Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potential for Osteoarthritis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Why Should We Pay Attention to MSC-Derived Exosomes for OA Management?
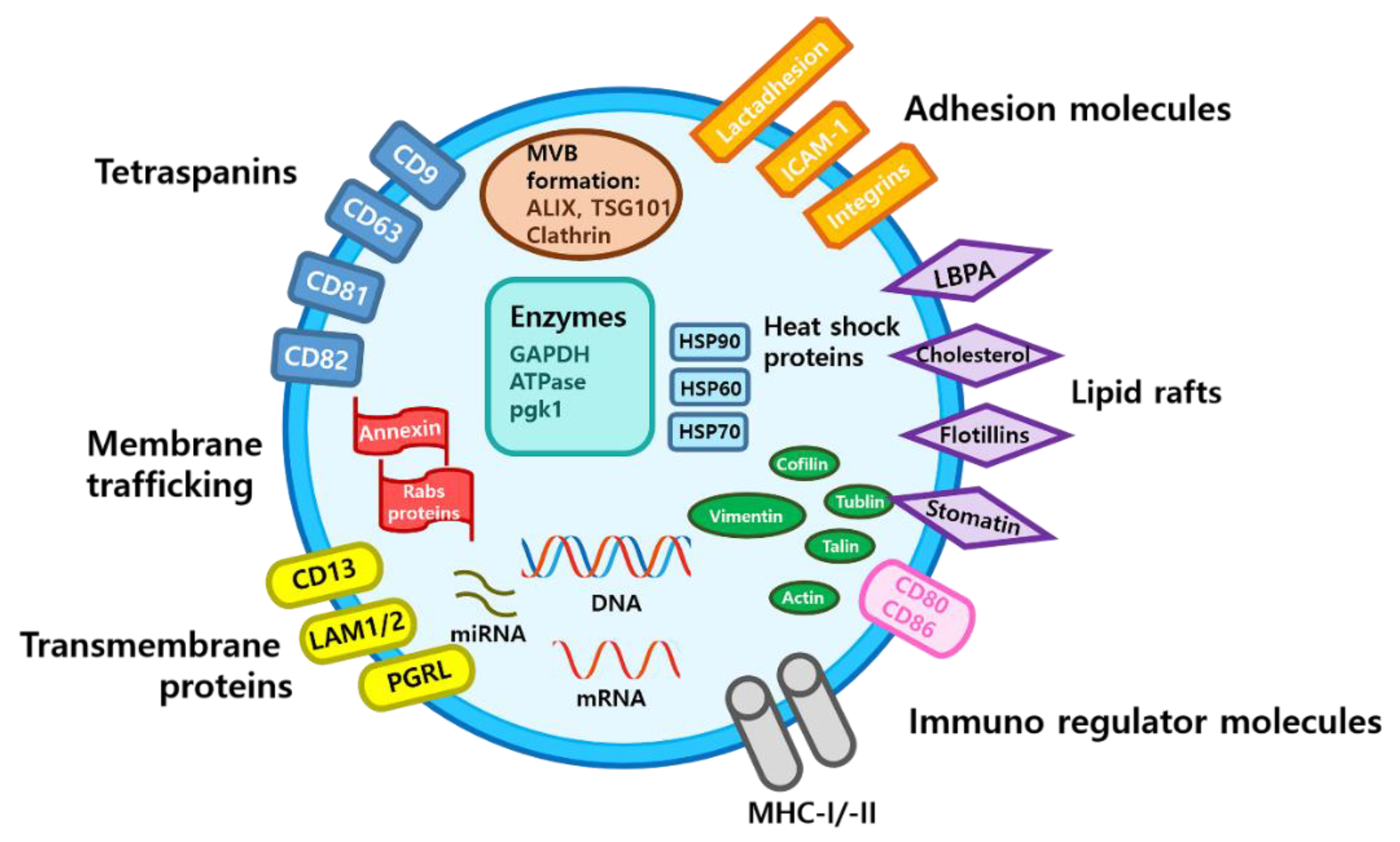
3. Characteristics of Exosomes
4. Technique for the Isolation of Exosomes from MSCs
4.1. Ultracentrifugation-Based Technique
4.2. Size-Based Technique
4.3. Immunoaffinity Interaction-Based Technique
5. Limitations of MSC-Based Therapies
6. MSC-Derived Exosomes and Osteoarthritis
7. Review of Current Studies with MSC-Derived Exosomes for OA Treatment
| Authors | Publications /Year | Type of Disease | Type of Cells | Type of EV | Model | Cargo | Function | Additional Manipulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tofiño-Vian et al. [103] | Cell Physiol Biochem 2018 | OA | AD-MSCs | Exosomes Microvesicles | In vitro | Proteins | TNF-α↓ IL-6↓ PGE2↓ NO↓ MMP-13↓ | Chondrocyte stimulated with IL-1β |
| Tofiño-Vian et al. [110] | Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017 | OA | AD-MSCs | Exosomes Microvesicles | In vitro | Proteins | β-galactosidase↓ γH2AX foci↓ IL-6↓ PGE2↓ | Osteoblast stimulate with IL-1β |
| Cosenza et al. [57] | Sci Rep 2017 | OA | BM-MSCs | Exosomes Microvesicles | Mice | Proteins | Type II collagen↑ Aggrecan↑ MMP-13↓ ADAMTS5↓ iNOS↓ | |
| Sun et al. [102] | J Cell Biochem 2019 | OA | BM-MSCs | Exosomes | In vitro | microRNA-320c | Chondrocyte proliferation↑ MMP-13↓ SRY-Box 9↑ | |
| Qi et al. [111] | In vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2019 | OA | BM-MSCs | Exosomes | Rabbit | Proteins | Chondrocyte apoptosis↓ (Phosphorylation of p38↓, ERK↓, AKT↑) | Induction of chondrocytes apoptosis with IL-1β |
| Mao et al. [112] | Stem Cell Res Ther 2018 | OA | BM-MSCs | Exosomes | Mice | microRNA-92a-3p | Cartilage development and homeostasis (direct targeting of WNT5A) | |
| Zhu et al. [100] | Stem Cell Res Ther 2017 | OA | iPSC-MSCs vs. SM-MSCs | Exosomes | Mice | CD9 CD63 TSG101 | iPSC-MSCs-exosomes have greater therapeutic effect on OA | Comparative study Intra-articular injection |
| Zhang et al. [101] | Biomaterials 2019 | OA | ESC-MSCs | Exosomes | Rat | Proteins | s-GAG synthesis impeded by IL-1β↑ IL-1 induced NO and MMP-13↓ | |
| Wang et al. [113] | Stem Cell Res Ther 2017 | OA | ESC-MSCs | Exosomes | Mice | Proteins | Type II collagen & aggrecan↑ ADAMTS5 with IL-1 β↓ |
8. Concluding Remarks and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lange-Brokaar, B.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; van Osch, G.; Zuurmond, A.-M.; Schoones, J.; Toes, R.; Huizinga, T.; Kloppenburg, M. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: A review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 1484–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Hawker, G.A.; Laporte, A.; Croxford, R.; Coyte, P.C. The economic burden of disabling hip and knee osteoarthritis (OA) from the perspective of individuals living with this condition. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, H.I.; Yamada, N.; Cheung, K.S.C.; Tilley, S.; Clarke, N.M.P.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Kokubun, S.; Bronner, F. Association between the abnormal expression of matrix-degrading enzymes by human osteoarthritic chondrocytes and demethylation of specific CpG sites in the promoter regions. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3110–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.A.; Buckwalter, J.A. The role of chondrocyte senescence in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and in limiting cartilage repair. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2003, 85, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime, P.; García-Guerrero, N.; Estella, R.; Pardo, J.; García-Álvarez, F.; Martinez-Lostao, L. Cd56+/cd16− natural killer cells expressing the inflammatory protease granzyme a are enriched in synovial fluid from patients with osteoarthritis. Osteo Arthritis Cartil. 2017, 25, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigrovic, P.A.; Lee, D.M. Mast cells in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2005, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, C.R.; Markovic, B.S.; Fellabaum, C.; Arsenijevic, A.