CYP2C19 Polymorphisms in Indonesia: Comparison among Ethnicities and the Association with Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
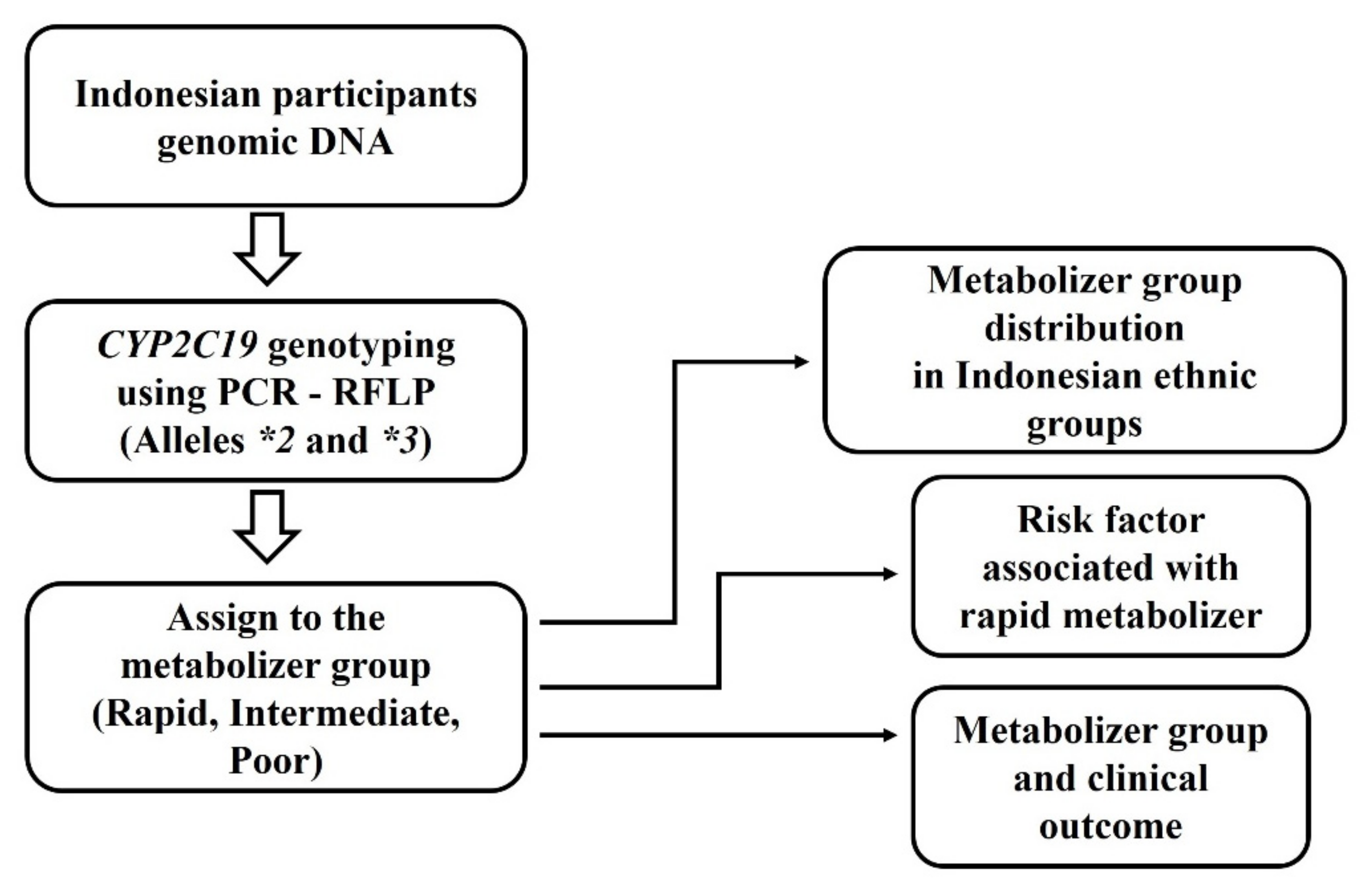
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Endoscopy Diagnosis and Gastritis Severity Score
2.3. CYP2C19 Polymorphism Genotyping
2.4. Classification of CYP2C19 Genotype Groups
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data and Endoscopy Results
3.2. CYP2C19 Polymorphism Genotyping
3.3. CYP2C19 Polymorphisms between Indonesian Ethnicities
3.4. CYP2C19 Polymorphisms and Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fock, K.M.; Katelaris, P.; Sugano, K.; Ang, T.L.; Hunt, R.; Talley, N.J.; Lam, S.K.; Xiao, S.D.; Tan, H.J.; Wu, C.Y.; et al. Second Asia-Pacific Consensus Guidelines for Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 1587–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Jung, H.K.; Lee, H.L.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.G.; Shin, W.G.; Shin, E.S.; Lee, Y.C. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in Korea, 2013 revised edition. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.Z.; Xie, Y.; Cheng, H.; Lu, N.H.; Hu, F.L.; Zhang, W.D.; Zhou, L.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Z.R.; Wang, C.W.; et al. Fourth Chinese National Consensus Report on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Dig. Dis. 2013, 14, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; O’Morain, C.A.; Gisbert, J.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Axon, A.T.; Bazzoli, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Atherton, J.; Graham, D.Y.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection-the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut 2017, 66, 6–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, E.J.; Nelis, G.F.; Klinkenberg-Knol, E.C.; Snel, P.; Goldfain, D.; Kolkman, J.J.; Festen, H.P.; Dent, J.; Zeitoun, P.; Havu, N.; et al. Cure of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with reflux oesophagitis treated with long term omeprazole reverses gastritis without exacerbation of reflux disease: Results of a randomised controlled trial. Gut 2004, 53, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, A.; Perri, F.; Leandro, G.; Franceschi, M. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the outcome of reflux esophagitis and chronic gastritis in the elderly. A randomized, multicenter, eight-month study. Gerontology 2006, 52, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenk, B.E.; Kuipers, E.J.; Nelis, G.F.; Bloemena, E.; Thijs, J.C.; Snel, P.; Luckers, A.E.; Klinkenberg-Knol, E.C.; Festen, H.P.; Viergever, P.P.; et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on chronic gastritis during omeprazole therapy. Gut 2000, 46, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagymasi, K.; Mullner, K.; Herszenyi, L.; Tulassay, Z. Update on the pharmacogenomics of proton pump inhibitors. Pharmacogenomics 2011, 12, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.H.; Lu, C.Y.; Shih, H.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Wu, M.C.; Hu, H.M.; Hsu, W.H.; Yu, F.J.; Wu, D.C.; Kuo, F.C. CYP2C19 polymorphism influences Helicobacter pylori eradication. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16029–16036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Syam, A.F.; Makmun, D.; Nusi, I.A.; Zein, L.H.; Zulkhairi; Akil, F.; Uswan, W.B.; Simanjuntak, D.; Uchida, T.; et al. Helicobacter pylori virulence genes in the five largest islands of Indonesia. Gut Pathog. 