult. Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.A.; Ahmadi, H.; Karimi Torshizi, M.A. Evaluating two multistrain probiotics on growth performance, intestinal morphology, lipid oxidation and ileal microflora in chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadde, U.; Oh, S.; Lee, Y.; Davis, E.; Zimmerman, N.; Rehberger, T.; Lillehoj, H.S. The effects of direct-fed microbial supplementation, as an alternative to antibiotics, on growth performance, intestinal immune status, and epithelial barrier gene expression in broiler chickens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balevi, T.; Ucan, U.; Coşun, B.; Kurtoğu, V.; Cetingül, I. Effect of dietary probiotic on performance and humoral immune response in layer hens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2001, 42, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil De Los Santos, J.; Storch, O.; Gil-Turnes, C. Bacillus cereus var. toyoii and Saccharomyces boulardii increased feed efficiency in broilers infected with Salmonella enteritidis. Br. Poult. Sci. 2005, 46, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountzouris, K.; Tsitrsikos, P.; Palamidi, I.; Arvaniti, A.; Mohnl, M.; Schatzmayr, G.; Fegeros, K. Effects of probiotic inclusion levels in broiler nutrition on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, plasma immunoglobulins, and cecal microflora composition. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, A.; Sarkar Ghosh, K.; Sen, S.; Ray, A. Evaluation of the nutritive value of Leucaena leucocephala leaf meal, inoculated with fish intestinal bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus circulans in formulated diets for rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings. Aquac. Res. 2004, 35, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.A.; Duc, L.H.; Cutting, S.M. The use of bacterial spore formers as probiotics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standen, B.; Peggs, D.; Rawling, M.; Foey, A.; Davies, S.; Santos, G.; Merrifield, D. Dietary administration of a commercial mixed-species probiotic improves growth performance and modulates the intestinal immunity of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 49, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, S.P.; Chiu, C.H.; Shiu, Y.L.; Huang, Z.L.; Liu, C.H. Effects of diets supplemented with either individual or combined probiotics, B acillus subtilis E20 and L actobacillus plantarum 7-40, on the immune response and disease resistance of the mud crab, S cylla paramamosain (E stampador). Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, Z.; Langa, R.; Aiyegoro, O.; Okoh, A. Effects of probiotics on growth performance, blood parameters, and antibody stimulation in piglets. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 47, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.; Martín-Orúe, S.M.; Nofrarías, M.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Gasa, J. Changes in caecal microbiota and mucosal morphology of weaned pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhouma, M.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Beaudry, F.; Letellier, A. Post weaning diarrhea in pigs: Risk factors and non-colistin-based control strategies. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, A.; Gibellini, M.; Gin, T.; Vangroenweghe, F.; Vandenbroucke, V.; Bauerfeind, R.; Bonilauri, P.; Labarque, G.; Hidalgo, Á. Prevalence of virulence factors in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with post-weaning diarrhoea in Europe. Porc. Health Manag. 2016, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlee, M.; Harder, J.; Köten, B.; Stange, E.; Wehkamp, J.; Fellermann, K. Probiotic lactobacilli and VSL# 3 induce enterocyte β-defensin 2. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 151, 528–535. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lillehoj, H.; Dalloul, R.; Park, D.; Hong, Y.; Lin, J. Influence of Pediococcus-based probiotic on coccidiosis in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brousseau, J.-P.; Talbot, G.; Beaudoin, F.; Lauzon, K.; Roy, D.; Lessard, M. Effects of probiotics Pediococcus acidilactici strain MA18/5M and Saccharomyces cerevisiae subsp. boulardii strain SB-CNCM I-1079 on fecal and intestinal microbiota of nursing and weanling piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 5313–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowska, E.; Jarosz, Ł.; Grądzki, Z. Effect of multi-microbial probiotic formulation Bokashi on pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines profile in the serum, colostrum and milk of sows, and in a culture of polymorphonuclear cells isolated from colostrum. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tawab, M.A.; Youssef, I.; Bakr, H.; Fthenakis, G.; Giadinis, N. Role of probiotics in nutrition and health of small ruminants. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adetoye, A.; Pinloche, E.; Adeniyi, B.A.; Ayeni, F.A. Characterization and anti-salmonella activities of lactic acid bacteria isolated from cattle faeces. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, D.; Kelton, D.; Weese, J.; Noble, C.; Duffield, T. Evaluation of a multispecies probiotic as a supportive treatment for diarrhea in dairy calves: A randomized clinical trial. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4498–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorini, M.; Soto, L.; Zbrun, M.; Sequeira, G.; Rosmini, M.; Frizzo, L. Impact of probiotic administration on the health and fecal microbiota of young calves: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of lactic acid bacteria. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, H.; Mulder, L.; Everts, H.; Van Espen, D.; Van Der Wal, E.; Klaassen, G.; Rouwers, S.; Hartemink, R.; Rombouts, F.; Beynen, A. Health and growth of veal calves fed milk replacers with or without probiotics. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2154–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Odhiambo, J.; Farooq, U.; Lam, T.; Dunn, S.; Ametaj, B. Intravaginal probiotics modulated metabolic status and improved milk production and composition of transition dairy cows. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olchowy, T.; Soust, M.; Alawneh, J. The effect of a commercial probiotic product on the milk quality of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 2188–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamali, M.; Nasiri, N.; Shavazi, N.T.; Jamilian, M.; Bahmani, F.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Asemi, Z. The effects of synbiotic supplementation on pregnancy outcomes in gestational diabetes. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güney-Varal, İ.; Köksal, N.; Özkan, H.; Bağcı, O.; Doğan, P. The effect of early administration of combined multi-strain and multi-species probiotics on gastrointestinal morbidities and mortality in preterm infants: A randomized controlled trial in a tertiary care unit. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2017, 59, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovachev, S.M.; Vatcheva-Dobrevska, R.S. Local probiotic therapy for vaginal Candida albicans infections. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2015, 7, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Zaneb, H.; Masood, S.; Khan, R.U.; Ashraf, S.; Sikandar, A.; Rehman, H.F.U.; Rehman, H.U. Effect of dietary supplementation of zinc and multi-microbe probiotic on growth traits and alteration of intestinal architecture in broiler. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).