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy of osteoarthritis: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2318–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.B.; Seo, M.-S.; Park, W.T.; Lee, G.W. Bone marrow aspirate concentrate: Its uses in osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.H.; Gil Lee, Y.; Shin, W.H.; Kim, H.; Chai, J.W.; Jeong, E.C.; Kim, J.E.; Shim, H.; Shin, J.S.; Shin, I.S.; et al. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: A proof-of-concept clinical trial. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, J.; Bates, D.; Boyd, R.; Shah, K.; Barnard, A.; Huguenin, L.; Tenen, A. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the treatment of osteoarthritis: Reparative pathways, safety and efficacy—A review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, A.; Martín-Ferrero, M.A.; Del Canto, F.; Alberca, M.; García, V.; Munar, A.; Orozco, L.; Soler, R.; Fuertes, J.J.; Huguet, M. Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: A randomized controlled trial. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, H.; Shimaya, M.; Muneta, T.; Nimura, A.; Morito, T.; Hayashi, M.; Suzuki, S.; Ju, Y.-J.; Mochizuki, T.; Sekiya, I. Local adherent technique for transplanting mesenchymal stem cells as a potential treatment of cartilage defect. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.W.; Seo, M.-S.; Kang, K.-K.; Oh, S.-K. Epidural fat-derived mesenchymal stem cell: First report of epidural fat-derived mesenchymal stem cell. Asian Spine J. 2019, 13, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prockop, D.J. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science 1997, 276, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.; Kim, G.B.; Jin, W. Intra-articular injection of autologous adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A phase iib, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. STEM Cells Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, L.; Munar, A.; Soler, R.; Alberca, M.; Soler, F.; Huguet, M.; Sentís, J.; Sánchez, A.; García-Sancho, J. Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with autologous mesenchymal stem cells: Two-year follow-up results. Transplant 2014, 97, e66–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, M.; Cosenza, S.; Maumus, M.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cells in osteo-arthritis. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, M.M.; Maxwell, J.S.; Weng, L.; Angelos, M.G.; Golzarian, J. Intra-articular treatment of knee osteoarthritis: From anti-inflammatories to products of regenerative medicine. Physician Sportsmed. 2016, 44, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.B.; Shon, O.-J. Current perspectives in stem cell therapies for osteoarthritis of the knee. Yeungnam Univ. J. Med. 2020, 37, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maumus, M.; Manferdini, C.; Toupet, K.; Peyrafitte, J.-A.; Ferreira, R.; Facchini, A.; Gabusi, E.; Bourin, P.; Jorgensen, C.; Lisignoli, G.; et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells protect chondrocytes from degeneration associated with osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res. 2013, 11, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraitchman, D.L.; Tatsumi, M.; Gilson, W.D.; Ishimori, T.; Kedziorek, D.; Walczak, P.; Segars, W.P.; Chen, H.H.; Fritzges, D.; Izbudak, I.; et al. dynamic imaging of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells trafficking to myocardial infarction. Circulation 2005, 112, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, C.; Wagner, W.R.; Bowry, S.; Schwartz, A.; Villanueva, F. Fate of culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cells in the microvasculature: In vivo observations of cell kinetics. Cir. Res. 2009, 104, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Van Balkom, B.W.; Bruno, S.; Choo, A.; Dominici, M.; Gimona, M.; Hill, A.F.; De Kleijn, D.; Koh, M.; Lai, R.C.; et al. Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1609206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, M.; Xu, J.; Woods, C.R.; Mora, A.L.; Spears, W.; Roman, J.; Brigham, K.L. Bone Marrow–Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Repair of the Injured Lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 33, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asari, S.; Itakura, S.; Ferreri, K.; Liu, C.-P.; Kuroda, Y.; Kandeel, F.; Mullen, Y. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress B-cell terminal differentiation. Exp. Hematol. 2009, 37, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, A.G.; Long, G.; Tyler, G.; Stefan, A.; Broadfoot, S.J.; Piccinini, A.M.; Middleton, J.; Kehoe, O. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium reduces disease severity and immune responses in inflammatory arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, J. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media suppresses inflammatory bone loss in a lipopolysaccharide-induced murine model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 15, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekkadan, B.; Van Poll, D.; Suganuma, K.; Carter, E.A.; Berthiaume, F.; Tilles, A.W.; Yarmush, M.L. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules reverse fulminant hepatic failure. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldring, N.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J.; Le Blanc, K.; Andaloussi, S.E. Therapeutic potential of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles. Hum. Gene Ther. 2015, 26, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschos, N.K.; Sennett, M.L. Update on mesenchymal stem cell therapies for cartilage disorders. World J. Orthop. 2017, 8, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnell, B.A.; Flaat, M.; Gagliardi, C.; Patel, B.; Ripoll, C. Adipose-derived stem cells: Isolation, expansion and differentiation. Methods 2008, 45, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, C.R.; Sadikot, R.; Pascual, J.; Fellabaum, C.; Jankovic, M.G.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy of inflammatory lung diseases: Current Understanding and Future Perspectives. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalu, M.M.; McIntyre, L.; Pugliese, C.; Fergusson, D.; Winston, B.W.; Marshall, J.C.; Granton, J.; Stewart, D.J. Safe ty of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (safecell): A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47559. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, M.; Bennaceur-Griscelli, A.; Nanbakhsh, A.; Oudrhiri, N.; Chouaib, S.; Azzarone, B.; Durrbach, A.; Lataillade, J.-J. TLR Ligands Stimulation Protects MSC from NK Killing. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blanc, K.; Mougiakakos, D. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, M.E.; Fibbe, W.E. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Sensors and Switchers of Inflammation. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterman, R.S.; Tomchuck, S.L.; Henkle, S.L.; Betancourt, A.M. A new mesenchymal stem cell (msc) paradigm: Polarization into a pro-inflammatory msc1 or an immunosuppressive msc2 phenotype. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, K.; Davies, L.C. Mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune response. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 168, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Mao, F.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Yan, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W. Mouse bone mar-row-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce macrophage m2 polarization through the nuclear factor-κb and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathways. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, N.; De Vries-van Melle, M.; Lehmann, J.; Wei, W.; Grotenhuis, N.; Farrell, E.; Van der Kraan, P.; Murphy, J.; Bastiaansen-Jenniskens, Y.; Van Osch, G. Human osteoarthritic synovium impacts chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via macrophage polarisation state. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Rajasingh, S.; Drosos, N.; Zhou, Z.; Dawn, B.; Rajasingh, J. Exosomes: New molecular targets of diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.-H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.