2015, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Lin, C.J. CYP2C19 genotypes in the pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of proton pump inhibitor-based therapy of Helicobacter pylori infection. Expert. Opin. Drug. Metab. Toxicol. 2010, 6, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, R.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, G. Effect of CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on the efficacy of proton pump inhibitor-based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2008, 13, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.H.; Hsu, P.I.; Kuo, F.C.; Wang, S.S.; Hu, H.M.; Liu, C.J.; Chuah, S.K.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsieh, M.C.; Wu, D.C.; et al. Comparison of 10 day bismuth quadruple therapy with high-dose metronidazole or levofloxacin for second-line Helicobacter pylori therapy: A randomized controlled trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.A.; Wang, H.; Gu, Z.J.; Wang, W.J.; Zeng, X.Y.; Du, Y.L.; Ying, S.S.; Zhang, B.H. Effect of CYP2C19 Gene Polymorphisms on Proton Pump Inhibitor, Amoxicillin, and Levofloxacin Triple Therapy for Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormeci, A.; Emrence, Z.; Baran, B.; Gokturk, S.; Soyer, O.M.; Evirgen, S.; Akyuz, F.; Karaca, C.; Besisik, F.; Kaymakoglu, S.; et al. Effect of cytochrome P450 2C19 polymorphisms on the Helicobacter pylori eradication rate following two-week triple therapy with pantoprazole or rabeprazole. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 879–885. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, T.; Chiba, K.; Ishizaki, T. Genotyping of S-mephenytoin 4′-hydroxylation in an extended Japanese population. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 60, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, M.; Mizuno, M.; Ishiki, K.; Nagahara, Y.; Maga, T.; Torigoe, T.; Nasu, J.; Okada, H.; Yokota, K.; Oguma, K.; et al. A randomized open trial for comparison of proton pump inhibitors, omeprazole versus rabeprazole, in dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection in relation to CYP2C19 genetic polymorphism. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 16, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Shiohira, H.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Tateishi, T.; Akamine, Y.; Uno, T. The (R)-omeprazole hydroxylation index reflects CYP2C19 activity in healthy Japanese volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 69, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jainan, W.; Vilaichone, R.K. Effects of the CYP2C19 genetic polymorphism on gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, peptic ulcer bleeding and gastric cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 10957–10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais, S.M.; Goldstein, J.A.; Xie, H.G.; Huang, S.L.; Lu, Y.Q.; Xia, H.; Xiao, Z.S.; Ile, N.; Zhou, H.H. Genetic analysis of the S-mephenytoin polymorphism in a Chinese population. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 58, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Morais, S.M.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Blaisdell, J.; Meyer, U.A.; Nakamura, K.; Goldstein, J.A. Identification of a new genetic defect responsible for the polymorphism of (S)-mephenytoin metabolism in Japanese. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 594–598. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, R.J.; De Morais, S.M.; Benhamou, S.; Bouchardy, C.; Blaisdell, J.; Ibeanu, G.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Sarich, T.C.; Wright, J.M.; Dayer, P.; et al. A new genetic defect in human CYP2C19: Mutation of the initiation codon is responsible for poor metabolism of S-mephenytoin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 284, 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdil, B.; Akkiz, H.; Bayram, S.; Bekar, A.; Akgollu, E.; Sandikci, M. Influence of CYP2C19 functional polymorphism on Helicobacter pylori eradication. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 21, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settin, A.; Abdalla, A.F.; Al-Hussaini, A.S.; El-Baz, R.; Galal, A. Cure rate of Helicobacter pylori infection in Egyptian children related to CYP2C19 gene polymorphism. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 33, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, J.K.; Bishop, J.R.; Sangkuhl, K.; Muller, D.J.; Ji, Y.; Leckband, S.G.; Leeder, J.S.; Graham, R.L.; Chiulli, D.L.; LLerena, A.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 Genotypes and Dosing of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 98, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, J.K.; Sangkuhl, K.; Swen, J.J.; Ellingrod, V.L.; Muller, D.J.; Shimoda, K.; Bishop, J.R.; Kharasch, E.D.; Skaar, T.C.; Gaedigk, A.; et al. Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, J.K.; Swen, J.J.; Thorn, C.F.; Sangkuhl, K.; Kharasch, E.D.; Ellingrod, V.L.; Skaar, T.C.; Muller, D.J.; Gaedigk, A.; Stingl, J.C. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 93, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Sangkuhl, K.; Stein, C.M.; Hulot, J.S.; Mega, J.L.; Roden, D.M.; Klein, T.E.; Sabatine, M.S.; Johnson, J.A.; Shuldiner, A.R. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for CYP2C19 genotype and clopidogrel therapy: 2013 update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikawati, Z.; Askitosari, T.D.; Hakim, L.; Tucci, J.; Mitchell, J. Allele frequency distributions of the drug metabolizer genes CYP2C9* 2, CYP2C9* 3, and CYP2C19* 17 in the Buginese population of Indonesia. Curr. Pharm. Pers. Med. (Former. Curr. Pharm.) 2014, 12, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makmun, D. Present status of endoscopy, therapeutic endoscopy and the endoscopy training system in Indonesia. Dig. Endosc. 2014, 26 (Suppl. 2), 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Waskito, L.A.; El-Serag, H.B.; Ajami, N.J.; Nusi, I.A.; Syam, A.F.; Matsumoto, T.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Doohan, D.; Fauzia, K.A.; et al. Gastric microbiota and Helicobacter pylori in Indonesian population. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.F.; Genta, R.M.; Yardley, J.H.; Correa, P. Classification and grading of gastritis: The updated Sydney system. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996, 20, 1161–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurso, G.; Lahner, E.; Marcheggiano, A.; Caruana, P.; Carnuccio, A.; Bordi, C.; Delle Fave, G.; Annibale, B. Involvement of the corporal mucosa and related changes in gastric acid secretion characterize patients with iron deficiency anaemia associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Morais, S.M.