-H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.J.; Jensen, S.S.; Lim, J.W.E. Proteomic profiling of exosomes: Current perspectives. Proteomics 2008, 8, 4083–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Properzi, F.; Logozzi, M.; Fais, S. Exosomes: The future of biomarkers in medicine. Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Chang, T.; Singh, S.P.; Lim, L.; Mannan, P.; Garfield, S.H.; Pendrak, M.L.; Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; Jin, S.; et al. CD47 Signaling Regulates the Immunosuppressive Activity of VEGF in T Cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-González, C.; Zuñiga, F.A.; Escudero, C.; Ormazabal, V.; Reyes, C.; Nova-Lamperti, E.; Salomón, C.; Aguayo, C. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote angiogenesis: Potencial clinical application. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, A.; Quast, T.; Keller, S.; Kolanus, W.; Knolle, P.; Altevogt, P.; Limmer, A. Transfer of T cell surface molecules to dendritic cells upon CD4+ T cell priming involves two distinct mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3965–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Grange, C.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Tumor Growth. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Okada, R.; Nagao, K.; Kawamata, Y.; Hanyu, A.; Yoshimoto, S.; Takasugi, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kanemaki, M.T.; Obuse, C.; et al. Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakasa, T.; Lotz, M.K.; Ochi, M. Exosomes from IL-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.H.; Alitalo, K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.A.; Sousa, L.P.; Pinho, V.; Perretti, M.; Teixeira, M.M. Resolution of Inflammation: What Controls Its Onset? Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashed, M.H.; Bayraktar, E.K.; Helal, G.; Abd-Ellah, M.F.; Amero, P.; Chavez-Reyes, A.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C. Exosomes: From garbage bins to promising therapeutic targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, R.; Huang, C.-C.; Ravindran, S. Hijacking the Cellular Mail: Exosome mediated differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 3808674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Omar, O.; Vazirisani, F.; Thomsen, P.; Ekström, K. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes have altered mi-croRNA profiles and induce osteogenic differentiation depending on the stage of differentiation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193059. [Google Scholar]
- Phinney, D.G.; Pittenger, M.F. Concise review: MSC-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosenza, S.; Ruiz, M.; Toupet, K.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.M.; Saleh, K.S.; Burdick, J.A.; Mauck, R.L. Bioactive factors for cartilage repair and regeneration: Improving delivery, retention, and activity. Acta Biomater. 2019, 93, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, H.C.; Mulhall, D.; Garimella, R. Role of extracellular membrane vesicles in the pathogenesis of various diseases, including cancer, renal diseases, atherosclerosis, and arthritis. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Sun, X.; Ding, Q. Exosomes derived from low-intensity pulsed ultrasound-treated dendritic cells sup-press tumor necrosis factor–induced endothelial inflammation. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 2081–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, W.S.; Foldager, C.B.; Pei, M.; Hui, J.H.P. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell-based strategies for cartilage repair and regeneration. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2014, 10, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, W.S.; Lai, R.C.; Hui, J.H.P.; Lim, S.K. MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration: Implications for osteoarthritis treatment. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 67, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chu, W.; Lai, R.C.; Lim, S.K.; Hui, J.H.P.; Toh, W. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chuah, S.J.; Lai, R.C.; Hui, J.H.P.; Lim, S.K.; Toh, W. MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials 2018, 156, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonk, L.A.; Van Dooremalen, S.F.J.; Liv, N.; Klumperman, J.; Coffer, P.J.; Saris, D.B.; Lorenowicz, M.J. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote human cartilage regeneration in vitro. Theranostics 2018, 8, 906–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of MicroRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andaloussi, S.E.; Mäger, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J. Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trams, E.G.; Lauter, C.J.; Salem, J.N.; Heine, U. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1981, 645, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camussi, G.; Deregibus, M.-C.; Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Fonsato, V.; Tetta, C. Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2010, 1, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer-Albers, E.-M.; Hill, A.F. Extracellular vesicles: Interneural shuttles of complex messages. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2016, 39, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Muth, C.; Dabrowski, O.; Krasemann, S.; Glatzel, M. Exosomes and the prion protein: More than one truth. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Wu, K.-C.; Harn, H.-J.; Lin, S.-Z.; Ding, D.-C. Exosomes and stem cells in degenerative disease diagnosis and therapy. Cell Transpl. 2018, 27, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christ, L.; Raiborg, C.; Wenzel, E.M.; Campsteijn, C.; Stenmark, H. Cellular Functions and Molecular Mechanisms of the ESCRT Membrane-Scission Machinery. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajimoto, T.; Okada, T.; Miya, S.; Zhang, L.; Nakamura, S.-I. Ongoing activation of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors mediates maturation of exosomal multivesicular endosomes. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Freitas, D.; Kim, H.S.; Fabijanic, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Martin, A.B.; Bojmar, L. Identi-fication of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willms, E.; Johansson, H.J.; Mäger, I.; Lee, Y.; Blomberg, K.E.M.; Sadik, M.; Alaarg, A.; Smith, C.E.; Lehtiö, J.; El Andaloussi, S.; et al. Cells release subpopulations of exosomes with distinct molecular and biological properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mianehsaz, E.; Mirzaei, H.R.; Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Rezaee, A.; Sahebnasagh, R.; Pourhanifeh, M.H.; Mirzaei, H.; Hamblin, M.R. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: A new therapeutic approach to osteoarthritis? Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Hwang, M.; Choi, B.; Jeong, H.; Jung, J.-H.; Kim, H.K.; Hong, S.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, Y. Exosome Classification by Pattern Analysis of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Data for Lung Cancer Diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6695–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzás, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J.; Nolte-‘t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeringer, E.; Barta, T.; Li, M.; Vlassov, A.V. Strategies for Isolation of Exosomes. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2015, 2015, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wong, D.K.; Hong, K.Y.; Raffai, R.L. Cushioned–Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation (C-DGUC): A Refined and High Performance Method for the Isolation, Characterization, and Use of Exosomes. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1740, pp. 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, M.F.; Otoc, N.; Sethi, J.K.; Gupta, A.; Antes, T.J. Integrated systems for exosome investigation. Methods 2015, 87, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deun, J.; Mestdagh, P.; Sormunen, R.; Cocquyt, V.; Vermaelen, K.; Vandesompele, J.; Bracke, M.; De Wever, O.; Hendrix, A. The impact of disparate isolation methods for extracellular vesicles on downstream RNA profiling. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauro, B.J.; Greening, D.W.; Mathias, R.A.; Ji, H.; Mathivanan, S.; Scott, A.M.; Simpson, R.J. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods 2012, 56, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, J.Z.; Lee, Y.; Vader, P.; Mäger, I.; Johansson, H.J.; Heusermann, W.; Wiklander, O.P.; Hällbrink, M.; Seow, Y.; Bultema, J.J.; et al. Ultrafiltration with size-exclusion liquid chromatography for high yield isolation of extracellular vesicles preserving intact biophysical and functional properties. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Kaslan, M.; Lee, S.H.; Yao, J.; Gao, Z. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics 2017, 7, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarovni, N.; Corrado, A.; Guazzi, P.; Zocco, D.; Lari, E.; Radano, G.; Muhhina, J.; Fondelli, C.; Gavrilova, J.; Chiesi, A. Integrated isolation and quantitative analysis of exosome shuttled proteins and nucleic acids using immunocapture approaches. Methods 2015, 87, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davatchi, F.; Abdollahi, B.S.; Mohyeddin, M.; Nikbin, B. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for knee osteoarthritis: 5 years follow-up of three patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 19, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretlow, J.D.; Jin, Y.-Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.J.; Hong, T.-H.; Zhou, G.; Baggett, L.S.; Mikos, A.G.; Cao, Y. Donor age and cell passage affects differentiation potential of murine bone marrow-derived stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnke, J.; Kremer, S.; Shahzad, T.; Chao, C.-M.; Böttcher-Friebertshäuser, E.; Morty, R.E.; Bellusci, S.; Ehrhardt, H. MSC Based Therapies—New perspectives for the injured lung. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.Y.; Bae, Y.-S.; Ryu, S.H.; Lee, T.G.; Kim, J.H. Proteomic Analysis of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced secretome of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddappa, R.; Licht, R.; van Blitterswijk, C.; de Boer, J. Donor variation and loss of multipotency during in vitro expansion of human mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, S.; Zhang, L.; Duan, L.; Wang, X.; Min, Y.; Yu, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis in a rat myocardial infarction model. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, L.A.; Borges, F.T.; Simões, M.J.; Borges, A.A.; Sinigaglia-Coimbra, R.; Schor, N. Bone Marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells repaired but did not prevent gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury through paracrine effects in rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeppner, T.R.; Herz, J.; Görgens, A.; Schlechter, J.; Ludwig, A.-K.; Radtke, S.; de Miroschedji, K.; Horn, P.A.; Giebel, B.; Hermann, D.M. Extracellular vesicles improve post-stroke neuroregeneration and prevent postischemic immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Niu, X.; Hu, B.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Comparison of exosomes secreted by induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells and synovial membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Teo, K.Y.W.; Chuah, S.J.; Lai, R.C.; Lim, S.K.; Toh, W.S. Msc exosomes alleviate temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation and restoring matrix homeostasis. Biomaterials 2019, 200, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lun, J.; Liao, W.; Zhang, Z. Expression of exosomal micrornas during chondrogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofiño-Vian, M.; Guillén, M.I.; del Caz, M.D.P.; Silvestre, A.; Alcaraz, M.J. Microvesicles from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a new protective strategy in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börger, V.; Bremer, M.; Ferrer-Tur, R.; Gockeln, L.; Stambouli, O.; Becic, A.; Giebel, B. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Potential as Novel Immunomodulatory Therapeutic Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, Z.; Webster, K.A.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z. Enhanced cardio-protection by human endometrium mesenchymal stem cells driven by exosomal microrna-21. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuda, T.; Tsuchiya, R.; Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takagaki, K.; Oki, K.; Takeshita, F.; Sakai, Y.; Kuroda, M.; Ochiya, T. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete functional neprilysin-bound exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, srep01197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, A.T.; Witwer, K.W.; Van Balkom, B.W.M.; De Beer, J.; Brodie, C.; Corteling, R.L.; Gabrielsson, S.; Gimona, M.; Ibrahim, A.G.; De Kleijn, D.; et al. Concise Review: Developing Best-Practice Models for the Therapeutic Use of Extracellular Vesicles. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yeo, R.W.Y.; Tan, K.H.; Lim, S.K. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gao, D.; Feng, C.; Yuan, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, S.; Fu, X. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress Fibroblast Proliferation and Reduce Skin Fibrosis Through a TGF-β3-Dependent Activation. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2015, 14, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofiño-Vian, M.; Guillén, M.I.; Pérez del Caz, M.D.; Castejón, M.A.; Alcaraz, M.J. Extracellular vesicles from adi-pose-derived mesenchymal stem cells downregulate senescence features in osteoarthritic osteoblasts. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Liu, D.-P.; Xiao, D.-W.; Tian, D.-C.; Su, Y.-W.; Jin, S.-F. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibit mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes via p38, ERK, and Akt pathways. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2019, 55, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Liao, W.; Kang, Y. Exosomes derived from miR-92a-3p-overexpressing human mesenchymal stem cells enhance chondrogenesis and suppress cartilage degradation via targeting WNT5A. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Dai, J.; Wu, B.; Zhou, J.; Heng, B.C.; Zou, X.H.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maumus, M.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine applied to rheumatic diseases: Role of secretome and exosomes. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Size (nm) | Morphology | Origin | Pathway Related | Biomarkers | Formation Mechanism | Ultracentrifugation Isolation (× g) | Contents | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exosomes | 50~150 nm, regular | Cup-shaped | Endosomal compartment of cells, Multivesicular body (MVB) | ESCRT-dependent Tetraspanin-Ceramide- | CD9,63,81 TSG101 Tetraspanins, ALIX, HSP70s | Exocytosis of MVB | 100,000~200,000 | mRNA, miRNA, IncRNA, protein, lipid, rarely DNA |
| Microvesicles | 100~1000 nm, Irregular | Heterogenous | Plasma membrane | Ca2+-dependent Various | Selectins, Integrins CD40 ligand | Budding from membrane | 10,000~60,000 | mRNA, miRNA, IncRNA, protein, lipid, rarely DNA |
| Apoptotic bodies | 1000~5000 nm, irregular | Heterogenous | Cells Plasma membrace | Apoptosis-related pathway | Histones, Annexin V | Budding from membrane | 10,000 (no standardized protocol) | Fragmented DNA, Cell organelles, Nuclear fraction |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.B.; Shon, O.-J.; Seo, M.-S.; Choi, Y.; Park, W.T.; Lee, G.W. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potential for Osteoarthritis. Biology 2021, 10, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040285
Kim GB, Shon O-J, Seo M-S, Choi Y, Park WT, Lee GW. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potential for Osteoarthritis. Biology. 2021; 10(4):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040285
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Gi Beom, Oog-Jin Shon, Min-Soo Seo, Young Choi, Wook Tae Park, and Gun Woo Lee. 2021. "Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potential for Osteoarthritis" Biology 10, no. 4: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040285
APA StyleKim, G. B., Shon, O.-J., Seo, M.-S., Choi, Y., Park, W. T., & Lee, G. W. (2021). Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potential for Osteoarthritis. Biology, 10(4), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040285