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Blaisdell, J.; Nakamura, K.; Meyer, U.A.; Goldstein, J.A. The major genetic defect responsible for the polymorphism of S-mephenytoin metabolism in humans. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 15419–15422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Shirai, N.; Kodaira, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Nogaki, A.; Kuriyama, S.; Iwaizumi, M.; Yamade, M.; Terakawa, I.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Pharmacogenomics-based tailored versus standard therapeutic regimen for eradication of H. pylori. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 81, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.H.; Dong, M.S.; Choi, M.G.; Yoo, H.W.; Lee, S.B.; Park, Y.I.; Chung, I.S. Effects of CYP2C19 and MDR1 genotype on the eradication rate of Helicobacter pylori infection by triple therapy with pantoprazole, amoxycillin and clarithromycin. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, G.Y.; Yu, C.Y.; Subramaniam, V.; Abdul Khalid, M.I.; Tuan Abdu Aziz, T.A.; Johari James, R.; Ahmad, A.; Abdul Rahman, T.; Mohd Nor, F.; Ismail, A.I.; et al. Detection of CYP2C19 Genetic Variants in Malaysian Orang Asli from Massively Parallel Sequencing Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.L.; Woad, K.J.; Woodfield, D.G.; Helsby, N.A. A high incidence of polymorphic CYP2C19 variants in archival blood samples from Papua New Guinea. Hum. Genom. 2008, 3, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masta, A.; Lum, J.K.; Tsukahara, T.; Hwaihwanje, I.; Kaneko, A.; Paniu, M.M.; Sapuri, M.; Takahashi, N.; Ishizaki, T.; Kobayakawa, T.; et al. Analysis of Sepik populations of Papua New Guinea suggests an increase of CYP2C19 null allele frequencies during the colonization of Melanesia. Pharmacogenetics 2003, 13, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hyun, Y.J.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, S.; Kim, J.M.; Oh, W.Y.; Na, H.S.; Lee, J.G.; Seo, D.W.; et al. Effects of CYP2C19 Genetic Polymorphisms on PK/PD Responses of Omeprazole in Korean Healthy Volunteers. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, N.; Sharanya, V.; Kanth, R.; Murthy, H.V.V.; Sasikala, M.; Banerjee, R.; Tandan, M.; Reddy, N. Rapid and ultra-rapid metabolizers with CYP2C19*17 polymorphism do not respond to standard therapy with proton pump inhibitors. Meta Gene 2016, 9, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Choi, K.D.; Song, H.J.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, J.H. The Influence of CYP2C19 Polymorphism on Eradication of Helicobacter pylori: A Prospective Randomized Study of Lansoprazole and Rabeprazole. Gut Liver 2010, 4, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Sheu, M.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Ho, H.O. Optimal dose regimens of esomeprazole for gastric acid suppression with minimal influence of the CYP2C19 polymorphism. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Furuta, T.; Shirai, N.; Nakamura, A.; Xiao, F.; Kajimura, M.; Sugimura, H.; Hishida, A. Different effects of polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta on development of peptic ulcer and gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunetta, K.L. Genetic association studies. Circulation 2008, 118, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K. Re: Association of polymorphism in cytochrome P450 2C9 with susceptibility to head and neck cancer and treatment outcome: Pragmatic use of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and statistical interaction analysis. Appl. Transl. Genom. 2014, 3, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shoemaker, J.; Painter, I.; Weir, B. A Bayesian characterization of Hardy-Weinberg disequilibrium. Genetics 1998, 149, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar]
- Yong Zou, G.; Donner, A. The Merits of Testing Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium in the Analysis of Unmatched Case-Control Data: A Cautionary Note. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2006, 70, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, V.M.; Del Tredici, A.L.; Hachad, H.; Ji, Y.; Kalman, L.V.; Scott, S.A.; Weck, K.E. Recommendations for Clinical CYP2C19 Genotyping Allele Selection: A Report of the Association for Molecular Pathology. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 20, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ethnicity | n | Age, Years | Sex | Gastritis | Gastric Ulcer | Duodenal Ulcer | GERD * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Range | Male | Female | ||||||
| Papuan | 14 | 43.4 ± 11.9 | 21–63 | 8 | 6 | 14 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Batak | 27 | 51.6 ± 16.3 | 17–78 | 13 | 14 | 24 (88.9) | 2 (7.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.7) |
| Balinese | 25 | 46.0 ± 12.6 | 23–70 | 15 | 10 | 25 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Dayak | 10 | 36.8 ± 11.8 | 22–54 | 5 | 5 | 9 (90) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (10.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Javanese | 28 | 42.5 ± 11.8 | 19–64 | 17 | 11 | 24 (85.7) | 1 (3.6) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (10.7) |
| Bugis | 37 | 47.5 ± 14.3 | 24–76 | 27 | 10 | 30 (81.1) | 2 (5.4) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (13.5) |
| Chinese | 17 | 46.8 ± 14.1 | 22–70 | 10 | 7 | 9 (52.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (47.1) |
| Timorese | 8 | 61.0 ± 12.1 | 44–80 | 6 | 2 | 8 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| CYP2 C19*2 | CYP2 C19*3 | CYP2C19 Genotype | Expected Phenotype | n (%) | Lower–Upper Proportion (95% CI) ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *1/*1 | *1/*1 | *1/*1 | Rapid Metabolizer | 64 (38.5) | 31.1–46.4 |
| *1/*2 | *1/*1 | *1/*2 | Intermediate Metabolizer | 60 (36.1) | 28.8–43.9 |
| *1/*1 | *1/*3 | *1/*3 | Intermediate Metabolizer | 9 (5.4) | 2.5–10.0 |
| *2/*2 | *1/*1 | *2/*2 | Poor Metabolizer | 23 (13.9) | 8.9–20.0 |
| *1/*1 | *3/*3 | *3/*3 | Poor Metabolizer | 4 (2.4) | 0.6–6.0 |
| *2/*2 | *1/*3 | *2/*3 | Poor Metabolizer | 1 (0.6) | 0.2–3.3 |
| *1/*2 | *1/*3 | *2/*3 | Poor Metabolizer | 5 (3.0) | 1.0–6.9 |
| Ethnicity | CYP2C19*2 (%) | CYP2C19*3 (%) | CYP2C19 Genotype (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *1/*1 | *1/*2 | *2/*2 | *1/*1 | *1/*2 | *2/*2 | RM | IM | PM | |
| Papuan | 4 (28.6) | 5 (35.7) | 5 (35.7) | 11 (78.6) | 1 (7.1) | 2 (14.2) | 2 (14.3) | 4 (28.6) | 8 (57.1) |
| Batak | 14 (51.9) | 10 (37.0) | 3 (11.1) | 22 (81.5) | 5 (18.5) | 0 (0.0) | 10 (37.0) | 13 (48.1) | 4 (14.8) |
| Balinese | 13 (52.0) | 8 (32.0) | 4 (16.0) | 24 (96.0) | 1 (4.0) | 0 (0.0) | 13 (52.0) | 8 (32.0) | 4 (16.0) |
| Dayak | 5 (50.0) | 3 (30.0) | 2 (20.0) | 9 (90.0) | 1 (10.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (40.0) | 4 (40.0) | 2 (20.0) |
| Javanese | 16 (57.1) | 8 (28.6) | 4 (14.3) | 23 (82.1) | 4 (14.3) | 1 (3.6) | 13 (46.4) | 8 (28.6) | 7 (25.0) |
| Bugis | 15 (40.5) | 19 (51.4) | 3 (8.1) | 35 (94.6) | 2 (5.4) | 0 (0.0) | 14 (37.8) | 19 (51.4) | 4 (10.8) |
| Chinese | 7 (41.2) | 7 (41.2) | 3 (17.6) | 15 (88.2) | 1 (5.9) | 1 (5.9) | 5 (29.4) | 8 (47.1) | 4 (23.5) |
| Timorese | 3 (37.5) | 5 (62.5) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (37.5) | 5 (62.5) | 0 (0.0) |
| Characteristic | Rapid Metabolizer (%) | OR | 95% CI | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 39 (38.6) | 1.006 | 0.530–1.910 | 0.984 |
| Female | 25 (38.5) | 1.000 | ||
| Ethnicity | ||||
| Papuan | 2 (14.3) | 1.000 | ||
| Batak | 10 (37.0) | 3.529 | 0.652–19.099 | 0.143 |
| Balinese | 13 (52.0) | 6.500 | 1.199–35.230 | 0.030 * |
| Dayak | 4 (40.0) | 4.000 | 0.563–28.396 | 0.166 |
| Javanese | 13 (44.4) | 5.200 | 0.978–27.653 | 0.053 |
| Bugis | 14 (37.8) | 3.652 | 0.710–18.785 | 0.121 |
| Chinese | 5 (29.4) | 2.500 | 0.403–15.501 | 0.325 |
| Timorese | 3 (37.5) | 3.600 | 0.454–28.562 | 0.225 |
| CYP2C19 | Gastritis | Gastric Ulcer | Duodenal Ulcer | GERD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion (%) | 95% CI ** | Proportion (%) | 95% CI ** | Proportion (%) | Proportion (%) | 95% CI ** | |
| RM | 55 (38.5) | 30.4–47.0 | 1 (20.0) | 0.5–71.6 | 0 (0.0) | 8 (47.1) | 23.0–72.2 |
| IM | 57 (39.9) | 31.7–48.4 | 4 (80.0) | 28.4–99.5 | 0 (0.0) | 8 (47.1) | 23.0–72.2 |
| PM | 31 (21.7) | 15.2–29.3 | 0 (0.0) | 0.0–52.2 | 1 (100) | 1 (5.9) | |
| Total | 143 | 5 | 1 | 17 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miftahussurur, M.; Doohan, D.; Syam, A.F.; Nusi, I.A.; Subsomwong, P.; Waskito, L.A.; Maulahela, H.; Akil, F.; Uwan, W.B.; Siregar, G.; et al. CYP2C19 Polymorphisms in Indonesia: Comparison among Ethnicities and the Association with Clinical Outcomes. Biology 2021, 10, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040300
Miftahussurur M, Doohan D, Syam AF, Nusi IA, Subsomwong P, Waskito LA, Maulahela H, Akil F, Uwan WB, Siregar G, et al. CYP2C19 Polymorphisms in Indonesia: Comparison among Ethnicities and the Association with Clinical Outcomes. Biology. 2021; 10(4):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040300
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiftahussurur, Muhammad, Dalla Doohan, Ari Fahrial Syam, Iswan Abbas Nusi, Phawinee Subsomwong, Langgeng Agung Waskito, Hasan Maulahela, Fardah Akil, Willy Brodus Uwan, Gontar Siregar, and et al. 2021. "CYP2C19 Polymorphisms in Indonesia: Comparison among Ethnicities and the Association with Clinical Outcomes" Biology 10, no. 4: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040300
APA StyleMiftahussurur, M., Doohan, D., Syam, A. F., Nusi, I. A., Subsomwong, P., Waskito, L. A., Maulahela, H., Akil, F., Uwan, W. B., Siregar, G., Fauzia, K. A., Rezkitha, Y. A. A., Rahman, A., Wibawa, I. D. N., Saudale, A. M. J., Richardo, M., Sugihartono, T., Chomariyati, A., Bramantoro, T., ... Yamaoka, Y. (2021). CYP2C19 Polymorphisms in Indonesia: Comparison among Ethnicities and the Association with Clinical Outcomes. Biology, 10(4), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040300







